Pin prick sized red dots skin
Pinprick Red Dots on Skin That Aren't Itchy: Causes, Next Steps
Your skin’s health and appearance shifts all the time depending on your environment, lifestyle, and health conditions, among other factors.
Sometimes skin problems have an obvious cause, like sunburn or a mosquito bite. But other times rashes or dots appear on your skin that are harder to identify.
Petechiae are red, purple, or brown dots on the skin that are generally painless and itch-free. These dots form when your tiniest blood vessels, called capillaries, break and leak blood under the skin. This blood pools under the surface, creating the appearance of spots.
Petechiae aren’t considered a medical condition on their own. They’re often a symptom of another underlying health problem, such as infection, allergic reaction, or autoimmune disease.
In this article, we will explore some common potential causes of petechiae, symptoms to watch out for, and when to see a doctor.
You can develop petechiae for a number of different reasons, including injuries and infection. In many of these cases, petechiae are a symptom of an underlying health issue.
Here’s an overview of common causes of petechiae:
Medication
An allergic reaction to certain medications may cause clusters of red dots to appear on your skin. This could be petechiae or hives. Hives are often itchy, raised welts that are generally larger than petechiae. Medications known to cause petechiae in rare cases include:
- antiplatelet medications
- aspirin
- steroids
Infections
Both viral and bacterial infections can cause red dots or other rashes to appear on your skin. Common infections linked to petechiae include:
- enterovirus infection
- parvovirus B19 infection
- dengue virus infection
- meningococcal infection (meningitis)
- scarlet fever
- infective endocarditis
- Rocky Mountain spotted fever
- septicemia/sepsis
- congenital TORCH syndrome (concurrent infection with toxoplasma gondii, other agents, rubella, cytomegalovirus, and herpes simplex virus)
Blood-related disorders
These include blood cancers, chronic conditions, and blood-related congenital disorders.
- thrombocytopenia
- leukemia
- types of anemia
- platelet dysfunction
- coagulation disorders
- vascular diseases
- Bernard-Soulier syndrome
- Glanzmann thrombasthenia
Other chronic conditions
Petechiae may come and go as a result of a chronic disease or illness. This includes autoimmune conditions, and certain congenital and connective tissue disorders. For example:
- Ehlers-Danlos syndromes (EDS)
- lupus
- chronic liver disease
- Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome
Acute injuries, allergic reactions, and a vitamin K deficiency are also associated with the symptom of petechiae.
Does COVID-19 cause petechiae?
Each new variant of SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, seems to appear with new symptoms. Different variants of the virus have caused some level of skin symptoms, including petechiae. This is believed to be related to bleeding and coagulation changes brought on by COVID-19.
Although petechiae has been observed in people with COVID-19, it’s not the most common skin manifestation. One study estimated that only about 3% of people with COVID-19 develop this symptom.
Petechiae may not always appear alongside other noticeable symptoms. These tiny dots are usually flat, red, brown, or purple in color, and measure less than 2 millimeters (mm).
A hallmark of petechiae is that they’re nonblanching. This means they don’t fade away or disappear when you apply pressure to your skin.
Size is what differentiates petechiae from purpura. Purpura are also caused by broken capillaries leading blood to pool under your skin, but they’re larger than petechiae (over 2 mm).
Although you may itch, be sore, or have a fever alongside petechiae, these symptoms are usually related more to the issue that caused your petechiae than these spots themselves.
Treatment for petechiae depends on the underlying cause, since the dots are usually a symptom of another condition.
Petechiae that appear from an injury or infection usually resolve on its own in 2 to 3 days. You’ll likely need to rest and take antibiotics for a bacterial infection. Treatment for most viral infections includes rest and over-the-counter pain medication (OTC NSAIDs).
If you have a blood-clotting disorder, your doctor will design an individualized treatment plan. This could include taking reversal agents to counter anticoagulation medications.
Steroids, chemotherapy, and immunosuppressant drugs may also be used to control a variety of autoimmune or inflammatory disorders that could be causing you to develop petechiae.
Immunosuppressant drugs work by suppressing or modifying your immune system so it doesn’t cause inflammation to joints, tissues, and organs.
