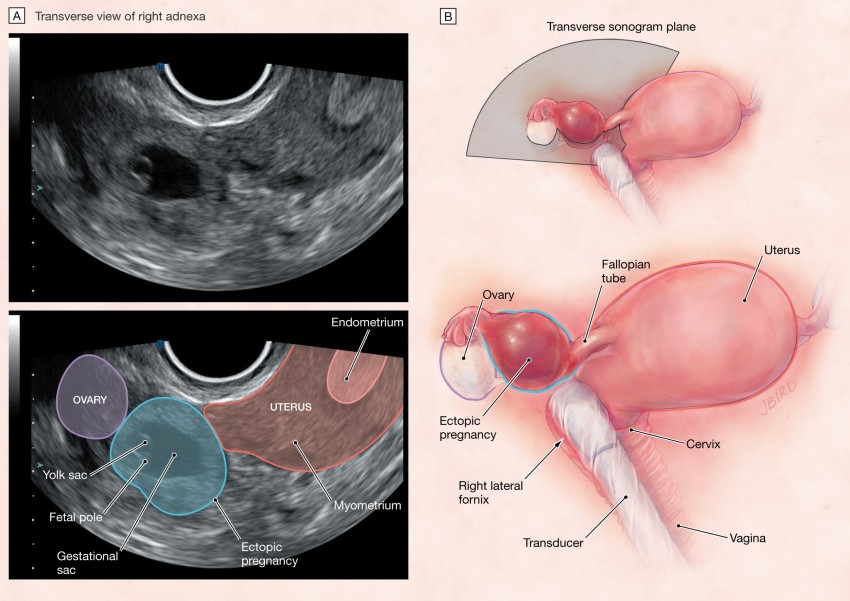
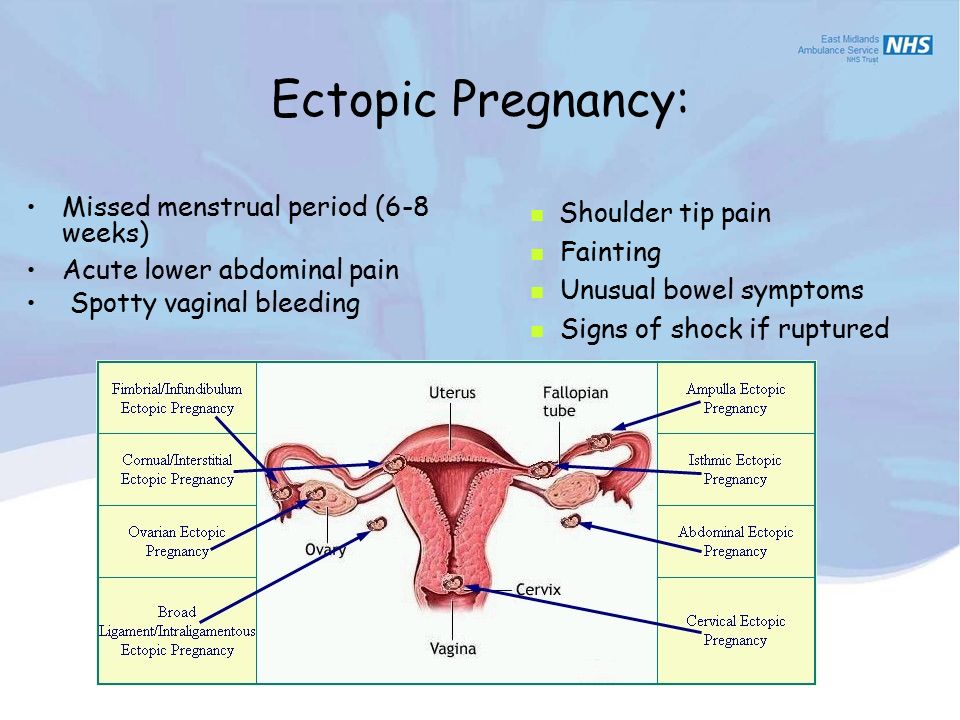
Ectopic pregnancy occurs when
Ectopic pregnancy - NHS
An ectopic pregnancy is when a fertilised egg implants itself outside of the womb, usually in one of the fallopian tubes.
The fallopian tubes are the tubes connecting the ovaries to the womb. If an egg gets stuck in them, it won't develop into a baby and your health may be at risk if the pregnancy continues.
Unfortunately, it's not possible to save the pregnancy. It usually has to be removed using medicine or an operation.
In the UK, around 1 in every 90 pregnancies is ectopic. This is around 11,000 pregnancies a year.
Symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy
An ectopic pregnancy doesn't always cause symptoms and may only be detected during a routine pregnancy scan.
If you do have symptoms, they tend to develop between the 4th and 12th week of pregnancy.
Symptoms can include a combination of:
- a missed period and other signs of pregnancy
- tummy pain low down on one side
- vaginal bleeding or a brown watery discharge
- pain in the tip of your shoulder
- discomfort when peeing or pooing
But these symptoms aren't necessarily a sign of a serious problem. They can sometimes be caused by other problems, such as a stomach bug.
Read more about the symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy.
When to get medical advice
Contact your GP or call NHS 111 if you have a combination of any of the above symptoms and you might be pregnant – even if you haven't had a positive pregnancy test.
An ectopic pregnancy can be serious, so it's important to get advice right away.
Your GP will ask about your symptoms and you'll usually need to do a pregnancy test to determine if you could have an ectopic pregnancy.
You may be referred to a specialist early pregnancy clinic for further assessment, where an ultrasound scan and blood tests may be carried out to confirm the diagnosis.
Read more about ectopic pregnancy tests.
When to get emergency help
Call 999 for an ambulance or go to your nearest accident and emergency (A&E) department immediately if you experience a combination of:
- a sharp, sudden and intense pain in your tummy
- feeling very dizzy or fainting
- feeling sick
- looking very pale
These symptoms could mean that your fallopian tube has split open (ruptured). This is very serious and surgery to repair the fallopian tube needs to be carried out as soon as possible.
This is very serious and surgery to repair the fallopian tube needs to be carried out as soon as possible.
A rupture can be life threatening, but fortunately they're uncommon and treatable, if dealt with quickly. Deaths from ruptures are extremely rare in the UK.
