Drinking monster while pregnant
How Much Caffeine is Safe During Pregnancy? | UNM Health Blog
June 17, 2022
200 MG of caffeine is the maximum amount a pregnant person should have, but the effects of caffeine are not fully understood. UNM Health experts can help you learn the right caffeine intake for your pregnancy
If you have always relied on a morning coffee or energy drink, you might be wondering if those things are still okay to have while pregnant.
About 90% of people in the U.S. drink caffeine daily. Here at UNM, we agree with the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG): Patients should consume less than 200 mg of caffeine during pregnancy.
One or two cups of coffee will put you at your daily limit. The average cup of coffee brewed at home has 95 mg of caffeine. But the amount will depend on the brand and size. Always check how much caffeine is in each serving.
Not all caffeinated drinks are safe for pregnant people. Doctors and midwives do not recommend energy drinks to anyone during pregnancy. Energy drinks contain a lot of caffeine and many other ingredients that could be unsafe for pregnant people.
Let’s discuss what drinks and foods contain caffeine and why it’s important to watch how much you have during pregnancy.
What Foods and Drinks Have Caffeine
Caffeine is a natural stimulant found in plants like tea leaves and coffee beans. It can also be made in a lab. Caffeine comes in common foods and drinks such as:
- Chocolate
- Coffee
- Coffee-containing foods like ice cream or yogurt
- Energy bars (sports bars)
- Energy drinks
- Pre-workout powders
- Soda
- Tea
- Yerba mate
Be sure to check food and drink labels for caffeine. During pregnancy, caffeine and other chemicals can cross the placenta and affect the pregnancy.
Here is a quick guide to how much caffeine one 8-ounce cup of coffee or tea contains on average:
- Brewed coffee = 96 mg
- Brewed decaf coffee = 2 mg
- Brewed black tea = 47 mg
- Brewed green tea = 28 mg
- Espresso = 64 mg
Many of these drinks contain a lot of extra sugar, too, which is not healthy for you or your pregnancy.
Problems from Drinking too Much Caffeine
During pregnancy, it takes up to three times longer for caffeine to leave your bloodstream. You could be more sensitive to its effects as a result. For example, your morning coffee could keep you awake at night.
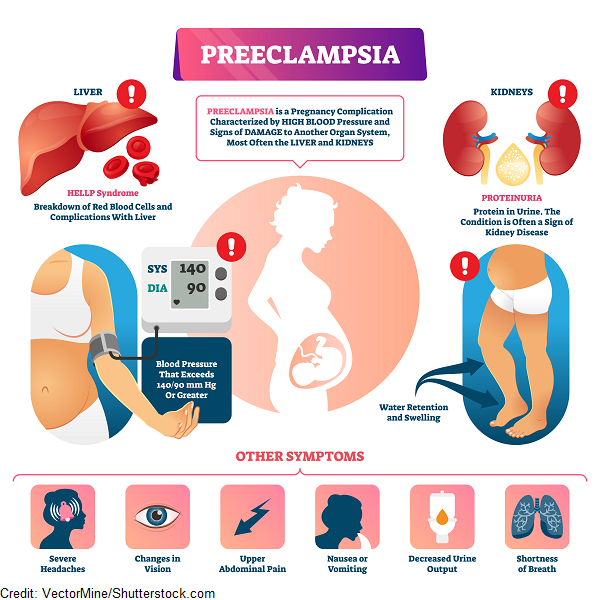
The effects of caffeine on pregnancy are not well understood. Some studies say that too much caffeine can put your pregnancy at risk. Problems with too much caffeine can include:
- Miscarriage
- Gestational diabetes
- Having children with behavioral or attention problems
- Having children with a low birthweight
- High blood pressure (preeclampsia)
You are higher risk for problems with caffeine if you have certain health conditions such as heart disease, diabetes or high cholesterol. Caffeine can also interfere with some medications, such as mental health drugs or medicines for HIV/AIDS.
