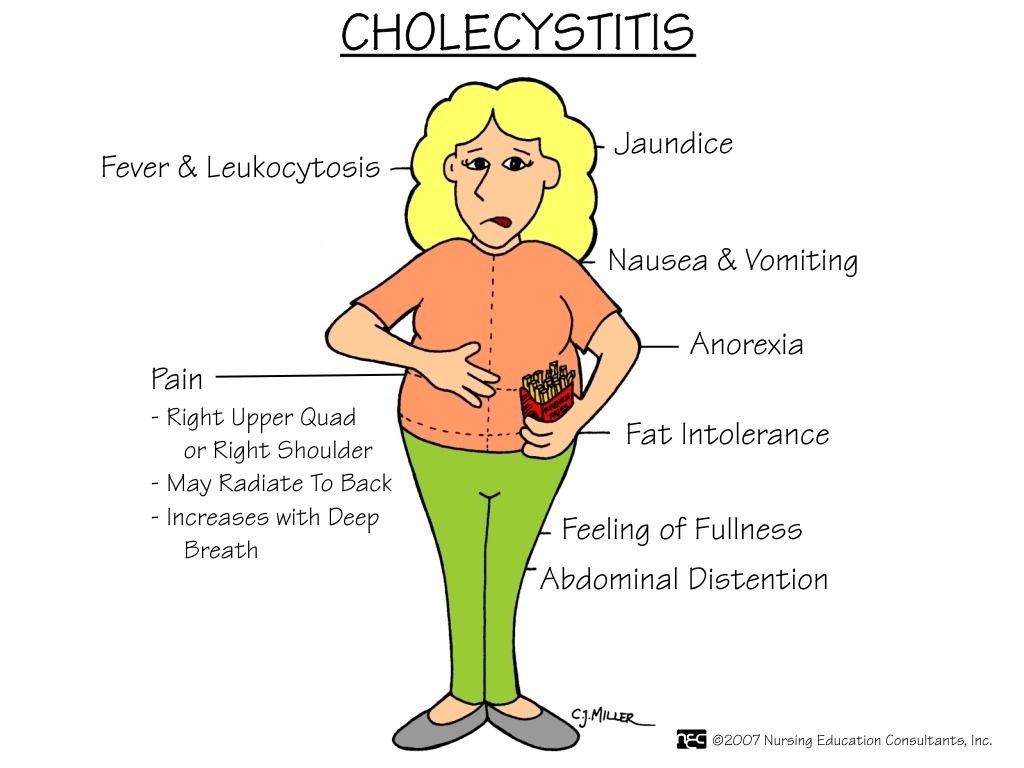
Different types of miscarriages
Miscarriage | Pregnancy Birth and Baby
The loss of a baby through miscarriage can be very distressing. A miscarriage generally occurs for reasons outside your control and nothing can be done to prevent or stop it from happening. Most women who have had a miscarriage will go on to have a healthy pregnancy in the future.
What is a miscarriage?
A miscarriage is the loss of your baby before 20 weeks of pregnancy. The loss of a baby after 20 weeks is called a stillbirth.
Up to 1 in 5 confirmed pregnancies end in miscarriage before 20 weeks, but many other women miscarry without having realised they are pregnant.
Common signs of miscarriage include:
- cramping tummy pain, similar to period pain
- vaginal bleeding
If you think you are having a miscarriage, see your doctor or go to your local emergency department.
Many women experience vaginal spotting in the first trimester that does not result in pregnancy loss.
What are the types of miscarriage?
There are several types of miscarriage — threatened, inevitable, complete, incomplete or missed.
Other types of pregnancy loss include an ectopic pregnancy, molar pregnancy and a blighted ovum.
Threatened miscarriage
When your body is showing signs that you might miscarry, that is called a 'threatened miscarriage'. You may have light vaginal bleeding or lower abdominal pain. It can last days or weeks and the cervix is still closed.
The pain and bleeding may resolve and you can go on to have a healthy pregnancy and baby. Or things may get worse and you go on to have a miscarriage.
There is rarely anything a doctor, midwife or you can do to prevent a miscarriage. In the past bed rest was recommended, but there is no scientific proof that this helps at this stage.
Inevitable miscarriage
Inevitable miscarriages can come after a threatened miscarriage or without warning. There is usually a lot more vaginal bleeding and strong lower stomach cramps. During the miscarriage your cervix opens and the developing fetus will come away in the bleeding.
Complete miscarriage
A complete miscarriage has taken place when all the pregnancy tissue has left your uterus. Vaginal bleeding may continue for several days. Cramping pain much like labour or strong period pain is common — this is the uterus contracting to empty.
If you have miscarried at home or somewhere else with no health workers present, you should have a check-up with a doctor or midwife to make sure the miscarriage is complete.
Incomplete miscarriage
Sometimes, some pregnancy tissue will remain in the uterus. Vaginal bleeding and lower abdominal cramping may continue as the uterus continues trying to empty itself. This is known as an 'incomplete miscarriage'.
Your doctor or midwife will need to assess whether or not a short procedure called a ‘dilatation of the cervix and curettage of the uterus’ (often known as a ‘D&C’) is necessary to remove any remaining pregnancy tissue. This is an important medical procedure done in an operating theatre.
