Contraction like cramps
Signs of Labor (Cervical Effacement) During Pregnancy
Written by WebMD Editorial Contributors
In this Article
- What Are the Signs of Labor?
- What's the Difference Between True Labor and False Labor?
- Time Your Contractions
- Try to Relax
- When Should I Call My Health Care Provider or Go to the Hospital?
What Are the Signs of Labor?
Labor is another word for your body’s natural process of childbirth. It starts with your first steady contractions and goes through the delivery of both your baby and placenta.
Some women have very distinct signs of labor, while others don’t. No one knows what causes labor to start or when it will start, but several hormonal and physical changes help indicate the beginning of labor.
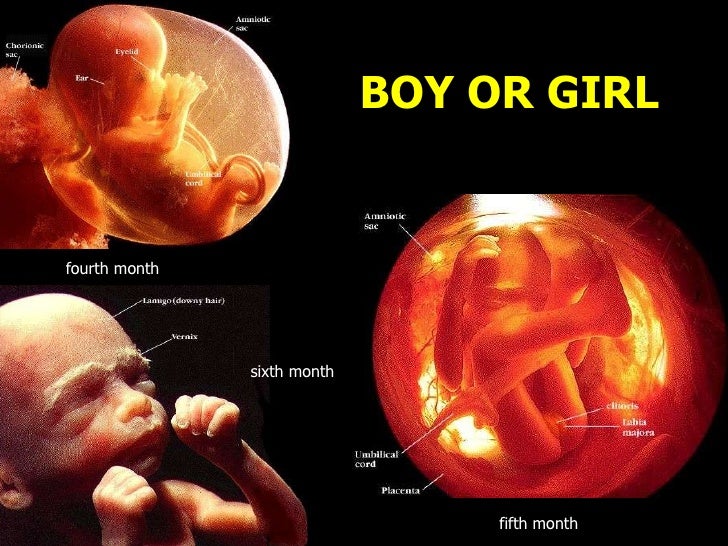
Lightening during labor
The process of your baby settling or lowering into your pelvis just before labor is called lightening. It’s also referred to as the baby “dropping. ”
- Lightening can happen a few weeks or a few hours before labor.
- Because the uterus rests on the bladder more after lightening, you may feel the need to urinate more often.
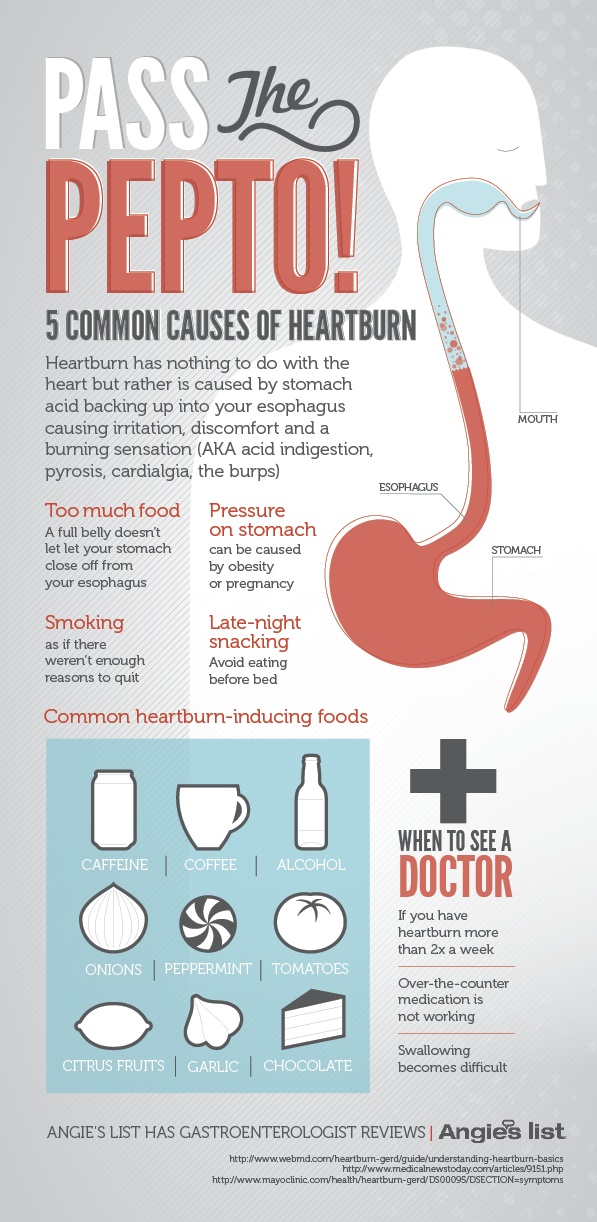
- But the extra room in your upper abdomen may make it easier to breathe and relieve heartburn.
Passing of the mucus plug
The mucus plug accumulates at the cervix during pregnancy. When the cervix begins to open wider, the mucus is discharged into the vagina. It may be clear, pink, or slightly bloody. This is also known as “show” or “bloody show.” Labor may begin soon after the mucus plug is discharged or one to two weeks later.
Labor contractions
Contractions are the tightening of the muscles of the uterus. During contractions, the abdomen becomes hard. Between contractions, the uterus relaxes and the abdomen becomes soft. The way a contraction feels is different for each woman, and it may feel different from one pregnancy to the next.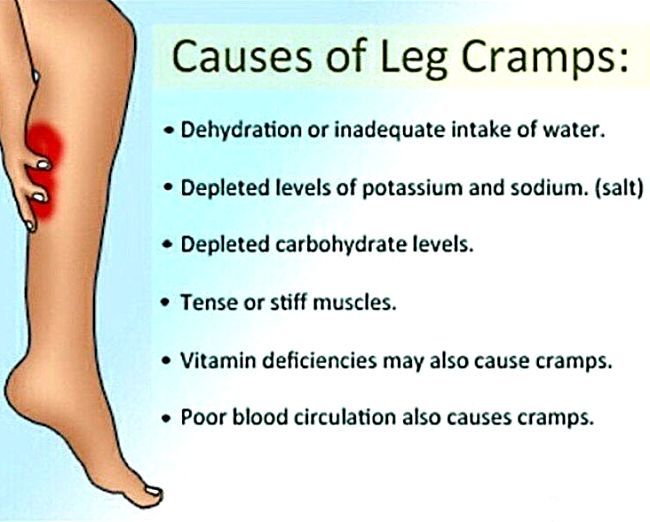
- Labor contractions usually cause discomfort or a dull ache in your back and lower abdomen, along with pressure in the pelvis.
- Contractions move in a wave-like motion from the top of the uterus to the bottom.
- Some women describe contractions as strong menstrual cramps.
- Unlike false labor contractions or Braxton Hicks contractions, true labor contractions don’t stop when you change your position or relax.
- Although they may be uncomfortable, you’ll be able to relax in between contractions.
Diarrhea
You may notice your poops are loose or watery. This may mean you are within a day or two of labor beginning.
Weight loss
While you’re pregnant, it may seem like you’re never going to stop gaining weight. But many women actually lose a few pounds in the days leading up to labor.
Nesting instinct
Some women find themselves with an urge to get ready shortly before their baby’s arrival. That’s known as the nesting instinct.
That’s known as the nesting instinct.
- You may have a sudden burst of energy after weeks of feeling more and more tired.
- You may feel like shopping, cooking, or cleaning the house.
- Be careful not to overdo it. Childbirth will take a lot of energy.
Activity of the baby
Your baby may move less as you get closer to the start of labor, but let your doctor know. It can sometimes be a sign of a problem.