Talk with your doctor or midwife if you feel any of these side effects from drinking too much caffeine:
- Anxiety
- Diarrhea
- Dizziness
- Headaches
- Heartburn
- Higher body temperature
- Irritability
- Nausea
- Rapid heartbeat
- Restlessness
- Sleeplessness
- Trembling hands
Drinking caffeine will make you need to urinate more. This will reduce the amount of fluid in your body. So, be sure to drink plenty of water after having caffeine.
This will reduce the amount of fluid in your body. So, be sure to drink plenty of water after having caffeine.
Keep Your Energy Up Safely in Pregnancy
Hormone changes in pregnancy can make you feel tired. Instead of drinking more coffee, talk with your doctor or midwife. We can recommend safe alternatives to caffeine such as:
- Adjusting exercise plans: We can help you determine if you are exercising enough or too much at any state of pregnancy.
- Changing your schedule: Allow yourself to say “no” to added responsibilities and new plans.
- Eating a healthy diet: We can check whether you are getting enough of the right calories, prenatal vitamins and nutrients to feel energized.
- Getting more rest: Give yourself permission to sleep in, nap, and rest whenever possible.
Make sure to skip caffeine after lunchtime if you have a hard time sleeping during pregnancy. Though caffeine can help you feel more alert and awake, it cannot give you more energy.
Your health is our top priority. Call your doctor or midwife if you are concerned about how much caffeine is safe during pregnancy. We are always here to answer your questions!
To find out whether you or a loved one might benefit from Ob/Gyn care
Call 505-272-2245.
Categories: Women's Health
Can I Drink Energy Drinks While Pregnant? Is It Safe?
Last Updated on December 16, 2021
Many women feel tired during pregnancy, and exhaustion is particularly common during the first trimester. You might have wondered if it’s safe to reach for your favorite energy drink during this time, or if it carries risks for you or your baby.
Energy drinks are not recommended for pregnant women, as they usually contain very high amounts of caffeine, sugar, and other additives. Caffeine can be harmful during pregnancy in very high doses, and consuming too much sugar during pregnancy may cause other health conditions such as diabetes.
In many countries, energy drinks carry warnings that they’re not suitable for pregnant women or those sensitive to caffeine.
In this article, I break down the reasons why you should avoid energy drinks when pregnant, and what you could do to boost your energy levels instead.
Covered in this Article:
What Are The Risks of Drinking Energy Drinks When Pregnant?
The main reason that pregnant women are told to avoid energy drinks is that they are usually classed as dietary or sports supplements, and they contain a variety of ingredients that aren’t recommended during pregnancy.
Caffeine
The biggest concern about drinking energy drinks during pregnancy is the high amount of caffeine that they contain. Pregnant women should reduce their caffeine consumption to 200mg-300mg a day, depending on individual government guidelines (source: WHO).
Depending on the brand, some energy drinks can contain up to 300 milligrams of caffeine per single serving, taking you up to or above the maximum recommended caffeine level in just one drink (source: Center for Science).
Caffeine overdose caused by energy drinks is one of the most prevalent problems seen in Emergency rooms in the USA (source: Journal of Public Health). People are often unaware of just how much caffeine these drinks contain.
If you really want an energy drink, you could check the food label and stick to lower caffeine options. However, it’s better to avoid them altogether, as they also have other ingredients that could also be harmful in high amounts, like sugar, covered below:
Sugar and Sweeteners
Another reason to avoid energy drinks when you’re pregnant is that they’re usually high in sugar or artificial sweeteners. Even a drink labeled ‘sugar-free’ or ‘zero-calorie’ is likely to contain sweeteners.
An Irish study found that some energy drinks can contain up to 17 teaspoons (69g) sugar in a single 500ml can, and contain as much caffeine as two espresso shots (source: SafeFood EU).
Excess sugar or sweeteners should be avoided during pregnancy, particularly if you have any risk of diabetes (including gestational diabetes) or have any insulin resistance (source: APA).
Even if you don’t have diabetes, the sugar content in energy drinks can add up to many calories – and excessive weight gain during pregnancy can cause many complications (source: Mayo Clinic).
