Foods to make baby poop
The Best Foods to Help Baby Poop (And a Few That Make It Worse)
Relieving your constipated baby can be as simple as feeding her the right thing. Load up on these foods to help baby poop (and avoid ones that worsen the problem).
1 / 11
SMarina/Shutterstock
Relieves Constipation: Prunes
No surprises here; prunes are one of the best high-fiber foods for a baby who’s having tummy troubles. If your little one is just starting solid foods, try cooking and mashing some prunes to feed her. You could also chop cooked prunes into small, bite-sized pieces—or use one of our other creative techniques for introducing new baby foods.
2 / 11
margouillat photo/Shutterstock
Relieves Constipation: Sweet potatoes
Sweet potatoes are delicious just about any way you prepare them, and they are also magic for a baby who needs to poop. They’re high in insoluble fiber, which will help your baby go right away. Try making your own baby food by cooking and mashing a sweet potato or roast fries in the oven for fun finger food.
This is how you know when to start feeding babies solid foods.
3 / 11
Mia Stern/Shutterstock
Relieves Constipation: Apples
An apple a day can keep constipation away! Apples (especially with the skin on) are high in fiber and can help pull water into your baby’s colon. This keeps baby’s poop soft and easy to pass. Try offering small pieces of cooked apple or pour some apple juice into a sippy cup to help get things back on track. Apples are a great stage 1 baby food. Learn more about what types of food to start feeding baby once they’re ready to go beyond formula or breastmilk.
4 / 11
mama_mia/Shutterstock
Relieves Constipation: Broccoli
If your baby hasn’t tried broccoli yet, there’s no time like the present! Broccoli is a vitamin powerhouse and is high in fiber. Try blending up cooked broccoli in a food processor or offering small, bite-sized pieces of soft, cooked broccoli. (Consider one of our recommended baby food makers.) If your baby is eating a variety of foods, try adding small pieces of broccoli to brown rice or scrambled eggs.
Try blending up cooked broccoli in a food processor or offering small, bite-sized pieces of soft, cooked broccoli. (Consider one of our recommended baby food makers.) If your baby is eating a variety of foods, try adding small pieces of broccoli to brown rice or scrambled eggs.
When he’s a little older, your kid will love these tasty broccoli side dishes.
5 / 11
nelea33/Shutterstock
Relieves Constipation: Pears
There is nothing more delicious than a ripe, juicy pear. Treat your baby to this seasonal treat to help relieve and even prevent constipation. Pears are one of the first foods babies can try and are high in fiber. They can be cooked, but are soft enough to be offered raw. Your baby can safely gum small pieces of ripe pear without teeth.
6 / 11
Sea Wave/Shutterstock
Relieves Constipation: Peas
If your baby is just starting solid foods, peas are usually one of the first options. This is good news if your baby needs help in the pooping department. Peas contain both soluble and insoluble fiber to help keep your baby’s poop soft and moving along. This makes it easier and quicker to pass without painful straining.
This is good news if your baby needs help in the pooping department. Peas contain both soluble and insoluble fiber to help keep your baby’s poop soft and moving along. This makes it easier and quicker to pass without painful straining.
7 / 11
nesavinov/Shutterstock
Relieves Constipation: Spinach
We usually save the fresh spinach for our own salads, but babies should be invited to the greens party, too. Spinach is loaded with fiber and vitamins that help make your baby’s poop easier to pass. Try blending up some fresh spinach in a fruit smoothie for both of you!
8 / 11
Brent Hofacker/Shutterstock
Causes Constipation: Cheese
Dairy products like small cubes of cheese or lightly flavored yogurt are easy foods for babies learning to eat solids. While safe and convenient, cheese is a low-fiber snack and can lead to constipation. Try cutting back on the dairy products for a few days and see if your baby improves.
Try cutting back on the dairy products for a few days and see if your baby improves.
You may think these foods are dairy-free, but they’re not!
9 / 11
Paulo Vilela/Shutterstock
Causes Constipation: Bananas
Bananas are a great first finger food for babies (and a yummy way to cut calories when baking). Unfortunately, they can also slow down your baby’s digestion, and thus slow down their pooping. Take a brief break from bananas and use this opportunity to give some new fruits a try.
10 / 11
images72/Shutterstock
Causes Constipation: Cereal
Whether your child is just starting out with rice cereal or has graduated to carrying a bag of Cheerios with her wherever she goes, babies and toddlers cannot get enough of this favorite first food. Cereal can lead to more formed poop, which could slow down the number of poopy diapers each day. Try cutting back on the amount of cereal and incorporating more fresh fruits and veggies.
Try cutting back on the amount of cereal and incorporating more fresh fruits and veggies.
Use up those Cheerios in one of these genius recipes.
11 / 11
Igor Dutina/Shutterstock
Causes Constipation: Processed foods
Processed foods like cookies, crackers and white bread are common snacks for growing babies and toddlers, but too much can quickly lead to constipation. While you don’t have to cut these foods out entirely, try to limit them if your baby is having tummy troubles. Or, try swapping out white flour for whole wheat. For example, brown rice is a tasty alternative to low-fiber white rice.
Originally Published: May 20, 2019
Carrie Madormo, RN
Now a freelance health and food writer, Carrie worked as a nurse for over a decade. When she isn't hunched over her laptop with a baby in hand, you will find her cooking her grandmother’s recipes, lacing up her running shoes or sipping coffee in the bathroom to hide from her three young children.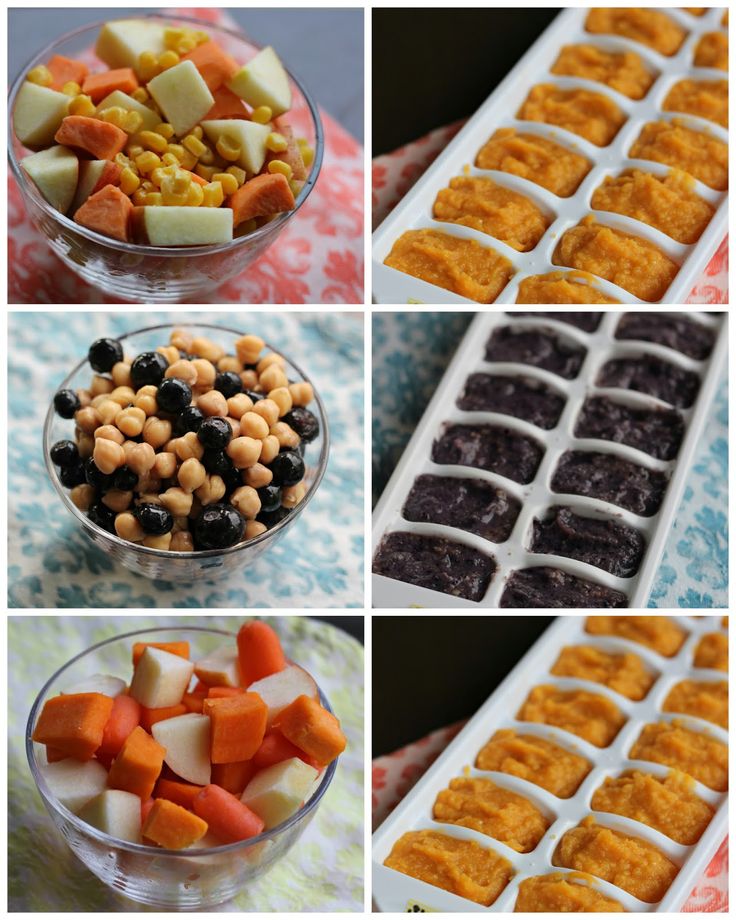
Are There Baby Foods that Help with Constipation?
While parenting brings many surprises, one of them is likely how much you’ll think about poop, or lack thereof, especially during that first year. But here you are worrying about your baby’s digestive tract and convinced that they’re constipated.
If you’ve recently introduced your baby to solid food, then your worries may be on target: solid foods can put a strain on your baby’s developing digestive tract and cause constipation. But there are things you can do to help!
Before you begin treating constipation you should determine if there is really an issue at all. So here’s the scoop on poop and how to tell if your worries are founded and your baby is constipated.
Breastfed babies
During the first few weeks, you’ll find yourself changing diapers with alarming regularity. Figure in every feed or so.
