Apgar for newborns
What Is the Apgar Score? (for Parents)
What Is the Apgar Score?
The Apgar score is a test given to newborns soon after birth. This test checks a baby's heart rate, muscle tone, and other signs to see if extra medical care or emergency care is needed.
Babies usually get the test twice: 1 minute after birth, and again 5 minutes after they're born. If there are concerns, a baby may get the test again.
What Does It Check?
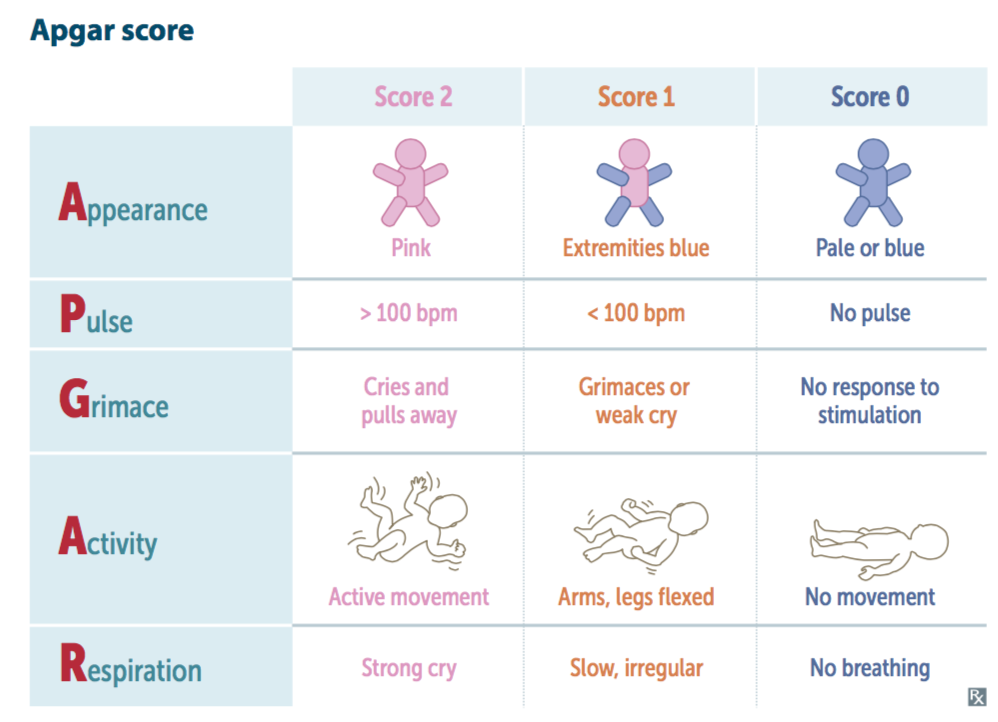
The Apgar score measures five things to check a baby's health. Each is scored on a scale of 0 to 2, with 2 being the best score:
- Appearance (skin color)
- Pulse (heart rate)
- Grimace response (reflexes)
- Activity (muscle tone)
- Respiration (breathing rate and effort)
Doctors, midwives, or nurses add up these five factors for the Apgar score. Scores are between 10 and 0. Ten is the highest score possible, but few babies get it. That's because most babies' hands and feet remain blue until they have warmed up.
| Apgar Sign | 2 | 1 | 0 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Appearance (skin color) | Normal color all over (hands and feet are pink) | Normal color (but hands and feet are bluish) | Bluish-gray or pale all over |
| Pulse (heart rate) | Normal (above 100 beats per minute) | Below 100 beats per minute | Absent (no pulse) |
| Grimace ("reflex irritability") | Pulls away, sneezes, coughs, or cries with stimulation | Facial movement only (grimace) with stimulation | Absent (no response to stimulation) |
| Activity (muscle tone) | Active, spontaneous movement | Arms and legs flexed with little movement | No movement, "floppy" tone |
| Respiration (breathing rate and effort) | Normal rate and effort, good cry | Slow or irregular breathing, weak cry | Absent (no breathing) |
What Does My Baby's Score Mean?
