Diamniotic dichorionic twins identical
Types of twins | Pregnancy Birth and Baby
beginning of content2-minute read
Listen
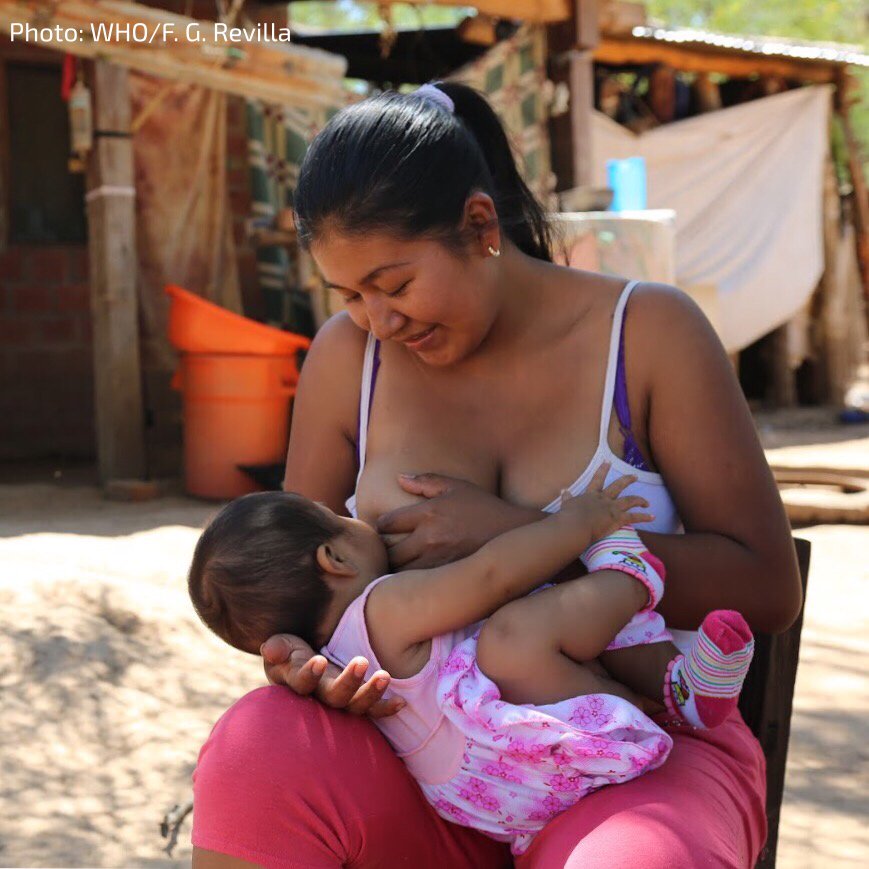
There are two types of twins - fraternal twins and identical twins. Find out more about the difference between the two types and twin-twin transfusion syndrome.
Fraternal twins
Fraternal twins are formed from the fertilisation of two eggs by two different sperm. They are also known as 'dizygotic twins', or 'non-identical twins'.
With fraternal twins, the two foetuses (developing babies) each have a separate placenta, inner membrane (the amnion) and outer membrane (the chorion). They don't usually look identical and might or might not be the same sex.
Identical twins
Identical twins are formed from the splitting of one embryo. They are also known as 'monozygotic twins'.
There are different types of identical twins, depending on what they share in the womb.
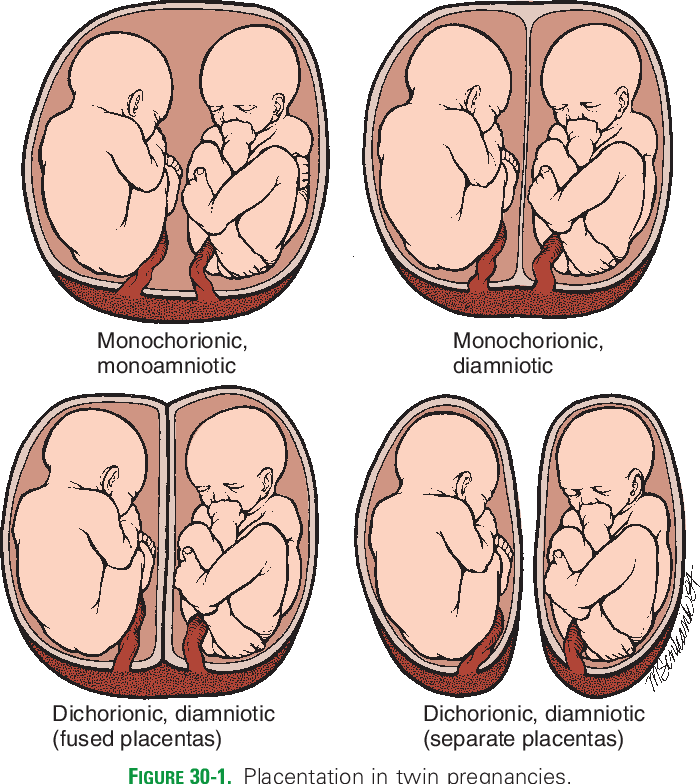
- Almost one third of identical twins have their own placenta, inner membrane, and outer membrane. The medical term for these twins is ‘dichorionic diamniotic’ or DCDA twins.
- Almost two-thirds of identical twins share the same placenta and chorion, but have their own amnion. These are ‘monochorionic diamniotic’ or MCDA twins.
- The rest — only about 4% of identical twins — share everything, and are called ‘monochorionic monoamniotic’ (MCMA) twins.
Although identical twins are the same sex and are genetically identical, they can develop quite different personalities. You can find a good description of the different types of monozygotic twins, with pictures, at the Twins Research Australia.
If you have triplets or more, the principles are similar.
Twin-twin transfusion syndrome
Identical twins who share the same placenta and chorion can sometimes share a condition called twin–twin transfusion syndrome (TTTS).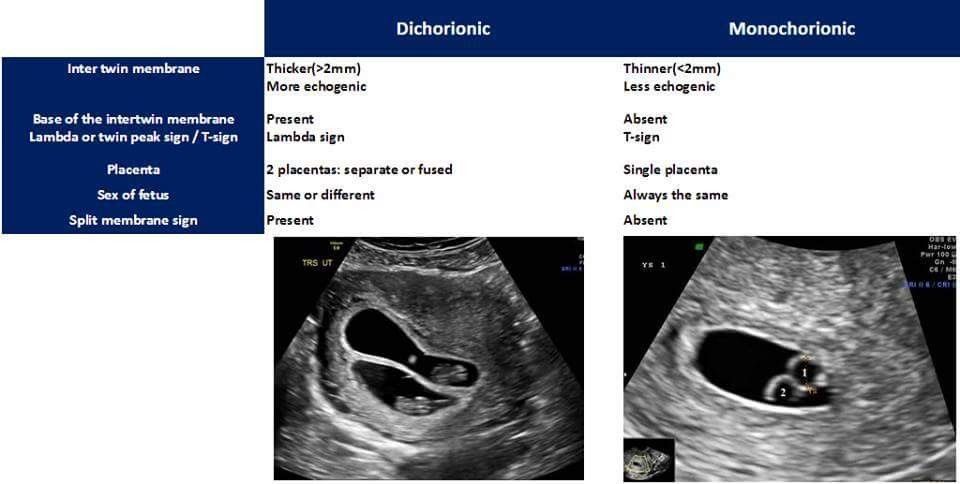 In this condition, blood flows from one twin to the other, resulting in one baby getting too much blood and the other baby not getting enough. This affects the health of both babies, sometimes severely.
In this condition, blood flows from one twin to the other, resulting in one baby getting too much blood and the other baby not getting enough. This affects the health of both babies, sometimes severely.
Most identical twins don’t get TTTS. But if they do, it is more likely to happen to MCDA twins than to MCMA twins.
If your twins have TTTS, there are many different ways to treat it - ask your doctor for advice.
More information
Find more information about twins at the Twins Research Australia and the Australian Multiple Birth Association.
