Changes in moles during pregnancy
Link and when to seek help
Pregnant people may develop new moles or other marks on their skin. Most are harmless. It is possible to develop melanoma during pregnancy, however, so have a doctor check any marks that are causing concern.
Moles form when clusters of cells, called melanocytes, overproduce melanin, the pigment that colors the skin.
The National Library of Medicine notes that people can develop new moles at any age and that hormonal changes during pregnancy can cause new moles to form.
This article explores the link between pregnancy and moles. It also looks at other common skin changes during pregnancy and why it is important to contact a healthcare professional about any difference in the appearance of a mole.
Moles can form at any time. They usually appear during childhood and puberty, and sometimes during pregnancy, due to hormonal changes.
Can moles disappear during pregnancy?
Moles can fade or completely disappear throughout a person’s lifetime.
The European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology reports that pregnancy does not significantly alter the way moles look. But changes in their appearance can occur.
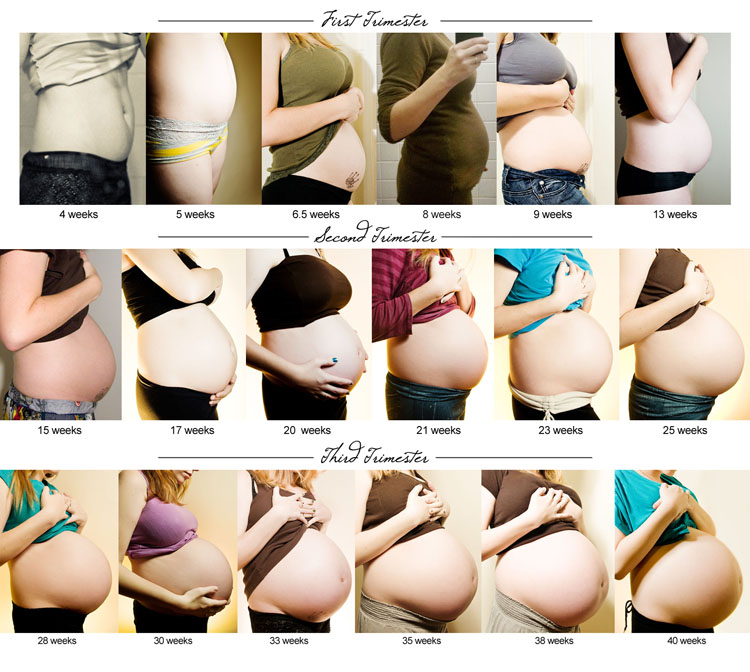
Existing moles may become more noticeable, particularly those on the chest or abdomen. As the skin expands to accommodate the growing fetus, moles may spread out and become larger and darker. More than 10% of pregnant people may find that this happens.
Moles on the back and limbs are unlikely to change in size due to pregnancy.
Melanoma is a type of skin cancer. As the American Academy of Dermatology (AAD) states that pregnancy does not increase the risk of developing melanoma.
However, as it notes, melanoma typically develops during child-bearing years.
If a doctor diagnoses melanoma during pregnancy or within 12 months of delivery, healthcare professionals refer to this as “pregnancy-associated melanoma”. This can affect 10–26 in 100,000 pregnancies.
How does melanoma affect pregnancy?
The AAD says that it is safe to test for melanoma during pregnancy. A doctor takes a biopsy using a local anesthetic, which is safe during pregnancy.
A doctor takes a biopsy using a local anesthetic, which is safe during pregnancy.
The outlook for both the pregnant person and the fetus is better with early detection and treatment.
If melanoma has spread, doctors may need further tests, and they should explain the risks and likely benefits. Some tests may not be possible during pregnancy.
Treatment options for early stage melanoma are safe during pregnancy. The doctor uses a local anesthetic and removes the melanoma.
In the later stages, the treatment options are limited. A doctor may recommend using interferon, a type of immunotherapy.
The best approach to treatment may depend on the location of melanoma. People who are pregnant and have melanoma on their face or neck may have radiation therapy. But radiation therapy may harm the fetus if a person receives it for melanoma around their abdomen.
Melanoma is a type of cancer that can cross the placenta. However, it is very rare, the AAD notes, for a baby to be born with it, even when the person giving birth has advanced melanoma.
The body changes in many ways during pregnancy. A person may develop acne or stretch marks.
