How fast do you gain weight when pregnant
Weight Gain During Pregnancy: How Much Is Normal?
Written by WebMD Editorial Contributors
In this Article
- Where Does the Extra Weight Go During Pregnancy?
- Is It Safe to Lose Weight When Pregnant?
- How to Gain the Right Amount of Weight During Pregnancy
- What if You Gain Too Much Weight During Pregnancy?
- When to Call Your Doctor
Eating a healthy, balanced diet will help your baby get the nutrients they need and grow at a healthy rate. But how many extra calories do you really need?
Though you do need some extra calories, it's not necessary to ''eat for two.'' The average pregnant woman needs only about 300 healthycalories more a day than they did before they were pregnant. This will help them gain the right amount of weight during pregnancy.
Ask your health care provider how much weight you should gain. A woman who was average weight before getting pregnant should gain 25 to 35 pounds after becoming pregnant. Underweight women should gain 28 to 40 pounds. And overweight women may need to gain only 15 to 25 pounds during pregnancy.
In general, you should gain about 2 to 4 pounds during the first 3 months you're pregnant and 1 pound a week during the rest of your pregnancy. If you are expecting twins you should gain 35 to 45 pounds during your pregnancy. This would be an average of 1 ½ pounds per week after the usual weight gain in the first 3 months.
It's especially important to gain the right amount of weight when you're expecting twins because your weight affects the babies' weight. And because twins are often born before the due date, a higher birth weight is important for their health. When carrying twins, you may need between 3,000 and 3,500 calories a day.
Where Does the Extra Weight Go During Pregnancy?
- Baby: 8 pounds
- Placenta: 2-3 pounds
- Amniotic fluid: 2-3 pounds
- Breast tissue: 2-3 pounds
- Blood supply: 4 pounds
- Stored fat for delivery and breastfeeding: 5-9 pounds
- Larger uterus: 2-5 pounds
- Total: 25-35 pounds
Is It Safe to Lose Weight When Pregnant?
If a woman is very overweight when they get pregnant, their doctor may want them to lose weight. They should only lose weight under their doctor's care. But in most cases, women should not try to lose weight or diet during pregnancy.
They should only lose weight under their doctor's care. But in most cases, women should not try to lose weight or diet during pregnancy.
How to Gain the Right Amount of Weight During Pregnancy
If your health care provider wants you to gain weight while you're pregnant, try these tips:
- Eat five to six small meals every day.
- Keep quick, easy snacks on hand, such as nuts, raisins, cheese and crackers, dried fruit, and ice cream or yogurt.
- Spread peanut butter on toast, crackers, apples, bananas, or celery. One tablespoon of creamy peanut butter gives you about 100 calories and 7 grams of protein.
- Add nonfat powdered milk to mashed potatoes, scrambled eggs, and hot cereal.
- Add extras to your meal, such as butter or margarine, cream cheese, gravy, sour cream, and cheese.
What if You Gain Too Much Weight During Pregnancy?
If you have gained more weight than your doctor recommended, talk to your doctor about it. In most cases, you'll want to wait until after delivery to lose weight.
Here are some tips to slow your weight gain:
- When eating fast food, choose lower-fat items such as broiled chicken breast sandwich with tomato and lettuce (no sauce or mayonnaise), side salad with low-fat dressing, plain bagels, or a plain baked potato. Avoid foods such as French fries, mozzarella sticks, or breaded chicken patties.
- Avoid whole milk products. You need at least four servings of milk products every day. However, using skim, 1%, or 2% milk will greatly reduce the amount of calories and fat you eat. Also, choose low-fat or fat-free cheese or yogurt.
- Limit sweet or sugary drinks. Sweetened drinks such as soft drinks, fruit punch, fruit drinks, iced tea, lemonade, or powdered drink mixes have lots of empty calories. Choose water, club soda, or mineral water to skip extra calories.
- Don't add salt to foods when cooking. Salt causes you to retain water.
