Can kids get stds
Sexually transmitted diseases in children
Review
. 1992 Dec;9(4):329-34.
doi: 10.1111/j.1525-1470.1992.tb00619.x.
G Lowy
- PMID: 1492047
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1525-1470.1992.tb00619.x
Review
G Lowy. Pediatr Dermatol. 1992 Dec.
. 1992 Dec;9(4):329-34.
doi: 10.1111/j.1525-1470.1992.tb00619.x.
Author
G Lowy
- PMID: 1492047
- DOI: 10.
1111/j.1525-1470.1992.tb00619.x
Abstract
Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) in children may be transmitted by sexual abuse, by accidental contact, or perinatally. Although only 2% to 10% of abused children become infected, childhood syphilis, gonorrhea, condylomata acuminata, and Chlamydia trachomatis must always be considered. We reviewed data from our hospital regarding the frequency, prevalence, routes of transmission, and clinical features of these infections. Ninety-five percent of acquired syphilis in children is transmitted by sexual abuse. The perpetrator is usually someone the child knows or trusts. Of our 21 patients under 14 years of age with acquired syphilis, most were 4 to 8 years old. Girls were infected twice as often as boys. Sexual contact was confirmed in 71.4%. A chancre sore was infrequent in children; condylomata lata was the most frequent cutaneous lesion (80. 9%). In the last 10 years, 102 cases of congenital syphilis were diagnosed in our hospital. The main clinical findings were bone involvement (78.7%), hepatosplenomegaly (68.8%), cutaneous lesions (50.8%), and jaundice (15.1%). Gonorrhea was detected in only nine children. Vulvovaginitis was the most common clinical manifestation. Sexual transmission was documented in three patients. Accidental contact with their infected mother occurred in two sisters. Three newborns acquired the disease during delivery. The STDs in children are a worrisome problem. Evaluation for sexual abuse should be done in all cases. Prevention and treatment of adults are the main steps to prevent these infections in children.
9%). In the last 10 years, 102 cases of congenital syphilis were diagnosed in our hospital. The main clinical findings were bone involvement (78.7%), hepatosplenomegaly (68.8%), cutaneous lesions (50.8%), and jaundice (15.1%). Gonorrhea was detected in only nine children. Vulvovaginitis was the most common clinical manifestation. Sexual transmission was documented in three patients. Accidental contact with their infected mother occurred in two sisters. Three newborns acquired the disease during delivery. The STDs in children are a worrisome problem. Evaluation for sexual abuse should be done in all cases. Prevention and treatment of adults are the main steps to prevent these infections in children.
Similar articles
-
Sexually transmitted diseases in sexually abused children: medical and legal implications.
Hammerschlag MR. Hammerschlag MR. Sex Transm Infect.
 1998 Jun;74(3):167-74. doi: 10.1136/sti.74.3.167. Sex Transm Infect. 1998. PMID: 9849550 Free PMC article. Review.
1998 Jun;74(3):167-74. doi: 10.1136/sti.74.3.167. Sex Transm Infect. 1998. PMID: 9849550 Free PMC article. Review. -
Sexually transmitted diseases in children.
Pandhi RK, Khanna N, Sekhri R. Pandhi RK, et al. Indian Pediatr. 1995 Jan;32(1):27-30. Indian Pediatr. 1995. PMID: 8617530
-
Sexually transmitted diseases in sexually abused children.
White ST, Loda FA, Ingram DL, Pearson A. White ST, et al. Pediatrics. 1983 Jul;72(1):16-21. Pediatrics. 1983. PMID: 6688126
-
Sexual assault and sexually transmitted diseases: detection and management in adults and children.
Schwarcz SK, Whittington WL.
 Schwarcz SK, et al. Rev Infect Dis. 1990 Jul-Aug;12 Suppl 6:S682-90. doi: 10.1093/clinids/12.supplement_6.s682. Rev Infect Dis. 1990. PMID: 2201079 Review.