Missed miscarriage
Sometimes, the fetus has died but stayed in the uterus. This is known as a 'missed miscarriage'.
If you have a missed miscarriage, you may have a brownish discharge. Some of the symptoms of pregnancy, such as nausea and tiredness, may have faded. You might have noticed nothing unusual. You may be shocked to have a scan and find the fetus has died.
If this happens, you should discuss treatment and support options with your doctor.
Recurrent miscarriage
A small number of women have repeated miscarriages. If this is your third or more miscarriage in a row, it’s best to discuss this with your doctor who may be able to investigate the causes, and refer you to a specialist.
A miscarriage can occur suddenly or over a number of weeks. The symptoms are usually vaginal bleeding and lower tummy pain. It is important to see your doctor or go to the emergency department if you have signs of a miscarriage.
The most common sign of a miscarriage is vaginal bleeding, which can vary from light red or brown spotting to heavy bleeding. If it is very early in the pregnancy, you may think that you have your period.
If it is very early in the pregnancy, you may think that you have your period.
Other signs may include:
- cramping pain in your lower tummy, which can vary from period-like pain to strong labour-like contractions
- passing fluid from your vagina
- passing of blood clots or pregnancy tissue from your vagina
What really happens during a miscarriage?
WARNING — This article contains some graphic descriptions of what you might see during a miscarriage.
What should I do if I think I’m having a miscarriage?
If you are concerned that you are having a miscarriage, call your doctor or midwife for advice and support.
Keep in mind that many women experience vaginal spotting in the first trimester of pregnancy that does not result in a miscarriage.
If you are alone, consider calling your partner or a friend for help and support.
If you have very heavy bleeding, strong pain or feel unwell, call triple zero (000) or have someone take you to your nearest emergency department.
How is a miscarriage managed?
Unfortunately, nothing can prevent a miscarriage from happening once it has begun. What happens now depends on your own health and what is happening to you.
Each approach has benefits and risks. You should discuss these with your doctor.
Expectant or natural management
Also called ‘watch and wait’, expectant management may be recommended in early pregnancy. This involves going home and waiting until the pregnancy tissue has passed from your womb by itself. This can happen quickly, or it may take a few weeks.
Medical management
You may be offered medication that speeds up the passing of the pregnancy tissue. You may be asked to stay in hospital until the tissue has passed, or you may be advised to go home.
Surgical management
You may be advised to have a form of minor surgery called a 'dilatation and curettage' (also called a D&C or a curette). This procedure is often recommended if you have heavy bleeding, significant pain or signs of infection. It may also be recommended if expectant or medical management has failed. You may also decide that you prefer this option.
It may also be recommended if expectant or medical management has failed. You may also decide that you prefer this option.
This procedure is done under general anaesthesia in an operating theatre. It takes 5-10 minutes once you are asleep. The doctor opens the cervix and removes the remaining pregnancy tissue.
How is a miscarriage treated?
Once it is confirmed that you are having a miscarriage, your doctor may offer or recommend treatment. There are many options. All have benefits and risks — discuss these with your doctor.
If the miscarriage is complete
If it seems the miscarriage is complete, you should still see your doctor for a check-up. You may be advised to have an ultrasound to make sure your uterus is empty.
If you go to hospital
If you go to your hospital’s emergency department, you will be seen first by a triage nurse, who will assess how urgently you need to be seen by a doctor. Depending on your symptoms, you will either be taken in to see a doctor immediately, or you will be asked to wait.
If you are waiting to be seen and your symptoms become worse or you feel like you need to go to the toilet, let the staff know immediately.
What happens if I miscarry at home?
Some women miscarry at home before they have a chance to see their doctor or get to the hospital.
If this happens, then:
- use pads to manage the bleeding
- if you can, save any pregnancy tissue that you pass, as your doctor may recommend it is tested to see why your miscarriage happened
- take medications such as paracetamol if you have pain
- rest
- call your doctor or midwife
There is a chance you may see your baby in the tissue that you pass, but often the baby is too small to recognise, or may not be found at all. It is normal to want to look at the remains, but you may decide you do not want to. There is no right or wrong thing to do.
Some women miscarry while on the toilet. This can also happen if you are out and about, or in hospital. There is no right or wrong way to handle this.
There is no right or wrong way to handle this.
Why do miscarriages happen?
Many women wonder if their miscarriage was their fault. In most cases, a miscarriage has nothing to do with anything you have or have not done. There is no evidence that exercising, stress, working or having sex causes a miscarriage.
Most parents do not ever find out the exact cause. However, it is known that miscarriages often happen because the baby fails to develop properly, usually due to a chromosomal abnormality that was spontaneous, not inherited.
Occasionally, miscarriage is caused by:
- hormonal abnormalities
- immune system and blood clotting problems
- medical conditions such as thyroid problems or diabetes
- severe infections causing high fevers (not common colds)
- physical problems with your womb or cervix
What are the risk factors for miscarriage?
Women are more likely to have miscarriages if they:
- are older
- smoke
- drink alcohol in the first trimester
- drink too much caffeine in coffee, tea or energy drinks
- have had several previous miscarriages
Can you prevent a miscarriage?