Other Ingredients and Regulation
In many countries, energy drinks aren’t regulated in the same way as normal food or beverages, and it’s left down to the manufacturers to accurately state the ingredients on the nutrition label.
Many energy drinks contain added ingredients such as herbal or fruit extracts, or amino acids such as taurine. Scientific studies are limited on the pregnancy safety of many of these additives.
What’s more confusing is that some brands DO get classed as beverages rather than supplements, and some don’t. For example, in the USA, Monster Energy is classed as a regular beverage, yet other similar drinks are classed as dietary supplements (source: FIDJ Law).
The law across the European Union is more strict, and any energy drink containing high levels of caffeine not only has to state the caffeine content on the food label, but also print a warning that the drink is “not recommended for pregnant or breastfeeding women” (source: UNESDA).
This warning often appears on drinks produced in the USA and elsewhere, too.
To summarize, it’s best to avoid energy drinks during pregnancy. The two common ingredients – caffeine and sugar/sweeteners, aren’t beneficial to you or your baby and could be harmful in large amounts.
If you have had an energy drink before realizing, there’s no need to panic as no single ingredient has been found to be directly harmful in moderation. However, it’s best to limit or stop drinking energy drinks for the duration of your pregnancy.
Energy Drink Brands During Pregnancy
I know that when you’re pregnant it’s good to have specifics, so here are a few of the most popular energy drink brands, and how much caffeine and sugar they contain.
Bear in mind that none of these are recommended during pregnancy, and there is no ‘best energy drink’ for pregnant women because it’s safer to get an energy boost in other ways – some ideas and tips for this are given later in this article.
| Energy Drink Brand | Caffeine | Sugar |
|---|---|---|
| Monster Energy (Original) 500ml can | 160mg | 55g |
| Red Bull (Original) 8.4 fl oz can (250ml) | 80mg | 27g |
| VPX Bang! (Star Blast) 16 fl oz (473ml) can | 300mg | None, but contains the sweetener sucralose |
| V8 Energy 8 fl oz can | 80mg | 10g |
| Rockstar Energy Original 16 fl oz can (473ml) | 160mg | 62g |
| 5 Hour Energy Shot 1.93 fl oz (57ml) | Not stated. Estimated to be around 215mgNone, but contains sweetener sucralose |
Sources: Monster, Red Bull, V8, Bang, Rockstar, Forbes
What To Drink For Energy When Pregnant
After reading this article, you might be understandably disappointed that it’s not recommended to battle pregnancy fatigue by having energy drinks.
When you’re feeling exhausted and listless during pregnancy, there are other ways of getting an energy boost that is much better for you and your baby.
Other good advice applies, like taking more naps or practicing better sleep hygiene, but for the purposes of this article, I’ll focus on drinks that can give you an energy boost – since you probably arrived here looking to see if energy drinks were okay.
Hydrate more – but it doesn’t have to be boring water.
Dehydration can sap your energy and leave you feeling tired (source: WebMD). Your fluid needs increase during pregnancy, so one of the first steps you can take to combat fatigue. For inspiration, check my article on ten drinks you can enjoy when pregnant, besides water.
Try to eat (or drink) protein and complex carbs – this will minimize any blood sugar spikes that can give you a ‘crash’ later and result in more tiredness (source: WebMD).
Good options during pregnancy include milk or smoothies that contain blitzed nuts or seeds, or other sources like peanut butter (source: Harvard Nutrition).
Choose lower sugar juices – if you want to drink juice to hydrate during pregnancy, opt for lower sugar options made from veg, include tomato or carrot juice. Check the label for added sugar or sweeteners, or make your own. Try to include the pulp to increase the fiber content, too.
Check the label for added sugar or sweeteners, or make your own. Try to include the pulp to increase the fiber content, too.
Remember that extreme fatigue can be a sign of another problem during pregnancy, such as anemia (low iron levels). If you’re experiencing extreme tiredness often, or if it’s severe, it’s wise to check in with your health provider to make sure there are no underlying problems (source: NHS).
Can Energy Drinks Affect A Pregnancy Test?
