Can you drink alcohol when pregnant
Alcohol and pregnancy: MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia
URL of this page: //medlineplus.gov/ency/article/007454.htm
To use the sharing features on this page, please enable JavaScript.
Pregnant women are strongly urged not to drink alcohol during pregnancy.
Drinking alcohol while pregnant has been shown to cause harm to a baby as it develops in the womb. Alcohol used during pregnancy may also lead to long-term medical problems and birth defects.
When a pregnant woman drinks alcohol, the alcohol travels through her blood and into the baby's blood, tissues, and organs. Alcohol breaks down much more slowly in the baby's body than in an adult. That means the baby's blood alcohol level remains increased longer than the mother's. This can harm the baby and can sometimes lead to lifelong damage.
DANGERS OF ALCOHOL DURING PREGNANCY
Drinking a lot of alcohol during pregnancy can lead to a group of defects in the baby known as fetal alcohol syndrome. Symptoms can include:
- Behavior and attention problems
- Heart defects
- Changes in the shape of the face
- Poor growth before and after birth
- Poor muscle tone and problems with movement and balance
- Problems with thinking and speech
- Learning problems
These medical problems are lifelong and can range from mild to severe.
Complications seen in the infant may include:
- Cerebral palsy
- Premature delivery
- Pregnancy loss or stillbirth
HOW MUCH ALCOHOL IS SAFE?
There is no known "safe" amount of alcohol use during pregnancy. Alcohol use appears to be the most harmful during the first 3 months of pregnancy; however, drinking alcohol anytime during pregnancy can be harmful.
Alcohol includes beer, wine, wine coolers, and liquor.
One drink is defined as:
- 12 oz of beer
- 5 oz of wine
- 1.5 oz of liquor
How much you drink is just as important as how often you drink.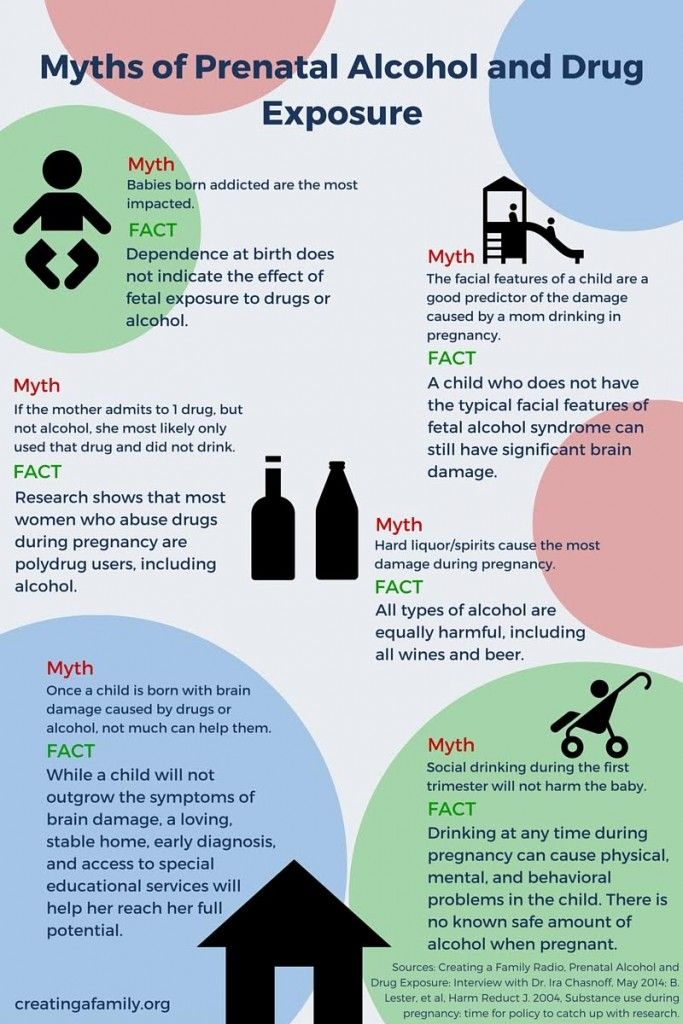
- Even if you don't drink often, drinking a large amount at one time can harm the baby.
- Binge drinking (5 or more drinks on one sitting) greatly increases a baby's risk of developing alcohol-related damage.
- Drinking moderate amounts of alcohol when pregnant may lead to miscarriage.
- Heavy drinkers (those who drink more than 2 alcoholic beverages a day) are at greater risk of giving birth to a child with fetal alcohol syndrome.
- The more you drink, the more you raise your baby's risk for harm.
DO NOT DRINK DURING PREGNANCY
Women who are pregnant or who are trying to get pregnant should avoid drinking any amount of alcohol. The only way to prevent fetal alcohol syndrome is to not drink alcohol during pregnancy.
