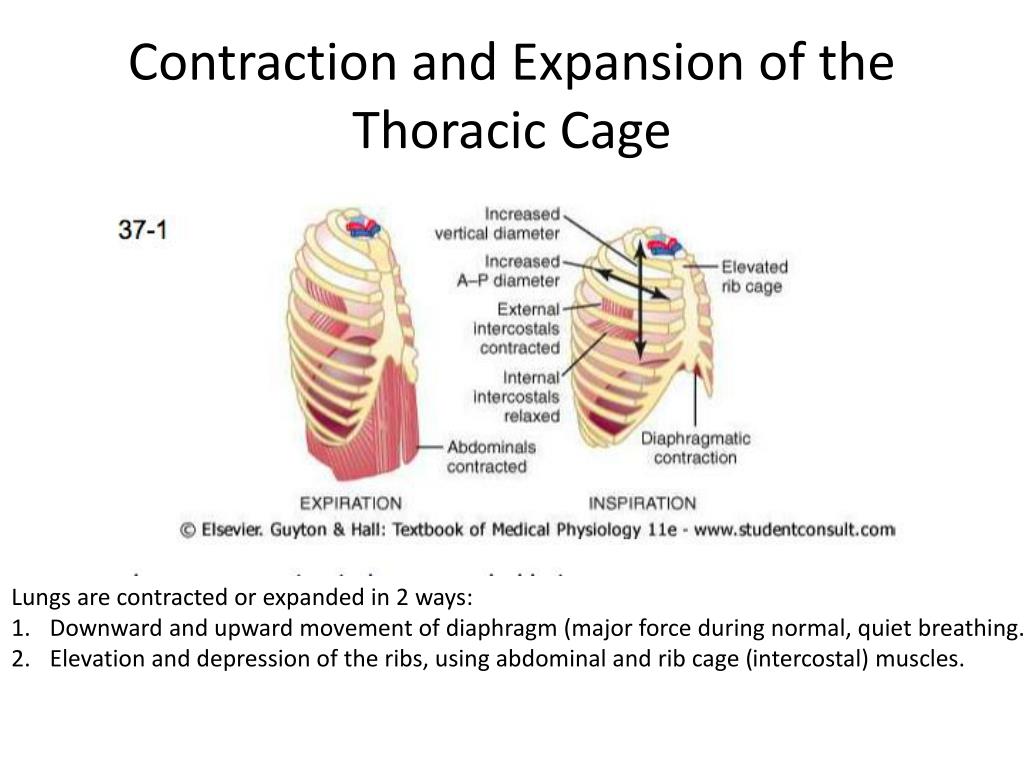
Contractions and dilation
Cervix Dilation Chart: Stages of Labor
The cervix, which is the lowest portion of the uterus, opens when a woman has a baby, through a process called cervical dilation. The process of the cervix opening (dilating) is one way that healthcare staff track how a woman’s labor is progressing.
During labor, the cervix opens to accommodate the passage of baby’s head into the vagina, which is around 10 centimeters (cm) dilated for most term babies.
If your cervix is dilated with regular, painful contractions, you’re in active labor and getting closer to delivering your baby.
The first stage of labor is divided into two parts: the latent and active phases.
Latent phase of laborThe latent phase of labor is the first stage of labor. It can be thought of more as the “waiting game” stage of labor. For first-time moms, it can take a while to move through the latent phase of labor.
In this stage, contractions aren’t yet strong or regular. The cervix is essentially “warming up,” softening, and shortening as it prepares for the main event.
You might consider picturing the uterus as a balloon. Think of the cervix as the neck and opening of the balloon. As you fill that balloon up, the neck of the balloon draws up with the pressure of the air behind it, similar to the cervix.
The cervix is simply the bottom opening of the uterus drawing up and opening wider to make room for the baby.
Active stage of laborA woman is considered to be in the active stage of labor once the cervix dilates to around 5 to 6 cm and contractions begin to get longer, stronger, and closer together.
The active stage of labor is characterized more by the rate of regular cervical dilation per hour. Your doctor will expect to see your cervix opening at a more regular rate during this stage.