A baby who scores a 7 or above on the test is considered in good health.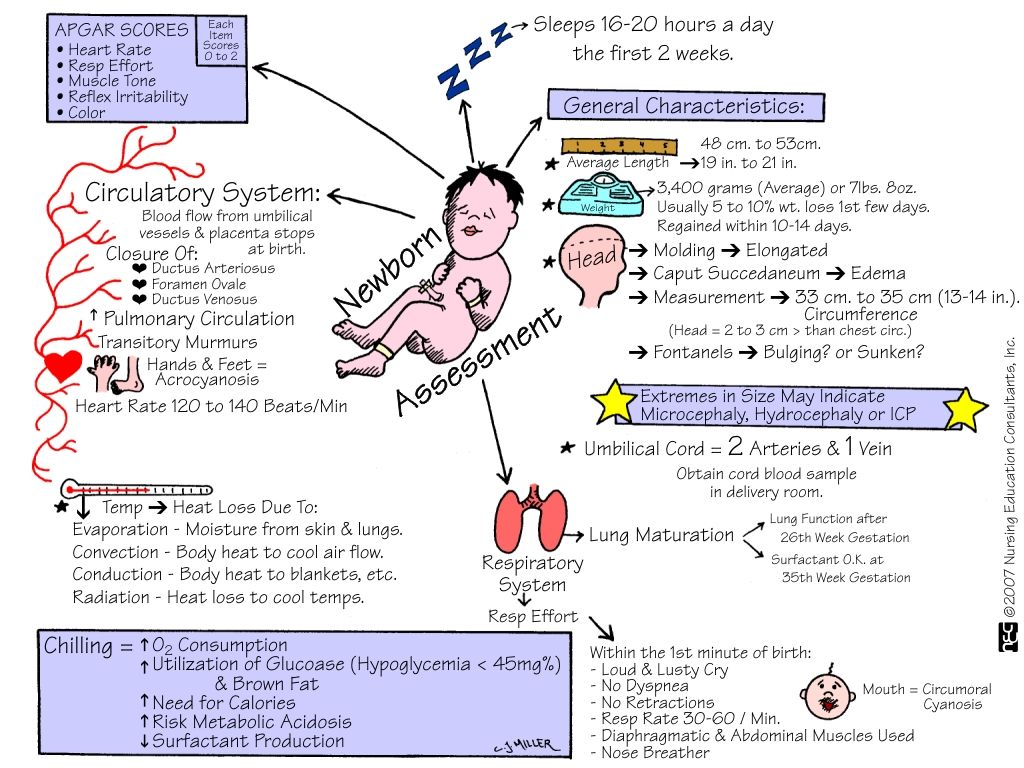 A lower score does not mean that your baby is unhealthy. It means that your baby may need some immediate medical care, such as suctioning of the airways or oxygen to help him or her breathe better. Perfectly healthy babies sometimes have a lower-than-usual score, especially in the first few minutes after birth.
A lower score does not mean that your baby is unhealthy. It means that your baby may need some immediate medical care, such as suctioning of the airways or oxygen to help him or her breathe better. Perfectly healthy babies sometimes have a lower-than-usual score, especially in the first few minutes after birth.
A slightly low score (especially at 1 minute) is common, especially in babies born:
- after a high-risk pregnancy
- through a C-section
- after a complicated labor and delivery
- early
At 5 minutes after birth, babies get the test again. If a baby's score was low at first and isn't better, or there are other concerns, the doctors and nurses will continue any needed medical care. They'll watch the baby closely.
What if My Baby Has a Low Score?
Many babies with low scores are healthy and do just fine after getting used to life outside the womb.
