Fruits to avoid during pregnancy first trimester
What Should Expecting Mothers Eat
- Home
- Pregnancy Prenatal Care
- Fruits During Pregnancy: The Good, the Bad, and the Unhealthy
It's wise for expecting mothers to watch what they eat, but what about fruit? All About Women physicians discuss which fruits to eat during your pregnancy, and which fruits to avoid.
When it comes to a pregnancy diet, it can feel like the restrictions never end: no caffeine, seafood, deli meat, etc. Women should certainly be cautious about what goes into their bodies because it's very possible that a baby's growth and development could be negatively affected by certain foods and drinks.
Fruits can provide women with a plethora of healthy vitamins and minerals that can be very beneficial for a newborn child; however, some fruits carry risks when they are eaten during a pregnancy.
Read on to learn which fruits should and should not be eaten while you are pregnant.
The Benefits of Fruit
Fruits are super, that's for sure! They provide vitamins and minerals that can help your baby along throughout your pregnancy. Pregnant mothers require foods rich in fiber, potassium, vitamin A and C, folic acid, and other nutrients in order to keep their bodies strong until baby arrives, and fruits can be an excellent and easy source.
Good Fruits for Pregnancy
Without further ado, here are some wonderful healthy fruits to eat while pregnant.
Apples
Apples are very high in fiber, which can help regulate a woman's digestion and prevent hemorrhoids – a common issue that many pregnant women face.
Citrus
Citrus fruits like lemons and oranges are chock full of vitamin C. Vitamin C is responsible for helping your baby's bones grow properly. Citrus can also help with a woman's digestion and deter morning sickness during pregnancy.
Bananas
Bananas are a wonderful source of potassium. Potassium can help greatly with regulating the fluid and blood pressure in a woman's body and preventing leg cramps or pain during the later stages of a pregnancy.
Kiwis
Kiwis contain a high level of folic acid and are delicious besides. Folic acid actively helps prevent fetal growth defects. In addition, kiwi helps expectant mothers absorb iron more efficiently, and this can prove essential for ensuring that a mother's blood carries enough oxygen to her baby.
Watermelon
Watermelon has it all: high levels of vitamins A, C and B6, as well as potassium for cramps and magnesium. Magnesium helps muscles relax, which can prevent premature contractions during pregnancy. In addition, watermelon can fight morning sickness, reduce heartburn, and prevent dehydration.
Berries
This includes strawberries, blueberries, raspberries, and pretty much any other berry your heart desire! Berries are rich in antioxidants that can help prevent serious diseases for both mother and baby.
Other Healthy Fruits
Besides those already listed, there are tons of healthy fruits that can give baby the nutrients he or she needs in the womb. They include:
- Mangoes
- Cantaloupe
- Cherries
- Pomegranates
- Apricots
Ask your doctor more about which fruits can be beneficial to you during your pregnancy and the recommended serving suggestions.
Bad Fruits for Pregnancy
This list is much shorter than the last, but there are a few fruits that do pose a potential risk to expectant mothers and unborn children.
Pineapple
Pineapples are shown to contain bromelain, which can cause the cervix to soften and result in an early labor if eaten in large quantities. Many doctors believe pineapple is safe when eaten in small portions, and the fruit contains many helpful nutrients that could prove beneficial. To be safe, however, it's recommended to limit pineapple intake to the first trimester of pregnancy.
Papaya
Papaya, when ripe, is actually pretty safe for expectant mothers to include in their pregnancy diets. However, an unripe papaya contains latex, which can cause premature contractions to occur. In addition, even ripe papaya skin and seeds are unsafe to eat. Many choose to cut out papaya altogether while pregnant to avoid these risks.
Grapes
This one is a bit up in the air, but it is sometimes advised that women avoid grapes during their pregnancy. This is because grapes contain resveratrol, a toxic compound that could cause poisoning or other pregnancy complications. Like pineapple, however, when eaten in moderation, grapes typically prove to be a low risk food.
Final Thoughts
- ALWAYS wash fruit before consuming. Any fruit has the potential to have pesticide residue or soil remaining from harvest, which can be unhealthy for both mother and child. For this reason, many mothers opt for organic produce, but it is still necessary to wash.