If you did not know you were pregnant and drank alcohol, stop drinking as soon as you learn you are pregnant. The sooner you stop drinking alcohol, the healthier your baby will be.
Choose nonalcoholic versions of beverages you like.
If you cannot control your drinking, avoid being around other people who are using alcohol.
Pregnant women with alcoholism should join an alcohol abuse rehabilitation program. They should also be followed closely by a health care provider.
The following organization may be of help:
- Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration -- 1-800-662-4357 www.findtreatment.gov
- National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism -- www.rethinkingdrinking.niaaa.nih.gov/about.aspx
Drinking alcohol during pregnancy; Fetal alcohol syndrome - pregnancy; FAS - fetal alcohol syndrome; Fetal alcohol effects; Alcohol in pregnancy; Alcohol related birth defects; Fetal alcohol spectrum disorders
Prasad MR, Jones HE. Substance abuse in pregnancy. In: Resnik R, Lockwood CJ, Moore TR, Greene MF, Copel JA, Silver RM, eds. Creasy and Resnik's Maternal-Fetal Medicine: Principles and Practice. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2019:chap 68.
Prasad M, Metz TD. Substance use disorder in pregnancy. In: Landon MB, Galan HL, Jauniaux ERM, et al, eds. Gabbe's Obstetrics: Normal and Problem Pregnancies. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 8.
Wallen LD, Gleason CA. Prenatal drug exposure. In: Gleason CA, Juul SE, eds. Avery's Diseases of the Newborn. 10th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2018:chap 13.
Updated by: John D. Jacobson, MD, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Loma Linda University School of Medicine, Loma Linda, CA. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
Drinking a little alcohol early in pregnancy may be okay
The usual message to pregnant women: Don't drink any alcohol. Clearly alcohol use can cause major problems for the pregnant woman and her baby.
While not drinking any alcohol during pregnancy is the safest choice, small amounts of alcohol early in pregnancy may be less risky to the mother’s health and the health of their babies than previously believed. Minimal alcohol use during the first trimester doesn’t appear to increase the risk for high blood pressure complications, or premature birth or low birth weights. That’s the findings of a study previously published in the journal Obstetrics and Gynecology.
Minimal alcohol use during the first trimester doesn’t appear to increase the risk for high blood pressure complications, or premature birth or low birth weights. That’s the findings of a study previously published in the journal Obstetrics and Gynecology.
Dr. Fergus McCarthy and colleagues from Ireland, England, New Zealand, and Australia compared birth outcomes among 5,628 women who were pregnant for the first time between 2004 and 2011. More than half of them reported drinking alcohol during the first three months of pregnancy. Some (19%) reported occasionally drinking alcohol. Twenty-five percent reported low alcohol consumption, or three to seven drinks per week ("a drink" defined as a glass of wine or a little less than a 12-ounce bottle of beer). Another 15% reported having more than seven drinks per week.
Rates of premature birth, babies with low birth weight or small size, and pre-eclampsia—a potentially life-threatening condition in which a pregnant woman develops high blood pressure—were similar across the alcohol consumption categories
The potential hazard of alcohol during pregnancy
For the past few decades, women have been urged to avoid alcohol during pregnancy. Respected medical societies like the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists and the United Kingdom's Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists Women both say women shouldn't drink any alcohol during pregnancy. The main reason for this is that heavy use of alcohol during pregnancy has been linked to a long-term and irreversible condition known as fetal alcohol syndrome (FAS).
Respected medical societies like the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists and the United Kingdom's Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists Women both say women shouldn't drink any alcohol during pregnancy. The main reason for this is that heavy use of alcohol during pregnancy has been linked to a long-term and irreversible condition known as fetal alcohol syndrome (FAS).
Babies with FAS may be born early. They are often underweight and don't grow well. Some have characteristic facial features like a thin upper lip and small eye openings, or the small vertical groove between the upper lip and the nose may be flattened. Other physical signs that go along with fetal alcohol syndrome include a small head, short nose, and problems with the way the heart or the joints are formed.
