When due pregnancy
Calculate your due date: How to find your baby's due date
Choose a calculation method Last periodConception dateI know my due date
First day of my last period
BabyCenter's Due Date Calculator
Use our pregnancy due date calculator by plugging in either the date of your last menstrual cycle or the date you know you conceived. The calculator will do the rest.
How is my due date calculated?
There are several ways your due date is determined. If you happen to know the day you conceived, you can count 38 weeks from that day to find your due date. (Human gestation takes about 38 weeks.)
But very few expectant moms know exactly when they conceived. Even if you only had sex once during your fertile period, you wouldn't conceive on that day unless you happen to be ovulating. Sperm can live for up to five days inside your fallopian tubes. So, it could be up to five days after you have sex that you release an egg (ovulate) and it gets fertilized by a waiting sperm. That's the day you conceive.
So, without knowing the day of conception, how does anyone determine a due date?
First day of your last period
The most common way to calculate your pregnancy due date is by counting 40 weeks from the first day of your last menstrual period (LMP). And that's how most healthcare providers do it.
If your menstrual cycle length is the average length (28-day cycle), your menstrual cycle probably started about two weeks before you conceived. This explains why pregnancies are said to last 40 weeks instead of 38 weeks.
This method doesn't take into account how long your menstrual cycle actually is or when you think you might have conceived. But generally speaking, women typically ovulate about two weeks after their menstrual cycle starts. And women are more likely to know when their last period started than the day they ovulated.
Conception date
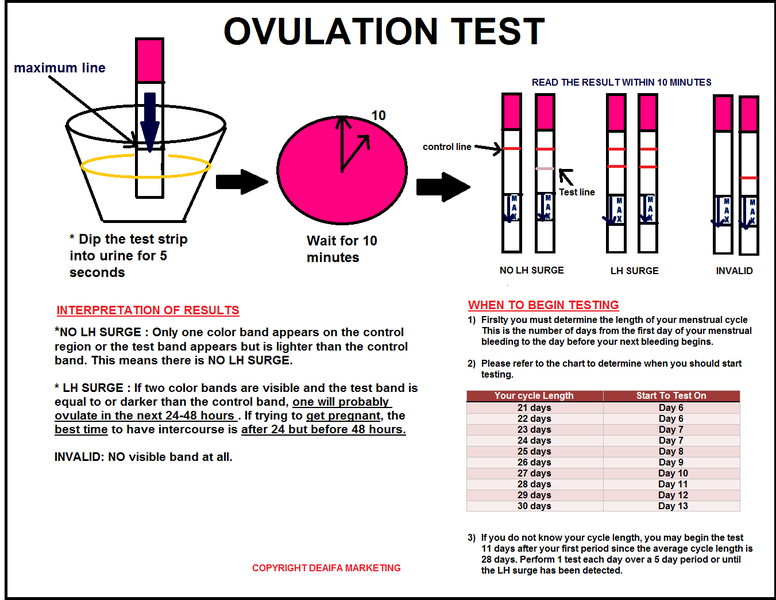
If you do happen to know precisely when you conceived – say, if you were using an ovulation predictor kit or tracking your ovulation symptoms – you can calculate your pregnancy due date based on your conception date. Just choose that calculation method from the pulldown above and put in your date.
Just choose that calculation method from the pulldown above and put in your date.
Note: Again, you don't necessarily conceive on the day you have sex.
IVF transfer date
If you conceived through IVF, you can calculate your due date using your IVF transfer date. If you had a Day 5 embryo transfer, count 261 days from your transfer date. If you had a Day 3 embryo transfer, count 263 days.
Can my due date change?
Your healthcare provider might revise your due date if your baby is measured during a first trimester ultrasound scan and found to be much bigger or smaller than expected for gestational age. This is more likely to happen if you have an irregular menstrual cycle length that makes it hard to pinpoint the date of conception.
Your healthcare provider will measure your baby during that ultrasound exam to figure out how far along your baby is and then provide you with a new due date.
