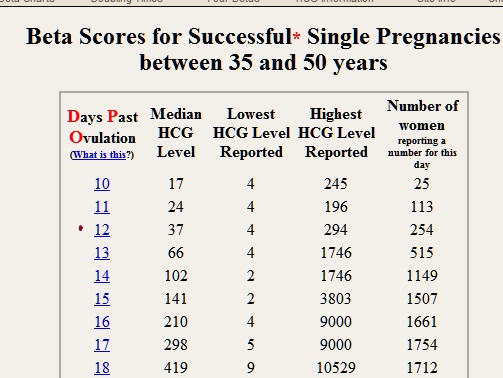
Beta level chart
hCG Levels | The American Pregnancy Association
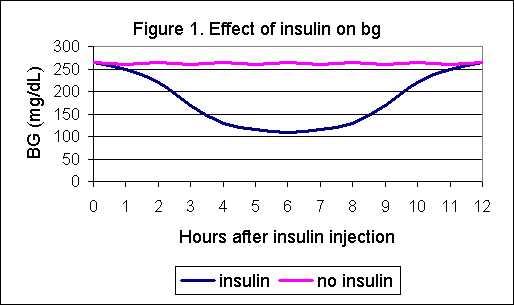
HCG (Human Chorionic Gonadotropin) is often called the pregnancy hormone because it is made by cells formed in the placenta, which nourishes the egg after it has been fertilized and becomes attached to the uterine wall. Levels can first be detected by a blood test about 11 days after conception and about 12-14 days after conception by a urine test.
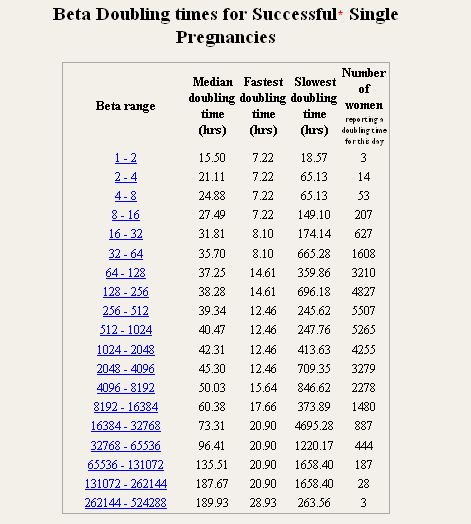
Typically, the hCG levels will double every 72 hours. The level will reach its peak in the first 8-11 weeks of pregnancy and then will decline and level off for the remainder of the pregnancy.
- As you get further along in pregnancy and the hCG level gets higher, the time it takes to double can increase to about every 96 hours.
- Caution must be used in making too much of hCG numbers. A normal pregnancy may have low hCG levels and result in a perfectly healthy baby. The results from an ultrasound after 5 -6 weeks gestation are much more accurate than using hCG numbers.
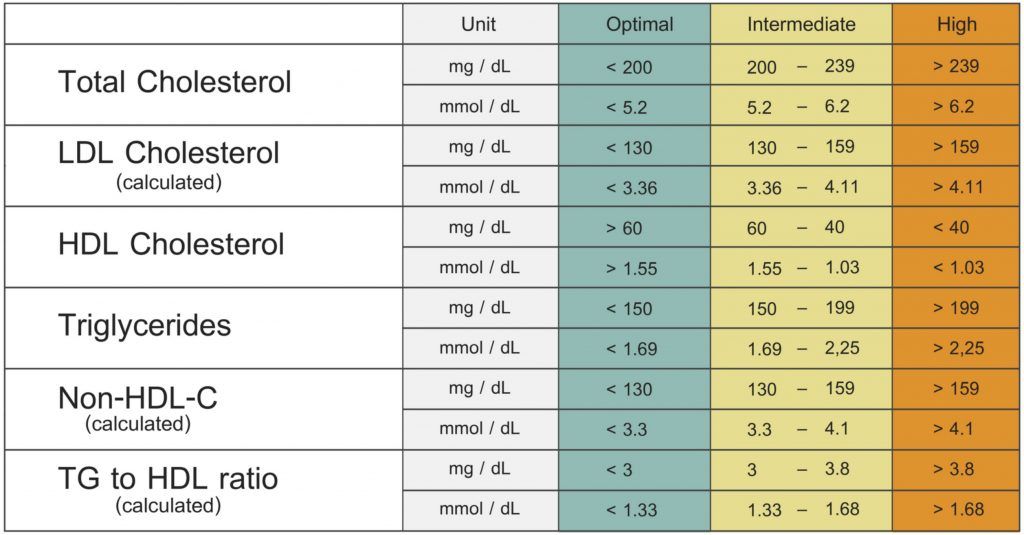
- An hCG level of less than 5 mIU/mL is considered negative for pregnancy, and anything above 25 mIU/mL is considered positive for pregnancy.
- An hCG level between 6 and 24 mIU/mL is considered a grey area, and you’ll likely need to be retested to see if your levels rise to confirm a pregnancy.
- The hCG hormone is measured in milli-international units per milliliter (mIU/mL).
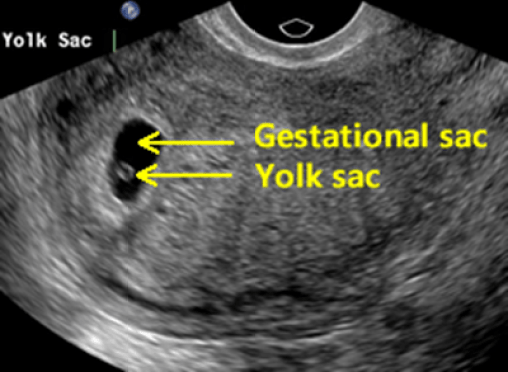
- A transvaginal ultrasound should be able to show at least a gestational sac once the hCG levels have reached between 1,000 – 2,000 mIU/mL. Because levels can differentiate so much and conception dating can be wrong, a diagnosis should not be made by ultrasound findings until the hCG level has reached at least 2,000 mIU/mL.
