Baby not viable
When a pregnancy fails early
From the start, pregnancy poses significant risk to a woman’s health, and differentiating normal from abnormal gestation may be challenging for a clinician. The time from a positive urine pregnancy test (UPT) to a confirmed viable pregnancy can be a few weeks, during which there can be cramping, spotting, and lack of early pregnancy signs, all of which may lead to anxiety for a patient.
The major goal for the clinician is to confirm the location and viability of the pregnancy. Diagnosing a normal intrauterine, an abnormal intrauterine, or abnormally located pregnancy may be complicated and is integral for management of pregnancy. Certain conditions (eg, ectopic pregnancy, molar pregnancy) can not only fail to result in a live birth but also impose significant maternal morbidity and mortality unless treated promptly. The term early pregnancy loss or failure (EPF) refers to a non-viable, intrauterine pregnancy with either an empty gestational sac or a gestational sac containing an embryo or fetus without heart activity within the first 12 6/7 weeks of gestation. 1 At the same time premature assumption of the non-viability of a pregnancy can result in over-diagnosis of EPF and irreversible treatment measures in cases of very early but potentially viable pregnancies. That can be detrimental when the pregnancy is desired. Since falsely diagnosing a pregnancy as failed carries potentially more harmful consequences than delay in diagnosing a failed pregnancy, the specificity goal for the criteria for the diagnosis of non-viability is 100%.2 The formulation of this goal in the context of several large multicenter studies necessitated challenging the prior diagnostic cutoffs and timelines. The consequence was a recent change in guidelines for diagnosis of EPF, which on one hand made the criteria more strictly outlined and, on the other hand, allowed for longer waiting time prior to making the final determination of non-viability.3,4 Here we review the current guidelines and available literature on early pregnancy diagnosis (up to 12 6/7 weeks’ gestation), localization and identification of viability as well as management options and counseling.

Pregnancy diagnosis
In most cases, the diagnosis of pregnancy is made with a positive pregnancy test (using urine or blood) in a reproductive-age women. This may be done when a woman is anticipating a pregnancy or she develops normal pregnancy-related symptoms (such as amenorrhea, nausea and vomiting, and breast tenderness) or abnormal pregnancy-related symptoms (unusual vaginal bleeding, back or lower abdominal pain) or even signs of clinical instability (life-threatening vaginal bleeding, syncopal episode, etc.).
Human chorionic gonadotropin
The pregnancy test in current use is based on detection of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) in a woman’s urine or blood. hCG is a 237 aminoacid glycoprotein hormone produced largely by syncytiotrophoblast cells and composed of alpha and beta subunits. Its main function is to stimulate progesterone production by the corpus luteum until approximately 14 weeks’ gestation. In normal singleton pregnancy hCG starts to rise as early as 6–12 days after ovulation and reaches its peak of 100,000 at ~10 weeks’ gestation, after which it slowly decreases to a plateau of 20,000 mIU/mL in the mid-second trimester, where it stays until delivery. 5,6
5,6
Although beta hCG is the predominant form of hCG in the urine of pregnant women, home pregnancy tests are designed to detect both hCG and beta hCG. The sensitivity of over-the-counter tests varies greatly among brands and ranges from 0.4 to 6.3 IU/L (despite manufacturer-claimed sensitivity of 25 IU/L).8
Most serum assays are now designed to measure hCG and hCG-beta equally. The sensitivities of current quantitative pregnancy tests are ~25 IU/L and 1 IU/L for enzyme-linked assays and fluoroimmunoassays, respectively. The upper limit of the reference range is ~3 IU/L in non-pregnant women <50 years old and ~5.4 IU/L in women >50 years old.9
Ultrasound evaluation of early pregnancy
Use of ultrasound (U/S) in obstetrics and gynecology dates back to 1958 when Donald et al. published their experience on identification of abdominal masses using U/S in the Lancet.10 Since then U/S evaluation has become nearly universal in developed countries as part of routine prenatal care and is used to diagnose pregnancy, establish its location and viability, and assess fetal anatomy and growth and placental position. Ultrasound has become a preferred modality for pregnancy viability assessment since 1987 when the transvaginal approach for this purpose became widely available.11,12 Since then criteria for a non-viable pregnancy have been suggested.
Ultrasound has become a preferred modality for pregnancy viability assessment since 1987 when the transvaginal approach for this purpose became widely available.11,12 Since then criteria for a non-viable pregnancy have been suggested.
A pregnancy is termed viable if it has the potential to result in a live-born neonate.2,12 The two major criteria that must be met for a pregnancy to be viable are a normally location within the uterus and a potentially viable fetus.
Location
Timely identification of a pregnancy’s normal location within the uterus is crucial. The diagnosis of intrauterine pregnancy is most commonly made with U/S, based on identification of an intrauterine gestational sac located toward the fundus with at least yolk sac or fetal pole with or without a heartbeat (Figure 1).
Findings of gestational sac but without yolk sac or fetal pole traditionally were not considered exclusive of abnormally located pregnancy due to a possibility of the visualized sac being a pseudosac in association with an ectopic pregnancy. This paradigm and thus the term pseudosac itself, however, have recently been challenged due to the predominance of occasions when a round fluid collection in the uterus in conjunction with a positive pregnancy test were indicative of an intrauterine pregnancy.13,14
This paradigm and thus the term pseudosac itself, however, have recently been challenged due to the predominance of occasions when a round fluid collection in the uterus in conjunction with a positive pregnancy test were indicative of an intrauterine pregnancy.13,14
Viability
Criteria for viability can vary at different gestational ages. In a viable singleton pregnancy, correlation between pregnancy dating, hCG level, and U/S findings has been described, though there is some variability in the milestones. The embryo is expected to grow by at least 0.2 mm/day, and the gestational sac at least 1 mm/day.15
In many instances a single point hCG measurement is not diagnostic of either the viability of pregnancy, or its location; rather hCG trend is much more helpful in distinguishing those. With a normal intrauterine pregnancy hCG is expected to rise by at least 53% over a 48-hour period, and a deviation from that trend may indicate a nonviable intrauterine or an abnormally located pregnancy. Importantly, observation of a normal rise does not necessarily exclude the possibility of an abnormal intrauterine or abnormally located pregnancy.18 Once a viable IUP is confirmed, hCG does not need to be trended further. To describe the correlation between the hCG level and U/S findings, the term “discriminatory zone” (Table) emerged and is used to determine the hCG value above which an intrauterine gestational sac is consistently seen on U/S in normal pregnancies.13 The discriminatory zone is institution-specific and usually ranges between 1500 and 3500 mIU/mL. However, care should be taken to personalize the use of discriminatory zone because there are certain clinical scenarios that result in deviation of the hCG curve and U/S findings from expected pattern. An example is early multiple-order gestations, which may not necessarily have the same association between the hCG level and U/S findings and higher discriminatory hCG level (~3000 mIU/mL).
Importantly, observation of a normal rise does not necessarily exclude the possibility of an abnormal intrauterine or abnormally located pregnancy.18 Once a viable IUP is confirmed, hCG does not need to be trended further. To describe the correlation between the hCG level and U/S findings, the term “discriminatory zone” (Table) emerged and is used to determine the hCG value above which an intrauterine gestational sac is consistently seen on U/S in normal pregnancies.13 The discriminatory zone is institution-specific and usually ranges between 1500 and 3500 mIU/mL. However, care should be taken to personalize the use of discriminatory zone because there are certain clinical scenarios that result in deviation of the hCG curve and U/S findings from expected pattern. An example is early multiple-order gestations, which may not necessarily have the same association between the hCG level and U/S findings and higher discriminatory hCG level (~3000 mIU/mL).
