Due date based on weeks pregnant
Calculate your due date: How to find your baby's due date
Choose a calculation method Last periodConception dateI know my due date
First day of my last period
BabyCenter's Due Date Calculator
Use our pregnancy due date calculator by plugging in either the date of your last menstrual cycle or the date you know you conceived. The calculator will do the rest.
How is my due date calculated?
There are several ways your due date is determined. If you happen to know the day you conceived, you can count 38 weeks from that day to find your due date. (Human gestation takes about 38 weeks.)
But very few expectant moms know exactly when they conceived. Even if you only had sex once during your fertile period, you wouldn't conceive on that day unless you happen to be ovulating. Sperm can live for up to five days inside your fallopian tubes. So, it could be up to five days after you have sex that you release an egg (ovulate) and it gets fertilized by a waiting sperm. That's the day you conceive.
So, without knowing the day of conception, how does anyone determine a due date?
First day of your last period
The most common way to calculate your pregnancy due date is by counting 40 weeks from the first day of your last menstrual period (LMP). And that's how most healthcare providers do it.
If your menstrual cycle length is the average length (28-day cycle), your menstrual cycle probably started about two weeks before you conceived. This explains why pregnancies are said to last 40 weeks instead of 38 weeks.
This method doesn't take into account how long your menstrual cycle actually is or when you think you might have conceived. But generally speaking, women typically ovulate about two weeks after their menstrual cycle starts. And women are more likely to know when their last period started than the day they ovulated.
Conception date
If you do happen to know precisely when you conceived – say, if you were using an ovulation predictor kit or tracking your ovulation symptoms – you can calculate your pregnancy due date based on your conception date. Just choose that calculation method from the pulldown above and put in your date.
Just choose that calculation method from the pulldown above and put in your date.
Note: Again, you don't necessarily conceive on the day you have sex.
IVF transfer date
If you conceived through IVF, you can calculate your due date using your IVF transfer date. If you had a Day 5 embryo transfer, count 261 days from your transfer date. If you had a Day 3 embryo transfer, count 263 days.
Can my due date change?
Your healthcare provider might revise your due date if your baby is measured during a first trimester ultrasound scan and found to be much bigger or smaller than expected for gestational age. This is more likely to happen if you have an irregular menstrual cycle length that makes it hard to pinpoint the date of conception.
Your healthcare provider will measure your baby during that ultrasound exam to figure out how far along your baby is and then provide you with a new due date.
What if I already know my due date?
If you already know your due date, you can use this calculator to see your pregnancy timeline. It will tell you when you'll hit various milestones, and when you may be due for prenatal tests and prenatal visits. You'll also find what your baby's sign and birthstone will probably be and which famous people were born on your due date.
It will tell you when you'll hit various milestones, and when you may be due for prenatal tests and prenatal visits. You'll also find what your baby's sign and birthstone will probably be and which famous people were born on your due date.
How likely am I to give birth on my due date?
Of course, a due date calculation is always approximate, whether it's from our tool or from your doctor or midwife. Only 1 in 20 women delivers on their due date. You're just as likely to go into labor any day during the two weeks before or after.
Want more information about how the weeks, months, and trimesters of pregnancy are counted? See our pregnancy timing chart.
How soon can I take a pregnancy test?
With all this talk about pregnancy due dates, you may be wondering when you can take a pregnancy test. To ensure you get the most accurate reading, it's best to wait a few days after your missed period to take a pregnancy test.
At-home urine tests measure the amount of hCG (human Chorionic Gonadotropin) present in your body. If you take a pregnancy test before you miss your period, you may not get an accurate result, despite what some tests advertise.
If you take a pregnancy test before you miss your period, you may not get an accurate result, despite what some tests advertise.
If you're getting a blood test in your provider's office, you may get results sooner. These tests also measure the amount of hCG in your bloodstream, but they're more sensitive than at-home urine tests. Blood tests may be able to detect pregnancy six to eight days after ovulation.
Read more
- Your pregnancy, week by week
- Your first trimester pregnancy checklist
- Pregnancy Weight Gain Calculator
- Ovulation Calculator
- See all tools
Pregnancy tests: How soon can you get a positive pregnancy test?