Learn about ways to prevent petechiae.
If your petechiae (or your child’s) develops alongside other symptoms like fever, talk with your doctor.
Febrile (feverish) conditions that appear with petechiae are especially common in children, accounting for about 2. 5% of visits to the pediatric emergency department each year.
5% of visits to the pediatric emergency department each year.
In these children, doctors will usually evaluate for a meningococcal infection first.
In a 2018 study, between 7% and 11% of cases of petechiae and fever in children were caused by meningococcal disease, and about 10% were caused by Group A staphylococcus infection. Overall, about 60% of these cases were linked to viral illnesses.
Learn more about when to see a doctor for petechiae.
There are many conditions that can cause red dots on your skin. You may need your doctor to help you differentiate between these conditions and petechiae.
Other conditions that can produce dots or skin irritation similar to petechiae include:
- hives
- acne
- bug bites
- eczema
- heat rash
- rosacea
Petechiae are usually a symptom of another health issue. These spots form after blood leaks from your capillaries. They don’t itch and won’t disappear if pressed.
Common causes for petechiae include infections, certain chronic diseases, and even injuries.
Your doctor may have to run several tests to identify what’s causing the dots to appear on your skin. Treatment depends entirely on the underlying cause.
Most of the time, these red, purple, or brown dots will resolve in a few days, especially if the condition causing them has been addressed and managed.
Causes, Treatments, Pictures, and More
We include products we think are useful for our readers. If you buy through links on this page, we may earn a small commission. Here’s our process.
Overview
Petechiae are tiny purple, red, or brown spots on the skin. They usually appear on your arms, legs, stomach, and buttocks. You might also find them inside your mouth or on your eyelids. These pinpoint spots can be a sign of many different conditions — some minor, others serious. They can also appear as a reaction to certain medications.
Though petechiae look like a rash, they’re actually caused by bleeding under the skin. One way to tell the difference is by pressing on the spots.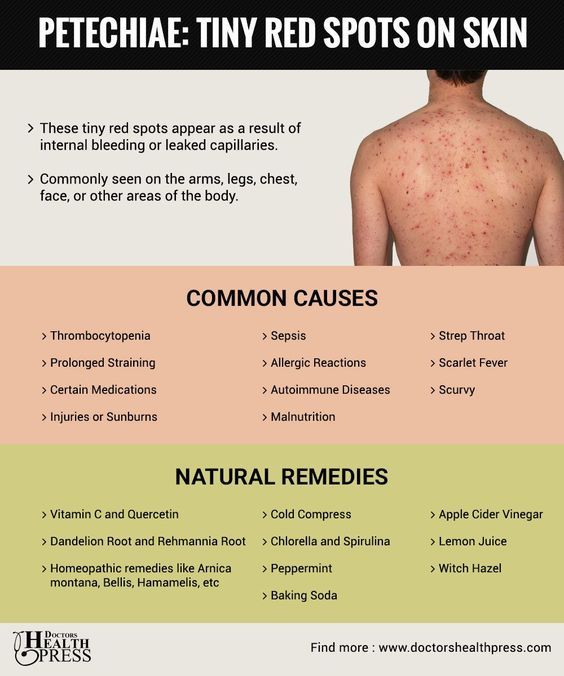 Petechiae won’t turn white when you press on them. A rash will turn pale.
Petechiae won’t turn white when you press on them. A rash will turn pale.
Petechiae are formed when tiny blood vessels called capillaries break open. When these blood vessels break, blood leaks into your skin. Infections and reactions to medications are two common causes of petechiae.
Conditions that may cause petechiae include:
If you or your child has petechiae, call a doctor. Some of the underlying causes of petechiae are serious and need to be treated. It’s hard to know whether you have something mild or serious until you see your doctor for a diagnosis.
You should also call if you have serious symptoms like these:
- high fever
- trouble breathing
- confusion
- change in consciousness
Petechiae themselves don’t cause complications, and they won’t leave scars. Some of the conditions that cause this symptom can have complications, such as:
- damage to the kidneys, liver, spleen, heart, lungs, or other organs
- heart problems
- infections in other parts of your body
If a bacterial or viral infection caused the petechiae, your skin should clear up once the infection gets better.![]() If a medication caused the petechiae, this symptom should go away once you stop taking the drug.
