Are nosebleeds common in pregnancy
What causes nosebleeds in pregnancy, and tips to manage them | Your Pregnancy Matters
Pregnant women are more likely to get nosebleeds due to increased blood volume, which may cause vessels in the nose to rupture.Pregnancy is full of quirky side effects – including nosebleeds. One in five patients get nosebleeds during pregnancy (epistaxis), compared with 6% of women who get them when not pregnant.
Over the course of pregnancy, your total blood volume doubles to support the growing baby. To accommodate this extra blood, the blood vessels in your body dilate. The pressure of the extra blood can sometimes cause the more fragile vessels to rupture and bleed more easily.
Your nose is rich in tiny blood vessels that can get dried out from normal breathing, which can lead to breakage and bleeding. For most pregnant patients, the occasional minor nosebleed is no cause for alarm. It’s mostly just annoying.
I've invited my colleague, Ashleigh Halderman, M.D., an ear, nose, and throat specialist from UT Southwestern's Otolaryngology Department, to talk about what causes nosebleeds during pregnancy, how women can prevent them, and how to stop them when they do occur.
Colds, medications, and unruly sinuses
Dr. Ashleigh HaldermanEven when you aren't pregnant, you're more likely to get a nosebleed with a cold, sinus infection, or allergies. But approximately 20% of women experience pregnancy rhinitis – inflammation and swelling of the mucous membranes in the nose.
Pregnancy rhinitis causes congestion, postnasal drip, and runny nose. And when you're constantly blowing your nose, you're more susceptible to having a bloody nose.
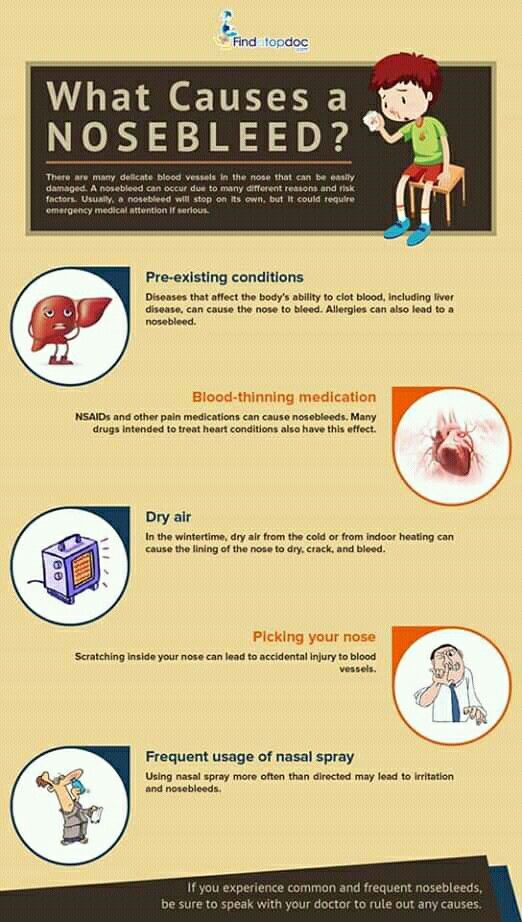
Certain medical conditions such as high blood pressure or clotting disorders can cause nosebleeds as well.
You may also get a nosebleed if the membranes in your nose dry out and crack due to cold weather, dry air, or intense air conditioning.
Pregnancy tumor: A rare cause of nosebleeds
Also known as a pyogenic granuloma, a pregnancy tumor is a noncancerous, rapidly growing mass of capillary blood vessels that bleeds easily. Research suggests the masses form due to the influx of hormones during pregnancy.
Approximately 5% of pregnant women develop pregnancy tumors, which typically form in the gums between the teeth but can also form in the nose. The masses can appear anywhere on the body and generally disappear after the baby is born.