Schwarcz SK, et al. Rev Infect Dis. 1990 Jul-Aug;12 Suppl 6:S682-90. doi: 10.1093/clinids/12.supplement_6.s682. Rev Infect Dis. 1990. PMID: 2201079 Review. -
Sexually transmitted diseases in children and evidence of sexual abuse.
Argent AC, Lachman PI, Hanslo D, Bass D. Argent AC, et al. Child Abuse Negl. 1995 Oct;19(10):1303-10. doi: 10.1016/0145-2134(95)00082-j. Child Abuse Negl. 1995. PMID: 8556444
See all similar articles
Cited by
-
Medical care for migrant children in Europe: a practical recommendation for first and follow-up appointments.
Schrier L, Wyder C, Del Torso S, Stiris T, von Both U, Brandenberger J, Ritz N. Schrier L, et al. Eur J Pediatr.
 2019 Sep;178(9):1449-1467. doi: 10.1007/s00431-019-03405-9. Epub 2019 Jun 26. Eur J Pediatr. 2019. PMID: 31240389
2019 Sep;178(9):1449-1467. doi: 10.1007/s00431-019-03405-9. Epub 2019 Jun 26. Eur J Pediatr. 2019. PMID: 31240389
Publication types
MeSH terms
Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs)
Nationwide Children’s Hospital
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) can be spread when a person is exposed to blood, skin, semen, vaginal fluids, or other bodily fluids that have a virus, bacteria, or parasite during sexual contact. Sexual contact includes vaginal, oral, or anal sex, or contact with the genitals. They can also be spread from an infected mother to her baby during a vaginal delivery. STIs are very common. It is thought that 20 million new cases of STIs happen in the United States every year. Half of these cases are teenagers and young adults.
Half of these cases are teenagers and young adults.
Types of STIs
STIs are caused by bacteria, viruses, or parasites.
- Bacterial and parasitic STIs can usually be treated with antibiotics.
- Viral STIs can stay in the body, sometimes for life. They cannot be cured, but symptoms can be managed with medicines.
| Bacteria/Parasite STI's | Virus STI's |
|---|---|
| Chlamydia | Herpes |
| Gonorrhea | Human Papilloma Virus (HPV) |
| Syphilis | HIV/AIDS |
| Trichomoniasis | Hepatitis |
Risk Factors for STIs
All sexually active teenagers and young adults should be tested for STIs at least once a year. Certain behaviors put males and females at a bigger risk for getting a STI. If you do any of these behaviors, you should consider getting tested more than once a year.
- Males having sex with other males
- Having a new sex partner or many sex partners
- Having sex with someone who has an STI
- Pregnancy
- Having unprotected oral, vaginal, or anal sex. This means sex without a condom.
- Getting a new STI. This puts you at greater risk of having another STI at the same time.
- Had an STI in the past.
- Trading sex for money, drugs, or anything else.
Signs and Symptoms of STIs
Most infections have no signs or symptoms. Most signs and symptoms will depend on which STI you have. You are able to spread STIs to partners even when you do not have symptoms of the STI.
- Sores on the mouth, genitals, or rectal areas
- Burning or pain during urination
- Discharge from the penis or vagina
- Vaginal smell (odor)
| Some of the most common EARLY signs and symptoms are: | Some of the most common LATE signs and symptoms are: |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Diagnosing STIs
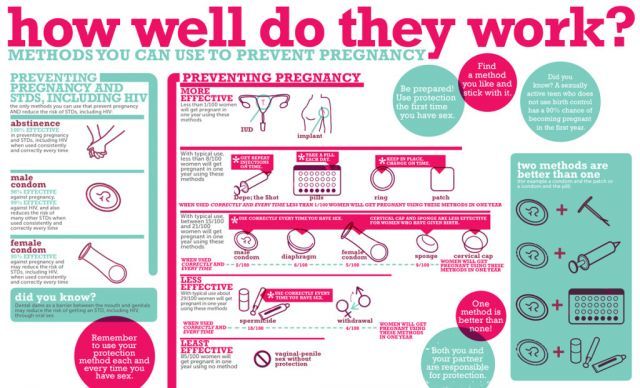
- There is not one test that looks for all STIs, so you may need 2 or more different tests.

