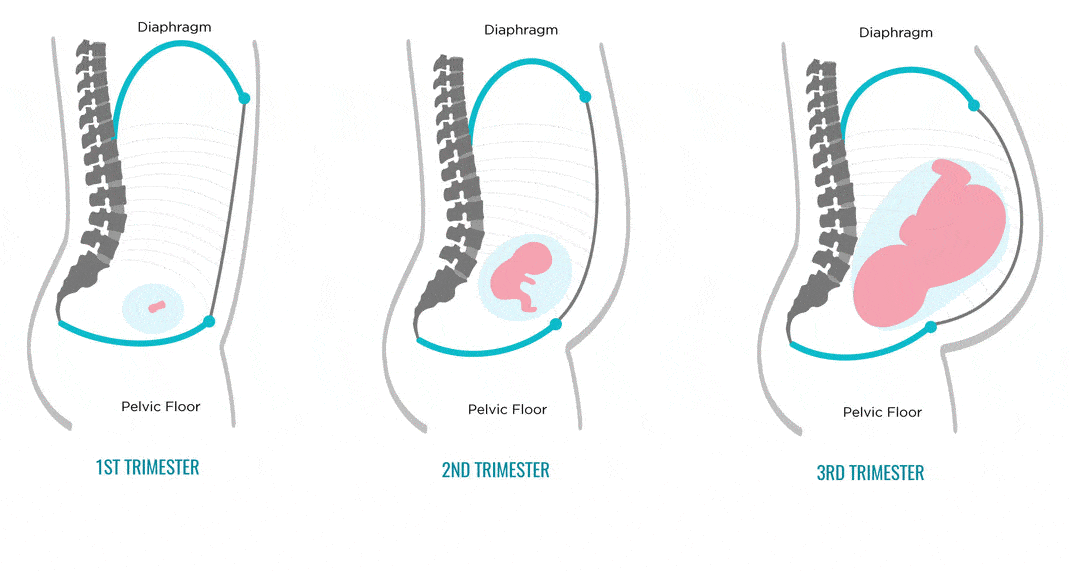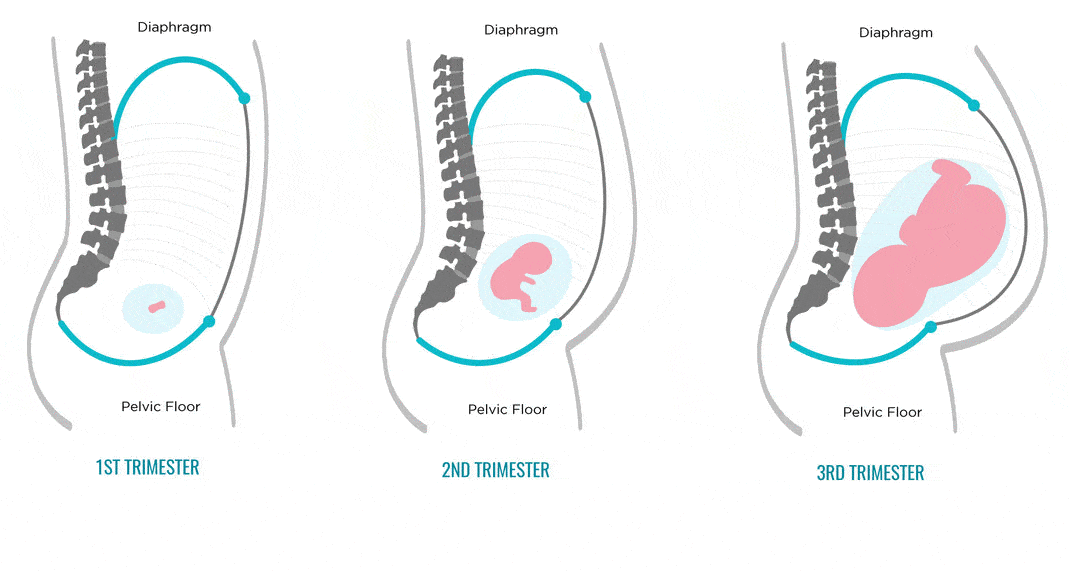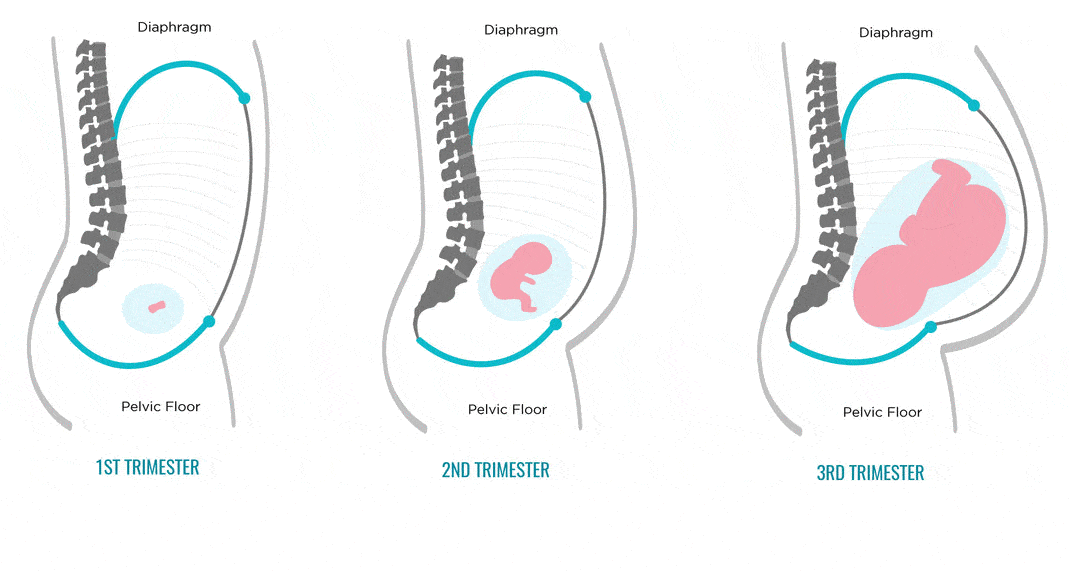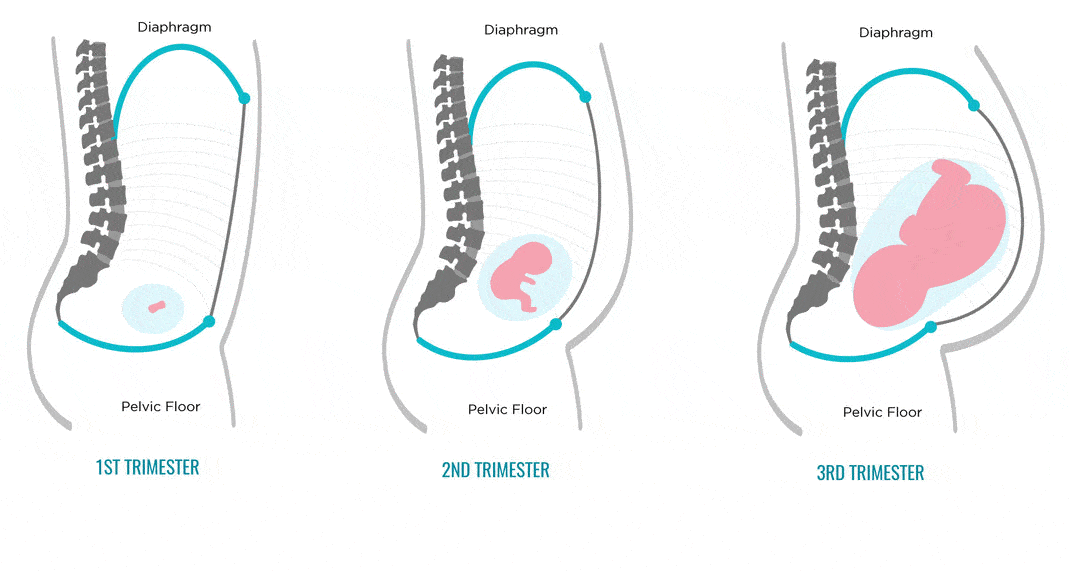
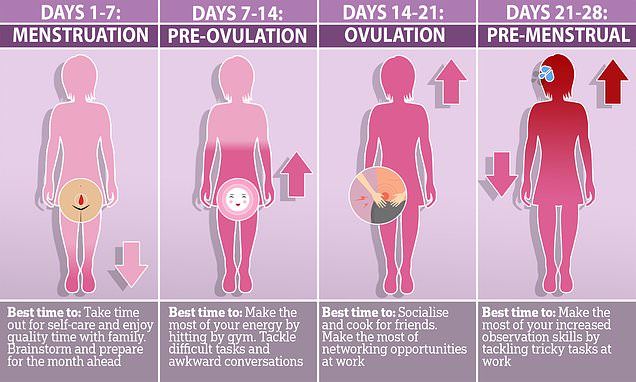
Average gestation period
Baby due date - Better Health Channel
Summary
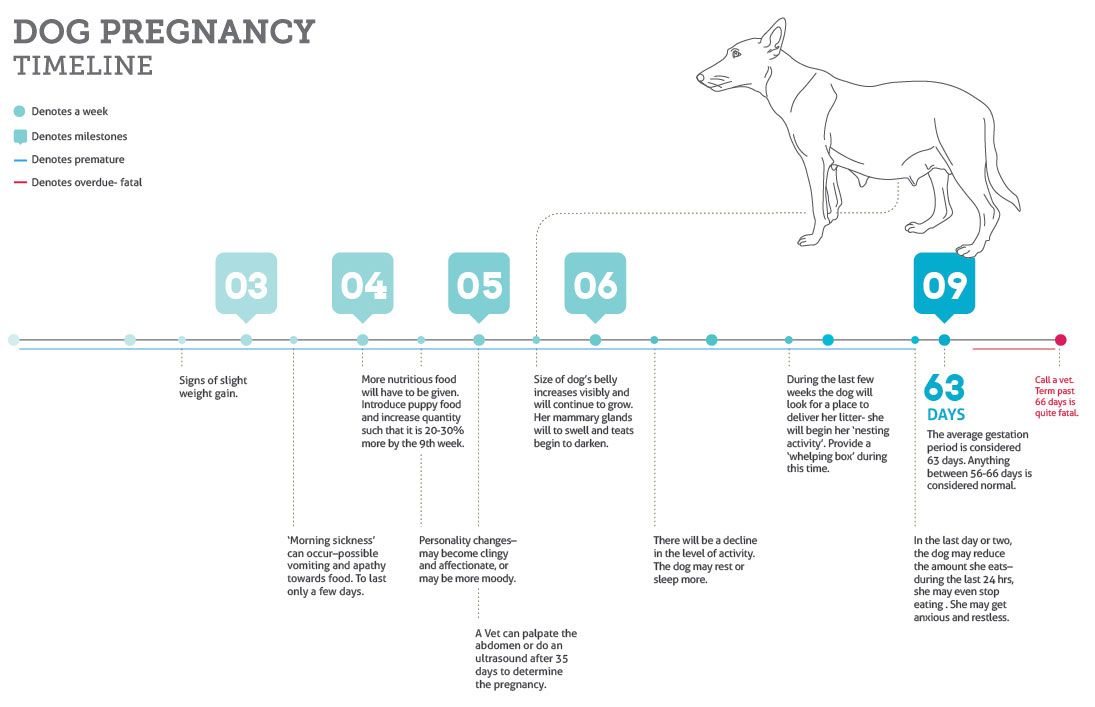
Read the full fact sheet- The unborn baby spends around 38 weeks in the uterus, but the average length of pregnancy, or gestation, is counted at 40 weeks.
- Pregnancy is counted from the first day of the woman’s last period, not the date of conception which generally occurs 2 weeks later.
- Since some women are unsure of the date of their last menstruation (perhaps due to period irregularities), a baby is considered full term if its birth falls between 37 to 42 weeks of the estimated last menstruation date.
The unborn baby spends around 37 weeks in the uterus (womb), but the average length of pregnancy, or gestation, is calculated as 40 weeks. This is because pregnancy is counted from the first day of the woman’s last period, not the date of conception which generally occurs 2 weeks later, followed by 5 to 7 days before it settles in the uterus.
Since some women are unsure of the date of their last menstruation (perhaps due to period irregularities), a pregnancy is considered full term if birth falls between 37 to 42 weeks of the estimated last menstruation date.
A baby born prior to week 37 is considered premature, while a baby that still hasn’t been born by week 42 is said to be overdue. In many cases, labour will be induced in the case of an overdue baby.
The average length of human gestation is 280 days, or 40 weeks, from the first day of the woman’s last menstrual period. The medical term for the due date is estimated date of confinement (EDC). However, only about 4 per cent of women actually give birth on their EDC.