Sources:
Cochrane Library (Planned caesarean section for women with a twin pregnancy), Cochrane Library (Regimens of ultrasound surveillance for twin pregnancies for improving outcomes), Cochrane Library (Interventions for the treatment of twin-twin transfusion syndrome), Twins Research Australia (Types of twins)Learn more here about the development and quality assurance of healthdirect content.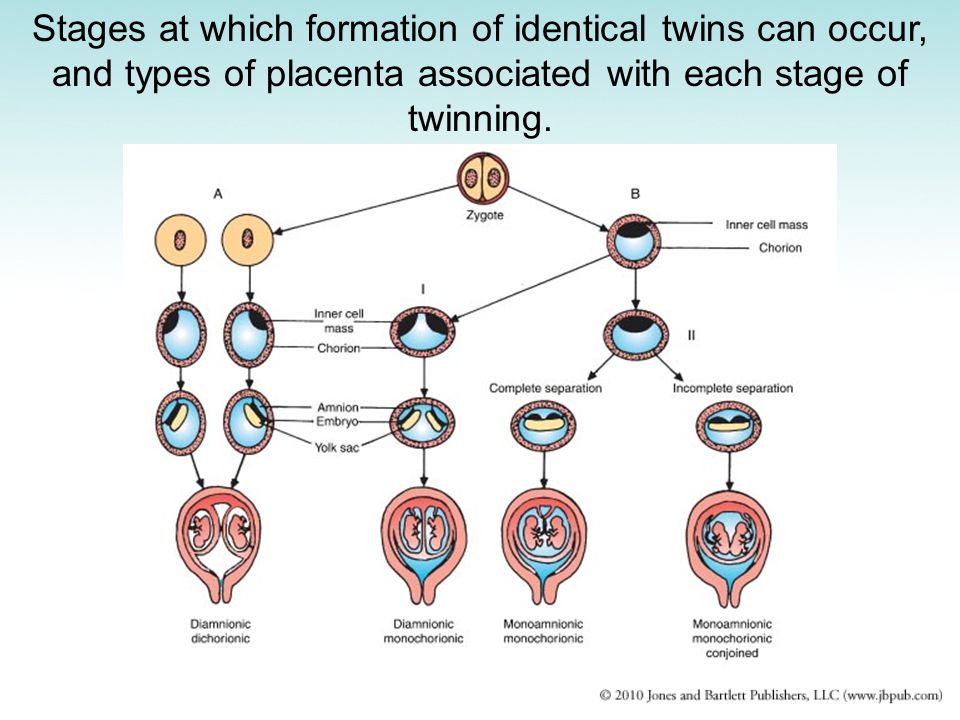
Last reviewed: October 2020
Back To Top
Related pages
- Preschool and twins
- Raising twins
- Giving birth to twins
- Pregnant with twins
This information is for your general information and use only and is not intended to be used as medical advice and should not be used to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any medical condition, nor should it be used for therapeutic purposes.
The information is not a substitute for independent professional advice and should not be used as an alternative to professional health care. If you have a particular medical problem, please consult a healthcare professional.
Except as permitted under the Copyright Act 1968, this publication or any part of it may not be reproduced, altered, adapted, stored and/or distributed in any form or by any means without the prior written permission of Healthdirect Australia.
Support this browser is being discontinued for Pregnancy, Birth and Baby
Support for this browser is being discontinued for this site
- Internet Explorer 11 and lower
We currently support Microsoft Edge, Chrome, Firefox and Safari. For more information, please visit the links below:
- Chrome by Google
- Firefox by Mozilla
- Microsoft Edge
- Safari by Apple
You are welcome to continue browsing this site with this browser. Some features, tools or interaction may not work correctly.
How will I know if my twins are identical?
In this article
- What's the difference between identical and non-identical twins?
- When will I find out if my twins are identical?
- How accurate are ultrasound scans for confirming identical twins?
- Can identical twins be a boy and a girl?
- What difference could it make to my care if I'm pregnant with identical twins?
- Will it be obvious if my babies are identical when they're born?
What's the difference between identical and non-identical twins?
Identical twins always develop from a single fertilised egg that's split and grown into two genetically identical babies. Non-identical (fraternal) twins grow from two eggs, separately fertilised by different sperm.
Non-identical (fraternal) twins grow from two eggs, separately fertilised by different sperm.
You're sure to be keen to find out if your twins are identical, but your obstetrician and midwife will be too. Whether or not your twins are identical can affect the type of medical care you and your babies receive. It can also affect the type of birth you have.
Defining twins as identical or not is more complicated than you may think. Medical definitions of twins are based on how the twins are conceived - from one fertilised egg or more - and how they are growing in the womb (uterus).
Within the womb, babies are surrounded by two membranes:
- The inner membrane, called the amnion. This membrane forms a bag that contains the amniotic fluid.
- The outer membrane, called the chorion. This membrane forms an extra layer around the amnion. The placenta grows from tissues in the chorion.
By carefully looking at these membranes, and the placenta or placentas, via an ultrasound scan, it's usually possible to tell whether twins may be identical. Your twins can then be placed into one of the following categories:
Your twins can then be placed into one of the following categories:
Dichorionic diamniotic (DCDA)
Each baby has their own placenta and their own separate outer membrane (chorion) and inner membrane (amnion). This is the case for about a third of identical twins and all non-identical twins (Davies 2014, 2019).
In DCDA identical twins, this happens when the fertilised egg completely splits within three days of conception (Davies 2014). This is early enough for the separate membranes and placentas to grow from the egg sac.
So, DCDA twins can be identical or non-identical.
Monochorionic diamniotic (MCDA)
Both babies share one placenta and one outer membrane (chorion), but they each have their own separate, inner membrane (amnion) (NHS 2019). This is the case for two-thirds of identical twins, so is the most common type of identical twin.
Monochorionic monoamniotic (MCMA)
Both babies share a single placenta, one single outer membrane (chorion) and one inner membrane (amnion) (NHS 2019).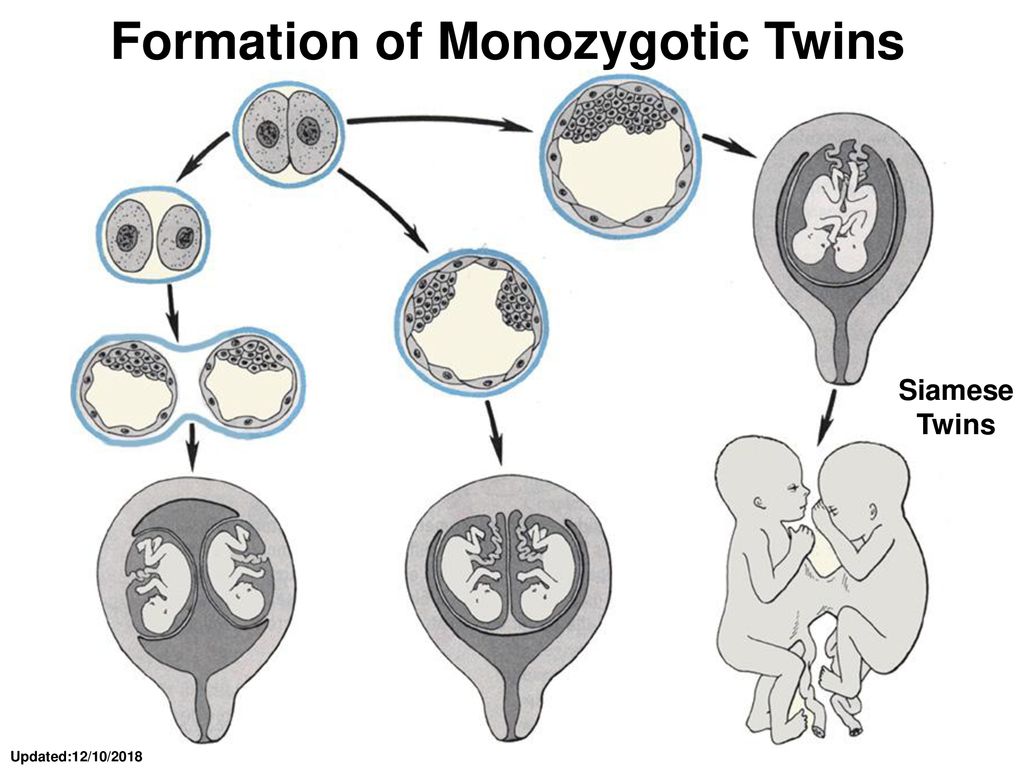 MCMA twins are extremely rare and only account for about one per cent of all identical twins (Davies 2014, MBF 2010, NHS 2019).
MCMA twins are extremely rare and only account for about one per cent of all identical twins (Davies 2014, MBF 2010, NHS 2019).
When will I find out if my twins are identical?
If you’re expecting MCDA or MCMA twins, you should find out whether they are identical at your dating scan, between 10 weeks and 14 weeks of pregnancy (NHS 2019, NICE 2011).
Before 14 weeks, it's easier to see on a scan whether your babies each have their own membranes (NICE 2011, RCOG 2016). Your sonographer will use this information to try to work out if your twins are identical.
If your sonographer identifies DCDA twins, you may not be able to find out for certain whether they are identical, during your pregnancy. You may have to wait until after they’re born to be sure. However, as all non-identical twins are DCDA, and a third of identical twins are DCDA, the chances are they are non-identical (NHS 2019).
How accurate are ultrasound scans for confirming identical twins?
Ultrasound scans are generally accurate for telling whether or not your twins share a chorion, particularly if done by 14 weeks (RCOG 2016).
If your sonographer is unsure, she will perform a second scan, and may seek a second opinion (NICE 2011, RCOG 2016). Sometimes, an immediate referral to a specialist at a bigger hospital is needed (RCOG 2016).
However, your sonographer may not be able to see everything accurately on the screen (NICE 2011, van Jaarsveld et al 2012). For example, it's possible for the placentas of non-identical twins to fuse together and look like one placenta (Davies 2014).
In addition, some health professionals may assume that two placentas means non-identical twins, when it's possible for identical twins to have a placenta each, if they are DCDA (Davies 2014, McAslan Fraser nd, van Jaarsveld et al 2012).
Can identical twins be a boy and a girl?
No, identical twins are genetically identical, so are always the same sex. However, you could have non-identical twins of the same sex. Scans later in pregnancy, when your babies' genitals have developed, may show your babies' sex. If a pregnancy scan clearly shows a boy and a girl then you can be sure that the twins are non-identical.