Living healthily — no cigarettes, no alcohol and little to no caffeine — can decrease your risk of miscarriage.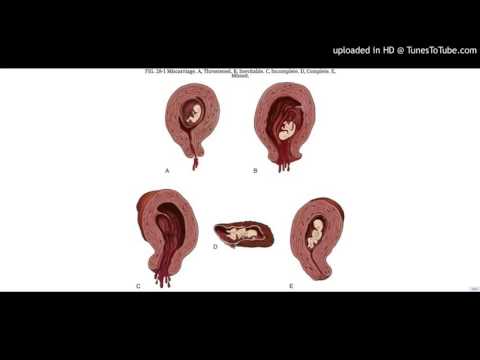 It’s a good idea to avoid contact with people who have a serious infectious illness when you’re pregnant.
It’s a good idea to avoid contact with people who have a serious infectious illness when you’re pregnant.
Who can I talk to for advice and support?
Talk to your doctor or midwife for information and advice on what do and how to look after yourself if you experience a miscarriage.
Your hospital should be able to provide details of available support services, such as bereavement support.
SANDS is an independent organisation that provides support for miscarriage, stillbirth and newborn death. You can call them on 1300 072 637 or visit www.sands.org.au.
You can also call Pregnancy, Birth and Baby on 1800 882 436, 7am to midnight (AET) to speak to a maternal child health nurse for advice and emotional support.
Speak to a maternal child health nurse
Call Pregnancy, Birth and Baby to speak to a maternal child health nurse on 1800 882 436 or video call. Available 7am to midnight (AET), 7 days a week.
Learn more here about the development and quality assurance of healthdirect content.
What Are the Different Types of Miscarriage?
A miscarriage, or “spontaneous abortion,” refers to the loss of a pregnancy before 20 weeks and occurs in 15 to 20 percent of all pregnancies. Most miscarriages occur during the first trimester but can also occur later on in the pregnancy.
Different types of miscarriages can occur at different stages of your pregnancy. The symptoms and treatments will depend on the type of miscarriage. Learn more about the different stages, signs and symptoms of, and treatment for miscarriage:
Chemical Pregnancy
A chemical pregnancy is a very early miscarriage which can occur before you even learn that you’re pregnant. As pregnancy tests have become more sensitive and more common, an increased number of chemical pregnancies have been diagnosed.
Chemical pregnancy is most likely the result of chromosomal abnormalities in the fertilized egg. An egg is fertilized, but is non-viable shortly after implantation, and is never visible on ultrasound.
Signs and Symptoms: There may be no signs of a chemical pregnancy. Most women simply begin to bleed around the time of their next period, though their period may arrive a few days late or be slightly heavier.
Blighted Ovum
Also known as anembryonic pregnancy, blighted ovum occurs very early in pregnancy, often before you even know you are pregnant. A fertilized egg attaches to the uterine wall, but an embryo does not develop.
Signs and Symptoms: You may feel signs of pregnancy, but when your doctor performs an ultrasound, he or she finds an empty gestational sac or cannot confirm a heartbeat.
You may miscarry the pregnancy or schedule a dilation and curettage (D&C) procedure, in which the cervix is opened, and the pregnancy is gently curetted, or removed, from the uterus.
Missed Miscarriage
A missed miscarriage, or a missed abortion, occurs when a fetus implants, but fails to develop.
The body does not expel the pregnancy tissue.
Signs and Symptoms: You may continue to feel signs of pregnancy if the placenta still releases hormones. Or, you may notice signs of pregnancy fade. Some women may experience some vaginal discharge and cramping, but many have no symptoms of miscarriage.
Sometimes the body will dispel the fetal tissue, but other times, a D&C procedure is necessary.
Threatened Miscarriage
A threatened miscarriage refers to vaginal bleeding that occurs during the first 20 weeks of pregnancy. It does not necessarily mean your pregnancy will end in a miscarriage — around half of threatened miscarriages result in a live birth.
Signs and Symptoms: Other symptoms of threatened miscarriage include lower back pain and abdominal cramps. If you have experienced unexplained bleeding during pregnancy, your doctor will want to perform an examination.
Cervix Dilation: In a threatened miscarriage, the cervix will remain closed. However, if an examination reveals the cervix has opened, a miscarriage is much more likely.
Inevitable Miscarriage
Inevitable miscarriage refers to unexplained vaginal bleeding and abdominal pain during early pregnancy.
Signs and Symptoms: Bleeding is heavier than with a threatened miscarriage and abdominal cramps more severe. Unlike threatened miscarriage, an inevitable miscarriage is also accompanied by dilation of the cervical canal. The open cervix is a sign that the body is in the process of miscarrying the pregnancy.
Incomplete Abortion
An incomplete abortion, which is also called an incomplete miscarriage, happens when some—but not all—of the pregnancy tissue is passed.
Signs and Symptoms: It is often accompanied by heavy vaginal bleeding and intense abdominal pain. The cervix will be open, and some remaining pregnancy tissue will be found in the uterus during an examination.
Complete Miscarriage
A complete miscarriage, also called a complete abortion, refers to a miscarriage in which all of the pregnancy tissue is expelled from the uterus.
Signs & Symptoms: A complete miscarriage is characterized by heavy vaginal bleeding, severe abdominal pain, and passage of pregnancy tissue. With a complete miscarriage, the bleeding and pain should subside quickly. Complete miscarriages can be confirmed through an ultrasound.
