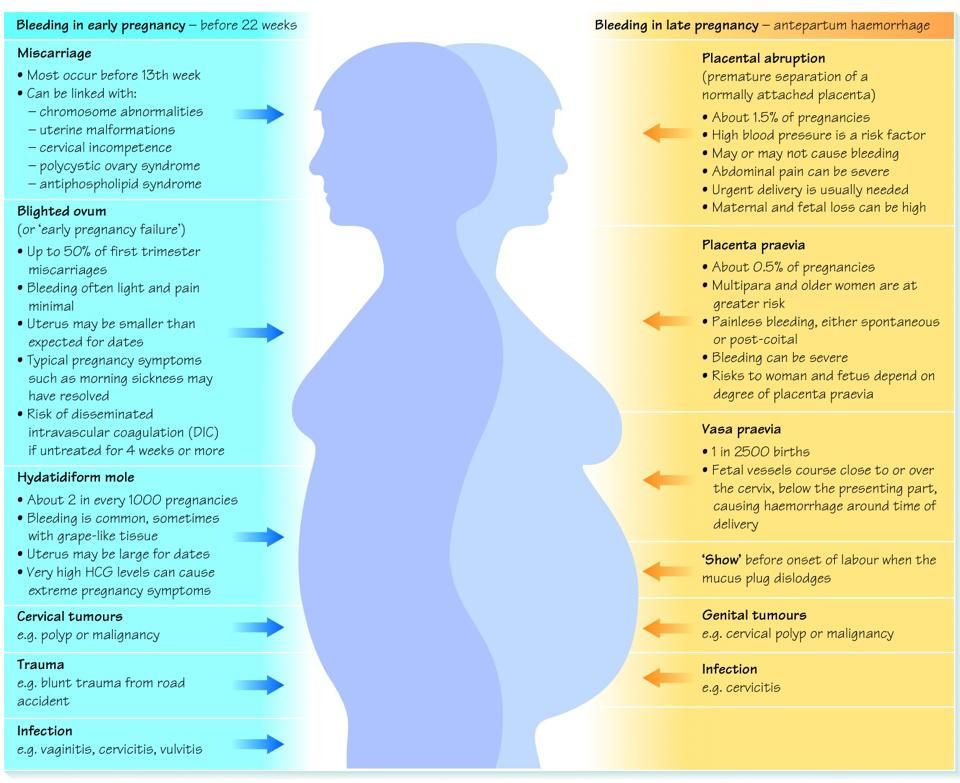
Fresh blood during pregnancy
Vaginal bleeding - NHS
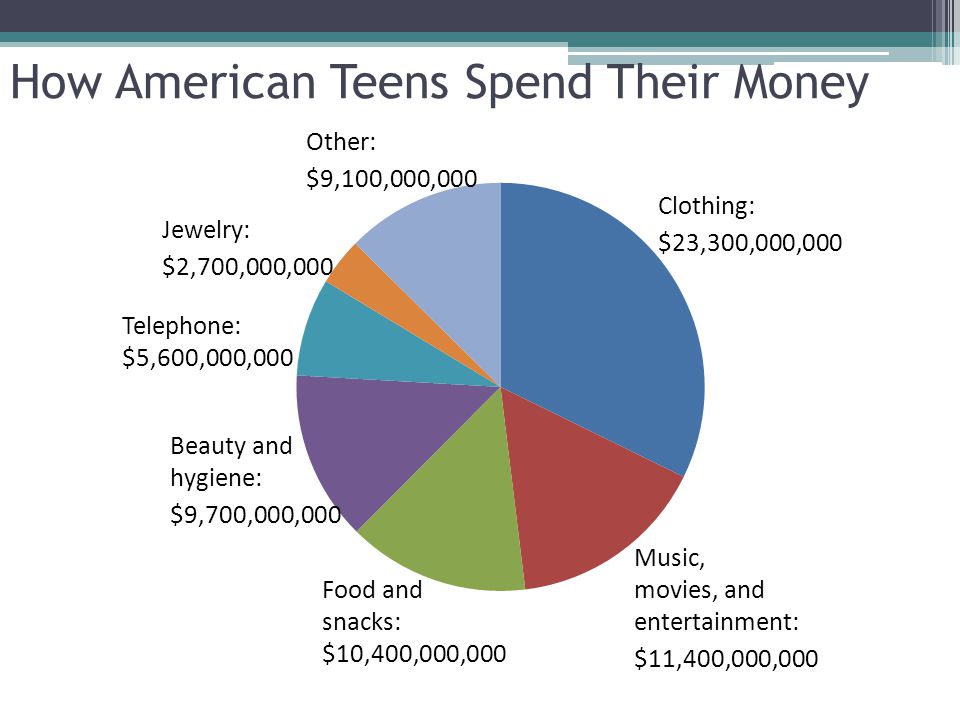
Bleeding during pregnancy is relatively common and does not always mean there's a problem – but it can be a dangerous sign.