How long does stage 1 of labor last?There’s no scientific hard and fast rule for how long the latent and active phases last in women. The active stage of labor can range from a woman dilating anywhere from 0.5 cm per hour up to 0.7 cm per hour.
The active stage of labor can range from a woman dilating anywhere from 0.5 cm per hour up to 0.7 cm per hour.
How fast your cervix dilates will also depend on if it’s your first baby or not. Mothers who have delivered a baby before tend to move more quickly through labor.
Some women will simply progress more quickly than others. Some women may “stall” at a certain stage, and then dilate very quickly.
In general, once the active stage of labor kicks in, it’s a safe bet to expect a steady cervical dilation every hour. Many women don’t start really dilating more regularly until closer to around 6 cm.
The first stage of labor ends when a woman’s cervix is fully dilated to 10 cm and fully effaced (thinned out).
The second stage of labor begins when a woman’s cervix is fully dilated to 10 centimeters. Even though a woman is fully dilated, it doesn’t mean that the baby is necessarily going to be delivered immediately.
A woman may reach full cervical dilation, but the baby may still need time to move down the birth canal fully to be ready for birth. Once the baby is in prime position, it’s time to push. The second stage ends after the baby is delivered.
Once the baby is in prime position, it’s time to push. The second stage ends after the baby is delivered.
In this stage, there’s again a wide range for how long it can take for the baby to come out. It can last anywhere from minutes to hours. Women may deliver with only a few hard pushes, or push for an hour or more.
Pushing occurs only with contractions, and the mother is encouraged to rest between them. At this point, the ideal frequency of contractions will be about 2 to 3 minutes apart, lasting 60 to 90 seconds.
In general, pushing takes longer for first-time pregnant people and for women who have had epidurals. Epidurals can reduce the woman’s urge to push and interfere with her ability to push. How long a woman is allowed to push depends on:
- the hospital’s policy
- the doctor’s discretion
- the health of the mom
- the health of the baby
The mother should be encouraged to change positions, squat with support, and rest between contractions. Forceps, vacuum, or cesarean delivery is considered if the baby isn’t progressing or the mother is becoming exhausted.
Forceps, vacuum, or cesarean delivery is considered if the baby isn’t progressing or the mother is becoming exhausted.
Again, every woman and baby is different. There’s no universally accepted “cut-off time” for pushing.
The second stage ends with the birth of the baby.
The third stage of labor is perhaps the most forgotten phase. Even though the “main event” of birth has occurred with the birth of the baby, a woman’s body still has important work to do. In this stage, she’s delivering the placenta.
A woman’s body actually grows an entirely new and separate organ with the placenta. Once the baby is born, the placenta no longer has a function, so her body must expel it.
The placenta is delivered the same way as the baby, through contractions. They may not feel as strong as the contractions that are needed to expel the baby. The doctor directs the mother to push and the delivery of the placenta is typically over with one push.
How long does stage 3 of labor last?The third stage of labor can last anywhere from 5 to 30 minutes.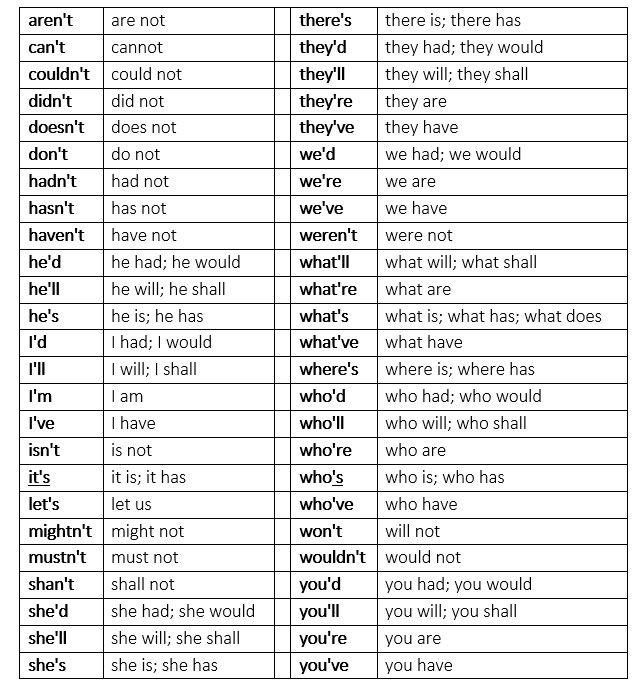 Putting the baby on the breast for breastfeeding will hasten this process.