Dr. Alan Copperman is a board-certified reproductive endocrinologist and infertility specialist with a long history of success in treating infertility and applying fertility preservation technologies. He serves as Medical Director of Progyny, a leading fertility benefits management company, and co-founded and serves as Medical Director of RMA of New York, one of the largest and most prestigious IVF centers in the country. Dr. Copperman is also the Vice Chairman and Director of Infertility for the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, and Chief Medical Officer of Sema4, a health information company. Dr. Copperman has been named to New York magazine’s list of Best Doctors 17 years in a row. He has been recognized by his peers and patient advocacy organizations for his commitment to patient-focused and data-driven care. He has published more than 100 original manuscripts and book chapters on reproductive medicine and has co-authored over 300 scientific abstracts on infertility, in vitro fertilization, egg freezing, ovum donation, and reproductive genetics.
He has been recognized by his peers and patient advocacy organizations for his commitment to patient-focused and data-driven care. He has published more than 100 original manuscripts and book chapters on reproductive medicine and has co-authored over 300 scientific abstracts on infertility, in vitro fertilization, egg freezing, ovum donation, and reproductive genetics.
Miscarriage, how to avoid - Planning and management of pregnancy in the gynecology of the Literary Fund polyclinic after a miscarriage
- Gallery
- News
- Blog
- Reviews
- Jobs
- Licenses
- Insurance partners
- Controlling organizations
- Schedule of reception of citizens on personal appeals
- What you need to know about coronavirus infection? nine0004
- Rules for patients
- Online doctor's consultation
- to corporative clients
- The documents
A miscarriage is always associated with serious consequences for the whole body of a woman and for her reproductive organs in particular, it also affects the family situation, disrupts the woman's work schedule. An unfavorable outcome of pregnancy requires great mental and physical costs on the part of parents. Therefore, turning to doctors to find out the causes of the problem is the very first and correct step towards the birth of a child. nine0033
An unfavorable outcome of pregnancy requires great mental and physical costs on the part of parents. Therefore, turning to doctors to find out the causes of the problem is the very first and correct step towards the birth of a child. nine0033
Any competent gynecologist will tell you that the problem of miscarriage can be solved. With proper preparation for pregnancy and its management, the next time you will have a successful pregnancy. Most girls after a miscarriage go to extremes: they try to get pregnant again as soon as possible. And if this succeeds, then the miscarriage is very often repeated. And you need to give the body a rest for 2-3 months, then identify and eliminate the cause. And only then try.
Causes of miscarriage
Many are convinced that miscarriages are due to a fall, bruise, or some other physical shock. Any woman who has had a miscarriage can remember that not long before she either fell or lifted something heavy. And I am sure that she lost her unborn child precisely because of this. However, those women whose pregnancy was normal also fall and lift heavy things. Most sudden miscarriages do not occur for this reason. The reason is in violations of the pregnancy itself. Approximately half of miscarriages are due to abnormal genetic development of the fetus, which can be hereditary or accidental. Merciful nature, following the principles of natural selection in everything, destroys the defective and unviable fetus. But you should not be afraid of this. The fact that there is a defect in one embryo does not mean at all that all the others will be the same. nine0033
However, those women whose pregnancy was normal also fall and lift heavy things. Most sudden miscarriages do not occur for this reason. The reason is in violations of the pregnancy itself. Approximately half of miscarriages are due to abnormal genetic development of the fetus, which can be hereditary or accidental. Merciful nature, following the principles of natural selection in everything, destroys the defective and unviable fetus. But you should not be afraid of this. The fact that there is a defect in one embryo does not mean at all that all the others will be the same. nine0033
The woman's body is almost always to blame for the other half of miscarriages. They are caused by various known and unknown factors, such as: acute infectious diseases suffered in the first trimester of pregnancy, poor environment or difficult working conditions, excessive psychological or physical stress, abnormal development of the uterus, radiation, alcohol, smoking and certain types of drugs.
The causes of early and late miscarriage may differ, although they may overlap. The most important thing is to find out and eliminate or compensate for your own cause of miscarriage. Having discovered the cause, the gynecologist will tell you how to avoid another loss. nine0033
The most important thing is to find out and eliminate or compensate for your own cause of miscarriage. Having discovered the cause, the gynecologist will tell you how to avoid another loss. nine0033
Miscarriage
Miscarriage statistics also include “missed pregnancy”. Sometimes it happens that the embryo dies and lingers in the uterine cavity. Most often, this fact is detected by ultrasound. The dead fetus may begin to decompose, and this, thereby, will lead to poisoning of the mother's body.
Doctors resort to surgical curettage, which is associated with a risk of inflammation and complications. With such a miscarriage, the next pregnancy is planned after the body is fully restored - not earlier than a year. During this year, you will have to find out the cause of the missed pregnancy and treat it. nine0033
Miscarriage up to 6 weeks
The main causes of miscarriage on this line are malformations of the embryo itself. Statistics say that from 70-90% of embryos had chromosomal abnormalities: they are random and will not occur in other pregnancies. You may have been ill, taken medication, or were under the influence of other harmful factors. Fate saved you from a child with malformations.