- A single reading is not enough information for most diagnoses. When there is a question regarding the health of the pregnancy, multiple testings of hCG done a couple of days apart give a more accurate assessment of the situation.

- The hCG levels should not be used to date a pregnancy since these numbers can vary so widely.
- There are two common types of hCG tests. A qualitative test detects if hCG is present in the blood. A quantitative test (or beta) measures the amount of hCG actually present in the blood.
Guideline to hCG levels in weeks during pregnancy
* These numbers are just a guideline – every woman’s level of hCG can rise differently. It is not necessarily the level that matters, but rather the change in the level.
What Does a Low hCG Level Mean?
A low hCG level can mean any number of things and should be rechecked within 48-72 hours to see how the level is changing. A low level can indicate:
- Miscalculation of pregnancy dating
- Possible miscarriage or blighted ovum
- Ectopic pregnancy
Is a High hCG Level a Bad Thing?
A high level of hCG can also mean a number of things and should be rechecked within 48-72 hours to evaluate changes in the level. A high level can indicate:
A high level can indicate:
- Miscalculation of pregnancy dating
- Molar pregnancy
- Multiple pregnancies
Should I Check My hCG level Regularly?
It’s not common for doctors to routinely check your hCG levels unless you are showing signs of a potential problem.
A health care provider may recheck your levels if you are bleeding, experiencing severe cramping, or have a history of miscarriage.
What Can I Expect After a Pregnancy Loss?
Most women can expect their levels to return to a non-pregnant range about 4 – 6 weeks after a pregnancy loss has occurred.
This can differentiate by how the loss occurred (spontaneous miscarriage, D & C procedure, abortion, natural delivery) and how high the levels were at the time of the loss.
Healthcare providers usually will continue to test hCG levels after a pregnancy loss to ensure they return back to <5.0.
What Can Interfere With My hCG Levels?
If you get a positive test result, you are most likely pregnant. False positives are extremely rare. However, there are some conditions that may cause a false positive, such as certain types of cancer and early miscarriage. Some antibodies may also interfere with test results.
False positives are extremely rare. However, there are some conditions that may cause a false positive, such as certain types of cancer and early miscarriage. Some antibodies may also interfere with test results.
Medications that contain hCG may interfere with hCG levels, as well.
These medications are often used infertility treatments, and your health care provider should advise you on how they may affect a test.
All other medications such as antibiotics, pain relievers, contraception or other hormone medications should not have any effect on a test that measures hCG.
Want to Know More?
- Pregnancy Calculator
- Calculating Gestation Age
- Concerns Regarding Early Fetal Development
Compiled using information from the following sources:
1. U.S. Food and Drug Administration
www.fda.gov
2. Bashir, I; Ihenetu, K; Miller, J.J.; Gim, M.; Lippmann, S. A Positive Pregnancy Test in the Post-Menopausal Psychiatric Patient — What to Think? Psychiatry (Edgemont). Feb. 2006.
Feb. 2006.
Beta hCG doubling time calculator and charts
First β-hCG level
mIU/mL
Second β-hCG level
mIU/mL
Time between tests
Days
Hours
We don’t collect, process, or store any of the data that you enter while using this tool. All calculations are done exclusively in your browser, and we don’t have access to the results. All data will be permanently erased after leaving or closing the page.
Difference
Doubling time
One day increase
Two day increase
Start over
Human chorionic gonadotropin, or hCG, is the hormone your body produces when you are pregnant. In fact, hCG showing up in your blood or urine is one of the earliest signs of pregnancy, which is why lots of people are eager to know more about normal hCG levels.
Get started with our hCG calculator now (above) to work out your hCG levels at home by entering the results of two blood tests and the time between those tests. Then scroll down for everything you need to know about hCG levels in early pregnancy.
Remember that hCG calculator tools and hCG level charts can help you learn more about the part hCG plays in pregnancy. But they are for informational purposes only, not a replacement for medical advice nor a self-diagnosis tool. Your doctor should always be your first port of call when it comes to tracking and explaining hCG progression.
Medically reviewed by
Dr. Angela Jones
Obstetrician and gynecologist, attending physician, Jersey Shore University Medical Center, New Jersey, US
When does hCG start?First up, you might be wondering when hCG starts to show up. The pregnancy hormone can be picked up in your urine and your blood once the embryo attaches itself to the uterine wall (between days 6 and 14 after the sperm has fertilized the egg).
A positive test confirms you’re pregnant. At-home pregnancy tests work by detecting hCG in your pee — normally from days 5 to 10 after your expected period, but some sensitive tests can detect it as early as 10 days after conception.
Dr. Sara Matthews, consultant gynecologist and fertility specialist at London’s Portland Hospital, says, “Home pregnancy tests using urine are very accurate. A positive result pretty much means you are pregnant, but before you celebrate or panic, make sure you are reading the test correctly — always check the instructions! A negative result may mean it’s simply too early to test, so if a period is delayed, the test should be repeated 2 to 3 days later.”
Your doctor can request an in-clinic blood test to check for hCG. “This can be useful if there has been bleeding and a miscarriage is possible,” Dr. Matthews explains. “It can also help the doctor if an ectopic pregnancy is suspected (a pregnancy that has implanted outside the womb). ”
”
We now know that hCG in your urine and blood can show you’re pregnant, but that’s not all. Your health care provider can also learn more about how your pregnancy might be progressing from the hCG levels in your blood.
“A pregnancy cannot be detected reliably by ultrasound until six weeks of pregnancy, so sometimes blood levels are monitored before then,” explains Dr. Matthews.
Beta hCG calculator: What if hCG levels are low?Let’s look at what different hCG levels can mean with a little help from Dr. Matthews:
- Higher than average hCG levels might indicate that you’re having twins or triplets, but you’ll need an ultrasound scan to confirm this. “A normal blood level for hCG on the day a period is due (14 days after ovulation) is 40 to 120 mIU/mL, but levels are up to 400 in multiple pregnancies!” she says. Higher than average hCG levels could also suggest your due date is wrong (you’re further along in your pregnancy than you thought!).