How an ectopic pregnancy is treated
There are 3 main treatments for an ectopic pregnancy:
- expectant management – you're carefully monitored and 1 of the treatments below is used if the fertilised egg doesn't dissolve by itself
- medicine – an injection of a powerful medicine called methotrexate is used to stop the pregnancy growing
- surgery – keyhole surgery (laparoscopy) is performed under general anaesthetic to remove the fertilised egg, usually along with the affected fallopian tube
You'll be told about the benefits and risks of each option. In many cases, a particular treatment will be recommended based on your symptoms and the results of the tests you have.
In many cases, a particular treatment will be recommended based on your symptoms and the results of the tests you have.
Some treatments may reduce your chances of being able to conceive naturally in the future, although most women will still be able to get pregnant. Talk to your doctor about this.
Read more about treating an ectopic pregnancy.
Help and support after an ectopic pregnancy
Losing a pregnancy can be devastating, and many women feel the same sense of grief as if they had lost a family member or partner.
It's not uncommon for these feelings to last several months, although they usually improve with time. Make sure you give yourself and your partner time to grieve.
If you or your partner are struggling to come to terms with your loss, you may benefit from professional support or counselling.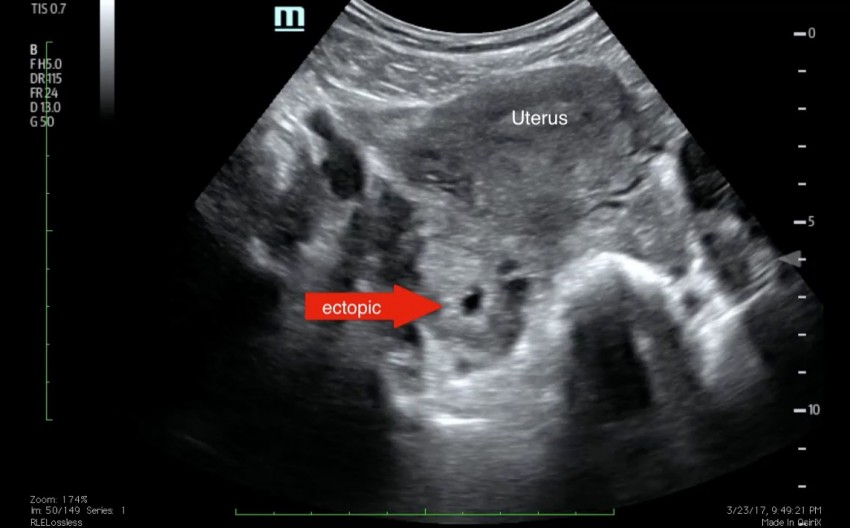 Speak to your GP about this.
Speak to your GP about this.
Support groups for people who have been affected by loss of a pregnancy can also help.
These include:
- The Ectopic Pregnancy Trust
- Ectopic Pregnancy Foundation
- Miscarriage Association
- Cruse Bereavement Care
Read more about dealing with loss and find bereavement support services in your area.
Trying for another baby
You may want to try for another baby when you and your partner feel physically and emotionally ready.
You'll probably be advised to wait until you've had at least 2 periods after treatment before trying again to allow yourself to recover.
If you were treated with methotrexate, it's usually recommended that you wait at least 3 months because the medicine could harm your baby if you become pregnant during this time.
Most women who have had an ectopic pregnancy will be able to get pregnant again, even if they've had a fallopian tube removed. Occasionally, it may be necessary to use fertility treatment such as IVF.
The chances of having another ectopic pregnancy are higher if you've had one before, but the risk is still small.
If you do become pregnant again, it's a good idea to let your GP know as soon as possible so early scans can be carried out to check everything is OK.
What can cause an ectopic pregnancy?
In many cases, it's not clear why a woman has an ectopic pregnancy. Sometimes it happens when there's a problem with the fallopian tubes, such as them being narrow or blocked.
The following are all associated with an increased risk of ectopic pregnancy:
- pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) – inflammation of the female reproductive system, usually caused by a sexually transmitted infection (STI)
- previous ectopic pregnancy – the risk of having another ectopic pregnancy is around 10%
- previous surgery on your fallopian tubes – such as an unsuccessful female sterilisation procedure
- fertility treatment, such as IVF – taking medicine to stimulate ovulation (the release of an egg) can increase the risk of ectopic pregnancy
- becoming pregnant while using an intrauterine device (IUD) or intrauterine system (IUS) for contraception – it's rare to get pregnant while using these, but if you do you're more likely to have an ectopic pregnancy
- smoking
- increasing age – the risk is highest for pregnant women aged over 35
You can't always prevent an ectopic pregnancy, but you can reduce your risk by using a condom when not trying for a baby to protect yourself against STIs, and by stopping smoking if you smoke.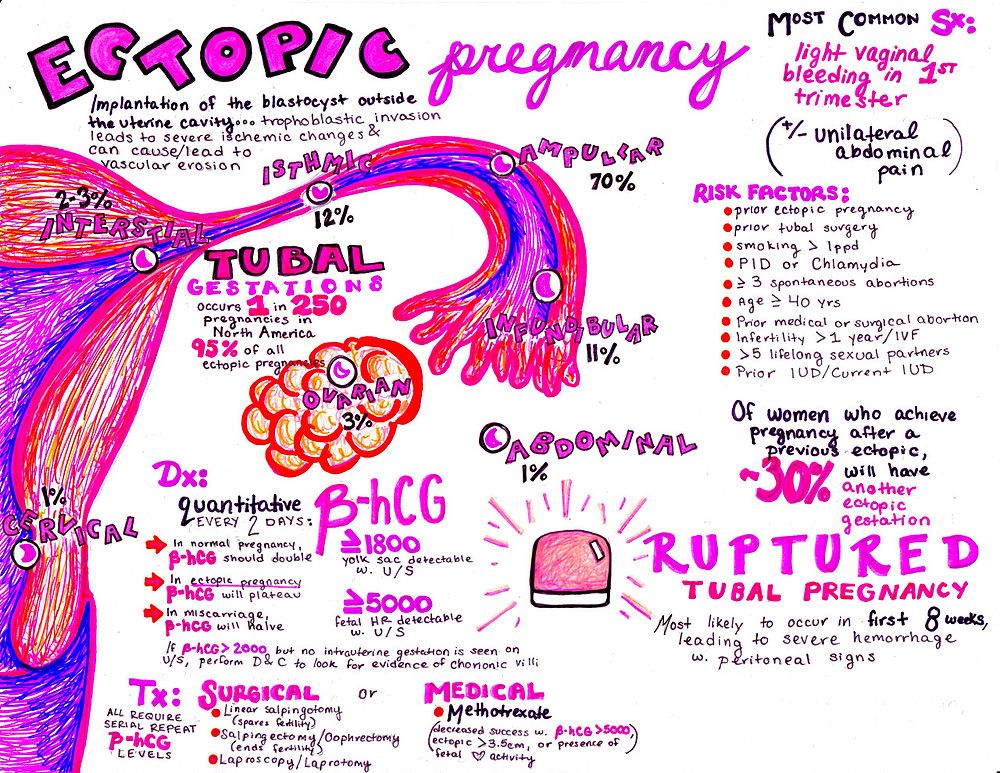
Page last reviewed: 23 August 2022
Next review due: 23 August 2025
What Is Ectopic Pregnancy? Tubal Pregnancy
What is an ectopic pregnancy?