If your doctor or midwife is concerned about your baby's score, they'll let you know and will explain how your baby is doing, what might be causing problems (if any), and what care is being given.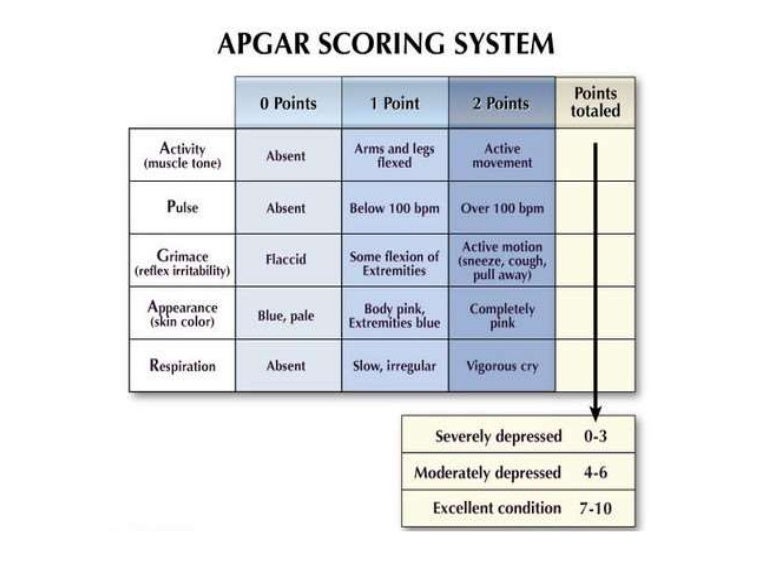
What Else Should I Know?
This test helps health care providers tell a newborn's overall physical condition so they can quickly decide if a baby needs medical care right away. It isn't meant to predict a baby's long-term health, behavior, intelligence, personality, or outcome.
With time to adjust to their new environment and with any needed medical care, most babies do very well.
Reviewed by: Mary L. Gavin, MD
Date reviewed: February 2018
Apgar score: MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia
URL of this page: //medlineplus.gov/ency/article/003402.htm
To use the sharing features on this page, please enable JavaScript.
Apgar is a quick test performed on a baby at 1 and 5 minutes after birth. The 1-minute score determines how well the baby tolerated the birthing process. The 5-minute score tells the health care provider how well the baby is doing outside the mother's womb.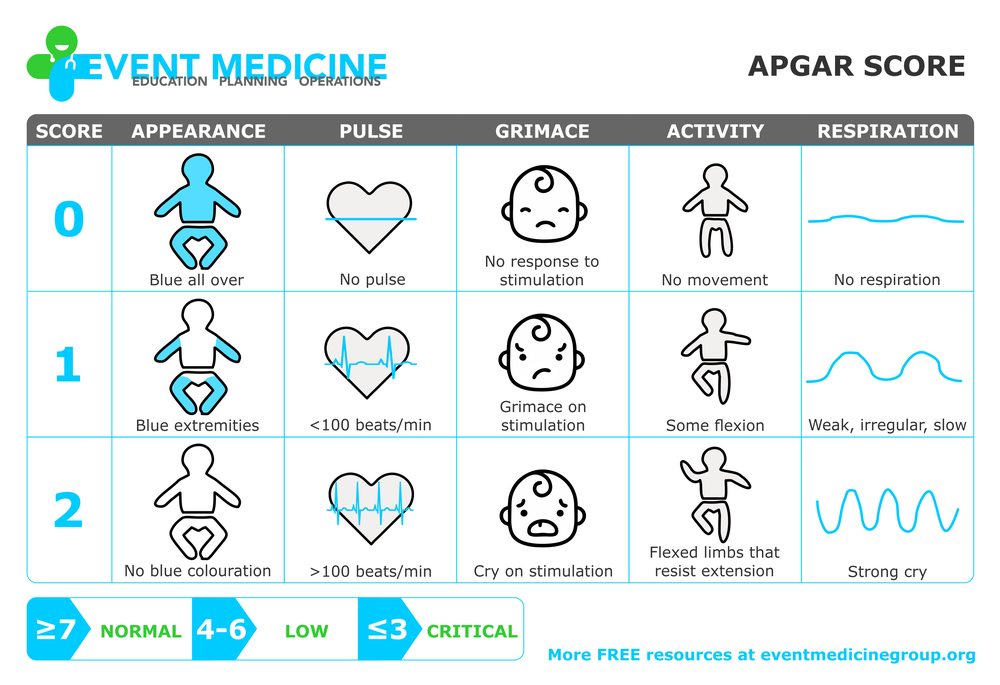
In rare cases, the test will be done 10 minutes after birth.