 Sadly, they can also indicate a molar pregnancy (when the placenta grows abnormally). “[Molar] pregnancy always ends in miscarriage, and careful monitoring of the hCG levels may be required for up to six months,” says Dr. Matthews.
Sadly, they can also indicate a molar pregnancy (when the placenta grows abnormally). “[Molar] pregnancy always ends in miscarriage, and careful monitoring of the hCG levels may be required for up to six months,” says Dr. Matthews. - Falling hCG levels within the first six weeks could mean you’re at higher risk of having a miscarriage. If you’re worried about your hCG levels, then speak to your doctor right away.
- Lower than average hCG levels “might indicate that the pregnancy implanted a day or two later than expected,” Dr. Matthews says. It could also mean an ectopic pregnancy or a “biochemical” pregnancy. A biochemical pregnancy is a very early miscarriage where the embryo implants, but only for a few days, and a late period happens before a scan to confirm a pregnancy can be done. Again, speak to your doctor if you think this might apply to you.
It’s important to remember that hCG levels are not a diagnosis on their own. They are just a sign that your doctor might need to do more tests.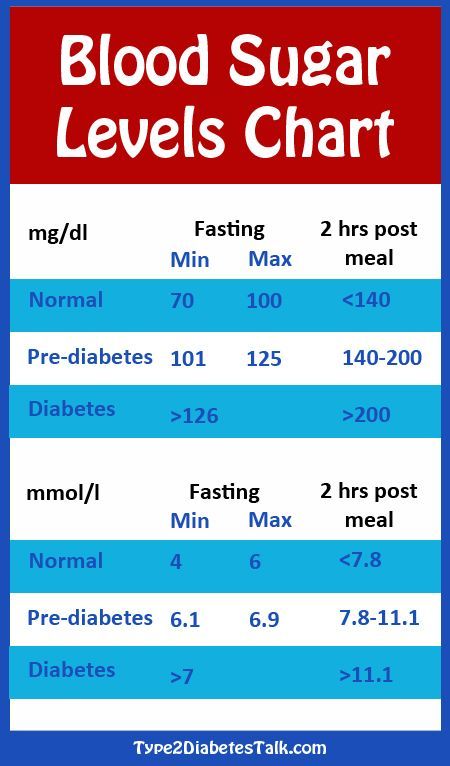 The tool above is designed for informational purposes only; you should always reach out to your health care provider for early pregnancy advice and support.
The tool above is designed for informational purposes only; you should always reach out to your health care provider for early pregnancy advice and support.
hCG levels in our blood change during the first trimester, rising rapidly.
Nonpregnant women have less than 5 milli-international units per milliliter (mIU/mL). “A normal blood level for hCG on the day a period is due (14 days after ovulation) is 40 to 120 mIU/mL,” Dr. Matthews says.
Levels should then double every 48 hours from weeks four to six, but that isn’t the case for everyone. hCG can vary from person to person and still mean a pregnancy is normal. In fact, a 2017 study into hCG found that “the slowest or minimal rise for a normal viable intrauterine pregnancy was 24% at one day and 53% at two days. More recently, a rise of 35% over 48 hours was proposed as the minimal increase consistent with a viable intrauterine pregnancy. ”
”
Dr. Matthews adds that “hCG levels peak at around eight [to ten] weeks of pregnancy. [They] are unreliable after that, but at that stage, ultrasound is used [anyway].”
hCG levels in early pregnancyRemember that hCG levels vary from person to person and can be lower than average, so the above beta hCG chart should only be used as a rough guide.
hCG doubling time: What does it mean?It’s important not to get fixated on hCG doubling time because, as we’ve learned, every pregnancy is different. That means your hCG levels might not double but are totally normal for you.
That said, it’s useful to know how hCG doubling time works in theory. Over to Dr. Matthews again: “An hCG level should double every 48 hours from four to six weeks [of pregnancy]. A level that does not double should be rechecked after another two days as it might indicate a failing pregnancy or a PUO (pregnancy of unknown origin).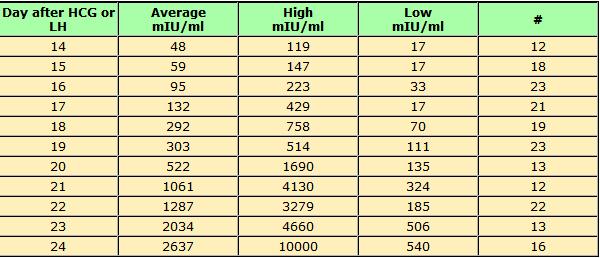
“But an initially high level can also fall in a multiple pregnancy when one baby stops growing. In this situation, the other baby is not affected by that unless twins or triplets are identical (they come from one embryo that split when it’s implanted).”
Speak to your doctor to put your hCG levels into context.
At what hCG level will I miscarry?“A miscarriage is likely if the hCG level falls in the first six weeks of pregnancy, but don’t forget that it can also fall from a high level with an early ‘vanishing twin,’ so if no bleeding has happened by six weeks, then always scan to find more information,” Dr. Matthews says.
“That is also of course an essential way to diagnose an ectopic pregnancy, commonly called a PUO (pregnancy of unknown origin), in the early stages that might be resolving itself without the need for an operation.
“A negative urine hCG pregnancy test is registered when the level of hormone drops below 4 mIU/mL [or the test sensitivity threshold]. A period will inevitably start within 1 to 2 days.”
A period will inevitably start within 1 to 2 days.”
In the early stages of pregnancy? We’ve got plenty of personalized information to help you track your baby’s development and changes to your body, week by week. Download the app now to get started.