If a medication caused the petechiae, this symptom should go away once you stop taking the drug.
Check the spots often to see if they change. If the number of spots increases, you might have a bleeding disorder.
Before recommending a treatment, your doctor will identify what’s causing your petechiae and other symptoms. Your doctor may prescribe any of these medicines to treat the cause of the spots:
- antibiotics to treat a bacterial infection
- corticosteroids to bring down inflammation
- medications that suppress your immune system, such as azathioprine (Azasan, Imuran), methotrexate (Trexall, Rheumatrex), or cyclophosphamide
- chemotherapy, biologic therapy, or radiation to treat cancer
You can also try these home remedies to relieve your symptoms:
- Rest.
- Take over-the-counter pain relievers such as ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin) or acetaminophen (Tylenol).
- Drink extra fluids to prevent dehydration.
To prevent petechiae, you need to avoid the conditions that can cause them. But you can’t prevent all of the possible underlying causes of petechiae.
But you can’t prevent all of the possible underlying causes of petechiae.
If you’ve had this reaction to a drug in the past, let your doctor know. Your doctor will probably recommend that you avoid the drug in the future.
To prevent infections that can cause petechiae:
- Wash your hands often with soap and water, or use an alcohol-based hand sanitizer.
- Try to stay away from anyone who appears to be sick.
- Don’t share glasses, utensils, and other personal items.
- Clean countertops and other common surfaces.
- Practice safe sex.
- Apply an insect repellant containing DEET before you go into wooded or grassy areas. Also, wear a long-sleeved shirt and long pants, and tuck your pants into your socks. Check your entire body for ticks when you get back home.
Red dots on the skin: causes, symptoms, care
Below are some of the various etiological factors for the appearance of red dots on the body.
Heat rash (prickly heat)
Obstruction of the sweat glands causes accumulation of sweat in the deep layers of the skin, which provokes the occurrence of prickly heat. This condition mostly affects young children who have underdeveloped sweat glands. The favorite places for the localization of a barely noticeable heat rash are the back, groin, chest, armpits, skin of the hands - the places of the most abundant accumulation of sweat deposits.
This condition mostly affects young children who have underdeveloped sweat glands. The favorite places for the localization of a barely noticeable heat rash are the back, groin, chest, armpits, skin of the hands - the places of the most abundant accumulation of sweat deposits.
Thermal rash may include the following symptoms:
- The totality of papules in the form of small tubercles
- itching and stabbing sensations
- of the skin of
- Generalization of
- Nausea
As a rule, prickly heat goes away on its own after 24 hours. To improve the condition of the skin, cooling home remedies (compresses, baths) are suitable, as well as preventive measures (wearing loose clothing made from natural fabrics). If a secondary infection has joined, it is necessary to prescribe a course of antibiotic therapy.
Keratosis pilaris
Keratosis pilaris (pilaris) is a common skin condition that presents as small white and red bumps on the surface of the skin. In most cases, the outer part of the shoulders, forearms and upper back are affected.
In most cases, the outer part of the shoulders, forearms and upper back are affected.
Symptoms of keratosis pilaris:
- Dryness and roughness of the skin
- Presence of itching
Contact dermatitis
Skin contact with an allergen results in an allergic reaction resulting in contact dermatitis. Manifestations of contact dermatitis can be different depending on the trigger factor.
Symptoms of contact dermatitis include:
➤ Pattern-like rashes
➤ Peeling, cracking and dryness
➤ Hyperemia of the skin
➤red spots0003
➤ Scarring of the skin
➤ Red color of the skin
➤ Presence of blisters with a crust
➤ Increased sensitivity to sunlight
In care, use products without the presence of aggressive components in the composition, wear jewelry made of natural metals. If large areas of the skin are affected, it is necessary to apply 1% hydrocortisone cream, complicated forms are treated with systemic antihistamines.
Atopic dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis (eczema) is a chronic inflammatory skin disease. There are several types of eczema - follicular and papular.
