Cravings meaning during pregnancy
Why Pregnancy Can Make You Have Weird Cravings
Gotta have pickles and ice cream? How about a juicy bacon cheeseburger, or the world’s biggest bowl of pineapple? Not all women get to fulfill their food dreams in a jar of pickles, but interesting food cravings are common when you’re expecting. So, along with changes in your body during your pregnancy, you can also expect some changes to your appetite.
Pregnancy cravings can be caused by a number of things, including hormones, a heightened sense of smell and taste, and nutritional deficiencies. Cravings typically begin during the first trimester and peak in the second trimester, but can happen anytime during pregnancy. If you find yourself reaching for something that makes your family and friends raise their eyebrows, know you’re not alone. Let’s explore some of the most common pregnancy cravings, and how to keep eating healthy during this important time.
Pickles
These salt-and-vinegar-soaked zingers are undoubtedly one of the most common food cravings for pregnant women. If you find yourself reaching for the dill pickles in the back of your fridge, it may because you have low sodium levels. Regardless of the cause, feel free to eat up. Pickles are low in calories and are an inexpensive snack to keep on hand.
Chocolate
Feeling low or depressed? Chocolate contains a naturally occurring chemical called tryptophan, which produces serotonin in your brain. Serotonin is responsible for secreting endorphins, which helps us experience positive emotion. Simply put, chocolate makes us feel happy. However, that chocolate bar is not all sunshine and roses. Chocolate is usually high in fat and calories and isn’t the best choice when consumed in large doses. Instead of eating an entire king-sized candy bar, try tossing some chocolate chips in your yogurt, or drizzling a little melted chocolate over some fresh strawberries.
Lemons
It may seem unusual but it’s common for pregnant women to crave lemons. Some women satisfy this craving by adding lemon to their water, which is a great way to stay hydrated. Some also crave eating the fruit itself. If you crave lemons like this, be sure to moderate your intake or use a straw. The juice from fresh lemons is known to erode tooth enamel, which can cause a number of uncomfortable dental problems.
Some also crave eating the fruit itself. If you crave lemons like this, be sure to moderate your intake or use a straw. The juice from fresh lemons is known to erode tooth enamel, which can cause a number of uncomfortable dental problems.
Soda
Many women drink soda to ease morning sickness. However, because soda contains large amounts of sugar, it’s not a great choice for pregnant women, especially women dealing with gestational diabetes. A healthier alternative is mineral water mixed with fruit juice or lime.
Red Meat
Red meats like beef are rich in iron and protein. Women who are experiencing iron or protein deficiencies often crave red meats to fulfill these mineral needs. Just remember, too much red meat may increase your risk of heart disease. The key to satisfying your craving for red meat without compromising your health is to choose leaner cuts. This means avoiding the fatty rib eye, and instead opting for sirloin cuts.
Spicy Food
During your pregnancy, you may feel so hot that even standing in a freezer couldn’t satisfy your inner volcano. Try eating some curry, hot wings, or red peppers. Spicy foods will make your body sweat, which will naturally bring down your body’s temperature. Our bodies trigger this on their own through cravings, or you can use this trick on purpose when you just want to cool off. If you find yourself reaching for spicy foods, just make sure they’re baked and not fried so you’re not consuming unwanted calories.
Try eating some curry, hot wings, or red peppers. Spicy foods will make your body sweat, which will naturally bring down your body’s temperature. Our bodies trigger this on their own through cravings, or you can use this trick on purpose when you just want to cool off. If you find yourself reaching for spicy foods, just make sure they’re baked and not fried so you’re not consuming unwanted calories.
Fruit
When you’re pregnant, your body is doing the best it can to make a healthy baby. Craving fruit is perfect because satisfying the craving provides your baby with vitamins and nutrients like vitamin C. Opt for fresh fruits instead of canned fruits in heavy syrup, since the canned option usually comes with a dose of sugar. If you’re struggling with gestational diabetes, talk to your doctor about which fruits are best for you. Fruits like grapefruit and berries are lower in natural sugars, which make them a great choice.
