Can vitamin k stop bleeding in pregnancy
Vitamin K at birth | Pregnancy Birth and Baby
Vitamin K at birth | Pregnancy Birth and Baby beginning of content5-minute read
Listen
Key facts
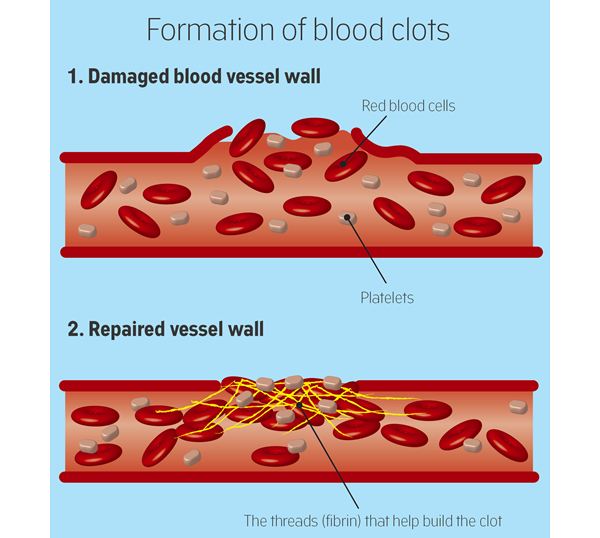
- Vitamin K helps your baby’s blood to clot.
- Babies need more vitamin K than they get from their mother during pregnancy or from breast milk.
- Parents of all newborns are offered a vitamin K injection for their baby soon after birth.
- This helps prevent babies from becoming vitamin K deficient.
- Without the injection, they are at risk of developing a condition called Vitamin K Deficiency Bleeding (known as VKDB).
What is vitamin K?
Vitamin K is an essential vitamin, and has an important role in maintaining good health by helping blood to clot. Vitamin K helps prevent serious bleeding.
Why is vitamin K important for my baby?
Vitamin K helps your baby’s blood clot and prevents serious bleeding. Babies do not get enough vitamin K naturally from their mother during pregnancy. Breast milk also does not provide babies with enough levels of vitamin K. This can result in vitamin K deficiency in newborns.
If your baby has vitamin K deficiency, they are at risk of developing a disease called Vitamin K Deficiency Bleeding, or VKDB. While VKDB is rare, it can be very serious as it can cause babies to bleed excessively and may cause them to bleed into their brain. This condition may result in brain damage and even death.
How is vitamin K given?
Vitamin K is usually given as a single injection in your baby’s leg muscle shortly after birth. If you prefer that your baby does not get an injection, they can have liquid vitamin K drops into their mouth. It is important to note that oral vitamin K drops are not absorbed as well by the body than injected vitamin K, so 3 doses of oral vitamin K are needed. The first dose is given at birth, the second at 3 to 5 days of age and the third when they are 4 weeks old.
The first dose is given at birth, the second at 3 to 5 days of age and the third when they are 4 weeks old.
Vitamin K injections are preferred over the oral drops for all babies. Some babies aren’t able to have oral vitamin K, such as if the mother was taking certain medications while pregnant, or if your baby is premature, unwell, taking antibiotics or has diarrhoea.
Can all babies have vitamin K?
Yes, all babies can have vitamin K. If your baby is premature or very small, they might need a smaller dose of vitamin K. You can discuss this with your doctor.
How much does vitamin K cost?
Vitamin K injections or drops are free. The cost is covered by the government for all babies born in Australia.
Does vitamin K have any side effects? What should I look out for?
Vitamin K in newborns is not associated with any side effects, and has been given to Australian babies for more than 30 years. Studies have investigated whether there is an association between injected vitamin K and childhood cancers. Doctors and scientists have concluded that vitamin K injections are safe and beneficial for babies, and that there is no link between vitamin K and childhood cancer.
Doctors and scientists have concluded that vitamin K injections are safe and beneficial for babies, and that there is no link between vitamin K and childhood cancer.
If your baby has not had a vitamin K injection or the full 3-dose course of vitamin K oral drops it is important that you look out for:
- unexplained bleeding or bruising
- showing signs of jaundice after they are 3 weeks old
If they show any of these symptoms, see your doctor or midwife immediately.
If your baby has liver problems, they may be at a higher risk of bleeding, even if they have had their recommended dose of vitamin K.
Does my baby need to have vitamin K?
It is your choice whether to give your baby vitamin K or not. However, giving vitamin K to your newborn is an easy way to prevent a very serious disease. Health authorities in Australia and throughout the world recommend giving vitamin K to all newborn babies — even babies who were born prematurely or are sick.
How do I get vitamin K for my baby?
During your pregnancy your doctor or midwife will talk to you about vitamin K, including the pros and cons of giving your baby vitamin K by injection or by mouth. Your doctor or midwife will then note this on your file. Your baby will receive vitamin K soon after birth by a doctor or a midwife, based on your decision.
If you have chosen to give your baby vitamin K by mouth then your baby will need to receive 2 more doses after the dose they receive at birth. The second dose can be given in hospital at the same time as your baby has their newborn screening test, or by your local doctor or healthcare worker. It is important to remember to arrange your baby’s third dose when they are 4 weeks old. This important final dose can also be given by your doctor or health care worker.
If you are having a home birth, be sure to discuss giving your baby vitamin K with your midwife. Homebirth midwives are required to have all essential equipment available for a planned home birth, including vitamin K injections.
Sources:
Australian Government, National Health and Medical Research Council (Vitamin K for Newborn Babies), South Australian Neonatal Medication Guidelines (Vitamin K), NSW Health (Having a baby - Labour and birth), SA Health (Planned Birth at Home in SA. 2018 Clinical Directive), The Royal Women Hospital Australia (Tests and Medicines for Newborn Babies)Learn more here about the development and quality assurance of healthdirect content.
Last reviewed: June 2022
Back To Top
Related pages
- Your baby in the first few days
- Baby's first 24 hours
Need more information?
