Hormone level test for pregnancy
HCG blood test - quantitative Information | Mount Sinai
Serial beta HCG; Repeat quantitative beta HCG; Human chorionic gonadotropin blood test - quantitative; Beta-HCG blood test - quantitative; Pregnancy test - blood - quantitative
A quantitative human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG) test measures the specific level of HCG in the blood. HCG is a hormone produced in the body during pregnancy.
Other HCG tests include:
- HCG urine test
- HCG blood test -- qualitative
Blood is drawn from a vein (venipuncture), usually from the inside of the elbow or the back of the hand. A needle is inserted into the vein, and the blood is collected in an air-tight vial or a syringe. Preparation may vary depending on the specific test.
How the Test is Performed
A blood sample is needed. This is most often taken from a vein. The procedure is called a venipuncture.
How to Prepare for the Test
No special preparation is needed.
How the Test will Feel
When the needle is inserted to draw blood, some people feel moderate pain. Others feel only a prick or stinging sensation. Afterward, there may be some throbbing.
Why the Test is Performed
HCG appears in the blood and urine of pregnant women as early as 10 days after conception. Quantitative HCG measurement helps determine the exact age of the fetus. It can also assist in the diagnosis of abnormal pregnancies, such as ectopic pregnancies, molar pregnancies, and possible miscarriages. It is also used as part of a screening test for Down syndrome.
Quantitative HCG measurement helps determine the exact age of the fetus. It can also assist in the diagnosis of abnormal pregnancies, such as ectopic pregnancies, molar pregnancies, and possible miscarriages. It is also used as part of a screening test for Down syndrome.
This test is also done to diagnose abnormal conditions not related to pregnancy that can raise HCG level.
Normal Results
Results are given in milli-international units per milliliter (mUI/mL).
Normal levels are found in:
- Non-pregnant women: less than 5 mIU/mL
- Healthy men: less than 2 mIU/mL
In pregnancy, HCG level rises rapidly during the first trimester and then declines slightly. The expected HCG ranges in pregnant women are based on the length of the pregnancy.
The expected HCG ranges in pregnant women are based on the length of the pregnancy.
- 3 weeks: 5 - 72 mIU/mL
- 4 weeks: 10 -708 mIU/mL
- 5 weeks: 217 - 8,245 mIU/mL
- 6 weeks: 152 - 32,177 mIU/mL
- 7 weeks: 4,059 - 153,767 mIU/mL
- 8 weeks: 31,366 - 149,094 mIU/mL
- 9 weeks: 59,109 - 135,901 mIU/mL
- 10 weeks: 44,186 - 170,409 mIU/mL
- 12 weeks: 27,107 - 201,165 mIU/mL
- 14 weeks: 24,302 - 93,646 mIU/mL
- 15 weeks: 12,540 - 69,747 mIU/mL
- 16 weeks: 8,904 - 55,332 mIU/mL
- 17 weeks: 8,240 - 51,793 mIU/mL
- 18 weeks: 9,649 - 55,271 mIU/mL
Normal value ranges may vary slightly among different laboratories. Talk to your provider about the meaning of your specific test result.
What Abnormal Results Mean
Higher than normal level may indicate:
- More than one fetus, for example, twins or triplets
- Choriocarcinoma of the uterus
- Hydatidiform mole of the uterus
- Ovarian cancer
- Testicular cancer (in men)
During pregnancy, lower than normal levels based on the gestational age may indicate:
- Fetal death
- Incomplete miscarriage
- Threatened spontaneous abortion (miscarriage)
- Ectopic pregnancy
Risks
Risks of having blood drawn are slight, but may include:
- Excessive bleeding
- Fainting or feeling lightheaded
- Blood accumulating under the skin (hematoma)
- Infection (a slight risk any time the skin is broken)
Jain S, Pincus MR, Bluth MH, McPherson RA, Bowne WB, Lee P. Diagnosis and management of cancer using serological and other body fluid markers. In: McPherson RA, Pincus MR, eds. Henry's Clinical Diagnosis and Management by Laboratory Methods. 23rd ed. St Louis, MO: Elsevier; 2017:chap 74.
Diagnosis and management of cancer using serological and other body fluid markers. In: McPherson RA, Pincus MR, eds. Henry's Clinical Diagnosis and Management by Laboratory Methods. 23rd ed. St Louis, MO: Elsevier; 2017:chap 74.
Jeelani R, Bluth MH. Reproductive function and pregnancy. In: McPherson RA, Pincus MR, eds. Henry's Clinical Diagnosis and Management by Laboratory Methods. 23rd ed. St Louis, MO: Elsevier; 2017:chap 25.
University of Iowa Diagnostic Laboratories. Test directory: HCG - serum, quantitative. www.healthcare.uiowa.edu/path_handbook/rhandbook/test446.html. Updated February 10, 2022. Accessed March 11, 2022.
Yarbrough ML, Stout M, Gronowski AM. Pregnancy and its disorders. In: Rifai N, ed. Tietz Textbook of Clinical Chemistry and Molecular Diagnostics. 6th ed. St Louis, MO: Elsevier; 2018:chap 69.