Cramps and back pain
It may be hard to recognize a contraction, especially with your first baby. Many women have what feels like menstrual cramps in the lower abdomen. They may stay the same or they may come and go. You might also have pain in your lower back that either stays or comes and goes.
Looser joints
If you find yourself “waddling” as your pregnancy winds down, that’s just your body getting ready for the job ahead. A hormone called relaxin loosens up the ligaments around your pelvis to make it easier for the baby to pass through.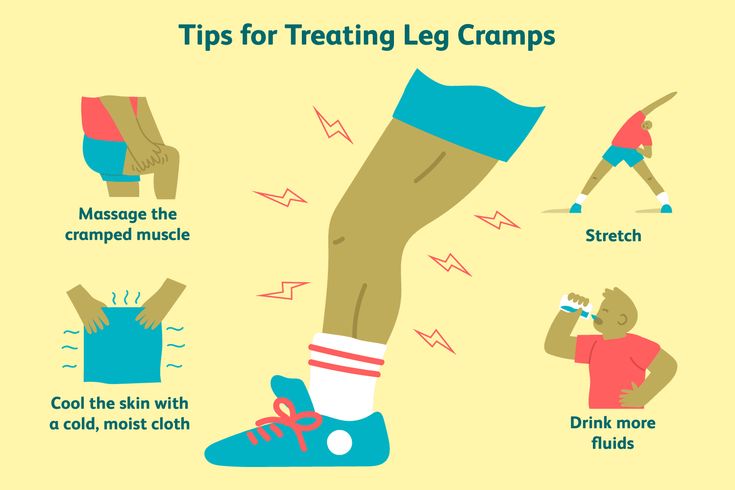
Water breaking
The rupture of the amniotic membrane (the fluid-filled sac that surrounds the baby during pregnancy) may happen before you get to the hospital.
- It may feel either like a sudden gush of fluid or a trickle of fluid that leaks steadily.
- The fluid is usually odorless and may look clear or straw-colored.
- If your "water breaks," write down the time this happens, how much fluid is released, and what the fluid looks like, then let your health care provider know. They’ll advise you what to do next.
- Not all women have their water break when they’re in labor. Many times the doctor will rupture the amniotic membrane in the hospital.
Effacement
During labor, your cervix gets shorter and thins out in order to stretch and open around your baby's head. The shortening and thinning of the cervix is called effacement. Your health care provider will be able to tell you if there are changes to the cervix during a pelvic exam.
Effacement is measured in percentages from 0% to 100%. If there are no changes to the cervix, it is described as 0% effaced. When the cervix is half the normal thickness, it is 50% effaced. When the cervix is completely thinned out, it is 100% effaced.
Dilation
The stretching and opening of your cervix is called dilation and is measured in centimeters, with complete dilation being at 10 centimeters.
Effacement and dilation are a direct result of effective uterine contractions. Progress in labor is measured by how much the cervix has opened and thinned to allow your baby to pass through the vagina.
What's the Difference Between True Labor and False Labor?
Before "true" labor begins, you may have "false" labor pains, also known as Braxton Hicks contractions. These irregular uterine contractions are perfectly normal and may start to occur in your second trimester, although more commonly in your third trimester of pregnancy. They are your body's way of getting ready for the "real thing."
They are your body's way of getting ready for the "real thing."
What do Braxton Hicks contractions feel like?
Braxton Hicks contractions can be described as a tightening in the abdomen that comes and goes. These contractions do not get closer together, do not increase with walking, do not increase in duration, and do not feel stronger over time as they do when you are in true labor.
How do I know when I am in true labor?
To figure out if the contractions you are feeling are the real thing, ask yourself the following questions.
| Contraction Characteristics | False Labor | True Labor |
| How often do the contractions occur? | Contractions are often irregular and do not get closer together.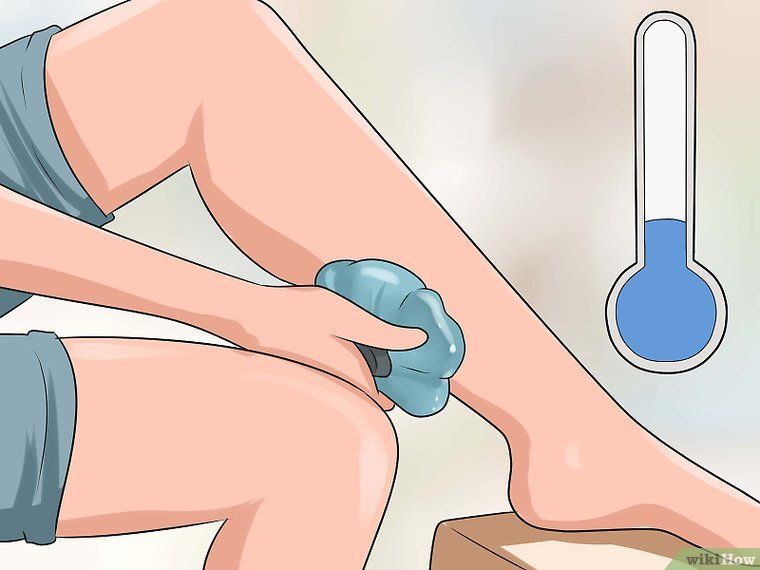 | Contractions come at regular intervals and last about 30-70 seconds. As time progresses, they get closer together. |
| Do they change with movement? | Contractions may stop when you walk or rest, or may even stop if you change positions. | Contractions continue despite movement or changing positions. |
| How strong are they? | Contractions are usually weak and do not get much stronger. Or they may be strong at first and then get weaker. | Contractions steadily increase in strength. |
| Where do you feel the pain? | Contractions are usually only felt in the front of the abdomen or pelvic region. | Contractions usually start in the lower back and move to the front of the abdomen. |
Time Your Contractions
When you think you are in true labor, start timing your contractions. To do this, write down the time each contraction starts and stops or have someone do it for you. The time between contractions includes the length or duration of the contraction and the minutes in between the contractions (called the interval).
To do this, write down the time each contraction starts and stops or have someone do it for you. The time between contractions includes the length or duration of the contraction and the minutes in between the contractions (called the interval).
Mild contractions generally begin 15 to 20 minutes apart and last 60 to 90 seconds. The contractions become more regular until they are less than 5 minutes apart. Active labor (the time you should come into the hospital) is usually characterized by strong contractions that last 45 to 60 seconds and occur 3 to 4 minutes apart.
Try to Relax
It’s best to go through the first stage of labor (called the Latent Phase) in the comfort of your home. Here are some tips to help you manage:
- Distract yourself -- take a walk, watch a movie.
- Soak in a warm tub or take a warm shower. But, ask your health care provider if you can take a tub bath if your water has broken.
- Rest. Try to sleep or take a nap if it is in the evening.
 You need to store up your energy for active labor.
You need to store up your energy for active labor.
When Should I Call My Health Care Provider or Go to the Hospital?
When you suspect you are in true labor, call your health care provider. Also, call:
- If you think your water has broken.
- If you’re bleeding (more than spotting).
- If the baby seems to be moving less than normal.
- When your contractions are very uncomfortable and have been coming every 5 minutes for an hour.
- If you have any of the signs of labor, but you haven’t reached your 37th week of pregnancy. You may be going into labor before your baby is ready and will need medical help right away.
Your health care provider will give you specific guidelines about when you should get ready to come to the hospital.
Signs of Labor (Cervical Effacement) During Pregnancy
Written by WebMD Editorial Contributors
In this Article
- What Are the Signs of Labor?
