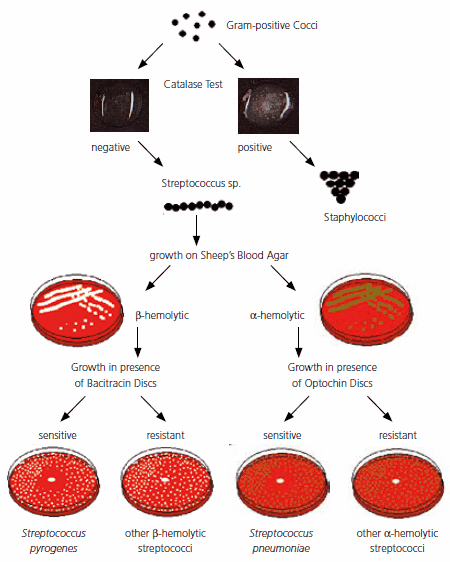
Group b streptococci test
Group B strep disease - Symptoms and causes
Overview
Group B strep (streptococcus) is a common bacterium often carried in the intestines or lower genital tract. The bacterium is usually harmless in healthy adults. In newborns, however, it can cause a serious illness known as group B strep disease.
Group B strep can also cause dangerous infections in adults with certain chronic medical conditions, such as diabetes or liver disease. Older adults are at increased risk of illness due to group B strep, too.
If you're a healthy adult, there's nothing you need to do about group B strep. If you're pregnant, get a group B strep screening test during your third trimester. If you have group B strep, antibiotic treatment during labor can protect your baby.
Products & Services
- Book: Mayo Clinic Family Health Book, 5th Edition
- Newsletter: Mayo Clinic Health Letter — Digital Edition
Symptoms
Infants
Most babies born to women carrying group B strep are healthy. But the few who are infected by group B strep during labor can become critically ill.
In infants, illness caused by group B strep can be within six hours of birth (early onset) — or weeks or months after birth (late onset).
Signs and symptoms might include:
- Fever
- Low body temperature
- Difficulty feeding
- Sluggishness, limpness or weak muscle tone
- Difficulty breathing
- Irritability
- Jitteriness
- Seizures
- Rash
- Jaundice
Adults
Many adults carry group B strep in their bodies — usually in the bowel, vagina, rectum, bladder or throat — and have no signs or symptoms.
In some cases, however, group B strep can cause a urinary tract infection or other more-serious infections. Signs and symptoms of infections that may be caused by group B strep include the following.
Urinary tract infection
- A strong, persistent urge to urinate
- A burning sensation or pain when urinating
- Passing frequent, small amounts of urine
- Urine that appears red, bright pink or cola colored — a sign of blood in the urine
- Pelvic pain
Blood infection (bacteremia)
- Fever
- Chills
- Confusion or lack of alertness
Pneumonia
- Fever
- Chills
- Cough
- Shortness of breath
- Chest pain when you breathe or cough
Skin or soft-tissue infection
- Swelling, warmth or redness in the area of the infection
- Pain in the area of the infection
- Lesions with pus or drainage
Bone or joint infection
- Fever
- Chills
- Swelling, warmth or redness over the area of the infection
- Pain in the area of the infection
- Stiffness or inability to use a limb or joint
When to see a doctor
If you have signs or symptoms of group B strep infection — particularly if you're pregnant, you have a chronic medical condition or you're older than 65 — contact your doctor right away.
If you notice your infant has signs or symptoms of group B strep disease, contact your baby's doctor immediately.
Request an Appointment at Mayo Clinic
From Mayo Clinic to your inbox
Sign up for free, and stay up to date on research advancements, health tips and current health topics, like COVID-19, plus expertise on managing health.