Virginia Apgar, MD (1909-1974) introduced the Apgar score in 1952.
The Apgar test is done by a doctor, midwife, or nurse. The provider examines the baby's:
- Breathing effort
- Heart rate
- Muscle tone
- Reflexes
- Skin color
Each category is scored with 0, 1, or 2, depending on the observed condition.
Breathing effort:
- If the infant is not breathing, the respiratory score is 0.
- If the respirations are slow or irregular, the infant scores 1 for respiratory effort.
- If the infant cries well, the respiratory score is 2.
Heart rate is evaluated by stethoscope. This is the most important assessment:
- If there is no heartbeat, the infant scores 0 for heart rate.
- If heart rate is less than 100 beats per minute, the infant scores 1 for heart rate.
- If heart rate is greater than 100 beats per minute, the infant scores 2 for heart rate.
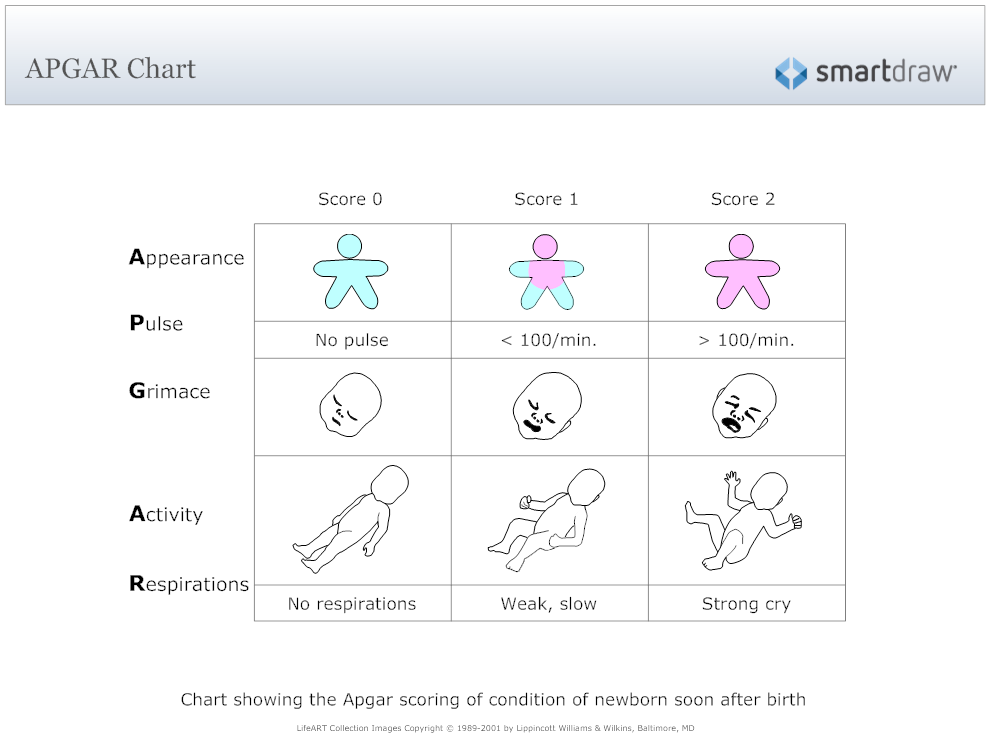
Muscle tone:
- If muscles are loose and floppy, the infant scores 0 for muscle tone.
- If there is some muscle tone, the infant scores 1.
- If there is active motion, the infant scores 2 for muscle tone.
Grimace response or reflex irritability is a term describing response to stimulation, such as a mild pinch:
- If there is no reaction, the infant scores 0 for reflex irritability.
- If there is grimacing, the infant scores 1 for reflex irritability.
- If there is grimacing and a cough, sneeze, or vigorous cry, the infant scores 2 for reflex irritability.
Skin color:
- If the skin color is pale blue, the infant scores 0 for color.
- If the body is pink and the extremities are blue, the infant scores 1 for color.
- If the entire body is pink, the infant scores 2 for color.
This test is done to determine whether a newborn needs help breathing or is having heart trouble.