- What's the Difference Between True Labor and False Labor?
- Time Your Contractions
- Try to Relax
- When Should I Call My Health Care Provider or Go to the Hospital?
What Are the Signs of Labor?
Labor is another word for your body’s natural process of childbirth. It starts with your first steady contractions and goes through the delivery of both your baby and placenta.
It starts with your first steady contractions and goes through the delivery of both your baby and placenta.
Some women have very distinct signs of labor, while others don’t. No one knows what causes labor to start or when it will start, but several hormonal and physical changes help indicate the beginning of labor.
Lightening during labor
The process of your baby settling or lowering into your pelvis just before labor is called lightening. It’s also referred to as the baby “dropping.”
- Lightening can happen a few weeks or a few hours before labor.
- Because the uterus rests on the bladder more after lightening, you may feel the need to urinate more often.
- But the extra room in your upper abdomen may make it easier to breathe and relieve heartburn.
Passing of the mucus plug
The mucus plug accumulates at the cervix during pregnancy. When the cervix begins to open wider, the mucus is discharged into the vagina. It may be clear, pink, or slightly bloody. This is also known as “show” or “bloody show.” Labor may begin soon after the mucus plug is discharged or one to two weeks later.
It may be clear, pink, or slightly bloody. This is also known as “show” or “bloody show.” Labor may begin soon after the mucus plug is discharged or one to two weeks later.
Labor contractions
Contractions are the tightening of the muscles of the uterus. During contractions, the abdomen becomes hard. Between contractions, the uterus relaxes and the abdomen becomes soft. The way a contraction feels is different for each woman, and it may feel different from one pregnancy to the next.
- Labor contractions usually cause discomfort or a dull ache in your back and lower abdomen, along with pressure in the pelvis.
- Contractions move in a wave-like motion from the top of the uterus to the bottom.
- Some women describe contractions as strong menstrual cramps.
- Unlike false labor contractions or Braxton Hicks contractions, true labor contractions don’t stop when you change your position or relax.
- Although they may be uncomfortable, you’ll be able to relax in between contractions.
Diarrhea
You may notice your poops are loose or watery. This may mean you are within a day or two of labor beginning.
Weight loss
While you’re pregnant, it may seem like you’re never going to stop gaining weight. But many women actually lose a few pounds in the days leading up to labor.
Nesting instinct
Some women find themselves with an urge to get ready shortly before their baby’s arrival. That’s known as the nesting instinct.
- You may have a sudden burst of energy after weeks of feeling more and more tired.
- You may feel like shopping, cooking, or cleaning the house.
- Be careful not to overdo it. Childbirth will take a lot of energy.
Activity of the baby
Your baby may move less as you get closer to the start of labor, but let your doctor know. It can sometimes be a sign of a problem.
It can sometimes be a sign of a problem.
Cramps and back pain
It may be hard to recognize a contraction, especially with your first baby. Many women have what feels like menstrual cramps in the lower abdomen. They may stay the same or they may come and go. You might also have pain in your lower back that either stays or comes and goes.
Looser joints
If you find yourself “waddling” as your pregnancy winds down, that’s just your body getting ready for the job ahead. A hormone called relaxin loosens up the ligaments around your pelvis to make it easier for the baby to pass through.
Water breaking
The rupture of the amniotic membrane (the fluid-filled sac that surrounds the baby during pregnancy) may happen before you get to the hospital.
- It may feel either like a sudden gush of fluid or a trickle of fluid that leaks steadily.
- The fluid is usually odorless and may look clear or straw-colored.
- If your "water breaks," write down the time this happens, how much fluid is released, and what the fluid looks like, then let your health care provider know. They’ll advise you what to do next.
- Not all women have their water break when they’re in labor. Many times the doctor will rupture the amniotic membrane in the hospital.
Effacement
During labor, your cervix gets shorter and thins out in order to stretch and open around your baby's head. The shortening and thinning of the cervix is called effacement. Your health care provider will be able to tell you if there are changes to the cervix during a pelvic exam.
Effacement is measured in percentages from 0% to 100%. If there are no changes to the cervix, it is described as 0% effaced. When the cervix is half the normal thickness, it is 50% effaced. When the cervix is completely thinned out, it is 100% effaced.
Dilation
The stretching and opening of your cervix is called dilation and is measured in centimeters, with complete dilation being at 10 centimeters.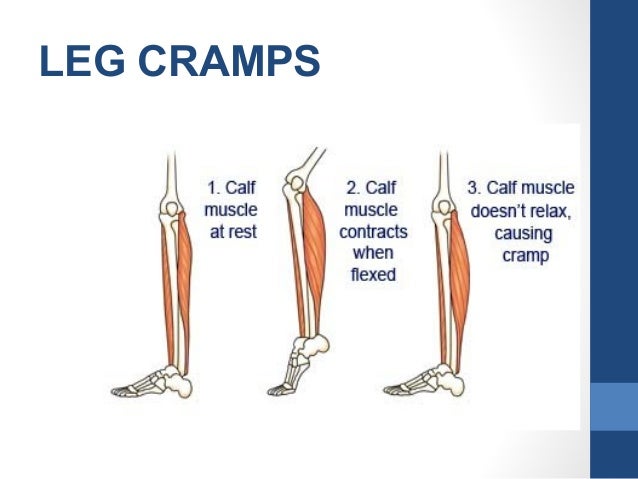
Effacement and dilation are a direct result of effective uterine contractions. Progress in labor is measured by how much the cervix has opened and thinned to allow your baby to pass through the vagina.
What's the Difference Between True Labor and False Labor?
Before "true" labor begins, you may have "false" labor pains, also known as Braxton Hicks contractions. These irregular uterine contractions are perfectly normal and may start to occur in your second trimester, although more commonly in your third trimester of pregnancy. They are your body's way of getting ready for the "real thing."
What do Braxton Hicks contractions feel like?
Braxton Hicks contractions can be described as a tightening in the abdomen that comes and goes. These contractions do not get closer together, do not increase with walking, do not increase in duration, and do not feel stronger over time as they do when you are in true labor.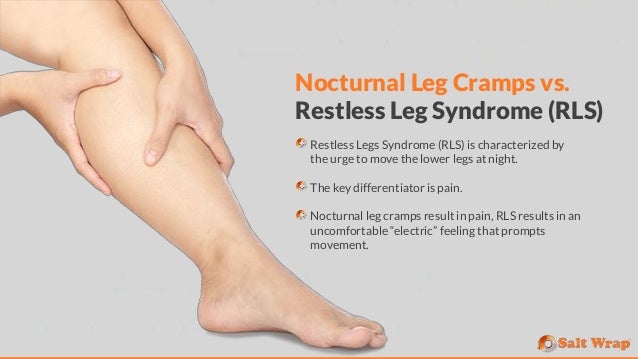
How do I know when I am in true labor?
To figure out if the contractions you are feeling are the real thing, ask yourself the following questions.
| Contraction Characteristics | False Labor | True Labor |
| How often do the contractions occur? | Contractions are often irregular and do not get closer together. | Contractions come at regular intervals and last about 30-70 seconds. As time progresses, they get closer together. |
| Do they change with movement? | Contractions may stop when you walk or rest, or may even stop if you change positions. | Contractions continue despite movement or changing positions. |
| How strong are they? | Contractions are usually weak and do not get much stronger. Or they may be strong at first and then get weaker. | Contractions steadily increase in strength. |
| Where do you feel the pain? | Contractions are usually only felt in the front of the abdomen or pelvic region. | Contractions usually start in the lower back and move to the front of the abdomen. |
Time Your Contractions
When you think you are in true labor, start timing your contractions. To do this, write down the time each contraction starts and stops or have someone do it for you. The time between contractions includes the length or duration of the contraction and the minutes in between the contractions (called the interval).