Pregnancy tests work by detecting the presence of a hormone called human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) in your urine. Some home pregnancy tests claim they're sensitive enough to give a positive result as early as five days before you would expect your next period. But you're more likely to get an accurate result (and avoid a false negative pregnancy test) if you wait to test until after the first day of your missed period.
How soon can you take a pregnancy test?
You're more likely to get an accurate result if you wait a few days to a week after you expect your period before taking a pregnancy test.
Some home pregnancy tests claim they're sensitive enough to give you a positive result as early as five days before you would expect your next period. And some women will have produced enough hCG to get a positive result at that point. So if you're anxious to know, go ahead and try it. If you get a negative result, you can just wait and test again later if you still haven't gotten your period.
Most home pregnancy tests claim to be accurate on the day you miss your period, but even then, the amount of hCG in the urine at this time can vary a great deal from one woman to another.
If you test too soon, you may get a false negative pregnancy test (a negative result even if you are pregnant) or an unclear result like a faint line on a pregnancy test.
How do pregnancy tests work?
Home pregnancy tests tell if you're pregnant or not by detecting the presence of hCG in your urine.
This hormone is produced by cells that will develop into the placenta. It first enters your bloodstream when the fertilized egg starts to implant in the lining of your uterus, as early as six days after fertilization.
The amount of hCG in your body then increases rapidly over the next few weeks, often doubling every two days or so. When a pregnancy test detects the hormone in your urine, it shows a positive result.
Home pregnancy tests are now about 99 percent accurate, when done correctly. And there's no reason to pay more for one test over another. As long as a test isn't expired, it should be equally as accurate as another test.
What will differ between tests is their sensitivity. Detecting hCG in the urine of someone 6 months pregnant (when there's plenty of hCG) versus 6 days past ovulation (when there's a very small amount of hCG) are two very different tasks. The ability of a test to pick up small amounts of hCG in your urine depends on the sensitivity of the test.
It's not always easy to tell which tests are the most sensitive. New products come out frequently, and manufacturers can make improvements at any time.
But some package inserts provide information about a test's sensitivity – that is, they report the lowest concentration of hCG in milli-International Units per milliliter (mIU/ml) of urine that the test can detect. For example, a pregnancy test that claims to be able to detect hCG at 20 mIU/ml should be more sensitive than one that claims to detect it at 50 mIU/ml.
How do I use a home pregnancy test?
For best results when using a home pregnancy test:
- Make sure the test is current. Check the expiration date on the package, especially if you've had it for a while. If you've been storing the test anywhere that gets moist or warm, like the bathroom, it may have deteriorated. If that's the case, it's better to throw it away and get a new one.
- Test first thing in the morning.
 Your urine is most concentrated when you first get up, so hCG levels (if present) will be easier to detect at that time.
Your urine is most concentrated when you first get up, so hCG levels (if present) will be easier to detect at that time. - Read the directions carefully. Directions vary with different brands. Some require you to urinate in a cup and then use the dropper provided to place a small sample in the testing well. With others, you can pee directly onto the testing device. And some let you do either.
The tests also vary in how they display the results. For example, some show pink or blue lines on the test strip, while others reveal a red plus or minus sign in a window. "Digital" tests tell you in words whether you're pregnant. Most have a control indicator (often a second line or symbol) to indicate whether the test is valid.
It may take up to 10 minutes to see results. If the control indicator doesn't show up properly, the test may be faulty. If this happens, you can usually call the manufacturer and have them send you a new one (though it probably won't arrive soon enough to use that same month).
If you have questions about how to use a test, call the manufacturer's toll-free number on the package instructions.
If the test shows a negative or a faintly positive result, wait another few days or a week and try again if you still haven't gotten your period. One possibility is that you ovulated later in your cycle than you thought and took the test too early to get a positive result.
Don't assume that one negative result means you're not pregnant. The amount of hCG produced is different for every woman and varies with each pregnancy. If you suspect that you're pregnant (for instance, if you're having early pregnancy symptoms) and still have a negative test, repeat a urine pregnancy test in a week if you still haven't gotten your period.
If you still haven't gotten either your period or a positive result two weeks or so after you would expect it, contact your healthcare provider.