References
Updated December 05 2022
Beta decay
|
Beta decay Beta decay - spontaneous transformation of the nucleus (A, Z) into isobar nucleus (A,Z + 1) as a result of the emission of leptons (electron and antineutrino, positron and neutrino), or absorption of an electron with emission neutrino (e-capture).
where M and are the masses of the nuclei, m e is the mass of the electron.
where M at are the masses of atoms. (Here we have neglected the energy difference bonds of electrons in the initial and final atoms.) Released as a result β-decay energy is mainly carried away by light particles - leptons (electron, electronic antineutrino, positron, electron neutrino). 3 H → 3 He + e − + e + 0.02 MeV up to ~20 MeV 11 Li → 11 Be + e − + e + 20.4 MeV Half-lives also vary widely from 10 -3 s to 10 16 years. Big life times β-radioactive nuclei are explained by the fact that β-decay occurs as a result of weak interaction.
given that the Coulomb energy and the energy pairing, you can get the equilibrium number of protons in the nucleus (at a fixed A), which is determined by the maximum binding energy.
Since A = N + Z, formula (2) determines the ratio between the number of protons Z and neutrons N for nuclei of the stability valley. For Z < Z is equal to the nucleus is unstable to β - decay, and for Z > Z is equal to to β + decay and E-capture. For all A, β-stable nuclei must cluster around the values Z is equal to . It can be seen from (2) that for small A Z is equal to ~ A/2 t. e. stable light nuclei should have approximately the same number of protons and neutrons (the role of the Coulomb energy is small). As A increases, the role of the Coulomb energy increases, and the number of neutrons in stable nuclei begins to exceed the number of protons.
As a result of beta decay, three particles: a finite nucleus and a pair of leptons. The energy imparted to the nucleus by virtue of its large mass is small and can be neglected. So the kinetic energy released during beta decay is almost entirely carried away by a pair of leptons, and the distribution of energies between them can be any. In this way, the energy spectrum of positrons (electrons) and neutrinos (antineutrinos) should be continuous in the range from 0 to Q b (see Fig. 2).
Beta decay occurs as a result of weak interactions. On fig. 3 shows the Feynman diagram for the β - decay. On the quark level in beta decay, a transition of a d-quark to a u-quark occurs, or vice versa. On the at the nucleon level, this corresponds to the transitions of a neutron into a proton or a proton into neutron. Moreover, if a neutron can pass into a proton in a free state, then the reverse transition is possible only for protons in the nucleus.
where R is the core radius, is the wavelength. On a nucleus with radius R is hit by a particle with momentum p and impact parameter b.
For the impact parameter b in the classical approximation, condition
Let us estimate under what l condition (5) is satisfied. The radii of even the heaviest nuclei less than 10 fm. For estimation, let's set the radius equal to 10 fm, and the beta decay energy 20 MeV. Then for electrons we can also use the ultrarelativistic approximation and rewrite (5) as
where T is the kinetic energy of the outgoing lepton.
It can be seen from (7) that the orbital momentum of leptons emitted during beta decay at semiclassical consideration can only be zero, and transitions with l ≠ 0 prohibited. However, the quantum properties of particles lead to the fact that such forbidden transitions occur, although they are strongly suppressed. Moreover, the stronger, the smaller the ratio R/. Probability the beta transition is proportional to (R/) 2l . Since in the beta decay of R << and more R + a << , where a is the width of the Coulomb barrier, it practically does not affect the probability beta decay, since the resulting electrons (positrons) immediately have a nonzero probability of being outside the nucleus. The effect of the Coulomb forces is that the emitted electrons are decelerated, and the positrons are accelerated by the Coulomb field of the nucleus, which leads to a change in the shape of their spectra.
where M fi - matrix element of beta decay, ρ f (E) - density of final states.
V fi - weak interaction Hamiltonian, ψ i and ψ* f - wave functions of the initial and final states of the system.
To calculate the matrix element, it is necessary to perform integration over the volume of the nucleus.
where G F is the Fermi constant of the weak interaction.
where p and q are the electron and antineutrino momenta. It can be shown that the density states of free motion of electron and neutrino
where p and q are the momenta of the electron and neutrino. Ignoring the recoil energy kernels, write Q b = T e +, dQ b = dT e = d, where T e and are the kinetic energies of the electron and neutrino.
Substituting (14-15) into (13), we get
where T e is the kinetic energy of the electron. Number distribution electrons depending on their energy has the form:
states and the square of the matrix element
describing beta decay. It should be noted that the beta spectrum is distorted the Coulomb field of the atom, which is composed of the field of the nucleus and the electron shells. Therefore, the factor F(T e ,Z) is added to expression (17), which is defined as the ratio of the probability of finding an electron in some point with the field of the atom (Z = 0) to the probability without the field (Z = 0). The distortion introduced into the beta spectrum by the Coulomb field of an atom is especially significant in the beginning of the spectrum, i.
Relation (17) was obtained under the assumption that the mass neutrino = 0. In this case in the high-energy part of the electron spectrum dN e /dT e 0. However, if 0 instead of (15b) for the end spectrum of electrons, when the neutrino energy is low, you need to write
Then instead of (17) we get
i.e. in case 0 in the high-energy part of the electron spectrum dN e /dT e (Fig. 5).
This dependence of the probability on the energy release is typical not only for beta decay, but also for other weak decays and is called Sargent rules .
where R is the core radius.
i.e., to an expression depending only on the states of the initial and final nuclei and independent of lepton momenta. The shape of the beta spectrum in this case is determined only by the density of final states. These are allowed beta transitions. If matrix element = 0 in (18), then you need to expand the exponent in a series in terms of the degree of the exponent. The degree of the first term in this series that contributes nonzero to matrix element, determines the order of transition prohibition. From relation (22) it follows that the probability of the β-transition should decrease at approximately 10 4 with an increase in the order of the prohibition on 1.
where f(T e ) - Curie or Fermi plot
The intersection of the linear function f(T e ) with the x-axis determines beta decay energy - Q b .
where l is the total orbital momentum of a pair of leptons, J i , P i , J f P f , are the spins and parities of the initial and finite nuclei, - spins of leptons. The probability of beta transitions is mainly determined by the minimum orbital moment of a pair of leptons l min , satisfying the selection rules (26). TASKS
12/14/17 |
The norm of hCG during pregnancy. Table of hCG values by week. Elevated HCG. Low HCG. HCG in ectopic pregnancy. hCG during IVF (hCG after replanting, hCG at 14 dpo).
hCG or beta-hCG or total hCG - human chorionic gonadotropin - a hormone produced during pregnancy. HCG is formed by the placenta, which nourishes the fetus after fertilization and implantation (attachment to the wall of the uterus).