What if I already know my due date?
If you already know your due date, you can use this calculator to see your pregnancy timeline. It will tell you when you'll hit various milestones, and when you may be due for prenatal tests and prenatal visits. You'll also find what your baby's sign and birthstone will probably be and which famous people were born on your due date.
It will tell you when you'll hit various milestones, and when you may be due for prenatal tests and prenatal visits. You'll also find what your baby's sign and birthstone will probably be and which famous people were born on your due date.
How likely am I to give birth on my due date?
Of course, a due date calculation is always approximate, whether it's from our tool or from your doctor or midwife. Only 1 in 20 women delivers on their due date. You're just as likely to go into labor any day during the two weeks before or after.
Want more information about how the weeks, months, and trimesters of pregnancy are counted? See our pregnancy timing chart.
How soon can I take a pregnancy test?
With all this talk about pregnancy due dates, you may be wondering when you can take a pregnancy test. To ensure you get the most accurate reading, it's best to wait a few days after your missed period to take a pregnancy test.
At-home urine tests measure the amount of hCG (human Chorionic Gonadotropin) present in your body. If you take a pregnancy test before you miss your period, you may not get an accurate result, despite what some tests advertise.
If you take a pregnancy test before you miss your period, you may not get an accurate result, despite what some tests advertise.
If you're getting a blood test in your provider's office, you may get results sooner. These tests also measure the amount of hCG in your bloodstream, but they're more sensitive than at-home urine tests. Blood tests may be able to detect pregnancy six to eight days after ovulation.
Read more
- Your pregnancy, week by week
- Your first trimester pregnancy checklist
- Pregnancy Weight Gain Calculator
- Ovulation Calculator
- See all tools
Home pregnancy tests: How to take a pregnancy test at home
Home pregnancy tests work by detecting the presence of a hormone called hCG in your urine. Some at-home pregnancy tests claim they're sensitive enough to give a positive result as early as five days before your next period. But you're more likely to get an accurate result (and avoid a false negative) if you wait until the first day of your missed period.
How do home pregnancy tests work?
All home pregnancy tests measure the amount of a specific hormone known as human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) in your urine. When the embryo starts to implant in the lining of your uterus, as early as six days after conception, cells that will later develop into the placenta begin to produce hCG.
As the placenta grows, the amount of hCG in your body doubles every two days or so during the first few weeks. When hCG levels are high enough, the hormone enters the bloodstream. That's when it starts to show up in the blood and urine. If the home pregnancy test detects enough hCG in your urine, it gives you a positive result.
Some tests are more sensitive than others. But in general, it's easier for any home pregnancy test to pick up hCG in the urine when you're 4 weeks pregnant (when there's more hCG) versus 6 days after fertilization (when there's a trace amount of hCG at best).
The best way to tell if a test is sensitive enough to pick up the smaller amounts is to read the fine print. Some urine pregnancy tests can detect lower levels of hCG. If you're wanting to test early, before you miss a period, check the package insert to learn more about how much hCG needs to be present in your urine to detect a pregnancy.
Some urine pregnancy tests can detect lower levels of hCG. If you're wanting to test early, before you miss a period, check the package insert to learn more about how much hCG needs to be present in your urine to detect a pregnancy.
How to use an at-home pregnancy test
For best results when using a home pregnancy test:
- Make sure the test is up to date. Check the expiration date on the package, especially if you've had it for a while. If you've been storing the test in the bathroom, the humidity may have ruined it. Better to throw it away and get a new one.
- Test first thing in the morning. Your urine is most concentrated when you first get up. If you're pregnant, hCG levels will be higher too. That makes it easier for the at-home test to spot it.
- Read the directions carefully. Different brands have different instructions. With some home tests you urinate in a cup and then use the dropper to place a small sample in the testing well.
 With others, you can pee directly onto the strip or stick. And some let you do either.
With others, you can pee directly onto the strip or stick. And some let you do either. - Wait 5 minutes to check. You get the most accurate results if you wait up to 5 minutes, though this can vary by brand. Read the package instructions to learn exactly how long you'll need to wait to confirm a negative or positive result.
