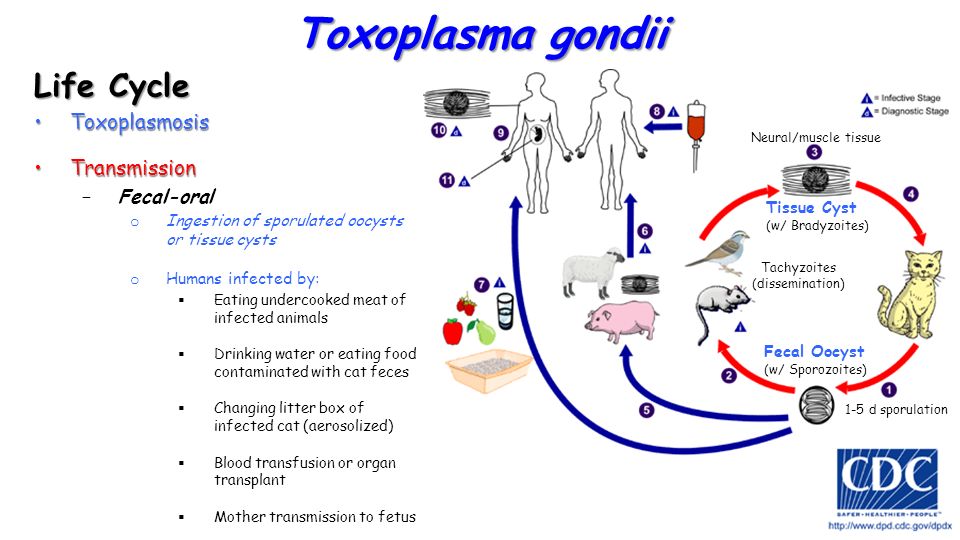
Boosting breast milk
Low Milk Supply | WIC Breastfeeding Support
Many moms worry about low milk supply, but most of the time your body makes exactly what your baby needs, even if you don't realize it. There are also ways to tell if your baby is getting enough milk. If you aren't making enough, there are ways you can build your supply. And your WIC breastfeeding staff is always there to help!
Am I Making Enough Milk?
First, look for these signs that your baby is getting enough milk. For example, pay attention to the number of wet and dirty diapers and your baby's weight gain.
Things you should NOT worry about:
- How your breasts feel. Your breasts will feel softer and less full as your milk supply adjusts to your baby's needs. This does not mean you have low supply.
- If your baby nurses for shorter periods of time, such as only 5 minutes on each breast.
- If your baby's feeds are bunched together. This is called cluster feeding and happens when your baby starts nursing more often and for longer.
This can happen in the evenings or because of growth spurts.
- Not getting much milk when you express. Your baby is much more effective than a pump or hand expression at getting out milk. Find tips to help you pump.
If you are still concerned, talk to your baby's doctor about their growth.
Causes of Low Milk Supply
While most moms make plenty of milk, some do have low milk supply. This might happen if you:
- Limit your baby's breastfeeding sessions. Remember, the more you feed on demand, the more milk you make.
- Give your baby infant formula instead of breastfeeding.
- Introduce solid foods before baby is 4-6 months old.
- Take certain birth control pills or other medicine.
- Don't get enough sleep.
- Drink alcohol or smoke.
- Have had breast surgery.
Talk to your doctor if you have hepatitis B or C, herpes, or diabetes. These conditions may also affect milk supply.
Increasing Your Milk Supply
Breastfeeding frequently—especially in the first hours, days, and weeks—is the main way to increase your milk supply. Your body will make milk to meet your baby's demand.
Try these tips to help you make more milk:
- Breastfeed every time your baby is hungry. In the early weeks, your baby will eat 8-12 times every 24 hours. It's best not to put your baby on a strict feeding schedule. Follow your baby's cues, and let your baby tell you when it's time to eat.
- Make sure your baby is latching well.
- Offer both breasts at each feeding. Let your baby finish the first side, then offer the other side.
- Empty your breasts at each feeding.
 Hand express or pump after a feeding to draw out all the milk and signal your body to make more.
Hand express or pump after a feeding to draw out all the milk and signal your body to make more. - Avoid bottles and pacifiers in the early weeks. Feed your baby from your breast whenever you can.
- Get plenty of sleep, and eat a healthy diet.