- Many fruits are known to have a high sugar content, which can be a problem for women with a risk of gestational diabetes. For this reason, it's recommended to completely avoid fruit juices and keep fruit intake to a small serving size in order to keep getting the nutrients without the excess sugars.
- If you have any questions about your pregnancy diet, do not hesitate to talk to your doctor about recommendations and ways to get the key nutrients to help your baby grow properly over your pregnancy. It's always better to be safe than sorry!
If you have questions about your pregnancy, the proper diet, or what to expect during each stage, the staff at All About Women can provide you with compassionate care and support both during and after your pregnancy.
Contact us at our Gainesville or Lake City offices to schedule an appointment today.
3 fruits to avoid during the first trimester of your pregnancy
Pregnancy is a journey with many changes. From morning sickness to rapid changes in body structure, pregnant women adapt to a different set of routines that they aren’t normally used to. One of the main changes is diet: Exactly what’s safe and beneficial to eat, and what isn’t? Are all fruits safe to eat, and if not, why? Here, we discuss three fruits to avoid during pregnancy first trimester. But first…
From morning sickness to rapid changes in body structure, pregnant women adapt to a different set of routines that they aren’t normally used to. One of the main changes is diet: Exactly what’s safe and beneficial to eat, and what isn’t? Are all fruits safe to eat, and if not, why? Here, we discuss three fruits to avoid during pregnancy first trimester. But first…
Why is the first trimester of pregnancy so important?
A woman’s pregnancy is divided into three parts, or trimesters. The first trimester is regarded as the first three months of your pregnancy.
The first trimester is important because even though your bump is barely showing, your baby is physically growing inside you. By the end of the first trimester, most of your tiny fetus’s organs have formed already.
Since the fetus is still developing, it is also defenseless as it still doesn’t have its own immune system. All of its growing organs can be injured by a variety of things, such as drugs, infections, radiation, tobacco and toxic chemicals.
Knowing all this, one way of keeping you and your fetus healthy is to refrain from alcohol, caffeine, smoking or drugs. Healthy fetal development also goes hand in hand with good lifestyle habits, such as exercising regularly, drinking adequate amounts of water and eating the right things.
When it comes to food that is not safe to eat during pregnancy, we know of the usual suspects: soft cheese, sushi, soft-serve ice-cream – anything that can result in food poisoning. However, did you know that there are some fruits too that you should avoid, especially in the first trimester?
3 Fruits to Avoid During Pregnancy First Trimester
1. Grapes
There are mixed opinions about grapes when it comes to fruits to avoid during pregnancy first trimester.
Some experts advise that’s it safe to eat while some say it should be avoided. While grapes do have high levels of vitamin A and C (which are important nutrients for pregnant moms), there are a few reasons why you might want to steer clear from grapes in your first trimester:
- Resveratrol toxicity.
 The outer skin of grapes is rich in a compound called resveratrol. Although scientific research identifies resveratrol as a healthy nutrient, it could be toxic to pregnant women. This is because resveratrol can react with disproportionate hormone levels a pregnant woman might have. A study also found out that pregnant monkeys fed with resveratrol supplements led to surprising results. Although more blood was directed from the pregnant monkey’s placenta to the fetus, the baby’s pancreas developed irregularly. The pancreas is important for controlling glucose levels in the blood, meaning that the babies were likelier to suffer from diabetes later on.
The outer skin of grapes is rich in a compound called resveratrol. Although scientific research identifies resveratrol as a healthy nutrient, it could be toxic to pregnant women. This is because resveratrol can react with disproportionate hormone levels a pregnant woman might have. A study also found out that pregnant monkeys fed with resveratrol supplements led to surprising results. Although more blood was directed from the pregnant monkey’s placenta to the fetus, the baby’s pancreas developed irregularly. The pancreas is important for controlling glucose levels in the blood, meaning that the babies were likelier to suffer from diabetes later on. - Pesticides that remain on the skin. Grapes are often sprayed with pesticides which aren’t easily washed away. These pesticides may contribute to health complications in the fetus.
- Grapes may cause constipation as its skin is difficult to digest.
- Heatiness which can affect both the mom and the baby.
If you are concerned about eating grapes while you are pregnant, please consult your doctor or gynecologist for further advice.