But don’t despair, because by the time your baby reaches 6 weeks old, they may have a bowel movement only once or twice a day. On the other hand, they may have one only every 7–10 days. (Yep, the frequency really can vary that much.)
On the other hand, they may have one only every 7–10 days. (Yep, the frequency really can vary that much.)
The poop is yellow, soft, runny and sometimes lumpy and the smell isn’t unpleasant.
Formula-fed babies
A newborn, formula-fed baby typically poops up to five times a day. At about 6 to 8 weeks, this may decrease to around once a day.
Formula-fed babies have poop that is a camel to brown color with a thicker consistency, more like paste. Most likely, the less-than-aromatic smell means you’ll hermetically seal soiled diapers before you toss them into the garbage.
Signs that your baby is constipated
You’ve noticed that your baby’s tummy isn’t following the schedule that you got used to. Could it be constipation? Here are the signs that could confirm your suspicions:
- You notice that they cry or fuss while they’re trying to have a hard bowel movement.
- The poop, when it does come, is like hard pellets.
- You notice streaks of red blood in the hard poop.

While it’s not easy for a baby on a liquid diet to become constipated, trouble can start when you start introducing your baby to solid foods at around 6 months. Here’s why:
New food types
Think of it as a learning curve: Your baby’s body is learning how to cope with a new kind of food to digest as they move away from their full liquid diet and you need to soften the learning curve. (Pardon the irresistible pun.)
Changes to fluid intake
Decreased fluids will make your baby’s poop harder and more difficult to push out. If they’ve started solids, they may need to up their fluid intake to offset the solid food. And if your baby is teething or feeling unwell, it can also lead to them taking in less fluid than usual.
Lack of fiber
Even though they’re just starting out, babies’ tummies work like ours. While initially the move to solids that have fiber (from breast milk or formula, which don’t) can cause temporary constipation, their tummies will adjust.
Make sure to monitor your baby’s fiber intake and pair it with plenty of hydration for a smooth ride the same way that you monitor yours.
OK, so you’ve confirmed that your baby is constipated. The next step is helping to alleviate the strain on their developing digestive system.
Remember that you can keep offering these foods as your baby develops into a toddler and beyond. In fact, there is little research or evidence to support specific foods (including high fiber ones) in treating or preventing constipation in infants. Most of these recommendations are based on evidence for older adults and children.
Keep in mind that good practice when introducing solids is to introduce foods as single ingredients. That way, if your baby is allergic to certain foods, you’ll be able to more easily trace the source.
If your little one hasn’t tried these foods before, don’t rush the process. Test out one at a time and then introduce combinations once you’re confident they’re well tolerated.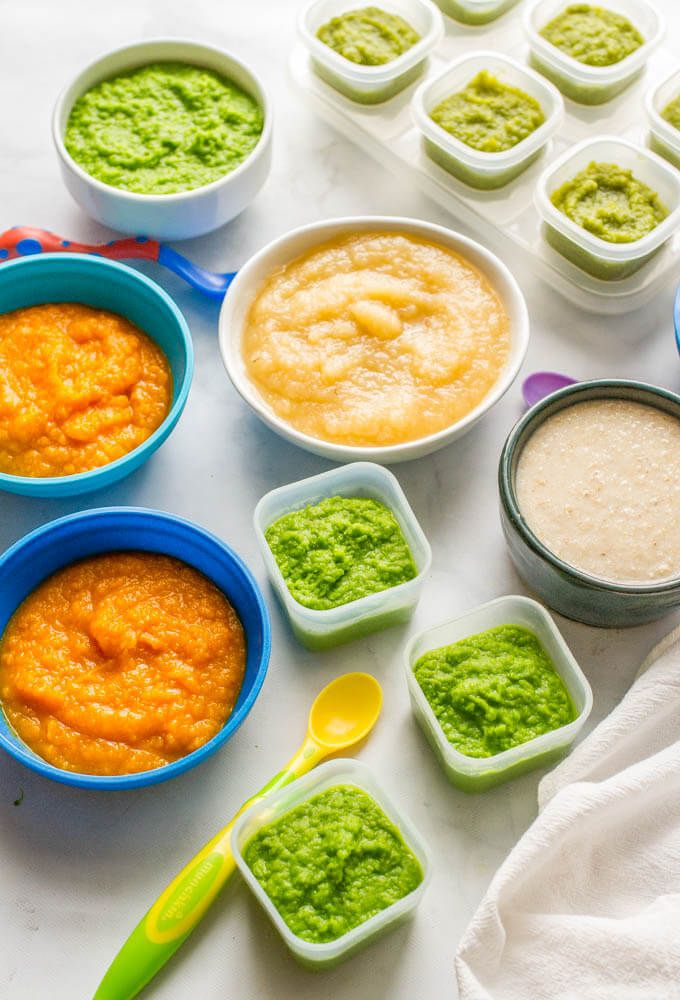
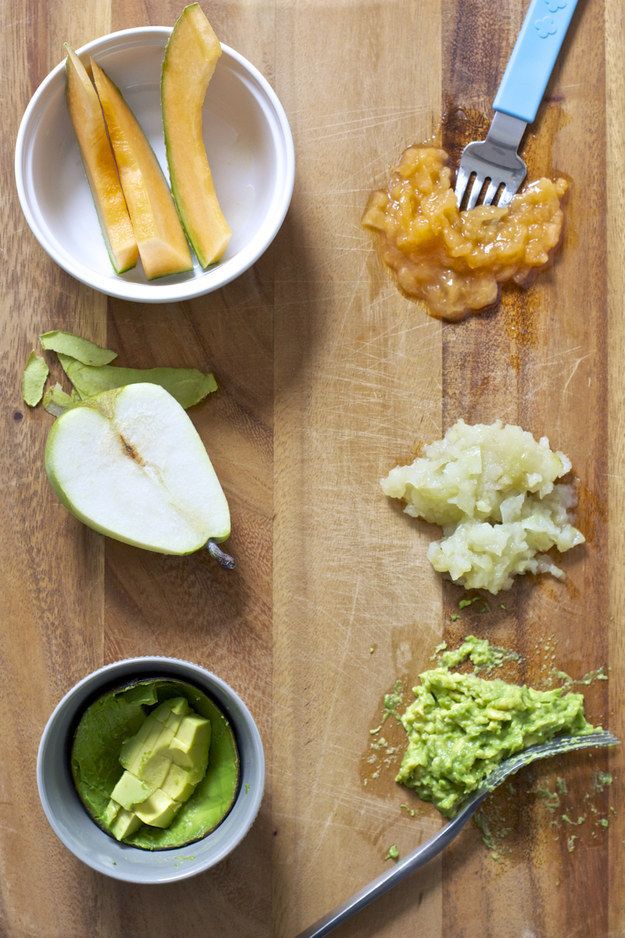
- Back to basics. Give your baby’s digestive tract a break by feeding them mashed avocado or sweet potato purée. These are easy to digest and may give your baby the kick start they need.
- B vegetables. Think broccoli, Brussels sprouts, and beans. Purée these for a meal filled with fiber.
- P fruits. Your grandmother was right — bring on the prunes for quick work. A purée that includes a mix of prunes plus pears, plums, or peaches should work magic. Try subbing the prunes with dates for a change.
- Bring on the fiber. If your baby is over 8 months, you can offer them whole grains like oatmeal, fiber-rich cereals, whole wheat pasta, and brown rice.
- Water intake. Until 6 months an exclusively breastfed or formula-fed baby doesn’t need to drink water. Above this age, you can introduce small amounts of water.
Plums and pears with cinnamon
Cut 2 or 3 pears and plums into small pieces.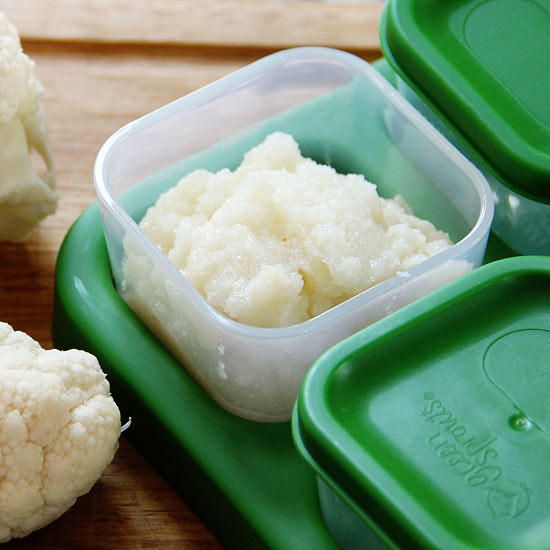 Place in a saucepan with a small amount of water and simmer until soft. Add in a sprinkle of cinnamon. Blend thoroughly.