If a pregnancy scan clearly shows a boy and a girl then you can be sure that the twins are non-identical.
What difference could it make to my care if I'm pregnant with identical twins?
It's not so much whether your twins are identical, but whether your twins share membranes and a placenta (monochorionic twins), that could make a difference.
If you are pregnant with monochorionic twins, you are more likely to experience complications (NICE 2011, RCOG 2016). Your specialist team will closely monitor you and your babies, and you should have more frequent antenatal appointments and scans (NICE 2011, RCOG 2016).
Though most monochorionic twins are born healthy, up to 15 per cent of twins who share a placenta have twin-to-twin transfusion syndrome (TTTS) (NICE 2011, NHS 2019, RCOG 2016, TAMBA nd).
TTTS happens when there is an imbalance in the placental blood vessels, meaning one twin gets too much blood and the other gets too little.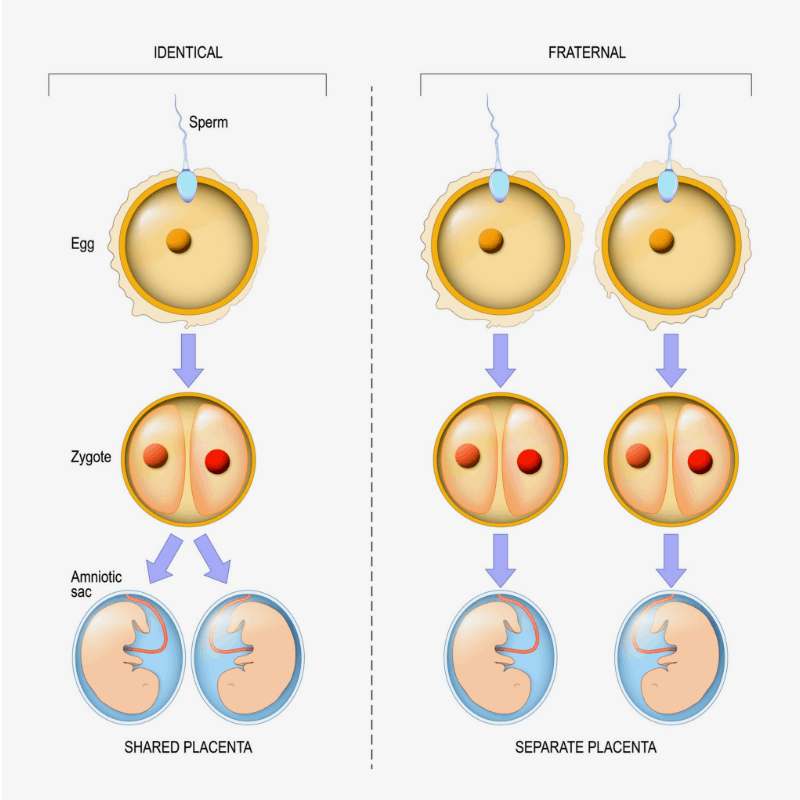 Your medical team will keep a close watch for TTTS, because it can be very harmful if it's not treated.
Your medical team will keep a close watch for TTTS, because it can be very harmful if it's not treated.
Will it be obvious if my babies are identical when they're born?
Occasionally it's not possible to tell whether babies are identical twins while they're still in the womb. In that case, you'll only find out for sure after your babies are born. But with newborns, it's difficult to tell just by looking. If your twins are the same sex, and each has their own placenta, they may or may not be identical (NICE 2011, NHS 2019, van Jaarsveld et al 2012).
Your obstetrician or midwife may be able to tell by examining the placenta closely (McAslan Fraser nd).
As your babies grow during their first year, other signs will show if they're identical, such as:
- eye colour
- hair colour and texture
- skin colour
- foot, hand and ear shape
- the exact timing and order in which they cut their teeth (MBF nd, McAslan Fraser nd)
If you want to know for sure early on whether your twins are identical, a DNA test is the most accurate way of finding out, but you will have to pay (McAslan Fraser 2012, NHS 2019).
The DNA test is called zygosity determination. It establishes whether your twins are identical (monozygotic) or fraternal (dizygotic). You'll just need to sweep a cotton bud inside your twins' mouths. DNA testing isn't usually available on the NHS, but is offered by the Multiple Births Foundation for about £100 per multiple tested (MBF nd, McAslan Fraser nd, Northgene nd).
Find out how many antenatal appointments twin pregnancies involve.
References
Davies M. 2014. Multiple pregnancy. In: Marshall J, Raynor M (eds). Myles textbook for midwives, 16th edn, Chapter 14. London: Elsevier.
MBF. 2010. Information for parents when twins share one placenta. Monochorionic twins. Multiple Births Foundation. www.multiplebirths.org.uk [Accessed June 2019]
MBF. nd. Are they identical? Multiple Births Foundation. www.multiplebirths.org.uk [Accessed June 2019]
McAslan Fraser E. nd. Expecting twins, triplets or more? The healthy multiple pregnancy guide.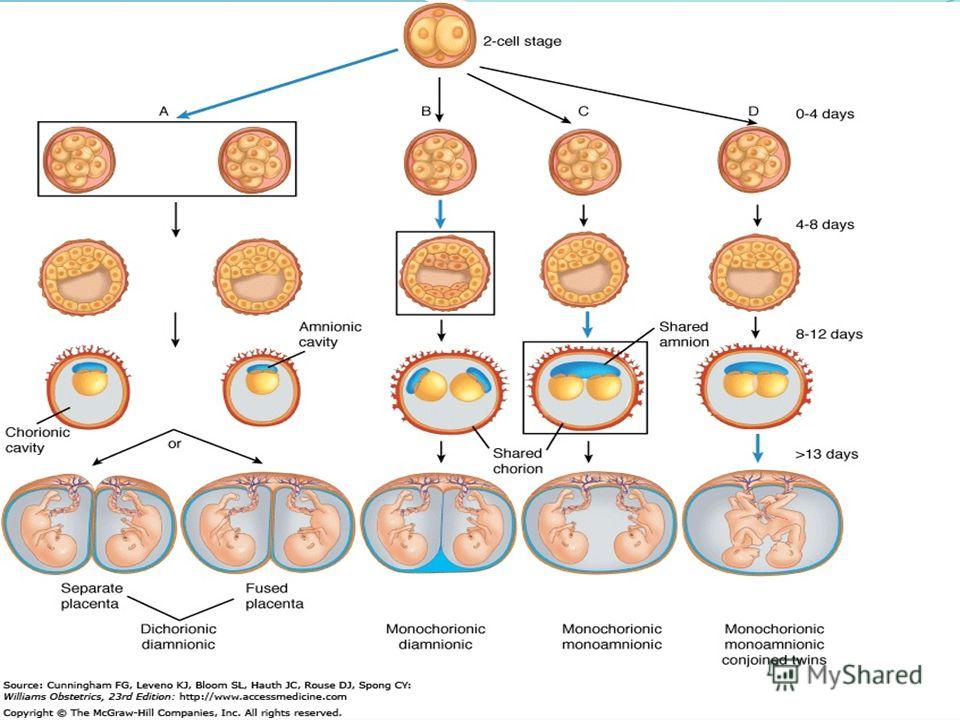 Tamba (Twins & Multiple Births Assocation). www.tamba.org.uk [Accessed June 2019]
Tamba (Twins & Multiple Births Assocation). www.tamba.org.uk [Accessed June 2019]
NHS. 2019. Antenatal care with twins. Health A-Z. www.nhs.uk [Accessed June 2019]
NICE. 2011. Multiple pregnancy: antenatal care for twin and triplet pregnancies. National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. CG129. www.nice.org.uk [Accessed June 2019]
Northgene nd. What relationship does zygosity testing prove? www.northgene.co.uk [Accessed June 2019]
RCOG. 2016. Management of monochorionic twin pregnancy. Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists, Green-top guideline 51. www.rcog.org.uk [Accessed June 2019]
Tamba nd. Key statistics on multiple births. Twins & Multiple Births Association. www.tamba.org.uk [Accessed June 2019]
Van Jaarsveld C, Llewellyn C, Fildes A, et al. 2012. Are my twins identical: parents may be misinformed by prenatal scan observations. BJOG . 119: 517–518. obgyn.onlinelibrary.wiley.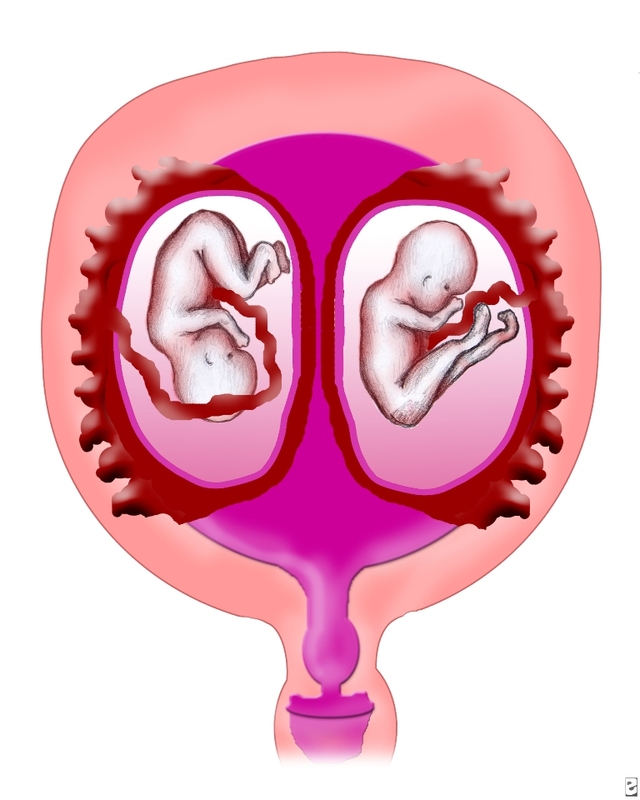 com/ [Accessed June 2019]
com/ [Accessed June 2019]
Show references Hide references
Multiple pregnancy
Author: Mikheeva Natalia Grigoryevna, Malyshok magazine
A multiple pregnancy is a pregnancy in which two or more fetuses develop simultaneously in the uterus. Multiple pregnancy occurs in 0.4 - 1.6% of all pregnancies. Recently, there has been an obvious trend towards an increase in the incidence of such pregnancies due to the active use of assisted reproduction technologies, including in vitro fertilization (IVF).