Mild contractions generally begin 15 to 20 minutes apart and last 60 to 90 seconds. The contractions become more regular until they are less than 5 minutes apart. Active labor (the time you should come into the hospital) is usually characterized by strong contractions that last 45 to 60 seconds and occur 3 to 4 minutes apart.
The contractions become more regular until they are less than 5 minutes apart. Active labor (the time you should come into the hospital) is usually characterized by strong contractions that last 45 to 60 seconds and occur 3 to 4 minutes apart.
Try to Relax
It’s best to go through the first stage of labor (called the Latent Phase) in the comfort of your home. Here are some tips to help you manage:
- Distract yourself -- take a walk, watch a movie.
- Soak in a warm tub or take a warm shower. But, ask your health care provider if you can take a tub bath if your water has broken.
- Rest. Try to sleep or take a nap if it is in the evening. You need to store up your energy for active labor.
When Should I Call My Health Care Provider or Go to the Hospital?
When you suspect you are in true labor, call your health care provider. Also, call:
- If you think your water has broken.
- If you’re bleeding (more than spotting).

- If the baby seems to be moving less than normal.
- When your contractions are very uncomfortable and have been coming every 5 minutes for an hour.
- If you have any of the signs of labor, but you haven’t reached your 37th week of pregnancy. You may be going into labor before your baby is ready and will need medical help right away.
Your health care provider will give you specific guidelines about when you should get ready to come to the hospital.
Muscle cramps - treatment, symptoms, causes, diagnosis
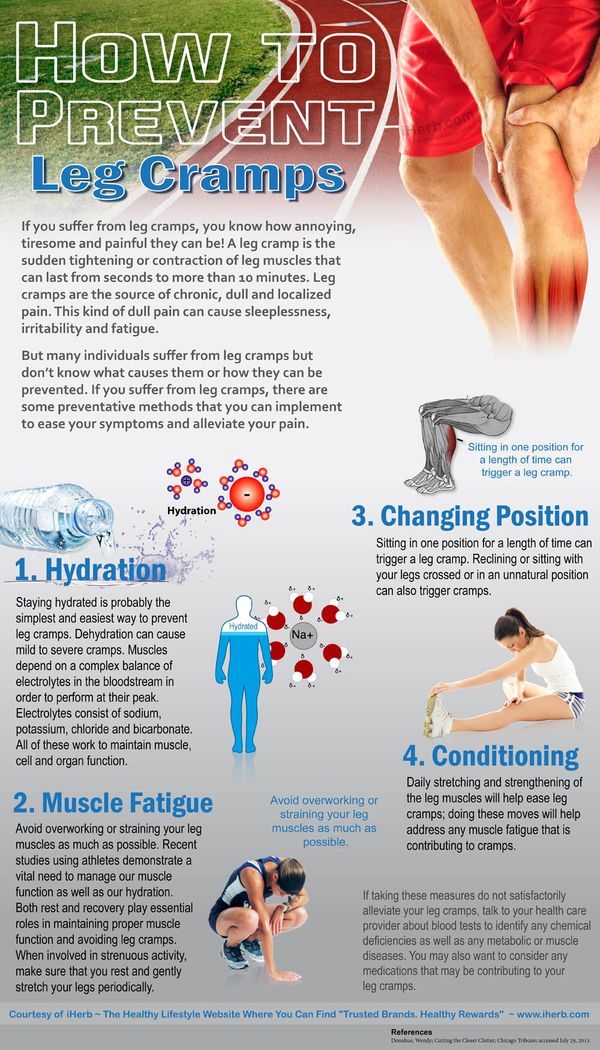
- Muscle cramps are involuntary and intense muscle contractions without a period of relaxation.
- Almost everyone has experienced a seizure episode at least once in their life.
- There are different types of seizures and different causes.
- Many different medications can cause muscle cramps.
- In most cases, muscle cramps can be stopped by relaxing (stretching) the muscle. nine0004
- Muscle cramps can often be prevented by measures such as good nutrition with sufficient micronutrients and adequate fluid intake.

Muscle cramps is an involuntary and violent contraction of a muscle without a period of relaxation. When muscles that can be controlled voluntarily, such as the muscles of the arms or legs, are used, they alternately contract and relax as certain movements are made in the limbs. The muscles that support the head, neck and torso work in synchrony and maintain the position of the body. A muscle (or even a few muscle fibers) can be involuntarily in a state of spasm. If the spasm is strong and persistent, then this leads to the appearance of convulsions. Muscle cramps are often visualized or palpated in the region of the muscle involved. nine0019
Muscle cramps can last from a few seconds to a quarter of an hour, and sometimes longer. It is also not uncommon for the seizures to recur until the muscle relaxes. The spasmodic contractions may involve part of a muscle, the entire muscle, or several muscles that usually contract at the same time when performing movements, such as flexing several fingers. In some cases, cramps can be simultaneously in the antagonist muscles responsible for movements in opposite directions. Muscle cramps are widespread. Almost all people (according to some studies about 95% of people) have experienced seizures at some point in their lives. Muscle cramps are common in adults and become more common with age, but cramps can still occur in children. In any muscle (skeletal) in which voluntary movements are performed, there may be cramps. Cramps of the limbs, legs and feet, and especially the calf muscle, are very common.
In some cases, cramps can be simultaneously in the antagonist muscles responsible for movements in opposite directions. Muscle cramps are widespread. Almost all people (according to some studies about 95% of people) have experienced seizures at some point in their lives. Muscle cramps are common in adults and become more common with age, but cramps can still occur in children. In any muscle (skeletal) in which voluntary movements are performed, there may be cramps. Cramps of the limbs, legs and feet, and especially the calf muscle, are very common.
Types and causes of muscle cramps
Skeletal muscle cramps can be divided into four main types. These include "true" seizures, tetanic seizures, contractures, and dystonic seizures. Seizures are classified according to the causes of the seizures and the muscle groups they affect. nine0019
Types of muscle cramps
True cramps . True cramps involve part or all of a muscle or group of muscles that normally function together, such as the muscles involved in flexing several adjacent fingers.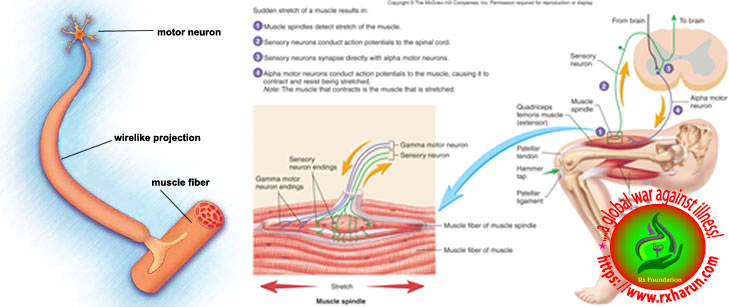 Most researchers agree that true cramps are caused by increased excitability of nerves that stimulate muscle contractions. They are overwhelmingly the most common type of skeletal muscle cramps. True seizures can occur in a variety of circumstances. nine0019
Most researchers agree that true cramps are caused by increased excitability of nerves that stimulate muscle contractions. They are overwhelmingly the most common type of skeletal muscle cramps. True seizures can occur in a variety of circumstances. nine0019
Injuries : Persistent muscle spasms may occur as a defense mechanism after an injury such as a broken bone. In this case, as a rule, spasm allows you to minimize movement and stabilize the area of injury. Injury to just the muscle can also lead to muscle spasm.