An ectopic pregnancy happens when a fertilized egg grows outside the uterus.
In a normal pregnancy, a fertilized egg implants and grows in the uterus (also called the womb). In an ectopic pregnancy, the fertilized egg doesn’t make it to the uterus. It implants somewhere else, most often in the fallopian tube. This is called a “tubal pregnancy.” It can also occur in the ovary, cervix, or abdomen.
An ectopic pregnancy can be dangerous for the mother. As the pregnancy grows, it could cause the organ it is implanted in to rupture (burst). This can cause major internal bleeding. That’s why it is important to find an ectopic pregnancy in its early stages.
Symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy
The early signs of an ectopic pregnancy are like those of a normal pregnancy:
- Missed periods
- Tender breasts
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Fatigue
- Frequent urination
- A positive home pregnancy test
The first warning signs of ectopic pregnancy may include:
- Abnormal vaginal bleeding
- Low back pain
- Mild pain in the abdomen or pelvis
- Mild cramping on one side of the pelvis
If you have any of these symptoms, you should call your doctor.
As an ectopic pregnancy grows, it may rupture. Then you may experience more serious symptoms. These could include:
- Sudden, severe pain in the abdomen or pelvis
- Shoulder pain
- Feeling weak, faint, or dizzy
If you experience these symptoms, get medical help right away.
What causes an ectopic pregnancy?
Usually, an ectopic pregnancy happens because the fertilized egg wasn’t able to move down the fallopian tube quickly enough. An infection or inflammation in the tube can cause it to be partially or completely blocked. This is commonly caused by pelvic inflammatory disease (PID).
Another common reason tubes get blocked is endometriosis. This is when cells from the lining of the uterus grow outside the uterus. The cells can grow inside the fallopian tube and cause blockages. Scar tissue from previous abdominal surgery or fallopian tube surgery can also block the tube.
Any pregnancy can be an ectopic pregnancy. But you’re more likely to have one if:
- You are older than 35 years of age.

- You have had infections (such as pelvic inflammatory disease) or operations in the pelvic area.
- You have endometriosis.
- You’re using assisted reproductive methods to become pregnant, such as in vitro fertilization (IVF).
- You smoke.
- You have a history of inflammation of the fallopian tubes or abnormally shaped fallopian tubes.
- You have had trouble getting pregnant or have had fertility treatment.
- You have had an ectopic pregnancy in the past.
How is an ectopic pregnancy diagnosed?
Ectopic pregnancies can be hard to diagnose because the first symptoms are the same as those of a normal pregnancy. If your doctor thinks you may have an ectopic pregnancy, he or she may do the following:
- Perform a pelvic exam to check the size and shape of your uterus.
- Order a urine test and a blood test to check your levels of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG). This is a hormone that is produced by the placenta.
 If you have an ectopic pregnancy, you may have a low hCG level.
If you have an ectopic pregnancy, you may have a low hCG level. - Perform a transvaginal ultrasound. During this procedure, a wand is inserted into your vagina. Sound waves from the wand make pictures of organs in the body. This will allow your doctor to see where the pregnancy is growing.
Can an ectopic pregnancy be prevented or avoided?
You can’t prevent an ectopic pregnancy, but you can try to control your risk factors. Don’t smoke. If you do smoke, plan on quitting before you get pregnant. Before getting pregnant, use a condom when having sex. This can help prevent sexually transmitted infections, such as chlamydia and gonorrhea, which can cause PID.
If you’re at higher risk of having an ectopic pregnancy, talk to your doctor. He or she may take extra steps to detect an ectopic pregnancy early. This could include checking your hormone levels or scheduling an early sonogram.
Ectopic pregnancy treatment
If a pregnancy is ectopic, the egg can’t develop. The ectopic tissue must be removed. This can be done with medicine or surgery.
The ectopic tissue must be removed. This can be done with medicine or surgery.
If an ectopic pregnancy is discovered early, your doctor can give you a shot of medicine called methotrexate. This medicine stops cells from growing and ends the pregnancy. Your body then absorbs the ectopic tissue.
Some ectopic pregnancies require surgery. These include those that aren’t discovered early enough, or that cause a pelvic organ to rupture. Surgery is usually done with laparoscopy. This procedure uses a tiny camera that is inserted into your body through small cuts in your abdomen. Special tools are used to remove the pregnancy. If your fallopian tube or another organ has burst, your doctor may remove that, as well.
Whether you’re treated with medicine or surgery, your doctor will want to see you regularly afterward. He or she will monitor your hCG levels to make sure they go back to normal. This can take several weeks.
Living with an ectopic pregnancy
Whether you’re treated with medicine or surgery, your recovery may take several weeks. You may feel tired and have abdominal pain or discomfort. You also might still feel pregnant for a while. It takes a while for the hCG levels in your body to drop. It will probably take a few cycles before your periods go back to normal.
You may feel tired and have abdominal pain or discomfort. You also might still feel pregnant for a while. It takes a while for the hCG levels in your body to drop. It will probably take a few cycles before your periods go back to normal.
If you’ve had an ectopic pregnancy, you’re more likely to have another one. You also may have trouble getting pregnant again. You should give yourself time to heal before you try to get pregnant after having an ectopic pregnancy.
Having an ectopic pregnancy can be emotionally hard. You may feel sad, angry, and confused. Talk about your feelings with your partner, a trusted family member, or friend. Allow yourself the chance to Find a family member or friend you can talk to about your feelings. Allow yourself to grieve the loss of a pregnancy.
Questions for your doctor
- Could vaginal bleeding in early pregnancy be a sign of ectopic pregnancy?