To provide you with the most relevant and helpful information, and understand which
information is beneficial, we may combine your email and website usage information with
other information we have about you. If you are a Mayo Clinic patient, this could
include protected health information. If we combine this information with your protected
health information, we will treat all of that information as protected health
information and will only use or disclose that information as set forth in our notice of
privacy practices.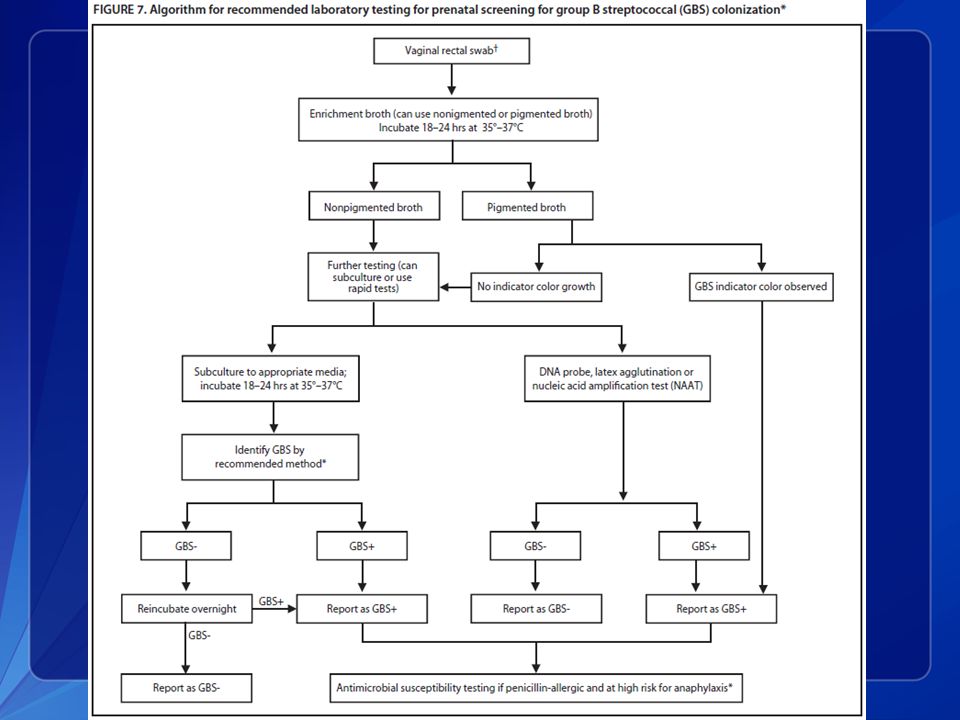 You may opt-out of email communications at any time by clicking on
the unsubscribe link in the e-mail.
You may opt-out of email communications at any time by clicking on
the unsubscribe link in the e-mail.
Causes
Many healthy people carry group B strep bacteria in their bodies. You might carry the bacteria in your body for a short time — it can come and go — or you might always have it. Group B strep bacteria aren't sexually transmitted, and they're not spread through food or water. How the bacteria are spread to anyone other than newborns isn't known.
Group B strep can spread to a baby during a vaginal delivery if the baby is exposed to — or swallows — fluids containing group B strep.
Risk factors
Infants
An infant is at increased risk of developing group B strep disease if:
- The mother carries group B strep in her body
- The baby is born prematurely (earlier than 37 weeks)
- The mother's water breaks 18 hours or more before delivery
- The mother has an infection of the placental tissues and amniotic fluid (chorioamnionitis)
- The mother has a urinary tract infection during the pregnancy
- The mother's temperature is greater than 100.
 4 F (38 C) during labor
4 F (38 C) during labor - The mother previously delivered an infant with group B strep disease
Adults
Adults age 65 and older are at increased risk of group B strep. You're also at increased risk of if you have a condition that impairs your immune system or other serious diseases, including the following:
- Diabetes
- HIV infection
- Liver disease
- Heart disease
- Cancer or history of cancer
Complications
Group B strep infection can lead to life-threatening disease in infants, including:
- Pneumonia
- Inflammation of the membranes and fluid surrounding the brain and spinal cord (meningitis)
- Infection in the bloodstream (bacteremia)
If you're pregnant, group B strep can cause the following:
- Urinary tract infection
- Infection of the placenta and amniotic fluid (chorioamnionitis)
- Infection of the membrane lining the uterus (endometritis)
- Bacteremia
If you're an older adult or you have a chronic health condition, group B strep bacteria can lead to any of the following conditions:
- Skin infection
- Bacteremia
- Urinary tract infection
- Pneumonia
- Bone and joint infections
- Infection of the heart valves (endocarditis)
- Meningitis
Prevention
If you're pregnant, the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists recommends a group B strep screening during weeks 36 to 37 of pregnancy. Your doctor will take swab samples from your vagina and rectum and send them to a lab for testing.
Your doctor will take swab samples from your vagina and rectum and send them to a lab for testing.
A positive test indicates that you carry group B strep. It doesn't mean that you're ill or that your baby will be affected, but that you're at increased risk of passing the bacteria to your baby.