Vitamin K for newborns | NHMRC
Vitamin K helps blood to clot and is essential in preventing serious bleeding in infants. Vitamin K deficiency bleeding can be prevented by the administration of vitamin K soon after birth. By the age of approximately six months, infants have built up their own supply of vitamin K.
Vitamin K deficiency bleeding can be prevented by the administration of vitamin K soon after birth. By the age of approximately six months, infants have built up their own supply of vitamin K.
Read more on NHMRC – National Health and Medical Research Council website
Vitamin K and newborn babies - Better Health Channel
With low levels of vitamin K, some babies can have severe bleeding into the brain, causing significant brain damage.
Read more on Better Health Channel website
At birth | Sharing Knowledge about Immunisation | SKAI
Most babies get two needles (injections) at birth. One is the hepatitis B vaccine and the other is a vitamin K injection. They are usually given in babies’ legs.
Read more on National Centre for Immunisation Research and Surveillance (NCIRS) website
Children and vitamins
Very few kids actually need to take vitamin and mineral supplements, they can get everything they need from a balanced diet.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Vitamin and mineral supplements - what to know - Better Health Channel
Vitamin and mineral supplements are frequently misused and taken without professional advice. Find out more about vitamin and mineral supplements and where to get advice.
Read more on Better Health Channel website
Vitamins & minerals for kids & teens | Raising Children Network
Children need vitamins and minerals for health and development. They can get vitamins and minerals by eating a variety of foods from the five food groups.
Read more on raisingchildren.net.au website
Itching during pregnancy
Mild itching is common in pregnancy because of the increased blood supply to the skin, but if the itching becomes severe it can be a sign of a liver condition called 'obstetric cholestasis'.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Baby's first 24 hours
There is a lot going on in the first 24 hours of your baby's life, so find out what you can expect.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
ACD A-Z of Skin - Intrahepatic Cholestasis of Pregnancy
A-Z OF SKIN Intrahepatic Cholestasis of Pregnancy BACK TO A-Z SEARCH What is it? Also known as … Recurrent Cholestasis of Pregnancy, Obstetric Cholestasis, Cholestasis of Pregnancy, Recurrent Jaundice of Pregnancy, Cholestatic Jaundice of Pregnancy, Idiopathic Jaundice of Pregnancy, Prurigo gravidarum, Icterus Gravidarum What is it? Intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy is a rare liver condition which causes an itchy skin
Read more on Australasian College of Dermatologists website
Pregnancy at week 40
Your baby will arrive very soon – if it hasn't already. Babies are rarely born on their due date and many go past 40 weeks.
Babies are rarely born on their due date and many go past 40 weeks.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Disclaimer
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is not responsible for the content and advertising on the external website you are now entering.
OKNeed further advice or guidance from our maternal child health nurses?
1800 882 436
Video call
- Contact us
- About us
- A-Z topics
- Symptom Checker
- Service Finder
- Linking to us
- Information partners
- Terms of use
- Privacy
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is funded by the Australian Government and operated by Healthdirect Australia.
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is provided on behalf of the Department of Health
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby’s information and advice are developed and managed within a rigorous clinical governance framework. This website is certified by the Health On The Net (HON) foundation, the standard for trustworthy health information.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
This information is for your general information and use only and is not intended to be used as medical advice and should not be used to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any medical condition, nor should it be used for therapeutic purposes.
The information is not a substitute for independent professional advice and should not be used as an alternative to professional health care. If you have a particular medical problem, please consult a healthcare professional.
Except as permitted under the Copyright Act 1968, this publication or any part of it may not be reproduced, altered, adapted, stored and/or distributed in any form or by any means without the prior written permission of Healthdirect Australia.
Support this browser is being discontinued for Pregnancy, Birth and Baby
Support for this browser is being discontinued for this site
- Internet Explorer 11 and lower
We currently support Microsoft Edge, Chrome, Firefox and Safari. For more information, please visit the links below:
- Chrome by Google
- Firefox by Mozilla
- Microsoft Edge
- Safari by Apple
You are welcome to continue browsing this site with this browser. Some features, tools or interaction may not work correctly.
Vitamin K during pregnancy | How Much Do You Need? | AptaclubVitamin K in Pregnancy – Prenatal Nutrition
Read time: 1 minute
Vitamin K is essential for blood clotting and helping wounds heal properly. It’s important to make sure you and your baby get enough in preparation for labour and your recovery afterwards. Although vitamin K deficiency is rare, an injection is given to all babies just after they’re born to minimise this risk.
Learn more about the importance of vitamin K in pregnancy, how much you need and which foods are the best sources.
Why is vitamin K so important during pregnancy?
As well as playing a key role in blood clotting, vitamin K is also needed for healthy bone development and protein formation in the liver1. This is particularly important during labour and just after you’ve given birth, when your body is recovering and starting to heal2.
Sufficient levels of vitamin K are also crucial for your baby immediately after birth, and while vitamin K deficiency in babies is very rare, it can lead to a condition called haemorrhagic disease that increases their risk of bleeding too much2.
Free 'Eating for 2' recipe e-book
Healthy, tasty recipes by chef Lorraine Pascale and our team of nutritionists
Join now for FREE
How much vitamin K do you need when you’re pregnant?
You should easily be able to get all the vitamin K that you and your baby need by eating a healthy, balanced pregnancy diet. The nutrient content of vitamin K-rich foods isn’t usually affected by cooking, and because it’s a fat-soluble vitamin, your body can build up stores of it in your liver, ready for when you need it.
The nutrient content of vitamin K-rich foods isn’t usually affected by cooking, and because it’s a fat-soluble vitamin, your body can build up stores of it in your liver, ready for when you need it.
It’s worth noting that some medical conditions and medications can affect your ability to absorb nutrients like vitamin K. If there’s a risk you’re not getting enough, you may need to take a supplement. If you have any concerns, talk to your GP or midwife, as taking a supplement unnecessarily can affect your baby3.
The exact amount of vitamin K you need depends on your size. According to the NHS, adults need approximately 1mcg a day of vitamin K for each kilogram of their body weight. So if you weigh 65kg, you need 65mcg of vitamin K each day1. Just half a cup of cooked broccoli contains 116mcg of vitamin K4.