None of the ingredients commonly found in energy drinks can directly affect a pregnancy test.
However, pregnancy tests rely on a sufficient concentration of a hormone called HCG (Human chorionic gonadotropin).
This hormone is produced when the embryo implantation has occurred and can be detected in urine about 12-14 days after conception. Most at-home pregnancy tests give a positive result after the hormone level reaches around above 25 mIU/mL (source: APA).
So, what has this got to do with energy drinks and pregnancy tests? The only way an energy drink can affect a pregnancy test is if you drank a large can (e. g. one of the bigger 500ml servings). Caffeine is a diuretic and makes you pee more (source: PubMed). This might alter the concentration of HCG in your urine.
g. one of the bigger 500ml servings). Caffeine is a diuretic and makes you pee more (source: PubMed). This might alter the concentration of HCG in your urine.
However, on the whole, if you follow the test instructions correctly (usually involving taking the pregnancy test in the morning, when HCG is typically more concentrated in your urine), then there’s little chance that energy drinks can interfere with a test.
If you suspect you may be pregnant, but keep getting negative tests, it’s a good idea to check with your doctor or healthcare provider.
Can Energy Drinks Induce Labor?
Drinking too much caffeine during pregnancy may increase the risk of pre-term birth (source: APA). For this reason, caffeine – such as that found in energy drinks – has been touted as one of the methods to induce labor, though there is no scientific evidence that caffeine or energy drinks can induce labor.
There are various myths and techniques floating around the internet, from simply drinking caffeine (like in energy drinks) or squatting over a hot cup of coffee to get the labor process going – but none of these are recommended as a way to induce labor, and may do more harm than good.
Trying to induce labor is best left to your doctor or midwife. If you have any concerns, it’s wise to speak to them before trying any untested or home remedies to induce labor.
You might also be interested in:
- The ultimate pregnancy guide to decaf coffee and tea
- The caffeine levels in chocolate – how much chocolate can you eat when you’re pregnant? Find out here.
- Ten drinks you can enjoy when pregnant, besides water
This article has been reviewed and approved for publication in line with our editorial policy.
What happens to the child if the mother drinks alcohol?
03.12.2019
Alcohol and pregnancy are incompatible - doctors do not get tired of talking about this to expectant mothers. But pregnant women sometimes allow themselves to skip a glass of wine, thinking that nothing bad will come of such an amount. However, alcohol can interfere with fetal development at any stage of pregnancy, even very early.
Studies show that excessive (four or more drinks at a time) and/or regular drinking by an expectant mother puts the fetus at the greatest risk of serious problems. But even a smaller amount of alcohol can be harmful, since there is no safe dose. nine0003
Alcohol easily passes from the mother's bloodstream into the child's bloodstream, which can affect the development of the brain and other vital organs, structures and physiological systems of the baby's body, leading to malformations that can begin in a child in early childhood and last a lifetime. The most profound effects of prenatal alcohol exposure are brain damage and associated behavioral and cognitive impairment.
Scientists define a wide range of effects and symptoms caused by in utero alcohol exposure, termed "fetal alcohol spectrum disorders". These include conditions such as intrauterine alcohol syndrome, alcohol-related nervous system disorder, and alcohol-associated birth defects. All these cases have one common feature - damage to the central nervous system (CNS) as a result of prenatal alcohol exposure to the fetus. nine0003
nine0003
The effects of alcohol on the CNS may be structural (eg, reduction in brain size, changes in certain areas of the brain) or functional (eg, cognitive and behavioral deficits, motor and coordination problems). Extended studies using modern imaging techniques (MRI, CT, etc.) have revealed differences in the structure and activity of the brain that are consistent with neuropsychological testing data, including a disorder in processing information from the senses, changes in cognitive processes and behavior in adults with the disorder alcohol spectrum of the fetus compared to healthy people. nine0003
The most profound effects of prenatal alcohol exposure are brain damage and associated impairments in behavioral and cognitive functioning.
How are the disorders different?