- STIs can be tested through urine (Picture 1), blood, or genital discharge and open sores. Usually you can collect the specimen yourself, in private.
- Test results usually come back within 2 to 3 days or sooner.
Treating STIs
Most STIs can be treated. Many STIs can be cured, but some do not have a known cure. These may still be managed with medicines.
- Antibiotics – only for STIs caused by bacteria or parasites. It is important that you take all of your medicine until it is gone, even if you feel better.
- Medicines – for STIs caused by viruses, like HPV, herpes, and HIV/AIDS. These can treat your symptoms and may lower the risk of giving the STI to a sex partner.
- If you have an STI, it is important to tell any partners you’ve had in the past 3 months. They will need to be tested and treated, as well.
- If your partner(s) does not have a regular doctor, he or she can be treated at the Columbus Public Health Sexual Health Clinic, 240 Parsons Avenue, Columbus, Ohio 43215.
 The phone number is (614) 645-7772. If you live outside the Columbus area, call your local health department.
The phone number is (614) 645-7772. If you live outside the Columbus area, call your local health department. - After being treated for an STI, do not have sex at all for the next week.
Preventing STIs
- NOT HAVING SEX (abstinence) is the only 100% way to make sure you do not get an STI.
- Limit the number of sexual partners. Know your partner and his or her sexual history.
- ALWAYS USE A LATEX CONDOM (Picture 2). Use it correctly. Use a condom every time you have sex, the whole time you have sex.
- Having only one, long-term partner that has tested negative for all STIs and using a condom, the right way, every time you have sex.
- Vaccines are available for two STIs (Hepatitis B and HPV). This can greatly lower your risk of getting either of these STIs.
- Avoid mind-altering substances such as alcohol and other drugs. You cannot make good decisions if you are drunk or high.

When to Call the Doctor
Call your doctor if your symptoms get worse or you get new symptoms, like pain in the lower belly (pelvis) or pain in the testicles.
Follow-ups and Appointments
You may need close follow-up and education after being diagnosed with some STIs. It is important to follow the doctor’s or healthcare provider’s orders.
- After treatment for chlamydia, gonorrhea, or trichomonas, you should be retested in three months to be sure you did not get that STI again, or any other STI.
- Some STIs make it easier for HIV to enter the skin and mucous membranes. If you have an STI, you should get tested for HIV.
- Write down all of your questions as you think of them. Bring the list with you when you see the doctor or healthcare provider.
- Call the clinic or doctor’s office if you cannot make your appointment.
- Be sure to tell your health care provider if there is any chance you may be pregnant.
- AVOID SEXUAL CONTACT until one week after you and your partner are both finished with the antibiotic treatments.
For More Information
- If you have any questions, call the Adolescent Medicine Clinic at (614) 722-2450.
- For more information, you may also call the National STD Hotline at 1-800-227-8922, Monday through Friday, 8 a.m. to 11 p.m.
- You can also get information at www.ashasexualhealth.org.
- Refer to these other Helping Hands:
- HH-I-38, Chlamydia
- HH-I-67, Gonorrhea
- HH-I-174, Herpes Simplex Virus
- HH-I-116, HIV Infection/AIDS
- HH-I-108, Trichomoniasis
- HH-I-102, Genital Warts
- HH-I-43, Hepatitis B
- HH-IV-46, Condoms
- HH-I-119, Vaginal Discharge
Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs) (PDF)
HH-I-428 4/17 Copyright 2017, Nationwide Children’s Hospital
You Might Also Be Interested In
Article
Birth Control: Depo Provera®
Article
Birth Control: Contraceptive Patch
Gonorrhea
Sexual diseases in children and adolescents - treatment, symptoms, diagnosis - GorPS.
 ru
ru Sexual diseases in children are now quite common. Statistical data suggest that infections characteristic of a more mature age are increasingly being diagnosed in infants. Sexually transmitted diseases in children can occur even in utero. If they are not immediately detected, the child may subsequently develop a dangerous pathology. It is important to know the specifics of all violations, identify them in time and immediately contact a specialist, since sexual diseases in children can be very life-threatening. If they are not treated in time, a fatal outcome is quite likely.