2. Unripe and Semi-Ripe Papaya Fruit
Fruits to avoid during pregnancy first trimester: stay away from unripe or semi-ripe papaya
Papayas are known for their sweet, juicy, orange flesh and as a natural remedy for indigestion. It is common in tropical countries and comes in a variety of types and sizes. However, the unripe and semi-ripe forms of this fruit aren’t particularly good for pregnant women for the following reasons:
- They are abundant in latex, which promotes early uterine contraction. This may result in a miscarriage.
- They contain large amounts of papain. One of papain’s side effects is that it can trigger early labor. The reason behind this is that papain looks very similar to another molecule that performs this role, which your body mistakes papain for.
- Latex is a common allergen. Common allergic symptoms include a runny nose, swelling in the mouth area and skin rashes. However, sometimes allergic reactions can cause breathing difficulties and anaphylaxis.
 In such cases, medical attention should be sought immediately.
In such cases, medical attention should be sought immediately.
Do avoid food or dishes that contain unripe or semi-ripe papaya (which have completely green skin), such as green papaya salads or papaya smoothies containing papaya seeds.
While the unripe versions are best not eaten during pregnancy, ripe papayas, on the other hand, are completely safe.
In fact, ripe papayas (with fully yellow skin) contain many nutrients that are important for a healthy pregnancy, such as:
- folate
- fiber
- cholene
- beta-carotin
- potassium
- and vitamins A, B and C
3. Pineapple
Who doesn’t like pineapple? It’s sweet, bright yellow and is tasty whether eaten ripe or used in dishes (like pineapple fried rice).
Sadly, this tropical fruit isn’t suitable for pregnant women. Pineapple is known to contain bromelain, an enzyme which breaks down protein. One of its side effects is that bromelain may soften the cervix, which could lead to early labor.
Studies also show that bromelain tablets are so potent in breaking down protein that they even can cause irregular bleeding!
However, do note that you need to eat massive amounts of pineapple (between seven to ten fresh ones at one go) to actually induce this effect. This means that while concentrated bromelain pills should be avoided, eating a few slices of pineapple while pregnant is okay.
Do note that eating too much pineapple can cause issues due to its acidic nature, such as acid reflux, heartburn, and even diarrhea (which leads to dehydration).
Also, if you haven’t eaten pineapple for some time, it’s possible that doing so will cause an allergic reaction. If you have symptoms like nasal congestion, itchy or swollen areas in your mouth or asthma after consuming pineapples, do book an appointment with your local doctor and discuss this.
More Tips About Eating Fruit when Pregnant
Clearly, unwashed fruits aren’t fit for consumption whether you are pregnant or not. However, they are especially risky for pregnant women.
However, they are especially risky for pregnant women.
The soil particles on fruits and vegetables can harbor bacteria such as toxoplasma, which makes infection possible for both the mother and baby.
Always wash your fruits and vegetables, ensuring that they are completely free of soil particles before eating them.
Why should pregnant women eat fruits as part of their diet?
Fruits are an essential part of a pregnant woman’s diet. Not only do they have nutrients that support your baby’s growth, but they also provide minerals, vitamins, antioxidants and fiber.
Furthermore, their rich nutrient content is counterbalanced by low calorie content, making it the ideal food for pregnant women! In addition, the following benefits have been linked to fruit consumption:
- Preventing cell damage. Fruits have antioxidants, which help to reduce any fetal cell injuries from damaging substances in the environment.
- Reduced infancy wheezing, which is associated with higher consumption of apples.

- Lower likelihood of childhood eczema, which is linked to eating citrus fruits during pregnancy.
What fruits are completely safe to eat during pregnancy?
1. Apples
Apples contain a variety of beneficial nutrients, like fibre, vitamins A & C, and potassium. In addition, previous research also highlights another added bonus: Most children born from mums who ate apples while pregnant did not develop childhood asthma or allergies.
2. Oranges
In addition to preventing childhood eczema, oranges also have:
- High water content, helping you stave off dehydration;
- Folate, a key vitamin that stops irregular development of the brain and spinal cord;
- Vitamin C, which not only has antioxidant properties, but also aids iron absorption.
3. Bananas
Bananas contain high levels of potassium, vitamin B-6, vitamin C and fibre. Fibre in bananas can help prevent constipation, whereas vitamin B6 can mitigate nausea and vomiting from morning sickness.