- Pump or express your milk. Pumping or expressing milk frequently between nursing sessions, and consistently when you're away from your baby, can help build your milk supply.
- Relax and massage. Relax, hold your baby skin-to-skin, and massage your breasts before feeding to encourage your milk to let down.
- Take care of yourself. Get plenty of rest, eat well, drink enough fluids, and let others help you.
Consider Charting Your Progress
Record how often your baby is breastfeeding, for how long, and on which sides. If you are supplementing with infant formula, record how much your baby is getting and decrease the infant formula as your milk supply increases. WIC breastfeeding staff can help you determine how much infant formula your baby needs.
WIC breastfeeding staff can help you determine how much infant formula your baby needs.
Still Have Questions?
Contact your WIC breastfeeding expert. They can talk to you about supply concerns and give you tips to increase your supply to meet your baby's needs.
How to Increase Breast Milk: Home Remedies, Diet, Supplements
We include products we think are useful for our readers. If you buy through links on this page, we may earn a small commission. Here’s our process.
Can you increase breast milk production?
If you’re worried that you’re not producing enough breast milk for your baby, you’re not alone.
Data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention shows that approximately 75 percent of new mothers start off breastfeeding their babies, but many stop either partially or completely within the first few months. One of the most common reasons for this is worry about insufficient milk production.
For many women, your milk supply is just fine. However, if you do need to increase your breast milk production, there are ways to do it.
However, if you do need to increase your breast milk production, there are ways to do it.
Read on to learn how to increase your breast milk production using several evidence-based methods and some practices mothers have sworn by for centuries.
How to increase breast milk production
The following are things that you can do to increase breast milk production. How long it’ll take to boost your milk supply depends on how low your supply is to begin with and what’s contributing to your low breast milk production. Most of these methods, if they’re going to work for you, should begin working within a few days.
1. Breastfeed more often
Breastfeed often and let your baby decide when to stop feeding.
When your baby suckles your breast, hormones that trigger your breasts to produce milk are released. That’s the “let-down” reflex. The let-down reflex is when muscles in your breasts contract and move the milk through the ducts, which happens shortly after your baby begins breastfeeding. The more you breastfeed, the more milk your breasts make.
The more you breastfeed, the more milk your breasts make.
Breastfeeding your new baby 8 to 12 times a day can help establish and maintain milk production. But this doesn’t mean that more or fewer feedings indicates a problem.
2. Pump between feedings
Pumping between feedings can also help you increase milk production. Warming your breasts before pumping can help make you more comfortable and pump easier, too.
Try pumping whenever:
- You have milk left over after a feeding.
- Your baby has missed a feeding.
- Your baby gets a bottle of breast milk or formula
3. Breastfeed from both sides
Have your baby feed from both breasts at each feeding. Let your baby feed from the first breast until they slow down or stop feeding before offering the second breast. The stimulation of having both breasts breastfed from can help increase milk production. Pumping milk from both breasts simultaneously has also been found to increase milk production and result in a higher fat content in the milk.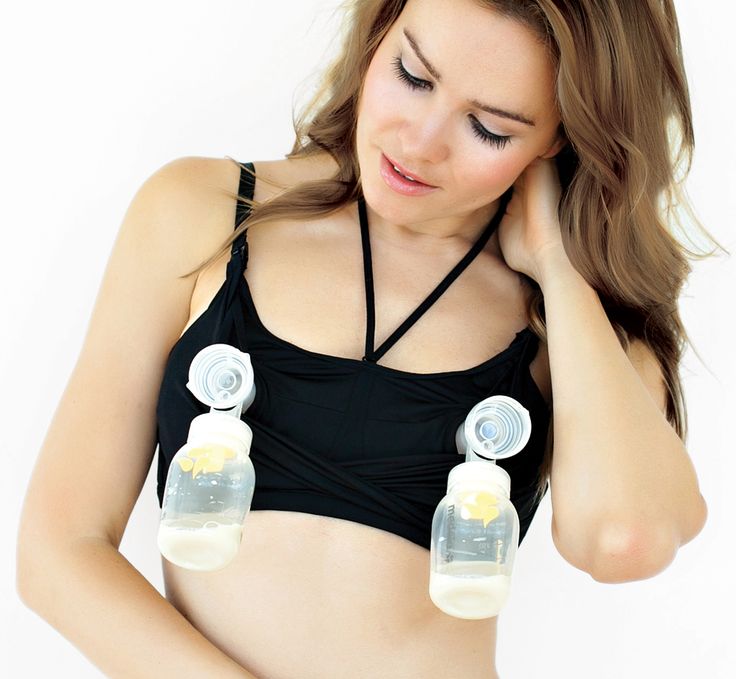
4. Lactation cookies
You can find lactation cookies in stores and online on Amazon or you can make your own. While there’s no research available on lactation cookies specifically, some of the ingredients have been linked to an increase in breast milk. These foods and herbs contain galactagogues, which may promote lactation. More research is needed, though.