Last reviewed on: 12/3/2020
Reviewed by: LaQuita Martinez, MD, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Emory Johns Creek Hospital, Alpharetta, GA.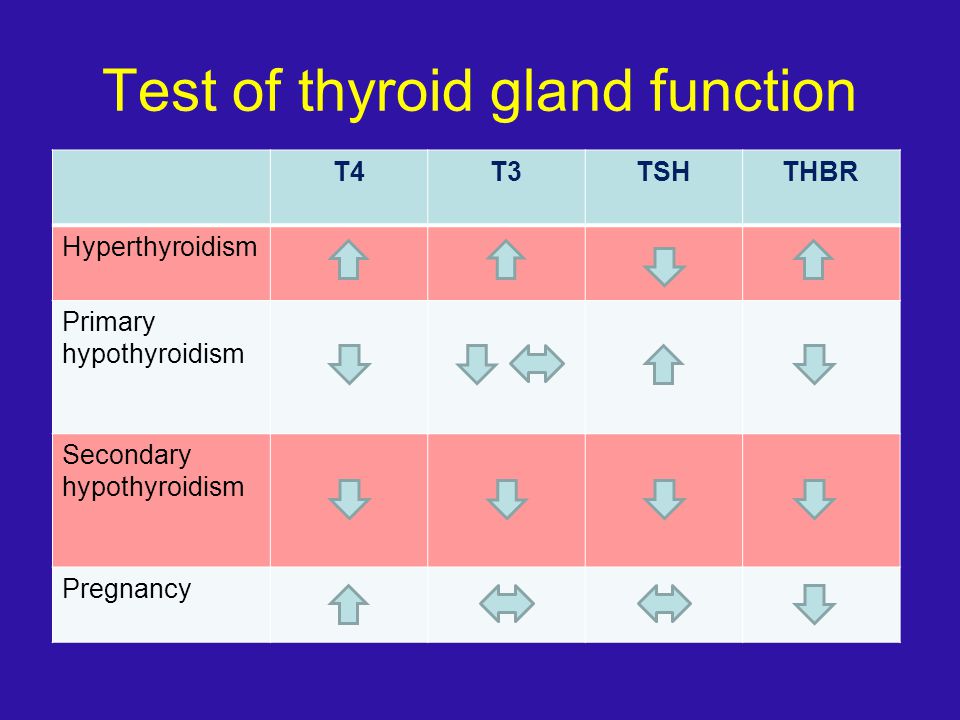 Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team. Editorial update 03/11/2022.
Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team. Editorial update 03/11/2022.
hCG Levels | The American Pregnancy Association
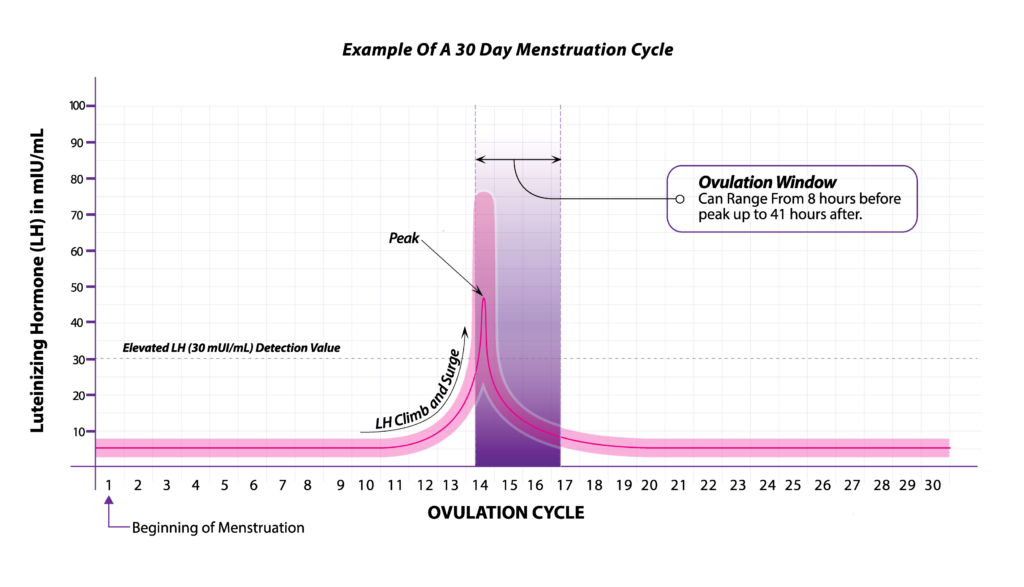
HCG (Human Chorionic Gonadotropin) is often called the pregnancy hormone because it is made by cells formed in the placenta, which nourishes the egg after it has been fertilized and becomes attached to the uterine wall. Levels can first be detected by a blood test about 11 days after conception and about 12-14 days after conception by a urine test.
Typically, the hCG levels will double every 72 hours. The level will reach its peak in the first 8-11 weeks of pregnancy and then will decline and level off for the remainder of the pregnancy.
- As you get further along in pregnancy and the hCG level gets higher, the time it takes to double can increase to about every 96 hours.
- Caution must be used in making too much of hCG numbers. A normal pregnancy may have low hCG levels and result in a perfectly healthy baby. The results from an ultrasound after 5 -6 weeks gestation are much more accurate than using hCG numbers.
- An hCG level of less than 5 mIU/mL is considered negative for pregnancy, and anything above 25 mIU/mL is considered positive for pregnancy.
- An hCG level between 6 and 24 mIU/mL is considered a grey area, and you’ll likely need to be retested to see if your levels rise to confirm a pregnancy.
- The hCG hormone is measured in milli-international units per milliliter (mIU/mL).
- A transvaginal ultrasound should be able to show at least a gestational sac once the hCG levels have reached between 1,000 – 2,000 mIU/mL. Because levels can differentiate so much and conception dating can be wrong, a diagnosis should not be made by ultrasound findings until the hCG level has reached at least 2,000 mIU/mL.
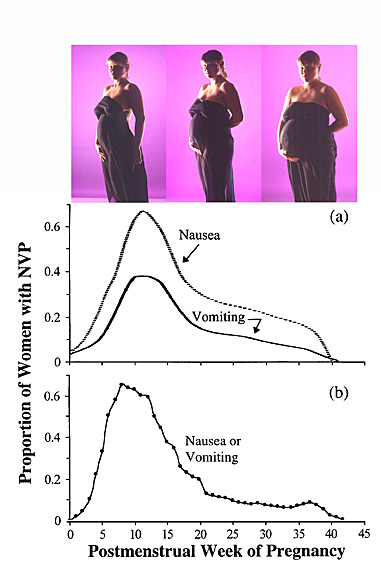
- A single reading is not enough information for most diagnoses. When there is a question regarding the health of the pregnancy, multiple testings of hCG done a couple of days apart give a more accurate assessment of the situation.
- The hCG levels should not be used to date a pregnancy since these numbers can vary so widely.
- There are two common types of hCG tests. A qualitative test detects if hCG is present in the blood. A quantitative test (or beta) measures the amount of hCG actually present in the blood.