Dairy Products
Ice cream and yogurt are go-to cravings for many pregnant women. This may be due to a calcium deficiency (or just loving ice cream). Head off these cravings with calcium supplements and calcium-rich food options like cheese and milk. If you just can’t shake your craving for ice cream, try non-fat frozen yogurt with fresh fruit instead.
This may be due to a calcium deficiency (or just loving ice cream). Head off these cravings with calcium supplements and calcium-rich food options like cheese and milk. If you just can’t shake your craving for ice cream, try non-fat frozen yogurt with fresh fruit instead.
Ice and Nonfood Substances
Okay, ice isn’t technically a “food,” but it’s a legitimate craving for many pregnant women. If you’re craving ice while you’re pregnant, it could be an indication of anemia, which is most often caused by an iron deficiency. Pregnant women with anemia crave ice because it helps relieve the inflammation of the mouth and tongue (a common symptom of anemia).
Some pregnant women are surprised to find they experience a phenomenon called Pica, which is the desire to eat nonfood substances. In these cases, you may crave things like laundry starch, crayons, or dirt. These cravings may be due to an iron or zinc deficiency and satisfying these cravings may be as simple as loading up on foods rich in these minerals.
Strange food Combinations
Weird food combinations aren’t uncommon for many pregnant women. Some women crave pickles wrapped in cheese, eggplant on pizza, and other strange food combinations they wouldn’t normally eat. As long as the food choices are healthy, go for it! The cravings will only last for a short time.
Beating Pregnancy Cravings
One of the best ways to head off pregnancy cravings is to make sure you have well-balanced meals throughout the day. Eat breakfast, get regular physical activity, and make sure you have a lot of emotional support.
When cravings hit you hard, distract yourself. Go for a walk, play a game, visit a friend. If that’s just not working, you can help satisfy cravings by paying attention to what your body is telling you, and finding an alternative.
If you still find yourself hankering for ice cream, have a little. Moderation is the key to a healthy diet during pregnancy. However, it’s best to consult your healthcare provider if you’re having cravings for things like starch, dirt, or Play-Doh. Having cravings for these non-food items could be a sign of a nutrient deficiency.
Having cravings for these non-food items could be a sign of a nutrient deficiency.
Pregnancy is a wonderful experience. Embrace the changes in your appetite, but make sure your cravings don’t compromise your or your baby’s health.
Food cravings during pregnancy | Pregnancy Birth and Baby
Food cravings during pregnancy | Pregnancy Birth and Baby beginning of content4-minute read
Listen
What are food cravings?
Food cravings are sudden urges to eat a certain type of food or non-food (pica). They are a real experience and affect many females during pregnancy.
Sometimes you might crave common foods such as chocolate cake or apples. Sometimes you might want to eat unusual food combinations or a foods that you normally don’t like.
Common food cravings include ice cream, chocolate, other sweet foods, fish, dairy products, and fruit.
Why do cravings develop?
No one really knows why food cravings develop. However, there is no evidence of a link between cravings and nutrient deficiency.
Many pregnant women also develop a sudden dislike for certain strong-tasting and strong-smelling foods.
Food cravings and sudden food dislikes may have something to with the effects of pregnancy hormones, which can change the way some foods taste and smell.
What to do about food cravings
It is OK to give in to the occasional food craving, as long as you continue to eat a good variety of healthy foods.
If you are craving a lot of unhealthy foods, such as sweets or chocolate, try not to over-indulge. Too much sugar can cause excessive weight gain and dental problems. Also, if you have gestational diabetes, it won’t help you manage your condition.
Your doctor, midwife, dietitian or maternal and child health nurse can provide more information about healthy weight gain during pregnancy. Generally, a healthy weight gain during pregnancy is 5kg to 12kg, depending on your starting weight.
Some tips for managing cravings
The following suggestions will help you to manage your food cravings:
- eat regular, healthy meals, to help prevent sudden feelings of hunger
- keep your pantry stocked with healthy snacks
- don’t do the grocery shopping when you are hungry
- choose healthy, low glycaemic index (GI) foods that keep you full for longer (such as unsweetened rolled oats (porridge), wholegrain breads, baked beans, and fresh fruit)
- get plenty of sleep (research has shown that people who are sleep deprived tend to crave junk food more often than healthy foods)
- remain physically active
- drink plenty of water
- clean your teeth regularly
If you would like to learn more about nutritional needs during your pregnancy you can see a dietitian.