Putting the baby on the breast for breastfeeding will hasten this process.
Postpartum recovery
Once the baby is born and the placenta has been delivered, the uterus contracts and the body recovers. This is often referred to as the fourth stage of labor.
After the hard work of moving through the stages of labor is finished, a woman’s body will need time to return to its nonpregnant state. On average, it takes about 6 weeks for the uterus to return to its nonpregnant size and for the cervix to return to its prepregnancy state.
Signs, Progression & What To Expect
What to expect during labor and delivery.How does labor work?
As your pregnancy begins to wrap up, your body will prepare for labor and delivery. This is the process through which your baby will be born. Labor is often different for each person.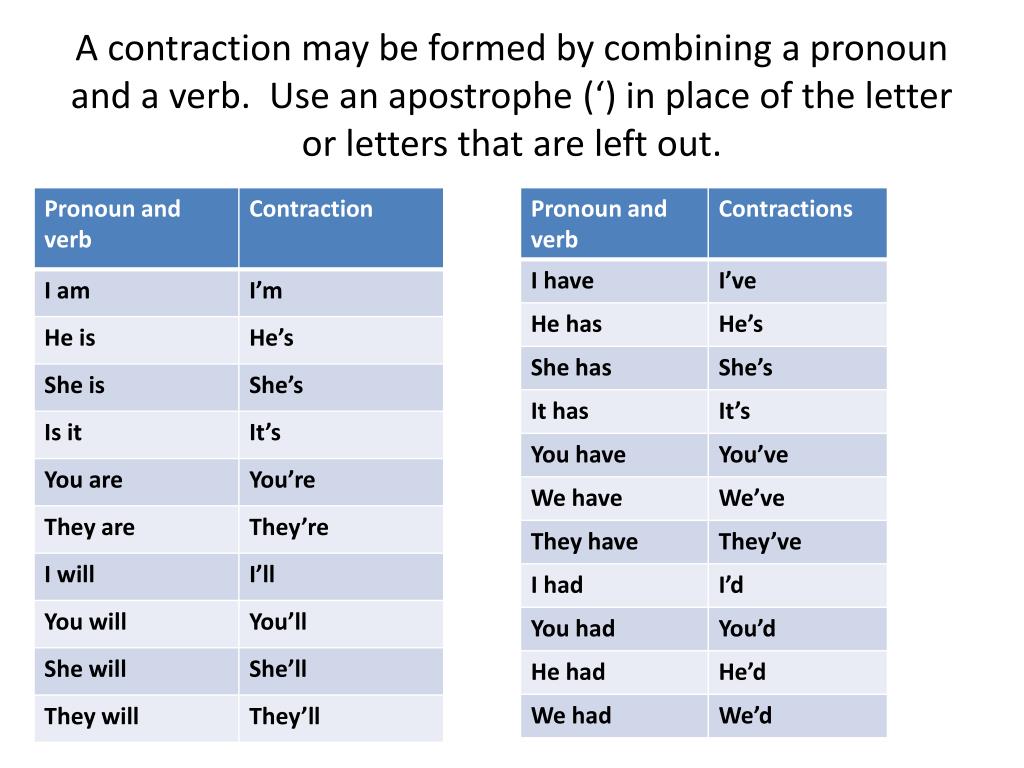 Some have quick labors and some long, difficult labors. Other people may even experience labor that stalls or stops, leading to medical intervention.
Some have quick labors and some long, difficult labors. Other people may even experience labor that stalls or stops, leading to medical intervention.
Early labor
The average labor lasts 12 to 24 hours for a first birth and is typically shorter (eight to 10 hours) for other births. Throughout this time, you’ll experience three stages of labor. The first stage of labor is usually the longest and it ranges from when you first go into labor until your cervix is open. The beginning of this stage is called early labor. Early labor is described as dilating from 0 to 6 centimeters.