There are many online pregnancy calculators (see Baby due date calculator) that can tell you when your baby is due, if you type in the date of the first day of your last period.
A simple method to calculate the due date is to add 7 days to the date of the first day of your last period, then add 9 months.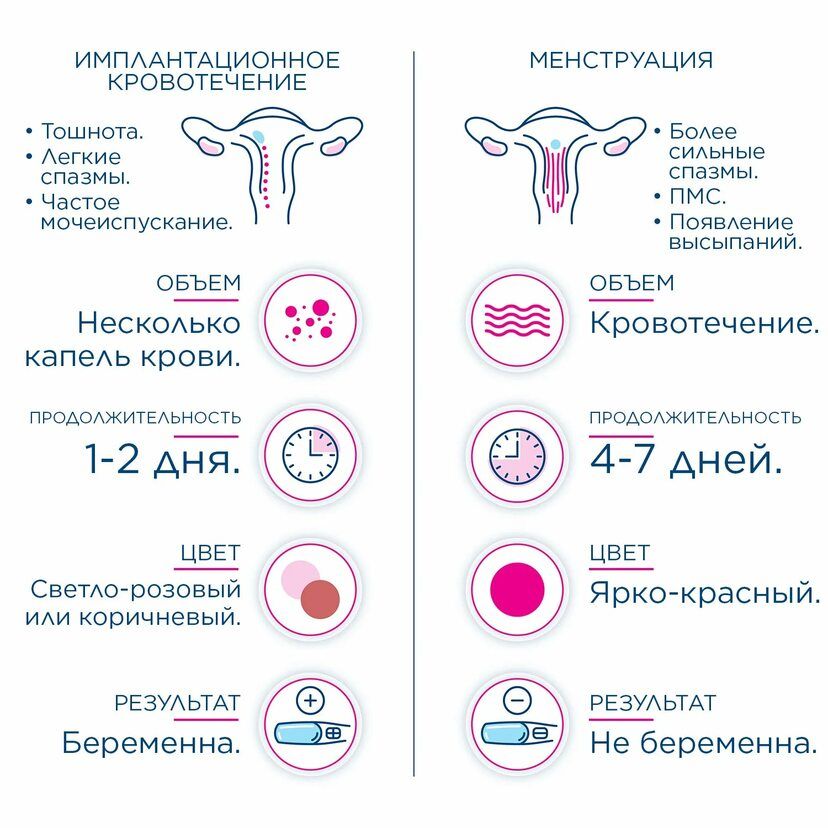 For example, if the first day of your last period was 1 February, add 7 days (8 February) then add 9 months, for a due date of 8 November.
For example, if the first day of your last period was 1 February, add 7 days (8 February) then add 9 months, for a due date of 8 November.
Determining baby due date
Irregular menstrual cycles can mean that some women aren’t sure of when they conceived. Some clues to the length of gestation include:
- Ultrasound examination (especially when performed between 6 and 12 weeks)
- Size of uterus on vaginal or abdominal examination
- The time fetal movements are first felt (an approximate guide only).
Pregnancy ultrasound
A pregnancy ultrasound is a non-invasive test that scans the unborn baby and the mother’s reproductive organs using high frequency sound waves.
The general procedure for a pregnancy ultrasound includes:
- The patient lies on a table.
- A small amount of a clear, conductive jelly is smeared on the abdomen.
- The operator places the small hand-held instrument called a transducer onto the abdomen.

- The transducer is moved across the abdomen. The sound waves bounce off internal structures (including the baby) and are transmitted back to the transducer. The sound waves are then translated into a two-dimensional picture on a monitor. The mother will not feel or hear the transmission of the sound waves.
- By measuring the baby’s body parts, such as head circumference and the length of long bones, the operator can estimate its gestational age.
The diagnostic uses of pregnancy ultrasound
Apart from helping to pinpoint the unborn baby’s due date, pregnancy ultrasounds are used to diagnose a number of conditions including:
- multiple fetuses
- health problems with the baby
- ectopic pregnancy (the embryo lodges in the fallopian tube instead of the uterus)
- Abnormalities of the placenta such as placenta previa, where the placenta is positioned over the neck of the womb (cervix)
- The health of the mother’s reproductive organs.
Premature babies
A baby born prior to week 37 is considered premature. The odds of survival depend on the baby’s degree of prematurity. The closer to term (estimated date of confinement, or EDC) the baby is born, the higher its chances of survival – after 34 weeks gestation with good paediatric care almost all babies will survive.
Premature babies are often afflicted by various health problems, caused by immature internal organs. Respiratory difficulties and an increased susceptibility to infection are common.
Often there is no known cause for a premature labour; however, some of the maternal risk factors may include:
- drinking alcohol or smoking during pregnancy
- low body weight prior to pregnancy
- inadequate weight gain during pregnancy
- no prenatal care
- emotional stress
- placenta problems such as placenta previa
- various diseases such as diabetes and congestive heart failure
- infections such as syphilis.

Overdue babies
Around 5 out of every 100 babies will be overdue, or more than 42 weeks gestation. If you have gone one week past your due date without any signs of impending labour, your doctor will want to closely monitor your condition.
Tests include:
- monitoring the fetal heart rate
- using a cardiotocograph machine
- performing ultrasound scans.
The placenta starts to deteriorate after 38 weeks or so, which means an overdue baby may not get enough oxygen. An overdue baby could also grow too large for vaginal delivery. Generally, an overdue baby will be induced once it is 2 weeks past its expected date.
Some of the methods of induction include:
- Vaginal prostaglandin gel - to help dilate the cervix.
- Amniotomy – breaking the waters, sometimes called an artificial rupture of membranes (ARM).
- Oxytocin – a synthetic form of this hormone is given intravenously to stimulate uterine contractions.
Where to get help
- Your GP (doctor)
- Obstetrician
- Midwife
- Your local maternal and child health service
- Common concerns and discomforts: overdue baby, Mother’s Bliss, UK.
- Going Overdue, Centre for Reproduction and Minimally Invasive Surgery.
- Premmie-L FAQ and advice sheets, Parents of Premature Babies Inc.(Preemie-L).
- Pregnancy: what to expect when it’s past your due date, Family Doctor, USA.
- Ultrasound, The Royal Women’s Hospital, Melbourne.
This page has been produced in consultation with and approved by:
Gestational age: MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia
URL of this page: //medlineplus.gov/ency/article/002367.htm
To use the sharing features on this page, please enable JavaScript.