Early pregnancy failure
The term “early pregnancy loss” or EPF refers to a nonviable, intrauterine pregnancy with either a gestational sac that is empty or contains an embryo or fetus without heart activity within the first 12 6/7 weeks of gestation. EPF occurs in 15% of all clinically recognized pregnancies and most frequently results from a spontaneous chromosomal abnormality of the embryo. Depending on clinical presentation and U/S findings EPF can be divided into several categories.
EPF occurs in 15% of all clinically recognized pregnancies and most frequently results from a spontaneous chromosomal abnormality of the embryo. Depending on clinical presentation and U/S findings EPF can be divided into several categories.
- Anembryonic pregnancy, also known as a blighted ovum: this EPF is characterized by no embryo development once a gestational sac reaches 25 mm (Figure 3A).
- Embryonic/fetal death is also known as missed abortion. This is characterized by an IUP with an embryo that either never developed a heartbeat or that previously had a heartbeat, but now lacks one (Figure 3B).
- Spontaneous abortion is characterized by a previously seen IUP, followed by cramping and bleeding. A spontaneous abortion may either be complete, as the uterus expels the products of conception (POCs) on its own, or inevitable, with an open os and gestational sac in the lower uterine segment.
Previous recommendations did not have a 0% false positive rate, and therefore a number of viable pregnancies were destined to be treated as though they were losses. Traditional data on EPF utilized a crown–rump length of 5 mm without cardiac activity, or an empty gestational sac of 16 mm as diagnostic criteria.11,12 Recent prospective studies, however, revealed an 8.3% false-positive rate with this crown–rump length and a 4.4% false-positive rate with this gestational sac diameter. In thoser studies, it was necessary to achieve a 0% false-positive rate, a crown–rump length of 5.3 mm without cardiac activity, or an empty gestational sac of 21 mm. The same group also found that an empty gestational sac 7 days from initial identification of the sac was 100% diagnostic of EPF.1,3,4 In response, the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) released in May 2015 an updated Practice Bulletin with diagnostic criteria of EPF incorporating guidelines from the Society of Radiologists in Ultrasound (SRU). The new guidelines allow for diagnosis of EPF in the situations summarized in Table 2 (from AGOG Bulletin #150, May 2015). The new criteria for EPF are less strict, allowing for lengthening of the waiting time prior to EPF diagnosis and thus minimizing the false-positive rate.
Traditional data on EPF utilized a crown–rump length of 5 mm without cardiac activity, or an empty gestational sac of 16 mm as diagnostic criteria.11,12 Recent prospective studies, however, revealed an 8.3% false-positive rate with this crown–rump length and a 4.4% false-positive rate with this gestational sac diameter. In thoser studies, it was necessary to achieve a 0% false-positive rate, a crown–rump length of 5.3 mm without cardiac activity, or an empty gestational sac of 21 mm. The same group also found that an empty gestational sac 7 days from initial identification of the sac was 100% diagnostic of EPF.1,3,4 In response, the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) released in May 2015 an updated Practice Bulletin with diagnostic criteria of EPF incorporating guidelines from the Society of Radiologists in Ultrasound (SRU). The new guidelines allow for diagnosis of EPF in the situations summarized in Table 2 (from AGOG Bulletin #150, May 2015). The new criteria for EPF are less strict, allowing for lengthening of the waiting time prior to EPF diagnosis and thus minimizing the false-positive rate. If the diagnosis is at all in doubt, serial U/S assessment is recommended.
If the diagnosis is at all in doubt, serial U/S assessment is recommended.
Certain U/S findings can be suggestive of a nonviable pregnancy. To add to the list above, additional findings concerning for EPF are: fetal bradycardia, expanded amnion sign, and yolk sac abnormalities (size >6 mm, abnormal location, number, or echogenicity).15,19,20 Importantly, both ACOG and the SRU state, “These are the radiologic criteria only and do not replace clinical judgment.” Other factors to account for are the risks of postponing diagnosis in medically complex patients, the patient’s desire to continue the pregnancy, or the patient’s desire to achieve 100% certainty prior to intervention. A discussion with the patient about the possible outcomes should be had, and should guide further diagnostic and clinical management.
Because assigning an estimated date of delivery is frequently challenging due to unknown/inaccurate LMP, most of the criteria in the chart are based on U/S findings and their changes over time rather than on gestational age. Thus the patient should be followed with serial hCG levels, and repeat U/S in 7–14 days. In addition, if no IUP is seen, the diagnosis of pregnancy of unknown location (PUL) is made and the patient should be told of the warning signs for ectopic pregnancy.
Thus the patient should be followed with serial hCG levels, and repeat U/S in 7–14 days. In addition, if no IUP is seen, the diagnosis of pregnancy of unknown location (PUL) is made and the patient should be told of the warning signs for ectopic pregnancy.
Disclosures:
None of the authors report a conflict of interest to report with respect to the content of this article.
References:
- Doubilet PM. Ultrasound evaluation of the first trimester. Radiol Clin North Am, 2014. 52(6):1191-9.
- Doubilet PM, et al. Diagnostic criteria for nonviable pregnancy early in the first trimester. Ultrasound Q, 2014. 30(1):3-9.
- Abdallah Y, et al. Gestational sac and embryonic growth are not useful as criteria to define miscarriage: a multicenter observational study. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol, 2011. 38(5):503-9.
- Abdallah Y, et al. Limitations of current definitions of miscarriage using mean gestational sac diameter and crown-rump length measurements: a multicenter observational study.
 Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol, 2011. 38(5):497-502.
Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol, 2011. 38(5):497-502. - Barnhart KT, et al. Symptomatic patients with an early viable intrauterine pregnancy: HCG curves redefined. Obstet Gynecol, 2004. 104(1):50-5.
- Wilcox AJ. Baird DD, Weinberg CR. Time of implantation of the conceptus and loss of pregnancy. N Engl J Med, 1999. 340(23):1796-9.
- Korevaar TIM, et al.,Reference ranges and determinants of total hCG levels during pregnancy: the Generation R Study. European Journal of Epidemiology, 2015. 30(9):1057-1066.
- Cervinski MA, et al. Qualitative point-of-care and over-the-counter urine hCG devices differentially detect the hCG variants of early pregnancy. Clin Chim Acta, 2009. 406(1-2): 81-5.
- Montagnana M, et al. Human chorionic gonadotropin in pregnancy diagnostics. Clin Chim Acta, 2011. 412(17-18):1515-20.
- Donald I. Clinical application of ultrasonic techniques in obstetrical and gynaecological diagnosis. J Obstet Gynaecol Br Emp, 1962. 69:1036.
- Brown DL, et al.
 ,Diagnosis of early embryonic demise by endovaginal sonography. J Ultrasound Med, 1990. 9(11): p. 631-6.
,Diagnosis of early embryonic demise by endovaginal sonography. J Ultrasound Med, 1990. 9(11): p. 631-6. - Pennell RG, et al. Prospective comparison of vaginal and abdominal sonography in normal early pregnancy. J Ultrasound Med, 1991. 10(2): p. 63-7.