Active labor
As you progress and your contractions become stronger, you’ll move into the second part of the first stage of labor called active labor. Active labor is dilating from 6 to 8 centimeters and then transitioning into the second stage as you dilate 8 to 10 centimeters. Your contractions will become even stronger during active labor and your cervix will open up quickly. The second stage of labor is when you push. This is the phase of your labor when you will actually give birth to your baby.
This is the phase of your labor when you will actually give birth to your baby.
Afterbirth
The third stage is the point when you deliver the placenta. This is also called afterbirth.
During these stages, your body prepares for childbirth by going through dilation and effacement.
- Dilation: This is a process where your cervix stretches and opens to make way for your baby’s birth. Dilation is measured from 1 to 10 centimeters. Your provider will do a vaginal exam to check how dilated you are throughout your labor. You’ll be 10 centimeters dilated in the second stage of labor for the delivery of your baby.
- Effacement: The cervix not only stretches during labor but it also becomes thinner. The shortening and thinning of your cervix are measured in percentages. You’ll progress from 0% to 100% effacement during your labor.
Think of your cervix as a round doorway that needs to stretch outward and get thinner before your baby can pass through it.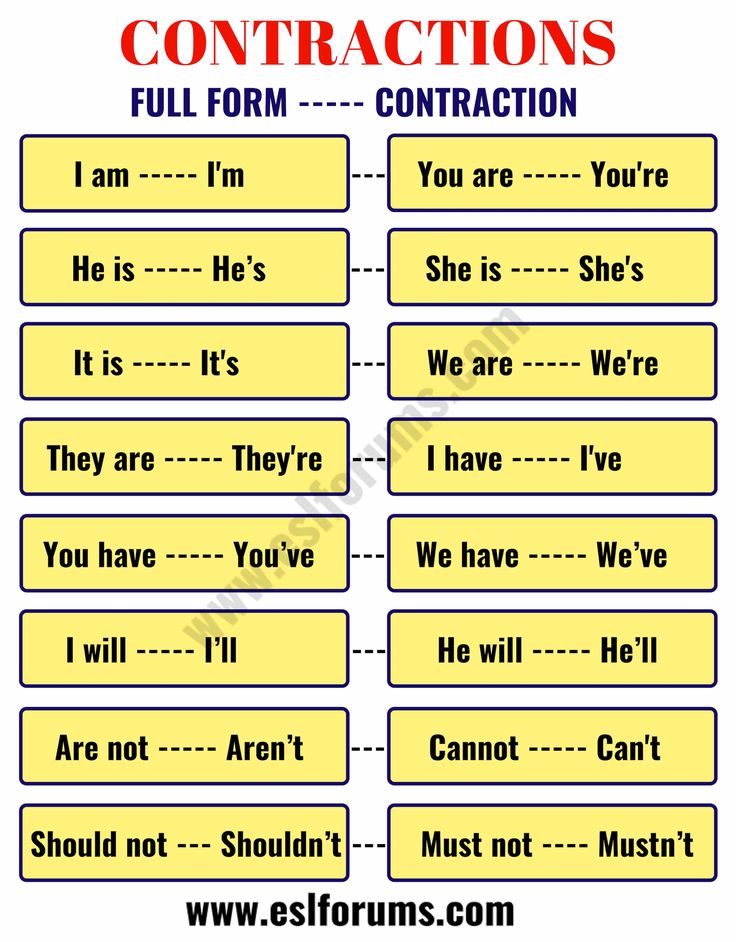 This stretching and thinning are caused by contractions. Contractions can be described in a variety of ways ranging from uncomfortable, period-like cramps to a painful tightening of your abdomen. You might also feel a dull ache in your back and lower abdomen, as well as pressure in your pelvis.
This stretching and thinning are caused by contractions. Contractions can be described in a variety of ways ranging from uncomfortable, period-like cramps to a painful tightening of your abdomen. You might also feel a dull ache in your back and lower abdomen, as well as pressure in your pelvis.
When you have a contraction, it’s actually the muscles of your uterus tightening at regular intervals to dilate and efface (open and thin) your cervix. During contractions, your abdomen becomes hard. Between contractions, your uterus relaxes and your abdomen becomes soft. Even though they can be painful, each contraction helps move you forward through your labor.