Sexually transmitted diseases in children alphabetically
Gonorrhea in children
Gonorrhea (gonorrhoea), also gonorrhea - a disease most common in adults, but children can also become infected. Disease requires the most...
Mycoplasmosis in children
Mycoplasmosis in children is not the most common, but unpleasant infection that causes a wide range of diseases of the reproductive and respiratory systems. ...
...
Trichomoniasis in children
Trichomoniasis is a common urinary tract infection systems. It is transmitted mainly through sexual contact, but in some cases it is possible to infect ...
Chlamydia in children
Having discovered chlamydia in children, parents often wonder why a child has a venereal disease? In reality chlamydia is transmitted to children ...
Sexual diseases in children are now quite common. Statistical data suggest that infections characteristic of a more mature age are increasingly being diagnosed in infants. Sexually transmitted diseases in children can occur even in utero. If they are not immediately detected, the child may subsequently develop a dangerous pathology. It is important to know the specifics of all violations, identify them in time and immediately contact a specialist, since sexual diseases in children can be very life-threatening. If they are not treated in time, a fatal outcome is quite likely.
Causes and consequences
Sexually transmitted diseases in children occur due to various factors. According to doctors, hereditary pathologies are increasingly observed. But there are also acquired disorders. Therefore, it is important to know how sexually transmitted diseases are transmitted to children. A child can become infected in the following ways:
- when breastfeeding a mother who is sick with HIV, syphilis, various types of hepatitis;
- by direct contact with infected household items or an infected person;
- during the passage of the fetus through the birth canal during childbirth;
- when the embryo is in the womb of an infected mother.
Sexually transmitted diseases in adolescents are no less common than in adults. Among the reasons are:
- early onset of sexual activity,
- lack of knowledge about ways to protect against STIs,
- failure to comply with preventive measures and sanitary rules,
- during medical procedures.

Childhood sexually transmitted diseases cause great damage to health. The consequences can be the most deplorable. They affect the formation of deformities, lag in development. At a more mature age, the slightest violations can develop into a serious illness. These can be ectopic pregnancies, and orgastic dysfunctions, and infertility, and disruptions in the menstrual cycle, and oncology.
Sexually transmitted diseases in adolescents may not manifest themselves in the early stages. Subsequently, they can lead to the chronic stage of the disease, cancer, and even death.
Symptoms
Children's sexual diseases may not reveal themselves until a certain period. As soon as the first symptoms appear, you need to make an appointment with a doctor.
Make an appointment
Save your time searching, we will call you back, select the nearest doctor of the required profile and make an appointment.
Sign up
I have read and agree to the terms of the User Agreement, including those relating to the work with personal data (section 5).
Small, at first glance, changes serve as a signal. The main signs of sexually transmitted diseases in children in the genital area:
- erosion,
- papillomas,
- ulcers,
- rash.
Diagnosis and types
Only experienced and qualified venereologists, urologists and gynecologists can detect childhood sexual diseases. That is why it is important to have regular check-ups. Only a doctor is able to determine the pathology and conduct a competent examination. Diagnosis includes a detailed survey of parents, a visual examination of the child. Then, biological material is taken for a general smear analysis for diseases of the genital organs in children. If necessary, the doctor can also take a bacterial culture of the material and take a blood sample. In some cases, ultrasound, X-ray and magnetic resonance examinations are performed. The course of treatment depends on which childhood diseases of the genital organs were identified.