False positive pregnancy tests
A false positive pregnancy test means that you get a positive result, but aren't pregnant. These are uncommon, but they can happen under certain circumstances:
These are uncommon, but they can happen under certain circumstances:
- You had a miscarriage or a pregnancy termination in the previous eight weeks or have a molar pregnancy.
- You've taken a fertility drug containing hCG (used to induce ovulation in fertility treatments).
- You have a rare medical condition, such as an hCG-secreting tumor.
- You're using an expired or faulty test.
- You're experiencing menopause or perimenopause.
If you have an early positive result and then get your period soon after, you may have had what's sometimes called a chemical pregnancy. This means a fertilized egg implanted in your uterus and developed just enough to start producing hCG, but then stopped developing for some reason. This form of early pregnancy loss usually happens when the fertilized egg has defects that prevent it from growing normally.
After a chemical pregnancy, your period may be a little heavier and a few days later than usual.
Note: An ectopic pregnancy usually results in a positive pregnancy test, even though these pregnancies show slower hCG rises. No matter what result you get from a pregnancy test, call your healthcare provider right away if you:
- Feel dizzy or faint.
- Have abdominal pain (especially a sharp or stabbing pain in your abdomen or on one side of your pelvis).
- Have abnormal bleeding.
Pregnancy blood tests
Most healthcare providers use a urine pregnancy test, just as you would at home – but your provider may use a blood test instead. It takes anywhere from an hour to a day or more to get the results.
There are two types of pregnancy blood tests:
- A qualitative hCG blood test simply detects whether there is hCG in your blood. It will give pregnancy results at about the same time as a urine test. The results return as "positive" or "negative."
- A quantitative blood test (beta hCG test or serum test) measures the exact amount of hCG in your blood.
 The results return as a number. This test is very accurate. It can detect hCG as early as six to eight days after ovulation, about a week before your period is due. It takes longer to get results from a quantitative blood test, though.
The results return as a number. This test is very accurate. It can detect hCG as early as six to eight days after ovulation, about a week before your period is due. It takes longer to get results from a quantitative blood test, though.
Some testing companies will let you pay online and then go to a lab and have a blood sample taken. The testing company will provide you with your result the next day by phone or online. These tests start at about $40. If you decide to use one of these companies rather than going through your healthcare provider, be sure to find out which type of blood test they're using.
What to do after a positive pregnancy test
Some women take more than one pregnancy test (or several) just to be sure – but that's not necessary. Once you've gotten a positive pregnancy test, call your healthcare provider to set up a prenatal visit or to discuss your options if you're uncertain about continuing the pregnancy.
For prenatal care, providers typically schedule the visit for when you're at least 8 weeks pregnant, but it varies. Some will see you sooner, particularly if you have a medical condition or have had problems with a pregnancy in the past. It's especially important to see a provider soon if you're having nausea and vomiting, vaginal bleeding, or abdominal pain.
Some will see you sooner, particularly if you have a medical condition or have had problems with a pregnancy in the past. It's especially important to see a provider soon if you're having nausea and vomiting, vaginal bleeding, or abdominal pain.
If you don't already have a family doctor, ob-gyn, or midwife, do some research and ask for recommendations. But don't delay your care while searching for a good fit, because you can always switch providers later. At your first prenatal visit, your provider will take your health history, explain your options, and more.
Learn more:
- I'm pregnant – now what?
- Implantation bleeding
- Pregnancy symptoms
Angarsk Perinatal Center: Pregnancy Calendar
Regardless of whether this is your first pregnancy or you already have a child and are expecting another one, an exciting period of life is coming for you. You began to feel the birth and development of a new life within yourself.

Calculation of due date
In most cases, women do not know the exact date of conception, but they can tell exactly when the last menstrual cycle began. This is the point from which pregnancy is usually counted. For most women, the most likely period of fertilization (ovulation) lies in the middle of their monthly cycle, in other words, two weeks before the start of the next menstrual cycle.
Based on this date, the pregnancy lasts about 280 days, or 40 weeks, from the start of the last menstrual period. So you can get your estimated due date by adding 280 days to the date you started bleeding in your last cycle. The same result can be obtained by adding 7 days to the date of the last menstrual period and subtracting 3 months. For example, if your last period started on February 20, then your due date is expected to be November 27.