How will I know I’m in labor?
It can be difficult to know when you’re in true labor. First-time parents, in particular, might mistake other symptoms or irregular practice contractions (called Braxton Hicks contractions) for true labor. True labor has a pattern and progresses steadily over time.
When you’re in true labor, you’ll notice a pattern in your contractions. Instead of the irregular Braxton Hicks contractions you might have felt during your pregnancy that showed up and then went away randomly, these contractions will keep coming for an extended period of time. There are three things you’ll want to look for when you are in true labor.
Instead of the irregular Braxton Hicks contractions you might have felt during your pregnancy that showed up and then went away randomly, these contractions will keep coming for an extended period of time. There are three things you’ll want to look for when you are in true labor.
- Frequency: How often are your contractions happening? Keep track of them with a journal or labor app on your phone to make sure they're coming at regular intervals.
- Duration: How long are each of your contractions? As your labor continues, your contractions will last longer and longer. Use a stopwatch, watch a clock or keep the timer on your phone handy so you can record the length of each contraction.
- Intensity: Are your contractions getting stronger? Contractions can get stronger and you might feel them more intensely as you move through the stages of labor. Keep track of how your contractions feel over time.
Are there any signs that I will go into labor soon?
Many women have several pre-labor signs that might hint that labor will start soon. These signs of labor include:
These signs of labor include:
- Backaches.
- Diarrhea.
- Weight loss.
- Nesting (cleaning and organizing your home).
No one knows for sure what causes labor to start, but several hormonal and physical changes may point to the beginning of labor.
What are Braxton Hicks contractions?
Often called practice contractions, Braxton Hicks are irregular contractions that don’t cause cervical change. Think of them as a test run for the real thing. They can start happening at the end of your pregnancy and can startle people into thinking they’re in labor. This is called false labor.
A Braxton Hicks contraction will feel like a sudden, sharp tightening of your abdominal muscles. Even though this is very similar to how a contraction feels, Braxton Hicks contractions don’t follow a pattern or progress over time. They may also stop when you lay down or relax. When you start to experience these practice contractions, keep track of them. Writing them down is the best way to tell the difference between true and false labor.
What is lightening?
Lightening is the process where your baby settles or lowers into your pelvis. This can happen a few weeks or a few hours before labor. When this happens, you may experience some increased lower pelvic pressure. Because your uterus rests on your bladder more after lightening, you might also feel the need to urinate more frequently. You might notice that you’re not as short of breath once your baby drops.
What’s the mucus plug and what does it mean when it falls out?
During pregnancy, a thick piece of mucus called a plug blocks the cervical opening. This plug keeps your uterus closed off from the birth canal and the outside of your body and prevents bacteria from traveling into your uterus. When your cervix begins to soften, thin, and open, the mucus is expelled into your vagina. Not every mucus plug will look the same. Possible colors of the mucus plug can include:
- Clear.
- Pink.
- Slightly bloody.
Labor could start shortly after you lose your mucus plug or it could begin several weeks later.
How do I time my contractions?
Once you’re in labor, it’s important to keep track of your contractions. Your healthcare provider will need to know how long your contractions are lasting (duration), how often they’re happening (frequency) and how intense they are. When you’re timing your contractions, you will want to have a way to record each one – pen and paper or through an app on your phone – and a timer or clock. Make sure you keep track of each contraction from start to end, as well as the time between each contraction. This second measurement will help your provider know the frequency of your contractions.
It can be difficult to record the intensity of your contractions. This can really vary from person to person. Often, an easy way to keep track of the intensity of your contractions is to record when you cannot walk, talk or laugh during contractions.
Is there anything I can do to cope with contractions?
As you approach the end of your pregnancy, it’s a good idea to talk to your healthcare provider about different ways to deal with pain and discomfort during labor. There are several options your provider will discuss with you to relieve pain.
There are several options your provider will discuss with you to relieve pain.
There are also ways to deal with the discomforts of labor at home or without medication, including:
- Distract yourself by taking a walk, going shopping or watching a movie.
- Soak in a warm tub or take a warm shower. Make sure to ask your healthcare provider if you should take a tub bath if your bag of water has broken.
- Sit on a birth ball.