Different tests reveal the results in different ways too. Some show pink or blue lines on the test strip, while others have a red plus or minus sign in a window. Digital tests give results in words ("You're pregnant"). Most have a control indicator (often a second line or symbol) that tells you whether the test is valid.
If the control indicator doesn't show up properly, the test is probably faulty. If this happens, call the manufacturer and see if they'll send you a new one. Also call the company if you have questions about how to use the test.
If the test shows a negative or a faintly positive result, wait another few days and try again if you still haven't gotten your period. Maybe you ovulated later in your cycle than you thought and took the test too early to get a positive result.
Maybe you ovulated later in your cycle than you thought and took the test too early to get a positive result.
Advertisement | page continues below
One negative result doesn't necessarily mean you're not pregnant. Every woman produces different amounts of hCG and it's not even the same for each pregnancy. If you suspect that you're pregnant (say, you're having early pregnancy symptoms) and still have a negative test, take another home pregnancy test in a week if you still haven't gotten your period.
If you still haven't gotten either your period or a positive result two weeks or so after you would expect it, reach out to your provider.
When can I take an at-home pregnancy test?
At-home pregnancy tests are getting better and better. But you're still more likely to get the most accurate results if you wait to take a pregnancy test until the morning of your expected period. Waiting a few more days after that may provide an even more accurate result.
Some home pregnancy tests claim they're sensitive enough to give you a positive result as early as five days before your next period. And some women will have produced enough hCG to get a positive result at that point. But, once again, every pregnancy is different.
And some women will have produced enough hCG to get a positive result at that point. But, once again, every pregnancy is different.
If you're eager (or anxious) to know if you're pregnant, go ahead and do the test 10 or 12 days after you think you've conceived. If you get a negative result, no problem. Wait a week and test again if you still haven't gotten your period.
How accurate are home pregnancy tests?
At-home pregnancy tests are 99 percent accurate. But you can still get what are called false negatives or false positives.
A false negative is when you're pregnant but the test results show up negative. Sometimes you get a faint line on the home pregnancy test, so the result is unclear. These things usually happen if you take the test too soon, before your hCG levels are high enough. If you get a faint line on a pregnancy test, wait a few days and test again.
A false positive pregnancy test means that you get a positive result but aren't pregnant. This doesn't happen very often, except for in the following circumstances:
- You've had a miscarriage or terminated a pregnancy in the past eight weeks, or have a molar pregnancy.

- You've taken a fertility drug with hCG (used to induce ovulation in fertility treatments).
- You have a rare medical condition, such as an hCG-secreting tumor.
- You're using an expired or faulty test.
- You're going through perimenopause or menopause.
If you have a positive result and then get your period soon after, you may have had what's called a chemical pregnancy. This means the embryo implanted in your uterus and developed just enough to start producing detectable levels of hCG, but then it stopped developing. This is most commonly caused by a genetic abnormality of the embryo.
An ectopic pregnancy can also result in a positive pregnancy test, even though these pregnancies often show slower rises in hCG.
No matter what result you get from a pregnancy test, call your healthcare provider right away if you:
- Feel dizzy or faint
- Have abdominal pain (especially a sharp or stabbing pain in your abdomen or on one side of your pelvis
- Have abnormal bleeding
These could be signs of a miscarriage or ectopic pregnancy.
What to do if you get a positive home pregnancy test
Some women take more than one home pregnancy test (or several) just to be sure – but that's not really necessary. Once you've gotten a positive pregnancy test, call your healthcare provider to set up a prenatal visit or to discuss your options if you're not sure about continuing the pregnancy.
If you don't already have a family doctor, ob-gyn, or midwife who can provide prenatal care, do some research to see who's covered by your insurance, and ask for recommendations.