Urgent advice: Call your midwife or GP immediately if:
- you have any bleeding from your vagina
Causes of bleeding in early pregnancy
Implantation bleeding
In early pregnancy, you might get some harmless light bleeding, called "spotting". This is when the developing embryo plants itself in the wall of your womb. This type of bleeding often happens around the time your period would have been due.
Cervical changes
Pregnancy can cause changes to the cervix, and this may sometimes cause bleeding – after sex, for example.
Miscarriage or ectopic pregnancy
During the first 12 weeks of pregnancy, vaginal bleeding can be a sign of miscarriage or ectopic pregnancy.
However, if you bleed at this stage of pregnancy it's likely you will go on to have normal and successful pregnancies.
Treating bleeding in early pregnancy
You may be offered a medicine called progesterone to stop bleeding in early pregnancy. This will only be recommended if you've had a scan to confirm you're pregnant and you've had a miscarriage before.
Your doctor may recommend you take the medicine twice a day until you're 16 weeks pregnant.
Miscarriage
If a pregnancy ends before the 24th week, it's called a miscarriage. Around 1 in 5 pregnancies ends this way.
Many early miscarriages (before 14 weeks) happen because there is something wrong with the baby. There can also be other causes of miscarriage, such as hormone or blood clotting problems.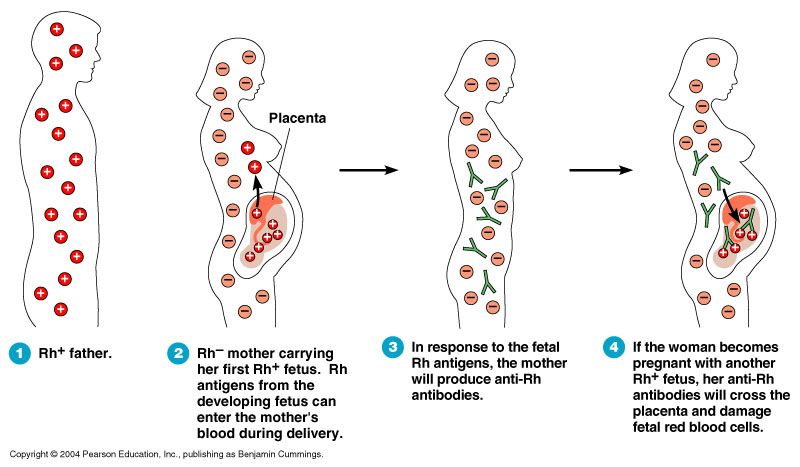
Most miscarriages occur during the first 12 weeks (3 months) of pregnancy and, sadly, most cannot be prevented. Other symptoms of miscarriage include:
- cramping and pain in your lower abdomen
- a discharge or fluid from your vagina
- a discharge of tissue from your vagina
- no longer experiencing the symptoms of pregnancy, such as feeling sick
If you have bleeding or any of the symptoms above, contact your midwife or GP straightaway.
Ectopic pregnancy
An ectopic pregnancy is when a fertilised egg implants outside the womb – for example, in the fallopian tube.
It can cause bleeding and is dangerous because the fertilised egg cannot develop properly outside the womb. The egg has to be removed, which can be done through an operation or with medicines.
Symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy tend to develop in the 6th week of pregnancy but can happen later.
Other signs of ectopic pregnancy can include:
- tummy pain low down which may be on one side
- vaginal bleeding or a brown, watery discharge
- pain in the tip of your shoulder
- discomfort when peeing or pooing
Call 111 if you have symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy.
Causes of bleeding in later pregnancy
Cervical changes
These can lead to bleeding, particularly after sex.
Vaginal infections
Your midwife or doctor can discuss tests and treatment with you.
A 'show'
This is when the plug of mucus that has been in the cervix during pregnancy comes away, signalling that the cervix is getting ready for labour to start. It may happen a few days before contractions start or during labour itself.
It may happen a few days before contractions start or during labour itself.
Find out about the signs of labour and what happens in labour.
Placental abruption
This is a serious condition in which the placenta starts to come away from the womb wall. Placental abruption usually causes stomach pain, and this may occur even if there is no bleeding.
Low-lying placenta (placenta praevia)
This is when the placenta is attached in the lower part of the womb, near to or covering the cervix. Bleeding from a low-lying placenta can be very heavy, and put you and your baby at risk.
You may be advised to go into hospital for emergency treatment, and a caesarean section will usually be recommended. The Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists has more information on placenta praevia.
Vasa praevia
This is a rare condition where the baby's blood vessels run through the membranes covering the cervix.
When your waters break, these vessels may be torn and cause vaginal bleeding. The baby can lose a life-threatening amount of blood.
Finding out the cause of bleeding in pregnancy
To work out what is causing the bleeding, you may need to have a vaginal or pelvic examination, an ultrasound scan or blood tests to check your hormone levels.
Your doctor will also ask you about other symptoms, such as cramp, pain and dizziness. Sometimes it might not be possible to find out what caused the bleeding.
If your symptoms are not severe and your baby is not due for a while, you'll be monitored and, in some cases, kept in hospital for observation.
How long you need to stay in hospital depends on the cause of the bleeding and how many weeks pregnant you are.
Being in hospital allows staff to keep an eye on you and your baby, so they can act quickly if there are further problems.
Find the answers to common health problems in pregnancy
Video: What should I do if I start bleeding during early pregnancy?
In this video, a midwife tells you what to do if you start to bleed during early pregnancy.
Media last reviewed: 20 March 2020
Media review due: 20 March 2023
Bleeding and spotting from the vagina during pregnancy
Bleeding and spotting from the vagina during pregnancy are common
If you bleed or spot during pregnancy, it doesn’t always mean there’s a problem but in some cases they may be signs of a problem for you or your baby’s health
If you have heavy bleeding, call your health care provider right away
Tell your provider about any bleeding or spotting you have during pregnancy
Bleeding and spotting from the vagina during pregnancy are common. Up to 1 out of 4 (up to 25%) of all pregnant women have some bleeding or spotting during their pregnancy.
Bleeding and spotting in pregnancy don’t always mean there’s a problem, but they can be a sign of miscarriage or other serious complications. Miscarriage is when a baby dies in the womb before 20 weeks of pregnancy.
Call your health care provider if you have any bleeding or spotting, even if it stops. It may not be caused by anything serious, but your provider needs to find out what’s causing it.
What’s the difference between bleeding and spotting?
Bleeding or spotting can happen anytime, from the time you get pregnant to right before you give birth. Spotting is light bleeding. It happens when you have a few drops of blood on your underwear. Spotting is so light that the blood wouldn’t cover a panty liner. Bleeding is when the blood flow is heavier, enough that you need a panty liner or pad to keep the blood from soaking your underwear and clothes.
What should you do if you have bleeding or spotting during pregnancy?
Call your health care provider if you have any kind of bleeding during pregnancy and do these things:
- Keep track of how heavy your bleeding is, if it gets heavier or lighter, and how many pads you are using.
- Check the color of the blood. Your provider may want to know. It can be different colors, like brown, dark or bright red.
- Don’t use a tampon, douche or have sex when you’re bleeding.