- Limit sweets and high-calorie snacks. Cookies, candies, donuts, cakes, syrup, honey, and potato chips have a lot of calories and little nutrition.
 Try not to eat these foods every day. Instead, try fresh fruit, low-fat yogurt, angel food cake with strawberries, or pretzels as lower-calorie snack and dessert choices.
Try not to eat these foods every day. Instead, try fresh fruit, low-fat yogurt, angel food cake with strawberries, or pretzels as lower-calorie snack and dessert choices. - Use fats in moderation. Fats include cooking oils, margarine, butter, gravy, sauces, mayonnaise, regular salad dressings, sauces, lard, sour cream, and cream cheese. Try lower-fat alternatives.
- Cook food the healthy way. Frying foods in oil or butter will add calories and fat. Baking, broiling, grilling, and boiling are healthier preparation methods.
- Exercise. Moderate exercise can help burn excess calories. Walking or swimming is usually safe for pregnant women. Ask your health care provider what exercise would be right for you before getting started.
When to Call Your Doctor
Talk to your doctor if you:
- Want to know a good target weight gain for you
- Think you are gaining too much weight
- Are losing weight during the second or third trimester
- Have an eating disorder that is keeping you from eating a healthy amount of food
- Need help setting a good menu plan to gain a healthy amount of weight
- Gain weight rapidly.
 This could be a sign of preeclampsia, pregnancy-related high blood pressure, a serious health issue
This could be a sign of preeclampsia, pregnancy-related high blood pressure, a serious health issue
Health & Pregnancy Guide
- Getting Pregnant
- First Trimester
- Second Trimester
- Third Trimester
- Labor and Delivery
- Pregnancy Complications
- All Guide Topics
How much weight should I gain while pregnant?
Weight gain is essential for a healthy pregnancy
Learning to eat well and manage your weight gain are key components to a healthy pregnancy. Weight gain helps your baby to grow and develop properly, and allows your body to make physical changes to support pregnancy, such as growth of your uterus, development of the placenta and an increase in blood volume. But how much weight is the right amount to gain? When determining a weight-gain range, some important things to consider are: your pre-pregnancy weight for height, commonly referred to as your Body Mass Index (BMI), your medical history, and whether you're carrying one baby, twins or multiples.
How much weight should I gain?
There is no set amount of weight gain that is right for everyone. Yet over time, some general guidelines have been accepted. For women carrying one baby, the first trimester is typically considered a time of minimal weight gain, regardless of your pre-pregnancy BMI. As you near the end of your first trimester, and begin the second, weight gain is expected to increase. Some providers like to see women with a "healthy" BMI prior to pregnancy, gain 10 pounds by 20 weeks. During the second and third trimester, guidelines often suggest gaining 1/2 to 1 pound per week. Whatever weight-gain range is determined to be right for you, try to gain the weight gradually. Below are some generally accepted total weight-gain guidelines based on pre-pregnancy BMI.
BMI below 19 prior to pregnancy
Of all categories, underweight women are at highest risk for delivering low birth-weight babies. If you were underweight before becoming pregnant, it's especially important to gain an adequate amount of weight during your pregnancy - 28 to 40 pounds is often recommended.
BMI of 19 to 25 prior to pregnancy
Your pregnancy is off to a healthy start if you're in the "recommended" BMI category. It's typically advised that you gain 25 to 35 pounds over the course of your pregnancy.
BMI of 25 to 30 prior to pregnancy
If you start your pregnancy in this BMI group, your weight gain range is slightly less, however, it's still important to gain weight to support a healthy pregnancy and provide your baby with adequate nourishment – 15 to 25 pounds is often recommended.
BMI above 30 prior to pregnancy
If your BMI is above 30 before you become pregnant, strive for a modest weight gain of 15 pounds – and remember that pregnancy is not a time to lose weight!
Pregnant with twins or multiples
Women who are pregnant with more than one baby typically need to gain additional weight to provide adequate nourishment for the babies. It's best to discuss your weight-gain range with your provider.