Vigorous activity: true cramps are usually associated with active muscle loading and muscle fatigue (during sports or unusual activities). Such convulsions can occur both during the activity and after, sometimes many hours later. In addition, muscle fatigue from sitting or lying down for a long period of time in an awkward position or any repetitive movement can also cause cramps. Older people are more at risk of seizures during vigorous or strenuous physical activity. nine0019
nine0019
Rest seizures : Rest seizures are very common, especially in the elderly, but can occur at any age, including childhood. Rest spasms often occur at night. Night cramps, while not life threatening, can be painful, disrupt sleep, and may recur frequently (i.e., many times a night and/or many nights a week). The actual cause of nighttime cramps is unknown. Sometimes these cramps are initiated by a movement that contracts the muscles. An example would be stretching the foot in bed, which shortens the calf muscle, where cramps are most common. nine0019
Dehydration : Sports and other strenuous exercise may cause excessive fluid loss through sweat. With this type of dehydration, the likelihood of true seizures increases. These cramps most often occur in warm weather and may be an early sign of heat stroke. Chronic dehydration due to diuretics and poor fluid intake can similarly lead to seizures, especially in the elderly. Seizures can also be associated with a lack of sodium.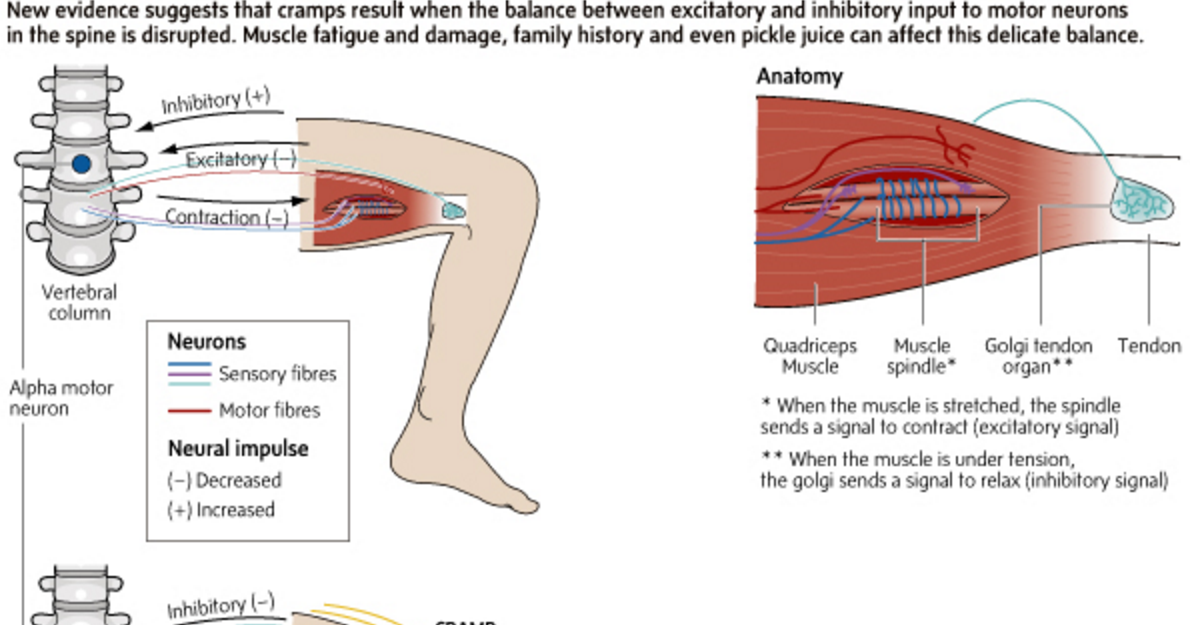 nine0019
nine0019
Redistribution of fluids in the body: true convulsions can also be noted in conditions where there is an unusual distribution of fluid in the body. An example is cirrhosis of the liver, in which there is an accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity (ascites). Similarly, seizures are a relatively common complication of the rapid changes in body fluids that occur during dialysis for kidney failure.
Low levels of electrolytes in the blood (calcium, magnesium): low blood levels of calcium or magnesium directly increase the excitability of the nerve endings innervating the muscles. This may be a predisposing factor for the spontaneous true seizures that many older people experience, and these seizures are also common in pregnant women. Low levels of calcium and magnesium are common in pregnant women, especially if these minerals are not getting enough from the diet. Seizures occur in any circumstance that reduces the availability of calcium or magnesium in body fluids, such as diuretics, hyperventilation, excessive vomiting, lack of calcium and/or magnesium in the diet, insufficient absorption of calcium due to vitamin D deficiency, reduced parathyroid function.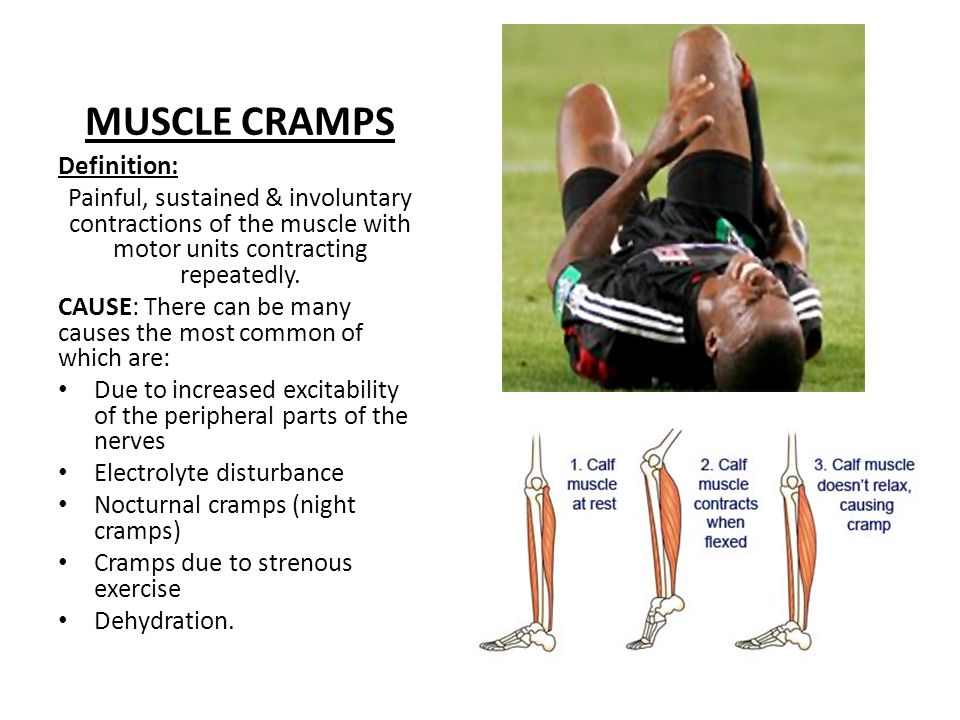 nine0019
nine0019
Low potassium levels: Low blood potassium levels sometimes cause muscle cramps, although muscle weakness is more common in hypokalemia.