Guideline to hCG levels in weeks during pregnancy
* These numbers are just a guideline – every woman’s level of hCG can rise differently. It is not necessarily the level that matters, but rather the change in the level.
What Does a Low hCG Level Mean?
A low hCG level can mean any number of things and should be rechecked within 48-72 hours to see how the level is changing.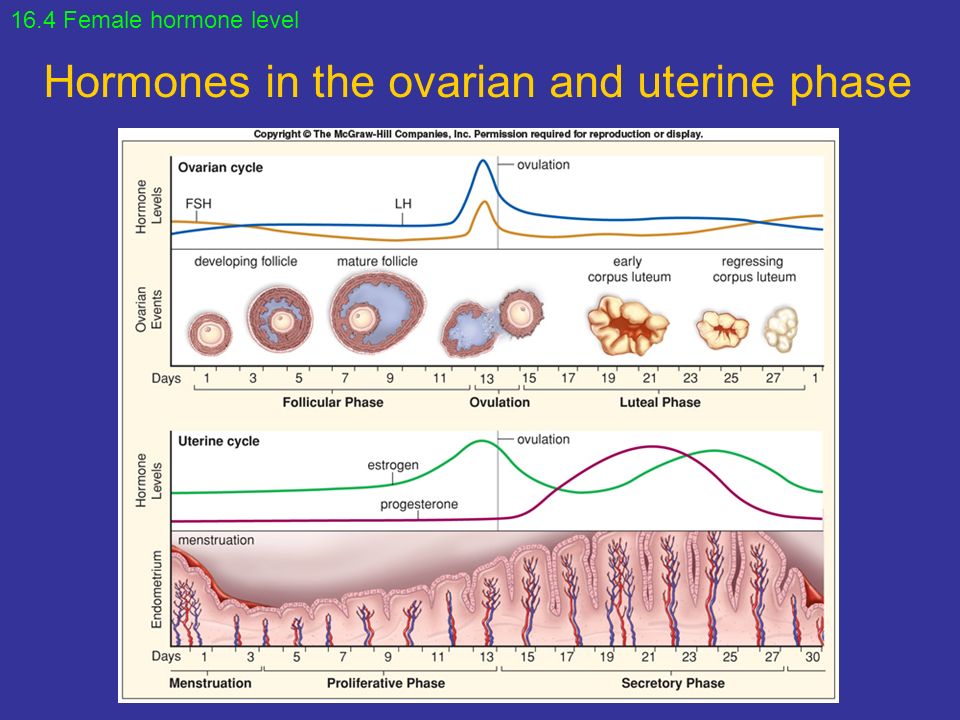 A low level can indicate:
A low level can indicate:
- Miscalculation of pregnancy dating
- Possible miscarriage or blighted ovum
- Ectopic pregnancy
Is a High hCG Level a Bad Thing?
A high level of hCG can also mean a number of things and should be rechecked within 48-72 hours to evaluate changes in the level. A high level can indicate:
- Miscalculation of pregnancy dating
- Molar pregnancy
- Multiple pregnancies
Should I Check My hCG level Regularly?
It’s not common for doctors to routinely check your hCG levels unless you are showing signs of a potential problem.
A health care provider may recheck your levels if you are bleeding, experiencing severe cramping, or have a history of miscarriage.
What Can I Expect After a Pregnancy Loss?
Most women can expect their levels to return to a non-pregnant range about 4 – 6 weeks after a pregnancy loss has occurred.
This can differentiate by how the loss occurred (spontaneous miscarriage, D & C procedure, abortion, natural delivery) and how high the levels were at the time of the loss.
Healthcare providers usually will continue to test hCG levels after a pregnancy loss to ensure they return back to <5.0.
What Can Interfere With My hCG Levels?
If you get a positive test result, you are most likely pregnant. False positives are extremely rare. However, there are some conditions that may cause a false positive, such as certain types of cancer and early miscarriage. Some antibodies may also interfere with test results.
Medications that contain hCG may interfere with hCG levels, as well.
These medications are often used infertility treatments, and your health care provider should advise you on how they may affect a test.
All other medications such as antibiotics, pain relievers, contraception or other hormone medications should not have any effect on a test that measures hCG.
Want to Know More?
- Pregnancy Calculator
- Calculating Gestation Age
- Concerns Regarding Early Fetal Development
Compiled using information from the following sources:
1. U.S. Food and Drug Administration
U.S. Food and Drug Administration
www.fda.gov
2. Bashir, I; Ihenetu, K; Miller, J.J.; Gim, M.; Lippmann, S. A Positive Pregnancy Test in the Post-Menopausal Psychiatric Patient — What to Think? Psychiatry (Edgemont). Feb. 2006.
Hormonal studies during pregnancy / Nyanya.ru
02/27/2012
Nona Hovsepyan, Consultant Physician, Independent Laboratory INVITRO
Why is it necessary to control the level of hormones?
Hormones are amazing biologically active substances that affect not only the state of health, but also the inner world of a person. Nature provides that in the female body immediately after conception, special pregnancy hormones are activated, which not only help the baby to fully develop, but also set up the expectant mother for the desired motherhood, teach them to love the baby growing inside and get used to taking care of him.
During the period of expectation of a baby, serious changes occur in the whole body of a woman, especially her hormonal levels.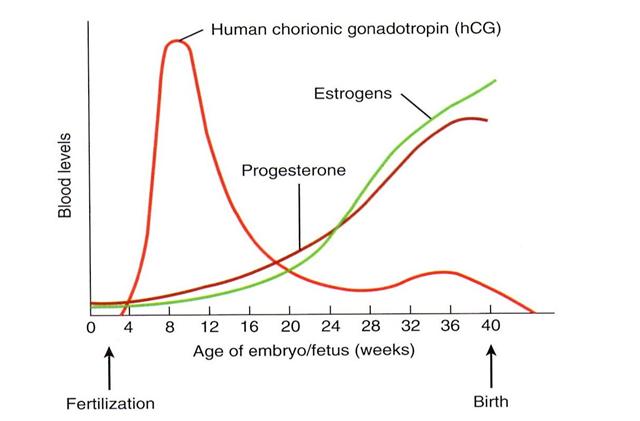 Changes occur throughout the endocrine system. The body of the future mother, completely rebuilding, creates the conditions for the bearing and normal development of the baby, and from the first days of pregnancy begins to prepare for childbirth.