- What is hCG (= beta-hCG)
- When to donate blood for hCG
- HCG norm. Deciphering the analysis of hCG. HCG level during pregnancy
- Normal HCG doubling time
- HCG norms by week.
 HCG table
HCG table - Low hCG. What does hCG below normal mean?
- Negative hCG or hCG indicative of non-pregnancy with missed period
- hCG and biochemical pregnancy
- hCG and ectopic pregnancy
- Elevated hCG. What can hCG levels above normal mean?
- HCG and multiple pregnancy. hcg and twins.
- Blister drift
- HCG test after embryo transfer. HCG for IVF
- hCG and ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome
- Elevated hCG levels in non-pregnant women and men
- How does hCG change after miscarriage, abortion, childbirth?
- What medications affect hCG levels?
What is hCG (= beta-hCG)
HCG or beta-hCG or total hCG - human chorionic gonadotropin - a hormone produced during pregnancy. HCG is formed by the placenta, which nourishes the fetus after fertilization and implantation (attachment to the wall of the uterus). HCG is measured in mIU/mL (mile international units per milliliter).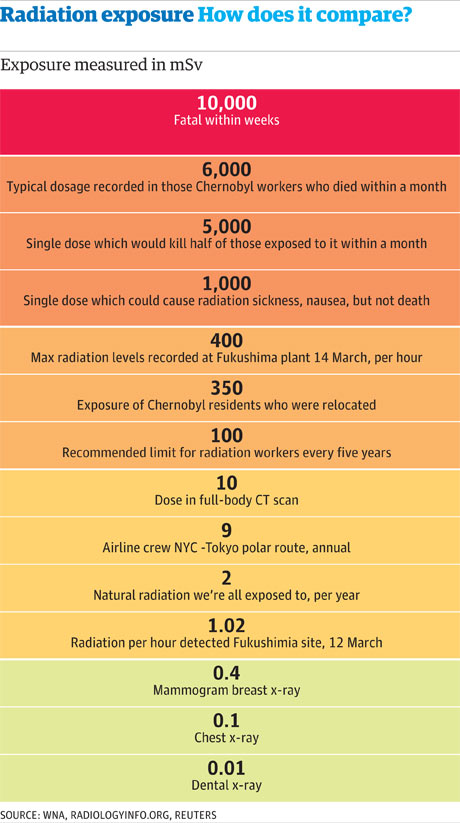
HCG partially crosses the placental barrier. The level of hCG in newborns is approximately 1/400 of the level in maternal blood. And it is approximately 10-50 mIU / ml at birth. The half-life is 2-3 days. Thus, at 3 months of life, the level in newborns corresponds to the norm of hCG for an adult.
When to donate blood for hCG
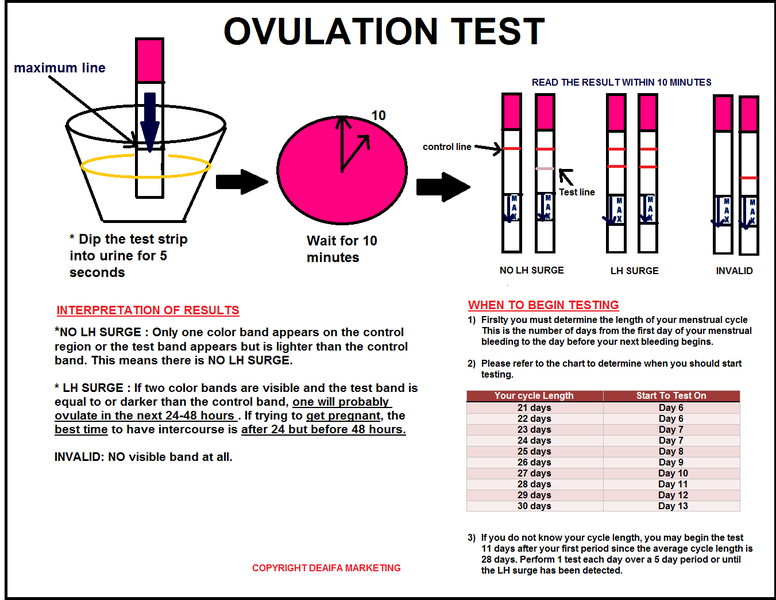
An increase in hCG in the blood can be detected a few days before the expected menstruation. The optimal time for a blood test to determine hCG is after a missed period.
A single determination of hCG cannot be used to diagnose miscarriage or ectopic pregnancy.
HCG norm. Deciphering the analysis of hCG. HCG level during pregnancy
An hCG level of less than 5 mIU / ml indicates the absence of pregnancy or that the test was taken too early. The level of hCG is above 25 mIU / ml - about the presence of pregnancy.
On average, a doubling of hCG levels occurs every 36-72 hours.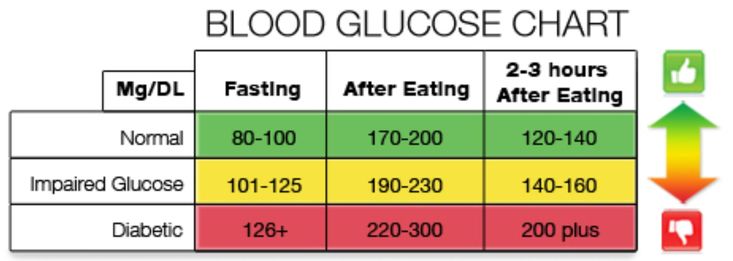 HCG levels peak at term 9-11 weeks of pregnancy (from the date of the last menstruation) and further decreases until the 15th week of pregnancy, remaining unchanged during the remainder of the pregnancy. In 85% of cases, the level of hCG in the early stages doubles every 48-72 hours. As pregnancy progresses, the doubling time for hCG levels increases to 96 hours.