4. Avocados
Avocados are the nutrient powerhouses of all fruits, containing a diverse array of nutrients such as:
- Vitamins B, C and K
- Fibre
- Magnesium
- Potassium
- Iron
- Choline
- Folate – avocados have much higher levels compared to your average fruit.
In particular, eating avocados can reduce the instances of:
- leg cramps from low potassium and magnesium levels
- nausea, perhaps due to its high magnesium and choline content
- abnormal brain and nerve development in your baby via supplying ample amounts of choline
5. Berries
These yummy fruits are also nutrient-dense superfoods which provide a lot of beneficial compounds, such as:
- carbohydrates
- vitamin C
- folate
- fiber
- flavonoids
- anthocyanins
To maintain healthy levels of energy during the day, pregnant women should consume 50 to 60% of their calories from carbohydrates. Berries pack a lot more nutrients than other “empty calories” from refined grains. Do consider limiting refined carbohydrates and eating more nutrient-rich sources of carbohydrates like berries, instead.
Berries pack a lot more nutrients than other “empty calories” from refined grains. Do consider limiting refined carbohydrates and eating more nutrient-rich sources of carbohydrates like berries, instead.
We hope this information on fruits to avoid during pregnancy first trimester has been useful to you, and helps you ensure a safe and smooth pregnancy!
References: Medical News Today, American Pregnancy,NHS, Healthline, Only My Health, Healthline, Lifecell, Hopkins Medicine, Healthline, Apta Club
This article appeared originally at theAsianParent Philippines.
Nutrition of a pregnant woman
So, your plans and decisions to give birth to a child have come true - you are pregnant! But this news causes you a double feeling: - on the one hand, a feeling of joy, and on the other hand, a feeling of certain fear and even fear of unknown trials for your life and the fate of the unborn baby. What will he be like? - healthy, beautiful, happy?. ..
..
And this largely depends on the woman herself, on what lifestyle she will lead during pregnancy and, most importantly, how she will eat.
Nutrition of a woman in different periods of pregnancy
The main thing in the menu of a future mother is variety. She should consume foods from all food groups: meat, fish, vegetables and fruits, dairy products, bread and cereals.
A woman's nutrition during pregnancy can be roughly divided into three periods (trimesters).
If before pregnancy a woman ate normally, felt comfortable, did not experience allergies to any products, then it is not worth changing her diet at an early stage of the first trimester of pregnancy.
During this period, all organs and systems in the child's body are formed, tissues are formed. The body needs complete proteins and vitamins: lean meat (rabbit, chicken, turkey), fish and seafood, dairy products. Be sure to eat rice, fresh or frozen vegetables, seasonal fruits. In the first trimester, many expectant mothers are still working. No matter how difficult it is to control your diet in the workplace, you need to do it - find time for a full breakfast and lunch.
No matter how difficult it is to control your diet in the workplace, you need to do it - find time for a full breakfast and lunch.
In the first trimester of pregnancy, there is an active restructuring of the body and adaptation to a new state. During this period, it is recommended to switch to a low-calorie diet, which includes more fruits, juices, decoctions of dried fruits, including rose hips. At the very beginning of pregnancy, especially if toxicosis torments, more frequent, but less plentiful meals are recommended.
Always keep a hematogen, a bag of nuts or dried fruit in your pocket to have a snack on the street. If your condition does not allow you to eat regular food, you should pay attention to baby food. Baby products literally save expectant mothers suffering from severe toxicosis. These are boxed cereals, children's curds, cookies and fruit purees.
In the first trimester, special attention must be paid to the quality of products. Gradually abandon sauces, semi-finished products and canned food containing harmful chemical additives. Do not forget that the placenta freely accumulates and passes chemistry. The importance of products containing folic acid is great, without it intensive metabolism is impossible, its deficiency can cause developmental abnormalities. Folic acid is found in greens, nuts, white cabbage and broccoli, beets, legumes, and eggs.
Do not forget that the placenta freely accumulates and passes chemistry. The importance of products containing folic acid is great, without it intensive metabolism is impossible, its deficiency can cause developmental abnormalities. Folic acid is found in greens, nuts, white cabbage and broccoli, beets, legumes, and eggs.