My baby only weighs 7 pounds – what makes up the rest?
Rest assured – it is not all fat. Most of the weight will go away gradually after delivery. Here's what you're carrying and approximately how it adds up:
Most of the weight will go away gradually after delivery. Here's what you're carrying and approximately how it adds up:
- Amniotic fluid and placenta: 4 pounds
- Increase in blood and other fluids: 8 pounds
- Fat reserves: 7 pounds
- Enlarged uterus and breasts: 4 to 6 pounds
How do the calories add up?
You may have heard the saying, "you're eating for two." Although it is true that the food you eat is nourishing two, your calorie needs only increase by about 300 per day after the first trimester. So if your goal is a healthy weight gain, keep in mind that your calorie needs don't increase that much. Here are three examples of healthy food choices that add up to 300 calories:
- Whole-wheat English muffin with two tablespoons peanut butter
- One cup of yogurt with one cup fresh fruit
- Bowl of high-fiber cereal with reduced-fat or skim milk
How will I lose the weight after delivery?
When you combine healthy eating with regular activity during your pregnancy, you'll feel better and shed those extra pounds easier once your baby is born. Gaining the recommended amount of weight during pregnancy can actually help you lose it more quickly afterward. If you're gaining at a faster rate, consult with your health care provider. Try these tips to increase activity and eat healthy during your pregnancy:
Gaining the recommended amount of weight during pregnancy can actually help you lose it more quickly afterward. If you're gaining at a faster rate, consult with your health care provider. Try these tips to increase activity and eat healthy during your pregnancy:
- Park further away from buildings; use the stairs instead of elevators.
- Avoid sitting for long periods of time – take short walk breaks.
- Snack on yogurt, string cheese, fresh fruit, or whole-grains (like popcorn and high-fiber cereal) instead of chips, candy and high-fat desserts.
- Eat regular meals and snacks.
In addition, women who choose to breastfeed may find it a bit easier to lose weight because of the extra calories (about 500 per day) it takes for their body to produce milk. However, the best approach to losing weight is always through healthy low-fat eating and regular moderate exercise.
Visit our pregnancy page to schedule an appointment and learn more about our services.
causes, influence of physique, growth rate, size of the fetus
An enlarged belly is one of the signs of a woman's pregnancy - by its size and shape, the doctor can determine how the fetus develops. The expectant mother's belly may look too large due to her physique, the size of the baby, and other factors.
Natalya Chebakova
legion-media
The type of abdomen in a pregnant woman depends on her height, weight, and pelvic structure. The size of the abdomen is greatly influenced by the rate of growth and development of the fetus, its location in the womb and the volume of amniotic fluid. Sometimes a big belly indicates a pathology.
Contents of the article
Do not self-medicate! In our articles, we collect the latest scientific data and the opinions of authoritative health experts. But remember: only a doctor can diagnose and prescribe treatment.
How a pregnant woman's belly grows by trimesters
First trimester
In the first months of pregnancy, a woman's belly practically does not change its shape. If there are changes, then they are minor. Only the woman herself can see them.
If there are changes, then they are minor. Only the woman herself can see them.
By the end of the first month of pregnancy, the woman's uterus is still small, it is no larger than a chicken egg.
At the eighth week of pregnancy, the uterus enlarges and becomes the size of a goose egg, but it does not yet extend beyond the pubic symphysis located in the lower abdomen.
Due to this, the belly of a pregnant woman is invisible in the early stages. And only at the end of the first trimester, after the twelfth week, the stomach becomes noticeable. The bottom of the uterus extends beyond the womb and begins to rise above it.
Second trimester
In the second trimester, the fetus begins to actively develop, grow and gain weight. The uterus is also getting bigger. The belly is growing.
By the end of the second trimester, the uterus rises 4-6 centimeters above the navel.
If a woman wears tight-fitting clothes, then the belly will be visible to others only after the 20th week of pregnancy.