What foods should I avoid?
When you are pregnant, there are a few foods that you should avoid.
Things like:
- raw or unpasteurised dairy products
- soft cheeses e.
 g. brie, goats cheese
g. brie, goats cheese - sushi
- raw eggs
- pate, meat spreads and smoked seafood
- ready to eat sliced deli meats
- undercooked food – especially meat
These can contain harmful bacteria, including salmonella and E. coli. and lead to harmful illnesses such as listeria or toxoplasmosis.
Make sure you prepare and store foods safely.
Read more about the foods to avoid during your pregnancy.
Alcohol
There is no safe level of alcohol that you can drink during your pregnancy. Alcohol can harm your unborn baby.
Whether you are planning a pregnancy, already pregnant or breastfeeding, not drinking is the safest option.
Non-food cravings
Some pregnant women develop a craving to eat substances that are not food, such as chalk, clay, laundry starch or soap. This is a condition called pica.
Pica may indicate a mineral deficiency or severe anaemia. Pica is rare in well-nourished women from developed countries such as Australia.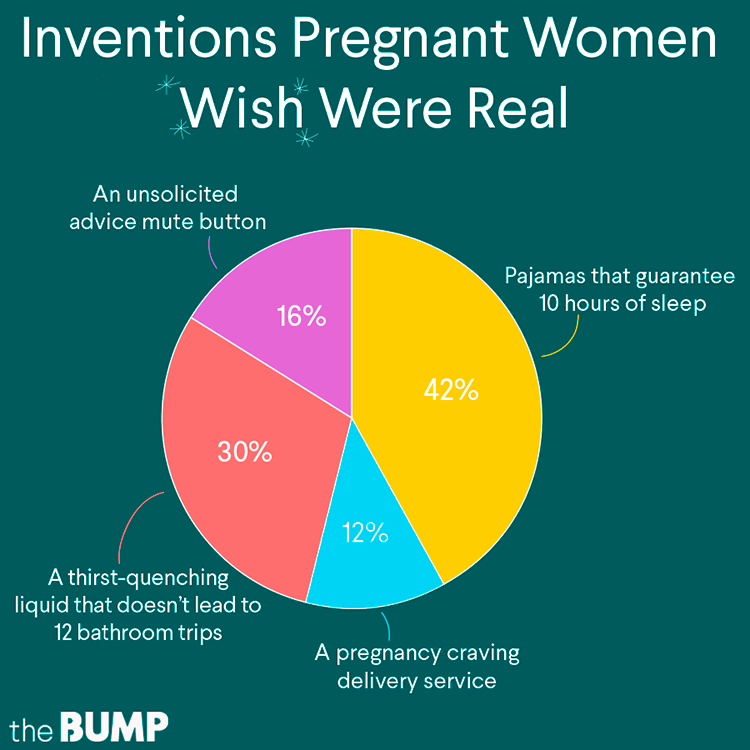
See your doctor, midwife, or nurse if you develop cravings for non-food items.
Speak to a maternal child health nurse
Call Pregnancy, Birth and Baby to speak to a maternal child health nurse on 1800 882 436 or video call. Available 7am to midnight (AET), 7 days a week.
Sources:
NSW Health (Common concerns in pregnancy), Australian Government Department of Health (Your Healthy Pregnancy), Dietitians Australia (Pregnancy and breastfeeding), Australian Government Department of Health (Healthy eating during your pregnancy)Learn more here about the development and quality assurance of healthdirect content.
Last reviewed: June 2022
Back To Top
Related pages
- Healthy diet during pregnancy
- Foods to avoid when pregnant
- Alcohol and pregnancy
- Food preparation and safety
- Guide to food and drink during pregnancy
Need more information?
Healthy diet during pregnancy
A healthy diet is an important part of a healthy lifestyle at any time, but especially vital if you're pregnant or planning a pregnancy.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Pregnancy health & wellbeing | Raising Children Network
Pregnant? Here’s all you need to stay healthy during pregnancy, including tips for healthy diet and lifestyle and a guide to pregnancy health care.