Tetany
Tetany activates all nerve cells in the body, which then stimulate muscle contraction. In this type, convulsive contractions occur throughout the body. The name tetany comes from the spasms that occur when tetanus toxin affects the nerves. However, this name for this type of cramp is now widely used to refer to muscle cramps in other conditions, such as low blood levels of calcium and magnesium. Low levels of calcium and magnesium increase the activity of the nervous tissue non-specifically, which can lead to the appearance of tetanic seizures. Often these seizures are accompanied by signs of hyperactivity of other nerve functions in addition to muscle hyperstimulation. For example, low blood calcium not only causes muscle spasm in the hands and wrists, but it can also cause numbness and tingling sensations around the mouth and other areas of the body.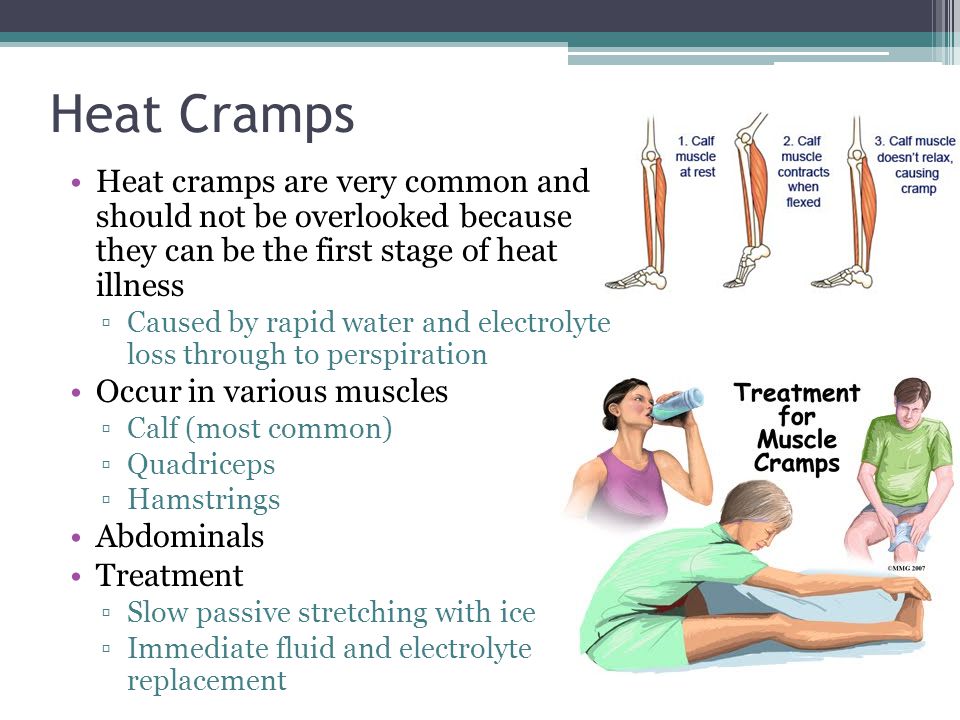 nine0019
nine0019
Occasionally, tetanic seizures are indistinguishable from true seizures. Additional changes in sensation or other nerve function may not be noticeable, as the pain of a cramp may mask other symptoms.
Contractures
Contractures occur when the muscles cannot relax for an even longer period than in the main types of muscle cramps. Constant spasms are caused by the depletion of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) - the energy intracellular substrate of the cell. This prevents relaxation of the muscle fibers. The nerves are inactive in this type of muscle cramp. nine0019
Contracture may be the result of genetic inheritance (eg, McArdle disease, which is a defect in the breakdown of glycogen to sugar in muscle cells) or acquired conditions (eg, hyperthyroid myopathy, which is a muscle disease associated with an overactive thyroid gland) . Convulsions of the type of contractures are rare.
Dystonic seizures
The last category of seizures are dystonic seizures, in which muscles not involved in the intended movement are affected and contracted. Muscles that are involved in this type of cramp include antagonistic muscles that usually work in the opposite direction of the intended movement and/or others that enhance the movement. Some dystonic spasms usually affect small muscle groups (eyelids, cheeks, neck, larynx, etc.). The arms and hands may be affected during repetitive movements such as writing (writer's cramp), playing a musical instrument. These activities can also lead to true cramps due to muscle fatigue. Dystonic seizures are not as common as true seizures. nine0019
Muscles that are involved in this type of cramp include antagonistic muscles that usually work in the opposite direction of the intended movement and/or others that enhance the movement. Some dystonic spasms usually affect small muscle groups (eyelids, cheeks, neck, larynx, etc.). The arms and hands may be affected during repetitive movements such as writing (writer's cramp), playing a musical instrument. These activities can also lead to true cramps due to muscle fatigue. Dystonic seizures are not as common as true seizures. nine0019
Other types of seizures
Some seizures are caused by a number of nerve and muscle disorders. For example, these are diseases such as amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (Lou Gehrig's disease), accompanied by muscle weakness and atrophy; radiculopathy in degenerative diseases of the spine (hernia, disc protrusion, osteophytes), when root compression is accompanied by pain, impaired sensitivity and sometimes convulsions. Seizures can also occur with peripheral nerve damage, such as diabetic neuropathy.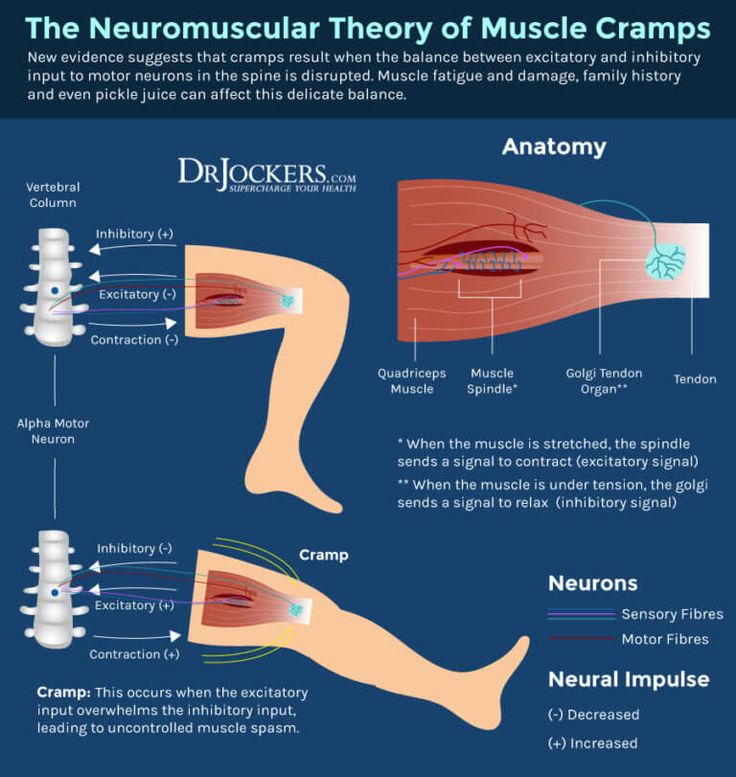 nine0019
nine0019
Crumpy . This type of cramps, as a rule, describes cramps in the calf muscle, and associate their appearance with muscle overstrain and the presence of degenerative changes in the spine (osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine, lumbar ischialgia). In addition, cramps are possible with disorders of the vascular circulation in the lower extremities (with obliterating endarteritis or post-thrombophlebitic syndrome). Also, various biochemical disorders in the triceps muscle of the leg can be the cause of cramps. nine0019
Many medicines can cause seizures. Strong diuretics such as furosemide or vigorous fluid removal from the body, even with less potent diuretics, can induce seizures as dehydration and sodium loss occur. At the same time, diuretics often cause loss of potassium, calcium and magnesium, which can also cause seizures.