Which foods contain vitamin K?
Foods rich in vitamin K include5:
- Green leafy vegetables – such as kale and spinach
- Broccoli
- Brussels Sprouts
- Asparagus
- Vegetable oils
- Cereal grains
Protecting your baby with vitamin K at birth
Although a significant deficiency is unlikely, babies are sometimes born with low vitamin K levels. They’ll usually be given a booster injection shortly after they’re born, just to be on the safe side6. If you don’t like the idea of your baby being injected, they can have an oral dose instead.
They’ll usually be given a booster injection shortly after they’re born, just to be on the safe side6. If you don’t like the idea of your baby being injected, they can have an oral dose instead.
Try increasing your intake with these vitamin K-rich snacks and meals:
- A bowl of vitamin K- fortified breakfast cereal
- Roast asparagus with a poached egg
- Steamed broccoli with your favourite salad dressing
- Oven-baked kale crisps
- Sesame-crusted tuna steaks with quinoa and baby spinach
View references
1. NHS UK. Vitamin K [Online]. 2012. Available at: www.nhs.uk/Conditions/vitamins-minerals/Pages/Vitamin-K.aspx[Accessed June 2014]
2. Shahrook S et al. Vitamin K supplementation during pregnancy for improving outcomes. The Cochrane Library, 2014.
3. Stazi AV, Mantovani A. A risk factor for female fertility and pregnancy: celiac disease. Gynecoll Endocrinol 2000;14(6):454-463.
4. Puckett RM, Offringa M. Prophylactic vitamin K for vitamin K deficiency bleeding in neonates. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 4, 2000.
Read next
- Aptaclub home
- Pregnancy
- Diet & nutrition
- Key vitamins and nutrients
- Importance of vitamin k
Uterine bleeding: description of the disease, causes, symptoms, cost of treatment in Moscow
Uterine bleeding is the discharge of blood from the uterine cavity. Unlike the normal menstrual cycle of a woman, it is characterized by abundance, intensity, and duration. Bleeding is due to a serious disease or pathology. In any case, the manifestation of this disease should not proceed without medical attention. Girls of any age are at risk. Even in the first days after uterine life, bloody discharge from the genitals can be observed.
In any case, the manifestation of this disease should not proceed without medical attention. Girls of any age are at risk. Even in the first days after uterine life, bloody discharge from the genitals can be observed.
Every woman should know her cycle. It is considered normal if it is regular, occurs monthly and lasts, on average, 5 days. They start out sparsely, gain in abundance towards the middle, and just as slowly go down. A healthy woman has no pain syndromes during menstruation. Everything else is a deviation or congenital pathology of the uterus. It can also mean a serious gynecological disease, hormonal failure. If menstruation occurs with pain, dizziness and weakness, contact your gynecologist immediately.
It should be understood that the onset of early menstruation in girls under the age of 11, as well as the resumption of bloody discharge in women after menopause (after 55 years), is a serious pathological abnormality, and should not proceed without medical supervision. There is no menstruation during pregnancy.
There is no menstruation during pregnancy.
Sometimes, within the normal range, there may be small blood discharge that occurs during periods of menstruation. The cause may be a hormonal failure as a result of ovulation. The walls of the vessels thin out a little, so blood blotches can come out along with the secretions. Duration 1 to 2 days maximum. Also, colds and inflammatory processes can have such a side effect.
This pathology has the first and main symptom - this is the discharge of blood from the vagina. The amount of blood loss in a woman increases dramatically. This can be noticed when changing special hygiene products too often. The cycle lasts more than 7 days. Its interval changes. After sexual intercourse, bleeding is observed. Bleeding after menopause, when the cycle has been stopped for a long time.
Cause. Types of bleeding.
The cause of uterine bleeding is ovarian dysfunction. There is a failure in the system of work of the hypothalamus, pituitary gland and ovaries. The release of the pituitary hormone is disrupted, which provokes the immaturity of the follicle. Ovulation and the menstrual cycle are disturbed. The follicle does not mature in the ovary and the corpus luteum does not mature. The production of estrogen and progesterone stops. The endometrium is shed, resulting in uterine bleeding. It stands out for a long time and plentifully.
The release of the pituitary hormone is disrupted, which provokes the immaturity of the follicle. Ovulation and the menstrual cycle are disturbed. The follicle does not mature in the ovary and the corpus luteum does not mature. The production of estrogen and progesterone stops. The endometrium is shed, resulting in uterine bleeding. It stands out for a long time and plentifully.
During bleeding, the risk of developing diseases of the uterus and adnexal system, cancer, mastopathy, and adenoma carcinoma increases.
There are many reasons that can cause uterine bleeding. It is necessary to determine the type of blood loss, and understand what caused it. The cause can be both a disease of the genital organs and a failure in their functions.
Non-genital disorders include the following:
-
Some infectious diseases (measles, influenza).
-
Cirrhosis of the liver.
-
Hypertension.
-
Atherosclerosis.

-
Urinary disorders.
-
Changes in the thyroid gland.
-
Blood diseases.