As The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists reports, other skin changes during pregnancy include:
- melasma, which are darker patches of skin on the face
- linea nigra, which is a dark line running from the belly button to the pubic area
- spider veins
- pruritic urticarial papules and plaques, which is an itchy, patchy rash of small bumps on the abdomen, thighs, buttocks, and breasts
- prurigo, which are tiny, itchy, bumps that look like insect bites
- intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy, which refers to itchiness of the palms and soles that can spread to the trunk of the body
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommend seeing a doctor about any sore that does not heal or any new or old growth that changes shape or size.
For people concerned about melanoma, the CDC recommends following the “ABCDE plan,” which involves contacting a doctor in any of these circumstances:
- Asymmetry: A mole has an unusual shape, and the two halves look different.
- Border: The mole has an uneven, possibly a jagged, edge.
- Color: Different parts of the mole are different colors.
- Diameter: The mole is bigger than a pea.
- Evolving: The mole changes over weeks or months.
Most moles are harmless patches of highly pigmented skin. They can appear at any time, particularly during periods of increased hormonal activity, such as pregnancy.
People who are pregnant may also notice that moles on the chest or abdomen become larger or darker during pregnancy.
As always, it is important to check for signs of skin cancer, including melanoma. Being pregnant does not increase the risk of melanoma, but it can develop during pregnancy. In the early stages, the treatment is safe for the person and their fetus.
Anyone concerned about a mark on their skin should contact a doctor.
Link and when to seek help
Pregnant people may develop new moles or other marks on their skin. Most are harmless. It is possible to develop melanoma during pregnancy, however, so have a doctor check any marks that are causing concern.
Most are harmless. It is possible to develop melanoma during pregnancy, however, so have a doctor check any marks that are causing concern.
Moles form when clusters of cells, called melanocytes, overproduce melanin, the pigment that colors the skin.
The National Library of Medicine notes that people can develop new moles at any age and that hormonal changes during pregnancy can cause new moles to form.
This article explores the link between pregnancy and moles. It also looks at other common skin changes during pregnancy and why it is important to contact a healthcare professional about any difference in the appearance of a mole.
Moles can form at any time. They usually appear during childhood and puberty, and sometimes during pregnancy, due to hormonal changes.
Can moles disappear during pregnancy?
Moles can fade or completely disappear throughout a person’s lifetime.
The European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology reports that pregnancy does not significantly alter the way moles look. But changes in their appearance can occur.
But changes in their appearance can occur.
Existing moles may become more noticeable, particularly those on the chest or abdomen. As the skin expands to accommodate the growing fetus, moles may spread out and become larger and darker. More than 10% of pregnant people may find that this happens.
Moles on the back and limbs are unlikely to change in size due to pregnancy.
Melanoma is a type of skin cancer. As the American Academy of Dermatology (AAD) states that pregnancy does not increase the risk of developing melanoma.
However, as it notes, melanoma typically develops during child-bearing years.
If a doctor diagnoses melanoma during pregnancy or within 12 months of delivery, healthcare professionals refer to this as “pregnancy-associated melanoma”. This can affect 10–26 in 100,000 pregnancies.
How does melanoma affect pregnancy?
The AAD says that it is safe to test for melanoma during pregnancy. A doctor takes a biopsy using a local anesthetic, which is safe during pregnancy.
The outlook for both the pregnant person and the fetus is better with early detection and treatment.
If melanoma has spread, doctors may need further tests, and they should explain the risks and likely benefits. Some tests may not be possible during pregnancy.
Treatment options for early stage melanoma are safe during pregnancy. The doctor uses a local anesthetic and removes the melanoma.
In the later stages, the treatment options are limited. A doctor may recommend using interferon, a type of immunotherapy.
The best approach to treatment may depend on the location of melanoma. People who are pregnant and have melanoma on their face or neck may have radiation therapy. But radiation therapy may harm the fetus if a person receives it for melanoma around their abdomen.
Melanoma is a type of cancer that can cross the placenta. However, it is very rare, the AAD notes, for a baby to be born with it, even when the person giving birth has advanced melanoma.
The body changes in many ways during pregnancy. A person may develop acne or stretch marks.
A person may develop acne or stretch marks.