Some of these include:
- whole oats
- wheat germ
- brewer’s yeast
- flaxseed meal
Easy lactation cookie recipe
Ingredients
- 2 cups white flour
- 2 cups oats
- 1 tbsp. wheat germ
- 1/4 cup brewers’ yeast
- 2 tbsp. flaxseed meal
- 1 cup butter, softened
- 3 egg yolks
- 1/2 cup white sugar
- 1/2 cup brown sugar
- 1/4 cup water
- 1 1/2 teaspoons pure vanilla extract
- 1 tsp. baking soda
- 1/2 tsp. salt
Directions
- Preheat oven to 350°F (175°C).

- Mix the flaxseed meal with water in small bowl and let soak for at least 5 minutes.
- Cream the butter and white and brown sugar in a large mixing bowl. Add egg yolks and vanilla extract. Beat on low for 30 seconds or until ingredients are combined. Stir in flaxseed meal and water.
- In a separate bowl, mix flour, baking soda, brewer’s yeast, wheat germ, and salt. Add to butter mixture, and stir just until combined. Fold in the oats.
- Roll dough into 2-inch balls and place 2 inches apart onto a baking sheet.
- Bake for 10 to 12 minutes or until edges start to golden. Let the cookies stand on the baking sheet for 1 minute. Cool on a wire rack.
You also can add dried fruit, chocolate chips, or nuts for some variety.
5. Other foods, herbs, and supplements
There are other foods and herbs that may increase breast milk production, according to the Canadian Breastfeeding Foundation. Some, such as fenugreek, have been found to take effect in as little as seven days. These foods and herbs include:
These foods and herbs include:
- garlic
- ginger
- fenugreek
- fennel
- brewer’s yeast
- blessed thistle
- alfalfa
- spirulina
Always talk to your doctor before taking a new supplement, especially when breastfeeding. Even natural remedies can cause side effects.
Potential causes for low milk supply
There are several factors that can interfere with the let-down reflex and cause low milk supply, including:
Emotional factors
Anxiety, stress, and even embarrassment can interfere with the let-down reflex and cause you to produce less milk. Creating a private and relaxing environment for breastfeeding and making the experience enjoyable and free of stress can help increase breast milk production. Try one of these 10 ways to relieve stress.
Medical conditions
Some medical conditions may interfere with milk production. These conditions include:
- pregnancy-induced high blood pressure
- diabetes
- polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS)
Certain medications
Medications that contain pseudoephedrine, such as sinus and allergy medications, and certain types of hormonal birth control may lower breast milk production.
Smoking and alcohol
Smoking and drinking moderate to heavy amounts of alcohol can lower your milk production.
Previous breast surgery
Not having enough glandular tissue because of breast surgery, such as breast reduction, cyst removal, or mastectomy, can interfere with lactation. Breast surgery and nipple piercings can damage the nerves that are connected to breast milk production.
Is your supply low?
You may be worried that your milk supply is low, but low breast milk production is rare. Most women make more than one-third more milk than their babies need, according to the Mayo Clinic.
There are many reasons your baby may cry, fuss, or seem distracted while breastfeeding, but it’s unlikely to be due to your milk supply. Teething, gas pains, or even just being tired can lead to fussiness. Babies are also more easily distracted as they age. This can interfere with feedings and cause them to pull away when you’re trying to breastfeed.
Every baby’s needs are different. Most newborns need 8 to 12 feedings in 24 hours, some even more. As your baby gets older, they’ll feed more efficiently. This means that even though feedings are much shorter, they may be getting more milk in less time. Other babies like to linger and suck longer, often until the flow of milk has almost stopped. Either way is fine. Take your cue from your baby and feed until they stop.
