Congestion with pregnancy
Relief for Ongoing Nasal Congestion Is Possible
If you're expecting a baby, you may be dealing with a stuffy nose that doesn’t seem to go away. This hassle is called pregnancy rhinitis. The cause of this condition isn’t really clear. However, it may be caused by hormonal changes.Having a history of allergies or asthma does not raise your risk of getting pregnancy rhinitis.
More than just a stuffy nose
Pregnancy rhinitis is an inflammation of the mucous membranes lining the nose. This causes nasal congestion. Increased blood flow to the nasal passages and enlargement of the nasal veins also play a role.
Symptoms occur during pregnancy. They can last for several weeks. On top of feeling uncomfortable, your sleep may be disrupted. This is because the congestion gets worse when you lie down. This may make you to feel more tired during the day. Long-lasting congestion also can lead to complications. These can include sinusitis and ear infections.
Be cautious when seeking treatment
Many women use non-prescription, over-the-counter (OTC) decongestant sprays to open up their nasal passages. Know that these medicines don’t work for pregnancy rhinitis. These medicines may give you temporary relief. However, they may actually make your symptoms worse and lead to a complete nasal blockage.
How can you get relief from pregnancy rhinitis? Experts say you can breathe easy with these measures:
-
Don’t use OTC nasal decongestants.
-
Drink plenty of fluids.
-
Increase the humidity levels in your home. Use a humidifier.
-
Don’t use nasal irritants, such as cigarette smoke.
-
Get moving. Regular, moderate-intensity exercise can reduce congestion. It can also help you sleep better. But first, check with your healthcare provider to see what exercises are safe for you.
-
When you go to sleep, raise the head of your bed. For instance, use an extra pillow or a wedge.
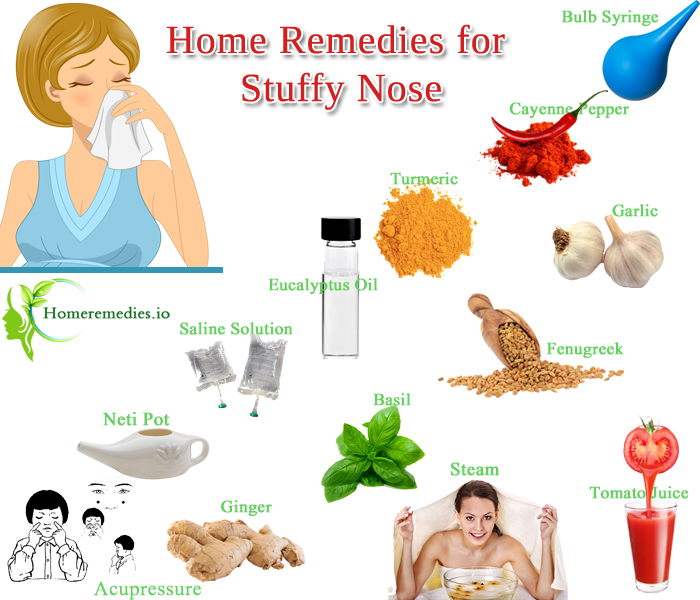
-
Ask your healthcare provider about using OTC nasal strips and saline sprays or drops.
The good news? Even if you don’t do anything, you can expect your stuffy nose to clear up soon after your baby is born. It often goes away within two weeks of childbirth.
Online Medical Reviewer: Bowers, Nancy, RN, BSN, MPH Foley, Maryann, RN, BSN
Date Last Reviewed: 4/12/2016
© 2000-2019 The StayWell Company, LLC. 800 Township Line Road, Yardley, PA 19067. All rights reserved. This information is not intended as a substitute for professional medical care. Always follow your healthcare professional's instructions.
© 2000-2019 The StayWell Company, LLC. 800 Township Line Road, Yardley, PA 19067. All rights reserved. This information is not intended as a substitute for professional medical care. Always follow your healthcare professional's instructions.
Baby (and tissues!) on board: Tips for managing pregnancy rhinitis | Your Pregnancy Matters
×
What can we help you find?Refine your search: Find a Doctor Search Conditions & Treatments Find a Location
Appointment New Patient Appointment
or Call214-645-8300
MedBlog
Your Pregnancy Matters
October 6, 2020
Your Pregnancy Matters
Robyn Horsager-Boehrer, M. D. Obstetrics and Gynecology
D. Obstetrics and Gynecology
When you think of side effects or symptoms brought on by pregnancy, nasal congestion and runny nose are not typically among the first to come to mind.