This calculation of pregnancy determines the so-called gestational, or menstrual, age of the fetus. It is on this “calendar” that doctors and nurses will track the development of the fetus. Gestational age is different from ovulation, or fertilization, age, which is two weeks earlier and is counted from the actual date of conception.
Gestational age is different from ovulation, or fertilization, age, which is two weeks earlier and is counted from the actual date of conception.
Many people calculate their pregnancy in weeks. This is the easiest and most convenient way to avoid confusion. For example, if your doctor says that you are 10 weeks pregnant (remember that the count is from the start of your last menstrual period), then you conceived about 8 weeks ago and will go into labor in 30 weeks because your total pregnancy is 40 weeks.
There is also a large unit of measurement - trimester. The trimesters divide the pregnancy into three phases. Each such phase, lasting 13 weeks, has its own characteristics.
You may also have heard of another unit of time, the lunar month. It corresponds to the cycle of lunar phases and is 28 days. The full gestation period, equal to 280 days, is 10 lunar months.
The calendar is based on a 42-week pregnancy schedule. The expected time of labor (ETD) is at the end of the 40th week. This way you will know the age of the developing fetus at any point during the pregnancy.
It is important to understand that the RID is an estimate, not a precise date. Only one woman in 20 gives birth on the exact day0 percent of women give birth a week earlier or a week later. Therefore, one cannot rely on the date of the OVR. It may turn out that it will come, and the child will not be born for some time. Consider this date as a guideline - a deadline for which you must prepare.
There is no fundamental difference how to count the time of pregnancy. Still, the process will not go faster. It will continue as long as nature allotted. After all, a miracle happens - a new life grows and develops in your body!
Your menstrual cycle
You estimate that your menstrual cycle probably ends at the beginning of the second week of pregnancy or a few days earlier. The usual interval between periods is 28 days, but they can occur after 21 and even after 35 days , and there is nothing abnormal in this.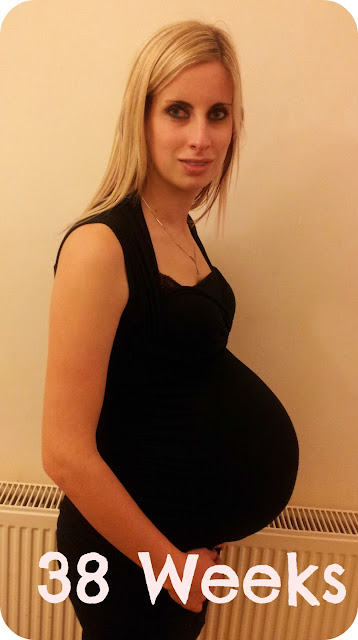 Actually menstruation in most cases lasts from 4 to 6 days. Discharge from the uterus is a mixture of sloughed uterine mucosa and blood. Clotted blood clots may also appear. On average, during menstruation, a woman loses 25-60 ml of blood. Blood loss can be different for different women, and for one woman it can change from one cycle to another.
Actually menstruation in most cases lasts from 4 to 6 days. Discharge from the uterus is a mixture of sloughed uterine mucosa and blood. Clotted blood clots may also appear. On average, during menstruation, a woman loses 25-60 ml of blood. Blood loss can be different for different women, and for one woman it can change from one cycle to another.
Two important biological cycles occur almost simultaneously in a woman's body. As a result of the ovulation cycle (ovulation), a mature egg appears, ready for fertilization, and during the endometrial cycle, the uterine wall is prepared for implantation of the fertilized cell. Both cycles are closely related to each other because endometrial changes are regulated by hormones that are released in the ovary.
The normal alternation of the ovulation and menstrual cycles (with the production of one egg for fertilization) is the rule, not the exception. Some women experience uneven cycles of egg production. Such cycles can take place without ovulation. This is quite rare compared to regular and predictable menstrual cycles and hormonal changes.
This is quite rare compared to regular and predictable menstrual cycles and hormonal changes.
Your body produces many hormones, including follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH) from the pituitary gland, as well as estrogen, progesterone and androgens (testosterone) from the ovary.
The natural purpose of the ovulation cycle is to produce an egg for fertilization. The body of a newly born girl contains about 2 million eggs. Their number is reduced to about 400 thousand by the beginning of puberty. But the maximum number of eggs is formed even before birth. When a fetus is only 5 months old (4 months before birth), it contains approximately 6.8 million eggs.