- Doubilet PM, et al. Diagnostic criteria for nonviable pregnancy early in the first trimester. N Engl J Med, 2013. 369(15):1443-51.
- Bradley WG, Fiske CE, Filly RA. The double sac sign of early intrauterine pregnancy: use in exclusion of ectopic pregnancy. Radiology, 1982. 143(1):223-6.
- Hamza A, et al. Diagnostic Methods of Ectopic Pregnancy and Early Pregnancy Loss: a Review of the Literature. Geburtshilfe Frauenheilkd, 2016. 76(4):377-382.
- Goldstein I, et al. Evaluation of normal gestational sac growth: appearance of embryonic heartbeat and embryo body movements using the transvaginal technique. Obstet Gynecol, 1991. 77(6):885-8.
- Bree RL, et al. Transvaginal sonography in the evaluation of normal early pregnancy: correlation with HCG level.
 AJR Am J Roentgenol, 1989. 153(1):75-9.
AJR Am J Roentgenol, 1989. 153(1):75-9. - Chung K, Allen R. The use of serial human chorionic gonadotropin levels to establish a viable or a nonviable pregnancy. Semin Reprod Med, 2008. 26(5):383-90.
- Horrow MM. Enlarged amniotic cavity: a new sonographic sign of early embryonic death. AJR Am J Roentgenol, 1992. 158(2):359-62.
- Bromley B, et al. Small sac size in the first trimester: a predictor of poor fetal outcome. Radiology, 1991. 178(2):375-7.
A Look at the Heartbreak and Way Forward
I won’t lie to you, mama. This topic is HARD. Non-viable pregnancy is sometimes a blessing but ALWAYS a tragedy.
Growing a little one is such a special thing, and you don’t need me to tell you: losing a pregnancy is one of the hardest things in the world to handle.
It’s my belief that knowing all there is to know in advance, or at least having the information from a source that gets you and feels for you, will help you to work through the worries or heartbreak that accompanies such a tough thing.
Table Of Contents
- Our Objective Regarding Non-Viable Pregnancy
- What is a Non-Viable Pregnancy?
- Determining Viability in Pregnancy
- Symptoms of a Non-Viable Pregnancy: What to Look For
- The Causes of a Non-Viable Pregnancy
- Non-Viable Pregnancy Options
- Making It Through a Non-Viable Pregnancy
Follow @mommy.labornurse on Instagram to join our community of over 580k for education, tips, and solidarity on all things pregnancy, birth, and postpartum!
Our Objective Regarding Non-Viable PregnancyAs a labor and delivery nurse, you can guess that I’ve seen every shade of non-viable pregnancy. I’m here to tell you, they are all hard. If you experience or have experienced a non-viable pregnancy, it can feel like no one understands.
But I’m with you, lady. As are millions of women before and beside you.
Your medical staff, the people you pass on the street, those somber-eyed ladies in black and white photos–we are all touched by this unique form of tragedy in one way or another at some point in our lives, even if we never know it.
So let’s take some time to review it all; it’s not always something to fear or something to dwell on, but knowledge and understanding can sometimes be our greatest hope. I firmly believe that context always provides a wider platform for acceptance and RECOVERY.
What Should You Do With This Information?If you are NOT working through a non-viable pregnancy at this time and are simply hoping to be well-informed, it’s my hope that I give you everything you need to feel good about your options–all without increasing your FEAR. Life’s too short for that, mama.
That said, be sure to ask about the pregnancy viability milestones your provider uses, as their information and how they relate that to you is going to more important than any other resource.
If, on the other hand, you are currently experiencing or are in danger of having a non-viable or at-risk pregnancy, my heart goes out to you–as does my hand.
I’ll be taking you through the definitions, causes, and treatment options necessary to cover ALL YOUR BASES.
I hope we’ll be able to examine non-viable pregnancy treatments together to ensure you have everything you need to make the best choices in what is easily a crucible for the best of us.
What is a Non-Viable Pregnancy?There’s a little push and pull when it comes to the definition of a non-viable pregnancy.
The reason for this is that there are legal implications if a radiologist or a practitioner uses a term like “non-viable pregnancy” or “non-viable fetus” outside of a very specific range of time.
It’s typically safer for medical staff to refer to it as a failed pregnancy.
This makes for pretty stale reading, but suffice it to say that we’re talking about a fetus that cannot be carried to term.
Because it’s simpler for our needs, we’ll stick to non-viable, but remember that your OB or radiologist might go a different way, mama.
If it becomes important to know the difference, your care provider will help you understand.
What Does Viability Mean Regarding Pregnancy?If non-viable means the baby can’t be carried to term, it follows that viability is the consideration of whether or not that little seed can actually grow into a plant.
Viability is determined by a lot of things, including:
- How and where the zygote (little baby bubble) attaches to the uterine wall
- What kind of conditions exist in the womb
- What kind of data mom and dad put into the sperm and egg that connected
In broader terms, “viable” means “capable of working successfully” or “feasible”. In biological terms, it’s more about being capable of surviving or living successfully, particularly in specific environmental conditions.
The Differences Between a Viable and a Non-Viable PregnancyThe viability of a pregnancy looks a little different depending on what term you’re in. As you can imagine, a lot goes into losing viability as a zygote.
As you can imagine, a lot goes into losing viability as a zygote.
That little seed pod needs very different conditions than a fully formed and growing embryo; even further still are the requirements for a legit fetus or an actual baby.
You can probably guess, but it’s a much more dangerous world for a tiny little zygote or an embryo than it is for a fetus or a baby.
The result is that you’re much more likely to have a failed pregnancy in the first trimester (the first 0-13 weeks of pregnancy).
Differences Between a Non-Viable Pregnancy and a MiscarriageView this post on Instagram
A post shared by Liesel Teen BSN, RN | Pregnancy + Birth (@mommy.labornurse)
A miscarriage is defined as the spontaneous loss of a fetus BEFORE 20 weeks of development.
Loss of the fetus after that would be considered a “stillbirth“.
There are a lot of similarities and correlations between a non-viable pregnancy and a miscarriage, mama. They overlap a lot, actually.
The reason for this is that miscarriage falls under the UMBRELLA of what we consider non-viable pregnancy.
But a non-viable pregnancy doesn’t have to be a miscarriage. Things like genetic issues may leave the zygote or fetus alive but with a low or null chance to survive beyond the womb.
Can You Have a Non-Viable Pregnancy Without MiscarriageYes, you CAN absolutely have a non-viable pregnancy but no miscarriage. The products of conception may have to be removed surgically if the pregnancy is non-viable.
Related Reading: Everything You Need to Know About Pelvic Pain During Pregnancy (Right Now!)
Determining Viability in PregnancyAs you can imagine, mama, a lot goes into determining whether or not a zygote, embryo, or fetus presents a viable pregnancy.
Because of the drastic nature of a non-viable pregnancy, it is very important for your health care provider to be as certain as possible before declaring the pregnancy non-viable.
Symptoms of a Non-Viable Pregnancy: What to Look ForIf you have excessive bleeding and cramping, it’s always a good idea to see your care provider as soon as possible.
Severe abdominal pain can be a strong indicator that something is wrong.