Read more on raisingchildren.net.au website
Having a healthy pregnancy
Having a healthy pregnancy means following a healthy diet, getting regular exercise, knowing what to avoid and making sure your vaccinations are up to date. Find out more here.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Pregnancy and Healthy Eating
It’s especially important to eat healthy food during pregnancy and while breast feeding.
Read more on Healthy Eating Active Living NSW website
Pregnancy healthy eating in pictures | Raising Children Network
Healthy eating for pregnancy means lots of fruit, vegetables and foods with calcium, protein and iron. Avoid sugary, fatty foods, and drink plenty of water.
Read more on raisingchildren.net.au website
Pregnancy: illustrated guides | Raising Children Network
Parenting in pictures provides step-by-step guides to pregnancy topics such as healthy eating, pelvic floor exercises and more.
Read more on raisingchildren.net.au website
Appetite changes and food aversions during pregnancy
It’s common to experience food cravings or a food aversion during pregnancy. Find out how to ensure you continue to eat healthily if this affects you.
Find out how to ensure you continue to eat healthily if this affects you.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Healthy eating when you’re pregnant or breastfeeding | Eat For Health
Eating well during pregnancy and while breastfeeding has health benefits for you and your baby.
Read more on NHMRC – National Health and Medical Research Council website
Gi and Pregnancy | GI Foundation
Home / Gi Health Benefits / Gi and Pregnancy Gi and Pregnancy Following a healthy low Gi diet during pregnancy helps protect your child’s future health and improves health and wellbeing for lifelong benefits
Read more on Glycemic Index Foundation website
Pregnancy and diet - Better Health Channel
Good nutrition during pregnancy can help to keep you and your developing baby healthy.
Read more on Better Health Channel website
Disclaimer
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is not responsible for the content and advertising on the external website you are now entering.
OKNeed further advice or guidance from our maternal child health nurses?
1800 882 436
Video call
- Contact us
- About us
- A-Z topics
- Symptom Checker
- Service Finder
- Linking to us
- Information partners
- Terms of use
- Privacy
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is funded by the Australian Government and operated by Healthdirect Australia.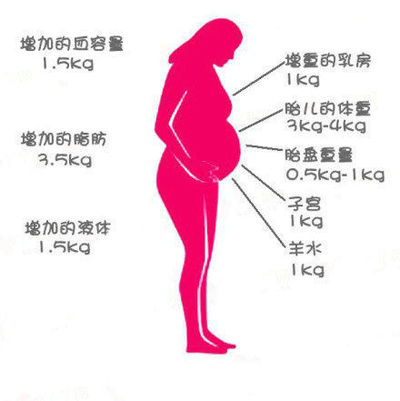
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is provided on behalf of the Department of Health
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby’s information and advice are developed and managed within a rigorous clinical governance framework. This website is certified by the Health On The Net (HON) foundation, the standard for trustworthy health information.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
This information is for your general information and use only and is not intended to be used as medical advice and should not be used to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any medical condition, nor should it be used for therapeutic purposes.
The information is not a substitute for independent professional advice and should not be used as an alternative to professional health care. If you have a particular medical problem, please consult a healthcare professional.
Except as permitted under the Copyright Act 1968, this publication or any part of it may not be reproduced, altered, adapted, stored and/or distributed in any form or by any means without the prior written permission of Healthdirect Australia.
Support this browser is being discontinued for Pregnancy, Birth and Baby
Support for this browser is being discontinued for this site
- Internet Explorer 11 and lower
We currently support Microsoft Edge, Chrome, Firefox and Safari. For more information, please visit the links below:
- Chrome by Google
- Firefox by Mozilla
- Microsoft Edge
- Safari by Apple
You are welcome to continue browsing this site with this browser. Some features, tools or interaction may not work correctly.
Cravings during pregnancy: myth or fact?
Almost everyone believes that this is a common occurrence associated with pregnancy cravings.
There are many myths about pregnancy. Among them, traction is often discussed. Let's find out more about them and find out if they are a myth or a reality.
Cravings are defined as a strong appetite and are hardly worthless for some nutrition. Cravings can be sweet, refreshing, unusual, or aberrant in a normal diet. Women are in constant hormonal change , which may be indicative but has no scientific basis. There may be psychological reasons, anxiety …, Or wishes for attention and body care.