Place in a saucepan with a small amount of water and simmer until soft. Add in a sprinkle of cinnamon. Blend thoroughly.
Sweet potato with apple and peach
Cut half a sweet potato, one apple, and half a peach into small pieces. Place in steamer basket and cook until tender. Blend until smooth.
Spinach and apple purée
Chop two apples into small chunks and cook in saucepan with about 1/2 cup of water. When they’re tender, add about 1 cup of spinach and cook another 2 to 3 minutes. Purée until smooth. Can be seasoned with cinnamon and ginger.
Some sources suggest prune, pear, and apple juices help to increase the water content in poop and can ease constipation.
However, the American Academy of Pediatrics recommends steering clear of fruit juice for children younger than 1 year old. You can stick with these fruits as purées for similar effects.
What is it about prune juice? The high levels of sorbitol and phenolic substances in prune juice and dried plums act as a laxative and diuretic properties. So if your child is over 1 year old, you can use small amounts of prune juice to encourage their system to run.
So if your child is over 1 year old, you can use small amounts of prune juice to encourage their system to run.
Some studies show that constipation may affect as much as 30 percent of children. If your child is part of the unlucky statistic, here are some foods that you may want to give them smaller amounts of until it passes:
- bananas
- dairy products such as cheese and yogurt
- low fiber foods like white rice, white bread, and white pasta
If you’re like most parents, you’ll be up for whatever you can try to help your baby get comfortable fast. Here are a few tricks that you can use to ease your baby’s constipation:
- Warm baths. These can relax those abdominal muscles and get them working.
- Exercise. Lay your baby on their back and push their legs alternately as if they’re cycling a bike. Alternatively, hold their knees and feet together and push their feet towards their belly.
- Massage.
 Use your fingertip to draw clockwise circles on your baby’s stomach.
Use your fingertip to draw clockwise circles on your baby’s stomach.
If you see that despite your home remedies, your baby still is having hard stools or hasn’t pooped after 2 or 3 days from their last hard stool, then contact your pediatrician. Especially if you consistently notice blood in their poop or your baby is extremely irritable and appears to be in pain.
While dealing with your baby’s toilet issues may seem a tad unsavory, you’ll soon be so used to it, that you’ll find yourself sharing your insights over coffee with other parents. And don’t be shy about sharing the yummy food combinations you discover to keep things moving.
Laxative products for constipation - KGBUZ City hospital No. 12, Barnaul: Articles
Nutrition is one of the constipation mechanisms. Therefore, complex treatment always requires one or two nutritional therapies, including adjustments to food intake and how to eat. In some cases, it is denied that this product has the effect of laxatives without laxatives or which can normalize this limited use and stools. He should n-about it in the article.
He should n-about it in the article.
Nutrition as a cause of constipation
The effect of food on intestinal motility and excrement may vary depending on mechanical, thermal and chemical effects. One product is weak, and on the contrary, it is connected. Those with shredded meat and dietary fiber reduce motor bowel function and slow stool progress. And because of the low content of organic acid and salt, this leads to moisture (from the intestines to the bloodstream) and reabsorption of the stool.
Delay in the chair contributes to the abuse of the following products.
- Gourmet food: the best foods, sweets, quick porridge, etc.
- Chopped meals and junk food: mashed soup, minced meat, a small amount of unions, vegetables and mashed fruits, jelly.
- Use of heated and chopped vegetables and fruits rather than raw vegetables in the vast majority of cases.
- Fast food, snacks, Dreabute first, chips.
- Dark tea, cocoa, chocolate.

- Eating multiple meals, eating on the go, overeating, many snacks 3.
Which Foods Weaken
Firstly, sexual nutrition contributes to the fact that foods with a laxative effect are included in the diet, that is, to ensure normal stool.
Food ingredients that make stools easier
1
Although rarely absorbed in the intestines, it loosens stools, increases quantity, mechanically stimulates large bowel movement and promotes defecation.
Crude fiber is used as a source of nutrition for the "beneficial" intestinal flora (Bifidobacteria, lactic acid bacteria), which is useful for improving 3. The configuration of the intestinal flora affects bowel movement 5, and the increase in dietary fiber in meals helps relieve constipation.
A "clean" product 2.3 that contains a lot of raw fiber
- Vegetables and fruits such as cheese, cooked food, baked food. Vegetables, cabbage, cucumber, carrots, beets, pumpkins, cutlets, onions and apples, pears, plums and bananas are especially effective.
- Coarse flour, i.e. cereal bread. It is found in grain film containing dietary fiber.
- Natamame and buckwheat "coarse" scattered porridge, automatic wheat (not tangled with oatmeal), "clear", bulgle, quinoa, etc.
- Meat containing tissues and skin fibres. Of course, animal ties not only belong to vegetable fibers, but are assimilated with difficulty.
- Dry fruits: prunes, dry application.
It must be borne in mind that wonderful fibers are contraindicated not only in the process of acute inflammation of the stomach and intestines, but also in intestinal movement, which increased bowel movements. Therefore, it is necessary to talk to a doctor who repeats the violation of the president.
2. Sugar substance
Sugar substance and products containing it (Tensai, sugar cane, honey, whole milk, jam, sweet fruits and its juice) also have a slowing effect. 2.3 Pulling a large amount of body fluid into the intestines. Ferring under the influence of the intestinal flora, the product increases in the intestinal cavity. For this reason, the stool contains a lot of water and becomes softer. Of course, do not abuse sweets, but they should not be discarded, because they have a positive effect on gastrointestinal function.
Ferring under the influence of the intestinal flora, the product increases in the intestinal cavity. For this reason, the stool contains a lot of water and becomes softer. Of course, do not abuse sweets, but they should not be discarded, because they have a positive effect on gastrointestinal function.
3. Organic acid
Organic acids increase intestinal excretion, increase the amount of water in the stool and activate peristalsis 2,3.
What is a weak "sour" food?
First, 3.
- Kefir, not fresh, 1-2 days old, low nutrition fermented dairy products such as yogurt, buttermilk, whey and Kinmizu.
- Acidic fruit and vegetable juice (tomato, rhubarb).
- Fruit drink 2.
The use of a product containing large organic acids increases the acidity of the stomach, causing high acid gastritis (high acid levels) and digestive ulcers in the stomach and duodenum.
4. Salt
Curries, pickles, corn and roe are rich in salt such as sodium chloride. Salt is 1.2, which draws body fluids into the intestines and dilutes the contents.
Salt is 1.2, which draws body fluids into the intestines and dilutes the contents.
Products containing salt contain mineral water that contains a lot of salt, eg hydrogen salt sulfate water, eg minerals up to 8 g per litre.
5. Fat
Lipids found in many foods make stools and bowel movements smooth.
Fatty laxatives are as follows.
- Butter, fresh cream, cream with 27% or more fat.
- Vegetable oil: sunflower oil, olive oil, corn, canola, rapeseed.
- Fish oil and high fat fish.
- Lard, thick pork, lamb, etc.
- Mayonnaise, fat sauce, dressing 2.3.
6. cold food
When the "cold" sensory container in the mouth is stimulated, the muscles of the digestive tract are reflexed and peristalsis is increased.
This is their “work style”.
- Cold drink
- Cold soup (beetroot, Okuroshka).
- Cold desserts such as ice cream
7.
 Carbonated (carbon dioxide)
Carbonated (carbon dioxide) Additive carbonated water, mineral water and horsemeat contain carbonic acid. In the binding state, it is rapidly decomposed by water and carbon dioxide, forming a large number of bubbles, stimulating the receptor, and increasing the volume of the intestinal content to stimulate peristalsis. Be careful when using "soda" for stomach and intestinal inflammatory diseases.
Surprising
- Diet therapy for constipation requires not only the selection of “relaxants”, but also sufficient water (2 to 2.5 liters per day).
- Diet and calorie balance 2.
- Meals a-necorono, at least 4 times a day, breakfast is higher than other meals.
- It is effective to drink cold drinking water, mineral water, freshly squeezed fruit juice and vegetable juice in the morning and on an empty stomach.