Bleeding may begin during gestation. This can carry a number of reasons, for example, an ectopic pregnancy, as well as:
-
scar on the uterus;
-
endometritis;
-
fibroids;
-
chorionepitheloma;
-
birth canal injuries;
-
ovarian pathology;
-
uterine rupture;
-
destruction of uterine tissue;
-
departed placenta;
-
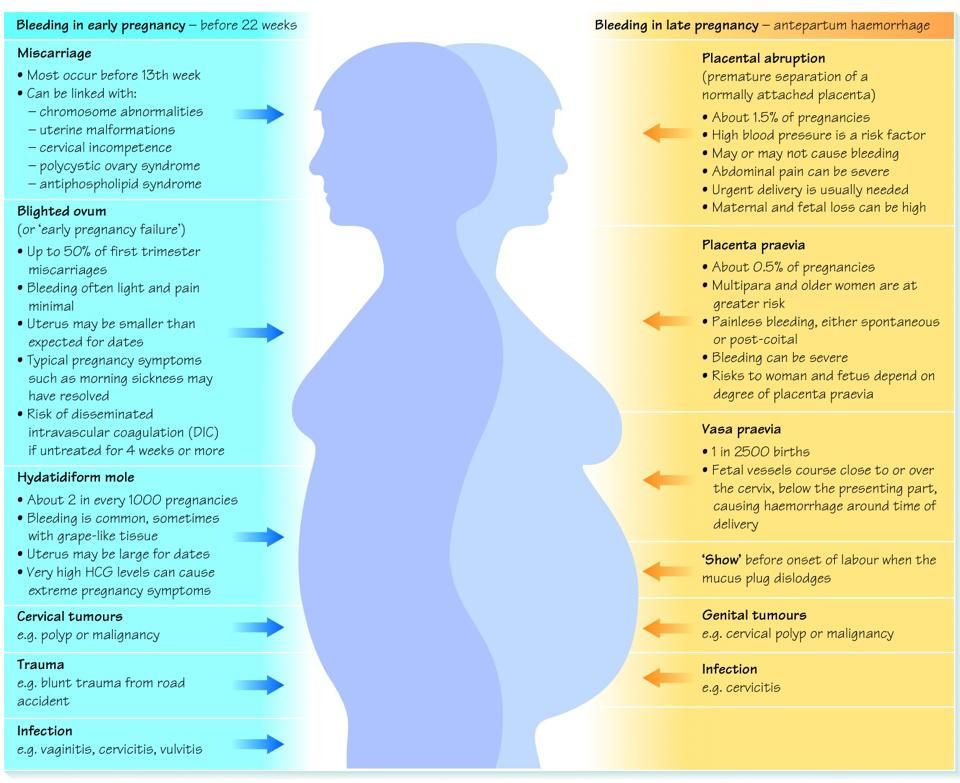
placental abruption or previa.
Bleeding during pregnancy
Bleeding can also occur in a woman who is not carrying a child. Can be called:
-
gross sexual activity;
-
taking contraceptives;
-
trauma to the external part of the genitals;
-
any injury to the uterus;
-
inflammatory processes such as vaginitis, erosion, cervicitis;
-
cyst and its rupture;
-
ovarian rupture;
-
intrusion of mucosa into uterus;
-
benign and malignant tumors, such as fibroids;
-
menopausal, juvenile and reproductive bleeding.

Menopausal bleeding
With menopause, women may experience uterine bleeding. They are of a different nature. This comes from the frequency of ovulation and the production of hormones. A fairly common occurrence, but you should consult a specialist. They may also indicate tumors. The reason for the urgent visit to the doctor is:
-
Abundant discharge that special hygiene products cannot cope with.
-
Discharge with clots.
-
Exceeding the duration of menstruation by more than 3 days.
-
Severe pain syndrome.
-
Remember that they can indicate polyps, fibroids, imbalances, tumors and other serious diseases of the female reproductive system.
Bleeding due to hormonal imbalance
With a change or violation of the hormonal system, a woman may experience uterine bleeding. Women of all ages are prone to this problem. With improper brain function, the level and production of the hormone is not controlled. An example of such a disease is the pathology of the pituitary gland.
With improper brain function, the level and production of the hormone is not controlled. An example of such a disease is the pathology of the pituitary gland.
Lethargy and chronic fatigue, malnutrition and exhaustion of the body can cause this problem. Violations of this type occur in the girl's body during the first menstrual cycle, as well as after abortion, childbirth and during pregnancy. Prolonged bleeding caused by medical abortion is gaining popularity. The use of hormonal drugs and heredity are attributed to a number of causes.
Treatment should be selected individually, it is necessary to determine the cause that caused the disease.
Bleeding during pregnancy
Uterine bleeding during pregnancy most often indicates a miscarriage, an ectopic pregnancy, or damage to the placenta. These causes are accompanied by severe pain in the lower abdomen, nausea, vomiting, and malaise. The blood is bright red or dark scarlet in color, most often with clots.
It is possible to damage the cervix during pregnancy during a gynecological examination or sexual intercourse. This bleeding is usually not prolonged or heavy. In the second or third trimester, bleeding may begin due to damage or placenta previa.
Bleeding poses a serious threat to the health and life of the mother and child. It should be understood that uterine bleeding is very dangerous for pregnant women. The woman should immediately call an ambulance.
Bleeding due to caesarean section
The cause of this bleeding is hemostasis. To do this, a medical intervention is carried out, in which the walls of the uterus are thoroughly cleaned. A caesarean section leaves behind a scar on the uterus, which prevents it from contracting normally. A caesarean section takes a long time to heal and can cause uterine bleeding. A woman should be under medical supervision, and after healing, when the first signs appear, immediately seek help.
Hypotonic bleeding is very difficult to stop, because it occurs at the moment after the contraction of the uterus. Hypotensive shock may occur. In this case, doctors must immediately proceed to rescue, and have a supply of blood for recovery.
Hypotensive shock may occur. In this case, doctors must immediately proceed to rescue, and have a supply of blood for recovery.
The last degree of severity of uterine bleeding after cesarean is the removal of the uterus. It is used in cases where the salvation of the patient directly depends on stopping the bleeding, and other methods are powerless.
Gynecologists classify bleeding according to various criteria. The most common are:
Hypotonic. The fertilized egg lingers in the myometrium of the uterus. The reason is hypotension. The contraction of the muscle tissue of the uterus after childbirth occurs spontaneously. A critical state occurs when it is completely absent. The bleeding should be stopped immediately. Replenish the volume of circulating blood. Continuous measurement of blood pressure and pulse. Treatment is aimed at the speedy restoration of the motor function of the uterus.
Hypotonic occurrence after childbirth requires removal of the placenta. It is this action that helps to restore the healthy functioning of the walls of the uterus. Massage if necessary. Apply ice or irritate the uterus with a swab dipped in ether. If hypotension does not stop, the therapy of atony is started.
It is this action that helps to restore the healthy functioning of the walls of the uterus. Massage if necessary. Apply ice or irritate the uterus with a swab dipped in ether. If hypotension does not stop, the therapy of atony is started.