As The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists reports, other skin changes during pregnancy include:
- melasma, which are darker patches of skin on the face
- linea nigra, which is a dark line running from the belly button to the pubic area
- spider veins
- pruritic urticarial papules and plaques, which is an itchy, patchy rash of small bumps on the abdomen, thighs, buttocks, and breasts
- prurigo, which are tiny, itchy, bumps that look like insect bites
- intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy, which refers to itchiness of the palms and soles that can spread to the trunk of the body
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommend seeing a doctor about any sore that does not heal or any new or old growth that changes shape or size.
For people concerned about melanoma, the CDC recommends following the “ABCDE plan,” which involves contacting a doctor in any of these circumstances:
- Asymmetry: A mole has an unusual shape, and the two halves look different.

- Border: The mole has an uneven, possibly a jagged, edge.
- Color: Different parts of the mole are different colors.
- Diameter: The mole is bigger than a pea.
- Evolving: The mole changes over weeks or months.
Most moles are harmless patches of highly pigmented skin. They can appear at any time, particularly during periods of increased hormonal activity, such as pregnancy.
People who are pregnant may also notice that moles on the chest or abdomen become larger or darker during pregnancy.
As always, it is important to check for signs of skin cancer, including melanoma. Being pregnant does not increase the risk of melanoma, but it can develop during pregnancy. In the early stages, the treatment is safe for the person and their fetus.
Anyone concerned about a mark on their skin should contact a doctor.
Moles appeared or enlarged during pregnancy
Moles and pregnancy Why did they appear Prevention What to do
Moles and Pregnancy
Moles (nevi) are benign growths on the skin that almost every person has. Someone has only a few of them, while others have dozens or even hundreds of nevi. Moreover: moles can appear, and sometimes disappear spontaneously. nine0003
Someone has only a few of them, while others have dozens or even hundreds of nevi. Moreover: moles can appear, and sometimes disappear spontaneously. nine0003
The most amazing phenomena occur with nevi against the background of hormonal changes. Women often notice that during pregnancy, moles appeared on absolutely smooth skin, and some time after childbirth, they disappeared without the slightest effort from a cosmetologist or dermatologist. However, this is not always the case, so the sudden appearance of nevi is a good reason to visit a doctor.
Causes of the appearance of moles during pregnancy
The main reason for the appearance of new moles in pregnant women is a change in hormonal levels. The main "guilt" in this lies with progesterone - a hormone necessary for conceiving and bearing a child. nine0003
Progesterone affects pigment cells (melanocytes), which, among other things, contributes to the appearance of moles. The number of neoplasms that appear during pregnancy is sometimes in the tens. The main place of their localization is the area of the chest, back and abdomen, but they can also appear on other parts of the body.
The main place of their localization is the area of the chest, back and abdomen, but they can also appear on other parts of the body.
As additional factors that activate the process of the appearance of moles during pregnancy, are:
- ultraviolet radiation; nine0020
- unbalanced diet and lack of vitamins;
- misuse of cosmetics.
Prevention of the appearance, injury and degeneration of moles during pregnancy
A visit to a dermatologist to examine the skin and diagnose neoplasms is an integral part of proper preparation for pregnancy. Therefore, it is reasonable to make an appointment with a specialist of the CELSIUM Clinic medical center even at the stage of pregnancy planning. nine0003
If you did not have time to visit a doctor before conception, do it as soon as possible, especially if moles appeared during pregnancy. Only a specialist (dermatologist) will be able to correctly determine the nature of the neoplasms, conduct dermatoscopy and decide whether the removal of the mole is required and whether histology is needed here.
Subsequently, follow his recommendations, for example:
- Limit sun exposure. It is better not to go on vacation to hot countries: acclimatization during this period is already a serious stress for the body, and then there is the scorching sun. In summer, you should wear closed, loose clothing made from natural materials, use protective equipment and refrain from sunbathing (especially in a solarium). nine0020
- Pay close attention to hygiene and comfort. Increased sweating, increased body weight and volume, swelling, tight clothing - all this contributes to the occurrence of itching and microtrauma. A frequent consequence of this is traumatization of moles. You need to wear loose clothing made from natural materials, take a shower more often and use special cosmetics recommended for pregnant women.
- Eat right and take your vitamins as recommended by your doctor. Taking drugs that regulate the synthesis of melanin (Aevit, Ascorutin, folic acid) can affect the formation of nevi and age spots.
 But you need to understand that any drug, even just vitamins, should not be taken on the advice of friends and the Internet, but only on the advice of a doctor. nine0020
But you need to understand that any drug, even just vitamins, should not be taken on the advice of friends and the Internet, but only on the advice of a doctor. nine0020
What should I do if I have moles during pregnancy?