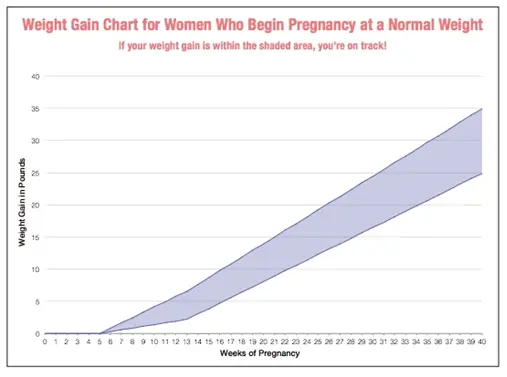
According to nutritionists, the diet of pregnant women should be 300 kcal / day higher than that of non-pregnant women, but in the first trimester there is no need to increase the energy value of the diet at all; in the second trimester, an additional 340 kcal / day is required; in the third trimester - 452 kcal / day. Pregnant women generally get enough calories, and more than 80% of women achieve and even exceed the required weight gain. These extra calories benefit the fetus. An underweight woman should gain 16–20 kg during her entire pregnancy, an overweight woman about 7 kg, and a normal body weight of 11–12 kg.
In the second trimester there are active jumps in the height and weight of the baby and uterus, so the caloric content of the diet needs to be increased. It is desirable to eat more and better. At this time, the need for trace elements increases: iron, magnesium, zinc, selenium, calcium, potassium. The child creates his own "reserve" of trace elements using the mother's resource, which means that the mother should have enough of them for two.
It is desirable to eat more and better. At this time, the need for trace elements increases: iron, magnesium, zinc, selenium, calcium, potassium. The child creates his own "reserve" of trace elements using the mother's resource, which means that the mother should have enough of them for two.
Very often in pregnant women in the second trimester hemoglobin drops, this is a normal physiological phenomenon, if it is not threatening to health. You can increase hemoglobin by eating red meat, chicken, fish, dried fruits, pomegranates, green vegetables and fresh herbs, buckwheat, citrus fruits (oranges, grapefruits, pomelo, lemons), rosehip and berry infusions.
In the second trimester, a pregnant woman should limit the intake of smoked and fried foods, as well as salt in her diet. In no case should you limit the liquid. Pure water is the best drink for a pregnant woman, and water should be consumed up to 2-2.5 liters per day. Water is a natural drink for the body, it does not cause complications and has no contraindications. Edema is caused not by water, but by salt, which we not only add in its pure form, but also consume with canned food, mayonnaise, cheese, and sausage. The absence of salt is not harmful, it is naturally found in many products: vegetables, bread, so the diet will not remain completely without it. Excess salt disrupts metabolism.
During this period, you can increase the calorie content of food. Childbirth must be approached physically strong. It is better to eat meat and fish in the morning, for breakfast and lunch, and for dinner, prepare dairy and vegetable dishes: cheesecakes, stewed vegetables, cottage cheese and vegetable casseroles. It is necessary to minimize the intake of canned food, smoked meats, pickles and marinades, hot spices and fatty foods. Frequent walks in the air, physical activity are recommended.
In the third trimester, it is necessary to reduce the calorie content of foods at the expense of confectionery and flour products, eat less fatty meat, as well as cheese and sour cream.
By the end of this period, many experts advise pregnant women to give up meat altogether in order to increase tissue elasticity and prevent ruptures.
During the entire period of pregnancy, special attention should be paid to the combination of products. If you combine foods wisely, you can ensure more efficient absorption of food. If the food is digested poorly, then this can lead to rotting and fermentation of products and the formation of substances harmful to the body of the mother and child. In addition, the fermentation process is accompanied by gas formation, which can lead to flatulence (bloating) and discomfort. This is especially harmful in the last stages of pregnancy.
Try not to take the first, second and third course at the same time; this overflows the stomach and presses on the fetus, the food is poorly digested and poorly absorbed. Eat little and often. It is not recommended to eat immediately before starting work, a long walk, before charging and immediately after it; it is advisable to rest for 10 minutes before eating.
Eat only when you are hungry, try not to snack on the go. Follow the diet, eat at about the same time.