HCG levels peak at term 9-11 weeks of pregnancy (from the date of the last menstruation) and further decreases until the 15th week of pregnancy, remaining unchanged during the remainder of the pregnancy. In 85% of cases, the level of hCG in the early stages doubles every 48-72 hours. As pregnancy progresses, the doubling time for hCG levels increases to 96 hours.
Normal HCG doubling time
HCG level Doubling time
1200 mIU/ml 48-72 hours
1200 – 6000 mIU/ml 72-96 hours
More than 6000 mIU/ml More than 96 hours
hcg calculator
At what hCG value should an ultrasound be done?
After reaching an hCG level of 1000 - 2000 mIU / ml, a fetal egg can be visualized by ultrasound. Since the level of hCG has a large variability, and the date of conception can be erroneous, the gestational age is determined by ultrasound or IVF data, but not by hCG.
A single determination of hCG is not enough, since it is important to evaluate the growth dynamics of the hormone every 48-72 hours.
HCG norms by week. HCG table
| Indicator (p.m. - from the date of the last menstruation) | Minimum | Maximum |
|---|---|---|
| Non-pregnant women | 0 | 5.3 |
| Pregnancy 3 - 4 weeks | 16 | 156 |
| Pregnancy 4 - 5 weeks | 101 | 4870 |
| Pregnancy 5 - 6 weeks | 1110 | 31500 |
| Pregnancy 6 - 7 weeks | 2560 | 82300 |
| Pregnancy 7 - 8 weeks | 23100 | 151000 |
| Pregnancy 8 - 9 weeks | 27300 | 233000 |
| Pregnancy 9 - 13 weeks | 20900 | 2 |
| Pregnancy 13 - 18 weeks | 6140 | 103000 |
| Pregnancy 18 - 23 weeks | 4720 | 80100 |
| Pregnancy 23 - 41 weeks | 2700 | 78100 |
These ranges are provided as a guide and should not be used to interpret a particular hCG assay.
Low hCG. What does hCG below normal mean?
- Not pregnant
- Error in calculation of gestational age
- Pregnancy arrest or miscarriage, biochemical pregnancy
- Ectopic pregnancy
- Threat of spontaneous abortion
Negative hCG or hCG indicative of non-pregnancy with missed period
It is necessary to repeat the analysis for hCG in 1-2 days, perhaps the pregnancy came later than expected. If the level of hCG does not rise, it is necessary to look for other reasons for the delay in menstruation.
hCG and biochemical pregnancy
The so-called "biochemical pregnancy" is a condition in which an increase in hCG above normal was detected, but the pregnancy did not continue to develop. The level of hCG in this case rises slightly, and then in a short time decreases to zero values.
HCG and ectopic pregnancy
An ectopic pregnancy is a pregnancy in which the fertilized egg is outside the uterine cavity. With an ectopic pregnancy, there may be pain in the lower abdomen, spotting. The level of hCG during an ectopic (ectopic) pregnancy may not increase as quickly and not as significantly as with a normally developing uterine pregnancy. However, the low level of hCG does not allow such a conclusion to be made unambiguously. Starting with an hCG level of 1000 mIU / ml, a fetal egg can be detected in the uterine cavity. With an hCG level of 2000 mIU / ml and the absence of a fetal egg in the uterine cavity during ultrasound, the likelihood of an ectopic pregnancy is significant.
With an ectopic pregnancy, there may be pain in the lower abdomen, spotting. The level of hCG during an ectopic (ectopic) pregnancy may not increase as quickly and not as significantly as with a normally developing uterine pregnancy. However, the low level of hCG does not allow such a conclusion to be made unambiguously. Starting with an hCG level of 1000 mIU / ml, a fetal egg can be detected in the uterine cavity. With an hCG level of 2000 mIU / ml and the absence of a fetal egg in the uterine cavity during ultrasound, the likelihood of an ectopic pregnancy is significant.
Increased hCG. What can hCG levels above normal mean?
- Error in calculation of gestational age
- Blister drift
- Multiple pregnancy
- Complications of pregnancy (preeclampsia)
- Maternal diabetes mellitus
- Taking synthetic progestogens
- Risk of fetal malformations
HCG and multiple pregnancy. hcg and twins.
The level of hCG in a multiple pregnancy is higher than in a single pregnancy, but the rate of increase in hCG is the same in both cases.
Blister
Vesicular drift is a rare complication of pregnancy in which the level of hCG will be significantly increased, on average 2 times higher than the average value for a given period. For example, the possible level of hCG with cystic mole for 36 days from the first day of the last menstruation can reach 200,000 mIU / ml, while with a normally developing pregnancy, hCG will be from 1,200 to 36,000 mIU / ml.
HCG test after embryo transfer. HCG in IVF
An hCG test is performed approximately 2 weeks after embryo transfer (12-14 days after transfer (dpp)). Usually the level of hCG at 14 dpo is more than 100 mIU / ml.
If the hCG level is less than 25 mIU / ml, pregnancy has not occurred. If the hCG level is more than 25, the test is repeated after 2 days, with the development of pregnancy, its level should increase. The hCG level will double approximately every 48 hours until 21 days after infusion.
The hCG level will double approximately every 48 hours until 21 days after infusion.
Higher hCG values (300-400 mIU / ml) are more likely to indicate multiple pregnancy.
hCG and ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome
In patients with ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome, hCG levels should be interpreted with caution. These patients may develop edema, which leads to thickening of the blood, which can lead to a false increase in the level of hCG, and when the blood composition is normal, to a false absence of an increase in the level of hCG.