Gestation is the period of time between conception and birth.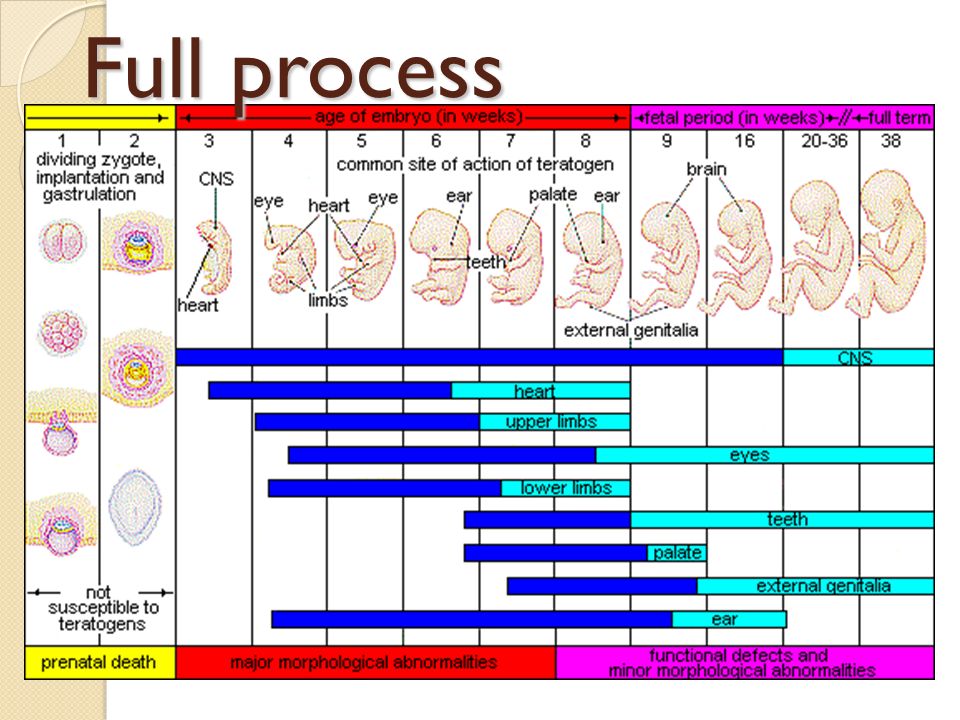 During this time, the baby grows and develops inside the mother's womb.
During this time, the baby grows and develops inside the mother's womb.
Gestational age is the common term used during pregnancy to describe how far along the pregnancy is. It is measured in weeks, from the first day of the woman's last menstrual cycle to the current date. A normal pregnancy can range from 38 to 42 weeks.
Infants born before 37 weeks are considered premature. Infants born after 42 weeks are considered postmature.
Gestational age can be determined before or after birth.
- Before birth, your health care provider will use ultrasound to measure the size of the baby's head, abdomen, and thigh bone. This provides a view on how well the baby is growing in the womb.
- After birth, gestational age can be measured by looking at the baby's weight, length, head circumference, vital signs, reflexes, muscle tone, posture, and the condition of the skin and hair.
If the baby's gestational age findings after birth match the calendar age, the baby is said to be appropriate for gestational age (AGA).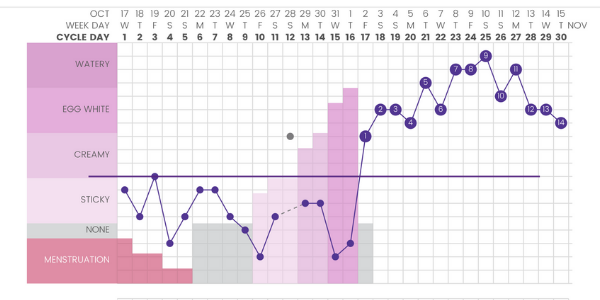 AGA babies have lower rates of problems and death than babies that are small or large for their gestational age.
AGA babies have lower rates of problems and death than babies that are small or large for their gestational age.
The weight for full-term infants that are born AGA will most often be between 2,500 grams (about 5.5 lbs or 2.5 kg) and 4,000 grams (about 8.75 lbs or 4 kg).
- Infants weighing less are considered small for gestational age (SGA).
- Infants weighing more are considered large for gestational age (LGA).
Fetal age - gestational age; Gestation; Neonatal gestational age; Newborn gestational age
Ball JW, Dains JE, Flynn JA, Solomon BS, Stewart RW. Growth and nutrition. In: Ball JW, Dains JE, Flynn JA, Solomon BS, Stewart RW, eds. Siedel's Guide to Physical Examination. 9th ed. St Louis, MO: Elsevier; 2019:chap 8.
Benson CB, Doubilet PM. Fetal measurements: normal and abnormal fetal growth and assessment of fetal well-being. In: Rumack CM, Levine D, eds. Diagnostic Ultrasound. 5th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2018:chap 42.
Graham GM, Park JS, Norwitz ER. Antepartum fetal assessment and therapy. In: Chestnut DH, Wong CA, Tsen LC, et al, eds. Chestnut's Obstetric Anesthesia: Principles and Practice. 6th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 6.
Goyal NK. The newborn infant. In: Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Blum NJ, Shah SS, Tasker RC, Wilson KM, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 21st ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 113.
Nock ML, Olicker AL. Tables of normal values. In: Martin RJ, Fanaroff AA, Walsh MC, eds. Fanaroff and Martin's Neonatal-Perinatal Medicine. 11th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:Appendix B, 2028-2066.
Walker VP. Newborn evaluation. In: Gleason CA, Juul SE, eds. Avery's Diseases of the Newborn. 10th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2018:chap 25.