Types of multiple pregnancies
Children born in multiple pregnancies are called TWINS. There are two main types of twins: monozygotic (identical, homologous, identical, similar) and dizygotic (fraternal, heterologous, different). African countries have the highest twin birth rate, Europe and the USA have an average rate, and Asian countries have a low rate.
Dizygotic (fraternal) twins are more common (in 66-75% of all twins). The birth rate of dizygotic twins varies from 4 to 50 per 1000 births. Dizygotic twins occur when two separate eggs are fertilized. The maturation of two or more eggs can occur both in one ovary and in two. The predisposition to develop dizygotic twins may be maternally inherited. Dizygotic twins can be either same-sex or opposite-sex, they look like each other like ordinary brothers and sisters. With fraternal twins, two placentas are always formed, which can be very close, even touching, but they can always be separated. Two fruit spaces (i.e., fetal bladders or two “houses”) are separated from each other by a septum consisting of two chorionic and two amniotic membranes. Such twins are called dizygotic dichorionic diamniotic twins.
The birth rate of dizygotic twins varies from 4 to 50 per 1000 births. Dizygotic twins occur when two separate eggs are fertilized. The maturation of two or more eggs can occur both in one ovary and in two. The predisposition to develop dizygotic twins may be maternally inherited. Dizygotic twins can be either same-sex or opposite-sex, they look like each other like ordinary brothers and sisters. With fraternal twins, two placentas are always formed, which can be very close, even touching, but they can always be separated. Two fruit spaces (i.e., fetal bladders or two “houses”) are separated from each other by a septum consisting of two chorionic and two amniotic membranes. Such twins are called dizygotic dichorionic diamniotic twins.
Monozygotic (identical) twins are formed as a result of the separation of one fetal egg at various stages of its development. The frequency of birth of monozygotic twins is 3-5 per 1000 births. The division of a fertilized egg into two equal parts can occur as a result of a delay in implantation (immersion of the embryo in the uterine mucosa) and oxygen deficiency, as well as due to a violation of the acidity and ionic composition of the medium, exposure to toxic and other factors.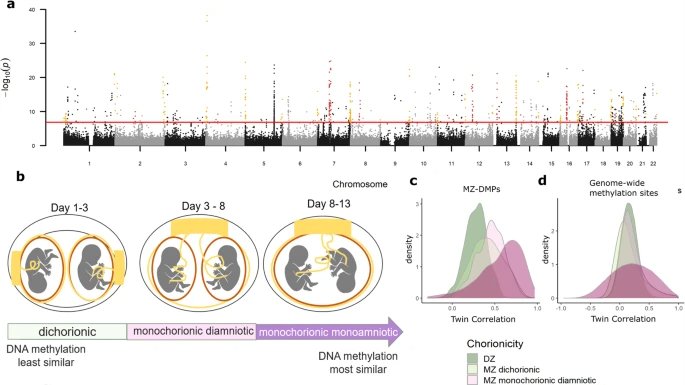 The emergence of monozygotic twins is also associated with the fertilization of an egg that had two or more nuclei. If the separation of the fetal egg occurs in the first 3 days after fertilization, then monozygotic twins have two placentas and two amniotic cavities, and are called monozygotic diamniotic dichoriones (Fig. A). If the division of the ovum occurs between 4 - 8 days after fertilization, then two embryos will form, each in a separate amniotic sac. Two amniotic sacs will be surrounded by a common chorionic membrane with one placenta for two. Such twins are called monozygotic diamniotic monochorionic twins (Fig. B). If division occurs by 9- 10th day after fertilization, then two embryos are formed with a common amniotic sac and placenta. Such twins are called monozygotic monoamniotic monochorionic (Fig. B) If the egg is separated at a later date on the 13th - 15th day after conception, the separation will be incomplete, which will lead to the appearance of conjoined (undivided, Siamese) twins.
The emergence of monozygotic twins is also associated with the fertilization of an egg that had two or more nuclei. If the separation of the fetal egg occurs in the first 3 days after fertilization, then monozygotic twins have two placentas and two amniotic cavities, and are called monozygotic diamniotic dichoriones (Fig. A). If the division of the ovum occurs between 4 - 8 days after fertilization, then two embryos will form, each in a separate amniotic sac. Two amniotic sacs will be surrounded by a common chorionic membrane with one placenta for two. Such twins are called monozygotic diamniotic monochorionic twins (Fig. B). If division occurs by 9- 10th day after fertilization, then two embryos are formed with a common amniotic sac and placenta. Such twins are called monozygotic monoamniotic monochorionic (Fig. B) If the egg is separated at a later date on the 13th - 15th day after conception, the separation will be incomplete, which will lead to the appearance of conjoined (undivided, Siamese) twins. This type is quite rare, approximately 1 observation in 1500 multiple pregnancies or 1: 50,000 - 100,000 newborns. Monozygotic twins are always the same sex, have the same blood type, have the same eye color, hair, skin texture of the fingers, and are very similar to each other.
This type is quite rare, approximately 1 observation in 1500 multiple pregnancies or 1: 50,000 - 100,000 newborns. Monozygotic twins are always the same sex, have the same blood type, have the same eye color, hair, skin texture of the fingers, and are very similar to each other.
Twin births occur once in 87 births, triplets - once in 87 2 (6400) twins, quadruples - once in 87 3 (51200) triplets, etc. (according to the Gallin formula). The origin of triplets, quadruplets, and more twins varies. So, triplets can be formed from three separate eggs, from two or one egg. They can be monozygotic and heterozygous. Quadruples can also be identical and fraternal.
Features of the course of multiple pregnancy
In case of multiple pregnancies, the woman's body is subject to increased requirements. All organs and systems function with great tension. In connection with the displacement of the diaphragm by the enlarged uterus, the activity of the heart becomes difficult, shortness of breath, fatigue occur. Enlargement of the uterus, especially towards the end of pregnancy, leads to compression of the internal organs, which is manifested by impaired bowel function, frequent urination, and heartburn. Almost 4-5 times more often there is the development of preeclampsia, which is characterized by an earlier onset, a protracted and more severe clinical course, often combined with acute pyelonephritis of pregnant women. Due to the increased need and consumption of iron, iron deficiency anemia often develops in pregnant women. Significantly more often than with a singleton pregnancy, complications such as bleeding during pregnancy and childbirth, anomalies in labor, and a low location of the placenta are observed. Often, with multiple pregnancies, abnormal positions of the fetus occur. One of the most common complications in multiple pregnancy is its premature termination. Preterm birth is observed in 25-50% of cases of such pregnancies.
Enlargement of the uterus, especially towards the end of pregnancy, leads to compression of the internal organs, which is manifested by impaired bowel function, frequent urination, and heartburn. Almost 4-5 times more often there is the development of preeclampsia, which is characterized by an earlier onset, a protracted and more severe clinical course, often combined with acute pyelonephritis of pregnant women. Due to the increased need and consumption of iron, iron deficiency anemia often develops in pregnant women. Significantly more often than with a singleton pregnancy, complications such as bleeding during pregnancy and childbirth, anomalies in labor, and a low location of the placenta are observed. Often, with multiple pregnancies, abnormal positions of the fetus occur. One of the most common complications in multiple pregnancy is its premature termination. Preterm birth is observed in 25-50% of cases of such pregnancies.