Call your health care provider right away at any time during pregnancy or go to the emergency room if you have:
- Heavy bleeding
- Bleeding with pain or cramping
- Dizziness and bleeding
- Pain in your belly or pelvis
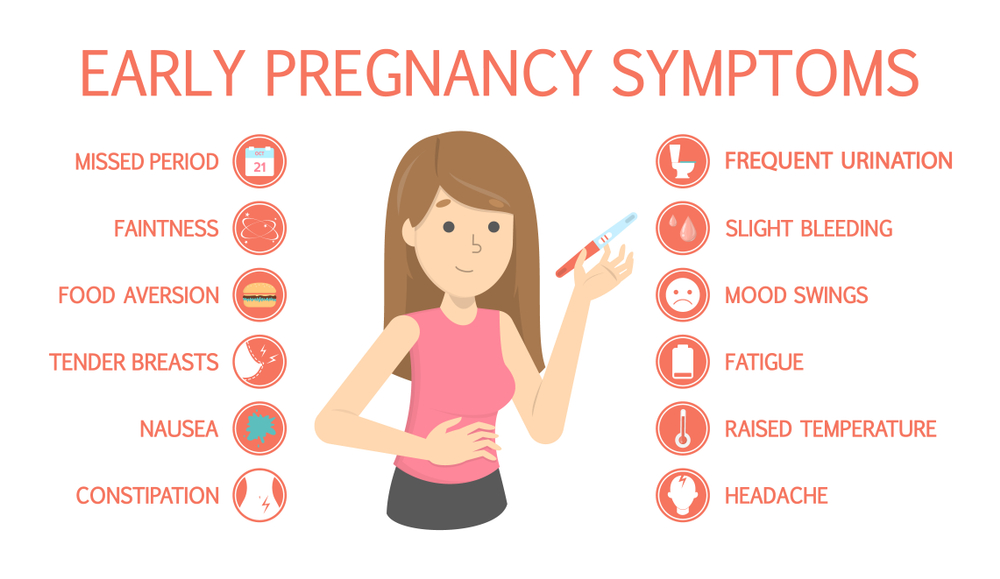
What causes bleeding or spotting early in pregnancy?
It’s normal to have some spotting or bleeding early in pregnancy. Bleeding or spotting in the first trimester may not be a problem. It can be caused by:
- Having sex
- An infection
- Implantation. When a fertilized egg (embryo) attaches to the lining of the uterus (womb) and begins to grow.
- Hormone changes. Hormones are chemicals made by the body.
- Changes in your cervix. The cervix is opening to the uterus that sits at the top of the vagina.

- Certain types of testing during pregnancy like an amniocentesis or Chorionic villus sampling (CVS). These are tests that are done to check for genetic abnormalities in your baby. Genetic abnormalities are changes in the genes that are passed down to a baby from mom or dad. These genetic changes can cause health problems for a baby.
- Problems related to smoking. If you smoke, it’s best to stop before pregnancy or as soon as you know you’re pregnant.
Sometimes bleeding or spotting in the first trimester is a sign of a serious problem, like:
- Miscarriage. Almost all women who miscarry have bleeding or spotting before the miscarriage.
- Ectopic pregnancy. This is when a fertilized egg implants itself outside of the uterus and begins to grow. An ectopic pregnancy cannot result in the birth of a baby. It can cause serious, dangerous problems for the pregnant woman.
- Molar pregnancy.
 This is when a mass of tissue forms inside the womb, instead of a baby. Molar pregnancy is rare.
This is when a mass of tissue forms inside the womb, instead of a baby. Molar pregnancy is rare.
What causes bleeding or spotting later in pregnancy?
Bleeding or spotting later in pregnancy may be caused by:
- Labor
- Having sex
- An internal exam by your health care provider
- Problems with the cervix, like an infection, growths, inflammation or cervical insufficiency. This is when a woman’s cervix opens too early. Inflammation of the cervix is when it may be painful, swollen, red or irritated.