Atonic. Atonic appear when the uterus is not able to contract. In gynecology, non-contractility of the uterus is called the uterus of Kuveler. Zero tone of the uterus does not make it possible to stop bleeding with the help of special injections and drugs. To clamp the uterine artery, a thick suture is placed on the lip of the uterus, secured with additional clamps. The inefficiency of the method is considered as preparation for the removal of the uterus. Critical blood loss is considered from 1.2 liters. Electrical stimulation makes attempts to reduce blood vessels. Constantly infuse blood to avoid fainting.
Juvenile. Occur during puberty. The main cause is ovarian dysfunction. Infection, psychological trauma, excessive physical activity, colds, malnutrition can cause juvenile bleeding. Climatic conditions are reflected. Treatment is carried out only in a hospital. Depending on the severity, this can lead to anemia. At the first detection, you should immediately call an ambulance, take a horizontal position, apply cold to the groin area and take a hemostatic drug.
Climatic conditions are reflected. Treatment is carried out only in a hospital. Depending on the severity, this can lead to anemia. At the first detection, you should immediately call an ambulance, take a horizontal position, apply cold to the groin area and take a hemostatic drug.
Dysfunctional. Occurs when the ovaries fail. The absence of menstruation for a long time and copious discharge are characteristic of this species.
Anuvulatory. Women undergo bleeding during menopause and adolescents. It is caused by a violation of the follicles and progesterone, during the absence of ovulation. It is also called single-phase, during bleeding, the corpus luteum does not form. A dangerous type of bleeding can cause the development of malignant tumors. Duration lasts more than 10 days. Bleeding is observed during a malfunction of the pituitary gland, after infections, poisoning and stress.
Profuse. Not accompanied by pain. The amount of fluid lost can vary. The reasons can be different, from a miscarriage to taking hormonal drugs.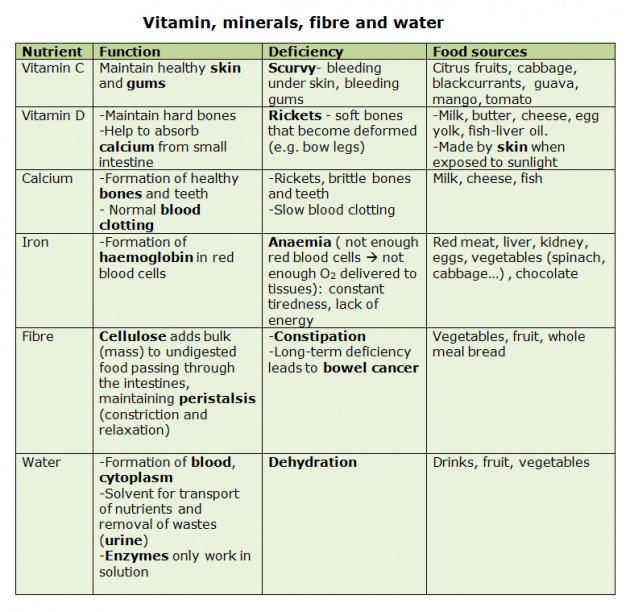
Clots in uterine bleeding
There are cases when a woman observes the presence of clots during bleeding. Doctors explain this with an anomaly that was transferred by the uterus in utero. The uterine cavity holds blood, forming clots. Such menstruation brings a lot of discomfort to a woman, especially during a hormonal crisis. This anomaly sometimes causes the appearance of a large number of clots. The anomaly can also be acquired. They are associated with lifestyle, profession and addiction to bad habits.
Menstruation with clots causes severe pain. To exclude an anomaly, you should apply for a gynecological consultation. To exclude the possibility of the appearance of clots on a hormonal background, take an analysis for hormones and check the thyroid gland. The presence of clots and pain indicate endometriosis. If the diagnosis is confirmed, then the disease requires urgent special treatment.
Stopping uterine bleeding
Upon arrival of the ambulance, the following actions are carried out:
-
apply cold to the abdomen;
-
with heavy bleeding, the woman is carried in a horizontal position;
-
urgent hospitalization;
-
specialist assistance;
-
the introduction of the desired solution, depending on the type of uterine bleeding.

If the patient has not given birth, and she does not have tumors, treatment in the hospital is carried out with the help of hormonal drugs. Treatment begins with an increased dose, gradually increasing from 6 tablets per day to 1 piece. In the absence of anemia, gestogens are used. Prescribe hemostatic drugs, such as Vikasol, Dicinon, Ascorutin.
During puberty, girls are prescribed drugs that strengthen blood vessels and stop the blood. It is recommended to take vitamins. Phytotherapy and hormonal preparations for regulating the menstrual cycle. Women of childbearing age undergo surgery for endometriosis, fibroids. Pathology of the uterus and ovaries, oncological diseases, after menopause, requires only surgical intervention, removal of the appendages and uterus.
It is very important for proper treatment to undergo an examination in time and establish the cause that caused the bleeding. Women experiencing this pathology should immediately seek medical help.
First aid
An ambulance should be called immediately. During pregnancy, the woman's condition deteriorates sharply, because blood loss is plentiful. Every minute counts. If it is not possible to contact the medical team, you should take the woman to the hospital yourself. The reaction should be quick, with uterine bleeding a serious threat to life looms. In case of dysfunctional bleeding, do not apply any warm heating pads to the stomach, do not use drugs, douching, taking a bath.
Before the ambulance arrives, a woman can be helped independently by the following actions:
1. We put the woman to bed. In a horizontal position, it is desirable to raise the legs above the head. Place a pillow or roll up a blanket. With impressive bleeding, this will help the patient not to lose consciousness.
2. Apply cold to the abdomen. If there is no heating pad or ice, replace it with any item from the refrigerator, after wrapping it in a cloth. A plastic cold water bottle will do. It is possible to achieve vasoconstriction and reduce bleeding with the help of cold for no more than 15 minutes. Take 5 minute breaks.
A plastic cold water bottle will do. It is possible to achieve vasoconstriction and reduce bleeding with the help of cold for no more than 15 minutes. Take 5 minute breaks.