Proper preparation of food will help to maximize the useful substances contained in the products. Do not overcook food, try not to reheat the same dish several times, it is better to set aside only the portion that will be used. Cook in the most gentle way: baking, steaming, stewing. Avoid frying, boiling in large amounts of water, with this method of processing products, many useful substances are lost. If possible, do not cook for several days at once. Do not use aluminum cookware when cooking. Remember that for a pregnant woman, it is not calories that are important, but the quality of food, its naturalness, primarily a “living cell” (whole cereals, raw vegetables and fruits, fresh meat and dairy products).
What can harm the pregnant woman and the fetus
Smoking and alcohol – quit smoking from the first days of pregnancy, if you have smoked before, avoid "passive" smoking, and do not consume alcoholic beverages in any doses.
Lack of vitamins and microelements in the body - their absence or deficiency can lead to irreparable consequences. So, for example, iodine deficiency can lead to mental retardation of a child, folic acid deficiency - to severe fetal deformities, calcium deficiency - to a violation of the formation of the child's skeleton, iron deficiency - to anemia and a delay in the physical and neuropsychic development of the child. It is necessary to consult a doctor, perhaps he will recommend switching to iodized salt, as well as supplementing your diet with a vitamin-mineral complex and folic acid.
Excess weight is the risk of having a large child, which means the risk of complications during childbirth and the child's tendency to become obese at an older age.
The use of food additives (sauces, seasonings such as vegeta, bouillon cubes), exotic fruits, semi-finished products, carbonated drinks - the risk of allergies and anomalies in a child, unfortunately, increases.
Recommended for pregnant women:
- Do not eat hot dogs and other snacks containing meat that has not been heated on fire or boiled in boiling water.

- Avoid soft cheeses. Hard cheeses are safe.
- Do not eat raw frozen pies and meat pastes, seafood. Canned analogues are safe.
- Do not consume raw vegetables, unpasteurized juices, liver, meat, poultry and eggs that have not been sufficiently cooked. These products may contain Salmonella taxins.
- Limit sweets.
- In no case do not resort to starvation and various diets.
- Regularly monitor blood pressure and do not miss visits to the gynecologist.
Remember!
Your child's development and health depend on your diet and lifestyle during pregnancy!
Nutrition in the first trimester of pregnancy
Times of change
You must change your old lifestyle and adapt to the new situation. It should be remembered that we are planning the nutrition of two organisms, whose need for energy and "building" materials will increase.
Due to the hormonal changes that are taking place, you may experience nausea and constant sleepiness. Instincts wake up in your body, which will have a great impact on the psycho-emotional balance. Frequent stressful situations and the lack of proper response to them are dangerous for you and your child.
Instincts wake up in your body, which will have a great impact on the psycho-emotional balance. Frequent stressful situations and the lack of proper response to them are dangerous for you and your child.
Proper nutrition will help you maintain optimal health and ensure the proper development of your child.
Basic nutrition rules
Rule 1: Eat regular and varied meals
1.1. During the day, you should eat 4-5 times.
1.2. Every meal should include grain products, eg. pastries made from coarse flour, porridge, pasta, rice, muesli or cereal (a source of dietary fiber, vitamins B, iron, manganese, selenium).
1.3. Dairy products are also advisable - fresh and sour-milk: fresh milk (avoid UHT), sour cream, natural yoghurts, sour-milk products (provide amino acids, are a source of acidophilus bacteria and lactose, which is necessary for the development of the correct bacterial flora in the intestine).
1.4. Eat a variety of meat, fish, eggs, vegetables, fruits daily.
Eat a variety of meat, fish, eggs, vegetables, fruits daily.
1.5. Eat vegetable fats - daily at least one tablespoon of different oils: from flax, olives, grape seeds, rapeseed, sunflower, etc.
1.6. It is advisable to avoid strong stimulants: cigarettes and alcohol (of course), strong black natural coffee, black tea.
1.7. It is worth giving up carbonated drinks and sweets (those that contain artificial preservatives, colors and flavors). When thirsty - drink still mineral water, natural fresh fruit and vegetable juices, herbal tea, fruit tea, green tea and coffee substitutes.
1.8. Avoid very fragrant and spicy spices and foods.
Rule 2: Always start the day with breakfast
Lack of breakfast causes low blood glucose, which can lead to dizziness or fainting. Therefore, breakfast will give strength for the whole day to you and your child.
For breakfast you can eat milk soup with muesli, oatmeal, dried fruit. Suitable eggs in any form and dairy products. You should also often eat fish for breakfast in combination with dairy products.