Bleeding or spotting later in pregnancy may be a sign of a serious problem, like:
- Preterm labor. This is labor that happens too early, before 37 weeks of pregnancy.
- Placenta previa. This is when the placenta lies very low in the uterus and covers all or part of the cervix.
- Placenta accreta.
 This is when the placenta grows into the wall of the uterus too deeply.
This is when the placenta grows into the wall of the uterus too deeply. - Placental abruption. This is when the placenta separates from the wall of the uterus before birth.
- Uterine rupture. This is when the uterus tears during labor. This happens very rarely. It can happen if you have a scar in the uterus from a prior cesarean birth (also called c-section) or another kind of surgery on the uterus. A c-section is surgery in which your baby is born through a cut that your doctor makes in your belly and uterus.
How are bleeding and spotting treated?
Your treatment depends on what caused your bleeding. You may need a medical exam and tests.
Most of the time, treatment for bleeding or spotting is rest. Your provider may also suggest treatments like:
- Take time off from work and stay off your feet for a little while
- You may need medicine to help protect your baby from Rh disease.
 Rh disease is when your blood and baby’s blood are incompatible (can’t be together). This disease can cause serious problems — even death — for your baby.
Rh disease is when your blood and baby’s blood are incompatible (can’t be together). This disease can cause serious problems — even death — for your baby. - Don’t have sex, douche or use tampons
- If you have heavy bleeding, you may need a hospital stay or surgery
Last reviewed April 2020
Signs, symptoms and causes of hemorrhoids in pregnant women - NEARMEDIC network of clinics
The main causes of hemorrhoids in pregnant women can be as follows:
- Chronic constipation. In this case, the stretching and tension of the walls of the rectum increases during defecation, which leads to the formation of hemorrhoids. In pregnant women, constipation occurs much more often due to a decrease in intestinal tone.
- Inactive lifestyle. With hypodynamia, blood stagnation occurs in the venous plexus of the rectum, which eventually leads to vein thrombosis and the formation of hemorrhoids. Features of the condition do not always allow pregnant women to be mobile, therefore they have a high risk of developing this disease.
 nine0006
nine0006 - Disturbance of blood circulation in the lower half of the body. During pregnancy, the uterus grows and compresses the inferior vena cava. This leads to stagnation of blood in the veins of the legs and rectum. During childbirth, a woman's intra-abdominal pressure rises greatly - this can cause hemorrhoids after pregnancy.
Signs of hemorrhoids in pregnant women
The longer the period, the higher the likelihood of developing the disease. Most often, hemorrhoids appear in the 3rd trimester or after childbirth. nine0003
The blood vessels of the hemorrhoidal plexus of the rectum gradually dilate. Over longer periods, the stretching of the veins becomes even stronger. With the expansion of the walls of the veins of the rectum, they lose their elasticity. This provokes protrusion of the veins under the mucous membrane.