Changes occur throughout the endocrine system. The body of the future mother, completely rebuilding, creates the conditions for the bearing and normal development of the baby, and from the first days of pregnancy begins to prepare for childbirth.
All hormonal indicators of the future mother's body play a huge role - namely, they are the most important indicators of fetal development. Therefore, the level of hormones is necessarily monitored by the attending physician with the help of special examinations - prenatal screenings, which a woman needs to undergo at least 2 times: in the first trimester (11-12 weeks) and in the second trimester (16-19weeks). Let's figure out what indicators are included in this mandatory examination, what the increase or decrease in the level of a particular hormone indicates, and what their role is.
Hormones that the body of the unborn baby "produces"
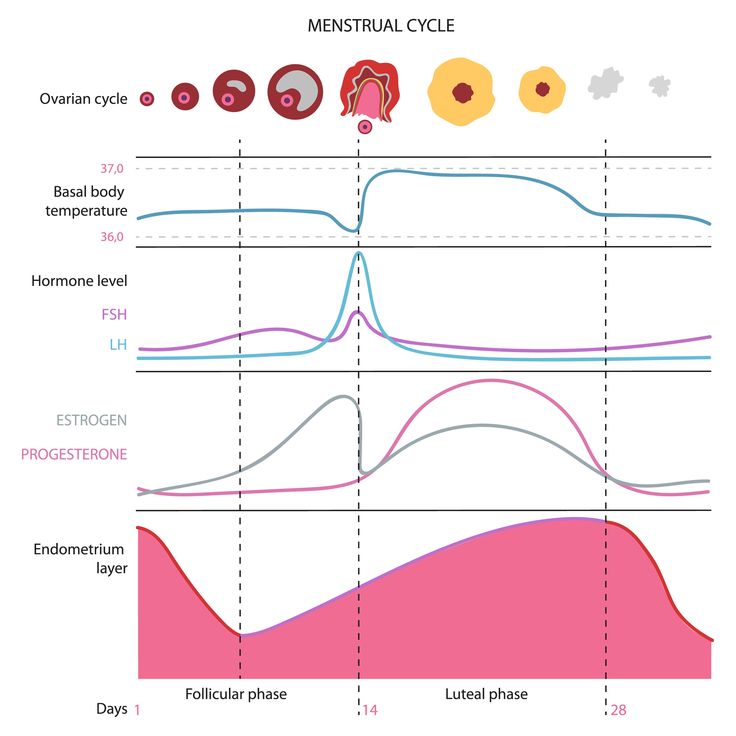
HCG. This is human chorionic gonadotropin, a hormone that is actively produced by the cells of the chorion (fetal membrane) immediately after it attaches to the wall of the uterus.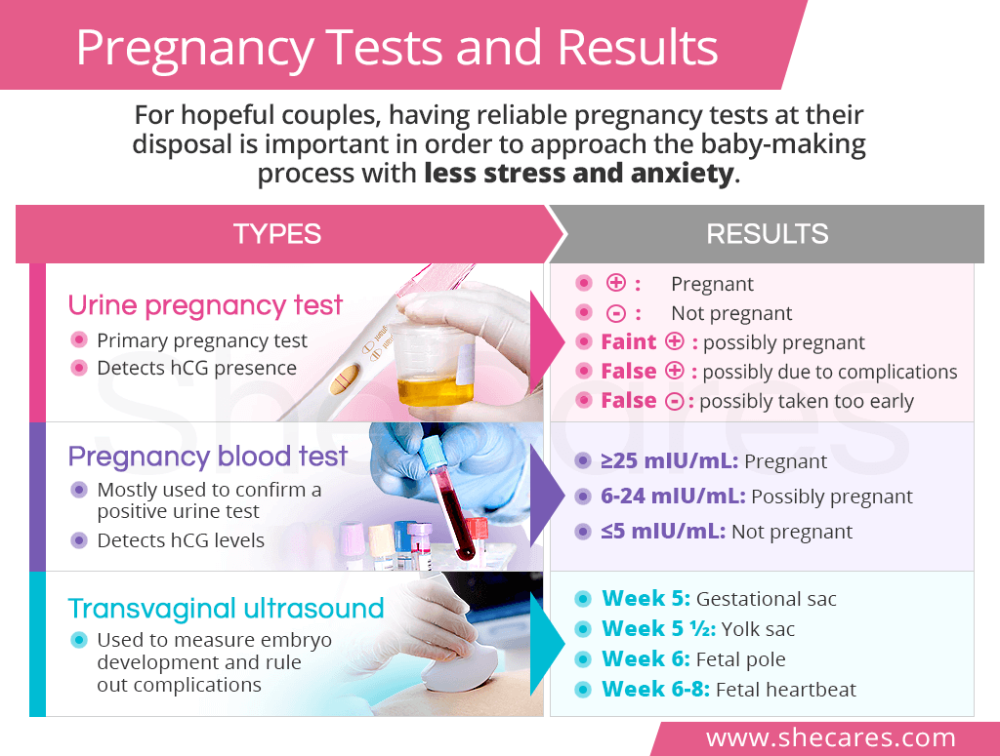 The "production" of this hormone is vital for the preservation and maintenance of pregnancy! It is hCG that controls the production of the main pregnancy hormones - estrogen and progesterone. With a serious lack of hCG, the fertilized egg is detached from the uterus, and menstruation occurs again - in other words, a spontaneous miscarriage occurs. Normally, the concentration of hCG in the blood of the expectant mother is constantly growing, reaching a maximum by the 10-11th week of pregnancy, then the concentration of hCG gradually decreases to remain unchanged until the very birth.
The "production" of this hormone is vital for the preservation and maintenance of pregnancy! It is hCG that controls the production of the main pregnancy hormones - estrogen and progesterone. With a serious lack of hCG, the fertilized egg is detached from the uterus, and menstruation occurs again - in other words, a spontaneous miscarriage occurs. Normally, the concentration of hCG in the blood of the expectant mother is constantly growing, reaching a maximum by the 10-11th week of pregnancy, then the concentration of hCG gradually decreases to remain unchanged until the very birth.