During the ovulation cycle, 20 or more follicles may begin the process leading to ovulation. And only one of them, bursting, can turn into a mature egg. Before the onset of ovulation, this follicle approaches the wall of the ovary, which becomes progressively thinner. At the time of ovulation, an egg is formed at the site of the burst follicle. The place of rupture of the follicle on the wall of the ovary is called the stigma.
Some women (approximately 25 percent) experience lower abdominal pain or discomfort on the day of ovulation or the next day. It is believed that they are caused by irritation of the ovary with fluid or blood of the follicle when it bursts. Pain is not necessarily felt with every cycle. By the presence or absence of this symptom, one can judge whether ovulation has occurred or not.
Most often, a woman becomes pregnant in the middle of the menstrual cycle, on the 12th-14th day from the beginning of the last menstruation. However, the beginning of the last menstruation is considered to be the starting point of ten obstetric months, or forty weeks of pregnancy. Therefore, we will start talking about the features of the development of the fetus from the third week of pregnancy, that is, after the moment of conception.
| FIRST TRIMESTER | SECOND TRIMESTER | THIRD TRIMESTER |
| 1st week | 15th week | 29th week |
| 2nd week | 16th week | 30th week |
| 3rd week | 17th week | 31st week |
| 4th week | 18th week | 32nd week |
| 5th week | 19th week | 33rd week |
| 6th week | 20th week | 34th week |
| 7th week | 21st week | 35th week |
| 8th week | 22nd week | 36th week |
| 9th week | 23rd week | 37th week |
| 10th week | 24th week | 38th week |
| 11th week | 25th week | 39th week |
| 12th week | 26th week | 40th week |
| 13th week | 27th week | 41st week |
| 14th week | 28th week | 42nd week |
How to determine the gestational age | Center for Fetal Medicine at Chistye Prudy
- Methods for determining the duration of pregnancy
- Embryonic term
- Obstetric term
- By last menstrual period
- By ovulation date or conception date
- According to the size of the uterus
- Ultrasound
- According to the level of hCG in the blood
- By the first movement of the fetus
Here is a pregnancy test showed the cherished two strips, the expectant mother is in a hurry to register in the antenatal clinic. The first thing that an obstetrician-gynecologist determines when registering is the gestational age. This indicator is extremely important in order to understand whether the pregnancy is proceeding correctly and the baby is developing, when it is necessary to take tests and undergo additional examinations, when to go on maternity leave and wait for the baby to be born.
The first thing that an obstetrician-gynecologist determines when registering is the gestational age. This indicator is extremely important in order to understand whether the pregnancy is proceeding correctly and the baby is developing, when it is necessary to take tests and undergo additional examinations, when to go on maternity leave and wait for the baby to be born.
It is also very important to know the exact gestational age for screening for the presence of genetic abnormalities in the fetus (ultrasound and blood tests), since these examinations are carried out strictly at certain times of pregnancy.
Turning to an obstetrician-gynecologist, many expectant mothers begin to worry about the difference in terms of pregnancy - what the doctor calculated and the woman herself. In order not to worry in vain, you need to know that there are 2 stages of pregnancy - obstetric and embryonic.
Fetal term
This is the true gestational age from conception, it usually lags behind the obstetric term by about 2 weeks.
Obstetric term
Doctors determine it from the first day of the last menstruation before pregnancy. It should be remembered that all doctors use only the obstetric term, all test results, the size of the fetus, the timing of examinations, maternity leave and the term of delivery are calculated taking into account only the obstetric term of pregnancy.
There are several ways to determine the gestational age.
Determination of the gestational age by the date of the last menstrual period
This is the most common method of calculating the gestational age. However, it can only be used if a woman's menstruation comes regularly at the same interval.
It is not always possible to accurately calculate the duration of pregnancy, guided only by the date of the last menstrual period. This happens in cases where a woman has irregular menstruation or in those patients who have a regular but long menstrual cycle. For example, if a woman has a typical cycle length of 35 days (and not 26 - 28, like most women), then most likely she will only be able to conceive on about the 21st day of the cycle (and not on the 14th, as on a 28 day cycle). Accordingly, the period calculated by menstruation will exceed the “real” obstetric gestational age by a week.