To prevent group B bacteria from spreading to your baby during labor or delivery, your doctor can give you an IV antibiotic — usually penicillin or a related drug — when labor begins.
If you're allergic to penicillin or related drugs, you might receive clindamycin or vancomycin as an alternative. Because the effectiveness of these alternatives is not well understood, your baby will be monitored for up to 48 hours.
Taking oral antibiotics ahead of time won't help because the bacteria can return before labor begins.
Antibiotic treatment during labor is also recommended if you:
- Have a urinary tract infection
- Delivered a previous baby with group B strep disease
- Develop a fever during labor
- Haven't delivered your baby within 18 hours of your water breaking
- Go into labor before 37 weeks and haven't been tested for group B strep
Vaccine in development
Although it's not available yet, researchers are working on a group B strep vaccine that could help prevent group B strep infections in the future.
By Mayo Clinic Staff
Related
Products & Services
Strep B Test: MedlinePlus Medical Test
What is a group B strep test?
Strep B, also known as group B strep (GBS), is a type of bacteria commonly found in the digestive tract, urinary tract, and genital area. It rarely causes symptoms or problems in adults but can be deadly to newborns.
In women, GBS is mostly found in the vagina and rectum. So a pregnant woman who is infected can pass the bacteria to her baby during labor and delivery. GBS can cause pneumonia, meningitis, and other serious illnesses in a baby. GBS infections are the leading cause of death and disability in newborns.
A group B strep test checks for GBS bacteria. If the test shows that a pregnant woman has GBS, she can take antibiotics during labor to protect her baby from infection.
Other names: group B streptococcus, group B beta-hemolytic streptococcus, streptococcus agalactiae, beta-hemolytic strep culture
What is it used for?
A group B strep test is most often used to look for GBS bacteria in pregnant women. Most pregnant women are tested as part of routine prenatal screening. It may also be used to test infants who show signs of infection.
Most pregnant women are tested as part of routine prenatal screening. It may also be used to test infants who show signs of infection.
Why do I need a group B strep test?
You may need a strep B test if you are pregnant. The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists recommends GBS testing for all pregnant women. Testing is usually done in the 36th or 37th week of pregnancy. If you go into labor earlier than 36 weeks, you may be tested at that time.
A baby may need a group B strep test if he or she has symptoms of infection. These include:
- High fever
- Trouble with feeding
- Trouble breathing
- Lack of energy (hard to wake up)
What happens during a group B strep test?
If you are pregnant, your health care provider may order a swab test or a urine test.
For a swab test, you will lie on your back on an exam table. Your health care provider will use a small cotton swab to take a sample of cells and fluids from your vagina and rectum.
For a urine test, you will most likely be told to use the "clean catch method" to ensure your sample is sterile. It includes the following steps.
- Wash your hands.
- Clean your genital area with a cleansing pad given to you by your provider. To clean, open your labia and wipe from front to back.
- Start to urinate into the toilet.
- Move the collection container under your urine stream.
- Collect at least an ounce or two of urine into the container, which should have markings to indicate the amounts.
- Finish urinating into the toilet.
- Return the sample container as instructed by your health care provider.
If your baby needs testing, a provider may do a blood test or a spinal tap.
For a blood test, a health care professional will use a small needle to take a blood sample from your baby's heel. After the needle is inserted, a small amount of blood will be collected into a test tube or vial. Your baby may feel a little sting when the needle goes in or out.
Your baby may feel a little sting when the needle goes in or out.
A spinal tap, also known as a lumbar puncture, is a test that collects and looks at spinal fluid, the clear liquid that surrounds the brain and spinal cord. During the procedure:
- A nurse or other health care provider will hold your baby in a curled-up position.
- A health care provider will clean your baby's back and inject an anesthetic into the skin, so your baby won't feel pain during the procedure. The provider may put a numbing cream on your baby's back before this injection.
- The provider may also give your baby a sedative and/or pain reliever to help him or her better tolerate the procedure.
- Once the area on the back is completely numb, your provider will insert a thin, hollow needle between two vertebrae in the lower spine. Vertebrae are the small backbones that make up the spine.
- The provider will withdraw a small amount of cerebrospinal fluid for testing.
 This will take about five minutes.
This will take about five minutes.
Will I need to do anything to prepare for the test?
You don't any special preparations for group B strep tests.
Are there any risks to the test?