Third trimester
By the end of the third trimester, the maximum height of the uterine fundus is located at the ribs.
A woman's pregnancy is visible to everyone around and is beyond doubt. A rounded belly cannot be hidden even under loose clothing.
From the second trimester, a gynecologist measures the height of the fundus of the uterus (the distance from the pubic bone to the upper part of the uterus) and the circumference of the abdomen every week. In this way, the development of the fetus and its approximate weight are monitored.
The height of the uterine fundus is multiplied by the circumference of the abdomen and the weight of the child is obtained. The error of this method is about 200 grams.
Child weight on average pregnancy weeks
- 8 - 11 week - from 2 to 10 grams
- 12 - 15 week - from 14 to 70 grams
- 16 - 19 week - from 100 to 240 grams
- 20 - 23 weeks - 300 to 500 grams
- 24 - 27 weeks - 600 to 900 grams
- 28 - 31 weeks - 1 to 1.5 kilograms
- 32 - 35 weeks - from 1.7 to 2, 5 kg
- 36 - 40 weeks - 2.6 to 3.5 kg
Reasons why your belly looks longer than your pregnancy
Every woman's body is different, and her belly during pregnancy may look completely different from that of her friend or acquaintance. Too big belly does not mean that there is some kind of pathology. Its size depends on many factors.
As long as your healthcare provider says your baby is developing well and you are gaining weight properly, there is no cause for concern.
Not the first pregnancy
Women who are expecting a second or subsequent child report that their belly begins to grow earlier because the muscles were stretched by a previous pregnancy.
Height
In tall, overweight women, the belly may be almost invisible until the last months of pregnancy.
In short and stocky women, the belly always seems to be larger than in tall and slender women, because they do not have enough space inside for the development of the child in the longitudinal direction.
Miniature and slender women have the opposite - the stomach seems to be very large.
Weight
Usually, doctors do not recommend gaining more than 7-13 kg during pregnancy. Such weight gain does not disturb the woman's metabolism, and the child develops well. However, the approach must be individual.
If the expectant mother has a small weight, then she can gain up to 18 kg during pregnancy, since the body first compensates for the weight deficit and only then proceeds to gain the kilograms that are needed for the development of the child.
A large woman who eats properly and rationally can gain only 3-5 kg in nine months, and this will not prevent the child from developing normally.
When pregnant, do not eat for two. Excess weight increases the load on the spine and blood vessels, causes swelling, increased pressure, which is not very good for the child and future birth.
Location of the baby
Very often the baby changes the shape of the mother's belly so that it becomes almost invisible. But as soon as he turns around, everything changes, and the stomach becomes noticeably larger.
If by the end of the third semester the child's head and legs are at their sides, natural childbirth is not possible.
Large child
A large belly may indicate that the child is large. But not necessarily. Large children are born both to very small women and to very fat ones, whose belly was not visible due to the size of the mother herself.
A large fetus may develop due to genetic characteristics, or may be due to diabetes in a pregnant woman. If a woman is diagnosed with diabetes, then it requires immediate treatment.
Multiple pregnancy
The number of children also affects the appearance of the abdomen. If twins or triplets develop normally, respectively, they take up more space in the womb.
Anomalies of pregnancy causing abdominal growth
Polyhydramnios during pregnancy
Or increased amniotic fluid. Most often, the pathology occurs in the 2-3 trimester.
Normally, the volume of amniotic fluid depends on the gestational age: at 10 weeks it is 30 ml, after 21 days - 100 ml, at 18 weeks - 400 ml, closer to childbirth - 800-1500 ml.
The danger of polyhydramnios during pregnancy lies in provoking multiple negative consequences for the woman and the child. In 36% of all cases, this condition causes severe toxicosis and contributes to a significant deterioration in the woman's condition.
In 36% of all cases, this condition causes severe toxicosis and contributes to a significant deterioration in the woman's condition.
A third of cases of polyhydramnios during pregnancy ends in spontaneous interruptions. The fetal membranes do not withstand the increased pressure of amniotic fluid and are damaged, which is accompanied by the death of the fetus.