Accordingly, the period calculated by menstruation will exceed the “real” obstetric gestational age by a week.
According to the date of ovulation or the date of conception
If the date of conception is known, two weeks must be added to this date - we will get the obstetric gestational age. However, it must be remembered that even if a woman knows exactly the date of ovulation or the date of sexual intercourse, after which pregnancy occurred, this does not mean that she absolutely knows the date of conception.
A spermatozoon that has entered the female body is capable of fertilization within 4-5 days, sometimes even within a week, and a mature egg retains the ability to conceive for 2 days after ovulation. Therefore, even knowing exactly the date of sexual intercourse or ovulation, it is impossible to say with accuracy that fertilization occurred on that day. It could have happened later. Therefore, the period calculated by ovulation or the date of conception cannot be considered completely accurate.
Doctors calculate the gestational age in a slightly different way in cases where pregnancy has occurred as a result of IVF. In this case, the fertilization of the egg by the spermatozoon is carried out "in vitro" by the embryologist. Embryos develop in the laboratory for 3-5 days, after which they are transferred to the uterus.
Doctors calculate the true duration of pregnancy after IVF from the date of ovarian puncture, that is, the stage of the procedure, when the follicular fluid and the follicles contained in it are taken with a special needle for subsequent fertilization “in vitro”, and to determine the “usual” obstetric period , add 2 weeks in the date of ovarian puncture.
If the transfer of the embryo into the uterus was preceded by its cryopreservation (that is, freezing in liquid nitrogen), to determine the exact gestational age, doctors add 5 days to the transfer date (this is the number of days the embryo develops before freezing), and to determine the obstetric period, to the received true date add 2 weeks.
According to the size of the uterus
Examining a woman in a gynecological chair, an obstetrician-gynecologist uses both hands to determine the size of the uterus. In this case, you can also determine the approximate gestational age.
This method is most accurate in early pregnancy, up to about 12 weeks. The earliest period that can be determined by the size of the uterus is 5 weeks of pregnancy. By this time, the uterus is slightly enlarged, softened and becomes rounded. At later dates, the size of the uterus may vary slightly depending on the size of the fetus, the amount of amniotic fluid, and the structure of the woman's pelvis. For example, it is believed that at 16 weeks the bottom of the uterus is located in the middle of the distance between the pubis and the navel, at 24 weeks of pregnancy the bottom of the uterus is at the level of the navel.
Ultrasound
In the early stages of pregnancy, by measuring the size of the ovum and embryo, the gestational age can be determined with great accuracy.
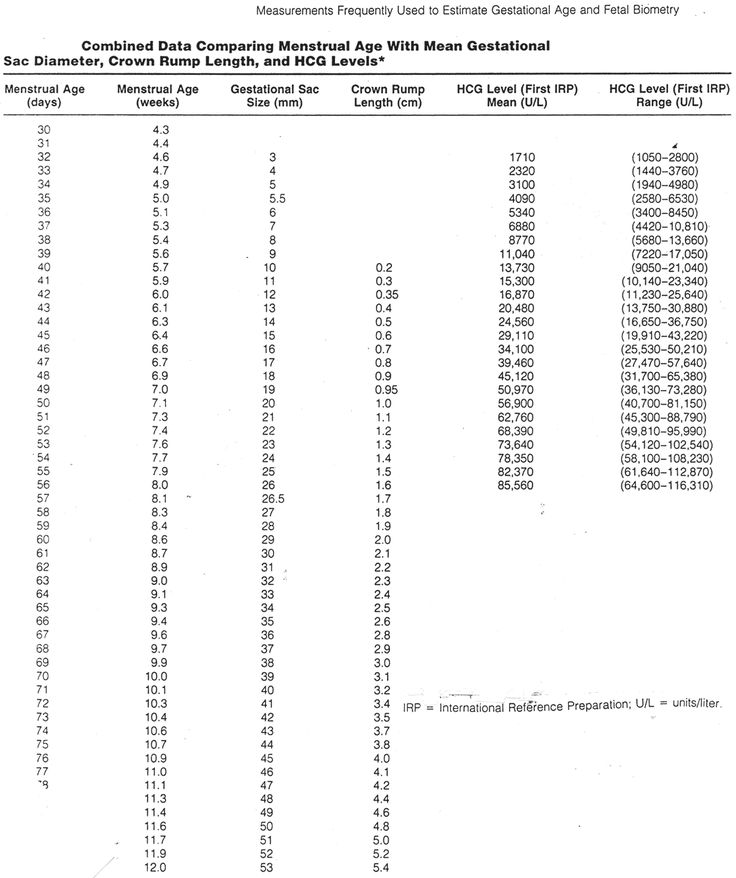
At 4-5 weeks in the uterus with ultrasound, a small “black circle” is determined - this is a fetal egg, in which an embryo will appear a little later. At about 6-7 weeks, the embryo appears in the form of a small “stripe” and you can see its heartbeat. More accurate is the period calculated by measuring the KTP of the embryo (KTP is the coccygeal-parietal size, that is, the maximum distance from the head end of the fetus to its tailbone), and not by the diameter of the fetal egg.