Cravings can be sweet, refreshing, unusual, or aberrant in a normal diet. Women are in constant hormonal change , which may be indicative but has no scientific basis. There may be psychological reasons, anxiety …, Or wishes for attention and body care.
Almost everyone thinks that pregnant women have food cravings, from mouth-watering strawberries and cream to the wildest pairings , like pickles and chocolate. The figure of the father always appears, the one who, at odd hours, gives his beloved the opportunity to enjoy a moment of gastronomic pleasure.
Index
- 1 History of cravings
- 2 More frequent cravings
- 3 Features of cravings
- 3.1 Truth of cravings
- 4 Relationship between desire and weight gain
- 4 Relationship between desire and weight gain 900 900
History of cravings
Some pregnant women crave certain foods, which can happen to other people at any point in their lives and without further complications. What is convenient is to be moderate in this regard, i.e. one should not give free rein to desires and eat uncontrollably whatever you want. In health, especially for the expectant mother in the first place.
What is convenient is to be moderate in this regard, i.e. one should not give free rein to desires and eat uncontrollably whatever you want. In health, especially for the expectant mother in the first place.
Around the 1960s and 70s, something affected the proper nutrition of pregnant women, which negatively affected the development of children. Years later The idea that pregnant women should overeat was still there to prevent it from happening again.
Today, pregnant women are fully supervised, they are even advised to gain weight and informed about the list of the most harmful foods for 9months. At this time, it may happen that during pregnancy the so-called "hunger hormone" is increased. This contributes to the regulation of energy metabolism.
More frequent cravings
The sweet taste of chocolate or pastry transcends the taste aspect and reaches the pregnant woman's brain for pleasure.
El the sweet taste surpasses the taste aspect and reaches the brain of a pregnant woman, giving pleasure That's why chocolate or pastries are so popular among pregnant women, and not only for them. Some examples :
Some examples :
- Ice : When taken, heat is better tolerated and they provide sugar. Cold helps with annoying nausea.
- Chocolates and chocolates : Enjoyment is guaranteed with them. This is a good antioxidant.
- Pretzels . They help to better cope with nausea.
- Pickles : Pregnant woman can choose any canned food. A strong aroma can cause appetite. It's the same with spicy food. They should be used with caution because they can cause stomach discomfort.
- Fruit, especially sour as in the case of strawberries. They contain a lot of vitamin C, and it is this level that decreases during pregnancy. He also provides the mother with sugar.
- Cheese and dairy products : It probably tastes so good that pregnant women need calcium. However, during pregnancy, you need to be very careful with cheeses and unpasteurized milk.
 They should be consumed in moderation. Yoghurts are healthy, fast and appetizing food.
They should be consumed in moderation. Yoghurts are healthy, fast and appetizing food.
Features of cravings
- There is such a thing as "Pica", in which pregnant women feel the desire to eat substances that are not food. eg dirt, chalk or stones. It has not been proven to have anything to do with the state of pregnancy.
- The traditional saying guarantees that the sex of the unborn child if she is a girl, this is due to the consumption of sweets such as cakes or chocolate. If I were a child, cravings would be more salty and spicy, like chili peppers, tabasco, pipe... Obviously, a person's gender does not depend on food.
- Legends say that this unusual appetite causes child and if it is not satisfied, the child may develop spots of the shape or color of inedible food.
- Another idea is that in order to be considered a craving, you must desire junk food .

True cravings
- Baby no will suffer the consequences of as a result of not eating the desired food.
- La the body's need for nutrients, minerals or Vitamins , weakness ..., can make you crave special foods rich in them.
- Longing desire may be healthy .
- Pregnant women should not indulge in appetite and self-control. They must not eat for two .
Relationship between desire and weight gain
They say that in order to be considered a craving, you have to crave junk food.