But maybe they should. Having a stuffy nose, difficulty breathing or sleeping, and snoring when pregnant can be alarming, especially amid the COVID-19 pandemic and the start of flu season.
Pregnancy rhinitis, also called gestational rhinitis, is a common ailment in the second and third trimesters, affecting approximately 20% of women. Characterized by inflammation and swelling of the mucous membranes in the nose, pregnancy rhinitis symptoms include congestion (nasal obstruction), sneezing, postnasal drip, and runny nose.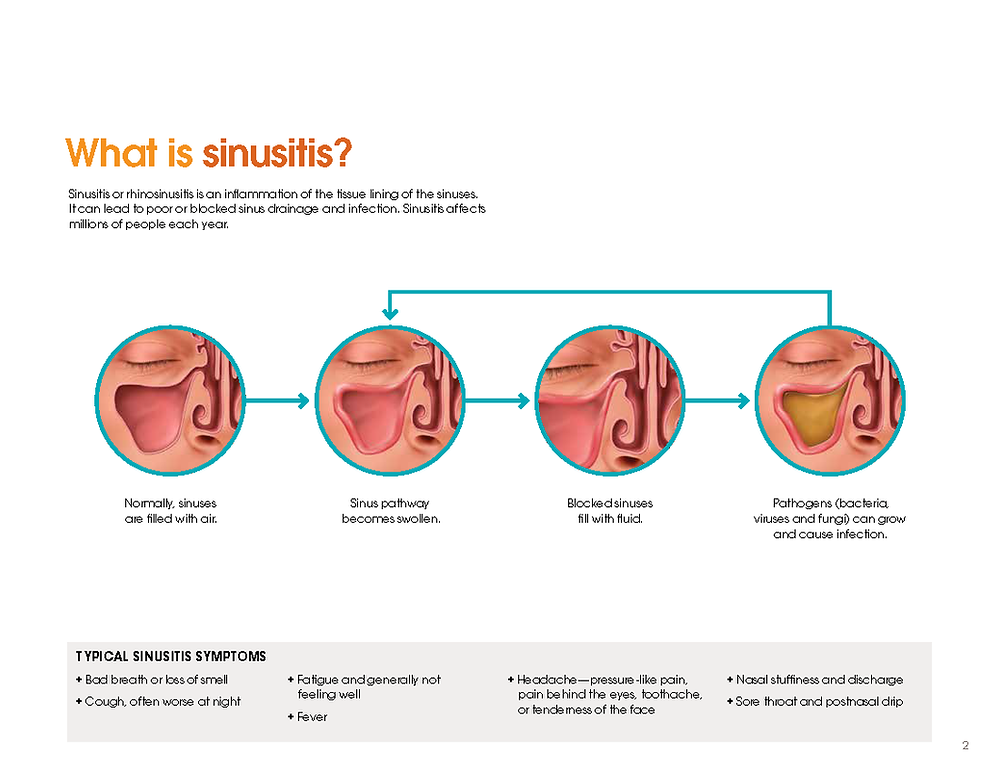 These symptoms can also lead to poor sleep when your growing belly might already be making it difficult to rest.
These symptoms can also lead to poor sleep when your growing belly might already be making it difficult to rest.
All these issues can dramatically affect your mood and quality of life. The good news is that, for most patients, pregnancy rhinitis is temporary and there are safe, effective treatments available.
I've invited my colleague, Ashleigh Halderman, M.D., an ear, nose, and throat specialist at UT Southwestern to explain in more detail the causes of pregnancy rhinitis and how patients can manage their symptoms.
What causes pregnancy rhinitis?
Dr. Ashleigh HaldermanThe root cause of rhinitis can be allergic (affected by environmental irritants) or non-allergic (caused by infection). However, we are still learning how rhinitis is related to pregnancy.