Also watch out for severe headaches (particularly with blurred vision), convulsions of any kind, a fever accompanied by extreme weakness or fast/labored breathing–they can all be indicators that something is wrong with your pregnancy.
You can read more details about when to call your doctor during pregnancy which might help!
Determining Whether or Not Your Pregnancy May Be Non-ViableAs with testing for the pregnancy itself, measurements of hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin) along with an early ultrasound can help in diagnosing the potential for complications.
Keep in mind that these methods aren’t 100% conclusive, though–this is important to note because a failed diagnosis could be catastrophic.
For this reason, and I hope your practitioner agrees, the investigation of viability should come to a screeching halt when the practitioner asks themselves “Is there a chance of viability”.
Diagnostic criteria for a non-viable pregnancy in the first trimester are imperfect enough that your doc should always be erring on the side of caution.
Ultimately, the consequences of your doctor giving you a false positive result (saying the pregnancy is non-viable when it’s not) blow the consequences of a false negative WAY out of the water.
Believing a pregnancy IS viable when it’s actually NOT may result in a slight delay in the correct treatment (and possibly a little more disappointment, if that’s possible), while the opposite can lead to birth defects and even CAUSING a non-viable pregnancy when a bit of waiting might have put your worries to bed for good.
Ultimately, there is no silver bullet amount of hCG that can tell us whether or not a pregnancy is non-viable.
There’s a lot of overlap between different conditions and the amount of hCG present in the body at any given time.
Can a Non-Viable Pregnancy be MisdiagnosedWe’ve covered it a bit here, but there is EVERY POSSIBILITY that a doctor may misdiagnose a non-viable pregnancy.
Technology has progressed a lot with the advent of things like the transvaginal probe, but we are still limited to what we can test for in the chemistry.
The Causes of a Non-Viable PregnancyThe various causes of a non-viable pregnancy range from significant defects preventing there from ever being a fetus to infections that erode the environment in which the fetus grows.
Some of these are pretty small potatoes, mama. But some of them can be really serious if left untreated.
Anembryonic Gestation is a condition where the gestational sac forms but no embryo grows within it. They used to call this a blighted ovum, but the term isn’t as widely used today. Some believe that it can be due to chromosomal abnormalities.
Chemical PregnancyView this post on Instagram
A post shared by Liesel Teen BSN, RN | Pregnancy + Birth (@mommy.labornurse)
A chemical pregnancy is when an egg gets fertilized but never attaches to the uterus. Chances are that you’ll never know you had one of these, honey, so don’t lose sleep over it.
Ectopic PregnancyAn ectopic pregnancy is when a fertilized egg implants inside of a fallopian tube or some other cavity, rather than inside the uterus. This one can actually be really dangerous if left untreated too long.
This one can actually be really dangerous if left untreated too long.
A molar pregnancy occurs when an already non-viable egg attaches to the uterine wall. Because the egg already can’t become a fetus for one reason or another, it grows into a non-cancerous mass instead.
Septic AbortionA septic abortion occurs when an infection takes hold in the placenta. This septic infection can transfer to the uterus and pelvis, potentially damaging organs nearby and even further away if left untreated.
Genetic / Congenital DefectsA genetic or congenital defect is an error in the DNA (or “code”) that comprises the substance of mommy or daddy.
These defects may be specific to a single specimen of sperm or ovum, or they can be substantial defects that affect all or most of a potential parent’s stuff.
Extremely Premature LaborThis one is what it is, mama. Premature labor short of about 24 weeks will be considered non-viable, as the fetus is insufficiently developed for survival outside of mom.
What options a mama has when the fetus is determined non-viable vary significantly depending on why the pregnancy is non-viable.
As always, the best recommendations are going to come directly from your care provider.
Hopefully, though, you can walk into that conversation armed to the teeth with the information necessary to ask the right questions and walk away fully satisfied by the outcome. Or at least as satisfied as can be under such circumstances.
First and foremost, you want to manage your expectations. If you know the little one is not viable, it’s important to frame your feelings and thoughts in a way that allows you to work through this difficult time.
If you suspect your pregnancy is not viable, be sure to walk in with hope but be prepared for the possibility of the worst news.
Management Options for a Non-Viable PregnancyYour doctor will have a very strong set of early pregnancy loss guidelines they follow.
When in doubt–if they aren’t entirely sure the pregnancy is non-viable, they will typically offer expectant management, which is a fancy way of saying “let’s do nothing and see what happens”.
That might sound messy, and even risky in some of the scenarios we worked through earlier.
What this recommendation DOES do for us is give a chance for a false positive to be determined false. Because some of this is a bit like educated guesswork, there’s always a chance that the pregnancy may be viable when the circumstances suggest otherwise.
But What Does That Mean For YOU?It’s a little bit of a waiting game.
Beyond that, there are medical treatments with medicine that can ensure your non-viable pregnancy will come to an end without much more effort and agony on your part.
In the worst case, a doctor may sometimes recommend surgical evacuation of the products of your non-viable pregnancy. It’s hard and drawn-out by comparison, but your doctor will know best if this is necessary.
Obviously, mama, this is the last place any of us want to be.
Losing a pregnancy, even early on, can be incredibly difficult for the strongest of us.
The most important thing you can do for yourself is trust in the science, trust in the people, and trust in the fact that these things happen for a reason–biologically speaking.
With the rare exception of something like an infection, you can basically assume that if your pregnancy becomes non-viable, that fetus would likely not have had much of a life given the complications that feed into most or all of these situations.
That’s small consolation if you’ve been there. Trust me, I get it. Your medical staff feels it too. We never get into the business to deal with the non-viable ones–but it’s worth all the tears in the world to be there for mamas like you in such a tough time.
As with anything, be sure to seek solace in the arms of loved ones and know that you have support.
With the right social interaction and a proper mindset, you stand a great chance of working through a non-viable pregnancy.
With a heavy heart, happy future-making, mama.
“His organs and systems are not ready” Why are they trying to save children in Russia who have almost no chance of surviving and being healthy: Society: Russia: Lenta.ru
period (less than 22 weeks) and extremely low weight (less than 500 grams). This happened after a series of criminal cases that the Investigative Committee initiated against obstetricians. So, neonatologist Elina Sushkevich from Kaliningrad was accused of killing a 22-week-old boy. Why are they trying to save 500-gram children in Russia at all today, what are their chances of surviving and whether they can grow up healthy - Lenta.ru learned from the doctor of medical sciences, head of the scientific department of neonatology and pathology of young children at the Research Clinical Institute of Pediatrics named after Yu.E. Veltishchev Elena Keshishyan.
Veltishchev Elena Keshishyan.
***
Lenta.ru: Now the minimum criteria for saving premature babies are 22-23 weeks and 500 grams of weight. Why?
Elena Keshishyan : In order to understand what is the limit of possibilities both in technical terms (creation of an environment close to intrauterine), and in terms of the maturity of the child's brain, which is able to develop out of utero, attempts were made in the world to give birth to premature babies of different ages. The greatest successes in this were achieved by the Japanese. They tried out babies born at 20 weeks. That is, the approximate gestational age was five months. The Japanese succeeded, but in isolated cases. And they saw that in children born at this age there is no differentiation of the brain, division into gray and white matter. Roughly speaking, this process determines the ability to think, to feel. This is called higher nervous activity. It is this ability that distinguishes man from animals.