A pregnant woman should take care of herself, follow a meal plan and eat the healthiest food possible. Gaining many kilograms is not optimal for either the mother or the child. , especially next day delivery. Ideally, gain about 10-12 kilograms, but medical control and the fact that it is he or she is important. The matron are those who guide the mother and help her in this process.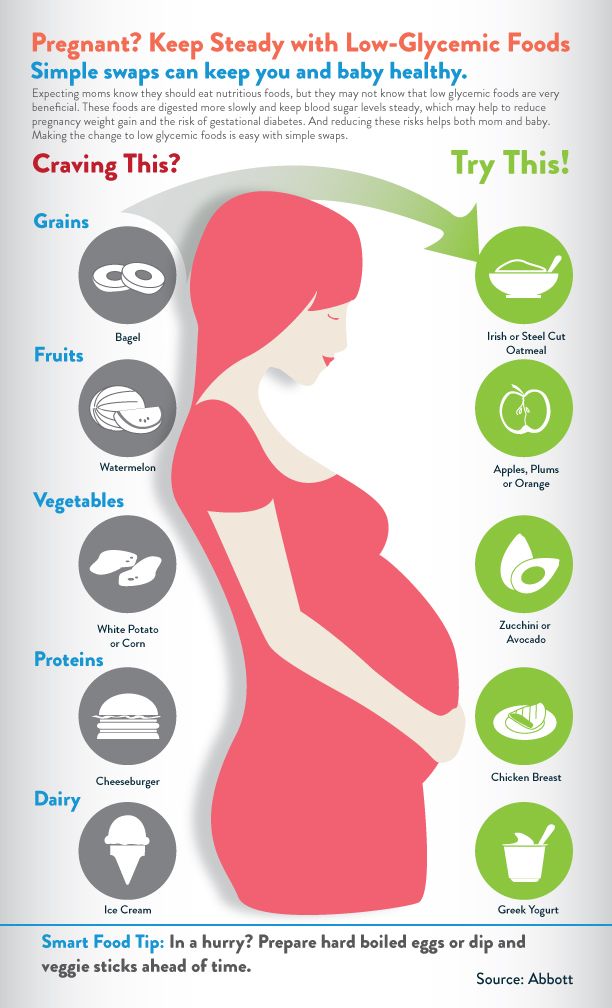
It is important to differentiate the age and starting weight from one pregnant woman to another, weigh whether she is doing sports normally, whether she leads an active lifestyle, whether she suffers from any disease, such as diabetes, obesity, and in this case, take the weight should be less than ... Cannot use the same scale for all . Even before pregnancy, a woman is advised, if she has not already done so, to start exercising and try to live as healthy a lifestyle as possible.
Drink plenty of water, eat plenty of fruits, vegetables, meat and fish. ... And avoid as many complex carbohydrates as possible, you need to eat rice or bread. Everything you need to fully nourish the table and meet the needs of mother and child. Weight is gained not only from eating, but also from the placenta amniotic fluid, baby, breast augmentation… everything will eventually make up the final weight, and on the day of delivery, some of this weight will disappear, and another in the following days, weeks or months.
How to deal with cravings?
In case of food cravings, it is best to make a meal plan and choose between foods with a higher nutritional content . You need to choose foods rich in proteins, vitamins ... and eradicate "junk food" that does not do anything good. It is extremely important that pregnant women eat 5 meals a day (and that breakfast is the best meal of the day) so that their meals are not superfluous.
It is important and necessary to exercise daily, drink plenty of water, if possible 2 liters a day, try to lead a quiet life and seek support from family and close friends. Some simple and healthy cravings options are:
- Yogurt creamy.
- Black chocolate , some daily portion. Lower sugar content.
- Unsalted nuts . They promote fluid retention.
- White bread and pastries - by user whole grain flour and cereals .
 Promotes intestinal transit.
Promotes intestinal transit.
The content of the article complies with our principles of editorial ethics. To report a bug, click here.
You may be interested in
Physiological changes in the body during pregnancy
From the very first days of pregnancy, a woman's body undergoes profound transformations. These transformations are the result of the coordinated work of almost all body systems, as well as the result of the interaction of the mother's body with the child's body. During pregnancy, many internal organs undergo significant restructuring. These changes are adaptive in nature, and, in most cases, are short-lived and completely disappear after childbirth. Consider the changes in the basic systems of the vital activity of a woman's body during pregnancy.