The development of term twins is normal in most cases.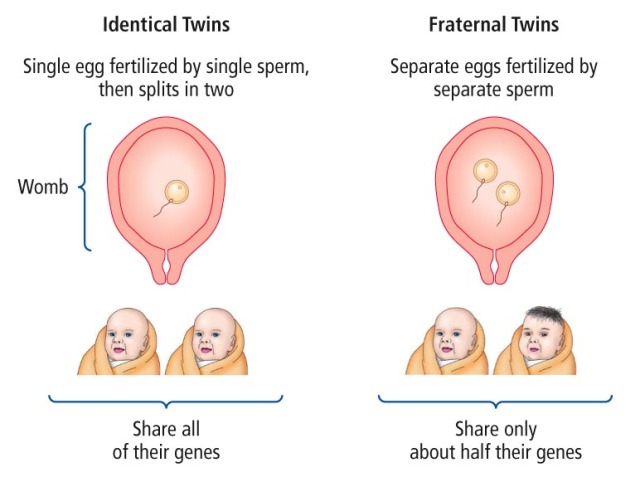 However, their body weight is usually less (by 10% or more) than in singleton pregnancies. With twins, the weight of children at birth less than 2500 g is observed in 40-60%. The low weight of twins is most often due to insufficiency of the uteroplacental system, which is not able to adequately provide several fetuses with nutrients, trace elements and oxygen. The consequence of this is a delay in the development of the fetus, which is a common occurrence in multiple pregnancies. The mass of twins, respectively, decreases in proportion to their number (triplets, quadruplets, etc.).
However, their body weight is usually less (by 10% or more) than in singleton pregnancies. With twins, the weight of children at birth less than 2500 g is observed in 40-60%. The low weight of twins is most often due to insufficiency of the uteroplacental system, which is not able to adequately provide several fetuses with nutrients, trace elements and oxygen. The consequence of this is a delay in the development of the fetus, which is a common occurrence in multiple pregnancies. The mass of twins, respectively, decreases in proportion to their number (triplets, quadruplets, etc.).
With monochorionic twins in the placenta, anastomoses are often formed between the vascular systems of the fetus, which can lead to a serious complication - the syndrome of feto-fetal transfusion. In this case, there is a redistribution of blood from one fetus to another, the so-called "stealing". The severity of feto-fetal transfusion (mild, moderate, severe) depends on the degree of redistribution of blood through the anastomoses, which vary in size, number and direction.
Diagnosis in multiple pregnancy
The most reliable method for diagnosing multiple pregnancies is ultrasound, which allows not only early diagnosis of multiple pregnancies, but also to determine the position and presentation of fetuses, localization, structure and number of placentas, the number of amniotic cavities, the volume of amniotic fluid, congenital malformations and antenatal fetal death, the state of the fetus from a functional point of view, the nature of the uteroplacental and fetal-placental blood flow.
In multiple pregnancies, due to the higher risk of complications, ultrasound monitoring is performed more frequently than in singleton pregnancies. With dizygotic twins, about once every 3-4 weeks, with monozygotic twins - once every 2 weeks.
In addition, examinations and control of clinical tests are carried out with great care, and CTG is regularly recorded from 28 weeks of pregnancy.
Birth management
Indications for caesarean section associated with multiple pregnancies are triplets (quadruple), the transverse position of both or one of the fetuses, breech presentation of both fetuses or the first of them, and not associated with multiple pregnancy - fetal hypoxia, anomalies labor activity, prolapse of the umbilical cord, extragenital pathology of the mother, severe gestosis, placenta previa and abruption, etc.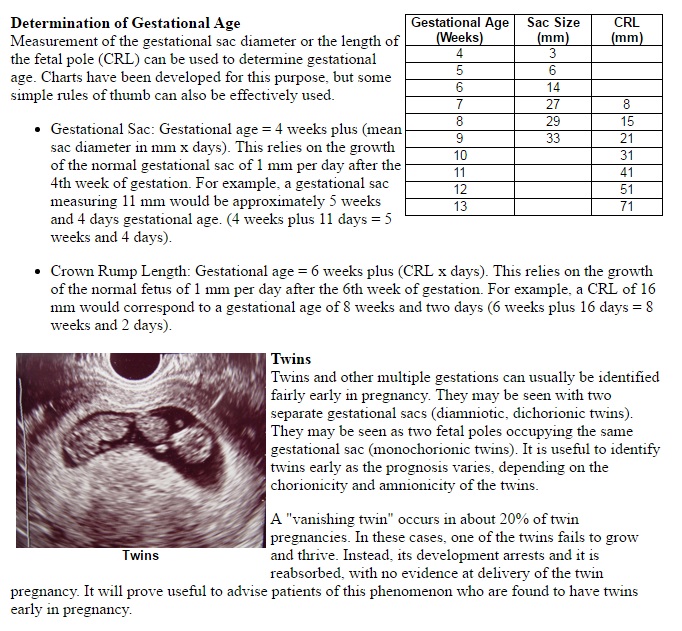
-
ECO
In the department of assisted reproductive technologies of the Maternity Hospital No. 2
, IVF is performed at the expense of the Republican budget for couples
who have received a positive decision from the Minsk city or regional commissions to provide one free IVF attempt.
No drug supply problem. There is no waiting list. -
Farewoman
-
Individual care for patients
-
Ultrasound diagnostics
Curious facts are
0
, how many are the Geminis? up to 80 million pairs of twins.
The number of twins born in relation to the total number of newborns in different countries and on different continents is different, but in general the trend is such that it continues to grow. Compared with the 60s, the percentage of twins has increased from 1.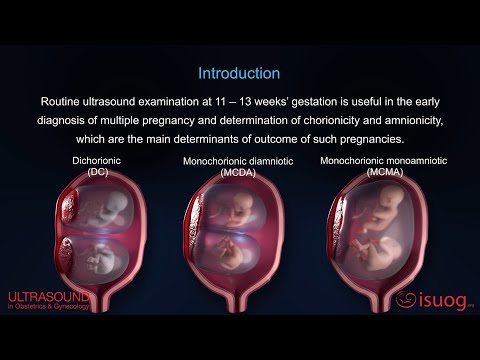 18 to 2.78, that is, almost 2.5 times.
18 to 2.78, that is, almost 2.5 times.
The largest number of children
The largest number of children born to one mother, according to official data, is 69. According to reports made in 1782, between 1725 and 1765. The wife of a Russian peasant Fyodor Vasiliev gave birth 27 times, giving birth to twins 16 times, triplets 7 times and 4 twins 4 times. Of these, only 2 children died in infancy.
The most prolific mother of our contemporaries is considered to be Leontina Albina (or Alvina) of San Antonio, Chile, who at 1943-81 years gave birth to 55 children. As a result of the first 5 pregnancies, she gave birth to triplets, and exclusively male.
Most birthed
The record 38 births are said to be Elizabeth Greenhillies Abbots-Langley, c. Hertfordshire, UK. She had 39 children - 32 daughters and 7 sons.
The largest number of multiple births in one family
Maddalena Pomegranate from Italy (b. 1839) had triplets born 15 times.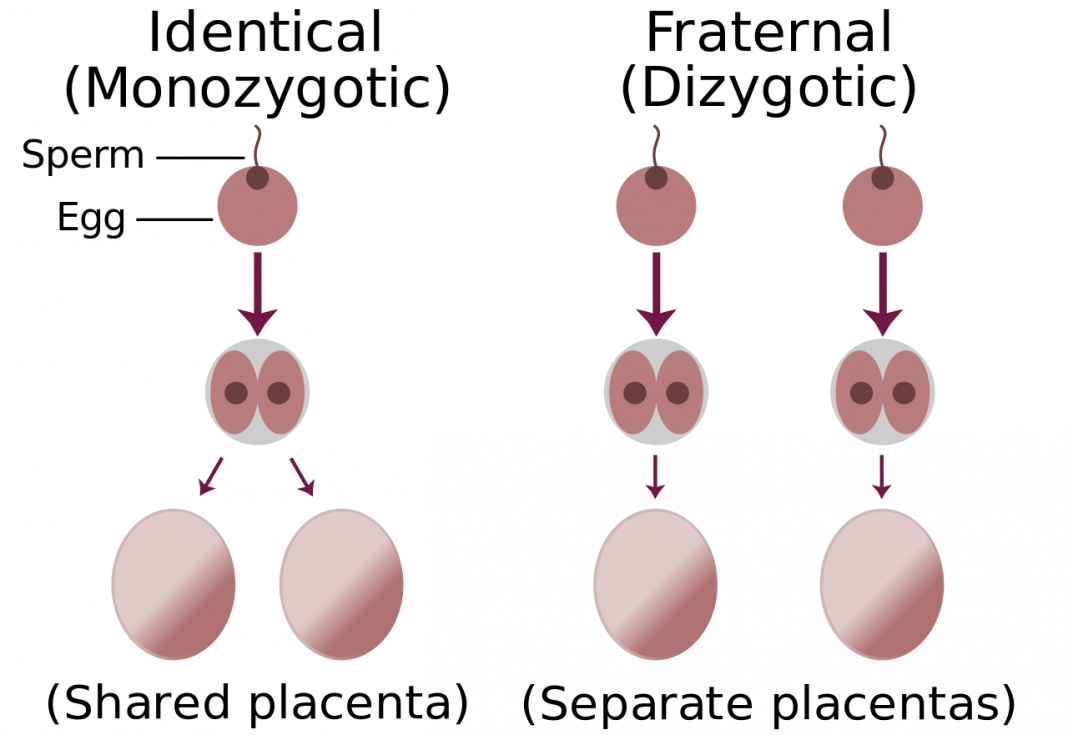
There is also information about the birth on May 29, 1971 in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, USA, and in May 1977 in Bagarhat, Bangladesh, 11 twins. In both cases, no child survived.