If hemorrhoids protrude only into the lumen of the rectum and do not come out of the anus, then we are talking about the treatment of hemorrhoids of the 1st stage.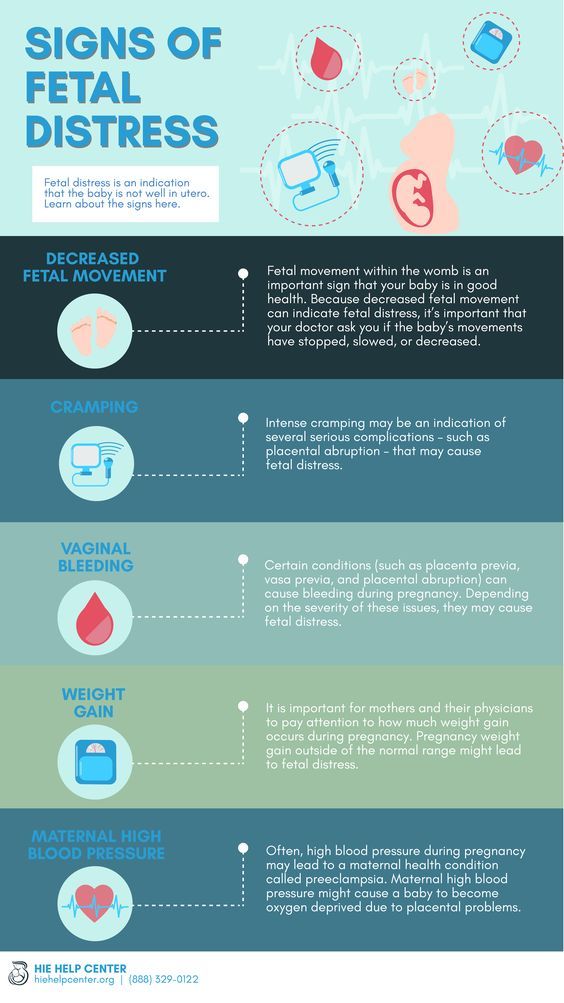 The farther, the larger the knots become and the more they sag from the anus. In the second stage of hemorrhoids, the nodes sag from the anus, but are easily set back on their own. The third stage occurs when the nodes can no longer cope back. nine0003
The farther, the larger the knots become and the more they sag from the anus. In the second stage of hemorrhoids, the nodes sag from the anus, but are easily set back on their own. The third stage occurs when the nodes can no longer cope back. nine0003
The symptoms of the disease depend on its stage.
- Internal hemorrhoids. Symptoms are mild, there is no sagging of hemorrhoids from the anus. At this stage, women may experience pain during bowel movements, slight bleeding or fresh blood in the stool, and itching and discomfort in the anus.
- External hemorrhoids. The main symptom is the sagging of one or more purple-red nodes from the anus. This manifestation is the main sign of what is required, and not of another disease, such as anal fissure. Walking, sitting and defecation in this case become extremely painful. nine0006
Urgent medical attention is required in case of infringement of the hemorrhoid - a pregnant woman experiences very severe pain in the anus with fever.
Treatment of hemorrhoids during pregnancy
If a woman already has any symptoms of hemorrhoids - itching, pain in the anus, bleeding from the anus, etc. - professional treatment is required.
At NEARMEDIC, the first stage of treatment is the preventive measures described above, which stop the progression of the disease. Then the woman is prescribed drugs, both local and systemic. But due to pregnancy, local therapy is preferable, as this reduces the risk of side effects, increases the effectiveness of treatment and reduces the negative effects of drugs on the child. In any case, the medicine is prescribed only by the attending physician who observes the woman during pregnancy. nine0003
In the case when a woman already has prolapsed nodes that cannot be set, an operation is prescribed. Other indications for surgical intervention are infringement or necrosis of the hemorrhoid, as well as acute inflammation. Most often, in NEARMEDIC surgery is postponed until the postpartum period, and during pregnancy they are limited to conservative treatment.
Prevention of hemorrhoids during pregnancy
Due to the fact that all pregnant women are at high risk of developing hemorrhoids, NEARMEDIC clinic doctors strongly recommend that preventive measures be taken throughout pregnancy, without waiting for symptoms to appear. nine0003
- Relief of constipation. To do this, you need to adjust your diet: eat more foods that contain coarse vegetable fiber - vegetables, fruits, cereals, cereals, prunes. Dairy products also have a beneficial effect on digestion. On the contrary, it is better to refuse meat and other foods rich in protein. As well as from an excess of fat, coffee and hot spices.