Medicines such as donepezil (Aricept, which is used to treat Alzheimer's disease) and neostigmine (Prostigmine, used for myasthenia gravis), asraloxifene (Evista) is used to prevent osteoporosis in postmenopausal women - may cause seizures. Tolcapone (Tasmar), which is used to treat Parkinson's disease, has been shown to cause muscle cramps in at least 10% of patients. True seizures have been reported with nifedipine and the drugs Terbutaline (Brethine) and albuterol (Proventil, Ventolin). Some medicines used to lower cholesterol, such as lovastatin (Mevacor), can also cause seizures. nine0019
Tolcapone (Tasmar), which is used to treat Parkinson's disease, has been shown to cause muscle cramps in at least 10% of patients. True seizures have been reported with nifedipine and the drugs Terbutaline (Brethine) and albuterol (Proventil, Ventolin). Some medicines used to lower cholesterol, such as lovastatin (Mevacor), can also cause seizures. nine0019
Seizures are sometimes observed in addicts during the cessation of sedatives.
A lack of certain vitamins can also lead directly or indirectly to muscle cramps. These include deficiencies in thiamine (B1), pantothenic acid (B5), and pyridoxine (B6). The exact role of deficiency of these vitamins in causing seizures is unknown.
Poor circulation in the legs leads to a lack of oxygen in the muscle tissue and can cause severe muscle pain (intermittent claudication) that occurs when walking. It usually occurs in the calf muscles. But the pain in vascular disorders in such cases is not caused by the muscle cramp itself. This pain may be more related to the buildup of lactic acid and other chemicals in muscle tissue. Cramps in the calf muscles can also be associated with a violation of the outflow of blood in varicose veins and, as a rule, cramps in the calf muscles occur at night. nine0019
This pain may be more related to the buildup of lactic acid and other chemicals in muscle tissue. Cramps in the calf muscles can also be associated with a violation of the outflow of blood in varicose veins and, as a rule, cramps in the calf muscles occur at night. nine0019
Symptoms and diagnosis of muscle cramps
Characteristically, a cramp is often quite painful. As a rule, the patient has to stop activities and urgently take measures to relieve seizures; the person is unable to use the affected muscle during the seizure. Severe cramps may be accompanied by soreness and swelling, which can sometimes persist for up to several days after the cramp has subsided. At the time of the cramp, the affected muscles will bulge, feel hard and tender to the touch. nine0019
Diagnosis of seizures is usually not difficult, but finding out the causes may require both a thorough medical history and instrumental and laboratory examinations.
Treatment
Most seizures can be interrupted by stretching the muscle. For many leg and foot cramps, this stretch can often be achieved by standing up and walking. With cramps in the calf muscles, it is possible to bend the ankle with the help of the hand, while lying in bed with the leg extended straight. In writing spasm, pressing the hand against the wall with the fingers down will stretch the flexors of the fingers. nine0019
For many leg and foot cramps, this stretch can often be achieved by standing up and walking. With cramps in the calf muscles, it is possible to bend the ankle with the help of the hand, while lying in bed with the leg extended straight. In writing spasm, pressing the hand against the wall with the fingers down will stretch the flexors of the fingers. nine0019
A gentle muscle massage can also be performed to relax a spasmodic muscle. If the cramp is associated with fluid loss, as is often the case with strenuous exercise, rehydration and restoration of electrolyte levels is necessary.
Muscle relaxants may be used in the short term in certain situations to allow muscles to relax during injury or other conditions (eg, radiculopathy). These drugs include cyclobenzaprine (Flexeril), orphenadrine (NORFLEX), and baclofen (Lioresal). nine0019
In recent years, injections of therapeutic doses of botulinum toxin (Botox) have been successfully used for certain dystonic muscle disorders that are localized in a limited group of muscles. A good response may last several months or more, and injections may be repeated.
A good response may last several months or more, and injections may be repeated.
Treatment of seizures that are associated with specific diseases, usually focuses on the treatment of the underlying disease.
In cases where seizures are severe, frequent, prolonged, difficult to treat, or not associated with an obvious cause, both additional investigation and more intensive treatment are required. nine0019
Prevention of seizures
Adequate nutrition with sufficient fluids and electrolytes is essential to prevent possible seizures, especially during strenuous exercise or during pregnancy.
Night cramps and other rest cramps can often be prevented with regular stretching exercises, especially if done before bed.
Magnesium and calcium supplements are also good for preventing seizures, but caution is required when prescribing them in the presence of renal insufficiency. In the presence of hypovitaminosis, it is necessary to take vitamins of group B, vitamin D, E. nine0019
nine0019
If the patient is taking diuretics, it is necessary to take potassium supplements.
Recently, the only drug that is widely used for the prevention, and sometimes for the treatment of seizures, is quinine. Quinine has been used for many years in the treatment of malaria. The action of quinine is due to a decrease in muscle excitability. However, quinine has a number of serious side effects that limit its use to all groups of patients (nausea, vomiting, headaches, heart rhythm disturbances, hearing impairment, etc.). nine0019
Seizures - Diseases - Medical Center Health Clinic
Description
Cramps are paroxysmal, involuntary contraction of muscles as a result of their overstrain. Convulsions occur suddenly and do not last long, but after a certain interval of time they can be repeated. They usually cause severe pain. Young people complain of painful cramps much less often than the elderly and children. Such muscle contractions occur predominantly at night when the body is warm and asleep, or during muscle activity. nine0019
nine0019
The calf muscles are most susceptible to cramps, less so are the hips, back, neck and abdomen. Cramps can be both in one muscle and cover a group of muscles.
Causes
Cramps appear due to insufficient blood circulation in the muscles, especially during physical exertion. For some, convulsions appear and intensify when exposed to external stimuli - pricking the body with a needle, sudden loud sounds, alcohol abuse.
A factor in the development of seizures in athletes is a lack of salt in the body, caused by increased sweating.
Even monotonous repetitive movements, such as typing on a keyboard or moving a computer mouse, can cause seizures.
Night cramps are the result of a complex of psychophysiological disorders (low blood circulation and stress).
If the same muscle groups are under load, then when tired, they can also be subject to convulsive contractions.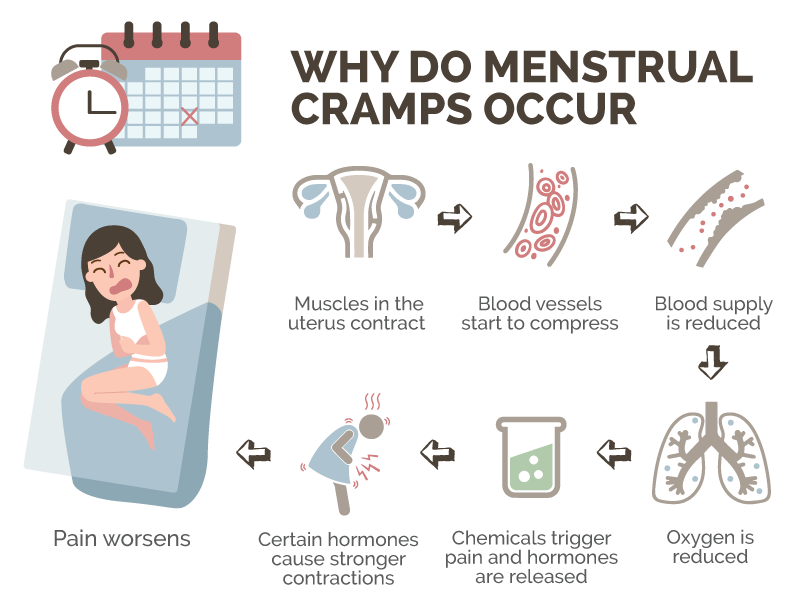 This is especially true for people who work standing up. nine0019
This is especially true for people who work standing up. nine0019
Sometimes convulsions are a consequence of diseases of the nervous system (epilepsy, tetanus, neurosis), poisoning, metabolic disorders or the activity of the endocrine glands.