Most fertile pregnancies
Dr. Gennaro Montanino, Rome, Italy, claimed to have removed, in July 1971, the embryos of 10 girls and 5 boys from the uterus of a 35-year-old woman who was 4 months pregnant. This unique case of 15-fertility was the result of infertility pills.
9 children - the largest number in one pregnancy - were born on June 13, 1971 by Geraldine Broadrick in Sydney, Australia. 5 boys and 4 girls were born: 2 boys were stillborn, and none of the rest survived more than 6 days.
The birth of 10 twins (2 boys and 8 girls) is known from reports from Spain (1924), China (1936) and Brazil (April 1946).
The father with many children
The largest father in the history of Russia is Yakov Kirillov, a peasant from the village of Vvedensky, who in 1755 was presented to the court in connection with this (he was then 60 years old). The first wife of a peasant gave birth to 57 children: 4 times four, 7 times three, 9once twice and 2 times once. The second wife gave birth to 15 children. Thus, Yakov Kirillov had 72 children from two wives.
The first wife of a peasant gave birth to 57 children: 4 times four, 7 times three, 9once twice and 2 times once. The second wife gave birth to 15 children. Thus, Yakov Kirillov had 72 children from two wives.
Longest Birth Intervals for Multiple Pregnancies
Peggy Lynn of Huntington Pennsylvania, USA, gave birth to a girl, Hanna, on November 11, 1995, and the second of the twins, Erika, only 84 days later (February 2, 1996).
Siamese twins
United twins became known as "Siamese" after Chang and Eng Bunkers were born fused in the area of the sternum on May 11, 1811 in the Maeklong region of Siam (Thailand). They married Sarah and Adelaide Yates of pc. North Carolina, USA, and had 10 and 12 children, respectively. They died in 1874, and with a difference of 3 hours.
The science of twins - gemellology.
"Secret language"
Twins often talk to each other in a language that others do not understand. This phenomenon is called cryptophasia.
This phenomenon is called cryptophasia.
Left-handed twins
18-22% of left-handed twins (for non-twins this percentage is 10).
Questions about multiple pregnancy: page 2
When can I find out about multiple pregnancy by ultrasound? What is the probability of multiple pregnancy with a genetic predisposition? Twins or twins? Doctors of medical clinics "Art-Med" answer questions about multiple pregnancy.
Ask a Question
Pregnancy 7 - 8 weeks. A monochorionic monoamniotic twin was placed. But one fetus lags behind in development from the other (one - 12 mm, the other - 9 mm). The uzist doctor scared me a lot, saying that this means the death of the second fetus and the pathology of the other, or the pathology of both. It was strongly recommended to have an abortion. What do you think? Is there a chance of having a healthy baby (one or both)?
You can still wait, maybe the situation with the second embryo will improve. Repeat ultrasound in 5-7 days. If one baby dies, then with monochorionic twins, the second will die. With dichorionic this would not have happened. Read more about multiple pregnancies in the Medical Publications section.
Repeat ultrasound in 5-7 days. If one baby dies, then with monochorionic twins, the second will die. With dichorionic this would not have happened. Read more about multiple pregnancies in the Medical Publications section.
Diamnotic mono- or dichorionic pregnancy, physicians disagree on diagnosis. At a period of about 16 weeks, one fetus froze, this was found out during an ultrasound scan at 18.5 weeks. What is the probability of damage to a healthy fetus, the development of neurological damage in him and what is the risk to the mother. What investigations and measures should be taken in this case?
If you had monochorionic twins, the second baby would have already died. In this situation, there is no reason for special concern - just monitor the condition of the remaining fetus.
My father had two or three twins in his family, but my mother never had twins. My husband's family on the paternal side had twins once.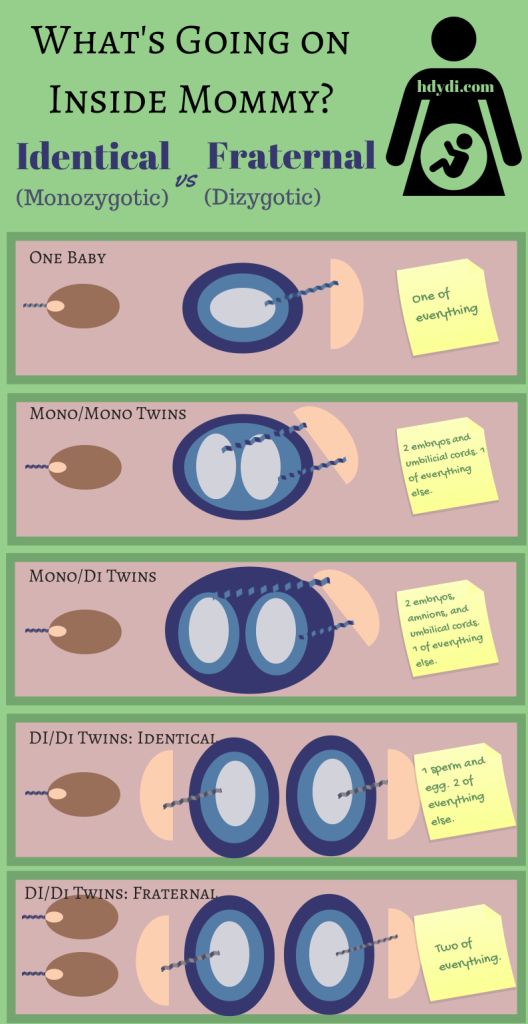 What is my chance of having multiple pregnancies?
What is my chance of having multiple pregnancies?
In your case, the probability of this event is higher than in the population, but it is impossible to calculate in numbers.
I had an ultrasound scan at 6 weeks of pregnancy, one fetus - 15 mm, and the second - 5.5 mm, hormones are lowered, now I am taking Duphaston and taking injections. Is it possible to keep the pregnancy?
Yes, there is a possibility. But not the fact that both embryos will develop.
Can identical twins be outwardly different and have different characters. After the birth, the doctor said that the children were identical twins, but already in the hospital they were not alike. Now we are six years old and they are absolutely not alike. The difference in height is a whole head, one is light, the second is swarthy, the shape of nails, ears, hair growth, everything is different, even the characters are not at all similar.
This is not typical for identical twins. Perhaps there was an error in determining the zygosity due to fused placentas. If this worries you, you can do a biological relationship test. Identical twins have exactly the same genes, while fraternal twins have differences in their genes.
Perhaps there was an error in determining the zygosity due to fused placentas. If this worries you, you can do a biological relationship test. Identical twins have exactly the same genes, while fraternal twins have differences in their genes.
I have monochorionic biamniotic twins, 12 weeks 1 day. The first fruit - 56 mm, the second - 50 mm. Will I have very young children?
At 12 weeks and 1 day, the CTE is in the range of 44 to 62 mm (53 mm on average), so that the babies on the CTE correspond to your gestational age. With monochorionic twins, the fetuses share the same placenta, so it is recommended to do an ultrasound examination more often to make sure that the fetuses develop normally.
The first pregnancy was multiple, at 13-14 weeks the fetuses died, what is the probability that the second pregnancy will be multiple (my husband and my family have twins)?
In your situation, the risk of multiple pregnancy is higher than in the general population, but it cannot be accurately calculated.
If my first pregnancy was multiple, but I had a spontaneous miscarriage at 17 weeks, can I have a second pregnancy with multiples, or is it still more likely that I will have one baby? My husband and I had twins.
If you and your spouse had twins in the family, then the probability of having a multiple pregnancy is significantly higher than in the general population, but still below 10%. With such a pregnancy, you will not necessarily have a miscarriage.
I am eight weeks away. One fertilized egg develops according to the term, and the second lags behind in development. If this continues further, is it possible to remove the non-developing and save another fetal egg.
Removal of a non-developing ovum is not required, it will not interfere with the development of the remaining baby.
I am 22 years old, third pregnancy, 16-17 weeks. Went for an ultrasound at 12 weeks.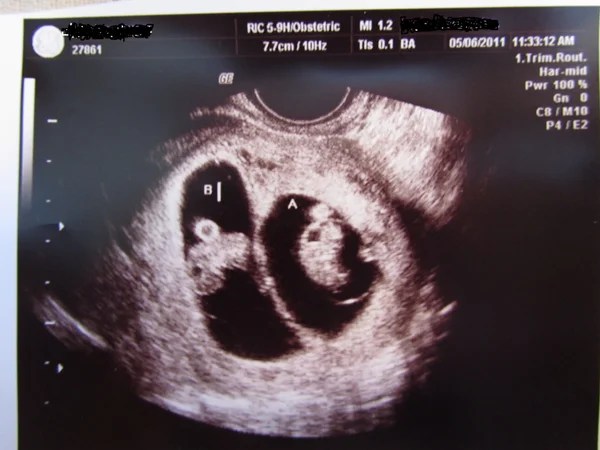 One fruit is determined, corresponds to the term. But for about a week I feel the movements of two children. Whether the error of US on such big term is possible or probable?
One fruit is determined, corresponds to the term. But for about a week I feel the movements of two children. Whether the error of US on such big term is possible or probable?