Testing for hCG during pregnancy plays a huge role.
Firstly, an analysis of the level of hCG in the blood can confirm that you will become a mother already 5-6 days after conception. This is much earlier and, most importantly, much more reliable than using conventional rapid tests.
Secondly, the test is needed to determine the exact gestational age. Very often, the expectant mother cannot give the exact date of conception, or she calls it, but incorrectly. At the same time, certain indicators of growth and development correspond to each period, deviations from the norm may indicate the occurrence of complications.
At the same time, certain indicators of growth and development correspond to each period, deviations from the norm may indicate the occurrence of complications.
Thirdly, the level of hCG in the blood can quite accurately “tell” whether your baby is developing correctly.
An unplanned increase in the level of hCG usually occurs with multiple pregnancy, preeclampsia, taking synthetic gestagens, diabetes in the expectant mother, and may also indicate some hereditary diseases in the baby (for example, Down's syndrome) and multiple malformations. An abnormally low level of hCG can be a sign of an ectopic and non-developing pregnancy, fetal growth retardation, the threat of spontaneous abortion, and chronic placental insufficiency.
However, do not rush to sound the alarm: increased or decreased values may also indicate that the gestational age was initially set incorrectly. Your doctor will help you interpret the test results correctly.
Placental lactogen and free estriol. Controlling the level of these hormones is extremely important for assessing the risk of developing hereditary chromosomal abnormalities in an unborn baby (these are Down, Edwards, Turner, Patau syndromes, neural tube defects, etc.)
Controlling the level of these hormones is extremely important for assessing the risk of developing hereditary chromosomal abnormalities in an unborn baby (these are Down, Edwards, Turner, Patau syndromes, neural tube defects, etc.)
Free estriol is "produced" by the placenta. This hormone improves blood flow through the vessels of the uterus, and also contributes to the development of the ducts of the mammary glands, preparing the body of the expectant mother to feed the baby. The level of free estriol changes in any pathological conditions:
- in fetoplacental insufficiency, when normal blood flow and nutrition in the placenta change;
- for fetal growth retardation;
- for suspected post-term pregnancy.
Placental lactogen (PL) is also “produced” by the placenta and can be detected in the blood of the expectant mother as early as 5-6 weeks of pregnancy. It reaches its maximum value by 37-38 weeks, then the hormone level gradually decreases. However, the level of PL must be monitored throughout the entire period of pregnancy - first of all, this is necessary to assess the condition of the placenta and timely diagnosis of placental insufficiency. A sharp decrease in the level of PL by more than 2 times (compared to the average level in accordance with the gestational age) may indicate a delay in fetal development. In this case, it is necessary to take emergency measures to prevent a decrease in the level of PL by 80 percent or more - this can lead to the death of the baby.
However, the level of PL must be monitored throughout the entire period of pregnancy - first of all, this is necessary to assess the condition of the placenta and timely diagnosis of placental insufficiency. A sharp decrease in the level of PL by more than 2 times (compared to the average level in accordance with the gestational age) may indicate a delay in fetal development. In this case, it is necessary to take emergency measures to prevent a decrease in the level of PL by 80 percent or more - this can lead to the death of the baby.
Pregnancy hormones
Estradiol and progesterone. Hormonal studies necessarily include tests for the level of progesterone and estradiol. It is they who take care of your unborn baby, maintaining the normal course of pregnancy, which is why they are called the main hormones of gestation (pregnancy).
Estradiol is produced by the ovaries and during pregnancy also by the placenta. During pregnancy, the level of the hormone rises sharply, and it is not surprising - estradiol is "responsible" for the normal course of pregnancy.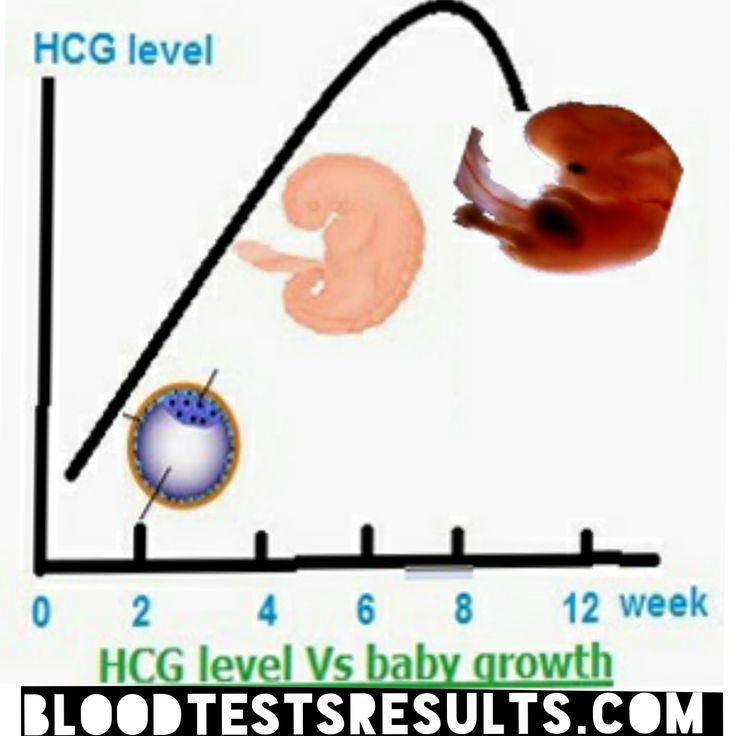 In the early stages, the concentration of this hormone evaluates the functioning of the placenta. A decrease in the level of estradiol indicates a serious threat of abortion.
In the early stages, the concentration of this hormone evaluates the functioning of the placenta. A decrease in the level of estradiol indicates a serious threat of abortion.
By the way, it is under the influence of this hormone that a woman feels a natural desire to “build a nest”, arrange everything and prepare for the birth of a baby. Before childbirth, the concentration of the hormone in the body of the expectant mother reaches its “peak”, which is also due to natural causes - estradiol, acting as the strongest natural pain reliever, helps to make the process of giving birth to a baby less painful.