Updated by: Neil K. Kaneshiro, MD, MHA, Clinical Professor of Pediatrics, University of Washington School of Medicine, Seattle, WA. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.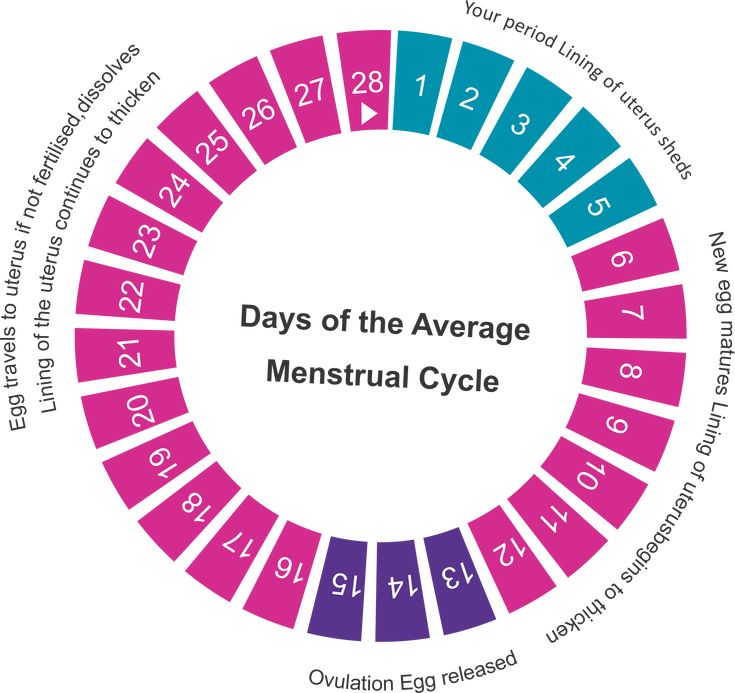 D.A.M. Editorial team.
D.A.M. Editorial team.
How long does pregnancy last: signs, terms and stages of fetal development
https://ria.ru/20210125/beremennost-1594527284.html
How long does pregnancy last: signs, terms and stages of fetal development
How long does pregnancy last: signs, terms and stages of fetal development - RIA Novosti, 01/25/2021
How long does pregnancy last: signs, terms and stages of fetal development
Pregnancy is the period when the formation and development of the fetus in the mother's body. About signs and duration - in the material of RIA Novosti. RIA Novosti, 01/25/2021
2021-01-25T18: 38
2021-01-25T18: 38
2021-01-25T18: 38
Health-Society
Pregnancy
Women
/HTML/Head/Meta [@name = Name = Name = Name = Name = Name = Name. 'og:title']/@content
/html/head/meta[@name='og:description']/@content
https://cdnn21.img.ria.ru/images/156254/97/
MOSCOW, January 25 - RIA Novosti.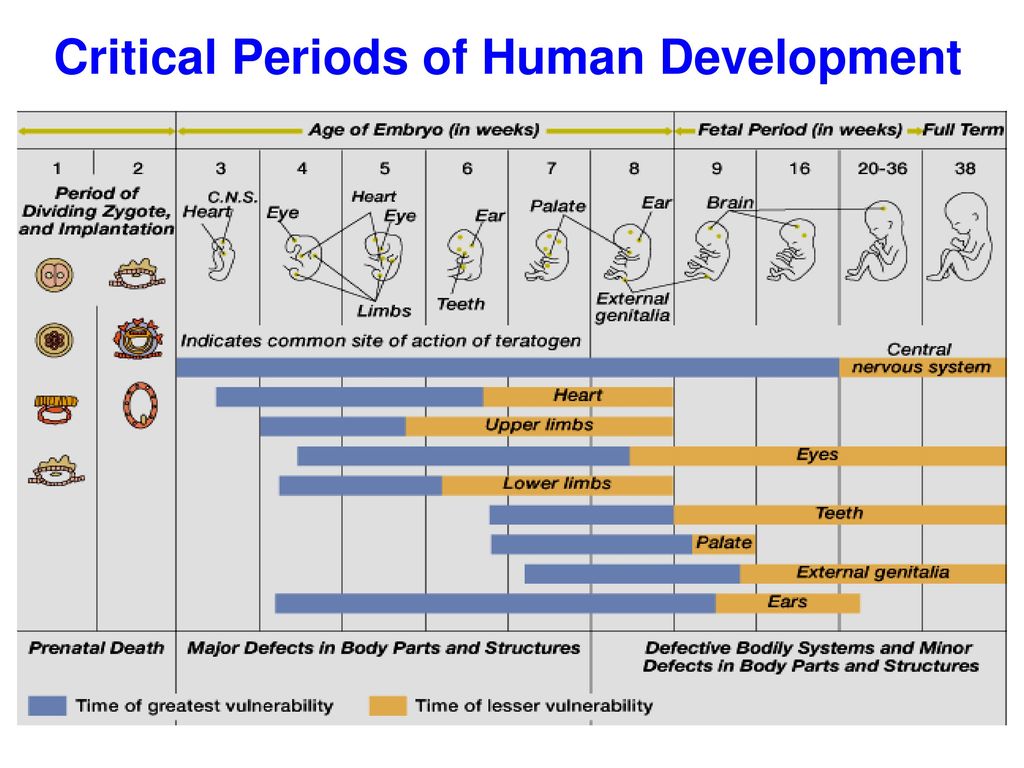 Pregnancy is a period when the formation and development of the fetus in the mother's body. About the signs and duration - in the material of RIA Novosti. Signs of pregnancy After conception, anatomical, physiological and hormonal changes occur in the body of a woman. There are a number of signals that may indicate pregnancy. Among the presumptive signs can be distinguished: - vomiting and nausea; - drowsiness; - aversion to certain smells; - frequent mood swings; - tearfulness; - dizziness. Also, a woman may experience frequent urination, an increase in the mammary glands. The most obvious indicator is the cessation of menstruation. Most often, pharmacy tests are used to determine pregnancy. Although they are reliable, they do not provide complete information. “A pregnancy test is one of the likely signs,” added Svetlana Ivanova. - He can tell that the patient is pregnant, but at the same time, he will not show whether this is a uterine or ectopic pregnancy. This can only be determined by ultrasound.
Pregnancy is a period when the formation and development of the fetus in the mother's body. About the signs and duration - in the material of RIA Novosti. Signs of pregnancy After conception, anatomical, physiological and hormonal changes occur in the body of a woman. There are a number of signals that may indicate pregnancy. Among the presumptive signs can be distinguished: - vomiting and nausea; - drowsiness; - aversion to certain smells; - frequent mood swings; - tearfulness; - dizziness. Also, a woman may experience frequent urination, an increase in the mammary glands. The most obvious indicator is the cessation of menstruation. Most often, pharmacy tests are used to determine pregnancy. Although they are reliable, they do not provide complete information. “A pregnancy test is one of the likely signs,” added Svetlana Ivanova. - He can tell that the patient is pregnant, but at the same time, he will not show whether this is a uterine or ectopic pregnancy. This can only be determined by ultrasound. ” How many weeks does a woman's pregnancy last? The expert answered the question about the pregnancy rate in weeks. According to her, pregnancy lasts 40 weeks, that is, ten obstetric months or nine calendar. Embryonic periodFrom the moment of fertilization, the embryonic period lasts until the tenth week of the obstetric period. At this time, the formation and development of the fetus in the mother's body begins. In particular, germ layers are formed in the embryo first, then tissues, organs and the placenta. During this period, the fetus increases to three centimeters, but it still does not resemble a baby, but only over time acquires the appropriate features. The fetal period The fetal period lasts from the 11th week of the obstetric period and ends with childbirth. At this time, the active growth of the fetus occurs, its proportions change, all organ systems begin to develop. In addition, the fetus begins to move in the womb. Physiological changes in the mother-fetus system Since the onset of pregnancy, two closely interconnected systems are formed.