The Apgar score is based on a total score of 1 to 10. The higher the score, the better the baby is doing after birth.
The higher the score, the better the baby is doing after birth.
A score of 7, 8, or 9 is normal and is a sign that the newborn is in good health. A score of 10 is very unusual, since almost all newborns lose 1 point for blue hands and feet, which is normal for after birth.
Any score lower than 7 is a sign that the baby needs medical attention. The lower the score, the more help the baby needs to adjust outside the mother's womb.
Most of the time a low Apgar score is caused by:
- Difficult birth
- C-section
- Fluid in the baby's airway
A baby with a low Apgar score may need:
- Oxygen and clearing out the airway to help with breathing
- Physical stimulation to get the heart beating at a healthy rate
Most of the time, a low score at 1 minute is near-normal by 5 minutes.
A lower Apgar score does not mean a child will have serious or long-term health problems. The Apgar score is not designed to predict the future health of the child.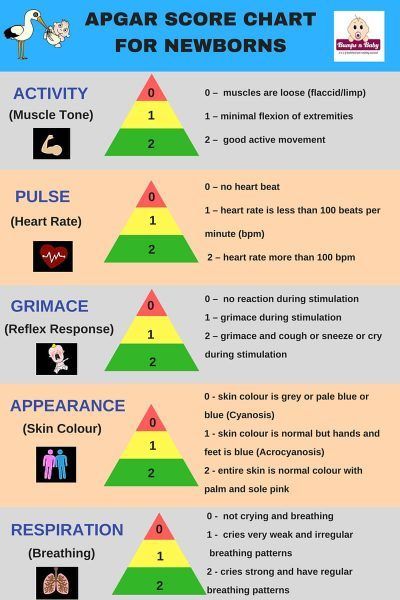
Newborn scoring; Delivery - Apgar
- Infant care following delivery
- Newborn test
Arulkumaran S. Fetal surveillance in labor. In: Arulkumaran SS, Robson MS, eds. Munro Kerr's Operative Obstetrics. 13th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 9.
Goyal NK. The newborn infant. In: Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Blum NJ, Shah SS, Tasker RC, Wilson KM, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 21st ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 113.
Updated by: Neil K. Kaneshiro, MD, MHA, Clinical Professor of Pediatrics, University of Washington School of Medicine, Seattle, WA. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
Apgar score
At each birth, the neonatologist tells the mother about the state of health of her baby at birth and necessarily talks about the grade with which her baby was born. This assessment is carried out on a special scale called Apgar. This scale has been used in obstetrics as a primary assessment of the condition of a newborn child since 1952. And today it is recognized as the simplest and most reliable method of comprehensively measuring the health status of an infant who has just been born. The Apgar scale helps to assess the physical condition of a newborn literally from the first minutes of life and, if necessary, provide him with high-quality medical care. The Apgar score is not a diagnosis. But this assessment allows the neonatologist to decide on the further routing of the baby: is it possible to combine him with his mother in the "Mother and Child" ward and standard care will be sufficient for him; perhaps the newborn needs to be placed in the ICU for intensive observation with the help of tracking equipment and additional examination and treatment, and perhaps the children's resuscitation team should be called with the subsequent evacuation of the newborn to a children's hospital or perinatal center.
This scale has been used in obstetrics as a primary assessment of the condition of a newborn child since 1952. And today it is recognized as the simplest and most reliable method of comprehensively measuring the health status of an infant who has just been born. The Apgar scale helps to assess the physical condition of a newborn literally from the first minutes of life and, if necessary, provide him with high-quality medical care. The Apgar score is not a diagnosis. But this assessment allows the neonatologist to decide on the further routing of the baby: is it possible to combine him with his mother in the "Mother and Child" ward and standard care will be sufficient for him; perhaps the newborn needs to be placed in the ICU for intensive observation with the help of tracking equipment and additional examination and treatment, and perhaps the children's resuscitation team should be called with the subsequent evacuation of the newborn to a children's hospital or perinatal center.
Neonatologists assess the condition of a newborn at the 1st and 5th, and if necessary, 10th minute of life after birth. The score is made up of the sum of the scores and the newborn's score at birth on the Apgar scale of 7-10 points is considered the norm. These points are made up of scores on 5 major indicators: heartbeat, breathing, muscle tone, skin color and reflexes.