You should also often eat fish for breakfast in combination with dairy products.
It is best to eat only meat of your own processing (fried, baked, boiled, etc.). Instead of natural morning coffee, it is better to drink a coffee bean drink (such as kurzeme), green tea or "bavarka" (black tea with milk).
For second breakfast you can eat baked fruit (apple, pear, plums) with nuts. In order to destroy mushrooms on the surface of nuts, it is necessary to scald them with boiling water.
Rule 3: Remember your supplements
Too little is bad, but too much can be worse.
Main supplements
Folic acid
Very important from the moment of fertilization. Its deficiency causes neural tube defects in the child (anencephaly, spina bifida, spinal hernia). These defects occur in the first 3-4 weeks of intrauterine life, when the woman does not know that conception has occurred. The lack of folic acid in the mother's body can cause miscarriages or other dangerous complications.
The lack of folic acid in the mother's body can cause miscarriages or other dangerous complications.
Most folic acid is found in: liver, eggs, wholemeal baked goods, fruits (e.g. bananas), green vegetables (e.g. brussels sprouts, spinach, asparagus, broccoli, cauliflower, to a lesser extent in lettuce, cucumbers and pepper).
The need for folic acid in the first trimester of pregnancy is high, it is necessary to take supplements that contain 400 to 1000 micrograms of folic acid.
Iron
Iron deficiency is common in children. Iron deficiency is the most common cause of anemia.
It is recommended to prophylactically give infants iron, but exactly the one that is contained in food or in the form of supplements. Anemia in a pregnant woman doubles the risk of anemia in a child compared to children of those mothers who did not have anemia.
Iron exists in two forms:
The best absorbed form is found in animal products such as red meat or liver.
A form that is less digestible - in products of plant origin, for example, in: nuts, pumpkin seeds, sunflower seeds, pastries from coarse flour.
Unfortunately, iron is poorly absorbed from food. Vitamin C, taken before meals, has a beneficial effect on its absorption. At the same time, a large amount of strong tea, coffee, sorrel, rhubarb, drinks such as cola should be avoided. The compounds contained in them, that is, tannin, oxalates, phosphates, practically prevent the absorption of iron.
Iron deficiency leads to anemia, which affects many women during pregnancy, especially in the third trimester. It is necessary to take care of supplementation with iron and vitamin C already before pregnancy. Pay attention to supplements with a dose of iron of 6-8 mg. You should be careful because too much iron is bad for our intestines, especially for the bacterial flora (black stools (feces) and even blood in the stools can appear).
Magnesium
Lack of magnesium during pregnancy leads to pathological conditions.
The processes of formation of the placenta and fetus in pregnant women proceed correctly only when the mother's body has the appropriate amount of magnesium. A four-month-old fetus increases its weight before delivery by 20 times, while the content of magnesium and calcium in the body of the fetus increases by 40 times.
Lack of magnesium leads to premature birth and the birth of children with too small weight, ie. hypotrophic children. It is also the main cause of pathology of the cardiovascular system, neurological diseases, metabolic disorders and complications during pregnancy.
Expectant mothers should take 300 mg of magnesium daily during pregnancy.
The daily requirement for magnesium must be provided with daily food intake, which is almost impossible. Even a balanced diet based on food from stores leads to a lack of magnesium (the glutamate and aspartame contained in these products accelerate the excretion of magnesium from the mother's body).
Magnesium deficiency in the body is also caused by prolonged stressful situations, the intake of natural coffee, alcohol, and the consumption of a large amount of sweets. Even those people who are convinced that they lead a healthy lifestyle are prone to obvious or hidden lack of magnesium.
Even those people who are convinced that they lead a healthy lifestyle are prone to obvious or hidden lack of magnesium.
Calcium
Calcium belongs to the group of basic "building materials" necessary for our body. It is found mainly in the bones, but approximately 5% calcium is a very important element that affects the maintenance of metabolic balance.
Calcium is necessary for the child to build bones, for the proper development of muscles, heart and nervous system.
If you are expecting a baby, remember that calcium deficiency has an adverse effect on the development of the fetus. At birth, a child may have a small weight, a tendency to rickets, and developmental defects may also occur.
In case of prolonged lack of calcium, the risk of preeclampsia and high blood pressure increases, blood clotting decreases.