Progesterone is also the main “pregnancy hormone”, the main task of which is to maintain pregnancy and create the necessary conditions for the development of the fetus. A normal level of progesterone is necessary for conception to occur. Together with estrogens, the hormone promotes the attachment of a fertilized egg to the endometrium and carefully reduces the increased tone of the uterus, preventing miscarriage. During the bearing of the baby, progesterone stimulates the growth and maturation of the mammary glands, “preparing” the body of the expectant mother for breastfeeding, and psychologically, it calms her down and morally supports her. Unfortunately, this hormone also has "side" effects that are familiar to every pregnant woman - this is increased drowsiness, nausea, frequent urination, soreness and swelling of the breast.
During the bearing of the baby, progesterone stimulates the growth and maturation of the mammary glands, “preparing” the body of the expectant mother for breastfeeding, and psychologically, it calms her down and morally supports her. Unfortunately, this hormone also has "side" effects that are familiar to every pregnant woman - this is increased drowsiness, nausea, frequent urination, soreness and swelling of the breast.
With a lack of progesterone, pregnancy can occur with serious complications. Hormone deficiency must be urgently replenished, otherwise the risk of non-developing pregnancy and miscarriage increases.
Important! Testing for estradiol and progesterone levels is carried out both during pregnancy and in preparation for the birth of a child, this is especially necessary in cases where a woman has already had a miscarriage.
Thyroid hormones
The normal functioning of the thyroid gland of the expectant mother plays an important role in the development of the baby.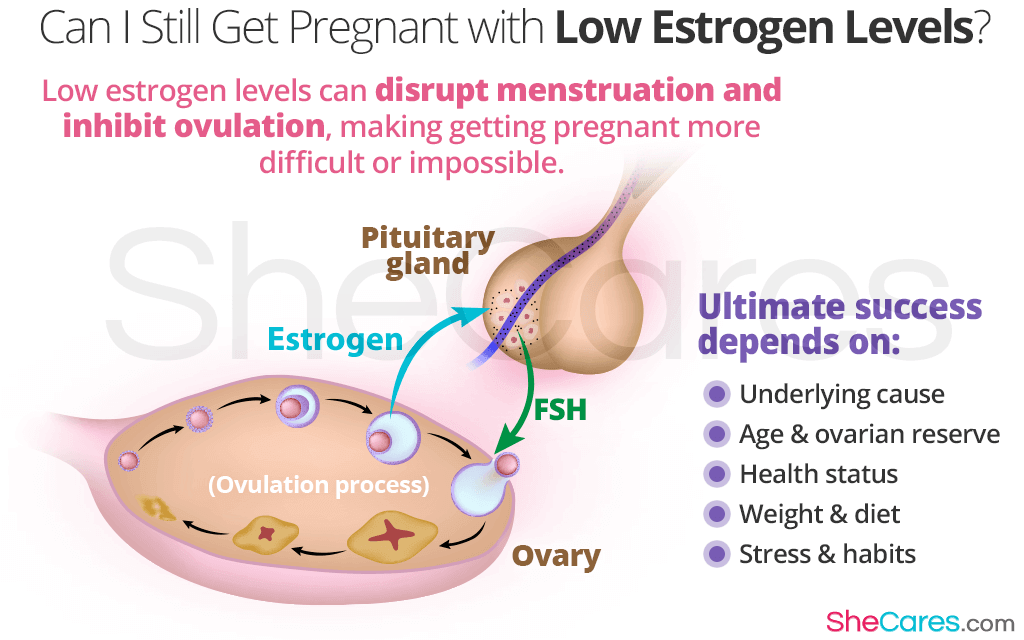 The corresponding hormones (TSH, T3 and T4) can also “tell” about the presence of hypo- or hyperfunction of the gland.
The corresponding hormones (TSH, T3 and T4) can also “tell” about the presence of hypo- or hyperfunction of the gland.
Motherhood hormones
The pituitary gland hormones (an endocrine gland located in the hypothalamic part of the brain) also play an indispensable role while expecting a baby. During childbirth, the pituitary gland releases the hormone oxytacin into the blood, which stimulates uterine contractions. And after childbirth, an active synthesis of the hormone prolactin begins, which is “responsible” for lactation. With a lack of prolactin, a woman simply would not be able to fully feed her baby with breast milk.
In addition, prolactin and oxytacin are also called "maternity hormones", because thanks to them, the mother's heart is filled with tenderness, she feels the pleasure of feeding and communicating with the child, which binds her to the baby even more. These hormones, in fact, provide a magical “transformation” of a woman into a mother - under their influence, priorities change dramatically, study, work, career and personal success fade into the background, and the main place in a woman’s heart is occupied by a small native creature. It is believed that the more a woman has these same "maternity hormones", the stronger her desire to constantly be with the baby, feel his warmth, take care of him. However, one should not expect that this “transformation” will happen as if by magic: normally, the level of hormones in a woman’s body changes gradually, so that her psyche has time to prepare for the changes without stress. The main thing during pregnancy is to make every effort to endure a strong and healthy baby.
It is believed that the more a woman has these same "maternity hormones", the stronger her desire to constantly be with the baby, feel his warmth, take care of him. However, one should not expect that this “transformation” will happen as if by magic: normally, the level of hormones in a woman’s body changes gradually, so that her psyche has time to prepare for the changes without stress. The main thing during pregnancy is to make every effort to endure a strong and healthy baby.
Hormonal studies during pregnancy / Nyanya.ru
02/27/2012
Nona Hovsepyan, Consultant Physician, Independent Laboratory INVITRO
Why is it necessary to control the level of hormones?