Doctors typically schedule the first prenatal visit when you're about 8 weeks pregnant. But some providers will see you sooner, especially if you have a medical condition or have had problems with a pregnancy in the past. It's especially important to see your provider sooner if you're having nausea and vomiting, vaginal bleeding, or abdominal pain.
Will you need a blood test to confirm your pregnancy?
Not necessarily. To make sure you're pregnant, most healthcare providers use a urine pregnancy test, just like your at-home pregnancy test . But your provider may use a blood test instead. Just note: It may take anywhere from an hour to a day or more to get the results.
But your provider may use a blood test instead. Just note: It may take anywhere from an hour to a day or more to get the results.
There are two types of pregnancy blood tests:
- A qualitative hCG blood test just shows whether there is hCG in your blood. The results return as "positive" or "negative." You usually get the results in about the same time you would with a urine test.
- A quantitative blood test (beta hCG test or serum test) measures the exact amount of hCG in your blood. The results return as a number. This test is very accurate. It can detect hCG as early as six to eight days after ovulation, or about a week before your period is due. It takes longer to get results from a quantitative blood test, though.
Again, your provider may not give you a blood test. Oftentimes, a positive home pregnancy test is enough to get started with the prenatal care you need.
Is it possible to have dental implants during pregnancy
home
Articles
Dental implants during pregnancy
Contents:
- Why pregnant women are not getting implants
- Is it possible to do dental implantation during pregnancy according to experts
- What to do if pregnancy becomes known during implantation
- When can dental implants be performed after childbirth
Women always strive to be beautiful regardless of the circumstances. Dental implantation during pregnancy may be required if a “hole” suddenly appears in the smile, which causes severe psychological discomfort. However, this period is included in the list of contraindications for almost all surgical interventions, including dental ones.
Dental implantation during pregnancy may be required if a “hole” suddenly appears in the smile, which causes severe psychological discomfort. However, this period is included in the list of contraindications for almost all surgical interventions, including dental ones.
Despite the relative safety of the procedure, implantation can be dangerous for the unborn baby and mother:
- an orthopanmogram or computed tomography is required, which means the patient will be exposed to x-rays;
- anesthetics are used for pain relief, which are not included in the list of permitted drugs;
- development of inflammatory, allergic reactions is possible;
- the osseointegration process requires calcium, which the fetus badly needs;
- low immunity, high risk of developing infectious diseases;
- psychological aspect: pain, anxiety, stress.
The greatest sensitivity to pain appears in the first trimester. The pain threshold is reduced and the patient may experience shock during the procedure. Also, postoperative pain is difficult to relieve with medication. Due to the high level of stress, a miscarriage is possible, and at a later stage, premature birth.
Also, postoperative pain is difficult to relieve with medication. Due to the high level of stress, a miscarriage is possible, and at a later stage, premature birth.
The most common complication during implantation is inflammation of the soft and bone tissues. To stop the infection, it is necessary to take antibiotics, which can adversely affect the formation of the fetus.
Since at this time the body is deficient in calcium, the process of engraftment of the implant may be delayed. In addition, this element is very necessary for the proper formation and growth of the child.
During pregnancy, the gums become loose and often inflamed. Gingivitis is also included in the list of contraindications for surgery.
In modern clinics, the treatment of single or multiple adentia is carried out according to one-stage protocols, with virtually no pain, with an easy recovery period. However, any dentist will categorically refuse to operate on a pregnant patient. The body of a woman during this period is unpredictable. Even if the health is near perfect and the procedure is well planned, there can always be complications.
Even if the health is near perfect and the procedure is well planned, there can always be complications.
Since the intrauterine development of a child directly depends on the state of the mother's body, no doctor will perform medical manipulations that can worsen the situation. Operations are possible only if the potential threat to the woman's life outweighs the risks to the fetus. However, implantation is not one of them.
If a doctor says that it is possible to install an implant during the period of bearing a child, then he pursues only financial gain, does not care about the interests and health of patients.
In some cases, the good news about motherhood comes at a time when the patient is already in the process of restoring her teeth. If this happened before the surgical stage, then the issue can be easily postponed until delivery. A few months after the birth of the baby or after stopping breastfeeding, you can return to him again.