3. A woman is given plenty to drink. This will replace the drip at home. Make sweet tea or water.
4. When carrying a child, take medication seriously. If it is not possible to consult a doctor, it is necessary to read the insert and find out the minimum dose. Be sure to read the side effects. Upon the arrival of medical workers, tell the name of the drug that the woman took and its dosage.
Diagnosis
At the first sign of uterine bleeding, contact your gynecologist immediately. Women should keep a calendar where the nature, symptoms, well-being and duration of the menstrual cycle are noted. This will help the gynecologist prescribe the correct treatment and complete the course of therapy faster. Performing ultrasound diagnostics, taking smears of the cervix for the presence of cancer. Blood tests are performed to determine the level of hormones. A biopsy is done to examine the endometrium under a microscope. Proper diagnosis is the key to optimal rehabilitation.
Blood tests are performed to determine the level of hormones. A biopsy is done to examine the endometrium under a microscope. Proper diagnosis is the key to optimal rehabilitation.
Treatment of uterine bleeding | Dobromed
Uterine bleeding - discharge of blood from the vagina, characterized by profuseness and duration. This pathological condition poses a danger to the life and health of a woman, is a sign of serious diseases of the reproductive system. In order to save the patient, it is important to immediately give her first aid, find out the cause of the outpouring of blood. Natural bleeding from the vagina is called menstruation. Menstrual bleeding is characterized by cyclicity, repeated at regular intervals. The period between menstruation usually lasts 25 - 30 days. Blood from the vagina should not stand out longer than 8 days, otherwise we can talk about pathology. Violation of the menstrual cycle is a reason to immediately contact a gynecologist. The doctor will find out the cause of the pathological phenomenon, help get rid of the disease at an early stage, until complications arise.
Causes of uterine bleeding
The likelihood of uterine bleeding depends on the age of the patient. In girls from 12 to 18 years old, abundant discharge of blood from the vagina is a consequence of a hormonal imbalance. And hormonal failures at a young age arise due to:
- physical trauma or emotional upheaval;
- deterioration of the endocrine glands;
- malnutrition, deficiency of vitamins in the body;
- pregnancy with complications, difficult delivery;
- genital tuberculosis;
- blood clotting disorders;
- severe infectious diseases.
In older women, uterine bleeding is rare and is usually associated with ovarian dysfunction. In this case, the provocateurs of the pathological condition are:
- stress, fatigue, nervous strain, mental disorders;
- uterine fibroids;
- endometriosis;
- advanced endometritis;
- uterine polyps;
- oncology of the uterus or cervix;
- tumor formations in the ovaries;
- ectopic pregnancy, miscarriage, medical or instrumental abortion;
- infectious diseases of the reproductive organs;
- climate change, unfavorable ecological situation in the place of residence, harmful working conditions;
- taking medications that can disrupt the systemic work of the hypothalamus and pituitary gland.
Uterine bleeding is common in menopausal women. This is due to a decrease in the synthesis of gonadotropin by the pituitary gland. As a result, the level of sex hormones in the female body begins to jump, the menstrual cycle goes astray, and the formation of follicles in the ovaries is disrupted. Common causes of uterine bleeding at reproductive age are:
Symptoms of uterine bleeding
- weakness;
- fainting;
- dizziness;
- nausea;
- blanching of the skin;
- cardiac tachycardia;
- lowering blood pressure.
- copious bleeding from the vagina;
- presence of clots in blood secretions;
- change pad every 2 hours, even more often;
- duration of bleeding more than 8 days;
- increased bleeding after intercourse;
- painless bleeding with a dysfunctional origin of the pathology;
- discrepancy between the onset of bleeding and the period of menstruation.

The duration of menstruation normally does not exceed 8 days, and bleeding that persists longer than the normal period is pathological. Unhealthy should be considered vaginal bleeding, the period between which is less than 21 days. During menstruation, 80-120 ml of blood flows out per day, with uterine bleeding, the daily volume of blood is more than 120 ml.
Types of uterine bleeding
Bleeding from the uterus, depending on the age of the patients, are divided into five types.
- During infancy. In the first week of life, a newborn girl may have slight bleeding from the vagina. This is not a pathological phenomenon, the child does not need medical intervention. Infant bleeding is caused by a sharp change in the hormonal background in a girl who was born, and disappear on their own.
- Before puberty. During this period, vaginal bleeding in girls is rare. The cause of the pathological condition is most often a hormone-dependent ovarian tumor, due to which the sex gland synthesizes too many hormones.
 As a result, the girl has a false maturation of the reproductive system.
As a result, the girl has a false maturation of the reproductive system. - During puberty. Uterine bleeding during puberty, attributable to 12-18 years, is called juvenile.
- During the reproductive period. Bleeding from the uterus, observed in the period of 18 - 45 years, are organic, dysfunctional, breakthrough, as well as due to pregnancy and childbirth.
- In menopause. During the period of extinction of the reproductive function, bleeding from the vagina is most often associated with pathologies of the genital organs or with a decrease in the synthesis of hormones.
Dysfunctional bleeding
This type of uterine bleeding during the reproductive period is the most common. The pathological condition is diagnosed in both girls and older women during menopause. The cause of dysfunctional blood secretions is the failure of the synthesis of sex hormones by the endocrine glands. The endocrine system, including the pituitary, hypothalamus, ovaries and adrenal glands, controls the production of sex hormones. If the work of this complex system fails, then the menstrual cycle is disturbed, the duration and abundance of menstruation changes, the likelihood of infertility and spontaneous abortion increases. Therefore, with any changes in the menstrual cycle, you should immediately contact a gynecologist. Dysfunctional uterine bleeding can be ovulatory and anovulatory. Ovulatory bleeding is manifested by a change in the duration and abundance of blood discharge during menstruation. Anovulatory bleeding occurs more often, due to the lack of ovulation due to a violation of the synthesis of sex hormones.
If the work of this complex system fails, then the menstrual cycle is disturbed, the duration and abundance of menstruation changes, the likelihood of infertility and spontaneous abortion increases. Therefore, with any changes in the menstrual cycle, you should immediately contact a gynecologist. Dysfunctional uterine bleeding can be ovulatory and anovulatory. Ovulatory bleeding is manifested by a change in the duration and abundance of blood discharge during menstruation. Anovulatory bleeding occurs more often, due to the lack of ovulation due to a violation of the synthesis of sex hormones.