The score is made up of the sum of the scores and the newborn's score at birth on the Apgar scale of 7-10 points is considered the norm. These points are made up of scores on 5 major indicators: heartbeat, breathing, muscle tone, skin color and reflexes.
1. If the baby's heart rate is 100 beats per minute or more, then he is given 2 points. With a heart rate of less than 100 beats per minute, the newborn is assessed by this criterion at 1 point.
2. Normally, at birth, a newborn baby should scream immediately and loudly, and the breathing criterion is estimated at 2 points. If the cry of the baby is weak and the breathing is uneven, the score is 1 point.
3. The third criterion is the assessment of the muscle tone of the newborn. The more rhythmic and clearer the baby's movements, the higher the score for this parameter. Active movements are worth 2 points. If the limbs are only slightly bent, and the movements are sluggish and rare, 1 point is given.
4. Normal skin color in a newborn is from pale to bright pink, which is estimated at 2 points. If the baby has cyanosis or pallor of the skin, then a score of 1 point is put.
Normal skin color in a newborn is from pale to bright pink, which is estimated at 2 points. If the baby has cyanosis or pallor of the skin, then a score of 1 point is put.
5. And the last fifth criterion is the assessment of reflexes. If the baby screams, grimaces, moves in every possible way, sneezes, then it definitely deserves 2 points. If the reflexes are sluggish, then a score of 1 point is given.
Assessment according to the Apgar score system for a newborn child, a neonatologist conducts in the delivery room immediately after birth on a heated neonatal table. The electronic system of the neonatal stage is automatically equipped with a timer that operates in three modes: clock, timer and Apgar. The results of the examination on the Apgar scale are necessarily entered in the history of the development of the newborn, in the discharge epicrisis and in the discharge from the maternity hospital.
Apgar score - articles from specialists of the clinic "Mother and Child"
first evaluation of the baby
As soon as the child is born, doctors immediately evaluate his condition and physical development. But not only weight and height are measured for the baby, there are other characteristics by which one can judge how healthy the child is. To do this, use a special scale proposed by the anesthesiologist Virginia Apgar and named after her.
But not only weight and height are measured for the baby, there are other characteristics by which one can judge how healthy the child is. To do this, use a special scale proposed by the anesthesiologist Virginia Apgar and named after her.
why
The Apgar score is used to determine which children need more attention. According to this scale, the health status of each newborn is assessed on five indicators: heart rate, respiration, muscle tone, reflexes and skin color of the baby.
The Apgar score, whether it be high or low, is not a diagnosis. This is a signal for the doctor about what measures are now needed or, conversely, the child does not need. Depending on the results of the assessment, an additional examination may be prescribed: blood tests, urine tests, a study for intrauterine infections, ultrasound, neurosonography. And after that, it is decided what to do next - to observe or treat the child.