The respiratory system during pregnancy works hard. The respiratory rate increases. This is due to an increase in the need of the mother and fetus for oxygen, as well as in the limitation of the respiratory movements of the diaphragm due to an increase in the size of the uterus, which occupies a significant space of the abdominal cavity.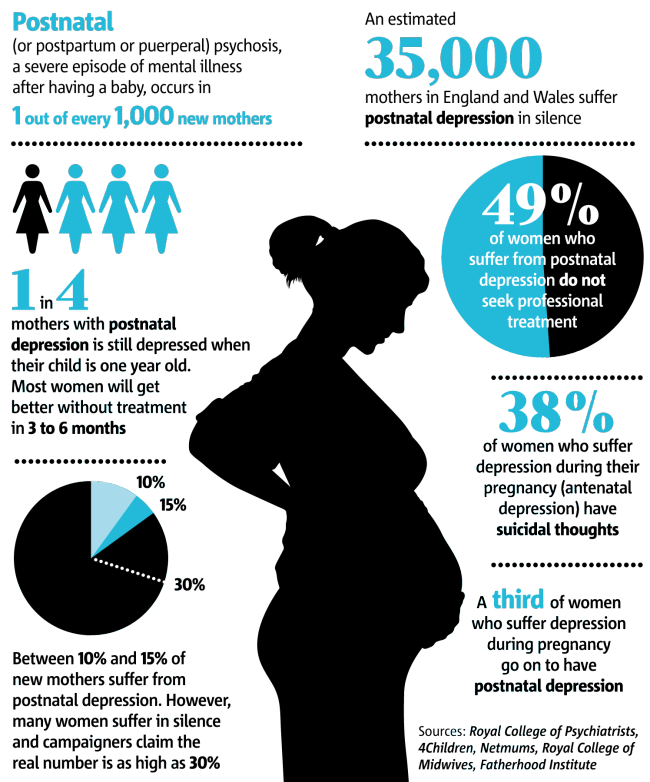
The mother's cardiovascular system during pregnancy has to pump more blood to ensure an adequate supply of nutrients and oxygen to the fetus. In this regard, during pregnancy, the thickness and strength of the heart muscles increase, the pulse and the amount of blood pumped by the heart in one minute increase. In addition, the volume of circulating blood increases. In some cases, blood pressure increases. The tone of blood vessels during pregnancy decreases, which creates favorable conditions for increased supply of tissues with nutrients and oxygen. During pregnancy, the network of vessels of the uterus, vagina, and mammary glands decreases sharply. On the external genitalia, in the vagina, lower extremities, there is often an expansion of the veins, sometimes the formation of varicose veins. Heart rate decreases in the second half of pregnancy. It is generally accepted that the rise in blood pressure over 120-130 and a decrease to 100 mm Hg. signal the occurrence of pregnancy complications. But it is important to have data on the initial level of blood pressure.
But it is important to have data on the initial level of blood pressure.
and changes in the blood system. During pregnancy, blood formation increases, the number of red blood cells, hemoglobin, plasma and bcc increases. BCC by the end of pregnancy increases by 30-40%, and erythrocytes by 15-20%. Many healthy pregnant women have a slight leukocytosis. ESR during pregnancy increases to 30-40. Changes occur in the coagulation system that contribute to hemostasis and prevent significant blood loss during childbirth or placental abruption and in the early postpartum period.
Kidneys work hard during pregnancy. They secrete decay products of substances from the body of the mother and fetus (the waste products of the fetus pass through the placenta into the mother's blood).
Changes in the digestive system are represented by increased appetite (in most cases), cravings for salty and sour foods. In some cases, there is an aversion to certain foods or dishes that were well tolerated before the onset of pregnancy. Due to the increased tone of the vagus nerve, constipation may occur.
Due to the increased tone of the vagus nerve, constipation may occur.
The most significant changes, however, occur in the genitals of pregnant women. These changes prepare the woman's reproductive system for childbirth and breastfeeding.