After 12 weeks, the gestational age during ultrasound is determined according to the so-called fetometry, that is, measurements of various sizes of the head and abdomen of the fetus, length of arms, legs, heart sizes, etc. are used to calculate the term.
Up to 9-10 weeks of pregnancy, the embryo grows proportionally, and its size in all women with the same gestational age will be approximately identical. In the future, the size of the fetus will differ in expectant mothers of different nationalities, with different body weights, the weight of the mother and father at birth will matter, and so on. That is, in the later stages of pregnancy, normally developing children of the same term may have different sizes (fluctuations can be about 2 weeks, sometimes more), and in such a situation, it is impossible to reliably determine the gestational age according to ultrasound data. In the later stages, the determination of the gestational age by ultrasound is only clarifying. In addition, the lag in the size of the fetus during ultrasound at long gestations is most often regarded by doctors as a developmental disorder due to the fact that the placenta does not transport oxygen and nutrients well enough.
That is, in the later stages of pregnancy, normally developing children of the same term may have different sizes (fluctuations can be about 2 weeks, sometimes more), and in such a situation, it is impossible to reliably determine the gestational age according to ultrasound data. In the later stages, the determination of the gestational age by ultrasound is only clarifying. In addition, the lag in the size of the fetus during ultrasound at long gestations is most often regarded by doctors as a developmental disorder due to the fact that the placenta does not transport oxygen and nutrients well enough.
At the Fetal Medicine Center in Moscow, all types of ultrasound during pregnancy are performed at an expert level, including ultrasound in early pregnancy.
Our center is organized in such a way that the whole range of services is concentrated in one place, where a woman receives the results of various types of examinations, including ultrasound, biochemical, and specialist consultation within 1-1. 5 hours.
5 hours.
Blood hCG level
HCG (human chorionic gonadotropin) is a hormone released during pregnancy by the placenta. It begins to be produced with the onset of pregnancy, gradually its amount increases, until about the 11th week of pregnancy, and then begins to decrease slightly.
Determining the concentration of hCG in the blood in the early stages of pregnancy helps to accurately determine the period. Having received the results of a blood test for hCG, it is worth paying attention that in the laboratory tables of the correspondence of the hormone level to the gestational age, the embryonic period is often indicated, that is, to determine the usual obstetric gestational age, 2 weeks should be added to the result.
Recently, tests have appeared to determine the duration of pregnancy by urine. They also determine the concentration of the hCG hormone in the urine of a pregnant woman and, in addition to confirming the very fact of pregnancy, show what period the hormone content corresponds to. The only thing to remember is that urine tests also show the fetal gestational age.
The only thing to remember is that urine tests also show the fetal gestational age.
The Fetal Medicine Center performs all types of tests for pregnant women.
Determining the term of pregnancy by the first movement of the fetus
This method of determining the term has recently been used less and less. It is based on the fact that nulliparous women begin to feel the first movements of the baby at 20 weeks of gestation, multiparous women a little earlier - at 18 weeks. That is why obstetrician-gynecologists recommend that a woman remember the date of the first movement of the fetus and enter this data into the exchange card.
However, this method of determining gestational age is often erroneous.
A mother who is expecting her first child, indeed, most often begins to feel the movements of the fetus a little later than a multiparous woman. This is due to the fact that "experienced" mothers know how the movements of the crumbs are felt at first and what they should feel.