Children with FAS are slower to learn language skills than other kids. When they reach school age they often have learning disabilities and difficulty with attention, memory and hyperactivity.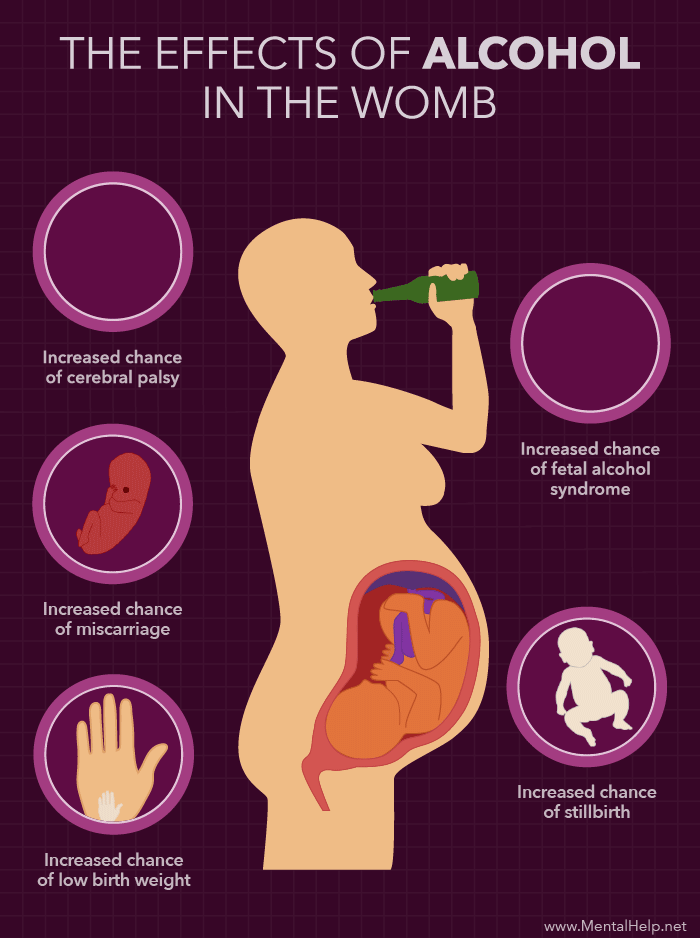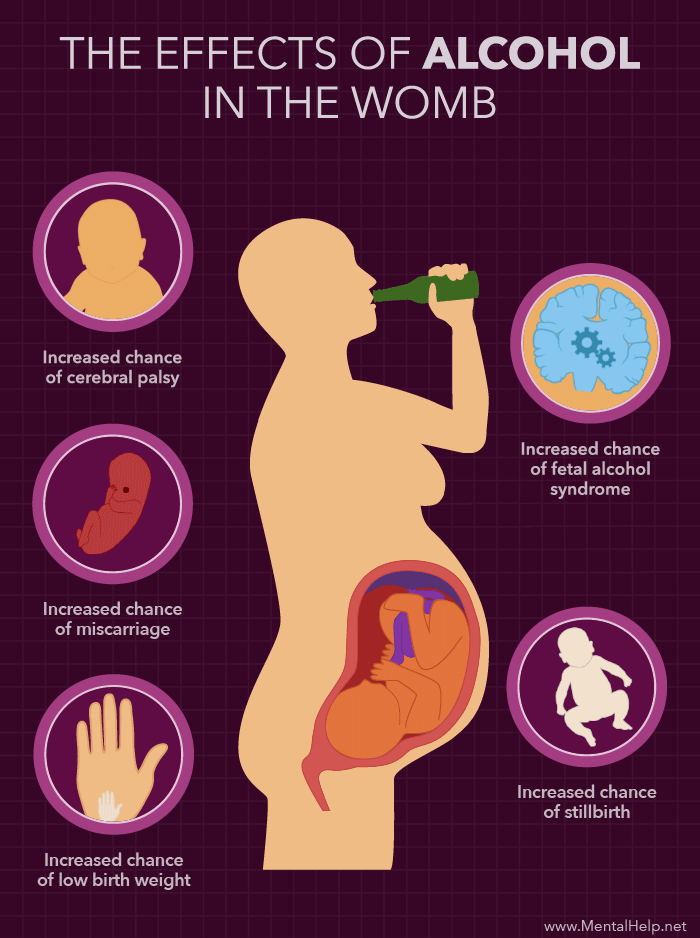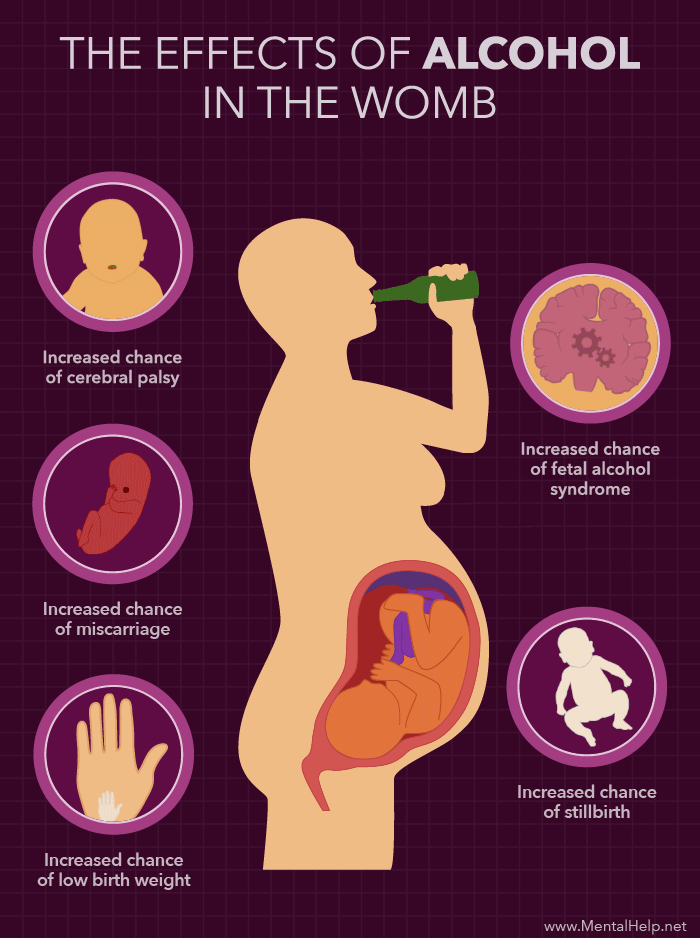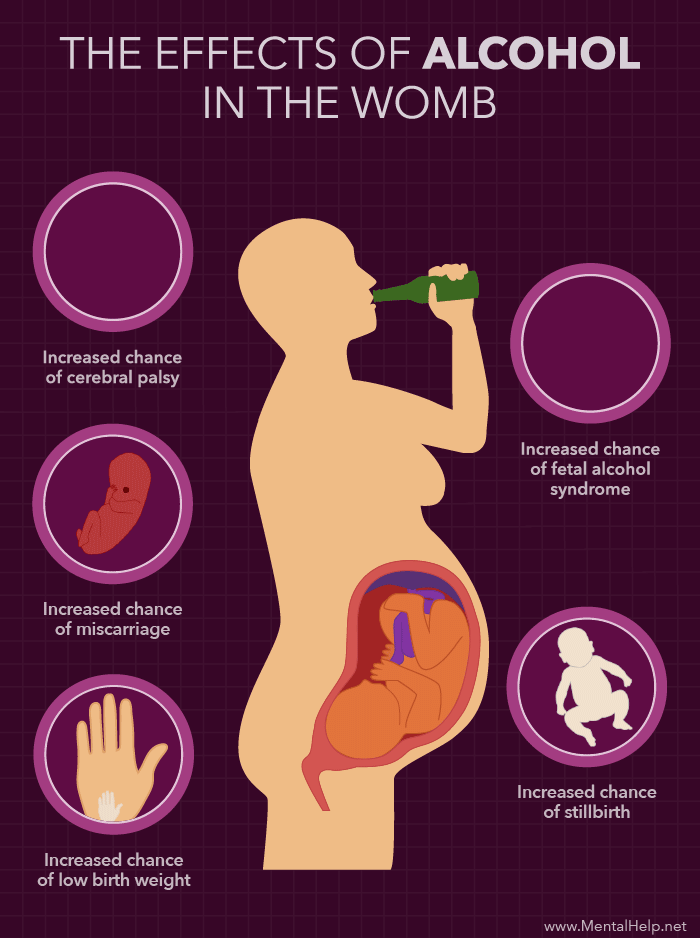 They are more likely to have poor coordination and a hard time with problem-solving. And some have trouble making friends and relating to other kids. All of which can make school a really difficult time.
They are more likely to have poor coordination and a hard time with problem-solving. And some have trouble making friends and relating to other kids. All of which can make school a really difficult time.
Despite this clear advice, up to half of women drink some alcohol during pregnancy.
Putting it into practice
How clear is the medical evidence supporting strict abstinence from alcohol during pregnancy? Not very strong. Other studies suggest pregnant women who have an occasional drink don't harm themselves or their baby. A 2012 Danish study, for example, found that low to moderate alcohol consumption during pregnancy did not affect executive functioning among 5-year-olds. Executive functioning is a catchall term that describes the ability to perform activities such as planning, organizing, strategizing, remembering details, and managing time.
However, since it's not clear how much alcohol it takes to cause problems, the best advice remains the same: women should avoid alcohol if they are pregnant or might become pregnant.
For the many women that drank some alcohol before they realized they were pregnant, this and other studies should reassure them. They almost surely did no harm to their unborn children.
Image: The Good Brigade/Getty Images
The effect of alcohol during pregnancy on the fetus: a modern view of the problem
Many women believe that it is possible to drink alcohol during pregnancy, albeit in small quantities. Of course, we are not talking about hard liquor like vodka or cognac, but a glass of red wine or beer is another matter.
However, everything is not as simple as it might seem at first glance, and even small doses of ethanol can cause irreversible changes in the development of the child. Medicine still does not give an exact answer about the permissible strength and volume of drinks that can be consumed during pregnancy without fear.
Important! Recent research has shown that even small amounts of alcohol during pregnancy can increase the chance of preterm birth and underweight babies (LBW).