- Where is my ectopic pregnancy located?
- What treatment do I need?
- Will I need surgery?
- I’m having a hard time dealing with my feelings.
 Is there someone I could talk to or a support group in my area?
Is there someone I could talk to or a support group in my area? - I’d like to get pregnant again. Is there anything I can do to minimize my risk of having another ectopic pregnancy?
Resources
National Institutes of Health, MedlinePlus: Ectopic Pregnancy
Ectopic pregnancy - causes and treatment
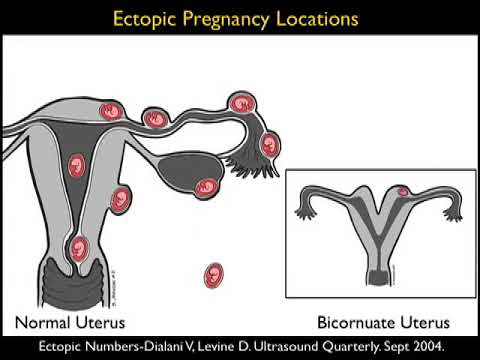
If the fixation and subsequent development of the ovum occurs outside the uterus, then the pregnancy is called ectopic (ectopic). It occurs in 2% of all pregnancies. The embryo can be fixed on the ovary, in the abdominal cavity, in the cervix, in the fallopian tubes. An ectopic pregnancy in the early stages is no different from a normal one.
An egg is released from the ovary during ovulation and enters the fallopian tube. Fertilization occurs when a sperm and an egg meet in the ampulla of the fallopian tube. Normally, at the end of the first week after fertilization, the embryo enters the uterine cavity and implantation occurs. A fertilized egg can develop normally only in the uterus. nine0003
nine0003
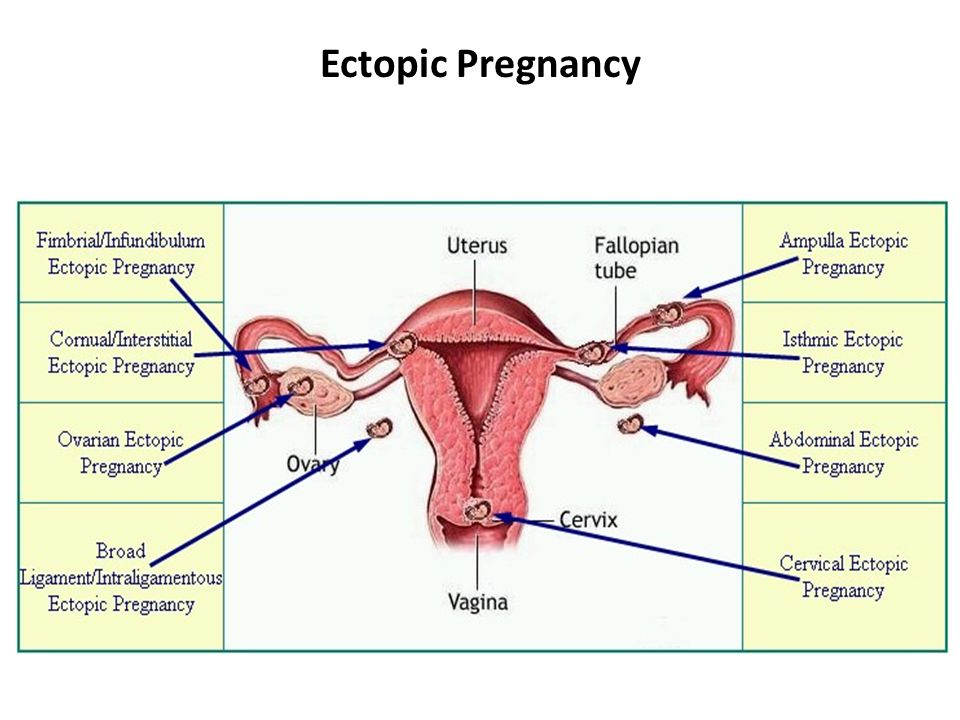
Types
- tubal - the embryo develops in the fallopian tubes;
- abdominal - the embryo is attached to the walls of the peritoneum;
- ovarian - the embryo is attached to the walls of the cervix;
- cervical - the embryo is attached to the cavity of the ovary.
Very rare bilateral ectopic pregnancy, as well as heterotopic pregnancy (combination of uterine and ectopic). An ectopic pregnancy of any type is considered a medical emergency. nine0003
Let's take a look at tubal pregnancy next, because it is the most common and accounts for 98-99% of all pregnancies outside the uterus.
Signs of ectopic pregnancy
Until the fetal egg overstretches the wall of the fallopian tube, pregnancy is no different from normal and is characterized by standard signs:
- delayed menstruation;
- positive test;
- early toxicosis;
- drowsiness; nine0010
- breast enlargement and soreness;
- change in taste preferences.
During menstruation, scanty dark-colored blood discharge is possible. It is impossible for a woman to determine an ectopic pregnancy at home, and diagnostics and specialist advice are required.
Until a certain point, the fertilized egg develops normally. But the embryo grows and it ceases to have enough nutrients. At some point, he ruptures the fallopian tube and bleeding occurs. At the same time, the blood practically does not flow out, only small spotting discharges may appear, the main bleeding occurs in the abdominal cavity. nine0003
An ectopic pregnancy may show symptoms after 2 weeks of delayed menstruation. A woman may feel:
- weakness, dizziness;
- pain in rectum radiating to back;
- loss of appetite;
- pain in the lower abdomen, sometimes with nausea and vomiting;
- scanty spotting.
Particular attention should be paid to pain in the lower abdomen. This symptom is also characteristic of a normal uterine pregnancy.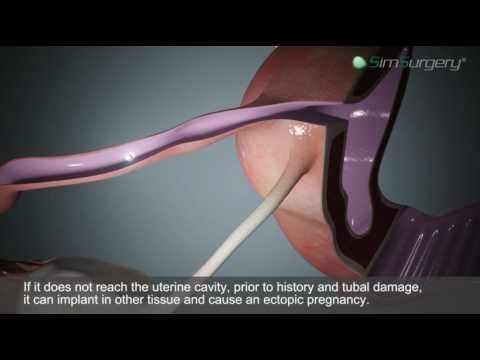 But in a normal pregnancy, the pain is temporary. With tubal, as a rule, the pain increases, intensifies and does not stop. nine0003
But in a normal pregnancy, the pain is temporary. With tubal, as a rule, the pain increases, intensifies and does not stop. nine0003
If you experience any of the symptoms listed, seek medical attention immediately. The condition can worsen sharply at any moment, which threatens the health and life of a woman.