Therefore, guided by research data and on the basis of a humanistic idea, the World Health Organization has established this limit for human live birth - 23 weeks, which corresponds to approximately 500 grams of weight. This is the minimum age at which the brain can differentiate into gray and white matter. And, accordingly, there is hope that it will already be a human person with mental abilities.
Countries with technological capabilities, including Russia, have agreed that those born at this gestational age can legally be considered human. That is, they have all human rights, including medical care.
Since 2012, Russia has moved to the WHO criteria for nursing premature babies. How many of these children have been saved during this time?
As a percentage of all those born, this is a minuscule amount. I don't have exact numbers. But I want to say that the body of children born almost half prematurely is very immature. And their survival rate, conditionally, is one in a hundred. Still, 22-23 weeks is not childbirth in the full sense. From the point of view of nature, this is a miscarriage, this is a critical situation that may be associated with the health of the mother or the sick child herself. Therefore, the readiness for independent existence in such fruits is close to zero. Even if we assume that the maximum efforts of doctors are thrown to save the child, all the necessary equipment is connected, the chance that he will get out is very small. In such an infant, the kidneys, gastrointestinal tract, heart and other organs may not work. This is a very, very complex, jewelry work of doctors.
Still, 22-23 weeks is not childbirth in the full sense. From the point of view of nature, this is a miscarriage, this is a critical situation that may be associated with the health of the mother or the sick child herself. Therefore, the readiness for independent existence in such fruits is close to zero. Even if we assume that the maximum efforts of doctors are thrown to save the child, all the necessary equipment is connected, the chance that he will get out is very small. In such an infant, the kidneys, gastrointestinal tract, heart and other organs may not work. This is a very, very complex, jewelry work of doctors.
One of the smallest surviving premature babies in the world. Amilya Taylor was born in 2006 in Miami, USA. She spent only 22 weeks in the womb and was born with a weight of 284 grams and a height of 24 centimeters.
Photo: Baptist Health South Florida / Reuters
And dear?
Of course. A day in a well-equipped neonatal intensive care unit costs several thousand dollars. And to leave such a child, months are needed. But I want to emphasize that the number of survivors in this period is minimal. And it is minimal in almost all countries where the WHO criteria apply.
And to leave such a child, months are needed. But I want to emphasize that the number of survivors in this period is minimal. And it is minimal in almost all countries where the WHO criteria apply.
If these children are not viable, cost too much, then why were these criteria established?
The medical task here is not at all to save without exception all children born at a term of five months. It is clear that there is not a single person who does not understand that this child is at risk of being blind, deaf and immobilized. The task of medicine in this situation is to acquire knowledge and experience.
Obstetricians learn how to prolong pregnancy as much as possible. There is a whole range of activities: prenatal diagnosis of genetic chromosomal diseases, various fetal malformations, identification of risk groups among pregnant women, their special monitoring, prenatal logistics and routing. They also hone the ability to properly take birth at this time. This must be done as carefully as possible and do not forget about the "golden hour". It is necessary to have time to give the child, without waiting until his condition worsens, what he could not get from his mother. That is, even if the child screamed, you need to understand that soon he will stop doing this and will not be able to breathe. The "golden hour" essentially determines whether or not there will be damage to brain cells. This means whether or not a child will have a full life.
It is necessary to have time to give the child, without waiting until his condition worsens, what he could not get from his mother. That is, even if the child screamed, you need to understand that soon he will stop doing this and will not be able to breathe. The "golden hour" essentially determines whether or not there will be damage to brain cells. This means whether or not a child will have a full life.
And the qualifications of resuscitators working with such children are growing today. All this led to an important point: the quality of nursing of children born a little later, at 26-28 weeks, has become much better. I see these babies regularly. And I can say that over time, many of them are no different from their peers.
And before?
About 30 years ago, about six or seven out of ten children would have become severely disabled. And today I had three 26-week-old babies at my appointment. And everyone is developing quite well, there is a slight backlog, but they will catch up. These children no longer have those possible malformations that, unfortunately, would have necessarily arisen in past years.
These children no longer have those possible malformations that, unfortunately, would have necessarily arisen in past years.
And this became possible thanks to the experience, the accumulation of knowledge about how such babies develop. There are no small things. This applies to everything - how to evaluate the heartbeat, how to interpret blood tests, and so on. Caring for a premature baby, both in the neonatal period and later, in the first or second year of life, is not the same as managing a normal, full-term baby. But knowledge allows timely adjustment of development, without even waiting for problems.
Photo: Science Photo Library / East News
It is important to understand that a premature baby is not a small copy of a normal one. This is a child who is forced to adapt to extrauterine life, when physiologically he should not do this. Its organs and systems are not prepared to function in the new conditions.
"This is painful love at the level of deep depression"
What do such children most often suffer from?
One of the typical pathologies is retinopathy of prematurity. In children, the mechanism that protects the eye from light has not yet matured. And they experience a real shock, suddenly falling into our bright world. Photons of light and the flow of oxygen begin to act on the retina, its vessels begin to grow rapidly, penetrate all the media of the eye, and, ultimately, exfoliate the retina, leading to total blindness. Earlier, even when I was just starting to work, although we knew about such a disease as retinopathy of prematurity, there were few children born and surviving at gestational ages of less than 30 weeks. Therefore, no one knew how to treat this disease. It's scary to remember, but premature babies were in wards with round-the-clock lighting. The light was needed so that doctors and nurses could observe the baby's condition and notice changes in time. At that time, six out of ten children whose birth weight was less than a kilogram went blind. Just then, the borders were opened in Russia, and we were amazed that in Europe, a maximum of two out of ten newborns had blindness.
In children, the mechanism that protects the eye from light has not yet matured. And they experience a real shock, suddenly falling into our bright world. Photons of light and the flow of oxygen begin to act on the retina, its vessels begin to grow rapidly, penetrate all the media of the eye, and, ultimately, exfoliate the retina, leading to total blindness. Earlier, even when I was just starting to work, although we knew about such a disease as retinopathy of prematurity, there were few children born and surviving at gestational ages of less than 30 weeks. Therefore, no one knew how to treat this disease. It's scary to remember, but premature babies were in wards with round-the-clock lighting. The light was needed so that doctors and nurses could observe the baby's condition and notice changes in time. At that time, six out of ten children whose birth weight was less than a kilogram went blind. Just then, the borders were opened in Russia, and we were amazed that in Europe, a maximum of two out of ten newborns had blindness.
But we started learning very quickly. Now in perinatal centers in all intensive care units for premature babies - twilight. The cuveuses are completely covered with dark blankets. The staff does not need to watch the baby all the time - all readings are automatically recorded by special devices. In good ICUs, nurses who approach babies have headlights. This is to avoid disturbing other children. In many intensive care units, a large “ear” hangs. If the decibel level in the room begins to exceed the allowable limit, the device lights up red.
After the birth of the child, every week they begin to look at the eyes with a special method. If there is proliferation of blood vessels, laser coagulation of the retina is performed. There are specialists in such operations in almost every major city.
Approximately 400-600 babies pass through me every year, born at 26-28 weeks. Over the past few years, not a single blind person has been among them. Although earlier in hospitals for such newborns it was necessary to open entire departments.
Is there any data on how many premature babies later became healthy?