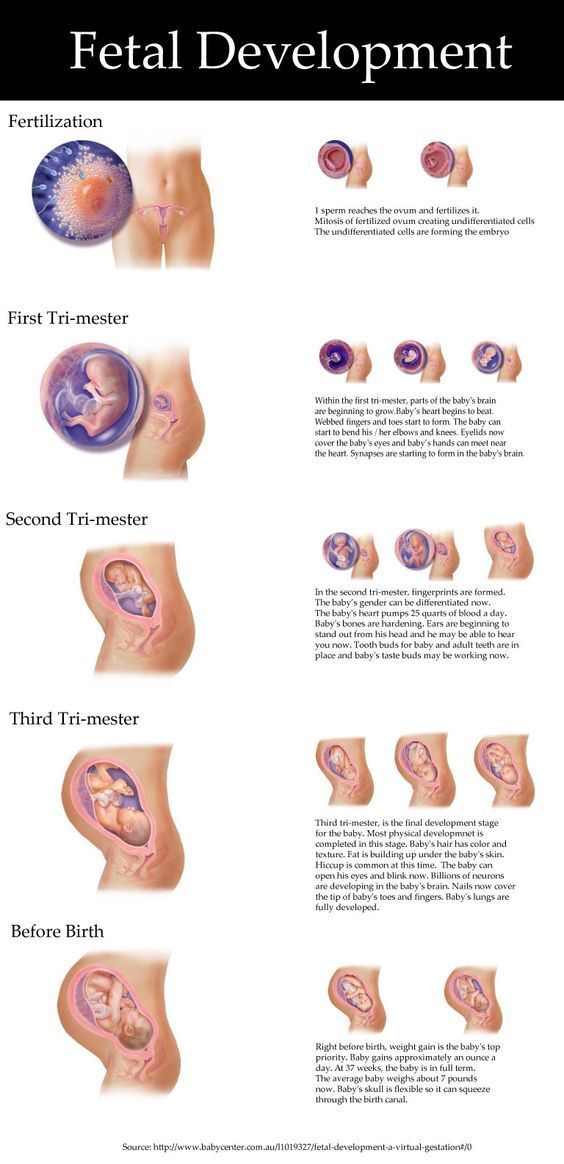
Alcohol in early pregnancy
When ingested by a pregnant woman, ethanol crosses the placental barrier and has a devastating effect on the fetal brain. If a mother regularly drinks alcohol during early gestation, it can lead to damage to the white matter, cerebellum, and brainstem.
Drinking alcohol during pregnancy in the early stages is fraught with a violation of the formation of the brain structures of the child, and also contributes to the development of such serious defects as:
- mental retardation;
- micro-, hydrocephalus;
- mental retardation, etc.
It is believed that in the first days and even weeks after pregnancy, alcohol is allowed. The placenta is not yet formed, which means that there will be no harm to the baby. However, ethanol makes it difficult for the embryo to attach, thereby increasing the risk of miscarriage.
Pregnant women in the first trimester are strongly discouraged from drinking alcohol, even in small quantities. This also applies to beer, wine and other low-alcohol drinks. Get a remote consultation from our gynecologists to protect yourself and your baby.
This also applies to beer, wine and other low-alcohol drinks. Get a remote consultation from our gynecologists to protect yourself and your baby.
The first week of pregnancy: a crucial stage
Alcohol is quite capable of harming the fetus in the first 5-7 days after conception, when it is only a fertilized egg. According to statistics, a huge number of miscarriages happen precisely in the early stages, when a woman does not yet know about pregnancy and, as they say, "misses a glass or two."
During the first week, the fertilized egg travels to the uterus through the fallopian tube. At this time, the drunk alcohol almost instantly enters the bloodstream and inevitably penetrates into the zygote. The result is very often spontaneous abortion, or miscarriage.
Case study:
When registering, the woman was worried that the child might be born handicapped, as there was alcohol consumption during pregnancy. She complained of nagging pain and heaviness in the lower abdomen, which was the reason for hospitalization. The pregnancy was saved.
She complained of nagging pain and heaviness in the lower abdomen, which was the reason for hospitalization. The pregnancy was saved.
What does "early" mean
By early is meant the gestation period in the first three months - that is, the 1st trimester. Conventionally, it can be divided into 2 periods:
- The first 10-12 days from the moment of conception.
- From 12-13 days to 13 weeks (end of the 1st trimester).
Effect of alcohol on the fetus during the first 10-12 days after pregnancy
Every woman from birth has a large set of follicles, of which there are about 500 thousand. New follicles no longer appear, and some die. This does not really matter, since no more than 500 of them will mature over the entire fertile period.
But under the influence of ethanol, the death of follicles is accelerated, and some are damaged. If a spermatozoon fertilizes a damaged egg, a child may develop congenital malformations.