You may have been ill, taken medication, or were under the influence of other harmful factors. Fate saved you from a child with malformations.
The human body is perfect and finds a way to correct the situation by miscarriage. Today is a tragedy for you. The real tragedy would be the preservation and birth of a sick, non-viable child. So don’t cry and understand: everything is for the best, you won’t help grief with tears ... And after three months, try again - it will almost certainly turn out to be successful. nine0033
It should also be noted that the fact of a miscarriage does not mean that you have lost something. So for a period of 7-8 weeks, the absence of an embryo in the fetal egg is found - "anembryony". It is believed that in 80-90% of cases, miscarriages are undiagnosed non-developing pregnancies.
Miscarriage between 6 and 12 weeks
Miscarriage in this period is also considered early. Its most common causes are:
Endocrine disorders
Endocrine disorders, when the ovaries do not synthesize enough hormones to keep the fetus in the womb, or the amount of male sex hormones is increased, is one of the most common causes of miscarriage and miscarriage. nine0033
nine0033
Imbalance of hormones in a woman's body is very likely to lead to an early termination of pregnancy. With a lack of the main hormone progesterone produced by the ovaries, this happens most often. Another hormonal problem is an increase in the tone of the uterus, which provokes the expulsion of the fetus.
Progesterone prepares the uterine mucosa for implantation and is the hormone for maintaining pregnancy in the first months. If conception occurs, the fetus cannot properly establish itself in the uterus. As a result, the fertilized egg is rejected. But pregnancy can be saved with the help of progesterone preparations if this problem is detected in time. nine0033
An excess of male sex hormones that suppress the production of estrogen and progesterone can also be the cause of an early miscarriage. Often, the cause of recurrent miscarriages are androgens that affect the formation and development of pregnancy; as well as thyroid and adrenal hormones. Therefore, a change in the function of these glands can lead to miscarriage.
Undertreated sexual infections
This problem must be solved before conception. Often the cause of miscarriage is sexually transmitted infections: syphilis, trichomoniasis, toxoplasmosis, chlamydia, cytomegalovirus and herpetic infections. Their effect on the fetus and the course of pregnancy is different for each woman and depends on the timing of infection, the activity of the microorganism, the degree of immune protection and the presence of other adverse factors. Depending on the situation, they can lead to the formation of fetal malformations, intrauterine infection, feto-placental insufficiency, early miscarriage or premature birth. Infection of the fetus and damage to the membrane of the fetus leads to miscarriage. To avoid this, infections should be treated before pregnancy. The use of therapy is possible during pregnancy as prescribed by a doctor. nine0033
Viral infections and other diseases
Any disease accompanied by intoxication and fever above 38 about C can lead to a miscarriage. Rubella, influenza and viral hepatitis occupy a leading position in this list. At a period of 4-10 weeks for pregnancy, ordinary tonsillitis can also become tragic, pneumonia carries a more serious risk. Pyelonephritis and appendicitis can cause early labor. When planning a pregnancy, it is imperative to undergo a medical examination in order to identify and treat foci of infections. nine0033
Rubella, influenza and viral hepatitis occupy a leading position in this list. At a period of 4-10 weeks for pregnancy, ordinary tonsillitis can also become tragic, pneumonia carries a more serious risk. Pyelonephritis and appendicitis can cause early labor. When planning a pregnancy, it is imperative to undergo a medical examination in order to identify and treat foci of infections. nine0033
Extremely dangerous during pregnancy rubella - it leads to severe fetal malformations, so infection during pregnancy is an indication for medical abortion.
Any disease during pregnancy can lead to non-viability of the fetus. And the body, through a miscarriage, insures you against unwanted offspring. With such a miscarriage, the next pregnancy has every chance of going well.
Immune causes of miscarriage
Sometimes antibodies that are hostile to the fetus are formed in the blood of a pregnant woman. This cause can be predicted and eliminated in advance. Most often, the conflict occurs when the embryo inherits the positive Rh factor of the father, and the negative Rh factor, the mother's body rejects the embryonic tissues that are alien to it. Constant monitoring of antibody titer and the introduction of anti-Rhesus immunoglobulins allows you to maintain and maintain pregnancy. In case of an immune conflict, progesterone preparations are also used to prevent miscarriage, which in this case has an immunomodulatory effect. nine0033
Most often, the conflict occurs when the embryo inherits the positive Rh factor of the father, and the negative Rh factor, the mother's body rejects the embryonic tissues that are alien to it. Constant monitoring of antibody titer and the introduction of anti-Rhesus immunoglobulins allows you to maintain and maintain pregnancy. In case of an immune conflict, progesterone preparations are also used to prevent miscarriage, which in this case has an immunomodulatory effect. nine0033
Reduced immunity
Reduced immunity during pregnancy also refers to immune causes. The body is simply not able to grow a new life in itself. You need to take care of yourself and recover before the next conception.
Anatomical causes of miscarriage
Anatomical causes of miscarriage are the most intractable. Malformations of the uterus are a serious reason for miscarriage. Sometimes you just have to deal with it.
Miscarriage between 12 and 22 weeks
Such a miscarriage is considered late. Its causes coincide with the causes of miscarriages in the early stages (anatomical, immune, infectious, endocrine).