- As a second breakfast, you should eat fresh vegetables and fruits and drink low-nutrition milk such as kefir and yogurt before going to bed.

- For constipation associated with a sedentary lifestyle, therapeutic exercises, swimming, massage, self-massage of the anterior abdominal wall are recommended.
Features of nutrition in certain types of constipation
Since stool impingement may be accompanied by a decrease and increase in intestinal motility, the choice of foods that affect peristalsis should be differentiated1,2,3.
For hypomotor (atonic) constipation, in which intestinal motility is impaired, a diet high in fiber is preferred 1,3. Stimulates peristalsis to improve intestinal tone and normalize stools 1 .
Hyperactive or spasmodic constipation is characterized by increased intestinal tone and associated abdominal pain. Eating foods high in indigestible fiber can overstimulate intestinal motility, aggravate symptoms, and increase discomfort.
Therefore, within 5-7 days after the start of treatment, doctors recommend avoiding a low-fiber diet for spastic constipation.
- Vegetables and fruits must be minced and cooked only.
- Flour products are made only from the highest quality flour.
- Milled grain Processed grain only 1.3.
Other laxatives are recommended to restore normal intestinal motility in spasm of the intestinal muscles 1.3:
- vegetable oil
- salty, sweet
- dairy products
- Berry puree and juice with pulp.
- degassed mineral water
Gradually introduce fiber into your diet.
Along with the diet, doctors prescribe laxatives if necessary 3 . Microclysters (MICROLAX® 4) are recommended for defecation, especially for acute and chronic constipation.
Microclysters begin to work in 5-15 minutes. Sodium citrate removes binding fluid from the intestine, sorbitol draws water into the intestinal lumen, and sodium lauryl sulfoacetate further thins the stool. This speeds up and facilitates bowel movements4.
Due to its high safety, it can be used not only by adults, including pregnant women, but also by infants. There is no need to achieve daily stool. Special diets should "accustom" the intestines to emptying.
There is no need to achieve daily stool. Special diets should "accustom" the intestines to emptying.
The information in this article is for guidance only and is not intended to replace professional medical advice. Consult a qualified physician for diagnosis and treatment.
Constipation is a dysfunction of the intestines, expressed in an increase in the individual physiological interval between bowel movements or in a systematic insufficiency of stool (1994).
The frequency of stools in healthy people is purely individual and depends on the diet, lifestyle and habits. Constipation is chronic retention of stool for 48 hours or more.
Treatment programs for constipation vary from person to person, of course, but general recommendations can be made.
Etiological treatment
There are many causes of constipation. Before you start treating constipation, you need to find out the cause.
Dietary constipation - develops with improper, unreasonable, monotonous nutrition, mechanically and chemically low-fiber products.
Foods that delay stool include shunting, rice porridge, slimy soup, jelly, ground food, strong tea, coffee, chocolate, and blueberries.
The inclusion of foods that promote eating habits and promote bowel movements in the diet may lead to the elimination of nutritional constipation (dietary therapy will be described later).
More constipation in-more occurs, and occurs in relation to disturbance of intestinal movement at any level of the nervous system. The maturation of defecation is under the control of the cerebral cortex, and the execution of defecation is involved in the lower back and the sacral nucleus.
It is divided into nerve causative constipation.
- Disconic
- Dyskinesia; Dyskinesia; Dyskinesia; Dyskinesia; Dyskinesia;
- Those who and because of the suppression of the desire to defecate (addictive constipation).
Constipation on exercise disorder is caused by primary disorders of bowel movement (motor reduction or spasms), and reflects constipation caused by various diseases such as gastrointestinal and urology (dysfunction of the secondary intestinal tract).
Weakness of the desire to defecate is the primary psychogenic effect (habitual constipation, suppressing the desire to defecate, for example, there is no way to recover from work), habitual defecation rhythm, morning rush. Defecation mechanisms may arise, especially when children are vulnerable.
If neurons or psychogenic constipation are found, rational psychotherapy is required, the habit of emptying the intestines every day (going to the toilet at the same time, see Exercises below), honey and lemon on an empty stomach. It is necessary to drink Cold water (this contributes to the development of gastrointestinal reflexes). It is also recommended for patients with neurosis or psychosomatic constipation to choose the optimal position for defecation (preferably squatting), during the first few days to facilitate defecation., Glycerin and a small oil enema (50-100 milliliters of vegetable oil) can be used. and in the future the need will disappear for them. When the effect of the above measures cannot be obtained. Complete the remaining modules of the treatment program.
Complete the remaining modules of the treatment program.
Low-artery-constipation due to low exercise, lack of exercise and weakness in the body. Nutritional constipation can occur not only in the elderly, but also in patients who rest in bed for long periods of time. Age and due to a sharp decrease in physical activity.
An active lifestyle, walking and physical education contribute to the elimination of low arterial constipation.
Constipation and due to inflammatory bowel disease is found in patients with chronic colitis, but not in many patients with chronic enteritis. Treatment of these diseases contributes to the restoration of the stool.
Patients with anus disease (hemorrhoids, anal line, rectal pain, etc.) have rectal constipation. Removing this condition will eliminate constipation.
Mechanical constipation in patients with intestinal tumors, stenosis of the colon, external mechanical pressure of the rectum, etc.
By removing these factors, it contributes to the normalization of the stool.
Constipation due to abnormal growth in large intestinal giant colon, specific giant colon, etc.
Occupational poisoning of chronic toxic constipation (lead, mercury, teric) and smoker's nicotine poisoning.
Medical constipation caused by certain medications. It contains a lot of sleeping pills, diuretics, adsorbent (activated carbon) and iron.
So if you stop these drugs, the constipation will be resolved.
Endocrine constipation p-Hypothyroidism (hypogenic constipation), hypothyroidism (hypertension, convulsive constipation), pituitary gland dysfunction, diabetes, non-sighted, sparkling cells, glucagonoma. This is not much observed and because of the menopause.
Constipation due to metabolic abnormalities and insufficiency, renal failure due to dehydration of all causes.
Physical activity regimen
If the general conditions are allowed, it is necessary to send an active lifestyle: physical education, sports, outdoor games, running, walking and swimming a lot, improve bowel emissions, and muscles containing ABS. Contribute to reinforcement.
Contribute to reinforcement.
Health food
For constipation, we recommend health food as part of meal number 3.
Energy value and composition: white c-100 g, fat r-100 g, carbohydrates 400-450 g, salty 8-10 g, free c-1.5 l, weight s-2. Kg (and due to the weight of the patient), energy value: 2900-3000 kcal.
This is a list of recommended meals.
Bread and bakery products: wheat bread with whole grain or wheat bran, yesterday; if there are no contraindications and good resistance, black bread is more suitable; it is better to add dry biscuits and bran. Cracker (if possible).
Soup: low fat, fish soup, vegetable soup. Borscht, beet soup (from existing vegetables), pearls, buckwheat, cauliflower.
Meat dishes: red meat (beef, vine, vandettes, chicken, rabbits, seven birds), boil, bake and basically banish them.
Fish dishes: low fat fish (Suzuki, sea bream, cod, carp, camas, melruza), white fish and nurelin resistant.
Gargle dishes and vegetables: salads with raw vegetables and boiled vegetables as garnishes. Plots, pumpkin, cauliflower, white cabbage, green peas, etc. Pleasant and acceptable bumps, carrots, tomatoes, lettuce, cutlet, pumpkin, cauliflower, white cabbage, green peas, etc. Except for vegetables rich in essential oils: cub, radish, onion, garlic, radish. Mushrooms.
Cooking and garnishing with cereals and pasta is allowed to limit the quantity and use of broken cereals such as buckwheat, barley and crushed grains.
Egg dishes: 1-2 per day (for soft, scrambled or gourmet dishes). Hard eggs cause constipation! ?
Sweet foods, fruits, berries: fresh, ripe sweet fruits and berries are used to increase the amount for cooking or juice.
Dried fruits and berries soaked in various dishes are especially recommended for plums, dry applications, apricots and figs.
Apple or grape juice is not recommended, plum juice is effective. Plums are recommended in any form, as plums contain organic acids that promote bowel movements.
Recommended to use 24 plums, 12 fruits, ½ cup and twice a day.