Now, among premature babies born at five or six months (25-26 weeks of pregnancy), 25-30 percent become disabled. The same is true in developed countries. And even 20-30 years ago there were 75-80 percent of them.
The risks for these children are still very high. They require long-term observation and treatment. But still today they have incommensurably or better chances than before.
Photo: East News
Do unfortunate parents regret insisting on resuscitation at all costs?
As a doctor, no one has ever told me this. Naturally, the families had very different hopes for childbirth. In the doctor's office they cry, but they don't moan. These children are madly loved. But this is painful love at the level of deep depression. Probably, some of these mothers may think at night what would happen if they knew in advance how everything would turn out. Perhaps they voice this to their mothers, husbands, girlfriends . .. But not to doctors. This is where people prefer to stay.
.. But not to doctors. This is where people prefer to stay.
When a child is one or two years old, from a moral point of view, the situation is more difficult than in three days. Newborns are all wonderful bags, it is only then that children begin to differ from each other. These families have a very specific and difficult life. When a child lies at home, does not move, does not swallow, never looks at you, does not speak - this is very difficult. And parents need to be helped to turn their life into at least a relatively social one, not to make them outcasts.
What family support can I expect now?
When Russia switched to WHO standards, doctors began to say that if we started caring for such children, there would be a high incidence of cerebral palsy, mental retardation and other pathologies leading to severe disability. Without the development of a specialized service that will help such children, we will inflict enormous damage on a society that will not accept such an increase in the number of people with disabilities. Then a follow-up system for premature babies began to develop, which leads them up to three years. Because in the usual polyclinic network there are not always doctors who understand how a child born with low or extremely low body weight grows and develops. In parallel with this, the system of medical rehabilitation is developing quite rapidly.
The worst situation is with the social service. Help for these children is minimal. Few people explain to families how to care for such a child, how to develop him, how to maintain motor skills. If in large cities at least some minuscule can be achieved, then what can we say about the province? All this turns one of the parents out of social life. There are no places where it would be possible to transfer such a child at least for a week, a month, so that the parents could have a little rest. Since the state has taken such a step, since we have legally recognized a 500-gram fetus as a person, then they themselves also need to act humanly in the future with his family.
Is there a support system in other countries?
I know that in Europe and in the USA it is built very well. The emphasis is not on medical rehabilitation, but on social rehabilitation. They have social workers who come and relieve these families of a significant part of their worries. Somewhere there are social centers where a child can be taken to a kindergarten. Moreover, they are zoned - parents do not need to go to the other end of the city.
Photo: Alexander Kondratyuk / RIA Novosti
“Even if it is clear that a child has pathologies that are incompatible with life, they must be saved to the last”
You say that some time ago, 1kg premature babies were also considered “non-residents”, but now they are quite promising. Is it possible that in 30-40 years the same can be said about 500-gram ones?
Indeed, even 30-40 years ago, when it was not possible to maintain breathing, children born before seven months of age survived very rarely.
Then, when some first mechanisms appeared, the bar was raised until the 28th week of pregnancy, which is about six months. But technological progress is always moving forward, and this has allowed us to further gradually reduce the age of survival. We can now at least partially simulate intrauterine conditions. For example, when a child is not born on time, he does not yet have a substance in his lungs, thanks to which he can breathe - surfactants. They can be introduced immediately at birth, start artificial ventilation of the lungs and thereby support gas exchange. It also became possible to give nutritional subsidies not through the gastrointestinal tract, but through a vein with special substances that are already ready for inclusion in metabolism. There are many other adaptations: the creation of a thermal regime, humidity close to intrauterine.
Technologically, the frontier could move indefinitely. If desired, you can simulate a situation where a woman is not needed at all to bear a child. But I have already said that scientists have established that the age of 22-23 weeks is the minimum period at which the cells of the cerebral cortex can develop postnatally. Still, the main criterion for the normal development of a child is not technological achievements, but the capabilities of the brain.
Is it true that they try to save all 500-gram children only in Russia and Turkey, and in other countries - only if the child has high chances for a normal life?
This is not true. In all countries where the WHO concept has been adopted, these children are subject to mandatory medical care. But there are nuances. If the baby was born between the 23rd and 25th weeks, parents can refuse resuscitation. To do this, in many countries there is a legal standard, reminiscent of the law on euthanasia.
There is a special service in perinatal centers. When it becomes clear that preterm labor has begun, representatives approach relatives - the father and, if possible, the mother. “We assume that a baby will be born with such and such parameters. In this case, there are such and such development risks ... You have the right to choose either full resuscitation or palliative care. And depending on what the parents decide, the doctors act.
Photo: Sergey Pyatakov / RIA Novosti
In Russia, you can also choose a palliative today, right?
This is not prescribed by law. Today, even if it is clear that a child has pathologies incompatible with life, they must be saved to the last. It happens that parents can sign a paper on their own that they would not like resuscitation, but this has no legal force. Parents can say, “Look, he is breathing, breathing. He opened his eyes. Let's revive him now!" And we lost time, which in this case is very important. This child initially has little chance, but it has become even less. And a situation may arise when parents accuse the doctors that their child was not specially treated, “talking teeth”.
The medical community is very concerned about this ambiguous position of doctors. And we have a number of proposals to solve the problem of their protection.
What exactly is offered?
Legislative initiative to allow parents to independently decide whether resuscitation care is appropriate for a child born between the 23rd and 25th weeks. Naturally, all this should be discussed. It is necessary to involve the public in the discussion: these are lawyers, doctors, patient communities, representatives of religious denominations.
The Ministry of Health has now prepared new criteria for newborns born too early. In particular, it is proposed not to register such a child until he has lived seven days. Maybe this will fix the situation, protect doctors from murder charges?
There are a lot of pitfalls here. In Russia, there was a similar law on kilogram children. They were assisted from birth, but until the age of seven days the child was considered a fetus. If he died, then his mortality already went into other criteria, it was not considered the death of a newborn.
There are not many children born with extremely low rates, they simply cannot influence the demographic structure in any way. But if there is such a situation that you can not register for up to seven days, it seems to me that even more claims may arise against doctors regarding the failure to provide assistance.
These are very difficult questions. On the one hand, parents can say: you did not save the child. And others, on the contrary, will say: why are you torturing him in vain? And imagine a resuscitator who may be faced with an ethical choice: he has only one ventilator in the hospital, and a 23-week-old baby has been on it for the 40th day. And then a 32-week-old is born in the hospital. He needs help, hold him for three days on the device, and then the baby will cope on his own. In the first case, there will certainly be a disabled person. And in the second - almost healthy. And what should a doctor do?
Are you speaking theoretically now or do such situations occur?
We cannot have this in federal centers. We have enough equipment. I just illustrated with an example that the issue of nursing such children is the most difficult, all aspects are in common in it - from medical to ethical and religious.
Photo: Sergei Krasnoukhov / RIA Novosti
“The issue of infant mortality has always been political”
The issue of infant mortality has recently become political. Perhaps that is why patient scandals associated with maternity hospitals are developing so sharply?
The issue of infant mortality has always been political. This is a socially significant parameter that determines the position of the country in terms of development. In our country as a whole, infant mortality has significantly decreased over ten years. However, in the last two years the rate of decline has slowed down. Our government says it's bad. From the point of view of doctors, this is not entirely true. There are objective reasons that cannot be overcome with a swoop.