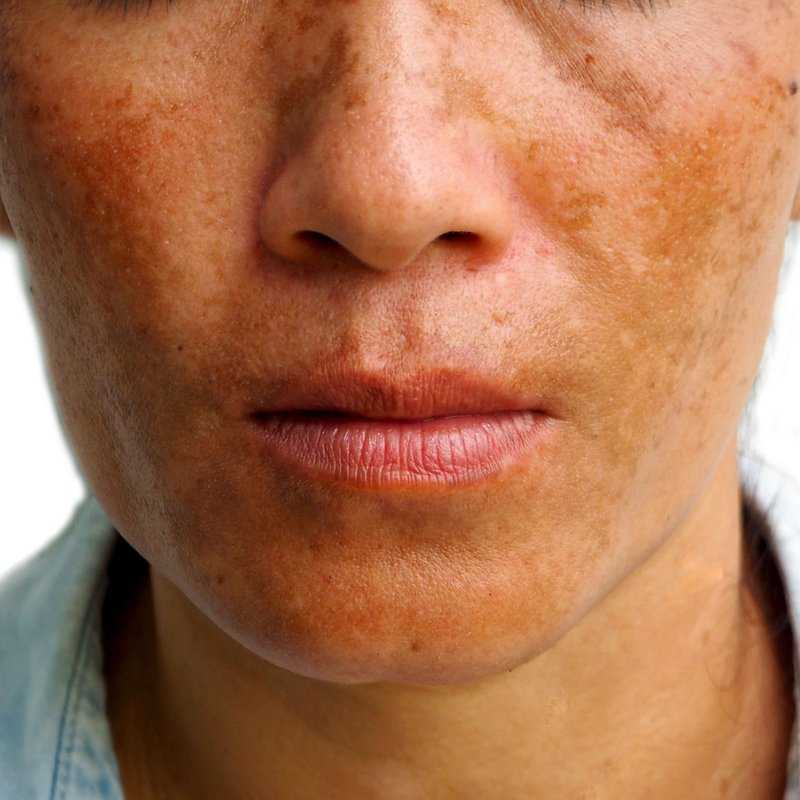
Fetal alcohol syndrome was the first form of alcohol spectrum disorder and is still the most well-known syndrome. It manifests itself with excessive alcohol consumption by the expectant mother during the first trimester of pregnancy. The impact of harmful substances on the fetus can disrupt the normal development of not only the brain, but also the face. Thus, in addition to CNS developmental anomalies, the child will have a specific pattern of three facial anomalies: narrow eye openings, a smooth area between the lip and nose (compared to a normal ridge), and a thin upper lip. Also, the baby may experience growth deficiency in utero and (or) after birth. nine0003
The impact of harmful substances on the fetus can disrupt the normal development of not only the brain, but also the face. Thus, in addition to CNS developmental anomalies, the child will have a specific pattern of three facial anomalies: narrow eye openings, a smooth area between the lip and nose (compared to a normal ridge), and a thin upper lip. Also, the baby may experience growth deficiency in utero and (or) after birth. nine0003
Partial fetal alcohol syndrome includes only some of the characteristics listed above.
An alcohol-related disorder of the nervous system is characterized by disorders of the central nervous system, which may be structural or functional. Functional impairments include a complex pattern of cognitive (mental) or behavioral problems that do not correspond to the standard level of development at any given age in a child. At the same time, the reasons for this discrepancy cannot be explained by factors other than prenatal alcohol exposure. Facial abnormalities and growth retardation should not be present. nine0003
Facial abnormalities and growth retardation should not be present. nine0003
Alcohol-related birth defects include heart, kidney, bone, and other malformations; difficulties with vision and hearing; decreased function of the immune system. They are rarely considered separately, but rather are a secondary disorder that accompanies other fetal alcohol spectrum disorders.
What will happen to the baby in the future?
Every person whose mother may have abused alcohol during pregnancy experiences a combination of everyday turmoil that includes medical, behavioral, educational, or social problems in the following areas: nine0003
- learning and memorization;
- understanding and following directions;
- ability to keep attention;
- the ability to control emotions;
- communication and socialization;
- performing daily life skills (eg, eating, bathing, counting money, taking care of personal safety).