” How many weeks does a woman's pregnancy last? The expert answered the question about the pregnancy rate in weeks. According to her, pregnancy lasts 40 weeks, that is, ten obstetric months or nine calendar. Embryonic periodFrom the moment of fertilization, the embryonic period lasts until the tenth week of the obstetric period. At this time, the formation and development of the fetus in the mother's body begins. In particular, germ layers are formed in the embryo first, then tissues, organs and the placenta. During this period, the fetus increases to three centimeters, but it still does not resemble a baby, but only over time acquires the appropriate features. The fetal period The fetal period lasts from the 11th week of the obstetric period and ends with childbirth. At this time, the active growth of the fetus occurs, its proportions change, all organ systems begin to develop. In addition, the fetus begins to move in the womb. Physiological changes in the mother-fetus system Since the onset of pregnancy, two closely interconnected systems are formed. Firstly, maternal, which provides the fetus with everything necessary, and, secondly, the functional system of the fetus. Significant changes take place in the mother's body. During pregnancy, a woman needs to receive vitamins, as the need for them increases. Therefore, the body needs one and a half times more zinc, iodine, vitamins B6 and B12. Lack of vitamins can affect the duration of pregnancy.
Firstly, maternal, which provides the fetus with everything necessary, and, secondly, the functional system of the fetus. Significant changes take place in the mother's body. During pregnancy, a woman needs to receive vitamins, as the need for them increases. Therefore, the body needs one and a half times more zinc, iodine, vitamins B6 and B12. Lack of vitamins can affect the duration of pregnancy.
2021
RIA Novosti
1
5
4.7
9000
7 495 645-6601
FSUE MIA "Today"
https: // xn- xn- -c1acbl2abdlkab1og.xn--p1ai/awards/
News
en-RU
https://ria.ru/docs/about/copyright.html
https://xn--c1acbl2abdlkab1og.xn--p1ai /
RIA Novosti
1
5
4.7
96
7 495 645-6601
FSUE MIA "Russia Today"
https: //xn--c1acbl2abdlkab1og.xn-p1ai/Awards/
1920 1920 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000
true
1920
1440
true
https://cdnn21.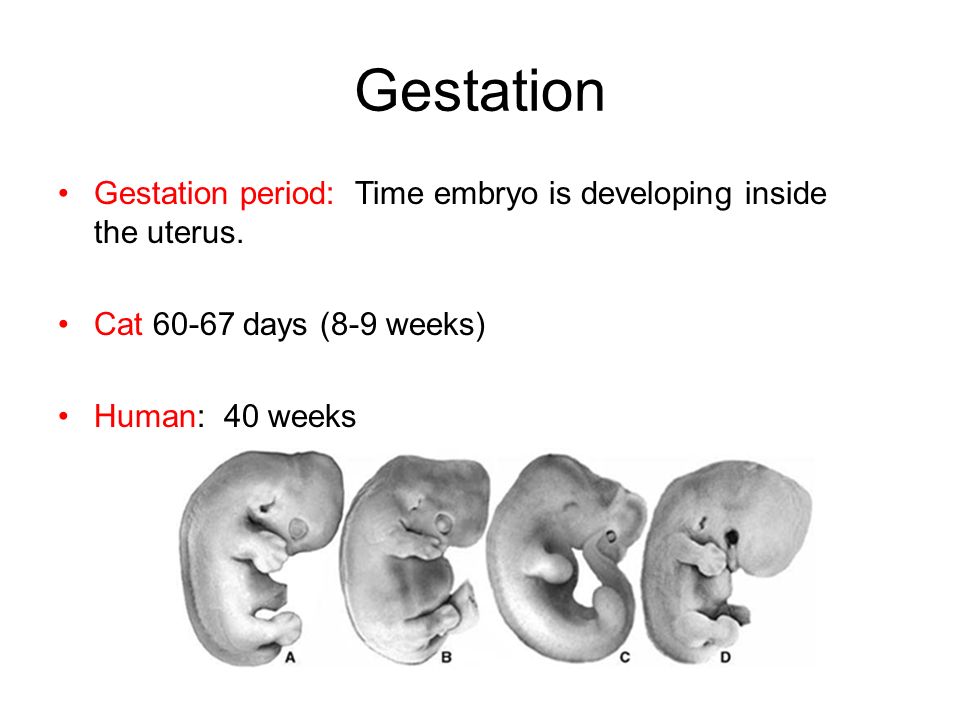 img.ria.ru/images/156254/97/1562549717_169:0:2900:2048_1920x0_80_0_0_15b447eb01248969392bfdc3b7477518.jpg
img.ria.ru/images/156254/97/1562549717_169:0:2900:2048_1920x0_80_0_0_15b447eb01248969392bfdc3b7477518.jpg
1920
1920
true
RIA Novosti
1
5
4.7
9000 9000
7 495 645-6601
FSUE MIA Russia Today
https: //xn--c1acbl2abdlkab1og.xn- P1AI/Awards/
RIA Novosti
1
5
4.7
9000
7 495 645-6601
FSUI MIA Russia Today
https :// xn--c1acbl2abdlkab1og.xn--p1ai/awards/
health - society, pregnancy, women
Health - society, pregnancy, women
MOSCOW, January 25 - RIA Novosti . Pregnancy is a period when the formation and development of the fetus in the mother's body. About signs and duration - in the material of RIA Novosti.
Signs of pregnancy
After conception, anatomical, physiological and hormonal changes occur in a woman's body. There are a number of signals that may indicate pregnancy. Among the presumptive signs can be identified:
Among the presumptive signs can be identified:
Pregnancy test: when and how to do it to get the right result
30 December 2020, 15:04
- vomiting and nausea;
- drowsiness;
- aversion to certain smells;
- frequent mood swings;
- tearfulness;
- dizziness.
Also, a woman may experience frequent urination, enlargement of the mammary glands. The most obvious indicator is the cessation of menstruation.