Causes of ectopic pregnancy
Causes are all conditions that disrupt the movement of a fertilized egg into the uterine cavity:
- chronic inflammatory processes of the pelvic organs;
- violation of patency - the appearance of adhesions and scarring of tissues; nine0010
- violation of the peristalsis of the fallopian tube
- the exit from the pipe is closed;
- endometrial pathology;
- transferred infectious diseases;
- congenital factor - pipes are twisted and very long;
- single fallopian tube.
Risk factors:
- history of ectopic pregnancy;
- adhesive process in the small pelvis;
- interventions on the fallopian tubes; nine0010
- intrauterine contraception;
- surgery;
- pregnancy after prolonged infertility, after IVF procedure;
- anatomical features;
- bad habits;
- age from 35 years;
- hormonal and endocrine disorders.

Diagnosis
It is very difficult to detect a tubal pregnancy during a routine gynecological examination. Methods for diagnosing ectopic pregnancy:
- beta-hCG test is the only biochemical indicator for diagnosing ectopic pregnancy. In a normal course, the increase in hCG should double every 2-3 days. Suspicion will be a sluggish increase in hCG, no more than 1.5 times every 2-3 days. A low rise in beta-hCG may be with an undeveloped uterine or ectopic pregnancy;
- An early ultrasound of an ectopic pregnancy should be transvaginal to determine where the embryo has attached. It is desirable to carry out for 5-7 days after the delay of menstruation. nine0010
Blood progesterone testing is not indicated for the diagnosis of tubal pregnancy. Only according to the beta-hCG data, it is impossible to make a diagnosis, it is necessary to do a transvaginal ultrasound.
Complications
Termination of an ectopic pregnancy usually occurs for 4-6 weeks and develops as a rupture of the tube or as a tubal abortion.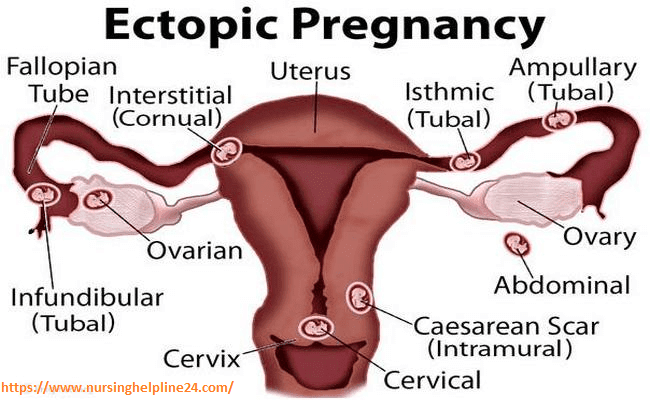
Signs of interruption by type of tube rupture:
- delayed menstruation; nine0009 intra-abdominal bleeding, characterized by a sharp decrease in blood pressure, pallor, cold sweat, dizziness, fainting, nausea, vomiting;
- sharp and very severe pain in the abdomen.
May occur after 6 weeks of pregnancy. An extremely dangerous situation for a woman's life and require immediate surgical intervention.
Signs of interruption by type of tubal abortion:
- delayed menstruation;
- bleeding from labia; nine0010
- constant aching, dull pain in the lower abdomen, may radiate to the lower back, groin, rectum.
Tubal abortion proceeds for a long time, without acute manifestations. With detachment of the fetal from the fallopian tube, blood enters the abdominal cavity in small portions and therefore there are no sharp symptoms. On gynecological examination, an increase in the size of the uterus and appendages, pain on palpation of the posterior fornix of the vagina is determined.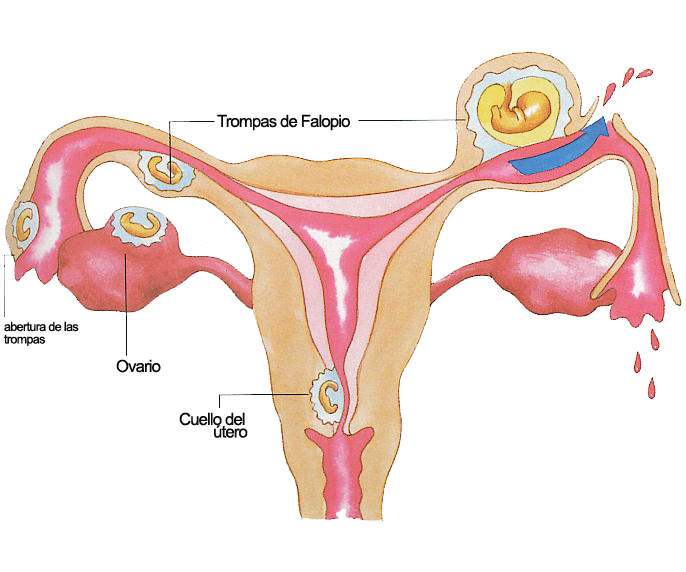
What complications can be:
- severe bleeding; nine0010
- repeated ectopic pregnancy;
- infertility.
Ectopic pregnancy and consequences
- probability of normal pregnancy and childbirth - about 50%;
- repeated ectopic pregnancy - about 20%;
- 15-20% miscarriages;
- 25% infertility.
Ectopic pregnancy, what treatment is used
If an ectopic pregnancy is suspected, a woman should be urgently hospitalized in a hospital, even if there are no complaints of well-being. The main threat is that the pregnancy can be terminated at any time. nine0003
The effectiveness of treatment is determined by timely diagnosis at an early stage and the choice of using laparoscopic access.