- Listen to music.
- Dim the lights.
- Use aromatherapy.
- Get a massage.
- Stay in an upright position. This can help with the descent and rotation of your baby.
- Try to sleep if it’s evening. You’ll want to store up your energy before active labor and delivery.
How will I know when my water breaks?
You may be familiar with the common phrase “my water broke.” This is actually the rupturing of your amniotic membrane. During pregnancy, your baby is inside a fluid-filled sac, also called your bag of water. When this membrane breaks, you might feel a sudden gush or trickle of fluid. Like many parts of labor and childbirth, this experience can be different for each person. The fluid is usually odorless and may look clear or straw-colored.
When this membrane breaks, you might feel a sudden gush or trickle of fluid. Like many parts of labor and childbirth, this experience can be different for each person. The fluid is usually odorless and may look clear or straw-colored.
Unlike urine leakage that some pregnant women experience, this won’t stop. The amniotic fluid will often continue to leak.
If your water breaks, call your healthcare provider. Let your provider know what time your water broke, the amount (trickle or gush), the color of the fluid and the odor. Don't use tampons if your water has broken. Your labor might start right after your water breaks. Some women are already in labor when their water breaks while others don’t experience the first stage of labor for a while after their water breaks.
When should I call my healthcare provider or go to the hospital?
If you ever have any questions, it’s always a good idea to call your healthcare provider. Your provider can answer any questions you have about true labor versus false labor and discuss how you’re feeling. When you start to notice that you’re having regular contractions, call your provider to talk about when you should go to the hospital. Some women are able to stay home throughout early labor, while others may need to come in sooner.
When you start to notice that you’re having regular contractions, call your provider to talk about when you should go to the hospital. Some women are able to stay home throughout early labor, while others may need to come in sooner.
You should also call your healthcare provider if you:
- Think your water has broken. This could be a sudden gush of fluid or a trickle of fluid that leaks steadily.
- Are bleeding (more than spotting).
- Experience contractions that are very uncomfortable and have been coming every five minutes, lasting for one minute and have been like this for one hour.
What happens when I get to the hospital?
When you get to the hospital, you will check in at the labor and delivery desk. Most people will be seen in a triage room first. This is part of the admission process. It’s usually recommended that you only bring one person with you to the triage room.
From the triage room, you will be taken to the labor, delivery and recovery (LDR) room. You’ll be asked to wear a hospital gown. Your pulse, blood pressure and temperature will be checked. An external fetal monitor will be placed on your abdomen for a short time to check for uterine contractions and measure your baby’s heart rate. Your healthcare provider will also examine your cervix to see how far labor has progressed. An intravenous (IV) line might be placed into a vein in your arm to deliver fluids and medications.
You’ll be asked to wear a hospital gown. Your pulse, blood pressure and temperature will be checked. An external fetal monitor will be placed on your abdomen for a short time to check for uterine contractions and measure your baby’s heart rate. Your healthcare provider will also examine your cervix to see how far labor has progressed. An intravenous (IV) line might be placed into a vein in your arm to deliver fluids and medications.
What does it mean to have labor induced?
Labor doesn’t always start naturally or progress as it should. In these cases, your provider might talk to you about inducing labor. This is a medical procedure where labor is started by your healthcare provider. This could happen if you:
- Are past your due date.
- Have health complications like high blood pressure, preeclampsia, infection or diabetes.
- Had your water break but labor didn’t start.
- Have low levels of amniotic fluid.
Your labor can be advanced or induced in several ways. Your provider will advise you about the best and safest option depending on your health. Inducing labor can be done by using:
Your provider will advise you about the best and safest option depending on your health. Inducing labor can be done by using:
- Medications (oxytocin) given through an IV (directly into your vein).
- Breaking your amniotic sac (water).
- Separating the amniotic membrane (the sac of fluid the baby is inside within your uterus) from your uterine wall. This is also called sweeping the membrane.
- Softening your cervix and encouraging it to open with a medication that can be placed directly in your vagina.
Labor induction can take longer than spontaneous labor because the cervical ripening process takes time.
What are the different types of delivery?