We know that smoking, as well as having chronic rhinitis before pregnancy, predisposes patients to developing pregnancy rhinitis. Research suggests a few more potential causes:
Research suggests a few more potential causes:
- Having extra fluid in the body: During pregnancy, the body makes more blood and fluids, which can cause swelling, even in unexpected places such as the nasal passages. Blood vessels in the nose can swell with this additional volume, causing stuffiness.
- Higher levels of estrogen: Estrogen in older formulations of birth control pills has been associated with a side effect of nasal obstruction. However, in studies of the menstrual cycle, we don't see congestion with fluctuating estrogen levels. So, the connection remains unclear for now.
- Creation of human growth hormone: The placenta creates a variant of the human growth hormone (HGH), which has been associated with nasal symptoms in other conditions. For example, tumors that grow on the pituitary glands secrete growth hormones, which can cause severe nasal congestion.
Gestational rhinitis is under-researched. Data to date suggest no known association of rhinitis with pre-existing asthma, maternal age, duration of pregnancy, or the number of times a patient has been pregnant.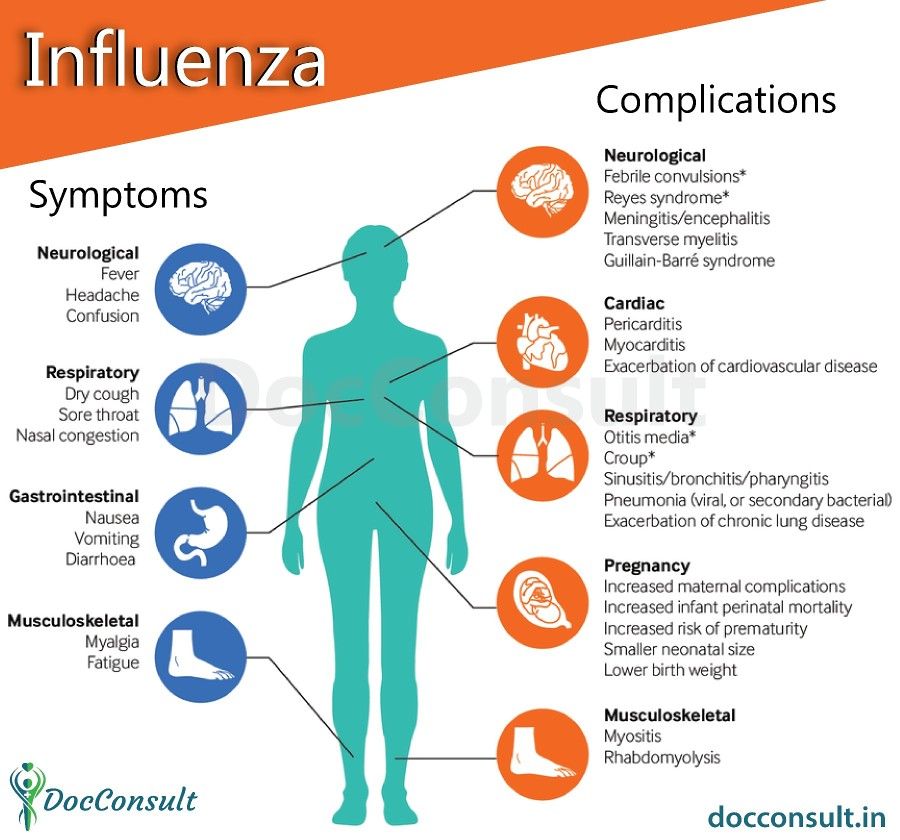 However, a recent study found that patients carrying female babies were diagnosed significantly more often than patients carrying male babies.
However, a recent study found that patients carrying female babies were diagnosed significantly more often than patients carrying male babies.
Related reading: How to manage allergies and asthma during pregnancy
How long do symptoms last?
The annoying, uncomfortable symptoms of pregnancy rhinitis typically last six weeks or longer. For most patients, symptoms typically resolve two weeks after delivery.
Approximately a third of patients who had chronic rhinitis before pregnancy will have the same level of symptoms during, and a third will experience worsening of rhinitis symptoms. However, the remaining third will have less severe or no symptoms during pregnancy. I've had many women tell me they've felt the best, sinus-wise, when they were pregnant. However, there's no specific reason why this occurs.
Related reading: 5 weird pregnancy symptoms you might not know about
What treatments are available?