In the hospital, after 48-72 hours, repeat ultrasound, determine the level of beta-hCG and conduct a gynecological examination. If the increase in beta-hCG is less than 50% in 48-72 hours and the fetal egg is not detected, then the patient will be shown a diagnostic laparoscopy.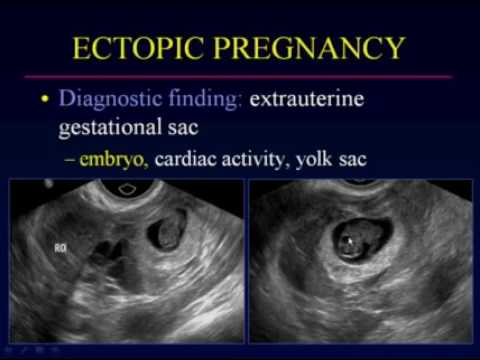 Such diagnostics will help not to wait for the rupture of the tube, blood loss and shock. nine0003
Such diagnostics will help not to wait for the rupture of the tube, blood loss and shock. nine0003
Currently in Russia, ectopic pregnancy is treated only surgically:
- radical (tubectomy) - removal of the tube along with ectopic pregnancy. It is used for rupture or overstretching of the pipe;
- organ-preserving (tubotomy) - the tube is cut and the fetal egg is removed. The method is used with timely detection and slight stretching of the pipe.
Only surgery can remove a fertilized egg that has attached itself outside the uterine cavity. The most common is laparoscopy. The surgeon removes the fetal egg and partially or completely the fallopian tube through small punctures. After 3 days, the woman is allowed to go home. nine0003
Opening of the abdominal cavity is usually used when laparoscopic access is difficult (pronounced adhesive process, a large amount of blood in the abdominal cavity, obesity).
The nature of the operation depends on the condition of the woman, the volume of blood loss, location and size of the ovum. With laparoscopic access, the incidence of recurrent ectopic pregnancy is lower than with laparotomy.
Recovering from an ectopic pregnancy
It is important to have a complete examination to understand the cause of an ectopic pregnancy and eliminate it. Observe physical and sexual rest for at least a month after surgery. Measures should be aimed at restoring reproductive function after surgery:
- prevention of adhesions - physiotherapy, reflexology, injections of longidase, lidase;
- oral contraceptives are recommended for the duration of rehabilitation therapy. As a rule, 6 months after an ectopic pregnancy, you can become pregnant again.
If a tubal pregnancy was diagnosed in time, then the chances of conceiving and carrying a healthy child are quite high. When planning a pregnancy, be sure to consult a doctor. nine0003
How to avoid ectopic pregnancy
Prevention involves reducing the likelihood of the causes that lead to the development of ectopic pregnancy:
- timely treatment of inflammatory diseases of the genital organs;
- reliable contraception as abortion prevention;
- use of contraceptives strictly under medical supervision;
- pregnancy planning, complete examination; nine0009 treatment of hormonal disorders.
Regular visits to the gynecologist and examination for various infections are also important. If you suspect pregnancy, contact the MEDICA Fetal Medicine Center, experienced specialists will consult, diagnose and determine the type of pregnancy.
If you suspect pregnancy or you are concerned about a delay, then contact the Medica Fetal Medicine Center, experienced specialists will consult, diagnose and determine the type of pregnancy. nine0003
Ectopic pregnancy - terms, causes, symptoms, signs, diagnosis, treatment (surgery, removal)
Ectopic pregnancy is one of the most dangerous pathological conditions in which the fetus develops outside the uterine cavity. The place of its implantation can be the fallopian (uterine) tubes, as well as other organs of the abdominal cavity and small pelvis.
Termination of an ectopic pregnancy is accompanied by intra-abdominal bleeding and severe complications requiring surgical intervention.
In the female body, normal gestation is possible only in the uterus, but in practice, the location of the embryo, in addition to the uterus, may vary.
There are several types of ectopic pregnancy: tubal, ovarian, abdominal, cervical and with a location in the rudimentary horn of the uterus.
The sites listed are unfavorable for gestation, so an ectopic pregnancy is terminated at 4 to 8 weeks to prevent serious complications. nine0003
Attached in an atypical place, the vessels of the fetal egg grow into the surrounding tissues. Other organs, besides the uterus, are not able to stretch and form blood vessels for the placenta. As a result, damage to surrounding tissues occurs, exfoliation of the fetal egg, as a result, severe bleeding occurs that threatens the life of the patient.
The appearance of a tubal form of pathology is associated with the presence of obstacles in the movement of a fertilized egg. If the fertilized egg does not reach the uterine cavity, then it is implanted in the fallopian tube. Ectopic fetal development occurs in approximately 2% of cases among all types of pregnancy, of which 9 fall on the tubal form. 8%. Fetal implantation in other parts of the uterus and appendages, as well as in the abdominal cavity, is much less common.
8%. Fetal implantation in other parts of the uterus and appendages, as well as in the abdominal cavity, is much less common.
The release of a fertilized egg into the abdominal cavity with further implantation to the omentum, peritoneum or intestine leads to the development of abdominal pregnancy. One of the causes of this pathology may be in vitro fertilization.
In cervical pregnancy, the egg is implanted in the columnar epithelium of the cervical canal. As a result of deep penetration of the embryonic villi into the muscular layer of the cervix, the pregnancy ends in very heavy bleeding. nine0259
Causes of pathology
The development of pregnancy outside the uterine cavity occurs as a result of failures of natural processes that prevent the penetration of a fertilized egg into it. The most common causes of ectopic pregnancy include:
- previously transferred infectious lesions of the appendages caused by pathogenic microflora;
- the presence of adhesions in the fallopian tubes;
- defects in the structure of the genital organs; nine0010
- installed IUD in the uterus;
- infantilism;
- the presence of a tumor in the appendages or uterus;
- use of assisted reproduction methods;
- use of hormonal contraceptives;
- the presence of an inflammatory focus in the pelvic cavity;
- previously transferred surgical interventions on the appendages;
- stimulation of the ovulation process;
- history of abortion; nine0010
- endometriosis.

Features
It is not possible to determine the pathology at home. In this regard, timely registration can play a decisive role in the correct diagnosis.
At an early stage of development, an ectopic pregnancy has no distinguishing features. As a rule, it is characterized by:
- absence of menstruation;
- breast engorgement; nine0009 manifestations or absence of toxicosis;
- a positive pregnancy test, although in the presence of ectopic pathology it is not pronounced;
- painful sensations in the lower abdomen with irradiation to the rectum, as well as "spotting" discharge from the vagina.