People with fetal alcohol spectrum disorder are more likely than others to make bad decisions, repeat the same mistakes, trust the wrong people, and have difficulty understanding the consequences of their actions. They are also more prone to disorders such as attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, depression, impulse control problems, alcoholism and drug addiction. nine0003
People with fetal alcohol spectrum disorder are more likely than others to make bad decisions, repeat the same mistakes, trust the wrong people, and have difficulty understanding the consequences of their actions.
Risk factors
Of course, it is impossible to argue that just one sip of champagne during pregnancy can provoke many anomalies in the development of the fetus and affect the psyche of the unborn child. But the medical community recommends completely avoiding any dose of alcohol during pregnancy. nine0003
There are risk factors that contribute to the development of undesirable consequences:
- the amount of alcohol a pregnant woman drinks at a time;
- frequency of drinking by a pregnant woman;
- the stage of pregnancy at which a woman drinks alcohol, and how much she drinks during the formation of one or another body system in the fetus.
Prenatal alcohol exposure to children can be exacerbated if their mothers are malnourished, overweight, underweight, or smoke…
In addition, studies show that prenatal alcohol exposure affects children more if their mothers live in unfavorable conditions and experience high levels of stress. These may include, for example, social isolation, living in a society where excessive drinking is common and acceptable, and living in a society where resources for prenatal care are limited.
The prenatal effects of alcohol on children can be exacerbated if their mothers are malnourished, overweight, underweight, smoke… nine0003
How to help a child?
First aid for a child is the refusal of the expectant mother from alcohol. But if during pregnancy a woman allowed herself to drink alcohol and the child has symptoms of a fetal alcohol spectrum disorder, special tactics of education and training should be applied. For example, a school may want to use specialized learning strategies that provide a consistent routine and allow children to continually practice learning skills. This will allow students to study better, remember lessons faster and keep up with the class. nine0003
First aid for a child is the refusal of the expectant mother from alcohol.
Other ways to help include family support groups and classes to help parents take better care of their baby, prenatal and postpartum supplements for their babies, mental health interventions for children that include social skills training, problem solving, and personal safety.
Of course, all these measures can be taken by specialists. You should not take dietary supplements and medications unless prescribed by a doctor. nine0003
A child whose mother drank alcohol during pregnancy may develop both physiological and mental disorders, which will affect his life. A woman's refusal to drink alcohol will help her child grow up healthy and happy.
What happens when an expectant mother drinks – DW – 29.09.2017
Photo: picture alliance
Culture
Gudrun Heise | Natalia Koroleva
29September 2017
Alcohol during pregnancy is taboo. Even in small quantities, it can cause serious pathology in a child.
https://p.dw.com/p/2kSDP
Advertising
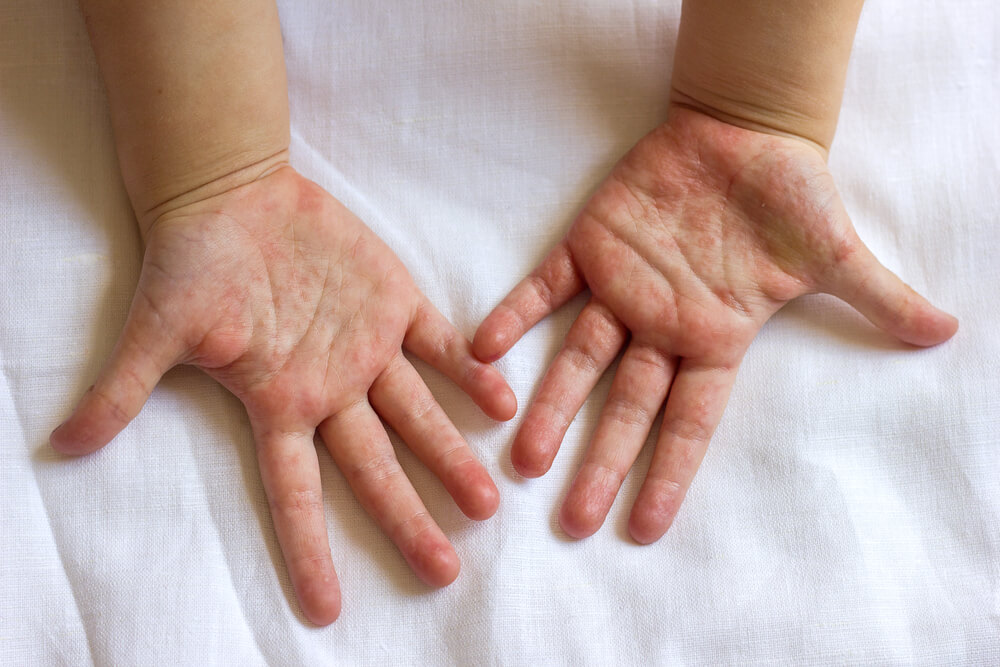