Its causes coincide with the causes of miscarriages in the early stages (anatomical, immune, infectious, endocrine).
At this time, miscarriage also occurs due to isthmic-cervical insufficiency - a weak cervix cannot hold the fetus and opens. For this reason, a miscarriage can occur in the 2nd or 3rd trimester. Isthmic-cervical insufficiency is observed in 15.0-42.7% of women suffering from miscarriage. Careful monitoring of the pregnant woman allows you to identify the problem in time and make surgical correction of the cervix before the onset of childbirth. nine0033
In isthmic-cervical insufficiency, there is only one method of treatment - mechanical narrowing of the cervical canal. To do this, the neck is either sewn up or a special ring is put on it. However, the latter method is less efficient, because the ring can easily slide off the neck, then it will no longer hold back the process of opening it.
After suturing, if necessary, it is possible to use antibiotics and drugs that normalize the microflora of the vagina. The treatment of the vagina and the control of the state of the seams are carried out daily for 5 days. Stitches are removed at 37-38 weeks and with premature onset of labor. nine0033
The treatment of the vagina and the control of the state of the seams are carried out daily for 5 days. Stitches are removed at 37-38 weeks and with premature onset of labor. nine0033
Isthmic-cervical insufficiency may be primary (for no apparent reason), may be the result of abortion or hormonal disorders (increased levels of androgens - male sex hormones or their precursors).
Miscarriage after 22 weeks
Such a loss is hard to forget. Obstetricians talk about premature birth after the 28th week of pregnancy. Traditionally, a child born after this period is considered viable. But medicine knows many cases when it was possible to save the life of earlier children. nine0033
We recommend that you be carefully examined for miscarriage, check the above factors. In addition to them, the cause of a miscarriage can be antiphospholipid syndrome, while the woman's body perceives the child as something alien and rejects it. This disease, like the others listed, can be corrected; you have a very real chance of bearing a child.
Miscarriages due to hemostasis disorders
All of the above causes account for only 30-40%. Up to 70% of miscarriages are caused by disorders in the blood coagulation system (hemostasis). nine0033
Blood coagulation disorders leading to pregnancy loss can be divided into thrombophilic (increased clotting) and hemorrhagic (bleeding tendencies). Both of these extremes are dangerous to the fetus. Various disorders leading to the formation of small blood clots lead to the fact that the fetus loses sufficient blood supply, development is disturbed and the fetus is rejected.
The main hemorrhagic changes can appear even in childhood in the form of increased bleeding during cuts, tooth extractions, the onset of menstruation. But sometimes they declare themselves only during pregnancy and are the cause of a miscarriage. Bleeding in the early stages and detachment of the chorion is difficult to stop. nine0033
You may not guess, but incomprehensible headaches, weakness, fatigue, temporary loss of smell or hearing may be symptoms of disorders in the blood coagulation system.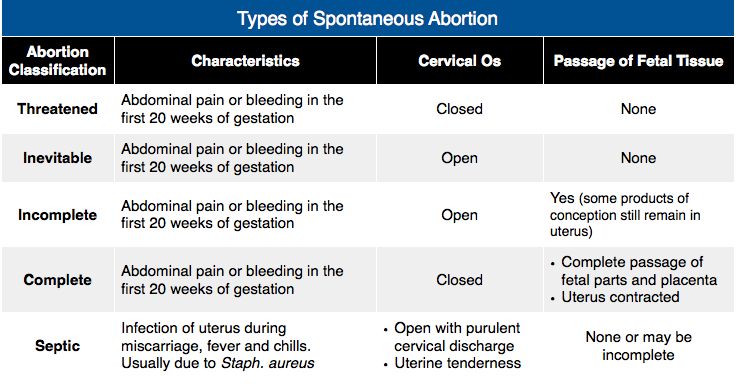
When planning a pregnancy, a genetic examination should be carried out and, if necessary, treatment should be started.
It is advisable to be examined for hidden hemostasis defects even for those who consider themselves healthy. This will allow you to predict the occurrence of complications and prevent loss. Early therapy can prevent miscarriage at 98% of cases. If defects in hemostasis are already detected during pregnancy, it can be difficult to maintain it.
What to do after a miscarriage?
Find the cause! The ideal option is to be examined by future parents: it is much more reasonable to postpone conception and spend two or three months to identify the causes than to risk getting pregnant again, spend two months waiting, and then lose everything again and still go to the doctors.