Treatment usually consists of either a medicated gel or nasal spray, which helps control bleeding. Some women need to have the tumor removed if it is causing breathing problems or excessive nosebleeds. The exact procedure to remove the tumor depends on where the tumor is located. For pregnancy tumors of the nose, most can be removed endoscopically without any external incisions or stitches.
Related reading: 5 weird pregnancy symptoms you might not know about
How can I prevent nosebleeds during pregnancy?
While it’s not possible to prevent all nosebleeds, there are few things you can do to avoid irritating the sensitive blood vessels in your nose.
● Moisturize the inside of your nose: Use a bit of saline nasal gel to lubricate dry or irritated nasal passages.
● Use a humidifier: Because dry air increases the risk of nosebleeds, adding a little moisture to the air can do wonders.
● Drink plenty of fluids: This keeps your mucous membranes well hydrated and less likely to dry out and crack.
● Treat colds and allergies: Talk to your doctor about which over-the-counter medications may be best.
Be especially gentle after a nosebleed. Your nose needs to heal, so don’t blow it too hard or stuff tissues in the nostrils, which can prolong bleeding.
How to stop a nosebleed and when to see your doctor
If you do get a nosebleed during pregnancy (or any other time):
● Sit or stand up to keep your head higher than your heart
● Lean forward slightly to stop the blood from running down the back of your throat into your mouth
● Pinch both nostrils and maintain pressure for 10 to 15 minutes
● To help constrict the blood vessels and slow bleeding, you also can apply a cold pack or ice over the bridge of your nose or use a nasal spray such as Afrin before pinching the nostrils together
Call your health care provider if you experience more than a couple nosebleeds during pregnancy, or if:
● Bleeding doesn’t stop after 30 minutes
● Blood flow is heavy
● You have trouble breathing
● You become lightheaded or disoriented
Pregnancy can cause strange things to happen to your body. While nosebleeds generally are nothing to be overly concerned about, talk to your doctor if you are worried. We're always available to help you feel more comfortable during pregnancy.
While nosebleeds generally are nothing to be overly concerned about, talk to your doctor if you are worried. We're always available to help you feel more comfortable during pregnancy.
To visit with an Ob/Gyn, call 214-645-8300 or request an appointment online.
Nosebleeds during pregnancy | Pregnancy Birth and Baby
Nosebleeds during pregnancy | Pregnancy Birth and Baby beginning of content3-minute read
Listen
Nosebleeds during pregnancy are fairly common. Although they can be alarming, in most cases there's no need to worry and you should be able to treat a bleeding nose yourself.
Why are nosebleeds common during pregnancy?
During your first trimester the amount of blood circulating in your body increases and your heart works harder. This means that the lining of your nasal passage (inside your nose) also receives more blood. You have tiny blood vessels inside your nose so the increased blood volume can sometimes damage those blood vessels and cause them to burst, resulting in a nosebleed.
This means that the lining of your nasal passage (inside your nose) also receives more blood. You have tiny blood vessels inside your nose so the increased blood volume can sometimes damage those blood vessels and cause them to burst, resulting in a nosebleed.
Changes in your hormones during pregnancy can also contribute to nosebleeds.
These changes can make your nose feel congested (stuffy) and it might get more blocked up than usual. Your gums may also feel swollen and may bleed.
A nosebleed may last for a few seconds or a few minutes, and can flow from one or both nostrils. The blood flow can be light or quite heavy. If a nosebleed happens at night, while you’re sleeping, you may wake up feeling the blood going down the back of your throat before you sit up. It will then come out of your nose.
Are nosebleeds during pregnancy a cause for concern?
Nosebleeds can give you a fright or be a nuisance, but as long as you don’t lose a lot of blood, they are generally nothing to be worried about. In most cases, a nosebleed won’t harm you or your baby.
In most cases, a nosebleed won’t harm you or your baby.
How do I stop a nosebleed if I have one?
- Sitting or standing, keep your head upright. This reduces the pressure in the blood vessels inside your nose and will help to slow down the bleeding.