Hormones are amazing biologically active substances that affect not only the state of health, but also the inner world of a person. Nature provides that in the female body immediately after conception, special pregnancy hormones are activated, which not only help the baby to fully develop, but also set up the expectant mother for the desired motherhood, teach them to love the baby growing inside and get used to taking care of him.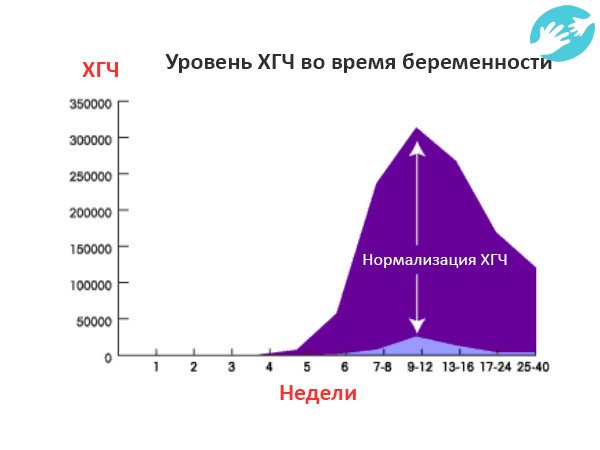
During the period of expectation of a baby, serious changes occur in the whole body of a woman, especially her hormonal levels. Changes occur throughout the endocrine system. The body of the future mother, completely rebuilding, creates the conditions for the bearing and normal development of the baby, and from the first days of pregnancy begins to prepare for childbirth.
All hormonal indicators of the future mother's body play a huge role - namely, they are the most important indicators of fetal development. Therefore, the level of hormones is necessarily monitored by the attending physician with the help of special examinations - prenatal screenings, which a woman needs to undergo at least 2 times: in the first trimester (11-12 weeks) and in the second trimester (16-19weeks). Let's figure out what indicators are included in this mandatory examination, what the increase or decrease in the level of a particular hormone indicates, and what their role is.
Hormones that the body of the unborn baby "produces"
HCG.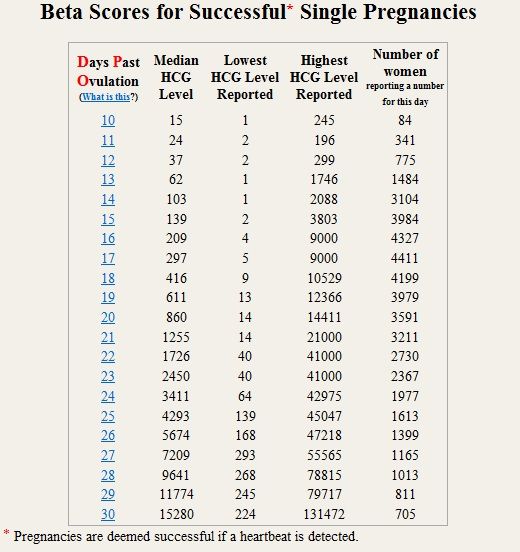 This is human chorionic gonadotropin, a hormone that is actively produced by the cells of the chorion (fetal membrane) immediately after it attaches to the wall of the uterus. The "production" of this hormone is vital for the preservation and maintenance of pregnancy! It is hCG that controls the production of the main pregnancy hormones - estrogen and progesterone. With a serious lack of hCG, the fertilized egg is detached from the uterus, and menstruation occurs again - in other words, a spontaneous miscarriage occurs. Normally, the concentration of hCG in the blood of the expectant mother is constantly growing, reaching a maximum by the 10-11th week of pregnancy, then the concentration of hCG gradually decreases to remain unchanged until the very birth.
This is human chorionic gonadotropin, a hormone that is actively produced by the cells of the chorion (fetal membrane) immediately after it attaches to the wall of the uterus. The "production" of this hormone is vital for the preservation and maintenance of pregnancy! It is hCG that controls the production of the main pregnancy hormones - estrogen and progesterone. With a serious lack of hCG, the fertilized egg is detached from the uterus, and menstruation occurs again - in other words, a spontaneous miscarriage occurs. Normally, the concentration of hCG in the blood of the expectant mother is constantly growing, reaching a maximum by the 10-11th week of pregnancy, then the concentration of hCG gradually decreases to remain unchanged until the very birth.
Testing for hCG during pregnancy plays a huge role.
Firstly, an analysis of the level of hCG in the blood can confirm that you will become a mother already 5-6 days after conception. This is much earlier and, most importantly, much more reliable than using conventional rapid tests.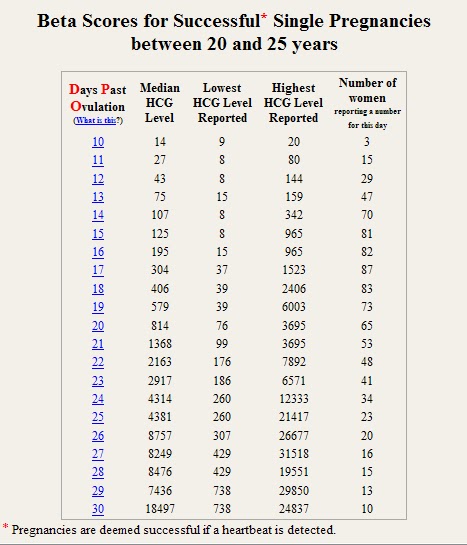
Secondly, the test is needed to determine the exact gestational age. Very often, the expectant mother cannot give the exact date of conception, or she calls it, but incorrectly. At the same time, certain indicators of growth and development correspond to each period, deviations from the norm may indicate the occurrence of complications.
Thirdly, the level of hCG in the blood can quite accurately “tell” whether your baby is developing correctly.
An unplanned increase in the level of hCG usually occurs with multiple pregnancy, preeclampsia, taking synthetic gestagens, diabetes in the expectant mother, and may also indicate some hereditary diseases in the baby (for example, Down's syndrome) and multiple malformations. An abnormally low level of hCG can be a sign of an ectopic and non-developing pregnancy, fetal growth retardation, the threat of spontaneous abortion, and chronic placental insufficiency.