Jam, rose, marshmallow, hard, milk and cream candy, jam, jelly, marmalade, sweet fruits, berries and honey are fine.
Dairy products: Kefir constant (raw), sourdough, curdled milk, fermented baked milk, fresh non-acidic cottage cheese (whole form, casserole, cheesecake, unhurried dumplings). Milk with broad tolerance for cooking and tea. Non-acidic sour cream in the form of seasoning is used in cooking in small quantities. The cheese is not spicy.
Sauces and spices: parsley, dill, coriander, celery, bay leaf, cinnamon, cloves. Fruit sauce, white sauce and some fresh cream.
Snacks: soft cheese, black caviar, lean ham, beef, chicken, fish, herring sauce, vegetable and fruit salad Seaweed is very healthy and effective.
Drinks: afternoon tea, rose soup, weak coffee substitutes, sweet fruit juices (plums, apricots), vegetables (tomatoes, carrots, etc.).
Fats: butter, olive oil (added to side dishes, served natural). Sunflower oil and other vegetable oils are allowed. Free of flame retardant animal fats: porcine, beef, lamb fats, mixed fats.
Sunflower oil and other vegetable oils are allowed. Free of flame retardant animal fats: porcine, beef, lamb fats, mixed fats.
In the absence of contraindications, it is reasonable to recommend a "green diet" consisting of 100 g of raw vegetable salad three times a day before meals.
When considering your daily diet, you need to consume at least 25-30 g of dietary fiber per day. Dietary fiber promotes intestinal peristalsis and promotes its emptying.
It indicates the content of dietary fiber in various foods in grams per 100 g of product (1992).
- Orange - 1.4
- carrots - 1.2
- Cherry - 0.5
- wheat bran — 8.2
- Canned peas…1.1
- Peach (pulp/skin)・・・0.9
- Dried mushrooms — 19.8
- Parsley - 1.5
- pear - 0.6
- Raw rhubarb - 1.0
- White cabbage - 1.0
- Turnip - 1.4
- Sauerkraut - 1.0
- Plum - 0.5
- Cauliflower - 0.
 9
9 - Fresh tomatoes・・・0.8
- potatoes - 1.0
- Bread - 2.1
- Strawberries - 4.0
- grain bread - 1.3
- buckwheat - 1.1
- Rye bread - 1.1
- Gooseberry - 2.0
- plums - 1.6
- dried apricots - 3.2
- Apples - 0.6
- Leek - 0.9
- Dried apples・・・5.0
- Blackberry - 5.0
Physiological effects of dietary fiber: increased satiety, appetite suppression, reduced hypercholesterolemia, increased choleresis, increased fecal volume, liquefaction of intestinal contents, increased intestinal transit.
Patients suffering from constipation may benefit from including laxative bran in their diet.
(1981) and (1983) recommend its use as follows.
Pour boiling water over “wheat bran” (to swell and soften) and drain off fat-free. Swollen bran (can be added to compotes, jelly, soups) 1 teaspoon 3 times a day for the first 2 weeks, then increase to 1-2 tbsp. once. Treatment continues for at least 6 weeks.
once. Treatment continues for at least 6 weeks.
Laxatives
For chronic constipation, laxatives should generally be avoided. Not indicated for alimentary neurogenic endocrine constipation. However, very persistent constipation, especially in elderly people with dysmotility or rectal constipation, requires the use of laxatives.
The most harmless laxative.
Lactulose (Normaz, Duphalac) - the drug does not undergo hydrolysis in the intestine, creating favorable conditions for the growth of lactic acid bacteria. Available in the form of a syrup containing 67 g of lactulose per 100 ml. Assign 1-3 tablespoons per day, then reduce to 1-2 tablespoons per day as desired.
Glycerin filled suppositories: Contains 1.44 g glycerol, 0.12 g stearic acid and 0.66 g sodium carbonate per suppository. When a suppository is introduced into the rectum, it has a slight irritating effect on the mucous membrane, causing reflex defecation and softening the stool. Enter 1 suppository 15-20 minutes after breakfast 1 time per day.
Enter 1 suppository 15-20 minutes after breakfast 1 time per day.
Glycerin suppositories are contraindicated in exacerbation of hemorrhoids, anal fissures, inflammatory and neoplastic diseases of the rectum.
Herbal preparations are widely used to treat constipation. Laxative medicinal plants include senna leaf, sea buckthorn bark, alfalfa fruit (sea buckthorn laxatives), rhubarb root, seaweed, licorice root/rhizome, fennel herb, oxalis root, dragontongue leaf, magnolia stem, rhubarb rhizome, wild rhubarb stem, flaxseed etc. .
Collection Part 1
- 3 parts senna leaves
- 2 parts sea buckthorn bark
- 2 parts chocolate fruit
- 1 anise pod
- 1 part licorice root
Brew 1 tablespoon with a glass of boiling water, leave for 30-40 minutes and drink half a glass in the evening.
Concentration #2
- 1 senna leaf
- 1 dill
- 1 part chamomile flower
- 1 peppermint leaf
- 1 part valerian root
- 1 immortelle flower
Prepare as set #1. Take 1 or 1/2 cup twice a day in the evening.
Take 1 or 1/2 cup twice a day in the evening.
Normalization of intestinal motility
Patients with constipation develop various types of colonic motility disorders.
Especially if the constipation is caused by suppression of the need to defecate, the patient must (absurdly) regain the self-defecation reflex.
You will be advised to drink cold water or fruit juice in the morning on an empty stomach. After 30 minutes, have breakfast, go to the bathroom, get into proper posture (lower back to belly) and exhale each time to try to induce a bowel movement.
During defecation, it is also effective to massage the abdomen with your hands, rhythmically draw in the anus, press between the coccyx and the anus. If this is not enough, add 0.5-1 teaspoon of Karlovy Vary salt to morning fruit juice or cold water (but in my opinion this is extreme) and insert a glycerin suppository into the anus after breakfast.
If the defecation reflex can be induced, stop suppositories and laxatives and continue to drink only cold water in the morning.
Treatment with mineral waters
For constipation, mineral waters are indicated: Essentuki No. 17 and No. 4, Batalinskaya, Slavyanovskaya, Jermuk.
Mineral water "Essentuki" No. 17 is prescribed for constipation, accompanied by hypomotility of the colon (tendency to spasms), and mineral water "Essentuki" No. 4 is prescribed for constipation, accompanied by hypermotility of the colon.
Drink 1 glass of cold mineral water 2-3 times a day 1-1.5 hours before meals for several weeks. Warm mineral water is preferred for constipation with hyperkinetic dyskinesia.
Physiotherapy
I can't do it at home. And the effect, to be honest, is not good.
Therapeutic exercise (LFK), special gymnastics, massage
Therapeutic exercise plays a very important role in the treatment of constipation.
The data show that exercise regimens specifically include diaphragmatic breathing, alternating bent leg pulls to the abdomen, bent leg lateral extension, cycling exercises, lifting the pelvis relative to the legs, and bending the legs to press against the anterior abdominal wall. movements such as pushing, rhythmic sphincter contractions, and withdrawals (repeated throughout the day) are needed.
movements such as pushing, rhythmic sphincter contractions, and withdrawals (repeated throughout the day) are needed.
The exercise can be performed lying on your back or in an upright position on all fours. In addition, people with constipation should exercise daily in the morning and lead an active lifestyle.
Exercises are also recommended, including special breathing techniques that increase intra-articular pressure, stimulate peristalsis, and serve as dependent stimuli.
The exercise is as follows.
Deep breath with protrusion of the abdominal wall - pause 5-10 s, full breath with retraction of the anterior abdominal wall - pause 5-10 s. Inhale deeply and exhale 3 times. After a few calm breaths, repeat the cycle again (7-10 times between trips to the toilet). Before starting a workout, it is recommended to drink cold water (with honey or lemon) on an empty stomach.
What does dysbacteriosis mean? What diagnostic methods are modern and reliable? What drugs are used for mycobacteria? There are more than 500 types of microorganisms in the human intestine, and the total number is
What is dysbacteriosis? What are the modern and reliable diagnostic methods? What drugs are used for mycobacteria?
There are more than 500 types of microorganisms in the human intestine, 1014 in total, which is an order of magnitude higher than the total cellular composition of the human body. The number of microorganisms increases in the peripheral direction, and the colon contains 10 11 bacteria per 1 g of feces, which corresponds to 30% of the dry residue of the intestinal contents.