The primary decrease in mortality occurred due to the high-quality saturation of hospitals with equipment, due to the construction of perinatal centers. This gave immediate results. And now these figures have reached a plateau. Another thing is that a plateau, for example, in Kaliningrad, St. Petersburg, is one thing. There mortality rates are at the European level. That is very low. And there are regions where mortality is high - the Altai Territory, the Jewish Autonomous Region, Magadan. There is a lack of doctors, a lack of equipment, very long distances, routing difficulties. And it's very difficult to do anything about it.
We are not compact Switzerland. We have a huge country with difficult geographical conditions. There are regions where we cannot even deliver a woman by helicopter. At one time I spent a lot of time in Chukotka, watching the obstetric service. Often, if a premature baby is born there, you will not help him in any way.
There are no good hospitals there?
Everything is there, but in one city - in Anadyr. And if a woman gave birth in another place, then often she can be cut off from the world. There are periods when even planes do not fly: a snowstorm, something else. And with routing too you will not guess. Because when you are expecting your first child, you are not going to give birth at 24 weeks. This is if the situation with childbirth repeats, then you can plan something, come closer to specialized care at the “dangerous” time . ..
Is it true that there have been more premature births lately?
No, their number is stable. This is approximately 7-10 percent of all newborns. Significantly increased their survival rate.
One of the most "inciting" topics on parenting Internet forums is that children who are "culled out" by nature have a bad effect on the quality of the gene pool. Is there any reason to think so?
In order for "survivors" to be able to influence the population, there must be a lot of them in percentage terms. For example, there are very few 26-week-olds - no more than two percent of all births. It can't affect anything in any way.
I know that at one time they discussed: what will happen if my child marries in the future someone who was once premature, will the gene pool suffer? Firstly, I can say that, as for children born after the 30th week, they are completely healthy, adapted and no different from others. They themselves give birth to beautiful healthy children, we have already seen many generations. The risk of preterm birth is not inherited. And usually premature babies are shaken, they are a lot of work. So in terms of development, these children can give odds to others.
As for children born at 5-6 months old, when they catch up with their peers, it is important that parents continue their active life with them, and not engage in a protective regime. We need songs, dances, sports. These children have behavioral patterns. But now there are centers that supervise such families. If you take care of children, everything will be fine. I look at these kids regularly. And I have a much more optimistic outlook. For example, the frequency of chronic diseases among them is approaching the norm. That is, it is not higher than in the population. Everyone has a chance for a full life, even the most hopeless, at first glance, child.
Miscarriage, how to avoid - Planning and management of pregnancy in the gynecology of the Literary Fund polyclinic after a miscarriage
- Gallery
- News
- Blog
- Reviews
- Jobs
- Licenses
- Insurance partners
- Controlling organizations
- What you need to know about coronavirus infection?
- Rules for patients
- Online doctor's consultation
- to corporative clients
- Documentation
A miscarriage is always associated with serious consequences for the whole body of a woman and for her reproductive organs in particular, it also affects the family situation, disrupts the woman's work schedule. An unfavorable outcome of pregnancy requires great mental and physical costs on the part of parents. Therefore, contacting doctors to find out the causes of the problem is the very first and correct step towards the birth of a child.
Any competent gynecologist will tell you that the problem of miscarriage can be solved. With proper preparation for pregnancy and its management, the next time you will have a successful pregnancy. Most girls after a miscarriage go to extremes: they try to get pregnant again as soon as possible. And if this succeeds, then the miscarriage is very often repeated. And you need to give the body a rest for 2-3 months, then identify and eliminate the cause. And only then try.
Causes of miscarriage
Many are convinced that miscarriages are due to a fall, injury, or some other physical shock. Any woman who has had a miscarriage can remember that not long before she either fell or lifted something heavy. And I am sure that she lost her unborn child precisely because of this. However, those women whose pregnancy was normal also fall and lift heavy things. Most sudden miscarriages do not occur for this reason. The reason is in violations of the pregnancy itself. Approximately half of miscarriages are due to abnormal genetic development of the fetus, which can be hereditary or accidental. Merciful nature, following the principles of natural selection in everything, destroys the defective and unviable fetus. But you should not be afraid of this. The fact that there is a defect in one embryo does not mean at all that all the others will be the same.
The woman's body is almost always to blame for the other half of miscarriages. They are caused by various known and unknown factors, such as: acute infectious diseases suffered in the first trimester of pregnancy, poor environment or difficult working conditions, excessive psychological or physical stress, abnormal development of the uterus, radiation, alcohol, smoking and certain types of drugs.
The causes of early and late miscarriage may differ, although they may overlap. The most important thing is to find out and eliminate or compensate for your own cause of miscarriage. Having discovered the cause, the gynecologist will tell you how to avoid another loss.
Miscarriage
Miscarriage statistics also include “missed pregnancy”. Sometimes it happens that the embryo dies and lingers in the uterine cavity. Most often, this fact is detected by ultrasound. The dead fetus may begin to decompose, and this, thereby, will lead to poisoning of the mother's body.
Doctors resort to surgical curettage, which is associated with a risk of inflammation and complications. With such a miscarriage, the next pregnancy is planned after the body is fully restored - not earlier than a year. During this year, you will have to find out the cause of the missed pregnancy and treat it.
Miscarriage up to 6 weeks
The main causes of miscarriage on this line are malformations of the embryo itself. Statistics say that from 70-90% of embryos had chromosomal abnormalities: they are random and will not occur in other pregnancies. You may have been ill, taken medication, or were under the influence of other harmful factors. Fate saved you from a child with malformations.
The human body is perfect and finds a way to correct the situation by miscarriage. Today is a tragedy for you. The real tragedy would be the preservation and birth of a sick, non-viable child. So don’t cry and understand: everything is for the best, you won’t help grief with tears ... And after three months, try again - it will almost certainly turn out to be successful.
It should also be noted that the fact of a miscarriage does not mean that you have lost something. So for a period of 7-8 weeks, the absence of an embryo in the fetal egg is found - "anembryony". It is believed that in 80-90% of cases, miscarriages are undiagnosed non-developing pregnancies.
Miscarriage between 6 and 12 weeks
Miscarriage in this period is also considered early. Its most common causes are:
Endocrine disorders
Endocrine disorders, when the ovaries do not synthesize enough hormones to keep the fetus in the womb, or the amount of male sex hormones is increased, is one of the most common causes of miscarriage and miscarriage.
Hormone imbalance in a woman's body is likely to lead to an early termination of pregnancy. With a lack of the main hormone progesterone produced by the ovaries, this happens most often. Another hormonal problem is an increase in the tone of the uterus, which provokes the expulsion of the fetus.
Progesterone prepares the uterine mucosa for implantation and is the hormone for maintaining pregnancy in the first months. If conception occurs, the fetus cannot properly establish itself in the uterus. As a result, the fertilized egg is rejected. But pregnancy can be saved with the help of progesterone preparations if this problem is detected in time.
An excess of male sex hormones that suppress the production of estrogens and progesterone can also be the cause of an early miscarriage. Often, the cause of recurrent miscarriages are androgens that affect the formation and development of pregnancy; as well as thyroid and adrenal hormones. Therefore, a change in the function of these glands can lead to miscarriage.