During pregnancy, 1000 - 1200 mg of calcium should be taken daily.
In order for calcium to be well absorbed, vitamin D should be consumed. On sunny days, a half-hour walk is enough for the body to produce the necessary amount of this vitamin. In autumn and winter, you need to eat fatty sea fish, eggs and dairy products.
On sunny days, a half-hour walk is enough for the body to produce the necessary amount of this vitamin. In autumn and winter, you need to eat fatty sea fish, eggs and dairy products.
Ideal for supplementing magnesium and calcium in the body of a future mother are preparations in the proportion of 2/1 or 3/2 calcium to magnesium. A good combination is alfalfa (alfalfa extract). It should be remembered that supplementation with omega 3 acids acts synergistically in the processes. The presence of these acids affects the proper development of the child's body, especially the nervous system. Only then can the intellect develop correctly in the child and all the senses can function correctly. Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) is of particular importance for the proper development of the brain and vision. Already from the fourth month of pregnancy, DHA is integrated into the retina of the child's eye and is involved in the conversion of light signals into nerve impulses that are transmitted to the brain. Polyunsaturated fatty acids are divided into two groups: omega 3 and omega 6. Humans need both groups of acids, but omega 3 acids play a special role in human development. These include ALA (alpha lipoic acid), DHA (docosahexaenoic acid) and EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid).
Polyunsaturated fatty acids are divided into two groups: omega 3 and omega 6. Humans need both groups of acids, but omega 3 acids play a special role in human development. These include ALA (alpha lipoic acid), DHA (docosahexaenoic acid) and EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid).
The recommended daily allowance is 2 g of ALA and 0.25 g of long-chain DHA and EPA.
A child's only source of DHA is his own mother. However, a pregnant woman's body cannot produce enough DHA on its own. The daily requirement for DHA quadruples during pregnancy. She passes DHA to her baby first through the placenta and then through breastfeeding milk. Supplementation from the third month of pregnancy helps the mother create an adequate supply of DHA, which the baby will use in the second half of pregnancy and while breastfeeding. The mother-to-be has two options to choose from: get DHA from plants or from fish. Fish do not produce omega-3s. The omega-3 in fish comes from the algae that the fish eat. Therefore, it is important that the fish is marine, for example - mackerel, salmon, cod, tuna, herring. The scientific literature draws attention to the possible presence of toxic compounds, including heavy metals, in fish and fish products. Therefore, pregnant women and children under four years of age should consume fish and fish products with caution. Choose only those that are not grown on farms and do not contain heavy metals. If you do not know where exactly the fish comes from, then it is better to take omega-3 supplementation instead of fish.
The scientific literature draws attention to the possible presence of toxic compounds, including heavy metals, in fish and fish products. Therefore, pregnant women and children under four years of age should consume fish and fish products with caution. Choose only those that are not grown on farms and do not contain heavy metals. If you do not know where exactly the fish comes from, then it is better to take omega-3 supplementation instead of fish.
Lecithin
Lecithin is a mixture of phosphatides phosphatidylcholine, phosphatidylserine, phosphatidylethanolamine and phosphatidylinositol derived from vegetable oils or from egg yolks. Phospholipids are found in all cells and are part of cell membranes. Participate in the metabolism of lipoproteins.
Indications for lecithin supplementation:
1. Degenerative processes of the nervous system (most of all lecithin is found in the membranes and intracellular structures of neurons).
2. With increased mental and physical stress, decreased concentration, memory impairment.
Lecithin is a precursor (precursor) of acetylcholine - a neurotransmitter that affects the expansion of blood vessels, lowering blood pressure, weakening the heart rate, enhancing the smooth muscles of the bronchi, intestines and bladder, increasing the secretion of glands. Lecithin protects a person from steatosis of the liver, kidneys and heart muscle. Regular supplementation with lecithin improves the lipid profile, which reduces the risk of heart attack.
How to survive the revolution in the digestive system?
During the first trimester of pregnancy, most mothers-to-be experience morning sickness and vomiting. This usually goes away by the 4th month of pregnancy.
To make it easier to get through this period, follow a few basic rules:
1. Before you get out of bed, drink one acerola (30 mg of vitamin C) and eat a snack prepared in the evening: a tablespoon of muesli with yogurt or fruit (not necessarily something from citrus).