The number of microorganisms increases in the peripheral direction, and the colon contains 10 11 bacteria per 1 g of feces, which corresponds to 30% of the dry residue of the intestinal contents.
Normal microflora in the intestines
In the intestines of a healthy person, there are up to 10 5 bacteria per 1 ml of intestinal contents. Most of these bacteria are streptococci, staphylococci, lactobacilli, other gram-positive aerobic bacteria and fungi. Enterococci, Escherichia coli, bacteroids, anaerobic bacteria, etc. increase to 10 7 - 10 8 in the peripheral ileum. Recently, we found that the concentration of the intestinal parietal microbiota is 10 11 cells/ml, which is six orders of magnitude higher than in the lumen. About 50% of the biomass of the parietal microbiota are actinomycetes, about 25% - aerobic granulococci (staphylococci, streptococci, enterococci, granulation tissue), 20-30% - bifidobacteria and lactobacilli.
Anaerobes (Pentostreptococci, bacteria, clostridia, propionobacteria) make up approximately 10% in the small intestine and up to 20% in the large intestine. Enterobacteriaceae make up 1% of the total mucosal microbiota.
Enterobacteriaceae make up 1% of the total mucosal microbiota.
Up to 90-95% of microorganisms in the large intestine are anaerobes (bifidobacteria and bacteria), strictly aerobic and any flora (lactobacilli, E. coli, enterococci, staphylococci, fungi, protists) They say it is only 5-10%.
Food coli, enterococci, bifidobacteria and acid bacilli have a clear antagonistic effect. Under conditions of normal functioning of the intestine, it is possible to suppress the growth of microorganisms of pathological microflora.
The area of the internal surface of the intestine is about 200 m2. Reliably interferes with penetration of food antigens, microorganisms and viruses. An important part of this defense organization is the body's immune system. Approximately 85% of human lymphoid tissue is concentrated in the intestinal wall, where secretory IgA is produced. The intestinal flora stimulates the immune defense. Intestinal antigens and intestinal bacterial toxins markedly increase IgA secretion in the intestinal lumen.
The decomposition of non-nutritional substances in the large intestine is carried out by bacterial enzymes with the formation of various amines, phenols, organic acids and other compounds. Toxic products of microbial metabolism (precipitates, amines, such as histamine) are excreted in the urine and usually have no effect on the body. Small fatty acids are formed during the utilization of uncovered carbohydrates (dietary fiber). Provides energy to the intestinal cells and improves the nutrition of the mucous membrane. Deficiency of dietary fiber can impair the permeability of the intestinal barrier due to the lack of short chain fatty acids. As a result, intestinal bacteria can enter the bloodstream.
In the distal ileum, microbial enzymes influence the degradation of bile acids and the conversion of primary bile acids to secondary bile acids. Normally, 80-95% of bile acids are reabsorbed, and the rest is excreted in the faeces as bacterial metabolites. The latter contribute to the normal formation of feces, delay the absorption of water and prevent excessive dehydration of feces.
dysbacteriosis
The concept of enterobacteriosis includes excessive microbial contamination of the small intestine and changes in the microbial composition of the large intestine. Most patients with pathology of the intestines and other parts of the gastrointestinal tract have some degree of microbiota disturbance. Thus, dysbacteriosis is a bacteriological concept. The disease can be considered as one of the symptoms or complications of the disease, but not as an independent condition.
If the intestinal environment becomes extremely abnormal, bacteria from the gastrointestinal tract (bacteria) may appear in the blood or sepsis may develop.
The composition of the intestinal microbiota is disturbed in intestinal and other gastrointestinal diseases, treatment with antibiotics and immunosuppressants, exposure to adverse environmental factors.
Whether it manifests itself as a clinical symptom depends on the localization of changes in biofortune telling.
Enterobacterial diseases of the small intestine
With enteromycosis, the number of microorganisms in the mucous membrane of the small intestine increases, and the number of others decreases. Eubacterium (30 times increase), α-turbulosis (25 times increase), Enterococcus (10 times increase), Candida (15 times increase), the appearance of bacteria of the genus Acinetobacter, herpes virus increased. Microorganisms such as most anaerobes, actinomycetes and cresel bacteria that naturally inhabit the intestines are reduced by 2-30 times.
Causes of intestinal bacterial disorders include: a) excessive entry of microorganisms into the small intestine due to dysfunction of the Achilles tendon and iliac valve and b) impaired intestinal digestion and absorption, for example, in conditions favorable for growth.
Increased microbial growth in the small intestine leads to premature degradation of bile acids and their loss in the faeces. An excess of bile acids promotes colonic motility, causing diarrhea and intestinal obstruction, and a lack of bile acids inhibits the absorption of vitamins from lipids, leading to the development of diseases of the biliary tract.
Bacterial toxins and metabolites such as phenols and biogenic amines can bind to vitamin B12.
Some microorganisms are cytotoxic and damage the epithelium of the small intestine. As a result, the height of the villi decreases and the crypts deepen. Electron microscopy reveals changes in microorganisms, mitochondria and the endoplasmic reticulum.
Insoluble colon
The composition of the microflora of the colon is affected by the weakening of the body's defense mechanisms (extreme climatic and geographical conditions, the biosphere of industrial waste and various chemicals, infectious diseases, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, malnutrition, ionizing radiation). various factors and adverse effects.
The development of colibacillosis is closely related to same-sex factors, including the use of antibiotics and sulfonamides, immunosuppressants, steroid hormones, radiation therapy, and surgical interventions. Antimicrobial drugs significantly suppress the development of not only pathogenic microflora, but also the normal microflora of the large intestine. As a result, external microbes and drug-resistant endogenous species (staphylococci, proteus, yeast fungi, enterococci, pseudonipple bites) develop.
As a result, external microbes and drug-resistant endogenous species (staphylococci, proteus, yeast fungi, enterococci, pseudonipple bites) develop.
Clinical signs of dysbacteriosis
Clinical manifestations due to microbial overgrowth in the small intestine is one of the etiologies of chronic recurrent diarrhea such as small intestine diverticulosis, partial intestinal obstruction, gastric and intestinal surgery, severe diarrhea, lipoma, 12- Acting in some diseases leading to anemia deficiency, it may not be at all.
Features of the clinical course of patients with escherichiosis in most cases cannot be established by bacteriological analysis of feces. Patients with chronic bowel disease are more likely to contract acute intestinal infections than healthy individuals. This is probably due to the reduced antagonism of the normal microflora, especially with the frequent deficiency of bifidobacteria.
Pseudomembranous colitis is particularly common and occurs in some patients treated with long-term broad-spectrum antibiotics.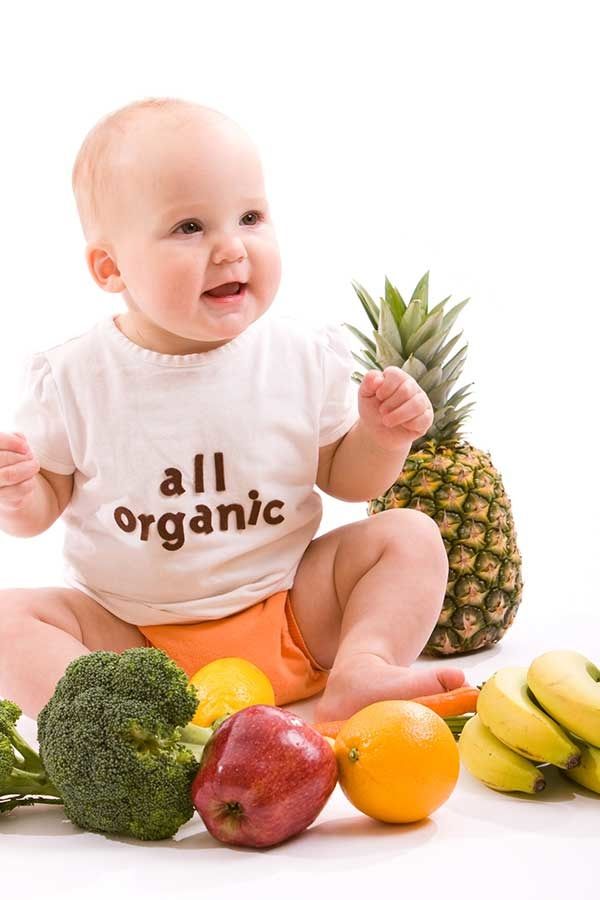 This is a severe variant caused by the suppression of the normal flora by toxins secreted by pseudomembranous rods Clostridium difficile that multiply in the intestine.