If moles appear during pregnancy, this is a good reason to visit a dermatologist in order to exclude and prevent risks and complications in a timely manner. And if the mole was injured, began to itch, or suddenly changed shape, size or color - you need to make an appointment with the doctor without delay at any stage of pregnancy.
A dermatologist at the CELSIUM Clinic medical center will conduct an examination and consultation, perform a dermatoscopy, and, if necessary, tell and show which moles should be urgently removed and which should not be touched before childbirth. Be attentive to your health and contact only professionals, because now you are responsible for two. nine0003
Article author
Pregnancy services
- Face cleaning
- Hair treatment
- Epilation
- Peelings
- Face massage
- Ear piercing
- Eyebrow correction nine0020
- Facial care
- Cryomassage of the face
Moles during pregnancy
The appearance of moles during pregnancy causes concern in women, but most often does not pose a threat to mother and baby.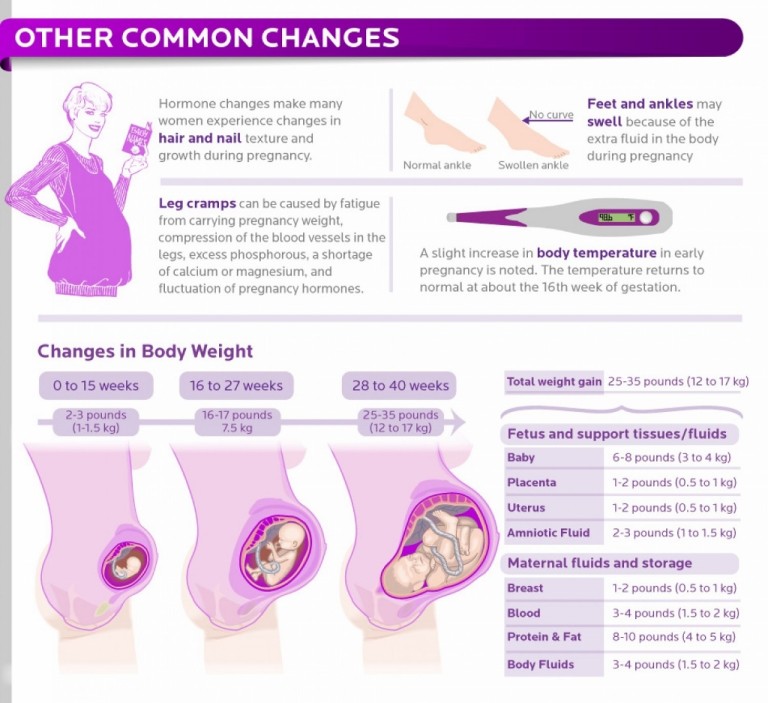 Only in the case of a malignant nature of the neoplasms, laser removal of moles is performed.
Only in the case of a malignant nature of the neoplasms, laser removal of moles is performed.
By carefully observing the changes in their body, many pregnant women notice the appearance of new moles or an increase in the size of existing neoplasms. Most often this happens in the second trimester, since during this period the restructuring of the hormonal background occurs most actively and causes the formation of nevi. nine0003
Like the size, the color of neoplasms can be different: flesh, brown, black. Moles are smooth or rough to the touch, in the form of pigmented areas or protruding above the surface of the skin. But regardless of their appearance, nevi do not pose a danger to mother and child and do not require removal. The only exceptions are those neoplasms that are disturbed by itching, peeling, painful sensations when touched, change color, become inflamed or bleed. Read more about how to deal with such moles in our article "Itchy and flaky mole. What to do?". Only in these cases, doctors can recommend laser removal of moles - a procedure in which the tissues of the neoplasm are evaporated by the energy of the laser beam. nine0003
nine0003
Prevention of moles during pregnancy
To prevent the appearance of moles pregnant women are advised to:
1. Limit sun exposure, especially in summer. You should also refuse to visit the solarium, as this not only dries the skin, but also activates the production of melanin in it. And there is a high probability that this pigment will begin to concentrate in the mole.
2. Take care of your skin. Due to changes in body volume, the skin in pregnant women begins to stretch and therefore often itches. This can cause scratching of already existing moles. Regular use of moisturizing cosmetics and soft bathing products will help to avoid injury to nevi. nine0003
3. Take multivitamin complexes. To maintain the vitamin and mineral balance of the body, pregnant women should take drugs prescribed by a doctor. In particular, they contain folic acid, the lack of which can provoke the formation of nevi.