Clinical manifestations of fetal development in the fallopian tube
An ectopic pregnancy can have a progressive form, in which case the growing fetal egg penetrates the muscular layer of the fallopian tube, leading to its gradual destruction. The patient has all the symptoms of pregnancy, but there are small bleeding from the genitals. nine0003
The patient has all the symptoms of pregnancy, but there are small bleeding from the genitals. nine0003
Also ectopic pregnancy can be terminated:
- as a tubal abortion. In this case, there is a partial or complete detachment of the membranes of the embryo from the wall of the tube and its entry into the abdominal cavity. Symptoms of manifestations depend on the severity of bleeding. Characterized by the presence of vaginal discharge in the form of blood clots. A pronounced soreness in the lower abdomen joins. Bimanual examination reveals an increase in the size of the uterus and appendages. Palpation of the posterior vaginal fornix is very painful; nine0010
- is like a ruptured fallopian tube. May occur after the 6th week of pregnancy. This condition is life threatening due to internal bleeding. Patients complain of very severe pain in the lower abdomen on both sides. There is a protrusion of the posterior fornix of the vagina and a "floating" uterus during a bimanual examination.

How to detect an ectopic pregnancy
In the initial period, it is difficult to diagnose pathology. Symptoms indicate, as a rule, the presence of pregnancy, but there are no signs typical for the pathology. nine0003
Diagnosis is carried out by examining a woman in a gynecological chair, as well as using additional research methods:
- blood test for B-hCG, which in case of ectopic pregnancy shows a shorter period than it actually is;
- Ultrasound, which will give more complete information about the development of the fetal egg and its location.
Interrupted tubal pregnancy is accompanied by intra-abdominal bleeding. Typical symptoms of a pipe rupture will be:
- acute pain in the lower abdomen radiating to the anus, lumbar region, legs;
- secretion of blood from the genital tract;
- rapid, weak pulse;
- sudden drop in blood pressure;
- loss of consciousness.
Clinical manifestations of an interrupted tubal pregnancy should be differentiated from appendicitis and ovarian apoplexy. When the embryo is located in the cervical region, pregnancy should be distinguished from incomplete abortion and tumors. nine0003
An ectopic pregnancy can be confirmed or denied after ultrasound diagnostics and a blood test for B-hCG.
Treatment
Treatment of ectopic pregnancy is carried out only by surgery. All the efforts of doctors are aimed at maintaining the integrity and function of the fallopian tube, into which the implantation of the fetal egg has occurred. With timely detection of pathology and a small blood loss, a laparoscopic operation is performed.
When localizing the embryo in the tube, the following types of surgical intervention are used:
- tubotomy (removal of the gestational sac while preserving the tube). In the case of choosing this method, the possibility of recurrence of the pathology is taken into account;
- tubectomy (excision of the tube) - performed in the presence of severe damage.
The choice of methodology is influenced by the following factors:
- whether the woman plans to have a child in the future;
- repeated ectopic pregnancy will require removal of the tube; nine0010
- whether there is an adhesive process in the small pelvis;
- change in the structure of the wall of the fallopian tube.
If the blood loss is large, then in order to save a life during an ectopic pregnancy, it is necessary to perform an abdominal operation, in which the fetal egg and tube are removed. Plasma transfusion may be required to restore blood loss. It is important that the remaining second pipe fully retains its function.
How to deal with an ectopic pregnancy
To avoid serious complications that can occur during a pathological pregnancy, a timely visit to an obstetrician-gynecologist will help. Attempts to save the fetus can lead to sad consequences: as a result of a ruptured tube, blood flows into the abdominal cavity, which leads to fatal hemorrhagic shock.
When a patient is diagnosed with an ectopic pregnancy, urgent hospitalization is required to terminate the pregnancy. nine0003
The author of the article:
Shklyar Aleksey Alekseevich
obstetrician-gynecologist, surgeon, KMN, head of the direction "Obstetrics and Gynecology"
work experience 10 years
reviews leave feedback
Clinic
reviews0263 Shklyar Aleksey Alekseevich
I turned to Shklyar Aleksey Alekseevich I want to express my deepest gratitude to the entire staff of the operating unit Aleksey Alekseevich Shklyar. You are all doctors with a capital letter. I never tire of thanking God for bringing me to you. I came to you on the recommendation of Sorvacheva M.V. We got in touch with the doctor by phone and appointed the day of the operation. For the first time, I was pleasantly surprised how Alexey Alekseevich told me everything in detail and reassured me.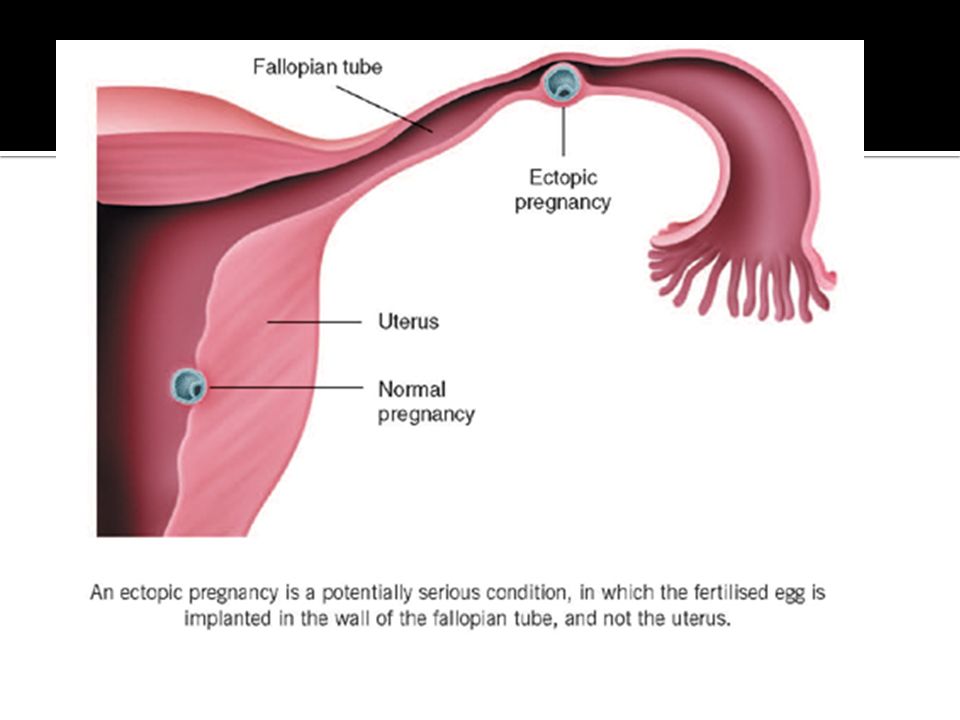 A couple of weeks later, I arrived at the clinic at 10.00 with a complete list of tests, and already at 11 I was lying on the operating table, to be honest, I didn’t even have time to get scared) Then the anesthetist magician came and I fell asleep sweetly. I woke up already in bed, nothing hurt, there were no side effects, just a normal morning awakening. I would never have believed that this was even possible, I am very grateful for a wonderful dream. Before that, I had more than one general anesthesia in state hospitals, and now I understand for sure that they apparently wanted to kill me there, but it didn’t work out. For the next two hours, until it was impossible to get up, wonderful nurses came to me asking how I felt and if I needed something, they put droppers, and I lay and did not believe that everything terrible was over)) 2 hours after the operation, I was already getting up and drank delicious broth and tea. The rest of the time before sleep, I walked around the ward, I didn’t feel any pain at all, a little weakness and nothing more.