- Pinch the soft part of your nose, underneath the bony ridge, between your thumb and forefinger. Once you have done this, the two sides of your nose should be pressed together.
- Keep pinching, without releasing, for 10 minutes.
- If your nose is bleeding a lot, you may want to lean slightly forward and breathe through your mouth so the blood runs out of your nose, rather than down the back of your throat.
- Spit out any blood that is in your mouth.
- You may also want to suck an ice cube or put an icepack on the back of your neck or forehead, or the bony part of your nose.
- After 10 minutes, gently release your pinch to see if the bleeding has stopped.
- If your nose is still bleeding, try this procedure again for another 10 minutes.

How can I avoid a nose bleed?
If you are blowing your nose, do so gently and try to avoid large sneezes. You should also avoid picking your nose. You could be more likely to get nosebleeds in winter months when the air is dryer, so you may like to use a dehumidifier in your home to moisten the air.
If you’ve recently had a nosebleed:
- Sneeze with your mouth open.
- Try to avoid bending down or vigorously exercising for at least 12 hours afterwards.
- Avoid hitting your nose on anything.
When should I see a doctor?
Let your doctor know straight away if your nosebleed happens after bumping your head.
You should also contact your doctor if:
- you have high blood pressure
- you have taken the steps above and your nosebleed hasn’t stopped after 20 minutes
- you have trouble breathing through your mouth
- there seems to be a large amount of blood
- you are getting nosebleeds frequently
- you have swallowed a lot of blood and vomited
- you have a fever or chill
For more information, or to discuss any concerns you might have about nosebleeds, call Pregnancy, Birth and Baby on 1800 882 436.
Sources:
Healthy WA (Healthy WA - Nose bleeds), Mater Mothers Hospital (Pregnancy information for women and families), NHS Choices (Nosebleeds in pregnancy), Raising Children Network (15 weeks pregnant), St John Ambulance Australia (First aid tip: nosebleeds)Learn more here about the development and quality assurance of healthdirect content.
Last reviewed: June 2021
Back To Top
Need more information?
Nosebleeds - MyDr.com.au
What causes nosebleeds? How can I prevent them? What first aid measures can I use to stop a nosebleed? Find out here.
Read more on myDr website
Nosebleeds in children: what to do | Raising Children Network
Nosebleeds in children are very common. Nosebleed treatment starts with staying calm and applying pressure to the nose. Nosebleeds aren’t usually serious.
Nosebleed treatment starts with staying calm and applying pressure to the nose. Nosebleeds aren’t usually serious.
Read more on raisingchildren.net.au website
Nosebleeds - Better Health Channel
betterhealth.vic.gov.au
Read more on Better Health Channel website
Nose bleeds
Nose bleeds can occur when the blood vessels or the lining or the nose become damaged.
Read more on WA Health website
Pale skin: babies, children & teens | Raising Children Network
Pale skin is usually nothing to worry about. But you might sometimes need to see your doctor if your child’s skin looks pale. This article explains.
Read more on raisingchildren. net.au website
net.au website
Using your allergy nasal spray correctly - National Asthma Council Australia
Many people with asthma also use allergy nasal sprays for their hay fever. Using your nasal spray properly is important. With the right tech
Read more on National Asthma Council Australia website
Bruises & bruising in children & teens | Raising Children Network
If your child falls over or bumps himself, he might get bruises. Bruising is when blood vessels are damaged and bleed into the skin. First aid can help.
Read more on raisingchildren.net.au website
Pregnancy health problems & complications | Raising Children Network
Many pregnancy health problems are mild, but always call your doctor if you’re worried about symptoms. A healthy lifestyle can help you avoid health problems.
A healthy lifestyle can help you avoid health problems.