As long as your baby is gaining weight as expected and needing regular diaper changes, then you’re probably producing enough milk.
When your baby is getting enough milk, they will:
- gain weight as expected, which is 5.5 to 8.5 ounces each week until 4 months
- have three or four stools every day by 4 days of age
- have two wet diapers over 24 hours by the 2nd day after birth, and six or more wet diapers after day 5
Regular checkups with your child’s pediatrician will help determine if your milk supply may be low or if your child is undernourished. Tracking feedings and diaper changes can also help your doctor determine whether or not your milk supply is lower than it should be.
Tracking feedings and diaper changes can also help your doctor determine whether or not your milk supply is lower than it should be.
If your milk supply is low, supplementing with formula may be an option. Speak to your doctor or a lactation specialist before supplementing feedings with formula to avoid accidental early weaning.
A lactation specialist can create a supplementation plan for you to follow so that you can increase your milk production and gradually decrease supplementation.
When to seek help
If you’re worried that your baby isn’t getting enough milk or feel that your baby isn’t thriving, speak to your doctor or consult a lactation specialist. If low milk production is the problem, correcting it may be as simple as making a few changes to your routine or feeding technique, or adjusting a medication you’re on.
If you’re supply is low or you’re having other trouble with breastfeeding, try to remember the motto “Fed is best.” As long as your baby is well-fed and getting the nourishment they need, breast milk or formula are both fine.
obstetrician-gynecologist Starostina Antonina Viktorovna.
For the normal development of lactation, first of all, it is necessary to organize the feeding of the child (feeding on demand, without a night break, the absence of nipples and pacifiers that suppress the suckling reflex of the baby), properly care for the breast, use a breast pump to stimulate and increase lactation, use according to indications other accessories for breastfeeding.
Sleep should be at least 10 hours a day - night and day. Outdoor walks for at least 2 hours. Frequent breastfeeding from birth (at least 10 times a day) with obligatory night feedings. Good nutrition and an increase in the amount of fluid consumed up to 1.5 - 2 liters per day (this is tea, soups, decoctions, milk, dairy products). Shower-massage: after feeding the baby and expressing milk, pour hot water (45 degrees) from the shower over the mammary gland that was fed, while massaging in circular motions from the nipple to the periphery and from top to bottom, while expressing milk. Duration 5-10 minutes.
Duration 5-10 minutes.
Perform the procedure 2 times for the left and 2 times for the right breast during the day. Drink hot tea with milk 30 minutes before feeding.
Drink in small sips throughout the day.
- Steep 3 teaspoons of dry nettle with 2 cups of boiling water and infuse for 10-15 minutes (we only infuse fresh herb for 2 minutes). The resulting drink should be used during the day.
- A very effective remedy that stimulates the flow of milk and helps increase lactation is an infusion of walnuts, which is prepared as follows: brew 0.5 cups of peeled walnuts with 0.5 liters of boiling milk in a thermos and infuse for 3-4 hours. Infusion take 1/3 cup 20 minutes before each feeding, but not daily, but every other day.
- A mixture that promotes lactation is very good: 100 g dried apricots, 100 g raisins, 100 g figs, 1 glass of walnuts. Grind everything and mix with 100 g of honey and 100 g of butter. Use 1 tbsp. spoon 15-20 minutes before feeding.
 Watch your child's reaction! Allergy is possible.
Watch your child's reaction! Allergy is possible. - Useful green tea with dill seeds, raspberry leaves, linden, oregano, lemon balm.
Be sure to use special multivitamin complexes for pregnant and lactating women, which also help improve lactation. They will improve the quality of milk and increase its quantity:
- Hipp tea for nursing mothers.
- Apilac 0.01 under the tongue and dissolve. Take 2-3 times a day. Pay attention to the child's reaction! Allergy is possible.
- Vitamin E capsules 0.1-0.2 - 2 times a day.
- Ascorbic acid (vitamin C) up to 1 g per day.
- Brewer's yeast - liquid 60 g 3 times a day, dry 1 tsp. 4 times a day.
- Calcium pantothenate 1 tab. 3 times a day.
- Asparkam 1 tab. 3 times a day
In European countries, homeopathic remedies are widely used to stimulate lactation. Of the many homeopathic remedies to enhance lactation, the following remedies can be recommended: before each feeding of the child (20 minutes) \ Urtika urens 3 and Agnus castus 3 alternately and at night - Pulsatilla 6. Take 5 grains until the effect is obtained (from 3 days to 3 weeks). But in any case, you need to consult a doctor.