how to test
During examination, each symptom (heart rate, respiration, muscle tone, reflexes, and skin color) is given 0, 1, or 2 points.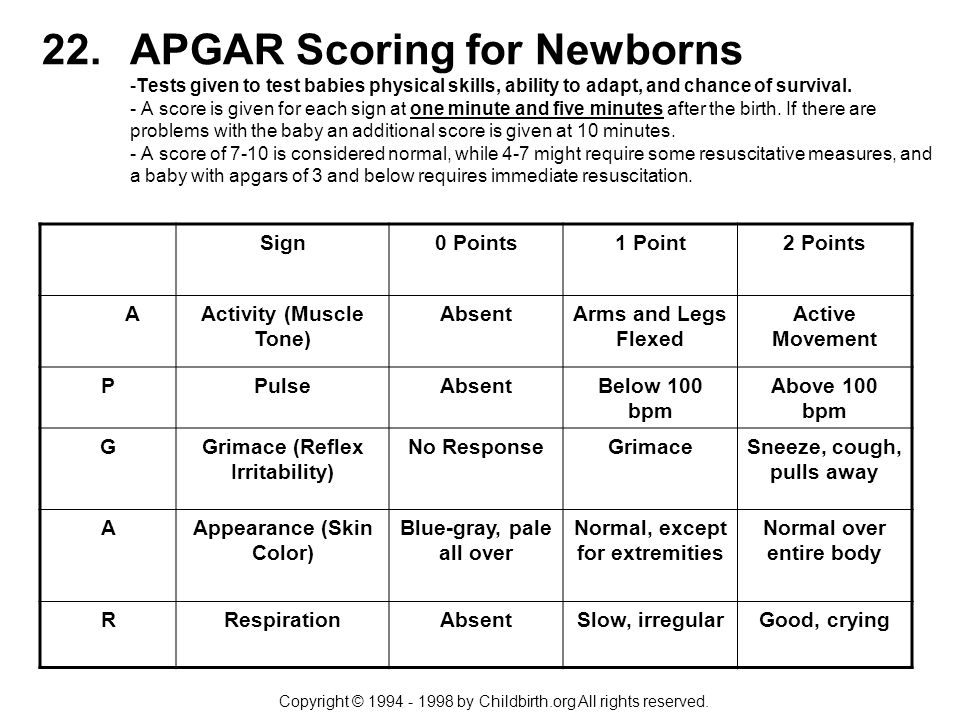 A score of 2 points in the delivery room is considered the highest and means that the sign is pronounced, 1 point - weakly expressed, 0 points - the sign is absent. The child is evaluated on the Apgar scale at the 1st and 5th minutes of life, so there are always two scores, for example, 8/9 points or 9/10 points. Children rarely score the maximum 10 points in the first minute of life, and usually the first score is always lower than the second. But the second assessment can just be equal to 10 points.
A score of 2 points in the delivery room is considered the highest and means that the sign is pronounced, 1 point - weakly expressed, 0 points - the sign is absent. The child is evaluated on the Apgar scale at the 1st and 5th minutes of life, so there are always two scores, for example, 8/9 points or 9/10 points. Children rarely score the maximum 10 points in the first minute of life, and usually the first score is always lower than the second. But the second assessment can just be equal to 10 points.
evaluation criteria
| 0 points | 1 point | 2 points | |
| Pulse | Missing | Less than 100 bpm | Over 100 bpm |
| Breathing | Missing | Slow, irregular | Good, cry |
| Muscle tone | Weak | Bends arms and legs | Actively moving |
| Reflexes | Missing | Weakly expressed | Called |
| Skin color | Blue, pale | Normal but bluish arms and legs | Normal throughout the body |
counting points
Children who score between 7 and 10 are considered to be in good condition and usually require only routine care. Those who score between 4 and 6 are in fair condition and may only need some resuscitation. Immediate life-saving assistance is needed for those who score below 4.
Those who score between 4 and 6 are in fair condition and may only need some resuscitation. Immediate life-saving assistance is needed for those who score below 4.
| Points | Result |
| 10–7 | Optimal, norm |
| 5-6 | Minor health problems |
| 3-4 | Average deviations in health status |
| 0–2 | Severe deviations in health |
let's be objective
In general, the Apgar score, although it is set according to objective criteria, still does not give an absolutely accurate forecast of the child's health in the future. It cannot be unequivocally said that a newborn who was given a 9or 10 Apgar scores, healthier than someone who got only 7 points. This only means that in the first case the baby breathes normally, he has pink skin and mucous membranes, he screams loudly enough, he has well-defined reflexes. And in the second case, one or two signs are less pronounced: for example, in the first minute the skin of the extremities is bluish, not pink, because the circulatory system takes about 5 minutes to get it working, or a healthy newborn loses points because he screams quietly in the first minutes life.