There are two main types of delivery: vaginal and cesarean section (C-section). During vaginal birth, your baby will pass naturally through the birth canal. A C-section is a surgical procedure where your provider makes an incision (cut) in your abdomen and delivers the baby in an operating room. Vaginal delivery is the most common type of birth. However, sometimes you might need a C-section for a variety of reasons, including:
Vaginal delivery is the most common type of birth. However, sometimes you might need a C-section for a variety of reasons, including:
- If your baby is not in the head-down position.
- If your baby is too large to naturally pass through your pelvis.
- If your baby is in distress.
- If the placenta blocks your cervix (a condition called placenta previa).
- If you have health issues or complications that make a C-section the safest option.
- If there’s an emergency situation that requires your baby to be delivered quickly.
In many cases, a cesarean delivery is not determined until after labor begins.
How long will I be in the hospital?
The length of your hospital stay can depend on the hospital where you deliver your baby and the type of delivery you have. Typically, you will stay in the hospital longer if you have a C-section delivery because it's a surgical procedure. You may also need to stay in the hospital for a longer period of time if you experience any complications or health issues during your delivery.
A note from Cleveland Clinic:
You're bound to a lot of feelings as you prepare to deliver your baby. It's normal to feel both excited and nervous. Discussing the signs and symptoms with your healthcare provider can help you know what to expect. Your partner and healthcare team are here to support you and will help you remain as comfortable as possible through the delivery process.
Rules for reducing and expanding fractions
- Arithmetic
- Geometry
- tables
- Arithmetic
- Rules for reducing and expanding fractions
To solve certain problems, it is often necessary to convert fractions using the extension method or the reduction method .
Since the value of a fraction remains unchanged, if the numerator and denominator of this fraction are multiplied or divided by the same non-zero number taken, the fraction can be changed depending on current requirements.
Fraction expansion
A fraction transformation in which the numerator and denominator are multiplied by a number with the same value is called fraction expansion .
| 1 2 | = | 1 × 2 2 × 2 | = | 2 4 |
Two-fourths fraction obtained by expansion by two.
| 1 5 | = | 1 x 5 5 × 5 | = | 5 25 |
Five twenty-fifths fraction obtained by expanding by five.
| 7 8 | = | 7 × 3 8 × 3 | = | 21 24 |
Fraction twenty-one twenty-fourths, obtained by expansion by three.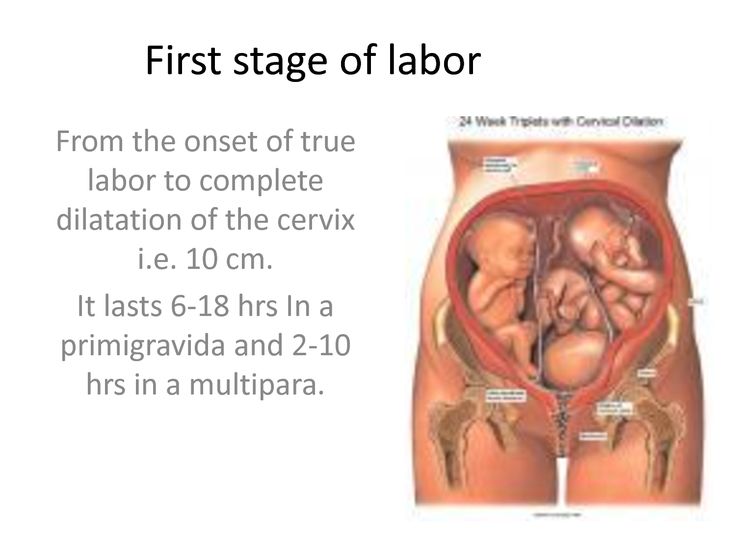
Fraction reduction
A fraction conversion in which the numerator and denominator are divided by a number with the same value is called fraction reduction .
| 2 4 | = | 2 : 2 4 : 2 | = | 1 2 |
One-half fraction obtained by reducing two-fourths by two.
| 5 25 | = | 5 : 5 25 : 5 | = | 1 5 |
One-fifth fraction obtained by reducing five from five-twenty-fifths.
| 21 24 | = | 21:3 24:3 | = | 7 8 |
Fraction seven-eighths, obtained by reducing by three from the fraction twenty-one twenty-fourth.