There is no risk to you from a swab or urine test. Your baby may have slight pain or bruising after a blood test, but that should go away quickly. Your baby will likely feel some pain after a spinal tap, but that shouldn't last too long. There is also a small risk of infection or bleeding after a spinal tap.
What do the results mean?
If you are pregnant and results show you have GBS bacteria, you will be given antibiotics intravenously (directly to your veins) during labor, at least four hours before delivery. This will prevent you from passing the bacteria to your baby. Taking antibiotics earlier in your pregnancy is not effective, because the bacteria can grow back very quickly. It's also more effective to take antibiotics through your vein, rather than by mouth.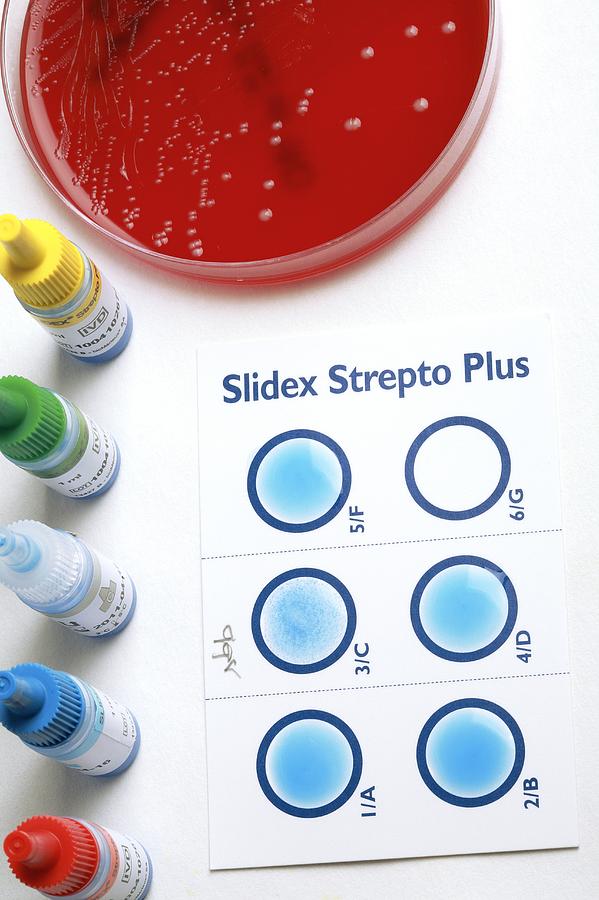
You may not need antibiotics if you are having a planned delivery by Cesarean section (C-section). During a C-section, a baby is delivered through the mother's abdomen rather than vaginally. But you still should be tested during pregnancy because you may go into labor before your scheduled C-section.
If your baby's results show a GBS infection, he or she will be treated with antibiotics. If your provider suspects a GBS infection, he or she may treat your baby before test results are available. This is because GBS can cause serious illness or death.
If you have questions about your results or your baby's results, talk to your health care provider.
Learn more about laboratory tests, reference ranges, and understanding results.
Is there anything else I need to know about a group B strep test?
Strep B is one type of strep bacteria. Other forms of strep cause different types of infections. These include strep A, which causes strep throat, and streptococcus pneumoniae, which causes the most common type of pneumonia.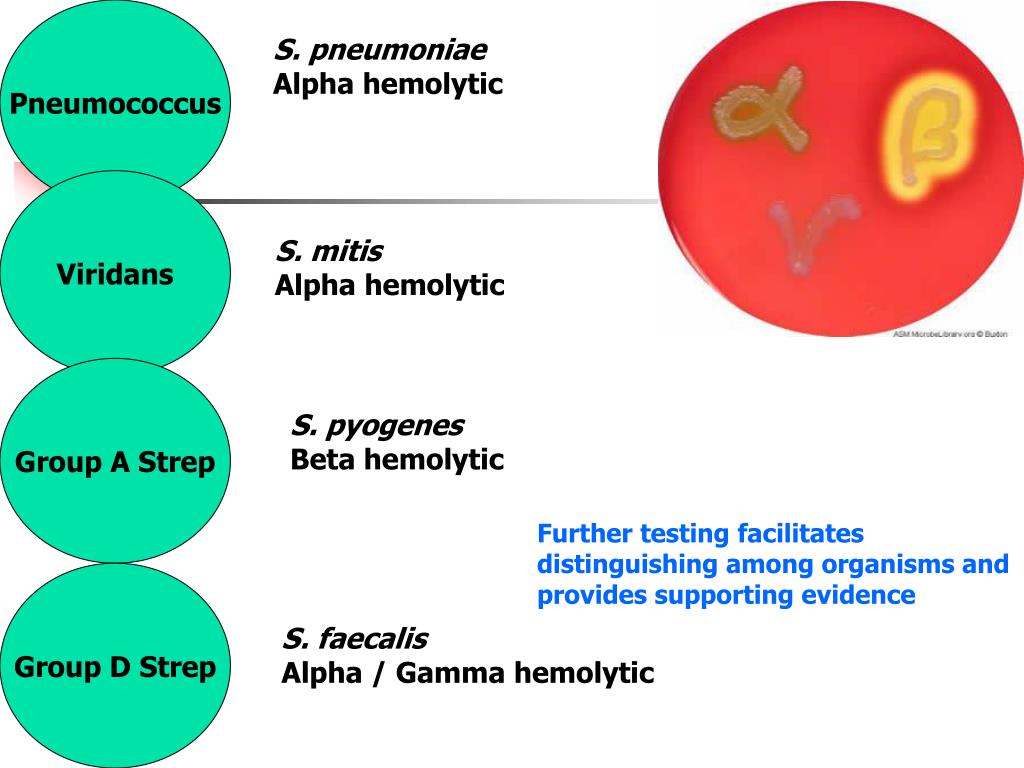 Streptococcus pneumonia bacteria can also cause infections of the ear, sinuses, and bloodstream.
Streptococcus pneumonia bacteria can also cause infections of the ear, sinuses, and bloodstream.
References
- ACOG: The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists [Internet]. Washington D.C.: American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists; c2019. Group B Strep and Pregnancy; 2019 Jul [cited 2019 Nov 15]; [about 3 screens]. Available from: https://www.acog.org/Patients/FAQs/Group-B-Strep-and-Pregnancy
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention [Internet]. Atlanta: U.S. Department of Health and Human Services; Group B Strep (GBS): Prevention; [cited 2019 Nov 15]; [about 4 screens]. Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/groupbstrep/about/prevention.html