- Hygiene. It is recommended to wash the perineum and anus after each act of defecation. In addition, once a day you can take sitz baths with antiseptics: chamomile infusion, a weak solution of potassium permanganate, etc. nine0006
Doctors
Who treat hemorrhoids during pregnancy
More doctorsClinics in Moscow
For all questions, you can contact the single contact center: +7 (495) 6-171-171
Bleeding in the first half of pregnancy - Information
|
Pregnancy is a complex physiological process that can be accompanied by various complications, including those that cause uterine or vaginal bleeding. Strange as it may seem, but not any bleeding at the beginning of pregnancy indicates a pathology that needs immediate medical intervention. nine0003 Moreover, it can be said that in the very early stages of pregnancy, slight bleeding is considered a normal symptom that is not a cause for concern and does not pose a danger to the normal course of pregnancy. The first weeks of pregnancy are the time of a global restructuring of a woman's body, hormonal and physiological. What could be the reasons for the discharge of blood from the genital tract of a pregnant woman? First of all, during the fixation of the ovum in the wall of the uterus, small fragments of its mucous membrane can be shed, which causes the appearance of small bloody discharge from the vagina. This vaginal discharge may be brown, brown, or intensely red. It is this kind of bleeding that sometimes becomes the first indication of pregnancy. We repeat that this does not happen when the pregnancy has already been established, but during the implantation of the fetal egg, that is, when the “real” uterine pregnancy has not yet begun. Most often, such spotting coincides with the time of the next menstruation, which leads to a fairly common belief that not everyone stops menstruating with the onset of pregnancy. nine0003 However, once the pregnancy is established, any bleeding should alert the pregnant woman and cause her to immediately report to the obstetrician-gynecologist leading the pregnancy. A fairly common cause of bleeding from the genital tract in pregnant women in early pregnancy is cervical erosion. This also happens for a completely understandable reason: due to increased blood flow to the uterus during pregnancy, the cervical mucosa may begin to bleed, turning into some kind of inflammatory ulcer. In case of cervical erosion in pregnant women, blood from the genital tract appears after sexual contact or without any apparent reason at all, such bleeding is not accompanied by pain, is insignificant and quickly stops spontaneously. In addition to erosion, the cause of bleeding in pregnant women in the first trimester of pregnancy can be polyps of the cervical canal and decidual polyps - harmless tumors that grow in the uterus or cervix. Bleeding is also insignificant and is not accompanied by pain. nine0003 Depending on the situation, the doctor may remove the polyp or wait for the polyp to fall off on its own, as is most often the case. Removal of a bleeding polyp does not harm the course of pregnancy, since curettage of the uterine cavity is not required when it is removed. In parallel with the removal of the polyp, treatment is necessarily carried out aimed at replenishing blood loss and maintaining pregnancy. However, there are other cases when bleeding in the first trimester of pregnancy serves as a signal that "not all is well in the Kingdom of Denmark. In particular, such severe complications of the first trimester of pregnancy as spontaneous miscarriage and ectopic pregnancy can begin with vaginal bleeding. In addition, the discharge of blood from the genital tract of a pregnant woman may indicate the development of any severe pathology of the cervix, up to oncological neoplasms. Other causes of bleeding include varicose veins in the vulva, vaginal infections. nine0003 Once again, in order not to miss the first signs of these complications, any bleeding in a pregnant woman should be a reason to see a doctor. Spontaneous miscarriage is a very serious complication of pregnancy that occurs early in pregnancy and usually begins with bleeding. Bleeding indicative of an incipient miscarriage may be minor and painless. However, it does not stop after a short time, but continues to grow both in intensity and in the unpleasant sensations that accompany it. nine0003 Spontaneous miscarriage occurs in several stages: threatened miscarriage, incipient miscarriage, abortion in progress, incomplete and complete miscarriage. In a threatened miscarriage, bloody discharge from the genital tract of a pregnant woman is extremely scarce, pain is usually absent or is manifested by aching sensations in the lower abdomen. At the same time, the uterus has not yet been changed, and with active and timely treatment, pregnancy can be maintained. nine0003 A miscarriage that has begun is characterized by slow bleeding, cramping pains. The cervix at this stage of the miscarriage may already be slightly shortened, and the external os is ajar. At the same time, the woman's condition remains satisfactory, and with proper treatment, pregnancy can be maintained. If this moment is also missed, then it is almost impossible to maintain the pregnancy, and, in addition, severe bleeding during an abortion in the course causes the need for urgent hospitalization, during which the uterine cavity is scraped, with compensation for blood loss, depending on its volume and the condition of the woman. Bloody discharge in incomplete miscarriage is significant, usually dark red in color, clots can be seen in them. Bleeding is accompanied by cramping pains in the lower abdomen. Emergency care consists in scraping the uterine cavity, removing the remnants of the fetal egg; compensation for blood loss, depending on its volume and the condition of the woman. If there is a complete miscarriage, then there is no bleeding, since the fetal egg is completely released from the uterus. The only thing that the doctor should do in this case is to scrape the uterine cavity so that there are no parts of the fetal egg left there. nine0003 Sadly, spontaneous miscarriages are a fairly common cause of uterine bleeding during pregnancy. Another cause of bleeding in pregnant women can be an ectopic pregnancy, that is, a situation in which the fetal egg is fixed not in the body of the uterus, but in the tubes or in the cervix. An ectopic pregnancy not noticed in time can lead to cervical rupture and even death. |
 As a rule, the first and last trimester of pregnancy, more precisely, the very first and last weeks of it, are the most dangerous from this point of view.