The less alcohol a woman drinks, the healthier her eggs are.
Even strong alcohol does not affect the state of the fertilized egg, if the pregnancy has already begun. A healthy oocyte is not threatened with damage, and the process of cell division will go according to the plan laid down by nature.
The danger lies in the fact that alcohol activates the production of a specific fluid in the fallopian tubes. The latter are the springboard through which the egg enters the uterus. If the fallopian tubes are blocked, the embryo will simply get stuck and attach to the wall of the tube before reaching the uterus.
On the 4-5th day after the onset of pregnancy, the embryo has about 58 cells and enters the uterus. It is built into its wall, and the formation of the chorion, the outer shell of the embryo, begins.
Up to 12-13 days, that is, before the circulatory system appears in the placenta, alcohol drunk by a pregnant woman can destroy the embryo, causing a miscarriage.However, he is not capable at this stage of pregnancy to cause any pathology.
All of the above does not apply to women suffering from alcoholism, and only applies to those who drink a little, rarely and only quality drinks.
If a pregnant woman drank alcohol at an early date, not yet knowing about her “interesting position”, you should not worry too much. It is unlikely that this will affect the health of the unborn child. However, you need to make sure that there is no ectopic pregnancy.
Why alcohol should not be drunk from the 12th-13th day to the 13th week of pregnancy
Around this time, the placental circulatory system begins to form. This means that the fetus takes oxygen and nutrition directly from the mother's body. If the mother drinks alcohol during pregnancy, the blood vessels will narrow, and the child will receive less oxygen: he will experience a state of hypoxia (oxygen starvation).
Even the liver of an adult perceives alcohol as a poisonous substance. In the fetus, the liver is just beginning to form and is not able to cope with the poison, the amount of which in his blood is similar to that in the blood of the mother, thanks to the placental circulatory system.
In the fetus, the liver is just beginning to form and is not able to cope with the poison, the amount of which in his blood is similar to that in the blood of the mother, thanks to the placental circulatory system.
Case study:
The patient turned to the gynecologist for advice about a possible pregnancy with the question "to save or not to save." She admitted that she drank alcohol, not knowing about her condition. The term is 12 weeks. Ultrasound showed the absence of fetal abnormalities and the threat of miscarriage. In due time, the woman gave birth to a healthy child.
Pregnant women cannot drink alcohol in the 1st trimester, as all systems and organs of the baby are laid. You should be especially careful in the period from 28 to 49the day when the laying of facial features occurs. Drinking alcohol can negatively affect a child's appearance.
Drinking alcohol during pregnancy at the very beginning of the term is highly undesirable. The consequences can be catastrophic:
The consequences can be catastrophic:
| No. p / p | Consequences of drinking alcohol |
| one. | fetal alcohol syndrome (FAS), which includes a whole set of congenital malformations |
| 2. | dysfunction of the brain and spinal cord |
| 3. | problems with the nervous system, the manifestations of which can range from mood swings to psychosis and suicidal tendencies |
| four. | defects in the structure of the genital organs - for example, undescended testicles in boys, doubling of the uterus and vagina in girls |
Alcohol during early pregnancy significantly increases the risk of miscarriage and premature birth. But it is important to know that even with the birth of a healthy child, the consequences may appear later. Most often they occur during puberty.
Most often they occur during puberty.
Important! It doesn't matter what the mother drinks - red or white wine, beer, cider, low-alcohol cocktails or homemade liquor.
Is it possible to drink wine during pregnancy in the second trimester
With the second trimester, everything is both easier and more difficult. The question is how much and when. Of course, it is better to completely refrain from alcohol, replacing them with tasty and healthy juices.
Intemperance in relation to alcohol can provoke a child:
- heart disease;
- distortion of facial features, disproportion of body parts;
- reduced muscle tone;
- impaired ability to concentrate, which will lead to learning difficulties;
- violation of diction, speech;
- weak immunity;
- hyperactivity, etc.
One of the consequences of drinking alcohol by a pregnant woman is the fading of the fetus.
However, there is no complete ban on wine during pregnancy in the second trimester. That's just to afford alcohol is allowed only in the middle of the 2nd trimester. At the beginning of this period, the fetus is not yet protected by the placenta, and its organs are actively developing.
1 sip of wine is allowed to drink at the beginning of the 2nd trimester if nausea is tormented.
A glass of wine during pregnancy can help:
- increase hemoglobin and prevent anemia;
- strengthen the cardiovascular system;
- improve mood, normalize the emotional background;
- replenish stocks of trace elements;
- stabilize blood pressure.
Pregnant women in the second trimester are allowed to drink a little wine no more than 1 time in 2 weeks.
However, towards the end of the 2nd trimester, you can’t drink at all, since alcohol can harm the baby and provoke various pathologies. Some experts believe that the intake of alcohol by the mother during this period can lead to alcoholism in the child in the future.