This is a severe variant caused by the suppression of the normal flora by toxins secreted by pseudomembranous rods Clostridium difficile that multiply in the intestine.
The main symptom of pseudomyomeomic colitis is a large amount of diarrhea in the form of water that develops before antibiotics are prescribed. After that, there is pain in the abdomen, such as cramps, fever, and white blood increases in the blood. Endoscopic imaging of pseudomacominia colitis is characterized by plaques, bands, and a continuous "film" and is soft but adherent to the mucosa. This change is most noticeable in the distortions of the colon and rectum. The mucous membrane is swollen, but there is no secretion. In an organizational test, there is infiltration of the subcutaneous epithelium, infiltration of circular cells in the plaque captain, and exit from erythrocytes outside the blood vessels. At the stage where pseudomia is formed under the epithelium of the mucosal surface, an infiltration of the secretion appears. The epithelium layer rises and is absent in some places. The bare part of the mucous membrane is covered only with epithelial epithelium. In the second half of the disease, these areas may occupy a segment of the large intestine.
The epithelium layer rises and is absent in some places. The bare part of the mucous membrane is covered only with epithelial epithelium. In the second half of the disease, these areas may occupy a segment of the large intestine.
Outbreak flash flow of false colitis resembling cholera is rare. Dehydration progresses within a few hours, which gives a fatal ending.
Therefore, the clinical significance of dysbiotic changes should be made on the basis of clinical symptoms as well as the results of a fecal microbial examination.
Diagnosis method
The diagnosis of dysbiosis is a difficult and frustrating task. For the diagnosis of square use, culture of the small intestine solution obtained using a sterile probe is used. Escherichia coli is detected by bacterial testing of fecal stool.
Microbial flora produces large amounts of hydrogen-containing gas. This phenomenon is used to diagnose disbaisis. The concentration of hydrogen in exhalation directly depends on the severity of d-oblomatofimer bacteria. In patients with bowel disease with chronic diarrhea and bacterial abscesses in the small intestine, expiratory hydrogen concentrations significantly exceed 15 ppm.
In patients with bowel disease with chronic diarrhea and bacterial abscesses in the small intestine, expiratory hydrogen concentrations significantly exceed 15 ppm.
Loading on racculose is also used to diagnose disbaisis. Normally, racculouses are not broken down in the small intestine and are metabolized in the microbial cells of the large intestine. As a result, the amount of hydrogen contained in the exhalation increases (Fig. 1).
| Figure 1. Exhaled hydrogen concentration |
The most common bacterial signs of Escherichia coli are the absence of bifidobacteria, which are the main bacterial symbiosis, and the number of lactic acid rods. Intestinal bacillus, ileum, crostia, staphylococcus aureus, fungus, yeast proteins are increased. Every bacterial symbiosis appears in a pathological form. Porilla blood cells, intestinal bacilli that have weak expression of enzymes, and intestinal intestinal. The main symptoms of Pseudomacomae colitis is a large amount of diarrhea in the form of water and develops prior to prescription of antibiotics. After that, there is pain in the abdomen, such as cramps, fever, and white blood increases in the blood. Endoscopic imaging of pseudomacominia colitis is characterized by plaques, bands, and a continuous "film" and is soft but adherent to the mucosa. This change is most noticeable in the distortions of the colon and rectum. The mucous membrane is swollen, but there is no secretion. In an organizational test, there is infiltration of the subcutaneous epithelium, infiltration of circular cells in the plaque captain, and exit from erythrocytes outside the blood vessels. At the stage where pseudomia is formed under the epithelium of the mucosal surface, an infiltration of the secretion appears. The epithelium layer rises and is absent in some places. The bare part of the mucous membrane is covered only with epithelial epithelium. In the second half of the disease, these areas may occupy a segment of the large intestine.
The main symptoms of Pseudomacomae colitis is a large amount of diarrhea in the form of water and develops prior to prescription of antibiotics. After that, there is pain in the abdomen, such as cramps, fever, and white blood increases in the blood. Endoscopic imaging of pseudomacominia colitis is characterized by plaques, bands, and a continuous "film" and is soft but adherent to the mucosa. This change is most noticeable in the distortions of the colon and rectum. The mucous membrane is swollen, but there is no secretion. In an organizational test, there is infiltration of the subcutaneous epithelium, infiltration of circular cells in the plaque captain, and exit from erythrocytes outside the blood vessels. At the stage where pseudomia is formed under the epithelium of the mucosal surface, an infiltration of the secretion appears. The epithelium layer rises and is absent in some places. The bare part of the mucous membrane is covered only with epithelial epithelium. In the second half of the disease, these areas may occupy a segment of the large intestine.
Outbreak flash flow of false colitis resembling cholera is rare. Dehydration progresses within a few hours, which gives a fatal ending.
Therefore, the clinical significance of dysbiotic changes should be made on the basis of clinical symptoms as well as the results of a fecal microbial examination.
The diagnosis of dysbiosis is a difficult and frustrating task. For the diagnosis of square use, culture of the small intestine solution obtained using a sterile probe is used. Escherichia coli is detected by bacterial testing of fecal stool.
Microbial flora produces large amounts of hydrogen-containing gas. This phenomenon is used to diagnose disbaisis. The concentration of hydrogen in exhalation directly depends on the severity of d-oblomatofimer bacteria. In patients with bowel disease with chronic diarrhea and bacterial abscesses in the small intestine, expiratory hydrogen concentrations significantly exceed 15 ppm. Normally, racculouses are not broken down in the small intestine and are metabolized in the microbial cells of the large intestine. As a result, the amount of hydrogen contained in the exhalation increases (Fig. 1).
Normally, racculouses are not broken down in the small intestine and are metabolized in the microbial cells of the large intestine. As a result, the amount of hydrogen contained in the exhalation increases (Fig. 1).
 This change is most noticeable in the distortions of the colon and rectum. The mucous membrane is swollen, but there is no secretion. In an organizational test, there is infiltration of the subcutaneous epithelium, infiltration of circular cells in the plaque captain, and exit from erythrocytes outside the blood vessels. At the stage where pseudomia is formed under the epithelium of the mucosal surface, an infiltration of the secretion appears. The epithelium layer rises and is absent in some places. The bare part of the mucous membrane is covered only with epithelial epithelium. In the second half of the disease, these areas may occupy a segment of the large intestine.
This change is most noticeable in the distortions of the colon and rectum. The mucous membrane is swollen, but there is no secretion. In an organizational test, there is infiltration of the subcutaneous epithelium, infiltration of circular cells in the plaque captain, and exit from erythrocytes outside the blood vessels. At the stage where pseudomia is formed under the epithelium of the mucosal surface, an infiltration of the secretion appears. The epithelium layer rises and is absent in some places. The bare part of the mucous membrane is covered only with epithelial epithelium. In the second half of the disease, these areas may occupy a segment of the large intestine. Diagnosis method
The diagnosis of dysbiosis is a difficult and frustrating task.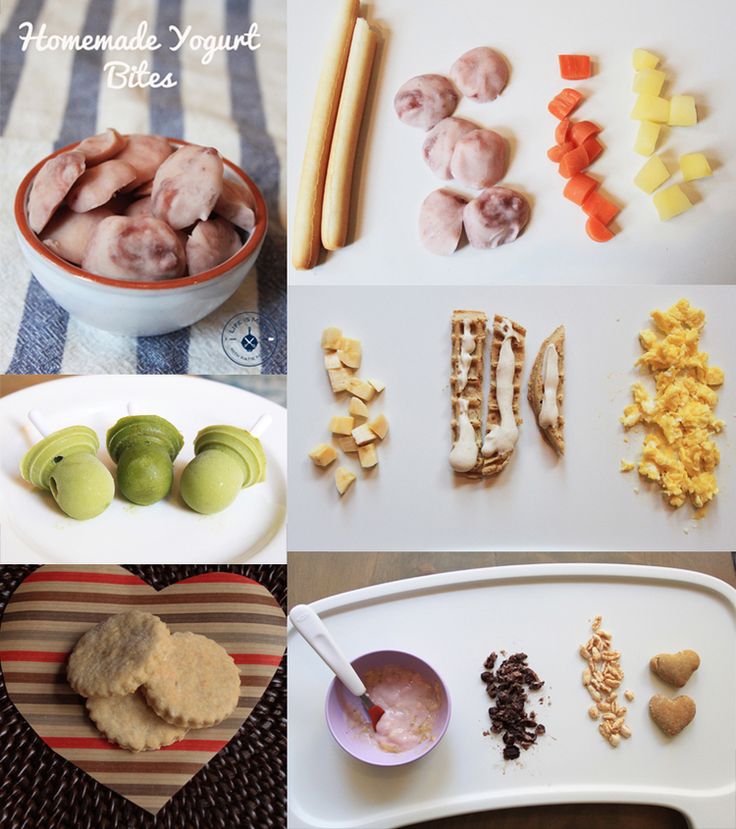 For the diagnosis of square use, culture of the small intestine solution obtained using a sterile probe is used. Escherichia coli is detected by bacterial testing of fecal stool.