However, do not rush to sound the alarm: increased or decreased values may also indicate that the gestational age was initially set incorrectly.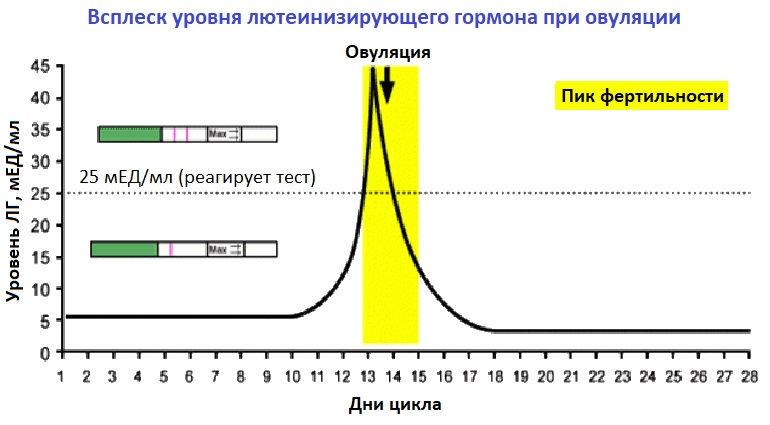 Your doctor will help you interpret the test results correctly.
Your doctor will help you interpret the test results correctly.
Placental lactogen and free estriol. Controlling the level of these hormones is extremely important for assessing the risk of developing hereditary chromosomal abnormalities in an unborn baby (these are Down, Edwards, Turner, Patau syndromes, neural tube defects, etc.)
Free estriol is "produced" by the placenta. This hormone improves blood flow through the vessels of the uterus, and also contributes to the development of the ducts of the mammary glands, preparing the body of the expectant mother to feed the baby. The level of free estriol changes in any pathological conditions:
- with fetoplacental insufficiency, when the normal blood flow and nutrition in the placenta changes;
- for fetal growth retardation;
- for suspected post-term pregnancy.
Placental lactogen (PL) is also “produced” by the placenta and can be detected in the blood of the expectant mother as early as 5-6 weeks of pregnancy. It reaches its maximum value by 37-38 weeks, then the hormone level gradually decreases. However, the level of PL must be monitored throughout the entire period of pregnancy - first of all, this is necessary to assess the condition of the placenta and timely diagnosis of placental insufficiency. A sharp decrease in the level of PL by more than 2 times (compared to the average level in accordance with the gestational age) may indicate a delay in fetal development. In this case, it is necessary to take emergency measures to prevent a decrease in the level of PL by 80 percent or more - this can lead to the death of the baby.
It reaches its maximum value by 37-38 weeks, then the hormone level gradually decreases. However, the level of PL must be monitored throughout the entire period of pregnancy - first of all, this is necessary to assess the condition of the placenta and timely diagnosis of placental insufficiency. A sharp decrease in the level of PL by more than 2 times (compared to the average level in accordance with the gestational age) may indicate a delay in fetal development. In this case, it is necessary to take emergency measures to prevent a decrease in the level of PL by 80 percent or more - this can lead to the death of the baby.
Pregnancy hormones
Estradiol and progesterone. Hormonal studies necessarily include tests for the level of progesterone and estradiol. It is they who take care of your unborn baby, maintaining the normal course of pregnancy, which is why they are called the main hormones of gestation (pregnancy).
Estradiol is produced by the ovaries and during pregnancy also by the placenta..jpg) During pregnancy, the level of the hormone rises sharply, and it is not surprising - estradiol is "responsible" for the normal course of pregnancy. In the early stages, the concentration of this hormone evaluates the functioning of the placenta. A decrease in the level of estradiol indicates a serious threat of abortion.
During pregnancy, the level of the hormone rises sharply, and it is not surprising - estradiol is "responsible" for the normal course of pregnancy. In the early stages, the concentration of this hormone evaluates the functioning of the placenta. A decrease in the level of estradiol indicates a serious threat of abortion.
By the way, it is under the influence of this hormone that a woman feels a natural desire to “build a nest”, arrange everything and prepare for the birth of a baby. Before childbirth, the concentration of the hormone in the body of the expectant mother reaches its “peak”, which is also due to natural causes - estradiol, acting as the strongest natural pain reliever, helps to make the process of giving birth to a baby less painful.
Progesterone is also the main “pregnancy hormone”, the main task of which is to maintain pregnancy and create the necessary conditions for the development of the fetus. A normal level of progesterone is necessary for conception to occur. Together with estrogens, the hormone promotes the attachment of a fertilized egg to the endometrium and carefully reduces the increased tone of the uterus, preventing miscarriage. During the bearing of the baby, progesterone stimulates the growth and maturation of the mammary glands, “preparing” the body of the expectant mother for breastfeeding, and psychologically, it calms her down and morally supports her. Unfortunately, this hormone also has "side" effects that are familiar to every pregnant woman - this is increased drowsiness, nausea, frequent urination, soreness and swelling of the breast.
Together with estrogens, the hormone promotes the attachment of a fertilized egg to the endometrium and carefully reduces the increased tone of the uterus, preventing miscarriage. During the bearing of the baby, progesterone stimulates the growth and maturation of the mammary glands, “preparing” the body of the expectant mother for breastfeeding, and psychologically, it calms her down and morally supports her. Unfortunately, this hormone also has "side" effects that are familiar to every pregnant woman - this is increased drowsiness, nausea, frequent urination, soreness and swelling of the breast.
With a lack of progesterone, pregnancy can occur with serious complications. Hormone deficiency must be urgently replenished, otherwise the risk of non-developing pregnancy and miscarriage increases.
Important! Testing for estradiol and progesterone levels is carried out both during pregnancy and in preparation for the birth of a child, this is especially necessary in cases where a woman has already had a miscarriage.
Thyroid hormones
The normal functioning of the thyroid gland of the expectant mother plays an important role in the development of the baby. The corresponding hormones (TSH, T3 and T4) can also “tell” about the presence of hypo- or hyperfunction of the gland.
Maternity hormones
Pituitary hormones (an endocrine gland located in the hypothalamic part of the brain) also play an indispensable role while waiting for a baby. During childbirth, the pituitary gland releases the hormone oxytacin into the blood, which stimulates uterine contractions. And after childbirth, an active synthesis of the hormone prolactin begins, which is “responsible” for lactation. With a lack of prolactin, a woman simply would not be able to fully feed her baby with breast milk.
In addition, prolactin and oxytacin are also called "maternity hormones", because thanks to them, the mother's heart is filled with tenderness, she feels the pleasure of feeding and communicating with the child, which binds her to the baby even more.