Sexual diseases in children are divided into several types:
- dropsy is an accumulation of fluid in the vaginal membrane of the testis in boys;
- disease of the gonads, manifested in the early onset of secondary sexual characteristics;
- AIDS characterized by fever, muscle and bone pain, rashes on the body;
- vulvitis - an inflammatory process in the vulva region in girls;
- gonorrhea, which manifests itself in copious purulent discharge of a greenish color;
- trichomoniasis characterized by thin, foamy discharge and itching;
- candidiasis, the main features of which are burning, white cheesy discharge;
- chlamydia in children manifests itself in the form of conjunctivitis and infections in the oral cavity;
- mycoplasmosis is expressed as itching in the genital area;
- papillomavirus infection reveals itself in the form of itching and the appearance of genital warts.
Sexually transmitted diseases in children cannot be cured on their own.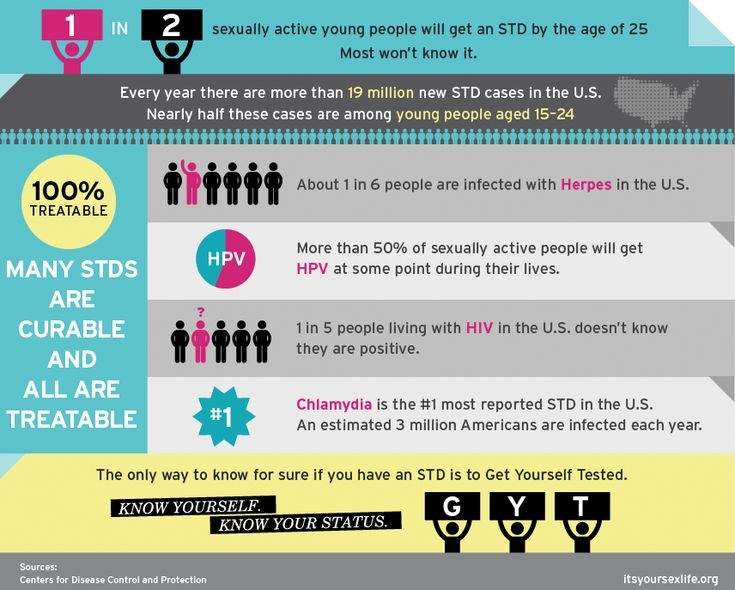 This can be hazardous to health. Only a knowledgeable doctor is able to recognize the disease and choose the right course of treatment. It takes place with the use of individually selected medications.
This can be hazardous to health. Only a knowledgeable doctor is able to recognize the disease and choose the right course of treatment. It takes place with the use of individually selected medications.
Prevention
It is easier, of course, to engage in prevention rather than cure sexual diseases in children and adolescents. To protect your child from infections, it is enough to follow simple recommendations:
- confidential conversations about how infection occurs and what are the signs of STIs;
- observance of hygiene rules;
- familiarity with methods of contraception;
- vaccination;
- scheduled examinations by a venereologist.
Sexual diseases in children can be avoided in most cases. The specialists of the clinic will help protect the baby from ailments. They are engaged in comprehensive examinations and the selection of optimal preventive measures. When a pathology is detected, doctors write out a treatment plan. Venereal disease in children is not yet a sentence. You can find a suitable venereologist yourself on our portal. Also call the free referral service, where they will help you find a doctor who knows everything about sexual diseases in children.
Venereal disease in children is not yet a sentence. You can find a suitable venereologist yourself on our portal. Also call the free referral service, where they will help you find a doctor who knows everything about sexual diseases in children.
This material is posted for informational purposes only, is not medical advice and should not be used as a substitute for consultation with a doctor. For diagnosis and treatment, please contact qualified doctors!
Please rate article
Rate
Make an appointment
Save your time searching, we will call you back, select the nearest doctor of the required profile and make an appointment.
Sign up
I have read and agree to the terms of the User Agreement, including those relating to the work with personal data (section 5).
See a doctor about your problem:
Top rated
Akhunova Nailya Rashitovna
Venereologist, dermatologist, mycologist.
Price − 2 300 ₽
Dobromed at the River Station
water stadium River Station Koptevo Khovrino Belomorskaya
Most Experienced
4 reviews
Naborova Vera Vyacheslavovna
Venereologist, dermatologist, cosmetologist, trichologist.