Read more on raisingchildren.net.au website
Childhood acute lymphoblastic leukaemia (ALL) - Leukaemia Foundation
Childhood acute lymphoblastic leukaemia (ALL) Listen What is childhood acute lymphoblastic leukaemia? Acute lymphoblastic leukaemia (ALL) is a type of cancer that affects immature lymphocytes developing in the bone marrow
Read more on Leukaemia Foundation website
Childhood acute myeloid leukaemia (AML) - Leukaemia Foundation
Childhood acute myeloid leukaemia (AML) Listen What is childhood AML? Acute myeloid leukaemia (AML) is a type of cancer that affects the blood and bone marrow
Read more on Leukaemia Foundation website
Disclaimer
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is not responsible for the content and advertising on the external website you are now entering.
Need further advice or guidance from our maternal child health nurses?
1800 882 436
Video call
- Contact us
- About us
- A-Z topics
- Symptom Checker
- Service Finder
- Linking to us
- Information partners
- Terms of use
- Privacy
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is funded by the Australian Government and operated by Healthdirect Australia.
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is provided on behalf of the Department of Health
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby’s information and advice are developed and managed within a rigorous clinical governance framework. This website is certified by the Health On The Net (HON) foundation, the standard for trustworthy health information.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
This information is for your general information and use only and is not intended to be used as medical advice and should not be used to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any medical condition, nor should it be used for therapeutic purposes.
The information is not a substitute for independent professional advice and should not be used as an alternative to professional health care. If you have a particular medical problem, please consult a healthcare professional.
Except as permitted under the Copyright Act 1968, this publication or any part of it may not be reproduced, altered, adapted, stored and/or distributed in any form or by any means without the prior written permission of Healthdirect Australia.
Support this browser is being discontinued for Pregnancy, Birth and Baby
Support for this browser is being discontinued for this site
- Internet Explorer 11 and lower
We currently support Microsoft Edge, Chrome, Firefox and Safari. For more information, please visit the links below:
For more information, please visit the links below:
- Chrome by Google
- Firefox by Mozilla
- Microsoft Edge
- Safari by Apple
You are welcome to continue browsing this site with this browser. Some features, tools or interaction may not work correctly.
reasons how to stop, is it dangerous?
Is nosebleed during pregnancy a cause for concern?
How to stop a nosebleed if it starts?
How to avoid nosebleeds?
Do I need to see a doctor?
Video
« I am pregnant and my nose bleeds all the time. Is it normal? »
Absolutely! And you are not alone. Nosebleeds affect one out of every five pregnant women and occur six times more frequently than non-pregnant women.
Of course you don't feel comfortable when this happens. But let me reassure you that in most cases, nosebleeds do not harm either your health or the health of your unborn child.
Why is nosebleed so common during pregnancy?
As usual, all the bad things that happen during pregnancy are due to hormones.
This is important to know!
As early as the first trimester of pregnancy, estrogen and progesterone levels rise and cause the tiny blood vessels inside the nose to dilate.
To provide both you and your baby with enough oxygen, the amount of blood circulating in the body increases and the heart works harder. All this together can sometimes damage the vessels of the nose and cause them to rupture, which leads to bleeding from the nose.
Is nosebleed during pregnancy a cause for concern?
In most cases, nosebleeds will not harm you or your baby.
Attention!
If the bleeding continues without stopping for more than 20 minutes or is very intense, it is a good idea to immediately go to the nearest medical facility where you will receive emergency treatment by stopping the bleeding with nasal packing or electrocoagulation.
How to stop a nosebleed if it has started?
- Sit comfortably and don't be nervous - stress raises blood pressure and can lengthen bleeding time.
- Keep your head upright - this will reduce the pressure in the blood vessels inside the nose and help slow down the bleeding. Do not tilt your head back - this can lead to blood entering the respiratory tract and coughing.
- Pinch the soft part of the nose under the bony part between the thumb and forefinger - both sides of the nose should be firmly pressed against each other.
- If the blood is coming out too hard and running down your throat so that you have to swallow it, lean forward a little - swallowed blood may cause vomiting.
- Have someone place an ice pack or frozen vegetables on the back of your head and hold it.