An error is unlikely. But to clarify the situation, repeat the ultrasound from an independent specialist.
I have monochorionic twins, on ultrasound (22 weeks) it was determined that I have 7 mm dilatation of the uterus. and a thick interfruit wall. Is it dangerous for my girls?
Yes, you can lose your pregnancy. In this situation, it is worth deciding on the surgical correction of CI.
I did the first ultrasound at 6 weeks, I was told that I had one fetal egg in the uterine cavity. Today I had a second ultrasound (12 weeks) I have a multiple pregnancy - 2 fetuses, can this be?
Apparently, the second ovum was not noticed the first time. To clarify the situation, repeat the ultrasound with an independent specialist.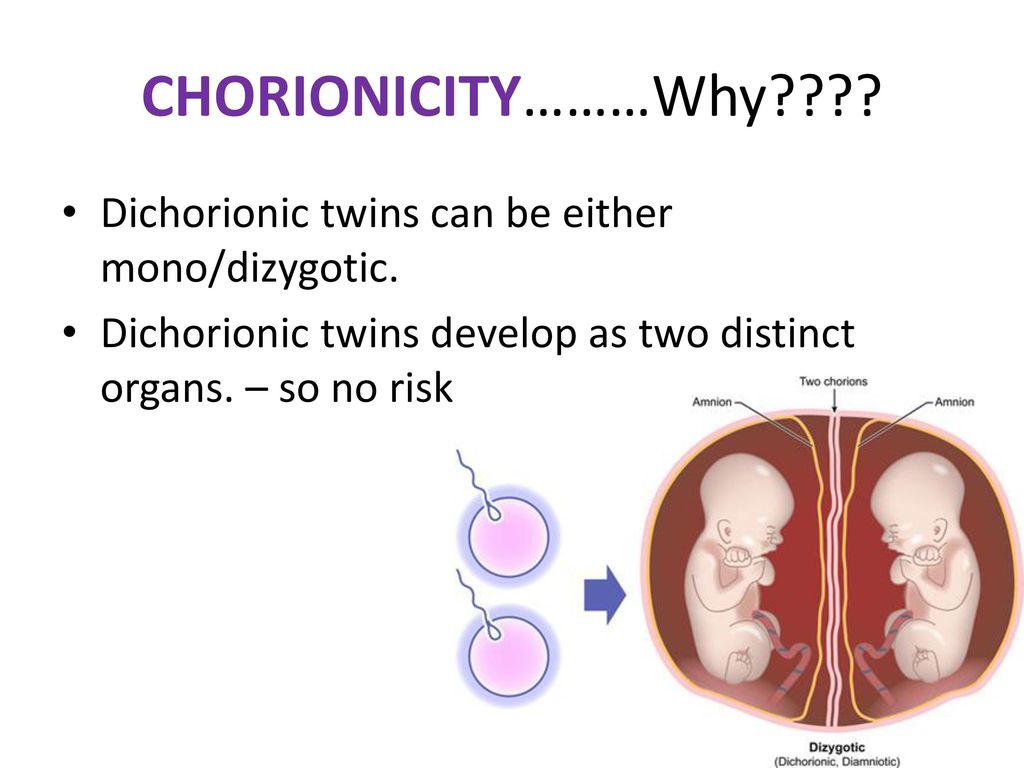
I had a dichorionic diamniotic twin questionable at a scheduled ultrasound at 12 weeks. Since there is a septum in the fetal egg, but only one fetus develops normally and is clearly visible. At the same time, the term for one fetus is set at 6-7 weeks, and the second is set for 12 weeks in accordance with the gestational age. They threatened to terminate the pregnancy. Is this situation dangerous? I was sent from the LCD to the hospital for an abortion, but in the hospital itself they advised me to wait a bit and do a second ultrasound to rule out all the questions.
Wait and repeat the ultrasound in 1-2 weeks. As a rule, with the spontaneous death of one of the fetuses, the second continues to develop normally.
Can the hCG level indicate a multiple pregnancy? I handed over hCG at 12 DPO - 299.2, at 14 DPO - 837.2. Could this mean that I have a multiple pregnancy?
Yes, it is possible. To clarify the situation, do an ultrasound of the pelvis.
Ultrasonography revealed two anechoic liquid formations 4.7x2.4x5 mm and 4.4x2.5x5.4 mm in the fundus projection. Does this mean a twin pregnancy in the short term or something else?
If there is a chorion corolla around these formations, then we are talking about a multiple pregnancy. If not, you need to decide what it looks like more: endometrial hyperplasia, internal endometriosis, emerging uterine fibroids, or something else.
I have dichorionic diamniotic twins at 22 weeks. At the last ultrasound, a single umbilical cord artery of one fetus was found, there are no malformations, the child corresponds to the term, uterine blood flow is normal. How dangerous is it?
The only umbilical artery usually does not adversely affect the development of the baby, but it is better to give birth by caesarean section.
Age 34, dichorionic twins. On ultrasound at 21-22 weeks, one fetus was diagnosed with varicose umbilical vein in the abdominal region of the fetus up to 7.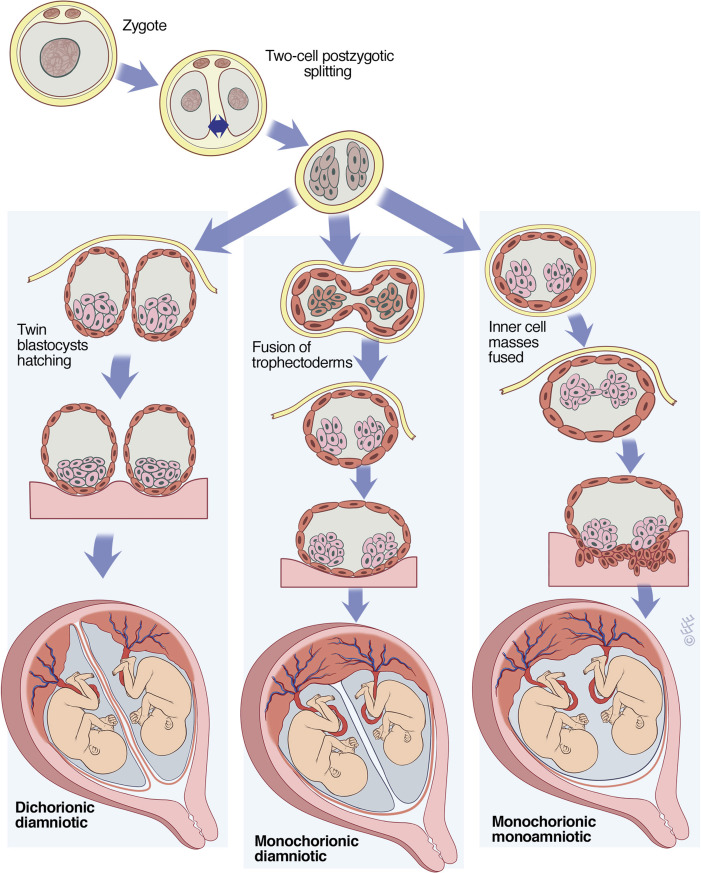 5 mm. Enlargement of the right atrium and reverse blood flow in the venous duct. How can this affect the development of the fetus and how dangerous is it? What to do in such cases?
5 mm. Enlargement of the right atrium and reverse blood flow in the venous duct. How can this affect the development of the fetus and how dangerous is it? What to do in such cases?
You need to go for a genetic consultation to decide whether these features are due to chromosomal abnormalities, heart defects, a normal variant or something else. After clarifying the situation, a decision can be made.
Have there been cases when ultrasound identified one fetus along the anterior wall, and during childbirth it turned out that there were twins and 2 fetuses along the posterior wall? Is it possible to not see the second fetus on ultrasound if it is under the first?
It is extremely difficult to make a mistake in the definition of twins, especially in the later stages.
The first ultrasound at 7 weeks showed that there were two embryos and two heartbeats in one fetal egg. On the second ultrasound at 12 weeks already one fetus.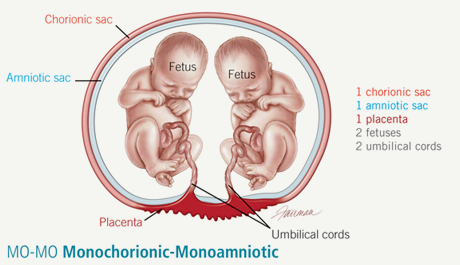 Can this be and how many children?
Can this be and how many children?
In early pregnancy, one of the twins often dies. To clarify the number of fetuses present, repeat the ultrasound from an independent specialist.
Two ultrasounds (at 7 and 9 weeks) identified one fetus, and blood tests for D-dimer and fibrinogen showed multiple pregnancies. What does it mean?
You have an activation of intravascular coagulation. Additional examination and adequate treatment are necessary.
I am 5-6 weeks pregnant. My husband has twins in every generation on his mother's side, and he himself is from twins. There were also twins in my family, passed down through generations. What is the probability of multiple pregnancy?
Higher than the population probability, but the exact percentage cannot be calculated.
Tell me, when and how can I find out that I have a multiple pregnancy?