Take 5 grains until the effect is obtained (from 3 days to 3 weeks). But in any case, you need to consult a doctor.
How to increase lactation of breast milk
To know if the baby is getting enough milk and to quickly increase lactation (breast milk production), it is necessary for the mother to understand where the milk comes from, how lactation develops and at what periods it is necessary to pay attention so that the baby receives enough nutrition.
What increases lactation in breastfeeding women
The secretion of breast milk (or lactation) is a clear and well-established mechanism that has been developed during evolution so that mothers can feed their children even in the most severe conditions. Therefore, knowing the mechanisms for launching and maintaining the production of breast milk, any mother can quickly increase lactation without any material costs and special efforts. They are simple - the more often a woman breastfeeds and the more the mammary gland is emptied, the more milk will be.
Let's immediately answer one key question - what to do to increase lactation? The answer is very simple - to breastfeed a child: often, for a long time and from the first minutes of his life. In the first days after the birth of the baby, milk arrives gradually, mother and baby adapt to each other. Breast overflow occurs with the beginning of the production of transitional milk, the baby cannot fully empty the breast, and therefore engorgement and leakage of milk may occur. As mature milk arrives, around the second week of feeding, lactation enters a stable phase.
After 4-5 weeks of feeding, strong leakage of milk from the breast gradually disappears (literally drops can be released) and a feeling of fullness, which frightens inexperienced mothers, it seems to them - there is less milk. In addition, the baby can sometimes act up at the breast, he begins a period of colic, or literally hangs on his chest (he can suck for 30-60 minutes or longer without a break), saves strength before a new stage in development. But this makes mothers think that there are probably problems, they are starting to look for ways to increase lactation and the fat content of breast milk. But you should not worry, the first thing you need to objectively assess is whether there really is a shortage of milk and you need to look for means that increase lactation (breast milk production).
But this makes mothers think that there are probably problems, they are starting to look for ways to increase lactation and the fat content of breast milk. But you should not worry, the first thing you need to objectively assess is whether there really is a shortage of milk and you need to look for means that increase lactation (breast milk production).
Does the baby have enough breast milk
The first mistake that many breastfeeding mothers make is to try to express milk from the breast (usually after feeding) to estimate the amount of milk, they get just a few drops and decide that the baby is malnourished, therefore it is naughty, and it is necessary look for ways to increase the amount of breast milk. We emphasize that pumping does not apply to the method of objectively assessing the sufficiency of milk when feeding a baby.
Not even the highest quality breast pump, let alone the manual method, can empty the breast as effectively as a baby does.
Plus, breast milk is actively produced during feeding, and the baby is actively satiated. The milk that is stored in the breast between feedings is the “forward milk”, this milk is rich in water, sugar and poor in fats. The baby quenches thirst with them and "snacks". During feeding, the breast synthesizes "hind" milk, it is thicker, fatty - this is already the "main dish" of the crumbs, with which he satisfies hunger.
The milk that is stored in the breast between feedings is the “forward milk”, this milk is rich in water, sugar and poor in fats. The baby quenches thirst with them and "snacks". During feeding, the breast synthesizes "hind" milk, it is thicker, fatty - this is already the "main dish" of the crumbs, with which he satisfies hunger.
But if the mother doubts whether the baby has enough food during breastfeeding, you need to evaluate his gains for the month. If the baby added more than 500g-600g - he gets enough milk. Another method of objective evaluation is the wet diaper count (while giving the baby nothing but breasts, not even water!). If in a day (in 24 hours) the baby wets more than eight to ten diapers, milk is enough for him.
If there are not enough diapers, in this case it is worth considering how to increase the amount of breast milk in a nursing mother. But it is important to emphasize - you do not need to immediately give the child supplementary feeding, it is possible to restore the volume of milk in case of its shortage in 3-4 days, you just need to be patient, give yourself and the baby more time.
How and how to increase the amount of milk during breastfeeding
If there is a problem of lack of milk, several useful tips can help to increase lactation in a nursing mother, which work and help women quickly and effectively normalize the situation.