The uterus of a pregnant woman increases significantly in size. Its mass increases from 50 g - at the beginning of pregnancy to 1200 g - at the end of pregnancy. The volume of the uterine cavity by the end of pregnancy increases by more than 500 times! The blood supply to the uterus is greatly increased. In the walls of the uterus, the number of muscle fibers increases. The cervix is filled with thick mucus that clogs the cavity of the cervical canal. The fallopian tubes and ovaries also increase in size. In one of the ovaries, there is a "corpus luteum of pregnancy" - a place for the synthesis of hormones that support pregnancy. Walls vaginas will loosen and become more elastic. External genitalia (labia minor and major), also increase in size and become more elastic. The tissues of the perineum are loosened. In addition, there is an increase in mobility in the joints of the pelvis and a divergence of the pubic bones. The changes in the genital tract described above are of extremely important physiological significance for childbirth. Loosening the walls, increasing the mobility and elasticity of the genital tract increases their throughput and facilitates the movement of the fetus through them during childbirth.
External genitalia (labia minor and major), also increase in size and become more elastic. The tissues of the perineum are loosened. In addition, there is an increase in mobility in the joints of the pelvis and a divergence of the pubic bones. The changes in the genital tract described above are of extremely important physiological significance for childbirth. Loosening the walls, increasing the mobility and elasticity of the genital tract increases their throughput and facilitates the movement of the fetus through them during childbirth.
Skin in the genital area and in the midline of the abdomen usually becomes darker in color. Sometimes "stretch marks" form on the skin of the lateral parts of the abdomen, which turn into whitish stripes after childbirth.
Mammary glands increase in size, become more elastic, tense. When pressing on the nipple, colostrum (first milk) is released.
Changes in the bone skeleton and muscular system . An increase in the concentration of the hormones relaxin and progesterone in the blood contributes to the leaching of calcium from the skeletal system. This helps to reduce the rigidity of the joints between the bones of the pelvis and increase the elasticity of the pelvic ring. Increasing the elasticity of the pelvis is of great importance in increasing the diameter of the internal bone ring in the first stage of labor and further reducing the resistance of the birth tract to fetal movement in the second stage of labor. Also, calcium, washed out of the mother's skeletal system, is used to build the skeleton of the fetus.
An increase in the concentration of the hormones relaxin and progesterone in the blood contributes to the leaching of calcium from the skeletal system. This helps to reduce the rigidity of the joints between the bones of the pelvis and increase the elasticity of the pelvic ring. Increasing the elasticity of the pelvis is of great importance in increasing the diameter of the internal bone ring in the first stage of labor and further reducing the resistance of the birth tract to fetal movement in the second stage of labor. Also, calcium, washed out of the mother's skeletal system, is used to build the skeleton of the fetus.
It should be noted that calcium compounds are washed out of all bones of the maternal skeleton (including the bones of the foot and spine). As shown earlier, a woman's weight increases during pregnancy by 10 -12 kg. This additional load against the background of a decrease in bone stiffness can cause foot deformity and the development of flat feet. A shift in the center of gravity of the body of a pregnant woman due to an increase in the weight of the uterus can lead to a change in the curvature of the spine and the appearance of pain in the back and pelvic bones. Therefore, for the prevention of flat feet, pregnant women are advised to wear comfortable shoes with low heels. It is advisable to use insoles that support the arch of the foot. For the prevention of back pain, special physical exercises are recommended that can unload the spine and sacrum, as well as wearing a comfortable bandage. Despite an increase in calcium loss by the bones of the skeleton of a pregnant woman and an increase in their elasticity, structure and bone density (as is the case with osteoporosis in older women).
Therefore, for the prevention of flat feet, pregnant women are advised to wear comfortable shoes with low heels. It is advisable to use insoles that support the arch of the foot. For the prevention of back pain, special physical exercises are recommended that can unload the spine and sacrum, as well as wearing a comfortable bandage. Despite an increase in calcium loss by the bones of the skeleton of a pregnant woman and an increase in their elasticity, structure and bone density (as is the case with osteoporosis in older women).
Changes in the nervous system . In the first months of pregnancy and at the end of it, there is a decrease in the excitability of the cerebral cortex, which reaches its greatest degree by the time of the onset of childbirth. By the same period, the excitability of the receptors of the pregnant uterus increases. At the beginning of pregnancy, there is an increase in the tone of the vagus nerve, in connection with which various phenomena often occur: changes in taste and smell, nausea, increased salivation, etc.