Some experts believe that the intake of alcohol by the mother during this period can lead to alcoholism in the child in the future.
In addition, along with the period, the body weight of the mother and child increases, therefore, products that contribute to weight gain are limited. Red wine is one of them.
Why pregnant women shouldn't drink champagne
Despite the fact that champagne is a type of wine, it is more harmful. Champagne is quite strong and is quickly absorbed into the bloodstream due to carbon dioxide bubbles, causing almost instant intoxication.
Alcohol and pregnancy are incompatible. To make your pregnancy go smoothly, get a consultation with an obstetrician-gynecologist by phone. He will give valuable advice and recommendations.
Beer for pregnant women - is it possible or not
It is undesirable to drink beer during pregnancy, and not only because of the alcohol content in it. There are many different additives in the foamy drink - in particular, cobalt is the foam stabilizer in it. And this element is harmful to the expectant mother and her child.
There are many different additives in the foamy drink - in particular, cobalt is the foam stabilizer in it. And this element is harmful to the expectant mother and her child.
The amount of cobalt in beer exceeds the permissible norm by 10 times.
Case study:
A pregnant woman from a drinking family regularly drank beer, believing that weak alcohol can be drunk and even healthy. By her own admission, sometimes she drank a little vodka. The result was the birth of a baby with fetal alcohol syndrome 1 degree (small head, low body weight). A full examination revealed a number of other irregularities.
Why You Shouldn't Drink Non-Alcoholic Beer While Pregnant
The so-called non-alcoholic beer contains from 0.5 to 1.5% ethanol, and drinking alcohol during pregnancy is not worth it, even such a weak one.
Any beer is also harmful because:
- contains many preservatives to ensure long-term storage;
- has a diuretic effect, undesirable for a pregnant woman;
- due to cobalt in its composition, it can cause inflammation in the esophagus and stomach.

Carbonated drinks
Doctors strongly advise pregnant women to exclude soda from the diet, as it adversely affects the stomach and increases gas formation in the intestines.
Carbonated water has a negative effect on the kidneys and gallbladder due to the content of phosphoric acid. This acid is responsible for the regulation of acidity and increases the risk of kidney and gallstone formation, especially in people with a predisposition to stone formation. During pregnancy, the load on the kidneys is already high, so it is better not to drink soda.
Alcohol in the 3rd trimester
Pregnant women in the third trimester are allowed to drink wine, but in an extremely limited amount. Half a glass of the drink can be drunk a maximum of 2 times a week.
The absence of a complete ban on alcohol is justified by the fact that by the third trimester all important processes in the fetal body have been completed, and the likelihood of a violation of its development is minimal.
FAQ
What is the best wine during pregnancy?
+
It is better for pregnant women to drink dry table wine. It helps to cope with low blood pressure, removes nausea, stimulates appetite. But for some, dry wines are too acidic, in which case they can be replaced with semi-sweet varieties.
Which is better - white or red wine during pregnancy?
+
There is not much difference here, a matter of personal preference. White wine has a positive effect on the functioning of the lungs and heart, but is inferior to red in the amount of antioxidants and the ability to increase hemoglobin. But after it, the head is less often dizzy and there is weakness in the body. Red wine reduces the risk of thrombosis, improves blood formation and helps to eliminate toxins from the body.
How about kvass?
+
Alcohol can be pregnant only at certain times described above. And in kvass, the volume of ethanol ranges from 0.3-2.5%. In addition, this drink can provoke an increase in the tone of the uterus due to active fermentation processes in the intestines and gas formation.
And in kvass, the volume of ethanol ranges from 0.3-2.5%. In addition, this drink can provoke an increase in the tone of the uterus due to active fermentation processes in the intestines and gas formation.
I drank homemade liqueur. What will happen to the child now?
+
If this happened after the start of the second trimester, and there is little alcohol consumed, then the chance of harming the baby is minimal. In addition, homemade drinks are prepared from quality products, and they do not contain harmful additives. Permissible dose - 150 ml.
Expert opinion:
Remember that alcohol and pregnancy are incompatible in principle. Even small doses of ethanol can cause irreversible changes in the development of the child. Alcohol at any stage of pregnancy has a negative impact on both the expectant mother and the baby. If you have been drinking alcohol, then in order to avoid unpleasant consequences, it is better to consult a doctor.
What happens to the child if the mother drinks alcohol?
03.12.2019
Alcohol and pregnancy are incompatible - doctors do not get tired of talking about this to expectant mothers. But pregnant women sometimes allow themselves to skip a glass of wine, thinking that nothing bad will come of such an amount. However, alcohol can interfere with fetal development at any stage of pregnancy, even very early.