Organic bleeding
Such bleeding is caused either by severe pathologies of the reproductive organs, or blood diseases, or serious disorders of the internal organs.
Breakthrough bleeding
Such uterine bleeding is also called iatrogenic. They are diagnosed after exceeding the dosage and course of taking certain medications, frequent use of hormonal contraceptives, as well as after surgery to install a spiral and after other surgical procedures on the organs of the reproductive system. synthetic hormones. In this situation, it is recommended to consult a doctor about changing the dosage of the medication. In most cases, with breakthrough bleeding, gynecologists advise patients to increase the dosage of the hormonal agent for a certain time. If after this measure the amount of blood released does not decrease, but increases, then you need to urgently undergo a medical examination. In this case, the cause of the pathological condition may be a serious disease of the reproductive system. If uterine bleeding occurred after the installation of the spiral, then the contraceptive device most likely injured the walls of the uterus. In this situation, you should immediately remove the spiral and wait for the healing of the uterine walls.
synthetic hormones. In this situation, it is recommended to consult a doctor about changing the dosage of the medication. In most cases, with breakthrough bleeding, gynecologists advise patients to increase the dosage of the hormonal agent for a certain time. If after this measure the amount of blood released does not decrease, but increases, then you need to urgently undergo a medical examination. In this case, the cause of the pathological condition may be a serious disease of the reproductive system. If uterine bleeding occurred after the installation of the spiral, then the contraceptive device most likely injured the walls of the uterus. In this situation, you should immediately remove the spiral and wait for the healing of the uterine walls.
Bleeding due to pregnancy and childbirth
In the first months of pregnancy, bleeding from the uterus is a sign of either threatened spontaneous abortion or ectopic location of the fetus. In these pathological conditions, there are severe pains in the lower abdomen.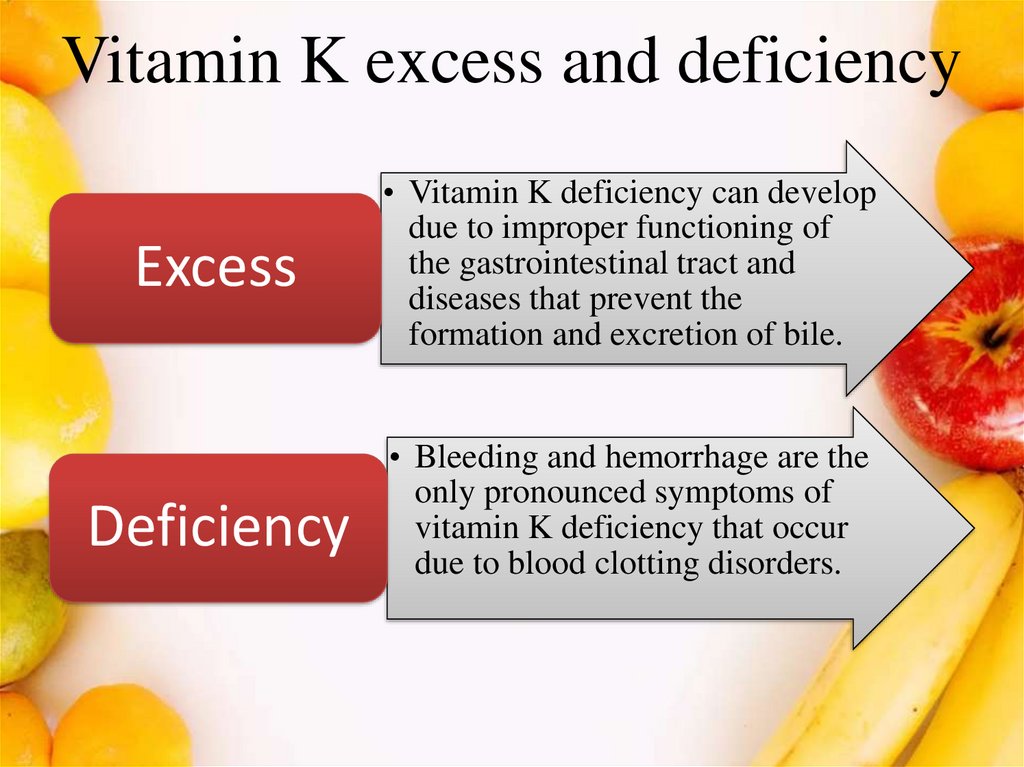 A pregnant woman who has begun uterine bleeding should immediately contact a supervising doctor. When a spontaneous abortion begins, the fetus can be saved if the correct treatment is started in time. In the last stages of a miscarriage, you will have to say goodbye to pregnancy, in this case, curettage is prescribed. In an ectopic pregnancy, the embryo develops in the fallopian tube or cervix. Menstruation is delayed, some symptoms of pregnancy are noted, but the embryo is not found in the uterus. When the embryo reaches a certain stage of development, bleeding occurs. In this situation, the woman needs urgent medical attention.
A pregnant woman who has begun uterine bleeding should immediately contact a supervising doctor. When a spontaneous abortion begins, the fetus can be saved if the correct treatment is started in time. In the last stages of a miscarriage, you will have to say goodbye to pregnancy, in this case, curettage is prescribed. In an ectopic pregnancy, the embryo develops in the fallopian tube or cervix. Menstruation is delayed, some symptoms of pregnancy are noted, but the embryo is not found in the uterus. When the embryo reaches a certain stage of development, bleeding occurs. In this situation, the woman needs urgent medical attention.
In the third trimester of pregnancy, uterine bleeding is deadly for both the mother and the developing child.
The causes of the pathological condition in the later stages of gestation are placenta previa or abruption, rupture of the uterine walls. In these cases, the woman urgently needs medical attention, usually a caesarean section is performed. Patients who have a high risk of the above pathologies should be kept. Uterine bleeding can also occur during childbirth. In this case, its causes may be the following pathological conditions:
Patients who have a high risk of the above pathologies should be kept. Uterine bleeding can also occur during childbirth. In this case, its causes may be the following pathological conditions:
- placenta previa;
- bleeding disorder;
- low uterine contractility;
- placental abruption;
- stuck in the uterus afterbirth.