- After 10 minutes (you can set the timer on your phone), release the sides of your nose and check if there is still blood.
- If so, try pinching your nose again and wait another 10 minutes.
Note
If bleeding occurs frequently and you find it difficult to wait 20 minutes each time, you can purchase a hemostatic sponge from a pharmacy and use it. It is a combination of collagen, hemostatic and antimicrobial agents.
Contraindications for the use of a hemostatic sponge during pregnancy and lactation have not been identified.
How to avoid nosebleeds?
- Dry nasal mucosa makes nosebleeds more likely. Use a humidifier in your home, especially during the winter months.
- Avoid mucosal injury when picking or blowing your nose. Try to open your mouth when sneezing so that air does not forcefully escape through your nose.
- Immediately after the bleeding stops, refrain from vigorous physical exercise so that it does not reopen.
- Handle your nose carefully, avoid punching or even playful nose-pulling.
Do I need to see a doctor?
If the nose bleeds for the first time, this is desirable. The doctor will check your blood pressure and, if the bleeding was significant, may order blood tests - general and clotting.
The doctor will check your blood pressure and, if the bleeding was significant, may order blood tests - general and clotting.
Seek medical attention if subsequent nosebleeds occur:
- your blood pressure is higher than usual;
- you are taking blood thinners;
- the bleeding was very difficult to stop;
- bleeding occurred after a blow to the head, not even a very strong one;
- after bleeding you have difficulty breathing, you feel dizzy or very pale;
- you think your nose might be broken.
If a medical examination has ruled out all serious causes of nosebleeds, but they continue to haunt you, use our advice and just try to wait out the bleeding like bad weather.
videos
Photo: © Depositphotos
* The information provided cannot be used for self-diagnosis, treatment determination and does not replace a visit to a doctor!
Heading Pregnancy
Important: experts told how and when it is best to get vaccinated against COVID-19pregnant women
Hypoplasia of the uterus: is pregnancy possible? 30 years old - you should have listened to your mother. .. child with a choice of profession? Safe Internet for a child Bulling at school: how to protect a child? Infectionist about vaccinations Gynecologist about COCs and not only Game: collect a first aid kit for a child First aid for SARS How not to spend autumn on sick leave?0005
.. child with a choice of profession? Safe Internet for a child Bulling at school: how to protect a child? Infectionist about vaccinations Gynecologist about COCs and not only Game: collect a first aid kit for a child First aid for SARS How not to spend autumn on sick leave?0005
Frequent nosebleeds: what are the causes and what to do?
Other related articles: otolaryngologist, therapist
-
"Sedentary" diseases
-
10 examinations
-
COVID-19
-
adenovirus infection
-
Adenoids
-
Angina
-
Anemia
-
Meniere's disease
-
Bronchitis
-
Bronchoscopy
-
Types of ELI tests
-
All about flu
-
Sinusitis
-
Nasal hemangioma
-
Hypertension
-
Flu and SARS
-
flu during pregnancy
-
Diarrhea (diarrhea)
-
Eustachitis
-
iron deficiency
-
Ear diseases
-
immunity to coronavirus
-
Nose curvature
-
Nosebleeds
-
Nosebleed
-
Laryngitis
-
Lungs after COVID
-
Treatment of adenoids
-
Lymphadenitis
-
ENT diseases in children
-
mastoiditis
-
Medical examinations
-
Uric acid
-
Runny nose
-
Nasal septum
-
Surveys in autumn
-
Complications after angina
-
Pneumonia
-
Defeat the Flu
-
Items in the nose
-
Taking antibiotics
-
Signs of COVID-19
-
Application of ozone
-
Washing lacunae
-
Rheumatism
-
Sinusitis
-
Vaccine testing
-
Tonsillitis
-
Tuberculosis
-
Sulfur Plug Removal
-
Tick bite
-
Bed bug bites
-
Pharyngitis
-
ferritin
-
Chronic fatigue
-
nasal endoscopy
Bleeding from the nose due to trauma usually does not raise questions, but if it occurs without any mechanical impact, and even more often, this should alert
What can be the causes of frequent nosebleeds and how they can be cured - tells otorhinolaryngologist of the clinic "Semeynaya" Olga Pavlovna Soloshenko.