Undertreated sexual infections
This problem must be solved before conception. Often the cause of miscarriage is sexually transmitted infections: syphilis, trichomoniasis, toxoplasmosis, chlamydia, cytomegalovirus and herpetic infections. Their effect on the fetus and the course of pregnancy is different for each woman and depends on the timing of infection, the activity of the microorganism, the degree of immune protection and the presence of other adverse factors. Depending on the situation, they can lead to the formation of fetal malformations, intrauterine infection, feto-placental insufficiency, early miscarriage or premature birth. Infection of the fetus and damage to the membrane of the fetus leads to miscarriage. To avoid this, infections should be treated before pregnancy. The use of therapy is possible during pregnancy as prescribed by a doctor.
Viral infections and other diseases
Any disease accompanied by intoxication and fever above 38 o C can lead to a miscarriage. Rubella, influenza and viral hepatitis occupy a leading position in this list. At a period of 4-10 weeks for pregnancy, ordinary tonsillitis can also become tragic, pneumonia carries a more serious risk. Pyelonephritis and appendicitis can cause early labor. When planning a pregnancy, it is imperative to undergo a medical examination in order to identify and treat foci of infections.
Extremely dangerous during pregnancy rubella - it leads to severe fetal malformations, so infection during pregnancy is an indication for medical abortion.
Any disease during pregnancy can lead to non-viability of the fetus. And the body, through a miscarriage, insures you against unwanted offspring. With such a miscarriage, the next pregnancy has every chance of going well.
Immune causes of miscarriage
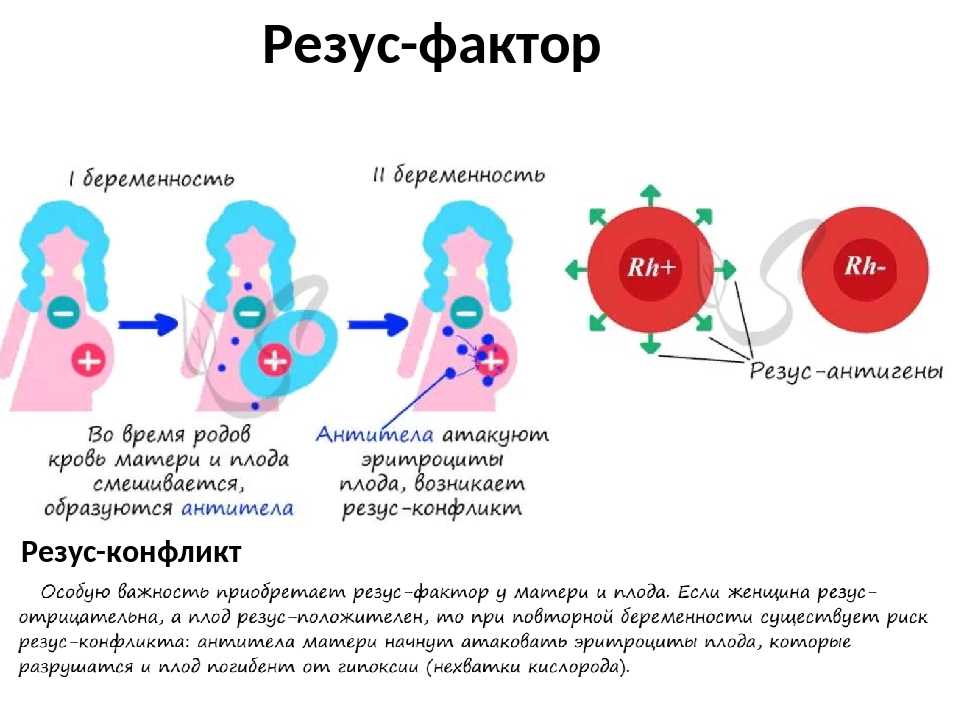
Sometimes antibodies that are hostile to the fetus are formed in the blood of a pregnant woman. This cause can be predicted and eliminated in advance. Most often, the conflict occurs when the embryo inherits the positive Rh factor of the father, and the negative Rh factor, the mother's body rejects the embryonic tissues that are alien to it. Constant monitoring of antibody titer and the introduction of anti-Rhesus immunoglobulins allows you to maintain and maintain pregnancy. In case of an immune conflict, progesterone preparations are also used to prevent miscarriage, which in this case has an immunomodulatory effect.
Reduced immunity
Reduced immunity during pregnancy also refers to immune causes. The body is simply not able to grow a new life in itself. You need to take care of yourself and recover before the next conception.
Anatomical causes of miscarriage
Anatomical causes of miscarriage are the most intractable. Malformations of the uterus are a serious reason for miscarriage. Sometimes you just have to deal with it.
Miscarriage between 12 and 22 weeks
Such a miscarriage is considered late. Its causes coincide with the causes of miscarriages in the early stages (anatomical, immune, infectious, endocrine).
At this time, a miscarriage also occurs due to isthmic-cervical insufficiency - a weak cervix cannot hold the fetus and opens. For this reason, a miscarriage can occur in the 2nd or 3rd trimester. Isthmic-cervical insufficiency is observed in 15.0-42.7% of women suffering from miscarriage. Careful monitoring of the pregnant woman allows you to identify the problem in time and make surgical correction of the cervix before the onset of childbirth.
In isthmic-cervical insufficiency, there is only one method of treatment - a mechanical narrowing of the cervical canal. To do this, the neck is either sewn up or a special ring is put on it. However, the latter method is less efficient, because the ring can easily slide off the neck, then it will no longer hold back the process of opening it.
After suturing, if necessary, it is possible to use antibiotics and drugs that normalize the microflora of the vagina. The treatment of the vagina and the control of the state of the seams are carried out daily for 5 days. Stitches are removed at 37-38 weeks and with premature onset of labor.
Isthmic-cervical insufficiency may be primary (for no apparent reason), may be the result of abortion or hormonal disorders (increased levels of androgens - male sex hormones or their precursors).
Miscarriage after 22 weeks
Such a loss is hard to forget. Obstetricians talk about premature birth after the 28th week of pregnancy. Traditionally, a child born after this period is considered viable. But medicine knows many cases when it was possible to save the life of earlier children.
We recommend that you be carefully examined for miscarriage, check the above factors. In addition to them, the cause of a miscarriage can be antiphospholipid syndrome, while the woman's body perceives the child as something alien and rejects it. This disease, like the others listed, can be corrected; you have a very real chance of bearing a child.
Miscarriages due to hemostasis disorders
All of the above causes account for only 30-40%. Up to 70% of miscarriages are caused by disorders in the blood coagulation system (hemostasis).
Disorders of the blood coagulation system leading to pregnancy loss can be divided into thrombophilic (increased clotting) and hemorrhagic (a tendency to bleed). Both of these extremes are dangerous to the fetus. Various disorders leading to the formation of small blood clots lead to the fact that the fetus loses sufficient blood supply, development is disturbed and the fetus is rejected.
The main hemorrhagic changes can manifest themselves even in childhood in the form of increased bleeding during cuts, extractions of teeth, the onset of menstruation. But sometimes they declare themselves only during pregnancy and are the cause of a miscarriage. Bleeding in the early stages and detachment of the chorion is difficult to stop.
You may not guess, but incomprehensible headaches, weakness, fatigue, temporary loss of smell or hearing may be symptoms of a blood clotting disorder.