Until you understand the reason, it will not evaporate. In most cases, the answers lie on the surface. Take care of your health and your future baby. nine0033
Sign up for a consultation with an obstetrician-gynecologist by phone +7 (495) 150-60-01
Tyan Oksana Alexandrovna
Head of the department, obstetrician-gynecologist Doctor of the highest category Work experience: 26 years
Volkova Polina Dmitrievna
Obstetrician-gynecologist, doctor of ultrasound diagnostics Doctor of the highest category Experience: 35 years
Postnikova Nadezhda Anatolyevna
Obstetrician-gynecologist, ultrasound specialist Work experience: 35 years
Moiseeva Alla Vitalievna
Obstetrician-gynecologist, doctor of ultrasound diagnostics Doctor of the first category Experience: 37 years
Zabolotnova Olga Valentinovna
Obstetrician-gynecologist Doctor of the first category Experience: 26 years
Shchelokova Elena Nikolaevna
Obstetrician-gynecologist Doctor of the highest category Experience: 38 years
Maksimova Tamara Anatolyevna
Obstetrician-gynecologist Work experience: 7 years
Pass or medical card number:
Contact phone: *
Select the day of your appointment:
Additional information: nine0033
I am not a robot
By clicking the "Submit Application" button, you agree to the terms Privacy Policy and User Agreement
terms, causes, signs and treatment in the medical clinic "Proxima", Sochi, Adler
Causes of miscarriage
Every spontaneous abortion is certainly a tragedy. After all, life, before it begins, stops. But in some cases, miscarriage should be considered as a protective and adaptive reaction. The fetus dies, and its non-viable tissues pose a threat to the health of the mother. And in order to protect itself from the action of embryonic toxins, to cleanse itself, the mother's body rejects these tissues. nine0033
After all, life, before it begins, stops. But in some cases, miscarriage should be considered as a protective and adaptive reaction. The fetus dies, and its non-viable tissues pose a threat to the health of the mother. And in order to protect itself from the action of embryonic toxins, to cleanse itself, the mother's body rejects these tissues. nine0033
There are a number of factors that affect the fetus. First of all, these are gene and chromosomal abnormalities of the fetus . Not all of them are inherited. Changes in the karyotype (set of chromosomes) and genotype (set of genes) can occur at any stage: during the maturation of gametes (sex cells), during the fertilization of the egg and its subsequent division. But these changes are so significant that they make it impossible for the further development of the embryo, and it dies.
The embryo is damaged by toxins. These can be exogenous toxins, toxic substances coming from outside, and endogenous toxins formed in the mother's body during various diseases and metabolic disorders. Many chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (gastrointestinal tract), liver, kidneys are also accompanied by endogenous intoxication.
Many chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (gastrointestinal tract), liver, kidneys are also accompanied by endogenous intoxication.
Exogenous toxins are industrial emissions, some household substances, medicines, as well as nicotine, alcohol, drugs. Salts of heavy metals, many groups of antibiotics, antifungal agents, psychotropic drugs have a particularly unfavorable effect on the fetus. Ionizing radiation, although not a toxin, also damages the fetus, and can lead to miscarriage. nine0033
The infection affects the fetus. In this regard, the TORCH group (in Russian transcription - TORCH) is especially dangerous. These include:
- herpes
- rubella
- cytomegalovirus
- toxoplasmosis
- gonorrhea, syphilis, chlamydia, trichomoniasis, and other sexually transmitted infections.
These types of infections have a direct teratogenic effect - they cause deformities that are often incompatible with further gestation (bearing a fetus). Other bacterial, viral infections, incl. and colds are accompanied by endogenous intoxication, deterioration of fetoplacental circulation and, ultimately, miscarriage. nine0033
Other bacterial, viral infections, incl. and colds are accompanied by endogenous intoxication, deterioration of fetoplacental circulation and, ultimately, miscarriage. nine0033
The following causes of miscarriages are related to hormonal imbalances. Normal gestation is provided by progesterone, which is also called the hormone of pregnancy. Progesterone relaxes the uterine muscles, and thereby prevents miscarriages. Consequently, with its deficiency, the risk of miscarriages will increase.
In this regard, the time interval of 8-12 weeks, corresponding to the second critical period of pregnancy, is dangerous. At this time, the placenta begins to form, and a physiological decrease in progesterone levels is noted. Changes in the levels of other hormones also often lead to miscarriages. In this regard, potentially dangerous are: diabetes mellitus, thyrotoxicosis, Itsenko-Cushing's disease, and other endocrine diseases. nine0033
Immune disorders also provoke miscarriages. After all, the fetus inherits paternal genes, and is alien in relation to the maternal organism. Therefore, the mother's body tries to reject it. To prevent this from happening, physiological immunosuppression, suppression of immunity, is formed during pregnancy.
Immunosuppression is provided by the same progesterone. Not only the deficiency of this hormone, but also some other factors strengthen the immune system. Sometimes this enhancement acquires pathological features. At the same time, autoimmune reactions develop when the secreted antibodies (autoantibodies) destroy their own tissues. The action of autoantibodies can also be directed to the fetal egg, which will entail a miscarriage. nine0033
Violations of fetoplacental blood flow lead to early termination of pregnancy. Specific causes of this condition:
- abnormal attachment of the placenta
- anemia in the mother
- disorders in the coagulation system leading to the occurrence of microthrombi in the vessels of the chorion
- deterioration of systemic blood flow in the mother's body in cardiovascular pathology (atherosclerosis, hypertension, heart failure, valvular disease).
 nine0004
nine0004
A number of structural changes in a woman's reproductive system also provoke spontaneous abortion. These changes can be congenital or acquired. With some congenital anomalies in the structure of the uterus, fertilization occurs, and the fetal egg is implanted in the endometrium. But in the future, the problems associated with the growth of the embryo increase, which makes further gestation impossible.