© 2012 – 2023
Extensions and reductions. NOTHING REGULAR
Extensions and abbreviations. NOTHING REGULARWikiReading
NOTHING REGULAR
Millman Dan
Contents
Extensions and reductions
Even if your bad mood is justified, do not forget about unreasonable happiness and try to experience it - just to make you feel better. Expand instead of contract.
Abbreviations
Abbreviations A. - Anguttara nikaya D. - Digha nikaya M. - Majjjhima nikaya Iti - "Itivutaka" S. - Samyutta nikaya
[13) The discrepancy between the expansion of production and the expansion of the market. Ricardo's concept of unlimited possibilities for the growth of consumption and for the expansion of the domestic market]
[13) The discrepancy between the expansion of production and the expansion of the market. Ricardo's concept of unlimited possibilities for the growth of consumption and for the expansion of the domestic market] [720] If we say that the continuously expanding production {which annually
Ricardo's concept of unlimited possibilities for the growth of consumption and for the expansion of the domestic market] [720] If we say that the continuously expanding production {which annually
Literature and abbreviations
Literature and abbreviations PS - Letter to P.B. Struve about the Eurasians (1922) // From the past of Russian thought. M., 1998. Open letter to VMI - In the world of searching and wandering. III. Paphos of false prophecy and imaginary revelations (1924) // From the past of Russian thought. M., 1998. Article in the scientific journal PN - Memory
Literature and abbreviations
Literature and abbreviations OSR — Fundamentals of medieval religiosity in the XII-XIII centuries. St. Petersburg, 1997 (1st edition 1915). Monograph S - Saligia (1919) // Karsavin L.P. Small essays. St. Petersburg, 1994. Brochure NP - Noctes Petropolitanae (1922) // Karsavin L.P. Small essays. Monograph FI - Philosophy of history. St. Petersburg, 1993 (1st edition 1923).
Brochure NP - Noctes Petropolitanae (1922) // Karsavin L.P. Small essays. Monograph FI - Philosophy of history. St. Petersburg, 1993 (1st edition 1923).
Abbreviations
Abbreviations APM 62 "Ayn Rand on Campus" radio broadcast discussing her lecture "America's Oppressed Minority: Big Businessmen" (1962). ARM 63 "America's Oppressed Minority: Big Businessmen" Lecture (1963). CBS March
Accepted abbreviations
Accepted abbreviations NL - New in foreign linguistics, vol., M. ZS - Scientific notes of Tartu University, vol. Works on sign systems. • Averintsev S. S. Water // Myths of the peoples of the world. M., 1981.• Bakhtin MM Problems of Dostoevsky's Poetics. M., 1963.• Bakhtin M. M. Francois Rabelais and folk
MAIN ABBREVIATIONS
KEY ABBREVIATIONS CITIES K. - Kyiv L. — Leningrad M - Moscow M—L. — Moscow—Leningrad Pg. — Petrograd SPb. - Saint Petersburg V. - Berlin Bait. — Baltimore Bdpst. — Budapest Berk. — Berkeley Brux.—Bruxelles bue. — Bucuresti Cambr. — Cambridge "VF" - "Questions of Philosophy" Lebedev. Fragments - Fragments
- Kyiv L. — Leningrad M - Moscow M—L. — Moscow—Leningrad Pg. — Petrograd SPb. - Saint Petersburg V. - Berlin Bait. — Baltimore Bdpst. — Budapest Berk. — Berkeley Brux.—Bruxelles bue. — Bucuresti Cambr. — Cambridge "VF" - "Questions of Philosophy" Lebedev. Fragments - Fragments
4. 4. The rule of expanding the boundaries of state system management
4. 4. The rule of expanding the boundaries of state system management (conditions of consistency and modeling of the boundaries of the public administration system, stages and key procedure of the method of systemic philosophy of modeling, modeling of the expansion of boundaries, general model
CHAPTER 24 HUMAN EXTENSION GAMES
CHAPTER 24 GAMES HUMAN EXTENSIONS Alcohol and gambling have very different meanings in different cultures. In our highly individualistic and fragmented Western world, "booze" is a social bond and a means of getting involved in the celebration.