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention [Internet]. Atlanta: U.S. Department of Health and Human Services; Group B Strep (GBS): Signs and Symptoms; [cited 2019 Nov 15]; [about 4 screens]. Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/groupbstrep/about/symptoms.html
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention [Internet].
 Atlanta: U.S. Department of Health and Human Services; Streptococcus Laboratory: Streptococcus pneumoniae; [cited 2019 Nov 15]; [about 3 screens]. Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/streplab/pneumococcus/index.html
Atlanta: U.S. Department of Health and Human Services; Streptococcus Laboratory: Streptococcus pneumoniae; [cited 2019 Nov 15]; [about 3 screens]. Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/streplab/pneumococcus/index.html - Centers for Disease Control and Prevention [Internet]. Atlanta: U.S. Department of Health and Human Services; Travelers' Health: Pneumococcal Disease; [updated 2014 Aug 5; cited 2019 Nov 15]; [about 3 screens]. Available from: https://wwwnc.cdc.gov/travel/diseases/pneumococcal-disease-streptococcus-pneumoniae
- Intermountain Healthcare: Primary Children's Hospital [Internet]. Salt Lake City: Intermountain Healthcare; c2019. Lumbar Puncture in a Newborn; [cited 2019 Nov 15]; [about 4 screens]. Available from: https://intermountainhealthcare.org/ext/Dcmnt?ncid=520190573
- Lab Tests Online [Internet]. Washington D.C.: American Association for Clinical Chemistry; c2001–2019. Blood Culture; [updated 2019 Sep 23; cited 2019 Nov 15]; [about 2 screens]. Available from: https://labtestsonline.
 org/tests/blood-culture
org/tests/blood-culture - Lab Tests Online [Internet]. Washington D.C.: American Association for Clinical Chemistry; c2001–2019. Prenatal Group B Strep (GBS) Screening; [updated 2019 May 6; cited 2019 Nov 15]; [about 2 screens]. Available from: https://labtestsonline.org/tests/prenatal-group-b-strep-gbs-screening
- Lab Tests Online [Internet]. Washington D.C.: American Association for Clinical Chemistry; c2001–2019. Urine Culture; [updated 2019 Sep 18; cited 2019 Nov 15]; [about 2 screens]. Available from: https://labtestsonline.org/tests/urine-culture
- Michigan Medicine: University of Michigan [Internet]. Ann Arbor (MI): Regents of the University of Michigan; c1995–2021. Group B Streptococcal Infections in Newborns[cited 2021 Aug 6]; [about 3 screens]. Available from: https://www.uofmhealth.org/health-library/zp3014spec
- University of Rochester Medical Center [Internet]. Rochester (NY): University of Rochester Medical Center; c2019. Health Encyclopedia: Group B Streptococcus Infection in Babies; [cited 2019 Nov 15]; [about 2 screens].