As a rule, the first and last trimester of pregnancy, more precisely, the very first and last weeks of it, are the most dangerous from this point of view. 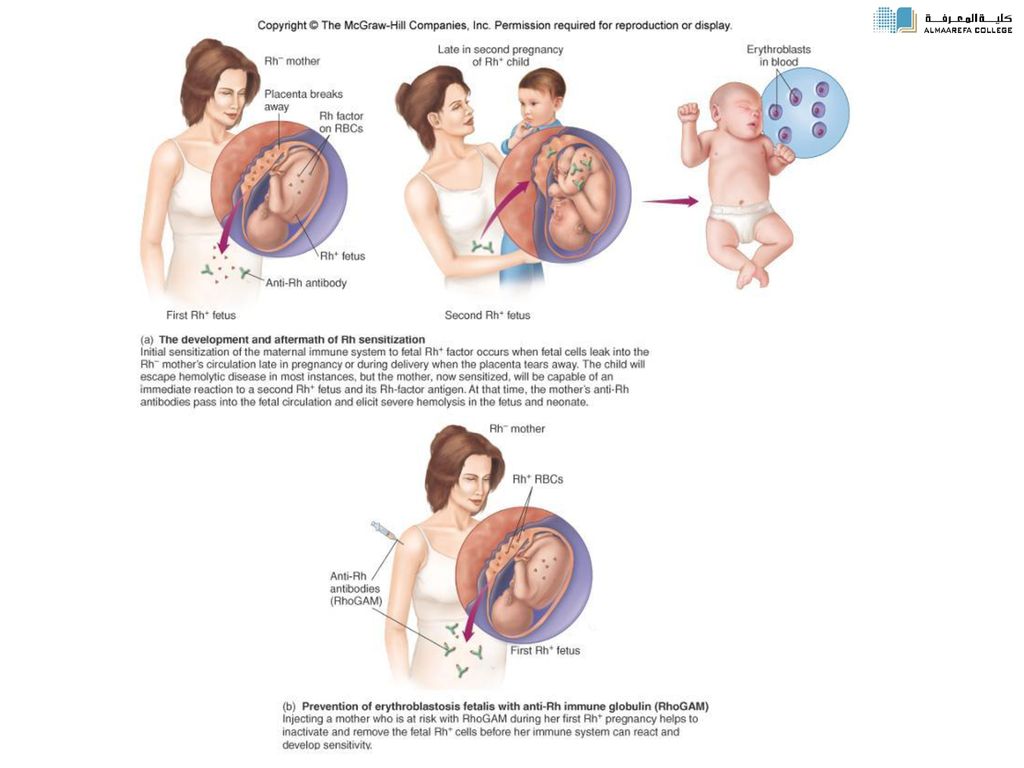 Most often, the discharge is not plentiful and does not last longer than a few days. Sometimes they are accompanied by minor spasms, sometimes they are completely painless for a pregnant woman. nine0003
Most often, the discharge is not plentiful and does not last longer than a few days. Sometimes they are accompanied by minor spasms, sometimes they are completely painless for a pregnant woman. nine0003  nine0003
nine0003  " nine0003
" nine0003  These stages differ just in the intensity of bleeding and the presence of pain.
These stages differ just in the intensity of bleeding and the presence of pain.  nine0003
nine0003