It cannot be unequivocally said that a newborn who was given a 9or 10 Apgar scores, healthier than someone who got only 7 points. This only means that in the first case the baby breathes normally, he has pink skin and mucous membranes, he screams loudly enough, he has well-defined reflexes. And in the second case, one or two signs are less pronounced: for example, in the first minute the skin of the extremities is bluish, not pink, because the circulatory system takes about 5 minutes to get it working, or a healthy newborn loses points because he screams quietly in the first minutes life.
what is important
As already mentioned, the first Apgar score is always lower than the second. In most newborns, the condition 1 minute after birth is estimated at 7-8 points on the Apgar scale, and after 5 minutes - at 8-10 points. And this suggests that the child was born in a satisfactory (normal) condition. If the Apgar score at the 1st minute is low, then the positive dynamics by the 5th minute will be important.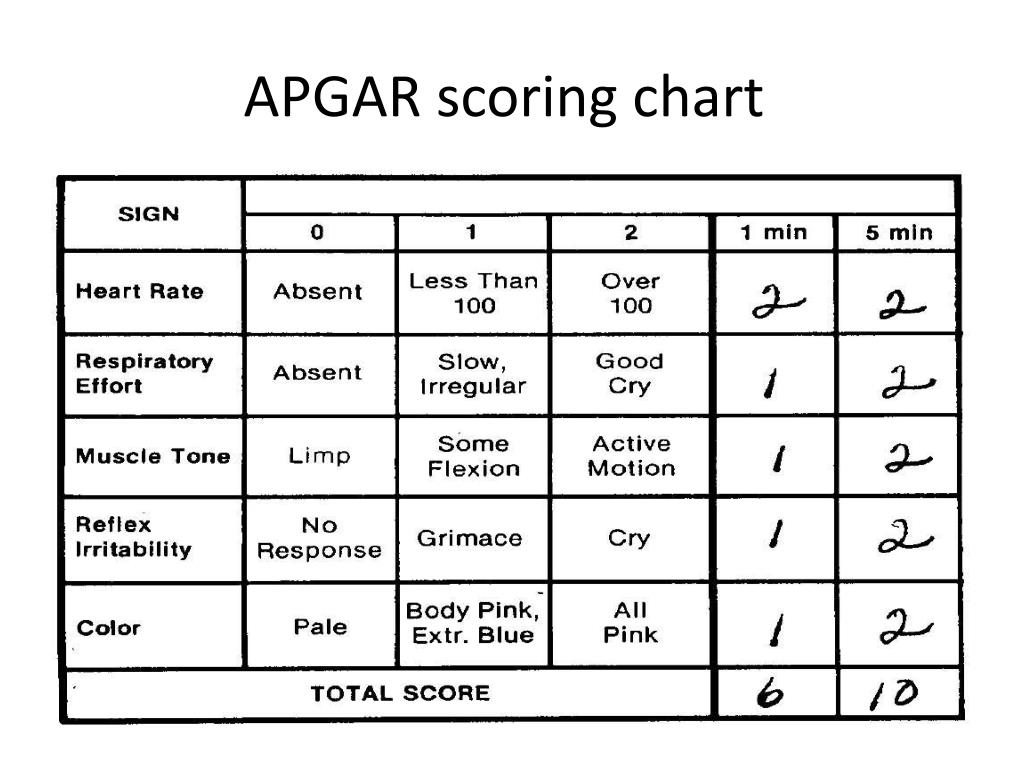 If the points increase by 2 or more by the 5th minute, then most likely the prognosis for health will be favorable. If, 5 minutes after birth, the Apgar score does not exceed 6 points, it will be necessary to carry out intensive therapy or continue resuscitation. So the main task of the Apgar scale is a quick assessment of whether a child needs medical help and how much.
If the points increase by 2 or more by the 5th minute, then most likely the prognosis for health will be favorable. If, 5 minutes after birth, the Apgar score does not exceed 6 points, it will be necessary to carry out intensive therapy or continue resuscitation. So the main task of the Apgar scale is a quick assessment of whether a child needs medical help and how much.
Whatever the Apgar score, the development of a child largely depends on love, care and upbringing in the family. So parental attention will always help the baby achieve the highest marks in life!
The maximum score of 10 in the first minute of life is rare for children, and usually the first score is always lower than the second. But the second assessment can just be equal to 10 points
With a low Apgar score at the 1st minute of a baby’s life, positive dynamics is extremely important - an increase of 2 or more points by the 5th minute of life
Most newborns have an Apgar score of 7–8 1 minute after birth, and 8–10 Apgar scores 5 minutes later
Attention! Prices for services in different clinics may vary.