Polyhydramnios during pregnancy is fraught with malposition of the fetus in the uterus due to the presence of a large space for its movements. Such a violation occurs in about 6-7% of cases.
The danger of polyhydramnios during pregnancy also lies in the fact that in every second case it provokes the development of postpartum hemorrhage, premature outflow of amniotic fluid, placental abruption.
Cystic mole
If the size of the abdomen is more than the given norms, then we can assume such a pathology as hydatidiform mole. This is a kind of tumor that consists of a large number of vesicles. Its development comes from placental tissue - degenerated chorionic villi - a fleecy membrane that forms the placenta.
This is a kind of tumor that consists of a large number of vesicles. Its development comes from placental tissue - degenerated chorionic villi - a fleecy membrane that forms the placenta.
Most often, such a pregnancy is terminated at an early stage, but sometimes the hydatidiform mole (MI) grows, increasing in size. A woman thinks that she is carrying a child, but in fact, instead of a fetus, a lump of small cysts develops in the uterus.
The cause of the disease is improper fertilization of the egg, during which the maternal chromosomes were “lost” or the egg was fertilized by two sperm at once.
The woman suffers from constant nausea and uncontrollable vomiting. Already in the first months, pressure rises, swelling occurs. Dark spotting appears from the genital tract, in which mole vesicles can be found.
With this pathology, the fetus is not viable, the uterus is cleaned using surgical curettage. and the woman is given treatment.
and the woman is given treatment.
Mole develops in 0.02-0.8% of all pregnancies.
Changes in the growth rate of the uterine fundus may indicate various pathologies of both the pregnant woman and the child. In this regard, if the gynecologist at the next appointment sees changes in the size of the uterine fundus that differ from the norm, then he sends the pregnant woman for additional studies. This helps to exclude pathology, or to diagnose it and take immediate measures.
MYTHS: Big belly - expect a big baby. The belly is small - wait for the girl.
youtube
Click and watch
Did you have a big belly during pregnancy?
What to do if you can't gain weight?
October 28, 2020 Answers
A variety of factors influence this - we analyze each one.
This question was sent by our reader. You can also ask your question to Lifehacker - if it is interesting, we will definitely answer.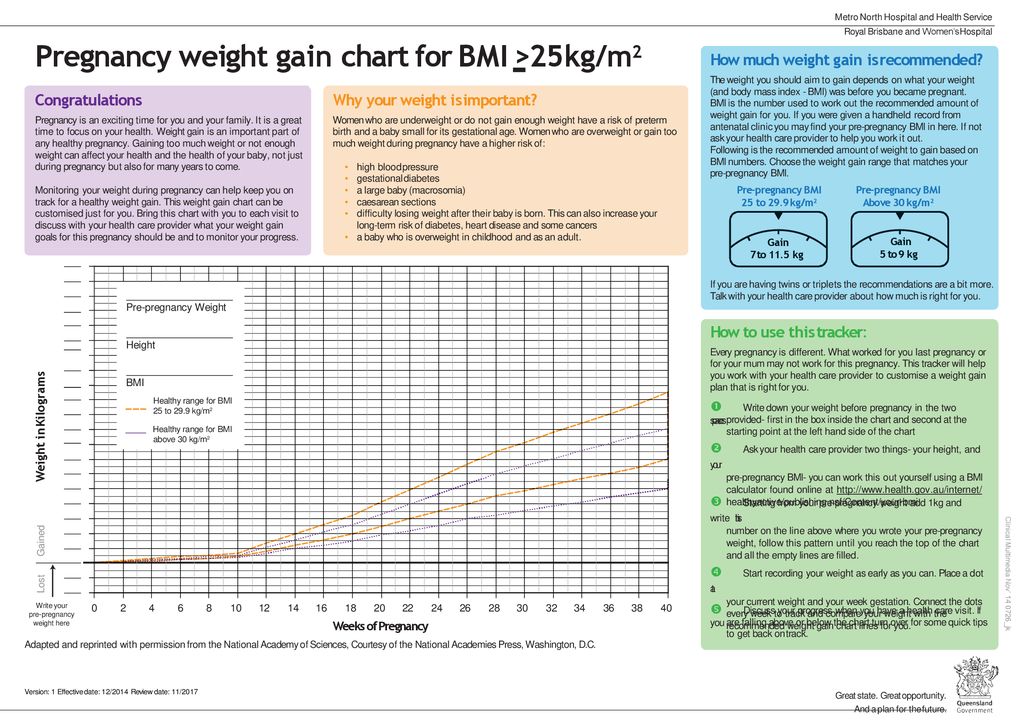
I want to gain weight, but I can't morally or psychologically because of the breakup of my parents, stress at work. How should I do it?