HCG in later pregnancy
The test for hCG is also included in the prenatal screening of the second trimester - an analysis that allows you to assess the risk of developing fetal defects.
Elevated hCG in non-pregnant women and men
Outside of pregnancy, hCG can be produced by the cells of some tumors (seminoma, testicular teratoma, neoplasms of the gastrointestinal tract (including pancreas, liver, colorectal cancer and stomach cancer).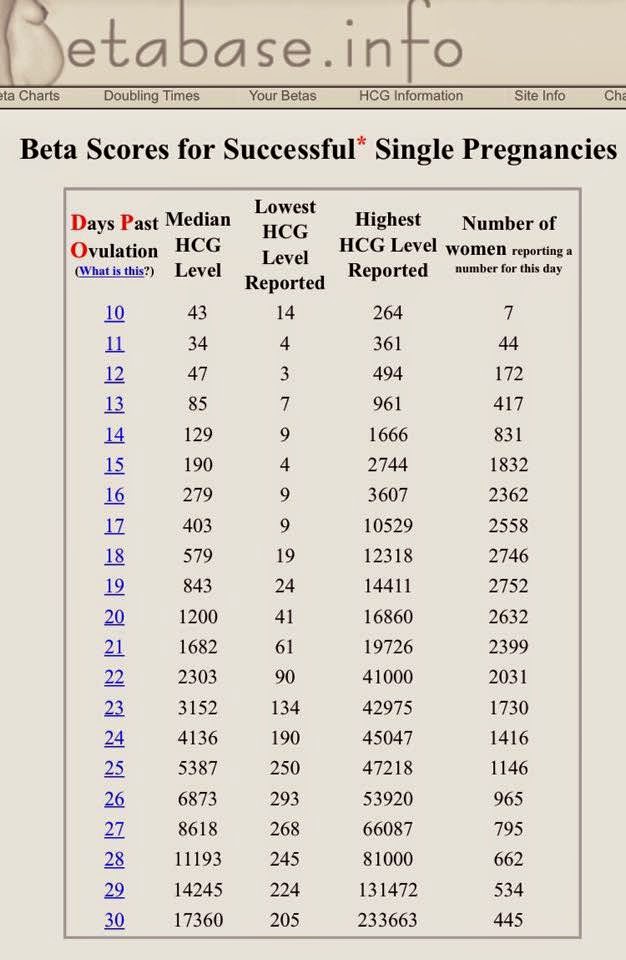
With successful treatment of an hCG-producing tumor, the hCG level should decrease to normal.
How does hCG change after miscarriage, abortion, childbirth?
In most cases, the level of hCG decreases. The half-life of hCG is 24-36 hours. The speed of reaching zero hCG values depends on what exactly happened: spontaneous miscarriage, abortion, childbirth, curettage) and how high the hCG level was at the time of pregnancy loss. Doctors recommend continuing to assess hCG levels until levels are below 5 mIU/mL. If the hCG level remains high, you should consult a doctor.
Which drugs affect hCG levels?
The level of hCG is affected by drugs that contain hCG (Pregnil, Horagon).
-
ToRCH infections and pregnancy
What are ToRCH infections, what are the dangers of these infections during pregnancy, how and when is the examination performed, how to interpret the results. Perinatal infections account for approximately 2-3% of all congenital fetal anomalies.

-
Pregnancy Tests in the CIR Laboratories
In our laboratory you can undergo a complete examination at the onset of pregnancy, take tests at any time, and in our clinics you can conclude an agreement on pregnancy management.
-
Pregnancy hCG calculator online
The hCG calculator is used to calculate the increase in hCG (the difference between two tests taken at different times).
The increase in hCG is important for assessing the development of pregnancy. Normally, in the early stages of pregnancy, hCG increases by about 2 times every two days. As the hormone levels increase, the rate of increase decreases.
-
False positive pregnancy test or why hCG is positive but not pregnant?
When can a pregnancy test be positive?
-
The norm of a complete blood count during pregnancy. Hemoglobin, platelets, hematocrit, erythrocytes and leukocytes during pregnancy. Clinical blood test during pregnancy.
 Hematological changes during pregnancy.
Hematological changes during pregnancy. Translation of materials from UpTodate.com
A normal pregnancy is characterized by significant changes in almost all organs and systems to adapt to the requirements of the fetoplacental complex, including changes in blood tests during pregnancy. -
Risk assessment of pregnancy complications using prenatal screening
Prenatal screening data allow assessing not only the risks of congenital pathology, but also the risk of other pregnancy complications: intrauterine fetal death, late toxicosis, intrauterine hypoxia, etc.
-
Parvovirus B19 and parvovirus infection: what you need to know when planning and getting pregnant.
What is a parvovirus infection, how is the virus transmitted, who can get sick, what is the danger of the virus during pregnancy, what tests are taken for diagnosis.
-
Pregnancy planning
Obstetrics differs from other specialties in that during the physiological course of pregnancy and childbirth, in principle, it is not part of medicine (the science of treating diseases), but is part of hygiene (the science of maintaining health).
 So as the masses or excess masses of atoms are tabulated, then for the energies of beta decays you can write
So as the masses or excess masses of atoms are tabulated, then for the energies of beta decays you can write  02 MeV
02 MeV 
 The left side of Fig. 1 shows the mass parabola for nuclei with odd A = 125. Stable kernel 125 Te is at the minimum mass parabolas (respectively, at the maximum of the parabola for the binding energy). 125 In, 125 sn, 125 Sb susceptible to β - decay, 125 I, 125 Xe, 125 Cs, 125 Ba - β + - decay. The greater the energy of beta decay of nuclei (mass difference between adjacent isobars), the farther they are from the line of stability.