Manifestations of eczema include:
- Redness and swelling of the skin
- Dryness and flaking of the skin after heavy scratching
- Blisters, followed by the release of fluid and the formation of a crust.
Therapy of atopic dermatitis is based on taking antihistamine drugs, moisturizing the skin, and using phototherapy.
Rosacea
Rosacea is a condition in which the skin becomes covered with small rashes and redness without itching. This pathology is more typical for fair-skinned people aged 30-50 years with a photosensitive skin type.
Symptoms of rosacea:
- Redness of the skin in the area of the nose, forehead, cheeks and chin
- Visible blood network and subcutaneous spots on the face
- Thickening of the skin
- Redness and tearing of the eyes0016
- Presence of bumps and pimples
To relieve rosacea, it is necessary to moisturize the skin, use pH-balanced cleansers and creams with SPF protection before going out, minimize exposure to provoking factors (UV light, harsh chemicals), limit consumption of spicy and hot food. As a drug treatment, azelaic acid, metronidazole, brimonidine tartrate are used.
As a drug treatment, azelaic acid, metronidazole, brimonidine tartrate are used.
Effective therapeutic and prophylactic remedies for rosacea and rosacea0012
Infections
Red spots on the skin may appear due to the following infectious diseases:
Chicken pox or shingles . The herpes virus that causes these diseases provokes the appearance of red itchy sores with localization throughout the body. Chickenpox usually occurs in infants and preschool children. Shingles affects adults and is characterized by a unilateral rash.
Rubella . Small bright red and pink dots on the skin are manifestations of rubella. The rashes are contagious and are localized mainly on the face, arms, legs and torso. Additional manifestations of rubella include lymphadenitis, fever, headache.
Meningitis . This disease is characterized by inflammation of the meninges and presents with a variety of symptoms, including headache, fever, neck stiffness, and, rarely, a microscopic single rash of red or brown small solitary lesions.
Scarlet fever . The causative agent is streptococcus, which causes red, rough specks in the neck, groin, and armpits.
Cherry angioma
A benign skin neoplasm of small size resembling a burgundy spot is called cherry angioma or capillary hemangioma. The shape of the tubercles can be varied, rashes are more typical for people over 30 years old. Angiomas are common on the trunk, arms and legs, and are similar to moles. Over time, they go away on their own and do not require treatment, but if desired, they can be removed with liquid nitrogen or a laser. Angiomas in the form of red droplets do not itch, sometimes they bleed, but this is a variant of the norm.
Ringworm
Mottled, red, raised, rounded dots are the result of ringworm (a fungal infection of the skin). Spots can be on any part of the skin, but most often they are on the arms and legs. The fungus is carried by both humans and pets. The rash is usually accompanied by flaking. Therapy for ringworm is the use of antifungal creams or drugs.
Therapy for ringworm is the use of antifungal creams or drugs.
Lichen planus
This disease has an autoimmune course and is characterized by the appearance of flat red purple spots that itch. Lichen planus occurs among females aged 35 to 60 years. It can often be found on the nails, genitals, throat, digestive tract, and even the inside of the mouth. In some cases, the disease goes away on its own. To get rid of lichen planus, it is necessary to use oral antihistamines and topical retinoids.
Red drug rash
Some medications may cause a red rash. Such rashes occur in the form of blisters or hives and are characterized by varying degrees of severity. If a drug allergic reaction is suspected, the drug should be stopped immediately. If the condition remains severe, antihistamines or steroids should be given.
Purpura
Since blood accumulates in the layers of the skin due to the fact that the vessels burst, red dots of different diameters form under the skin, which can even be observed in the oral cavity. In the presence of such ruby points, an immediate consultation with the attending physician is necessary. In simple cases, red vascular dots on the skin are treated with steroids, and platelet levels are also normalized.
In the presence of such ruby points, an immediate consultation with the attending physician is necessary. In simple cases, red vascular dots on the skin are treated with steroids, and platelet levels are also normalized.