 Available from: https://www.urmc.rochester.edu/encyclopedia/content.aspx?contenttypeid=90&contentid=P02363
Available from: https://www.urmc.rochester.edu/encyclopedia/content.aspx?contenttypeid=90&contentid=P02363 - University of Rochester Medical Center [Internet]. Rochester (NY): University of Rochester Medical Center; c2019. Health Encyclopedia: Pneumonia; [cited 2019 Nov 15]; [about 2 screens]. Available from: https://www.urmc.rochester.edu/encyclopedia/content.aspx?contenttypeid=85&contentid=P01321
- WHO Guidelines on Drawing Blood: Best Practices in Phlebotomy [Internet]. Geneva (SUI): World Health Organization; c2010. 6. Paediatric and neonatal blood sampling; [cited 2019 Nov 15]; [about 3 screens]. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK138647
RED rapid test Streptococcus group A
Express test immunochromatographic RED for the detection of group A streptococcus in respiratory secretions. Can be used at home. There are 10 tests in the set.
FUNCTION
The "RED streptococcus A" test is intended for in vitro one-stage rapid qualitative detection of group A streptococci in secretions from the human larynx.
SUMMARY
Group A Streptococcus (Streptococcus pyogenes) is a genus of spherical or ovoid asporogenic Gram-positive facultative anaerobic bacteria. Streptococci live in the respiratory and digestive tracts, especially in the mouth, nose, and large intestine.
Streptococcal infection can present as a moderate skin infection or sore throat, and can cause severe, life-threatening injuries such as toxic shock syndrome (multiple organ damage), necrosis of fasciitis (soft tissue disease).
The main routes of transmission of streptococci are contact (putting into the mouth with dirty hands) and airborne droplets, as well as through infected food stored at room temperature (for example, milk).
METHOD PRINCIPLE
The determination is based on the principle of immunochromatographic analysis. The analyzed sample of liquid biological material is absorbed by the absorbing area of the test strip. If there are group A streptococcal cells in the sample, they react with specific monoclonal antibodies against group A streptococci labeled with colored particles applied to the starting zone and continue to move with the fluid flow.
In the assay zone of the test strip, interaction occurs with specific monoclonal antibodies against group A streptococci immobilized on the membrane surface, forming stained immune complexes.
In the control zone of the test strip, a specific colored immune complex is formed regardless of the presence of group A streptococcal cells in the tested biological material. (red analytical, marked with the letter T, and blue control, marked with the letter C), indicating a positive test result.
If there is no group A streptococcal cells in the test sample, a single blue control line (C) will form on the test strip, indicating a negative test result.
COMPOSITION
One set of tests "RED streptococcus A" includes:
- immunochromatographic test strips "RED streptococcus A" in white plastic cassettes - 10 pcs.;
- vial with dropper cap containing pink reagent A - 1 pc.;
- vial with dropper cap containing colorless reagent B – 1 pc.
 ;
; - disposable plastic test tubes - 10 pcs.;
- sterile cotton swabs on the probe - 10 pcs.;
- disposable plastic pipettes - 10 pcs.;
- adhesive-based labels for labeling tubes - 10 pcs.;
- instructions for use of the test "RED streptococcus A" - 1 pc.
- Test strip cassettes and disposable plastic pipettes individually packaged
- aluminum foil vacuum packs containing silica gel sachets.
The RED streptococcus A test kit is packed in a cardboard box.
ANALYZED SPECIMENS
Freshly collected biological material (discharge from the human larynx) that does not contain preservatives.
Samples of secretions from the larynx before determination can be stored at a temperature of 2–4 ° C for no more than 24 hours.
Prior to analysis, biological samples should be brought to room temperature.