«
“Probable signs include an increase in the uterus,” Svetlana Ivanova, a teacher of obstetrics and gynecology of the highest category, told RIA Novosti. - When the doctor examines the patient, he can see the blueness of the vaginal cervix and the vagina itself. In general, the size of the uterus, shape and consistency changes.
Most often, pharmacy tests are used to determine pregnancy. Although they are reliable, they do not provide complete information.
“A pregnancy test is one of the likely signs,” added Svetlana Ivanova. - He can tell that the patient is pregnant, but at the same time, he will not show whether this is a uterine or ectopic pregnancy. This can only be determined by ultrasound.
- He can tell that the patient is pregnant, but at the same time, he will not show whether this is a uterine or ectopic pregnancy. This can only be determined by ultrasound.
The gynecologist named the ideal age for the birth of the first child
July 3, 2020, 02:53
How many weeks does a woman's pregnancy last
The expert answered the question about the pregnancy rate in weeks. According to her, the pregnancy lasts 40 weeks, that is, ten obstetric months or nine calendar months.
«
“In general, her term is 280 days, counting from the first day of the last menstruation,” added Svetlana Ivanova. - It is believed that timely delivery occurs from the 37th week to the 42nd. Childbirth before 37 weeks is considered premature, after the 42nd week - belated. Both are deviations from the norm.”
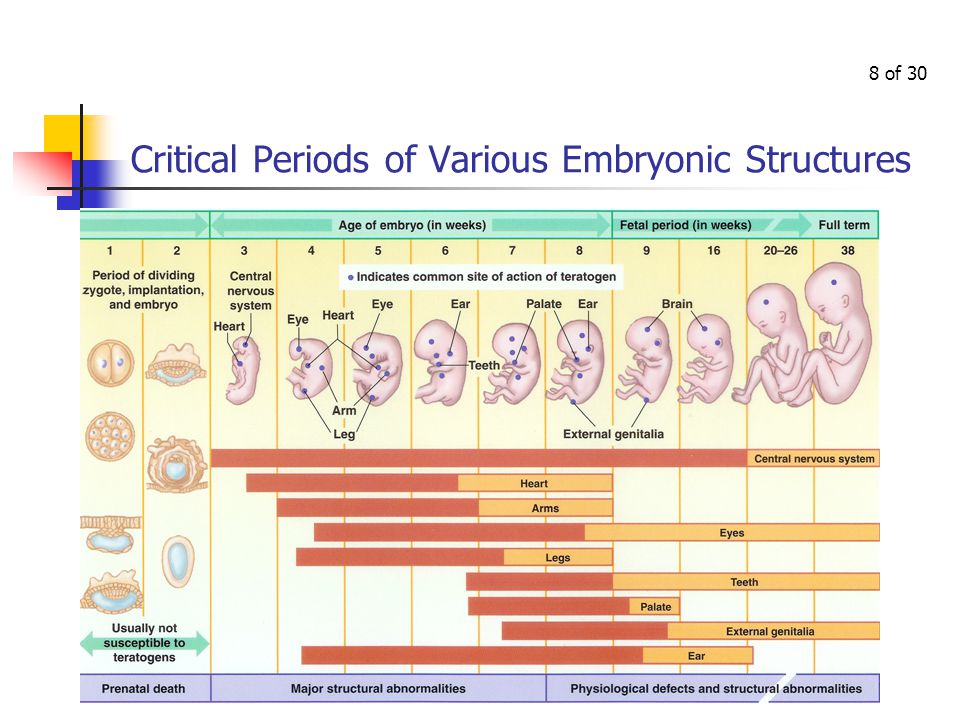
Embryonic period
From the moment of fertilization, the embryonic period lasts until the tenth week of the obstetric period. At this time, the formation and development of the fetus in the mother's body begins. In particular, germ layers are formed in the embryo first, then tissues, organs and the placenta. During this period, the fetus increases to three centimeters, but it still does not resemble a baby, but only over time acquires the appropriate features.
At this time, the formation and development of the fetus in the mother's body begins. In particular, germ layers are formed in the embryo first, then tissues, organs and the placenta. During this period, the fetus increases to three centimeters, but it still does not resemble a baby, but only over time acquires the appropriate features.
What you need to take with you to the maternity hospital for the child and mother: a list for 2021
January 19, 2021, 20:07
Fetal period
The fetal period starts from the 11th week of the obstetric period and ends with childbirth. At this time, the active growth of the fetus occurs, its proportions change, all organ systems begin to develop. In addition, the fetus begins to move in the womb.
Physiological changes in the mother-fetus system
Since the onset of pregnancy, two closely interconnected systems are formed. Firstly, maternal, which provides the fetus with everything necessary, and, secondly, the functional system of the fetus. Significant changes take place in the mother's body.
Significant changes take place in the mother's body.
«
“The level of progesterone, the main hormone responsible for gestation, increases, while estrogen decreases,” the expert explains. - They are responsible for the tone of the uterus. If there are too many hormones, a miscarriage may occur. During pregnancy, the heart, as well as the kidneys, work with increased stress. They excrete the urine of the mother and fetus. The thyroid and parathyroid glands increase in size, calcium production is disrupted, so pregnant women often experience brittle nails, hair loss, and teeth can crumble. Because of this, it is necessary to regularly check with the dentist for the presence of caries. This is a source of infection that can lead to infection of the fetus.”
During pregnancy, a woman needs to receive vitamins, as the need for them increases. Therefore, the body needs one and a half times more zinc, iodine, vitamins B6 and B12. Lack of vitamins can affect the duration of pregnancy.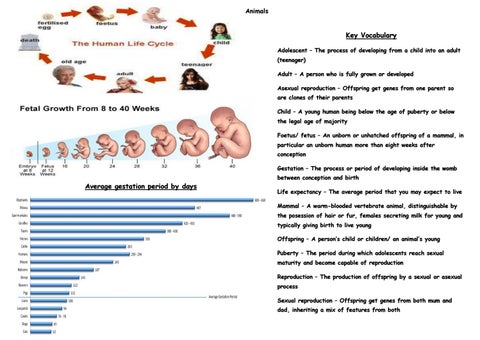
Instant large families. Family stories of quadruplets
September 26, 2020, 08:00
How long does a person's pregnancy last? | Blog
Several studies have been done on how many weeks a pregnancy lasts. The results of these studies were published in the journal Human Reproduction.
How does pregnancy begin?