The first step toward relief is a visit with your doctor to rule out infection, such as COVID-19, influenza, or sinusitis. We may also recommend testing for concerns such as sinusitis or pregnancy tumor (pyogenic granuloma) – a non-cancerous growth of blood vessels that may appear during pregnancy.
We may also recommend testing for concerns such as sinusitis or pregnancy tumor (pyogenic granuloma) – a non-cancerous growth of blood vessels that may appear during pregnancy.
From there, your doctor and Ob/Gyn may suggest:
- Getting regular exercise: Working out has been shown to significantly help relieve nasal congestion and regulate the sleep cycle. All the more reason to bust a move during pregnancy!
- Elevating your mattress: Try positioning the mattress so your whole body is situated at a 45-degree angle. While not widely studied, patients have reported that this helps clear the nasal passages enough to sleep.
- Using a humidifier: Adding a little moisture to the air can help alleviate nasal irritation. Many patients use them at night to wake up feeling less stuffy.
- Trying a sinus wash: Nasal saline sprays or sinus irrigation systems such as a neti pot can help clear the sinuses. Make sure to use distilled or boiled (and cooled) water – using water straight from the tap is not recommended.

Topical decongestants such as Afrin can be incredibly and immediately effective, but there is a risk of dependency. If you use this type of treatment more than once or twice a week, your nose can become "addicted" to it, which can lead to rhinitis medicamentosa – the spray will stop working as well, and your symptoms may get worse. Also, unlike gestational rhinitis, rhinitis medicamentosa won’t resolve after you deliver. It will only resolve when you stop using topical decongestants.
In general, pregnant patients can take decongestants that include pseudoephedrine as directed. However, we always recommend talking with your Ob/Gyn first, especially if you have high blood pressure.
Your Ob/Gyn might also recommend a steroid nasal spray, such as Flonase or Rhinocort, for severe symptoms. If you were using a spray to manage chronic rhinitis prior to pregnancy, your Ob/Gyn might advise you to keep using it during pregnancy. It is generally considered safe to use these products while breastfeeding, under your Ob/Gyn's guidance.
Your body will change in interesting ways during pregnancy. If you have new or unusual symptoms, call your doctor. We'll help you sort out what's normal from what could be a sinus infection or respiratory illness.
To talk with a doctor about nasal symptoms during pregnancy, call 214-645-8300 or request an appointment online.
More in: Your Pregnancy Matters
Your Pregnancy Matters
- Robyn Horsager-Boehrer, M.D.
December 20, 2022
Your Pregnancy Matters
- Robyn Horsager-Boehrer, M.
 D.
D.
December 13, 2022
Pediatrics; Your Pregnancy Matters
- Jessica Morse, M.D.
December 6, 2022
Your Pregnancy Matters
- Shivani Patel, M.
 D.
D.
November 22, 2022
Your Pregnancy Matters
- Robyn Horsager-Boehrer, M.D.
November 15, 2022
Your Pregnancy Matters
- Robyn Horsager-Boehrer, M.D.
November 7, 2022
Mental Health; Your Pregnancy Matters
- Robyn Horsager-Boehrer, M.
 D.
D.
October 11, 2022
Prevention; Your Pregnancy Matters
- Robyn Horsager-Boehrer, M.D.
October 4, 2022
Mental Health; Your Pregnancy Matters
- Meitra Doty, M.
 D.
D.
September 27, 2022
More Articles
Constipation during pregnancy: causes, recommendations
In addition, constipation in pregnant women may be caused by changes in the nature of food, the use of smooth muscle-relaxing drugs (lowering uterine activity, progesterone) 3 or mineral supplements containing iron and calcium4. Sometimes a woman has to lie down all the time, and at least minimal physical activity is necessary to maintain a normal bowel movement 3 . Another reason for the formation of constipation in pregnant women can be a decrease in fluid intake, starting from the earliest dates 4 .
In addition, constipation in pregnant women may be caused by changes in the nature of food, the use of smooth muscle-relaxing drugs (lowering uterine activity, progesterone) 3 or mineral supplements containing iron and calcium4. Sometimes a woman has to lie down all the time, and at least minimal physical activity is necessary to maintain a normal bowel movement 3 . Another reason for the formation of constipation in pregnant women can be a decrease in fluid intake, starting from the earliest dates 4 .