Studies show that excessive (four or more drinks at a time) and/or regular drinking by an expectant mother puts the fetus at the greatest risk of serious problems. But even a smaller amount of alcohol can be harmful, since there is no safe dose.
Alcohol easily passes from the mother's bloodstream into the child's bloodstream, which can affect the development of the brain and other vital organs, structures and physiological systems of the baby's body, leading to malformations that can begin in a child in early childhood and last a lifetime. The most profound effects of prenatal alcohol exposure are brain damage and associated behavioral and cognitive impairment.
The most profound effects of prenatal alcohol exposure are brain damage and associated behavioral and cognitive impairment.
Scientists define a wide range of effects and symptoms caused by prenatal alcohol exposure, termed "fetal alcohol spectrum disorders". These include conditions such as intrauterine alcohol syndrome, alcohol-related nervous system disorder, and alcohol-associated birth defects. All these cases have one common feature - damage to the central nervous system (CNS) as a result of prenatal alcohol exposure to the fetus.
The effect of alcohol on the CNS may be structural (eg, reduction in brain size, changes in certain areas of the brain) or functional (eg, cognitive and behavioral deficits, motor and coordination problems). Extended studies using modern imaging techniques (MRI, CT, etc.) have revealed differences in the structure and activity of the brain that are consistent with neuropsychological testing data, including a disorder in processing information from the senses, changes in cognitive processes and behavior in adults with the disorder alcohol spectrum of the fetus compared to healthy people.
The most profound effects of prenatal alcohol exposure are brain damage and associated impairments in behavioral and cognitive functioning.
How are the disorders different?
Fetal alcohol syndrome was the first form of alcohol spectrum disorder and is still the most well-known syndrome. It manifests itself with excessive alcohol consumption by the expectant mother during the first trimester of pregnancy. The impact of harmful substances on the fetus can disrupt the normal development of not only the brain, but also the face. Thus, in addition to CNS developmental anomalies, the child will have a specific pattern of three facial anomalies: narrow eye openings, a smooth area between the lip and nose (compared to a normal ridge), and a thin upper lip. Also, the baby may experience growth deficiency in utero and (or) after birth.
Partial fetal alcohol syndrome includes only some of the characteristics listed above.
An alcohol-related disorder of the nervous system is characterized by disorders of the central nervous system, which may be structural or functional. Functional impairments include a complex pattern of cognitive (mental) or behavioral problems that do not correspond to the standard level of development at any given age in a child. At the same time, the reasons for this discrepancy cannot be explained by factors other than prenatal alcohol exposure. Facial abnormalities and growth retardation should not be present.
Alcohol-related birth defects include heart, kidney, bone, and other malformations; difficulties with vision and hearing; decreased function of the immune system. They are rarely considered separately, but rather are a secondary disorder that accompanies other fetal alcohol spectrum disorders.
What will happen to the baby in the future?
Every person whose mother may have abused alcohol during pregnancy experiences a combination of everyday turmoil that includes medical, behavioral, educational, or social problems in the following areas:
- learning and memorization;
- understanding and following directions;
- ability to keep attention;
- the ability to control emotions;
- communication and socialization;
- performing daily life skills (eg, eating, bathing, counting money, taking care of personal safety).

People with fetal alcohol spectrum disorder are more likely than others to make bad decisions, repeat the same mistakes, trust the wrong people, and have difficulty understanding the consequences of their actions. They are also more prone to disorders such as attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, depression, impulse control problems, alcoholism and drug addiction.
People with fetal alcohol spectrum disorder are more likely than others to make bad decisions, repeat the same mistakes, trust the wrong people, and have difficulty understanding the consequences of their actions.
Risk factors
Of course, it is impossible to argue that just one sip of champagne during pregnancy can provoke many anomalies in the development of the fetus and affect the psyche of the unborn child. But the medical community recommends completely avoiding any dose of alcohol during pregnancy.
There are risk factors that contribute to the development of undesirable consequences:
- amount of alcohol a pregnant woman drinks at a time;
- frequency of drinking by a pregnant woman;
- the stage of pregnancy at which a woman drinks alcohol, and how much she drinks during the formation of one or another body system in the fetus.

Prenatal alcohol exposure to children can be exacerbated if their mothers are malnourished, overweight, underweight, or smoke…
In addition, studies show that prenatal alcohol exposure affects children more if their mothers live in unfavorable conditions and experience high levels of stress. These may include, for example, social isolation, living in a society where excessive drinking is common and acceptable, and living in a society where resources for prenatal care are limited.
The prenatal effects of alcohol on children can be exacerbated if their mothers are malnourished, overweight, underweight, smoke…
How to help a child?
First aid for a child is the refusal of the expectant mother from alcohol. But if during pregnancy a woman allowed herself to drink alcohol and the child has symptoms of a fetal alcohol spectrum disorder, special tactics of education and training should be applied.