If bleeding from the uterus occurs several days after delivery, an ambulance should be called immediately. The young mother will need emergency hospitalization.
First aid before the arrival of doctors
Excessive bleeding from the vagina must be stopped or at least reduced before the arrival of doctors. This is a matter of life and death for a woman. In most cases, with competent first aid, bleeding stops, but in 15% of cases, the pathological process ends in death.
Every woman should know how to help herself before the arrival of the doctors, what can and cannot be done.
A sick woman, waiting for doctors at home, should do the following:
- lie on her back, remove the pillow from under her head;
- place a high roll made of towels or a blanket under the shins;
- place a cold water bottle or ice-filled heating pad on the abdomen;
- drink cold still water.
It is strictly forbidden:
- to stand or sit;
- lie with your legs pressed to your stomach;
- take a hot bath;
- douching;
- put a heating pad on the stomach;
- drink hot drinks;
- take any medication.
Drug therapy
Treatment of diseases that caused bleeding from the uterus is carried out in a hospital. In addition, the doctor prescribes medicines to the patient to help stop the bleeding. Hemostatic drugs are taken only on the recommendation of a medical specialist, taking drugs at one's own discretion is strictly prohibited. Below is a list of medicines most commonly used to stop bleeding.
- Etamzilat - This drug stimulates the synthesis of thromboplastin, changes the permeability of blood vessels. Blood clotting increases, as a result, bleeding is weakened. The drug is intended for intramuscular injection.
- Oxytocin - A hormonal drug often used during childbirth to improve uterine contractility.
 As a result of contraction of the uterine muscles, bleeding stops. The drug oxytocin is prescribed for intravenous administration with the addition of glucose, has a large list of contraindications.
As a result of contraction of the uterine muscles, bleeding stops. The drug oxytocin is prescribed for intravenous administration with the addition of glucose, has a large list of contraindications. - Aminocaproic acid - This medicinal substance prevents blood clots from dissolving under the influence of certain factors, due to this, bleeding is reduced. The medicine is either taken orally or given intravenously. Treatment of uterine bleeding with aminocaproic acid is carried out under close medical supervision.
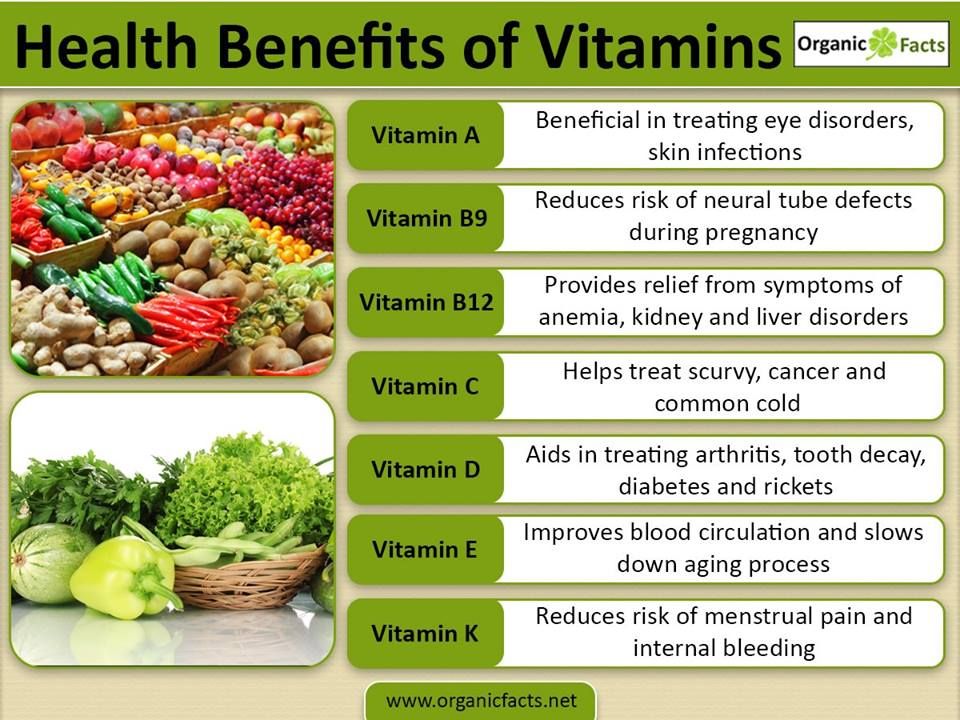
- Vikasol - The drug is based on vitamin K. With a deficiency in the body of this vitamin, blood clotting worsens. The drug is prescribed to patients who have a tendency to uterine bleeding. However, vitamin K begins to act only 10-12 hours after it enters the body, so it is not advisable to use the drug to stop the blood in emergency cases.
- Calcium gluconate - The drug is prescribed for calcium deficiency in the body. Deficiency increases the permeability of the vascular walls, worsens blood clotting.
 This drug is also not suitable for emergency use, but is used to strengthen blood vessels in patients prone to bleeding.
This drug is also not suitable for emergency use, but is used to strengthen blood vessels in patients prone to bleeding.
Treatment with folk remedies
Decoctions and infusions of medicinal plants can be used to stop and prevent uterine bleeding. Listed below are the most popular and effective folk recipes for stopping blood.
- Yarrow infusion - You need to take 2 teaspoons of dried plant material, pour a glass of boiling water. The solution is infused for about an hour, then filtered. The infusion is taken in a quarter cup 4 times a day before meals.
- Nettle decoction - Take a tablespoon of dried nettle leaves, pour a glass of boiling water. The solution is boiled over low heat for 10 minutes, then filtered. Ready decoction is taken in a tablespoon 3 times a day before meals.
- Infusion of shepherd's purse - Take a tablespoon of dried plant materials, pour a glass of boiling water. The container with the solution is wrapped in a warm towel, left for an hour to infuse.