Frequent feedings: the baby should be fed frequently, every one and a half to two hours, including during the night's sleep. If the child is fast asleep, it is applied to the chest in a dream and the heel or cheek is slightly scratched. The baby, half asleep, will attach to the breast and empty it. It is not worth skipping feedings for more than two to three hours because of the sound sleep of the baby.
Long stay at the breast: Do not limit the time your baby stays at the breast. If he has completely emptied one gland, he should be offered a second if he shows a desire to eat more. This allows the baby to get to the fatty “hind” milk, and stimulates the activity of the mammary gland. If the baby suckles for a short time, he receives mostly foremilk. It saturates worse, and short feeding stimulates the breast less actively.
It saturates worse, and short feeding stimulates the breast less actively.
Is it possible to increase lactation if the baby quickly falls asleep at the breast and sucks very sluggishly? This is a common problem. For such little ones, there is a method of alternate feeding. It is necessary to attach the crumb to the breast, while the milk flows from it actively, the baby swallows it quickly. As soon as the sucking activity slows down, move the baby to the other breast so that he suckles actively. As the tension in the chest eases, reattach the baby to the first mammary gland. This allows the baby to remain awake, to empty the chest more actively.
How to increase the amount of breast milk when pumping
Expressing milk is great for stimulating lactation, because the mammary glands work on a supply-demand basis. The more milk is removed from the breast, the more actively the production of its new portion starts. It is possible to increase lactation during pumping for mothers of babies who are weakened and cannot fully attach to the breast.
As the baby gets stronger and older, the mother can help maintain adequate milk levels in her breasts by pumping. Manually expressing large volumes of milk is quite difficult and tiring, so you need to know how to increase lactation when expressing with a breast pump.
Important!
It is important to express the breast when it is very full, after feeding the baby and between sucklings. Excess milk can be stored in the freezer as a spare.
What products increase lactation (breast milk) in a nursing woman
In pharmacies and children's stores, in advertisements for women's clinics, you can find various supplements, vitamin complexes and other products that increase lactation (breast milk) in a nursing woman. But it is important to understand that the effectiveness of these drugs is low, since milk synthesis is a hormone-dependent and reflex process, which is stimulated by frequent and maximally complete emptying of the breast.
However, many foods and drinks and other methods work like a placebo, allowing the mother to remove the internal “clamp” in her head and reduce stress, which positively affects milk flow.
Herbal teas and drinks for nursing: although many herbs and plants have a lactogenic effect, it is not so pronounced that lactation is restored only by taking these compounds without frequent and prolonged feeding of the child. Any warm liquid that the mother takes before feeding has a lactogenic effect. The flow of blood to the chest gives a sensation of a rush of milk within the glands.
Undoubted advantages of teas - they give confidence, contain mild sedative components, are a source of additional liquid. Obvious disadvantages - an allergy is possible to any herbs, negative effects in a mother or baby are possible.
Vitamin-mineral complexes and dietary supplements for nursing: they do not have a lactogenic effect, but help to support the woman's body, replenishing the supply of essential minerals (especially calcium, iron) and vitamins that are actively consumed during the synthesis of breast milk.
No breast simulators
To ensure that breast milk supply does not decrease, the baby should not have any breast simulators. Soothers, bottles with nipples are excluded. They reduce the time of breast stimulation, and also form the so-called "nipple confusion". When sucking on a bottle and pacifier, the baby uses other muscles, which can cause problems with attachment. Instead, you need to apply crumbs to the chest more often.
Soothers, bottles with nipples are excluded. They reduce the time of breast stimulation, and also form the so-called "nipple confusion". When sucking on a bottle and pacifier, the baby uses other muscles, which can cause problems with attachment. Instead, you need to apply crumbs to the chest more often.
- 1. Penny F, Judge M, Brownell E, Mcgrath JM. What Is the Evidence for Use of a Supplemental Feeding Tube Device as an Alternative Supplemental Feeding Method for Breastfed Infants? Adv Neonatal Care. 2018;18(1):31-37. doi:10.1097/ANC.0000000000000446
- 2. Riordan J, Wambach K. Breastfeeding and Human Lactation Fourth Edition. Jones and Bartlett Learning. 2014.
- 3. American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Breastfeeding Your Baby. 2019.
- 4. Heidarzadeh M, Hosseini MB, Ershadmanesh M, Gholamitabar tabari M, Khazaee S.