Multiple pregnancies can be detected by ultrasound starting at 6 weeks (obstetric term).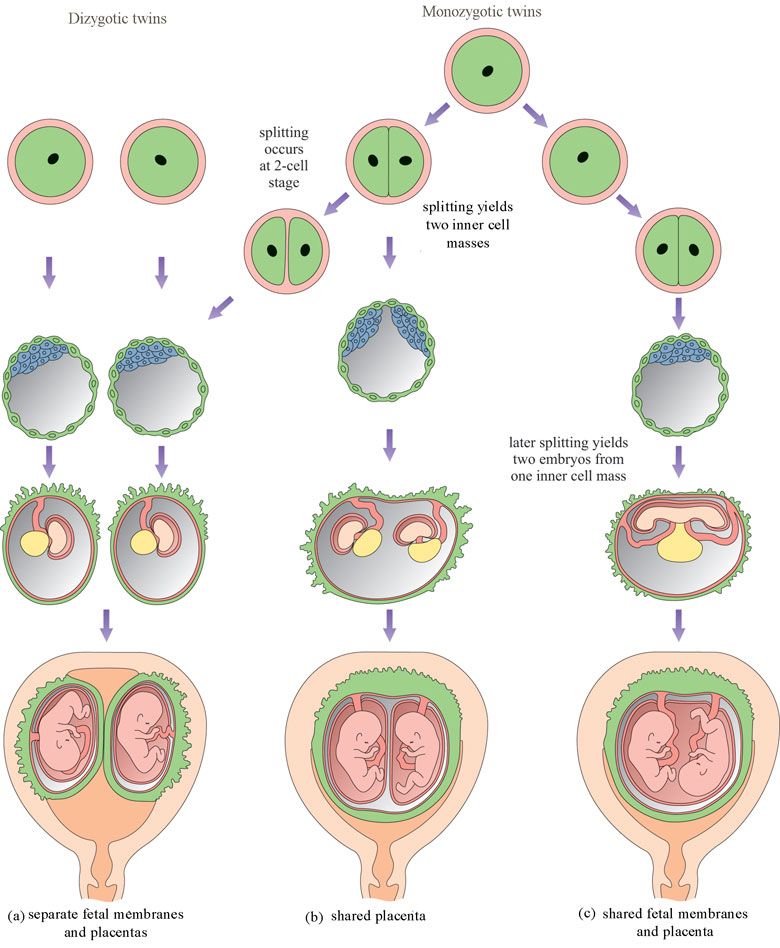
I am 29 weeks pregnant and have pain in my right hypochondrium. I went to the doctor and they told me that it was the liver and they prescribed a choleretic drug. The pain does not go away, I have twins.
It is possible that pain in the right hypochondrium is due to hypomotor dyskinesia of the gallbladder, in which case the appointment of choleretic drugs prescribed by a doctor will be useful. In addition, pain may be associated with the pressure of the pregnant uterus on the costal arch, in such a situation, choosing a position in which the pressure will be the least can help.
In monochorionic pregnancy, can children be of different sexes?
They cannot.
Can my husband and I have twins if his mother is from fraternal twins, and his father has a grandfather from twins? There were no twins on my side.
Yes, maybe the probability of such an event is slightly higher than the general population.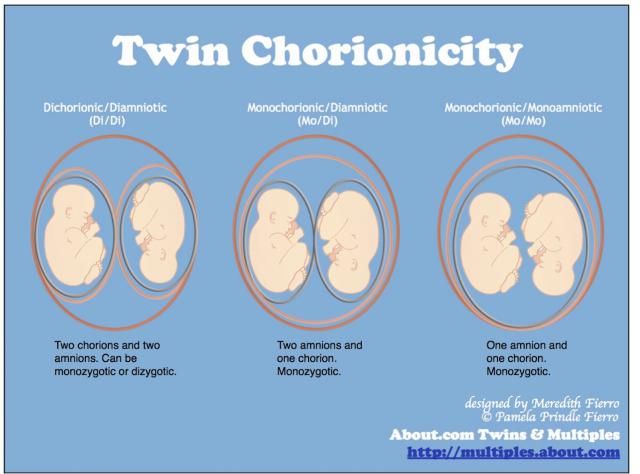
I have two boys, they don't look alike. You can't call them twins, only twins. The doctor said that all children born from multiple pregnancies are twins. Is it so?
They are indeed twins. Children are fraternal twins if they are descended from the fertilization of two different eggs by two different sperm. They can be of different sexes and differ in appearance. There are also identical twins, originating from the same egg and the same sperm, they have the same genetic composition (two identical embryos simply formed). They are always the same sex and share a common placenta.
Several twins were born in my father's family: my father is one of them himself, he has a twin sister. Also, triplets were born in his family (2 girls and a boy), and 1 more couple - a girl and a boy. What is my chance of having twins?
It can be argued that you are more likely to conceive a multiple pregnancy than in the general population.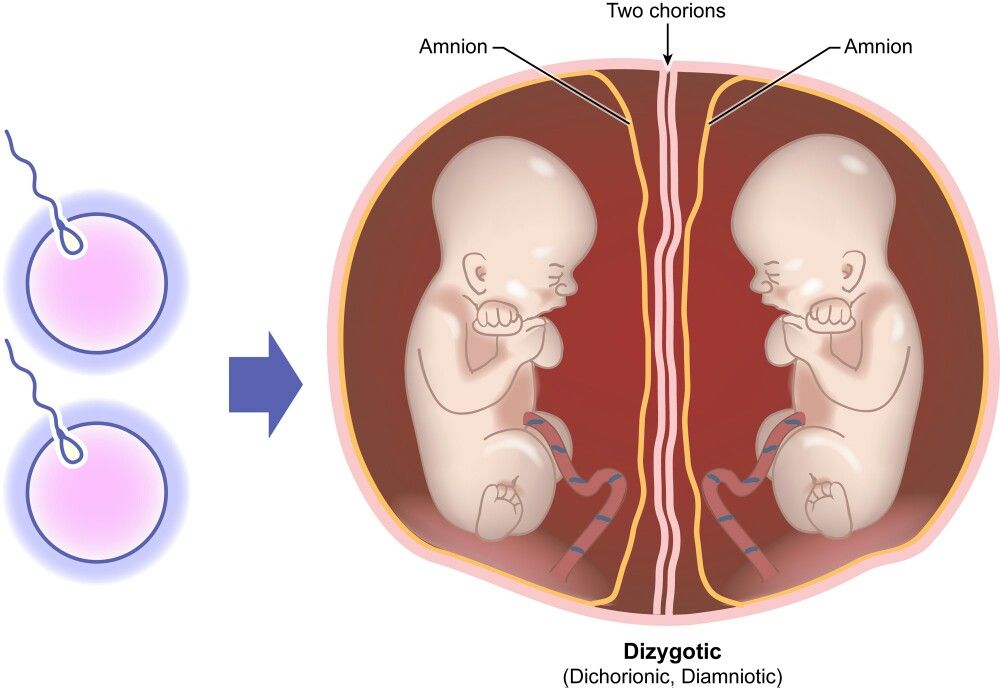 On average, among the European population, fraternal twins are born 5-6 per thousand births, among Asian peoples - 1-2 per thousand, among Africans - much more - 15-20 per thousand births. It is difficult to speak more precisely, and there is little practical sense in this. Multiple pregnancy with high certainty can be established by ultrasound from 5-7 weeks of pregnancy.
On average, among the European population, fraternal twins are born 5-6 per thousand births, among Asian peoples - 1-2 per thousand, among Africans - much more - 15-20 per thousand births. It is difficult to speak more precisely, and there is little practical sense in this. Multiple pregnancy with high certainty can be established by ultrasound from 5-7 weeks of pregnancy.
Dichorionic, diamniotic twins, intrauterine death of one of the fetuses (presumably 4-5 weeks ago). According to the results of ultrasound, the second fetus is all right. In the family, my grandmother on the mother's side had twins. What could be the reason for the death of one of the fetuses? Is there a threat to the second child? Is there an error in this case?
Self-reduction (spontaneous death) of one of the fetuses from twins - a fairly common situation in multiple pregnancies - is a manifestation of natural selection. As a rule, the further development of the second fetus is normal. An error in the diagnosis of such a condition is unlikely, but you can always get another independent opinion by doing an ultrasound in our medical center.
An error in the diagnosis of such a condition is unlikely, but you can always get another independent opinion by doing an ultrasound in our medical center.
Pregnancy 16 weeks, monochorionic monoamniotic twins. Severe pathology of one fetus on ultrasound - low intestinal obstruction, liquid formations in the abdominal cavity, echo-shadow of the bladder, liquid formation in the perineum, umbilical cord cyst. There is a single umbilical artery. The umbilical cord forms a true knot. The second fetus is absolutely normal. Passed genetics - 46 XX. There was only one hope for the ligation of the umbilical cord of the sick fetus. Do you perform such operations?
We do not perform such operations, I recommend that you contact the Center for Family Planning and Reproduction No. 1 in Moscow, Sevastopolsky Prospekt, 24-a, tel. 332-08-45.
Ultrasound results at 12 and 22 weeks: monochorionic biamniotic twins. When determining the sex: one fetus is a boy, and the second did not appear.