Spasms of the calf muscles are also an independent disease, and may be accompanied by any disease (for example, varicose veins). They occur during a long walk, swimming.
Convulsive contractions of the muscles of the glottis can be caused by irritating odors or gases. Often they lead to malnutrition and changes in the functions of the brain and heart, respiratory arrest. nine0019
Seizure symptoms
Symptoms of seizures range from mild to very severe. With a mild form, confusion, darkening of the eyes, snorting, convulsive twitching and tingling in a certain part of the body are possible. Moderate severity - when urinary and fecal incontinence is added to the previous symptoms, short-term fainting.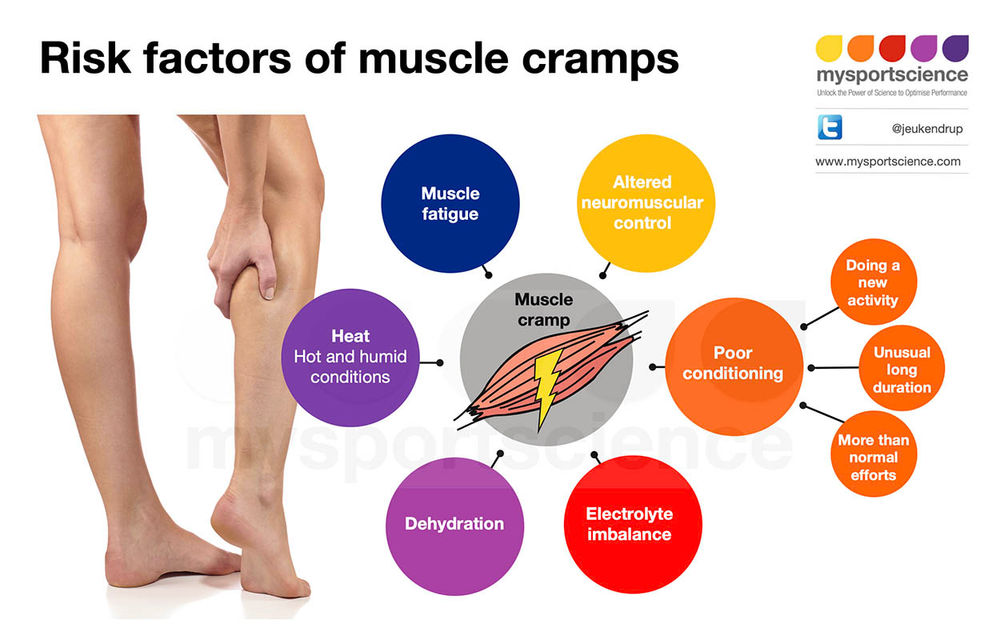
The most dangerous form of seizures is an epileptic seizure. In this case, there is an inexplicable feeling of fear and numbness, nausea, dizziness, salivation, foam from the mouth, deviation of the direction of the eyes and head. Convulsions last more than two minutes, after which there is a loss of consciousness. nine0019
Seizure treatment
Treatment of seizures is carried out depending on the underlying disease. Applicable anticonvulsants: phenobarbital, hexamidine, benzonal, diphenin. Thermal procedures, local massage, a clear mode of work and rest have a positive effect. With convulsive status or recurrent convulsions, emergency medical care is necessary, otherwise there is a risk of developing cerebral edema, respiratory depression and other vital functions.
In order to prevent dehydration in hot weather, the patient is advised to drink cold water with table salt dissolved in it (1 teaspoon of salt per liter of water).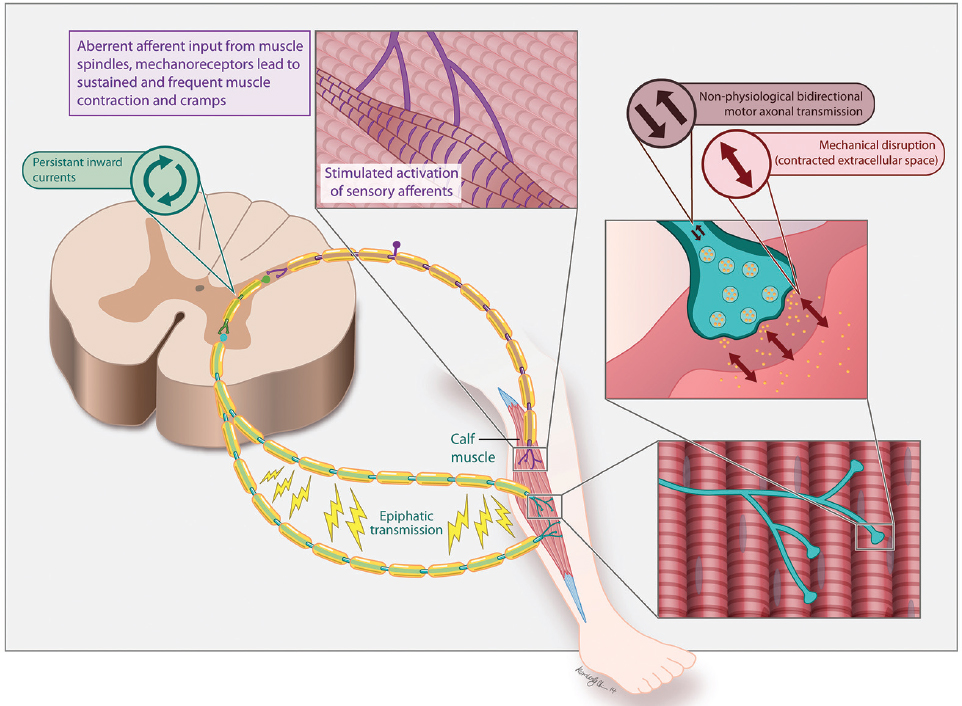
Another way to improve local circulation with recurring cramps is to apply alternately hot and cold compresses to the affected area.
If the cramp has already begun, the attack cannot be stopped. Those around are able to call for medical help as soon as possible, as well as protect the patient from injuries and bodily harm that he can inflict on himself. nine0019
Self-help in the event of a cramp is stretching the affected muscle. For example, to get rid of a spasm in the calf muscle, you need to overcome the pain and push the heel down to lengthen the muscle.
General convulsions and loss of consciousness are symptoms of epilepsy. Before the doctor arrives, you need to create a calm environment for the patient, lay him down in such a way as to help the muscles relax. If breathing problems are observed, provide fresh air or give oxygen from an oxygen bag. A person suffering from epilepsy should always have a note with him with information about the number and duration of epileptic seizures.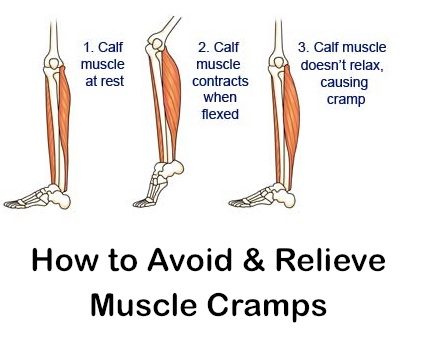




1.jpg)