Sometimes a woman has to lie down all the time, and at least minimal physical activity is necessary to maintain a normal bowel movement 3 . Another reason for the formation of constipation in pregnant women can be a decrease in fluid intake, starting from the earliest dates 4 .
Thus, low bowel tone during pregnancy is generally initially protective, but may result in constipation 1 .
Possible complications of constipation in pregnancy
Gestational constipation can not only drastically reduce the quality of life, but also pose a certain threat to the well-being of the pregnant woman and the fetus.
Prolonged stagnation of feces can lead to a series of disorders, among other things, to the activation of opportunistic microorganisms. The penetration of microbes and their metabolic products through the intestinal wall can be at least a predisposing factor, and sometimes a direct cause of complicated pregnancy, problems in childbirth and the postpartum period 1 .
Disruption of the normal balance of the colonic microbiota during constipation may later cause a change in the composition of the microflora of the cervical canal.
This condition can cause intrauterine ascending infection and the occurrence of various complications of the gestation period. The course of pregnancy against the background of stagnation in the large intestine can lead to the threat of interruption, untimely discharge of amniotic fluid, inflammation of the uterine mucosa 1 .
The pathological increase in intestinal permeability caused by constipation impairs its barrier function, and even after childbirth it may not fully recover. That is why constipation is a situation that cannot be ignored and must be treated 1 .
Disruption of the normal balance of the colonic microbiota during constipation may later cause a change in the composition of the microflora of the cervical canal.
 nine0029
nine0029 This condition can cause intrauterine ascending infection and the occurrence of various complications of the gestation period. The course of pregnancy against the background of stagnation in the large intestine can lead to the threat of termination, untimely discharge of amniotic fluid, inflammation of the uterine mucosa 1 .
The pathological increase in intestinal permeability caused by constipation impairs its barrier function, and even after childbirth it may not fully recover. That's why constipation is a situation that cannot be ignored and must be treated 1 .
Treatment of gestational constipation
The main rules for the prevention and treatment of constipation in pregnant women are primarily diet and recommendations for increasing physical activity 4 . Treatment of constipation, especially in pregnant women, begins with dietary measures 4 .
Treatment of constipation, especially in pregnant women, begins with dietary measures 4 .
For a laxative purpose, foods rich in indigestible plant fibers (fiber) are introduced into the menu. There are many such substances in raw fruits and vegetables, wholemeal bread 4 .
In terms of nutritional properties, wheat bran is considered the most acceptable for human consumption, which can be added 2-3 teaspoons to prepared meals 3 .
Prunes, kefir, dried apricots are considered products that help relieve constipation. The menu is recommended to include beets, zucchini, cabbage, lettuce, cucumbers and tomatoes. It is recommended to limit the consumption of strong tea and coffee, sweets and cocoa, flour dishes in the diet 3 . nine0009
It may also be necessary to correct the mode of motor activity, the amount of which is discussed with the doctor 3 . Gymnastics, walking or swimming in the pool may be recommended for a pregnant woman, if this is not contraindicated for health reasons 4 .
In some cases, despite following all recommendations, it may be necessary to use laxatives 4 . The choice of a possible drug cannot be made independently, because self-medication with laxatives during pregnancy is especially undesirable 1 .
The use of any medicine during pregnancy carries certain risks that only a doctor can weigh.
Therefore, only with medical permission, laxatives may be recommended. One of the laxatives that can be prescribed by a doctor to pregnant women starting from the 2nd trimester is Guttalax®: in the 1st trimester of pregnancy, the drug is contraindicated, in the 2nd and 3rd trimesters of pregnancy it is used with caution. Guttalax® is available in drops and tablets5,6. In view of the lack of studies, the use of Guttalax® tablets during pregnancy is recommended only in cases where the potential benefit to the mother outweighs the possible risk to the fetus. During pregnancy, the drug can be used only after consultation with a specialist. nine0009
During pregnancy, the drug can be used only after consultation with a specialist. nine0009
More about the drug
To increase the efficiency of preparation for the study, the individual functional state of the large intestine is also taken into account. If you have chronic constipation, you need to pay special attention to diet. In preparation for research, Guttalax® Express can be used in suppositories 8 . nine0102 The active substance - bisacodyl - becomes active and acts only in the lumen of the large intestine, therefore it does not affect the digestion and absorption of nutrients in the small intestine 8 . The drug Guttalax® Express enhances peristalsis, stimulates the natural process of bowel movement, and softens the stool. The development time of the laxative effect of the drug is 20 minutes (from 10 minutes to 30 minutes, in some cases - 45 minutes) 8 . nine0009
nine0009
THERE ARE CONTRAINDICATIONS. IT IS NECESSARY TO CONSULT WITH A SPECIALIST.