For the diagnosis of square use, culture of the small intestine solution obtained using a sterile probe is used. Escherichia coli is detected by bacterial testing of fecal stool.
Microbial flora produces large amounts of hydrogen-containing gas. This phenomenon is used to diagnose disbaisis. The concentration of hydrogen in exhalation directly depends on the severity of d-oblomatofimer bacteria. In patients with bowel disease with chronic diarrhea and bacterial abscesses in the small intestine, expiratory hydrogen concentrations significantly exceed 15 ppm.
Loading on racculose is also used to diagnose disbaisis. Normally, racculouses are not broken down in the small intestine and are metabolized in the microbial cells of the large intestine. As a result, the amount of hydrogen contained in the exhalation increases (Fig. 1).
Figure 1. Exhaled hydrogen concentration
The most common bacterial signs of Escherichia coli are the absence of bifidobacteria, which are the main bacterial symbiosis, and the number of lactic acid rods. Intestinal bacillus, ileum, crostia, staphylococcus aureus, fungus, yeast proteins are increased. Every bacterial symbiosis appears in a pathological form. Porilla blood cells, intestinal bacilli that have weak expression of enzymes, and intestinal intestinal.
Intestinal bacillus, ileum, crostia, staphylococcus aureus, fungus, yeast proteins are increased. Every bacterial symbiosis appears in a pathological form. Porilla blood cells, intestinal bacilli that have weak expression of enzymes, and intestinal intestinal.
Careful study of the microbiota shows that traditional methods do not provide reliable information about the state of the intestinal microbiota. Of the 500 known species of microorganisms, only 10-20 are commonly studied for diagnostic purposes. It is important to determine in which part of the intestine, ileum or large intestine to examine the microbial composition. Therefore, it is currently expected that the identification of microorganisms by chemical methods, which allow obtaining universal information about the state of the bacterial flora, will lead to the development of clinical problems of bacteriosis. The most widely used for this purpose are gas chromatography (GC) and chromato-mass spectrometry (GC-MS). This method provides unique information about the composition of monomeric chemical components and metabolites in microbial cells. Such markers can be identified and used to detect microorganisms. The main advantage of this method and its fundamental difference from bacteriological methods is the possibility of quantitative determination of more than 170 taxa of clinically significant microorganisms in various body media. In this case, conclusions can be obtained within a few hours.
Such markers can be identified and used to detect microorganisms. The main advantage of this method and its fundamental difference from bacteriological methods is the possibility of quantitative determination of more than 170 taxa of clinically significant microorganisms in various body media. In this case, conclusions can be obtained within a few hours.
In the study of microbiota in the blood and biopsy specimens of the mucous membrane of the small and large intestines of patients with irritable bowel syndrome, we were able to identify 30-fold deviations from the norm in many components. Using the method of GC-MS-microbial markers, changes in the intestinal flora can be assessed according to blood tests.
About the treatment of enterobacteriosis
Care
Treatment of dysentery should be complex (scheme) and include the following measures:
Elimination of excess bacterial infection of the small intestine.
restores the normal microflora of the large intestine;
Improves intestinal digestion and absorption.

Recovery of reduced intestinal motility.
Stimulate the body's reactivity.
antibacterial
Antibiotics are needed primarily to control the overgrowth of small intestinal flora. The most widely used antibiotics are from groups such as tetracyclines, penicillins, cephalosporins, quinolones (tarivid, nitroxoline) and metronidazole.
However, broad-spectrum antibiotics have a significant impact on colonic ubiquity. Therefore, it should be used only in diseases associated with impaired absorption and intestinal motility, and in principle only with a significant development of the microbial flora in the lumen of the small intestine.
Antibiotics given by mouth regularly for 7-10 days.
Diet for constipation in children | Mamovediya
Constipation is a fairly common problem among children of all ages from infants to teenagers.
One of the main causes of constipation in a child is improper or poor nutrition. If the child has constipation, then in order to normalize the baby's stool, it is necessary to develop the habit of emptying the intestines at the same time, as well as to make the right diet.
If the child has constipation, then in order to normalize the baby's stool, it is necessary to develop the habit of emptying the intestines at the same time, as well as to make the right diet.
When preparing a diet for a child who suffers from constipation, it is necessary to include in the diet foods that increase the volume of feces and improve intestinal motility, foods that have an enveloping effect and help food slide well into the lower sections, foods rich in potassium, necessary for a good the work of the intestinal muscles, as well as fermented milk products containing bifidobacteria, which contribute to the development of beneficial intestinal microflora.
Parents need to carefully review their baby's diet and avoid foods that may contribute to constipation.
Foods that can interfere with a child's bowel movement include dried blueberries, sticky foods, rice and semolina, foods that are too hot, and drinks such as cocoa and strong tea.
Also constipation can be promoted by muffins, fresh bread and other products made from white wheat flour dough, including dumplings, dumplings, yeast pies.
Bread with bran, buckwheat, oatmeal, raw vegetables and fruits, dried fruits, especially prunes, dried apricots and apricots are very helpful in the fight against constipation.
From vegetables and fruits with constipation, it is necessary to use carrots, pumpkins, beets, zucchini, cauliflower, greens, baked apples.
Also, in case of constipation, it is necessary to include in the diet low-fat varieties of meat and fish, dairy products, sour cream, jelly and fruit and berry compotes.
From dairy products, sour-milk products containing biocultures, one-day kefir, fermented baked milk and yogurt are best suited.
Since the diet for constipation in a child requires limiting sweets and starchy foods, instead of sweets, you can prepare a healthy and tasty dried fruit dessert for your child.
When compiling a diet for a child with constipation, it is necessary to try to increase the amount of ballast substances in the diet , which will swell in the intestines, and contribute to an increase in the volume of feces. These substances include fiber, pectin, seaweed, cellulose, bran.
If a child has bloating due to constipation, then in his diet it is necessary to exclude food that is rich in dietary fiber.
It is very important to avoid gas-producing foods while dieting . Such products include cabbage, beans, cucumbers, eggplants, pears, lingonberries, spinach, sorrel, apple and grape juice.
It is very important for a diet in case of constipation in a child to maintain an optimal drinking regimen and make sure your child is drinking enough fluids throughout the day. For drinking, mineral water without gas, juice with pulp, dried fruit compote, herbal tea are best suited.
If a child has a pronounced painful contraction of the intestines, then he should not be given coarse fiber for food. All fruits and vegetables should be given to the baby without the skin. Juices with pulp, mashed potatoes, sour-milk products, low-fat boiled meat and fish, honey, jams, jams can also help such a child very well.
All fruits and vegetables should be given to the baby without the skin. Juices with pulp, mashed potatoes, sour-milk products, low-fat boiled meat and fish, honey, jams, jams can also help such a child very well.
For infants who are bottle-fed, it is necessary to choose a therapeutic mixture for constipation in a child .
If the baby is breastfed, then in this case, the nursing mother needs to consume a lot of fresh vegetables and fruits, as well as dairy products.
The introduction of complementary foods to a child with constipation is best to start with one-component vegetable puree and pumpkin, zucchini, carrots, beets are well suited for this.
It is not possible to choose one general diet for all children, since it is necessary to take into account the individual characteristics of the baby's body and his state of health.
It is very important to remember that constipation that persists for a long time in a child is a reason for immediate medical attention, because in such cases one diet is not enough.