The development of pregnancy in humans begins with the fertilization of a female egg by a male spermatozoon. Fertilization is possible after ovulation - the release of the egg from the ovary. Usually, ovulation occurs on the 10-16th day of the menstrual cycle (from the 1st day of the last menstruation), but can be significantly shifted. The life span of an egg is about a day, and that of a sperm cell is 3-5 days. After ovulation, the egg enters the fallopian tube, where it meets the sperm and fertilization occurs. Then, within 14 days, the fertilized egg moves into the uterus in order to implant (fix) in the uterine cavity and continue to develop.
How to calculate the due date and what affects how many weeks the pregnancy lasts?
Estimated due date is calculated by adding 280 days to the first day of your last menstrual period. However, the duration of pregnancy is influenced by the age of the mother, the time of implantation of the embryo, the weight of the mother herself at the time of birth. It was found that with every year of her life, a woman bears a child for 1 day longer. And for every “extra” 100 grams of weight at birth, we also add 1 day to the duration of pregnancy. During the study, it was also found that embryos require different times for implantation (fixation in the uterus). And those embryos that took longer to implant also require more time from implantation to birth. More precisely, the date of birth can be determined using ultrasound.
What is term pregnancy?
In obstetric practice, full-term, it is customary to consider pregnancy lasting from 37 to 42 weeks. Up to 37 weeks is a premature pregnancy, and the birth is premature, and after 42 weeks it is a post-term pregnancy, and the birth is late.
Are there methods for accurately determining the duration of pregnancy?
A team of researchers, in order to more accurately calculate the duration of pregnancy, determined the level of hormones in the urine of women who plan to conceive naturally, which made it possible to determine the time of ovulation and implantation of a fertilized egg. Thus, scientists found that the duration of pregnancy was no more than 268 days, that is, 38 weeks. And the duration of pregnancy itself can vary by 37 days. It was also found that previous and subsequent pregnancies lasted approximately the same length as the pregnancy that was investigated.
Based on the results of this study, it was found that there are currently few mechanisms in the world that allow you to accurately determine the date of birth and how long the pregnancy lasts. And giving the exact due date is not a good idea, because. this causes a woman’s extra anxiety if the birth does not occur on the specified date.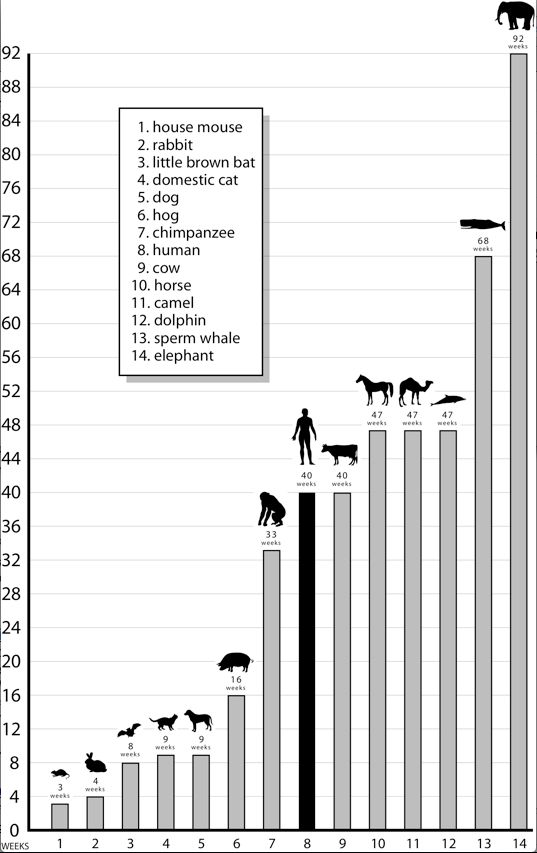 The poet, women should be told that you will give birth around this time.
The poet, women should be told that you will give birth around this time.
How often do women give birth on their due date?
It is statistically known that only 4% of women give birth on the expected date of delivery, and 70% within 10 days of the due date.
How is the estimated date of delivery determined at the Leleka Maternity Hospital?
In the Leleka Maternity Hospital, doctors use the first day of the last menstruation, to which we add 280 days, as well as the ultrasound diagnostic method to determine the expected date of birth. The most accurate time to determine the gestational age on an ultrasound scan is 11-13 weeks. During an ultrasound examination, the doctor will measure the coccyx-parietal size of the fetus, and using special tables, determine the gestational age to days and, accordingly, the expected date of birth. And, if the difference between the period calculated from the first day of the last menstruation and using ultrasound is less than 5 days, then we focus on the date according to the last menstruation, and if the difference is more than 5 days, then on the date that turned out during the ultrasound examination .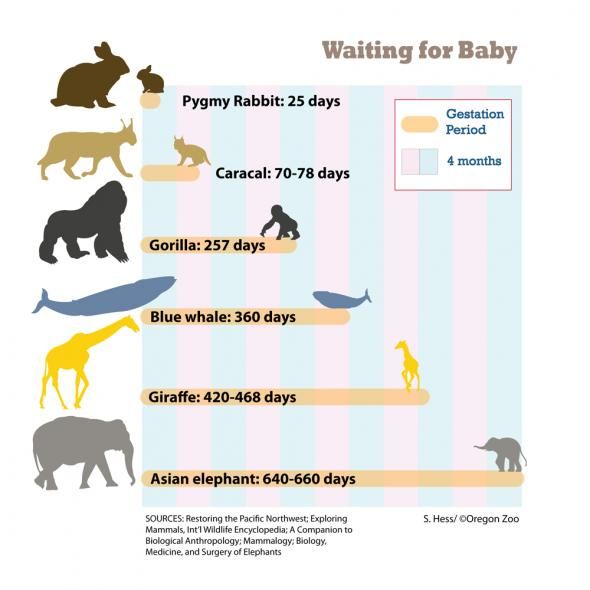
What to do if the expected date of delivery has come, but the birth has not happened?
If the date of delivery has come, but the birth does not occur, there is no need to panic. Come for a consultation with the doctors of the Leleka Maternity Hospital. During this consultation, the doctor will conduct a series of studies to make sure that everything is in order with the condition of the fetus and the pregnant woman. And will determine the date of induction of labor, if labor does not begin on its own. Experience shows that most women start giving birth before this date.
Remember that how many weeks a pregnancy lasts is a very individual value and can vary quite widely.
Pregnancy planning and childbirth are very important periods of life. The Leleka Maternity Hospital will provide informational and practical support. The institution provides professional obstetric-gynecological and non-anthological services that meet international standards. The company employs qualified narrow specialists who will provide support at all stages: from pregnancy planning, conception to postpartum rehabilitation.