Price − 1 900 ₽ 1 615 ₽
Medical Center Medline-Service on Molodyozhnaya
Krylatskoe Kuntsevskaya Youth Kuntsevskaya
Less price per visit
Derkach Snezhana Aleksandrovna
Venereologist, dermatologist, cosmetologist.
Price − 1 100 ₽
100Med (Stomed) in Lyubertsy
Kotelniki
Online booking
6 reviews
Medical Center He Clinics on the Culture Park
Culture Park
Shabolovskaya
9025 Zubovsky Br.
Online booking
111 reviews
EURDLICK
Pervomaiskaya
Shchelkovskaya
Lilac Bulvar, 32a
Online booking6 reviews0003
Alma-Ata
Borisovo
Bratislava
Maryino
Address: st. Lyublinskaya, 104
Lyublinskaya, 104
Online booking
75 reviews
Family on Skhodnenskaya
Planner
Skhodnenskaya
Tushinskaya
Address: st. Geroev Panfilovtsev, 1
Online booking
All clinics specializing in venereology
Venereal diseases
Take care of health, like honor, from a young age
Sexually transmitted diseases currently include a large number of infections. The most dangerous of them is syphilis.
Treponema pallidum is the causative agent of syphilis. The disease is characterized by a chronic, undulating course and damage to all organs and systems in the body. The disease manifests itself 3-4 weeks after infection in the form of a painless ulcer or erosion at the site of the introduction of the pathogen (usually on the genitals). A week later, nearby lymph nodes (often inguinal) become inflamed. Around the same time, positive blood tests for syphilis appear.
3 months after infection, a secondary period of the disease develops, characterized by the appearance of various rashes and foci of hair loss on the skin.
In the absence of treatment, after 2-4 years, the tertiary period of the disease develops, which is characterized by a malignant course, resistance to treatment and is manifested by the formation of infiltrates on the skin and in internal organs that are prone to decay. Manifestations of the tertiary period of syphilis lead to dysfunction of blood vessels, bones, muscles, nervous system and other organs.
Syphilis in a pregnant woman often leads to fetal death due to similar damage to all organs. When a live baby is born, it is usually small and low birth weight. Damage to organs and systems can be varied: blindness, deafness, dementia, epilepsy, paralysis of the limbs, heart defects, etc.
Persons leading a promiscuous sexual life should be periodically tested for syphilis. Treatment of syphilis is carried out in a dermatovenerological dispensary with an examination of family members and everyone who was in contact with the patient.
Gonorrhea is an infectious sexually transmitted disease characterized by inflammation of the mucous membranes of the urogenital organs, rectum, oral cavity, and eyes. Often, gonorrhea affects the joints, internal organs, and the nervous system.
Gonorrhea is usually transmitted through sexual contact. Non-sexual (domestic) infection is observed in children when using common beds with gonorrhea patients, wet washcloths, towels, diapers. It is possible to bring microbes into the eyes with hands contaminated with secretions of the genital organs. In newborns, microbes enter the mucous membranes of the eyes, oral cavity, and occur when sick mothers pass through the birth canal.
It is possible to bring microbes into the eyes with hands contaminated with secretions of the genital organs. In newborns, microbes enter the mucous membranes of the eyes, oral cavity, and occur when sick mothers pass through the birth canal.
A few days after infection there is a discharge from the urethra, sometimes pain when urinating. In case of damage to the eyes - pain in the eyes and blurred vision. If you do not see a doctor in a timely manner, gonorrhea becomes chronic.
This disease leads to serious complications (infertility, inflammation of the uterus and appendages in women, inflammation of the prostate gland and sexual dysfunction in men), which can subsequently cause a break in family relationships.
You can get gonorrhea at any age, there is no immunity to it.
Treatment should be carried out only in a specialized medical institution - a dermatovenerological dispensary. The success of treatment depends on timely treatment to the doctor. Self-medication leads to serious consequences and further spread of the infection.