Swimmer's itch
A bumpy red rash that occurs after swimming in a body of water infected with schistosomes (parasites of the genus trematodes) is called swimmer's itch or cercarial dermatitis. As a rule, the rash appears during the day and is not transmitted to others. For treatment, antihistamines and steroids are used, in complicated cases, antibiotics.
Psoriasis
Psoriasis is considered an autoimmune disease and occurs due to exposure to a trigger factor (stress, infection). The rash is crimson itchy lesions with silvery plaques, localized mainly on the elbows and knees. For the treatment of psoriasis, cold compresses, topical steroids, immunosuppressants are used.
Petechiae
Petechiae are located on the arms, abdomen, legs and buttocks and very much resemble red capillary dots. These blood points occur due to the fact that small blood vessels under the skin are injured. This occurs as a result of a blood clotting disorder due to an allergy, infection, or other pathological condition. Treatment depends on the etiological factor that caused the petechiae.
These blood points occur due to the fact that small blood vessels under the skin are injured. This occurs as a result of a blood clotting disorder due to an allergy, infection, or other pathological condition. Treatment depends on the etiological factor that caused the petechiae.
Pimples
Pimples or acne vulgaris look like inflammatory red bumps that occur due to excessive work of the sebaceous glands and their subsequent blockage. Often localized on the face, acne on the back or chest. Acne requires complex treatment to remove antibiotics, steroids, hormonal contraceptives and over-the-counter products.
Why do red dots appear on the body? – Family consultation
Why do red dots appear on the body? – Family consultationSmall red dots on the body can be both neoplasms and the result of skin damage. Let's see how dangerous it is and when you need to see a doctor immediately.
HEMANGIOMA AND MICROHEMATOMA
Small red dots on the body may occur after skin injury. For example, often such superficial capillary injuries are obtained during epilation. If the skin is strongly affected, then the surface of small vessels located close to the surface is injured. And outside there is a small bruise due to the fact that the blood goes into the subcutaneous fat layer. Such points are also called microhematomas. If you did epilation with a novice master, then there may be quite a lot of them.
Small hematomas may appear in other places. Outwardly, these red dots on the body look like moles. If you see a cluster of dots, or if they appear periodically without being tied to any procedures, then this may be due to increased fragility of the vessels. Usually it occurs due to a lack of vitamin C and K in the body. If any injuries, strong friction of the skin against tissue cause such “redness”, then this is most likely the reason. You will need to undergo the necessary tests and drink the course of vitamins recommended by the doctor.
As for hemangiomas, these are benign vascular tumors. Their features are as follows:
Their features are as follows:
- They can be up to several centimeters in diameter.
- If we are talking about dilated capillaries that provoked the disease, then the hemangioma is called capillary.
- But cavernous hemangiomas can often occur on the face and trunk. These are large cavities filled with blood, they look like swelling and can cause significant discomfort and change appearance.
- Hemangiomas can appear at any age, even in infants.
Here you can't expect the tumor to go away on its own. Be sure to consult a doctor, and he will help you choose the treatment.
RED DOTS WITH VASCULAR BRANCHES AND IN THE FORM OF SMALL RASHES
There are other reasons for the appearance of such skin imperfections:
- Red dots on the body can be spider veins and occupy a fairly large area. In this case, you should also not postpone a visit to the doctor. The fact is that such reddening in the form of capillary branches may indicate the development of dangerous diseases - cirrhosis of the liver and viral hepatitis.
- If we are talking about red dots resembling small rashes on the chest and back, then most likely the person has problems with the pancreas. Interestingly, when pressed, they do not disappear. Also, their number may increase or decrease.
- Often these rashes can be the result of autoimmune diseases, such as rheumatism. Then they do not resemble bruising, but rather a skin allergy. By the way, allergies can also lead to the appearance of red dots on the body, and in this case they will have different localization. It is easiest to distinguish an allergic disease by the presence of itching, but a doctor's consultation does not fit here either.
We think that we have answered your question “Red dots on the body - what is it?”. If you still have doubts about your own health, you can always come to us for a consultation. Also, do not forget that a person needs to maintain health with proper nutrition and vitamins. For example, a lot of vitamin C is found in cauliflower and green peas, parsley, tomatoes and apples.