Acquired changes are associated with chronic inflammatory diseases of the uterus and appendages, surgical interventions on the pelvic organs, previous medical, and even criminal abortions. nine0033
Isthmic-cervical insufficiency often leads to late pregnancy termination. This is a decrease in the tone of the muscles located in the isthmus of the uterus, isthmus. Isthmus directly passes into the cervix, cervix. The failure of the muscular valve in this area is accompanied by the opening of the cervix, and the expulsion of the fetus. If this happens in the third trimester, a premature but live fetus is born, and if earlier, a miscarriage.
If this happens in the third trimester, a premature but live fetus is born, and if earlier, a miscarriage.
There is an opinion that intense physical activity can negatively affect gestation. Maybe you are right. But these should be really prohibitive loads, for example, jumping from a height, lifting weights, which is rare in practice. On the contrary, walking, housework, and even travel contribute to the normal bearing of the fetus. The same goes for intimacy. Sex, at least in the early stages, is unlikely to cause an abortion. nine0191
Signs of miscarriage
The main symptoms of miscarriage are local pain and bloody vaginal discharge. An interesting fact: in the early stages of a few weeks, pregnancy, as a rule, is not recognized. Accordingly, its interruption is not recognized either. And discomfort and spotting are interpreted as menstrual irregularities with profuse painful menstruation. According to experts, a significant number of pregnancies end in an unrecognized termination in the early stages. nine0033
According to experts, a significant number of pregnancies end in an unrecognized termination in the early stages. nine0033
In the future, with an increase in the size of the embryo, the departed fetal egg looks like a blood clot. In appearance, it can be mistaken for a fragment of the endometrium with heavy menstruation. The severity of manifestations depends not only on the term, but also on the stage of spontaneous abortion.
- Threatened abortion
Initial reversible stage. A woman complains of pulling pains in the lower abdomen, which often radiate to the lower back. The tone of the uterus is increased (hypertonicity). But no bleeding yet. At this stage, if you take measures, you can save the pregnancy. nine0033
- Complete or incomplete abortion
In a complete abortion, the fertilized egg is completely expelled. And with incomplete placental fragments remain in the uterine cavity. The first option is more favorable. After the fetal egg is completely expelled, the uterus contracts and the lumen of the damaged blood vessels closes. As a result, the bleeding stops.
The first option is more favorable. After the fetal egg is completely expelled, the uterus contracts and the lumen of the damaged blood vessels closes. As a result, the bleeding stops.
In an incomplete abortion, parts of the membranes interfere with uterine contractions. The blood vessels gape and the bleeding continues. Complete abortion is mostly characteristic of early terms. In the later stages, when the fetus increases in size, abortion, as a rule, is accompanied by its incomplete rejection. nine0033
Due to heavy bleeding, obstetrical hemorrhagic shock develops . Uncontrolled bleeding is fraught with the death of the patient. Another complication of spontaneous abortion is sepsis. After all, the damaged bleeding uterine mucosa serves as an entrance gate for a pyogenic infection.
Diagnosis and treatment of miscarriages
Diagnosis is based on clinical observations, ultrasound, and laboratory parameters. During a gynecological examination, the size and tone of the uterus, the expansion of the uterine os are determined. Ultrasound assesses the condition of the embryo in the early stages, and the fetus and placenta in late pregnancy
During a gynecological examination, the size and tone of the uterus, the expansion of the uterine os are determined. Ultrasound assesses the condition of the embryo in the early stages, and the fetus and placenta in late pregnancy
Laboratory diagnosis at the time of miscarriage does not play a significant role. Only after the lapse of time, retrospectively, the level of hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin) decreases, and signs of anemia are noted.
At the slightest suspicion of an incipient miscarriage, you should immediately seek help. Much depends on how quickly a woman or her relatives do this, perhaps even life itself. Threatened abortion is an indication for emergency hospitalization in an obstetric hospital. The hospital provides bed rest, physical and emotional rest. To reduce the tone of the uterus, antispasmodics are prescribed. Also shown are progestins - synthetic analogues of progesterone. The effect of treatment is enhanced by sedatives. nine0033
When bleeding occurs, which indicates an abortion that has begun, hemostatics and hemostatic agents are included in conservative treatment. With isthmic-cervical insufficiency, a good result is the fixation of the cervix with sutures. If the threat of abortion has passed, the woman undergoes treatment with antispasmodic, hormonal and anti-inflammatory drugs, after which she is discharged. In the future, she is under the outpatient supervision of an obstetrician-gynecologist right up to the birth itself. nine0033
With isthmic-cervical insufficiency, a good result is the fixation of the cervix with sutures. If the threat of abortion has passed, the woman undergoes treatment with antispasmodic, hormonal and anti-inflammatory drugs, after which she is discharged. In the future, she is under the outpatient supervision of an obstetrician-gynecologist right up to the birth itself. nine0033
If the pregnancy does not persist, the uterine cavity is inspected for fragments of the ovum, which are removed by curettage. To avoid sepsis and bleeding, it is important that everything is completely removed from the uterine cavity by means of curettage. Curettage is carried out under general anesthesia, i.e., under anesthesia.
After that, the woman undergoes a course of treatment with antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs, hemostatics. Sometimes a woman comes to the hospital already in a state of hemorrhagic shock. In this case, intensive therapy is carried out using plasma-substituting solutions, donated blood, plasma or erythrocyte mass.