Every morning, approaching her baby's crib and carefully looking at his face, this woman cannot hold back her tears. “I know for sure: if I had not drunk during pregnancy, my son would have been born healthy,” she says bitterly. Her little son was diagnosed with fetal alcohol syndrome (FAS). The boy had deviations in psychophysical development. The reason is his mother's use of alcohol both before and during pregnancy. FAS disease is incurable. nine0003
Illness for life
Social educator Gisela Michalowski is the chairman of the German Fetal Alcohol Syndrome Society (FASD Deutschland), where those in need can apply for support, consult on various issues, and obtain the necessary information.
According to Michalowski, children whose mothers did not give up alcohol during pregnancy, there are serious disorders of the nervous system and abnormal growth of the body. Such children lag behind their peers in both height and weight. They also have a small head and specific facial features - a smoothed philtrum, a thin upper lip, and narrow eyes. nine0003
In addition, there are dysfunctions of the central nervous system - a syndrome of hyperactivity and attention deficit. “These children have difficulty learning, they cannot concentrate, they have functional and cognitive impairments, and it is difficult for them to control their behavior,” explains Heike Hoff-Emden, head physician of the Social and Pediatric Center in Leipzig.
The fetus is very sensitive to everything the mother-to-be consumes Photo: Fotolia/shootingankauf There are no specific treatments for FAS because there is no single neuropsychological profile in affected children. Therefore, the course of therapy is prescribed strictly individually, with an eye to specific symptoms. But, one way or another, the disease remains with a person for life, emphasizes pediatrician and psychologist Mirjam Landgraf from Munich. nine0003
Terrible consequences
If a pregnant woman drinks alcohol, no matter how much, it does not bypass the child in her womb. Alcohol penetrates the unborn child with blood through the placenta. And this happens in the shortest possible time - already a few moments after the pregnant woman drank an alcoholic drink. As a result, the blood alcohol level of the fetus is exactly the same as that of its mother.
After alcohol enters the body, the process of alcohol neutralization begins in the liver. But if in adults it proceeds quickly enough, then in an unborn child the liver is still underdeveloped, so alcohol is not excreted from his body much longer than from his mother's body. A fetal alcohol syndrome entails damage to the cells of his liver, vascular system, heart, brain. nine0003
Timely diagnosis
"Alcohol and pregnancy are absolutely incompatible!" - convinced social educator Gisela Michalovski. She urges women planning a pregnancy to completely abandon alcohol even before conception, because its consumption, even in small quantities, can fatally affect the health of the unborn child. Alcohol is especially harmful at the initial stage of pregnancy, when all the main organs and systems are laid, facial features are formed. nine0003
Gisela Michalowska has four children of her own. In addition to them, she has four more adopted babies, and each of these four has fetal alcohol syndrome. According to the teacher, it is very important to make a diagnosis in a timely manner and prescribe the necessary treatment. Indeed, many parents whose children suffer from FAS do not even suspect what is happening with their babies, and only wonder why their child is noticeably different from other children.
Where people drink more
Pediatrician and psychologist Miriam Landgraf knows many sad examples when children became disabled for life because of their mothers' drunkenness.