A couple of weeks later, I arrived at the clinic at 10.00 with a complete list of tests, and already at 11 I was lying on the operating table, to be honest, I didn’t even have time to get scared) Then the anesthetist magician came and I fell asleep sweetly. I woke up already in bed, nothing hurt, there were no side effects, just a normal morning awakening. I would never have believed that this was even possible, I am very grateful for a wonderful dream. Before that, I had more than one general anesthesia in state hospitals, and now I understand for sure that they apparently wanted to kill me there, but it didn’t work out. For the next two hours, until it was impossible to get up, wonderful nurses came to me asking how I felt and if I needed something, they put droppers, and I lay and did not believe that everything terrible was over)) 2 hours after the operation, I was already getting up and drank delicious broth and tea. The rest of the time before sleep, I walked around the ward, I didn’t feel any pain at all, a little weakness and nothing more.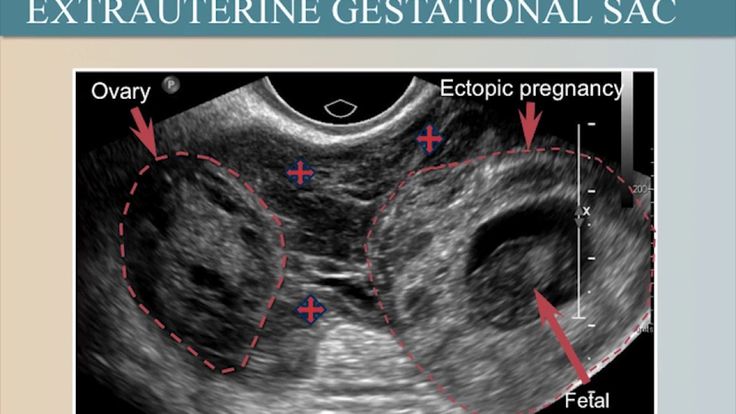 The next morning I was fed deliciously and discharged home. After being discharged, Aleksey Alekseevich is constantly in touch, he worries about my well-being more than even my relatives. I needed further treatment, he even helps me with this by calling the best doctors and clinics, supporting me. And now I know for sure that I am in the most reliable hands. Thank you very much again. Prosperity to your clinic and low bow to all your doctors. You are the best!!! nine0003
The next morning I was fed deliciously and discharged home. After being discharged, Aleksey Alekseevich is constantly in touch, he worries about my well-being more than even my relatives. I needed further treatment, he even helps me with this by calling the best doctors and clinics, supporting me. And now I know for sure that I am in the most reliable hands. Thank you very much again. Prosperity to your clinic and low bow to all your doctors. You are the best!!! nine0003
Lilia
05/15/2021 15:21:57
Clinic
m. Sukharevskaya
Doctor
Shklya Alekseevich
, May 7, 2021, underwent a male gynecological surgery, and would like to express gratitude to the attending physician, a doctor, a doctor. to the head of the gynecological department Shklyar Aleksey Alekseevich, - for high professionalism, and exceptionally friendly attitude, understandable recommendations. The doctor communicates very correctly, clearly and with explanations. nine0259 Special thanks to the anesthetist Alexey Valeryevich Fomin, for the quality anesthesia (I was more afraid of anesthesia than the operation itself), but everything went well, I was “not present” at the operation, and the condition after anesthesia was normal, as after waking up in the morning, no “side effects” ' did not feel.
nine0259 Special thanks to the anesthetist Alexey Valeryevich Fomin, for the quality anesthesia (I was more afraid of anesthesia than the operation itself), but everything went well, I was “not present” at the operation, and the condition after anesthesia was normal, as after waking up in the morning, no “side effects” ' did not feel.
After the operation, nothing hurt after half an hour, and after an hour and a half, I went home.
The attitude in the hospital was the most friendly, including from the nurses and the administrator at the reception (unfortunately, I did not ask for names). nine0259 It's already a week after the operation, and only the discharge summary # 140035314 reminds of it.
I'm very glad that I trusted the experience of the Polyclinic.
Services
- Title
- Initial appointment, consultation with an obstetrician-gynecologist3590
- Reception, consultation of an obstetrician-gynecologist repeated2200
- Reception, consultation of the doctor of the head of the department of gynecology / Ph.
 D. primary4300 905 years. Red Gates. AvtozavodskayaPharmacy. Glades. Sukharevskaya. st. Academician Yangelam. Frunzenskaya Zelenograd
D. primary4300 905 years. Red Gates. AvtozavodskayaPharmacy. Glades. Sukharevskaya. st. Academician Yangelam. Frunzenskaya Zelenograd Okocha Victoria Alexandrovna
obstetrician-gynecologist, reproductologist, gynecologist-endocrinologist, ultrasound doctor
reviews Make an appointment
Clinic
m. Frunzenskaya
Ellinskaya Anastasia Aleksandrovna
obstetrician-gynecologist, ultrasound doctor
reviews Make an appointment
Clinic
m. Smolenskaya
m. PolyankaAkabirova Shakhlooy Anvarovna
obstetrician-gynecologist, endocrinologist, ultrasound doctor, KMN
reviews Make an appointment
Clinic
m.
 Red Gate
Red Gate
m. AvtozavodskayaGazdieva Irina Khasanovna
obstetrician-gynecologist
reviews Make an appointment
Clinic
m. Street 1905 Goda
Zharova Natalya Anatolyevna
obstetrician-gynecologist
reviews Make an appointment nine0003
Clinic
m. Street 1905 Goda
Zotova Natalya Yurievna
obstetrician-gynecologist
reviews Make an appointment
Clinic
m. Street 1905 Goda
Meshcheryakova Elena Aleksandrovna
obstetrician-gynecologist, ultrasound doctor, online consultations
reviews Make an appointment nine0003
Clinic
m.