If the bleeding does not occur from trauma and recurs periodically, it is better not to delay the visit to the ENT. After all, bleeding can be anterior and posterior - the second happens less often, but it is much more dangerous. With anterior bleeding, blood only goes out, with posterior bleeding, it flows into the mouth or stomach along the back of the pharynx. Posterior is usually caused by damage to larger vessels that are located deep in the nasal cavity. It is very difficult to stop back bleeding without a doctor.
Causes of nosebleeds:
- Injuries. Injury to the nose is often fraught with cartilage fractures. As a rule, this is accompanied by swelling and pain.
- High blood pressure. Very common cause. Due to a sharp jump, the walls of the capillaries easily burst. Pressure rises due to overload, as well as in the presence of diseases of the cardiovascular system.
- Sunstroke and any sudden increase in body temperature.

- Overwork.
- Hormonal changes. Bleeding may occur in women during the months of pregnancy or menopause, and in adolescents at puberty.
- Dry air. It causes dryness of the mucous membranes.
- Poor blood clotting.
- ENT diseases. Sinusitis, sinusitis, rhinitis - all of them can cause bleeding, especially with the constant use of drugs that thin the mucous membrane.
- Vascular problems. Even infectious diseases such as chickenpox, measles, influenza, etc. can lead to them.
- Polyps, adenoids, tumors. In addition to periodic bleeding, they simply make breathing difficult.
- Foreign body - can damage the mucous membranes and blood vessels.
- Deficiency of vitamins K, C and calcium.
First aid rules for nosebleeds:
- Lie down (or position the patient) with legs down
- Tilt your head forward
- Place a cold compress on the bridge of the nose for a few minutes
- Cover nose with hand or insert swab pre-moistened with hydrogen peroxide
- Drops for vasoconstriction can be instilled
Attention, this must not be done!
- Throwing the head back (contrary to popular belief) - blood can enter the respiratory tract
- Blow your nose - so as not to increase the bleeding.

Which cases require an immediate call to a doctor and an ambulance
- In case of loss of consciousness
- For excessive bleeding
- Blood flows with clear fluid (this may occur after trauma and indicate a skull fracture)
- If you vomit blood (possibly indicating bleeding in the esophagus or stomach)
- Foamy blood (possible with lung injury)
- In a patient with diabetes mellitus
- If the patient is known to have poor blood clotting
Treatment
Treatment of bleeding is carried out in a complex manner. Often, an otorhinolaryngologist works in conjunction with a general practitioner, neurologist, endocrinologist, and hematologist.
At the first examination, the doctor determines the type of bleeding - anterior or posterior. Also, the patient is required to pass a general blood test and a coagulogram (analysis of blood coagulation indicators). In addition, it is important to measure the pressure, because if it is above the norm (the absolute norm is 120/80 mm Hg, but these figures change depending on age), the blood will not stop until it decreases.
In case of significant blood loss, the patient may be left in the hospital.
As a treatment for bleeding, it is possible to pack the nasal cavity, cauterize vessels (with drugs, laser, ultrasound, etc.), remove polyps. If there is no result, surgical ligation of vessels in problem areas is performed. In addition, drugs are prescribed that increase blood clotting.
Prophylaxis
- Taking drugs that strengthen the walls of blood vessels
- Nutrition rich in vitamins and minerals
- Air humidification during the heating season
- Injury Prevention
- Monitoring blood pressure and taking medications to lower it
Nosebleeds are not only unpleasant, but also dangerous. Therefore, as soon as it begins to bother you regularly, it is important to see a doctor as soon as possible. It is better to exclude all the most terrible causes of such a phenomenon as soon as possible and then it is already calmer to engage in further treatment.