Anonymous
Anastasia Makarova
Head of the pathopsychological laboratory of the Eating Disorders Therapy Center, PKB No. N. A. Alekseeva.
Hello! Weight loss and difficulty gaining it can be due to both medical and non-medical problems, and sometimes a combination of both. In any case, this is a signal that requires immediate attention.
Modern research indicates that weight gain is influenced by various factors: genetic, biological, behavioral (including eating habits). At the heart of the problem may be difficulty with appetite, weight gain, or eating.
What are the causes of underweight
Physiological
1. The development of serious diseases
Sometimes weight loss can be associated, for example, with Addison's disease, cancer, disorders of digestion, smell and/or taste, type I diabetes , hyperthyroidism, HIV.
2. Muscle Loss
This happens when you don't use your muscles as a result of injury, stroke, burns, osteoporosis, osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis, or nerve damage.
3. Endocrine system disorders
Often, weight loss and the inability to return to healthy levels are due to an imbalance of such hormones: insulin (regulates glucose levels, affects hunger), leptin (responsible for appetite and satiety), ghrelin ( responsible for hunger signals), cortisol (increases appetite during stress), adrenaline (speeds up metabolism in response to emotional arousal), estrogen (responsible for the deposition of adipose tissue) and thyroxine (speeds up metabolism).
5. Features of genetics
It is important to consider the genetic predisposition to high or low weight. More than 600 genes are now isolated that can affect weight.
Mental
1. Mood disorders
For example, mood disorders - depression and anxiety disorder.
2. Eating disorders
Eating disorders, or eating disorders, are deadly and difficult to treat. EDD (eg, anorexia nervosa and bulimia nervosa) is characterized by fear of gaining weight, placing a high value on appearance, and negative beliefs about one's weight and body shape.
Behavioral
1. Lifestyle considerations
For example, vegetarian or vegan diets can make it impossible to gain weight because the body does not get all the nutrients it needs. Also, excessive physical activity can lead to difficulties in gaining weight.
2. Substance and alcohol abuse
It affects the function of a person's metabolism. For example, alcohol, when ingested, breaks down and disrupts the body's ability to produce nutrients, irritates the intestines, and slows down the digestion process. This can cause loss of appetite and disruption of the digestive tract. Alcohol is high in calories and in some cases can lead to weight gain, but with prolonged use it still causes weight loss.
Substance use affects appetite, physical activity levels, and metabolism. Depending on the principle of action, certain groups of drugs will reduce control and lead to overeating, while others will suppress appetite, speed up metabolism and promote weight loss.
What to do to gain weight
The assistance program is structured depending on the cause of the difficulty in gaining a healthy body weight. It is necessary to conduct examinations, determine the body mass index and the amount of weight loss at a certain point in time.
Whatever the cause of weight loss and difficulty in gaining it, it signals a malfunction of the body and leads to poor health. Therefore, I recommend contacting a specialist if you lose more than 5% of body weight within 6-12 months and have a body mass index of less than 18.5.
First of all, it is worth visiting a therapist - he will prescribe the necessary examinations and exclude a physiological disease as the cause of low body weight.