SAMPLE PREPARATION
1. Using a sterile cotton swab, take a smear from the surface of the tonsils and / or the back wall of the larynx,
Using a sterile cotton swab, take a smear from the surface of the tonsils and / or the back wall of the larynx,
avoiding contact with teeth, gums, tongue, and cheeks (Figure 1-1).
2. Add 5 drops of pink reagent A (Fig. 1-2) and 5 drops of
to a disposable plastic tube colorless reagent B (Fig. 1-3). The solution will turn pale yellow.
3. Place the swab with the sample into the test tube. Wash off the sample by swirling the swab against the walls of the tube at least 10 times. Leave the swab in the test tube for 1 min. Squeeze the liquid out of the swab by squeezing it with the walls of the test tube (Fig. 1-4). Throw away the swab.
TESTING
Analyzed samples of secretions from the larynx and tests "RED streptococcus A" should be brought to room temperature (15-25 ° C) before analysis.
4. Immediately before starting the analysis, open the package of the "RED streptococcus A" test, tearing it along the slit. Remove the test strip cassette and place it on a flat horizontal surface.
Remove the test strip cassette and place it on a flat horizontal surface.
5. Using a disposable plastic pipette, add 4 drops (approximately 100 µl) of the liquid sample to the round window of the cassette marked with the letter S (Fig. 2). For each sample, it is necessary to use a separate tube, a separate pipette and a separate Streptococcus A RED test.
6. After 10 minutes, visually evaluate the result of the reaction.
INTERPRETATION OF THE RESULTS
The detection of one blue control line (C) in the test window of the cassette indicates a negative result of the analysis, i.e. indicates the absence of group A streptococcal cells in the analyzed sample (Fig. 3-1).
The detection of two parallel colored lines (blue and red) in the test window of the cassette indicates a positive result of the analysis, i.e. indicates the presence of group A streptococcal cells in the analyzed sample (Fig. 3-2). The intensity of the red analytical line (T) in the test window of the cassette may vary depending on the concentration of group A streptococcal cells in the sample.
In cases where no colored line is formed in the test window of the cassette, or only a red analytical line (T) is formed, the analysis result is considered invalid (Fig. 3-3). In this case, the analysis should be repeated using another test "RED streptococcus A".
The results obtained using the RED streptococcus A test are preliminary. To confirm them, it is necessary to conduct additional studies of samples using alternative methods.
Streptatest rapid test for the diagnosis of B-hemolytic streptococcus group a 2 pcs.
Characteristics
- Form of release
- Test for the diagnosis of beta-hemolytic streptococcus - aluminum foil sachets with test strips - 2 pcs per pack.
- Country of manufacture
- France
- Manufacturer0113
- Keep out of the reach of children.
- 2.2 CE marked swabs.
- 3.2 extraction tubes.
- 4.
 2 CE marked tongue holders.
2 CE marked tongue holders. - 5. Jar with extractive reagent A (sodium nitrite 2M), 10 ml.
- 6. Jar with extraction reagent B (acetic acid 0.4M), 10 ml.
- 7. Abstract
Description
- Streptatest is a universal express test for a doctor and a patient, which allows diagnosing the presence or absence of a dangerous group A beta-hemolytic streptococcus in the throat within 5 minutes. - diagnosis of streptococcus will help protect against unreasonable treatment, will not allow the passage of streptococcal tonsillitis, and most importantly - will prevent the development of severe complications!
- Streptatest is an immunochromatographic membrane test that works according to the sandwich principle.
Indications
- Inflammation of the mucous membrane and lymphoid tissue of the pharynx.
- If you suspect angina, pharyngitis, scarlet fever.
Dosage and administration
- 1. Preparation of the reagent (drop 4 drops from the red vial into the extraction tube).
- 2. Preparation of the reagent (drop 4 drops from the yellow bottle into the extraction bottle).
- 3.Sampling (take a smear from the surface of the tonsils and the back of the throat without touching the gums, tongue, palate).
- 4. Place the swab with the material in the test tube, swirl 10 times and leave for 1 minute.
- 5. Squeeze the cotton swab into the solution.
- 6. Dip the test strip with the arrows down into the solution for 5 minutes, read the results.
Special instructions
- Precautions
- Since extractants A and B are potentially hazardous, in case of improper use and/or contact with skin, eyes, immediately rinse the affected area with plenty of water, ingestion of reagent A - provoke vomiting, then drink plenty of water; if reagent B is swallowed, rinse mouth, then drink plenty of water.