The left side of Fig. 1 shows the mass parabola for nuclei with odd A = 125. Stable kernel 125 Te is at the minimum mass parabolas (respectively, at the maximum of the parabola for the binding energy). 125 In, 125 sn, 125 Sb susceptible to β - decay, 125 I, 125 Xe, 125 Cs, 125 Ba - β + - decay. The greater the energy of beta decay of nuclei (mass difference between adjacent isobars), the farther they are from the line of stability.  Some odd-odd kernels (e.g. 128 I) can experience both β - decay and β + decay and e-capture. There are significantly more stable even-even nuclei than stable nuclei with odd A and, moreover, stable odd-odd nuclei, of which there are only four ( 2 H, 6 Li, 10 B, 14 N ). For a given A, stable there can be several even-even nuclei (for example, 136 Xe, 136 Ba, 136 Ce). Elements with odd Z rarely have more than one stable isotope, while for elements with even Z this is not uncommon ( 112 sn, 114 Sn, 115 Sn, 116 Sn, 117 Sn, 118 Sn, 119 Sn, 122 Sn, 124 Sn). In some cases, when for even-even nuclei, beta decay into an odd-odd nucleus is impossible, it turns out energetically possible transition with a change in Z by two units - double beta decay. Such an exotic decay is experienced by 128 Te and 130 Te.
Some odd-odd kernels (e.g. 128 I) can experience both β - decay and β + decay and e-capture. There are significantly more stable even-even nuclei than stable nuclei with odd A and, moreover, stable odd-odd nuclei, of which there are only four ( 2 H, 6 Li, 10 B, 14 N ). For a given A, stable there can be several even-even nuclei (for example, 136 Xe, 136 Ba, 136 Ce). Elements with odd Z rarely have more than one stable isotope, while for elements with even Z this is not uncommon ( 112 sn, 114 Sn, 115 Sn, 116 Sn, 117 Sn, 118 Sn, 119 Sn, 122 Sn, 124 Sn). In some cases, when for even-even nuclei, beta decay into an odd-odd nucleus is impossible, it turns out energetically possible transition with a change in Z by two units - double beta decay. Such an exotic decay is experienced by 128 Te and 130 Te. Their content in the natural mixture of this element is 31.7% and 33.8% respectively. The probability of double beta decay is very small, periods half-life T 1/2 ( 128 Te) = 7.7 10 28 years,
Their content in the natural mixture of this element is 31.7% and 33.8% respectively. The probability of double beta decay is very small, periods half-life T 1/2 ( 128 Te) = 7.7 10 28 years, 
 Many years passed until Cowan and Reines managed to fix the electron antineutrino.
Many years passed until Cowan and Reines managed to fix the electron antineutrino.  If l = 1, then it is forbidden first order transition, l min = 2 - second order, etc. Other equal conditions for the ratio of the probabilities of emission of a particle with orbital momentum l = 0 (w 0 ) and l ≠0 (w l )
If l = 1, then it is forbidden first order transition, l min = 2 - second order, etc. Other equal conditions for the ratio of the probabilities of emission of a particle with orbital momentum l = 0 (w 0 ) and l ≠0 (w l )  The classical angular momentum pb is equal to the value of the orbital momentum
The classical angular momentum pb is equal to the value of the orbital momentum  Substituting into (6) numerical values, we get
Substituting into (6) numerical values, we get 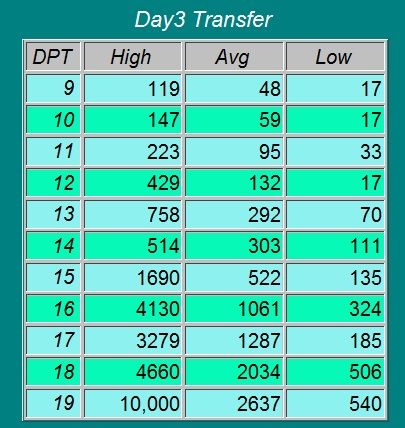
 As a first approximation, this matrix element can be replaced by as follows (Fermi's guess):
As a first approximation, this matrix element can be replaced by as follows (Fermi's guess):  Assuming the neutrino mass to be zero, we can write
Assuming the neutrino mass to be zero, we can write 
 e., for particles with low energy. In this case, the center of gravity of the curve distribution shifts towards low energies for electrons and high energies for positrons (Fig. 4). This shift is greater, the greater the nuclear charge.
e., for particles with low energy. In this case, the center of gravity of the curve distribution shifts towards low energies for electrons and high energies for positrons (Fig. 4). This shift is greater, the greater the nuclear charge. 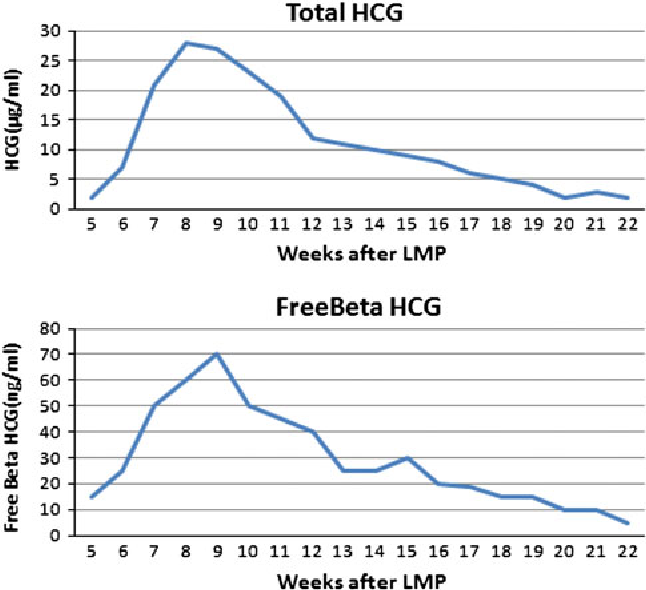
 In this case, the exponent in the matrix element differs little from 1 (integration is carried out over the inner region of the kernel, i.e. for r << R ) and matrix element reduces to
In this case, the exponent in the matrix element differs little from 1 (integration is carried out over the inner region of the kernel, i.e. for r << R ) and matrix element reduces to