If an artificial root is already in place, the following rules must be followed:
- Keep calm, as stressful situations are harmful.
 You need to tune in positively, because the operation took place before conception, and the processes of osseointegration are already in full swing. In addition, before implantation, the oral cavity is necessarily sanitized, so the condition of the dentoalveolar system must be good.
You need to tune in positively, because the operation took place before conception, and the processes of osseointegration are already in full swing. In addition, before implantation, the oral cavity is necessarily sanitized, so the condition of the dentoalveolar system must be good. - Report the situation to the gynecologist and implantologist. If treatment is necessary, doctors will take this fact into account and prescribe the safest drugs.
- Take vitamin and mineral complexes, especially those with a high content of calcium, fluorine, phosphorus. At the same time, you cannot choose vitamins on your own, it is better to leave this choice to your doctor.
- During the rehabilitation period, it is necessary to strengthen oral hygiene to prevent the risk of inflammatory and infectious processes. In addition to brushing your teeth twice, it is recommended to use mouthwash after meals. It is advisable to change your toothbrush once a month.
Placement of the Healing Abutment and Abutment will have to wait as these are traumatic procedures requiring anesthesia.
Pregnancy planning is essential to avoid such complications.
Dentists differ on this issue. Some doctors believe that three or four months is enough for recovery, others recommend waiting at least a year.
If an implant needs to be placed urgently, for example in the anterior row, the operation can be performed even during breastfeeding. In this case, the child is transferred to artificial nutrition, and a day after the procedure, breastfeeding is resumed.
Caries in pregnancy, prevention and treatment of caries in pregnant women
Caries in pregnancy, prevention and treatment of caries in pregnant womenServices
Pregnant women can develop dental caries due to hormonal changes and mineral and vitamin deficiencies. Microbes that cause caries Streptococcus mutans and Streptococcus sanguis destroy tooth tissues.
Specialists of the "Professor's Author's Dental Clinic on Arbat" do not recommend postponing a visit to the doctor, since untreated caries or a fallen filling can cause not only discomfort, but also complete loss of a tooth, so the therapy is selected depending on the patient's condition and the nature of the problem.
The impact of caries during pregnancy on health
According to statistics, the disease is detected in 92% of cases with a normal pregnancy and 94% with toxicosis. Caries is caused by pathogenic microorganisms that can enter the bloodstream and affect the health of the mother and fetus. The probability of their penetration through the placental barrier is negligible, so the baby is not in danger.
However, teeth should be treated because:
- Caries during pregnancy causes pain that cannot be relieved by pills
- The emotional state of a woman worsens, and this affects the fetus and leads to uterine tone
- Possible indigestion, fever, exacerbation of toxicosis
- There is a risk of developing pulpitis and periodontitis, which are much more difficult to treat
- Cariogenic bacteria can cause uterine contractions in early pregnancy
Peculiarities of caries treatment during pregnancy
When selecting therapy, specialists take into account the duration of pregnancy, the stage and type of caries (cervical, contact, fissure, cement caries). It is important for the expectant mother to visit the dentist before the 22nd week.
It is important for the expectant mother to visit the dentist before the 22nd week.
During the appointment, the doctor will assess the condition of the oral cavity, determine whether there is caries and the nature of the disease, tell about the necessary procedures, take into account undesirable factors, including:
- general anesthesia
- radiography
- extraction of teeth
- inflammation and swelling of the gums after intervention
- most antibiotics, painkillers
Therapy is not recommended for the first 12 weeks. In the second trimester, the negative effect of medications decreases. During this period, it is good to carry out the prevention of caries in pregnant women and dental treatment, the condition of which threatens to worsen in the third trimester. In the later stages, dental manipulations are carried out in exceptional cases.
Qualified treatment of caries in pregnant women in Moscow
Dentists of our clinic have all the necessary equipment for safe and painless manipulations, conduct observation and urgent therapy in difficult cases.