Treatments for constipation during pregnancy
What's the problem?
The term "constipation" is defined as difficulty in passing stools and decreased frequency of stools (defecations - bowel movements to empty it). Constipation is characterized by discomfort, excessive straining, hard or lumpy stools, a feeling of incomplete emptying, and infrequent bowel movements. Constipation is a common symptom during pregnancy. This may be the result of a combination of factors including hormonal changes (shifts) during pregnancy affecting the digestive system, physical inactivity, and dietary changes during pregnancy. Also, as the fetus (baby) grows, it can compress the mother's intestines and thereby cause bowel delays/obstructions. nine0009
Why is this important?
Constipation during pregnancy is associated with impaired quality of life and distress for pregnant women, as well as physical problems, including the development of hemorrhoids. A number of treatment options have been suggested, including the use of medications, nutritional supplements, or dietary changes.
A number of treatment options have been suggested, including the use of medications, nutritional supplements, or dietary changes.
Non-pharmacological interventions (changes in diet, water intake and exercise) are generally recommended initially, and if these are ineffective or insufficient, medical (pharmacological) interventions are recommended. Medical interventions include a wide range of drugs: lubricants (lubricants), bulking agents, osmotic and stimulant laxatives, stool softeners (emollient laxatives), enemas and suppositories (laxatives in suppositories and enemas). nine0009
This review looked at the benefits of drug and non-drug interventions for constipation in pregnancy and whether they are safe for women and children.
What evidence did we find?
We identified four studies, but only two studies (a total of 180 women) provided data for analysis. These studies compared stimulant laxatives with bulk laxatives and dietary supplements (dietary fiber) with no intervention.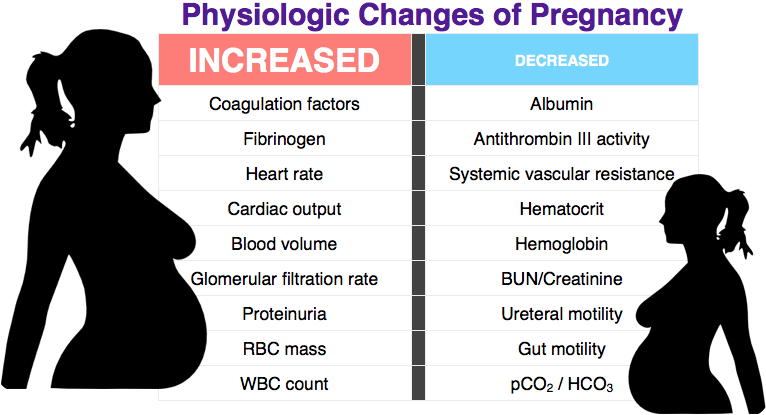 The included studies were considered to be of moderate (moderate) quality. nine0009
The included studies were considered to be of moderate (moderate) quality. nine0009
We have considered two main comparisons. In the first comparison, we found that stimulant laxatives may be more effective in treating constipation than bulk laxatives ( moderate-quality evidence ). However, it can also lead to more abdominal discomfort ( low-quality evidence ) and diarrhea ( moderate-quality evidence ). We found no difference in women's satisfaction ( moderate quality of evidence ). A second comparison between fiber supplementation and no intervention found that fiber supplementation may be effective in increasing stool frequency ( moderate-quality evidence ). The use of dietary supplements (fibers) was associated with improved stool consistency as defined by the testers (hard stool frequency decreased by 11% to 14%, normal stool frequency increased by 5% to 10%, and loose stool frequency increased by 0% to 6 %).
There were no studies looking at other interventions such as osmotic laxatives, stool softeners (stool softener laxatives), lubricants (lubricating laxatives), enemas, and suppositories (suppositories).