4. Wear comfortable clothing. With constant injury to the skin, the likelihood of a mole appearing on it increases many times over, so it is important for a pregnant woman to choose underwear and clothes in accordance with changing body volumes. nine0003
nine0003
Methods for removing moles in modern cosmetology
If a nevus causes discomfort and discomfort: it bleeds, itches, hurts or becomes inflamed, a decision can be made to remove it. To do this, modern cosmetology uses several techniques:
- laser removal;
- cryodestruction;
- electrocoagulation;
- surgical excision;
- radio wave removal. nine0025
- allergic dermatitis;
- infectious diseases of the skin;
- the presence of certain chronic diseases of the blood and cardiovascular system.
But not all of these methods can be used during pregnancy. Surgical excision and electrocoagulation are accompanied by pain and require anesthesia, radio wave radiation can adversely affect the development of the fetus, and cryodestruction does not always help to completely get rid of the neoplasm in one procedure.
Therefore, laser removal of moles is considered the most effective and safest method. In this procedure, neoplasms are treated with a laser beam of a certain intensity, under the influence of which the cells evaporate in layers from the surface of healthy skin.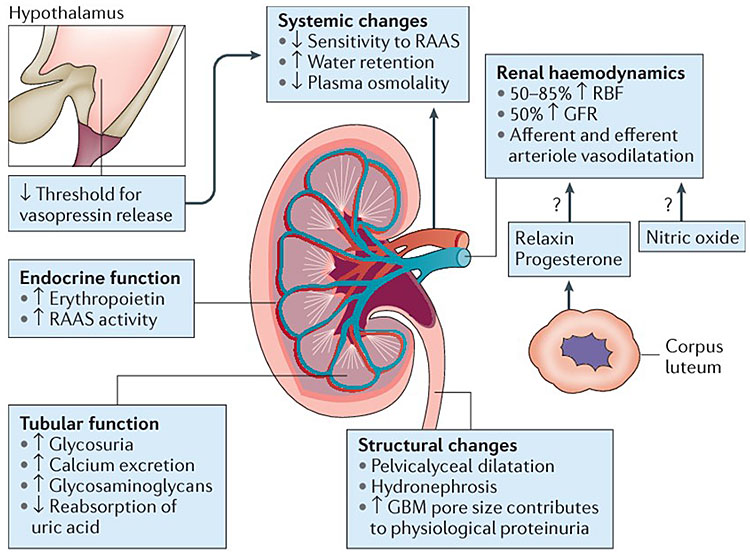 nine0003
nine0003
Advantages of laser mole removal
1. Less traumatic. The laser beam directly affects the melanin contained in the mole and does not affect healthy tissues. Therefore, the processing area is clearly limited.
2. Painless. In most cases, the procedure does not require anesthesia, but if the pregnant woman fears discomfort, an anesthetic cream may be used.
3. No chance of recurrence. Since all altered epidermal cells are completely removed, it is extremely unlikely that a new mole will form on the treated area. nine0003
4. Manipulation accuracy. Modern laser systems allow you to perform manipulations with great accuracy and prevent damage to the tissues located around the nevus.
5. No bleeding. Under the action of a laser beam, the capillaries located in the skin are instantly sealed, so the process of removing a mole with a laser is not accompanied by blood loss.
6. Possibility to remove several neoplasms in one session.
7. Minimum duration of the procedure. Removal of one nevus takes only a few minutes. nine0003
Minimum duration of the procedure. Removal of one nevus takes only a few minutes. nine0003
8. No rehabilitation period. At the site of removal of the mole, a crust forms, which spontaneously disappears after a few days. No special skin care in the affected area is required.
Side effects and contraindications
The laser mole removal procedure is almost never accompanied by side effects, therefore it is recommended for women during pregnancy. The impact of the laser does not cause allergic reactions, does not extend to the main systems of the body, and does not adversely affect the fetus. Only on very sensitive skin after treatment, slight hyperemia and redness may occur. You can learn more about the procedure for laser removal of neoplasms in our article "Laser removal of benign skin neoplasms". nine0003
For pregnant women, the possibility of using this procedure is determined by the doctor and is based on examination data. There are a number of contraindications to the use of the laser: