40 weeks pregnant baby very active sign of labour
4 ways your body gets ready for labour
1. You have Braxton Hicks contractions
During your pregnancy, you may feel your tummy tighten for a few seconds, then relax again. This can happen from the middle of your pregnancy and are thought of as 'practice' contractions. They do not mean you are in labour and are nothing to worry about.
As the end of pregnancy approaches, Braxton Hicks contractions may become more powerful, so it's easy to mistake them for the start of labour. Braxton Hicks contractions are irregular and don't last very long. Although they can be uncomfortable, they aren’t painful.
Find out more about the difference between Braxton Hicks and labour contractions.
Contact your midwife, birth centre or labour ward for advice if you're worried that the tightenings you're feeling might be the start of labour.
2. Your baby settles into position
Babies move around a lot in your womb during pregnancy but at some point in late pregnancy your baby will get into position for birth. If this is your first baby, you may find he or she is already in position by 35 weeks.
Remember, you should continue to feel your baby move right up to the time you go into labour and during labour. If you think your baby’s movements have slowed down, stopped or changed, contact your midwife or maternity unit immediately. Find out more about your baby’s movements.
The most common position for birth is head down with your baby's back facing outwards, which is called an anterior position. The is the ideal position for giving birth, because your baby may fit through your pelvis more easily.
If your baby is head-down but facing your tummy, this is called the posterior position. Some midwives and antenatal teachers believe that spending time leaning forwards (for example, being on your hands and knees or leaning forward over a beanbag or birth ball) can help encourage them to turn.
Whether your baby turns or not, you may find it comfortable to be in this during late pregnancy and labour, so it's worth a try.
Find out more about getting your baby in the best position for birth.
Breech position
Your baby is in breech position if they are sitting bottom or feet down in the womb. If your baby is in a breech position at 36 weeks, you may be offered an external cephalic version (ECV). This is when a doctor tries to turn the baby into a head-down position by putting pressure on your stomach.
This is a safe procedure that will be done at the hospital. Around 50% of breech babies can be turned using ECV.
Find out more about what happens when your baby is breech.
Engaging
If this is your first baby, they will usually may move down into your pelvis before the birth. This is called 'engaging' and when it happens any breathlessness you've been feeling will probably ease. Second or later babies may also do this, but it may not happen as early.
Multiple pregnancy
If you're having twins or triplets, your babies may be in different positions. All the babies’ positions are important, but your healthcare team will be more interested in the position of the first baby when considering how you will give birth.
3. You have a 'show'
When you are pregnant, a small plug of mucus blocks the entrance to your cervix (the neck of your womb).
As your cervix begins to stretch and get ready for the birth, this mucus plug starts to come away and you may notice it on your underwear. This is called a ‘show’, although not everyone will experience this.
The show is pink because it’s bloodstained. It’s normal to lose a small amount of blood with the mucus, but if you’re losing more blood it may be a sign something is wrong. Call your hospital or midwife straight away if you’re concerned.
Your labour may not start for hours or even days after you lose the mucus plug. Or you could already be in early labour. If you're full term when the mucus plug comes out, you may have other signs that labour has started.
If you think the mucus plug has come out before you're 37 weeks pregnant, call your midwife. You may not be in labour, but it’s best to get checked out.
4. Your waters break
Your baby develops inside a bag of fluid called the amniotic sac. When your baby is ready to be born the sac breaks and the fluid comes out through your vagina. This is your waters breaking. Your waters may break at any time during labour. Some babies are even born in their waters.
When your baby is ready to be born the sac breaks and the fluid comes out through your vagina. This is your waters breaking. Your waters may break at any time during labour. Some babies are even born in their waters.
You may have a big gush of water or just a trickle, so you may not be sure whether your waters have broken or you've just wet yourself. If you think your waters have broken, contact your midwife or hospital straight away as they may want to give you a check-up.
It is a good idea to make a note of when your waters broke so you can tell the midwife.
Tell your midwife straight away if:
- the waters are smelly or coloured
- you’re losing blood.
This could mean you and your baby need urgent attention. It may help to wear a sanitary pad (not a tampon) so you can show the midwife what’s happening.
If your waters break before you go into labour
Sometimes your waters may break before you go into labour. Most women go into labour on their own within 24 hours. If this doesn’t happen your midwife will offer to induce labour and you’ll be advised to give birth in hospital, if you’re not there already.
If this doesn’t happen your midwife will offer to induce labour and you’ll be advised to give birth in hospital, if you’re not there already.
This is because your waters breaking before labour starts increases your baby’s risk of infection.
Find out more about what to expect when your waters break.
40 Weeks Pregnant | Pregnancy
The wait is nearly over. Within days, you'll get to meet your baby. It's been quite a journey, but the real adventure starts when your little one is born.
What's happening in my body?
If this is your first baby, then you'll have an antenatal appointment this week. Your blood pressure will be checked, your bump will be measured and you'll hand over a urine sample. Your midwife or doctor will be checking for signs of pre-eclampsia, a dangerous condition that's characterised by high blood pressure and protein in the urine.
You're probably getting a lot of practice contractions now, which should not be painful. These are Braxton Hicks contractions. When you start getting labour pains, you'll know all about it! Real contractions hurt when your bump goes tight, and then the pain goes away when the muscles relax.
When you start getting labour pains, you'll know all about it! Real contractions hurt when your bump goes tight, and then the pain goes away when the muscles relax.
Labour is divided into 3 stages. The first stage is when you have contractions and your cervix opens up until it's 10cm across (fully dilated). The 1st stage lasts 6 to 12 hours, or less if you've had other children. The 2nd stage is where the baby is delivered – and the 3rd stage is when the placenta comes out.
Read about what happens during labour on the NHS website.
When your contractions last for at least 60 seconds and come every 5 minutes, call your hospital or midwife.
From breathing to bananas: 8 tips for your labour
These tips could help you feel in control and manage your pain:
-
If your contractions start at night, try to sleep your way through as much as possible. The rest will help to prepare you for the birth, and your cervix will dilate while you sleep.
-
If your contractions start in the day, then keep upright and active as this helps the baby to move down and your cervix to open up.
 This could speed up your labour and reduce the need for painkilling drugs.
This could speed up your labour and reduce the need for painkilling drugs. -
Try different positions. Rock on a birth ball, or put your arms around your birth partner's neck and lean on them. Just keep moving.
-
Have a warm bath or shower – it's a tried and tested method of pain relief.
-
Focus on breathing. You can practise your breathing techniques now. Take deep breaths in through your nose and out through your mouth. Keep your jaw relaxed.
-
Ask your birth partner for a massage and involve them in your labour. Having their support and reassurance will encourage your body to produce more endorphins, which are brilliant natural painkillers. Here are some more ways that your partner could support you.
-
Eat something healthy to keep up your energy levels, like a banana or low-fat yoghurt. Avoid fatty foods, as they could make you feel sick, and steer clear of sugary foods as they'll only give you a quick hit before a slump.

-
Do something that helps you to relax. If you feel calm, you will be able to manage your labour and pain much better than if you're stressed.
Will curries and sex bring on labour?
You've probably searched the internet for ways to bring on labour and found tips that range from sex to vindaloos. There's a Tommy's has information on what might help bring on labour from raspberry leaf tea to nipple stimulation.
There are no proven ways to safely bring on labour at home. Get advice from your doctor or midwife before trying anything other than watching and waiting.
3rd trimester pregnancy symptoms (at 40 weeks)
Do you feel like you've got PMT? Or do you have lower backache? These could be early signs of labour. Check out these 5 signs that your baby is on the way.
Your signs of pregnancy could also include:
- painless contractions around your bump, known as Braxton Hicks contractions
- sleeping problems (week 19 has information about feeling tired)
- stretch marks (read about stretch marks on week 17's page)
- swollen and bleeding gums (week 13 has information about gum health during pregnancy)
- pains on the side of your baby bump, caused by your expanding womb ("round ligament pains")
- piles (read about piles on week 22's page)
- headaches
- backache
- indigestion and heartburn (week 25 talks about digestive problems)
- bloating and constipation (read about bloating on week 16's page)
- leg cramps (week 20 explains how to deal with cramp)
- feeling hot
- dizziness
- swollen hands and feet
- urine infections
- vaginal infections (see week 15 for vaginal health)
- darkened skin on your face or brown patches – this is known as chloasma or the "mask of pregnancy"
- greasier, spotty skin
- thicker and shinier hair
You may also experience symptoms from earlier weeks, such as:
- mood swings (week 8's page has information on mood swings)
- morning sickness (read about dealing with morning sickness on week 6's page)
- weird pregnancy cravings (read about pregnancy cravings on week 5's page)
- a heightened sense of smell
- sore or leaky breasts (read about breast pain on week 14's page)
- a white milky pregnancy discharge from your vagina and light spotting (seek medical advice for any bleeding)
Read Tommy's guide to common pregnancy symptoms.
40th week of pregnancy - what happens at the fortieth week of pregnancy: nausea, discharge, signs of labor
WHAT HAPPENS
There is very little space in the uterus now, so do not be surprised if the number of movements is reduced. Be sure to listen to every movement of the baby: both excessive activity and complete cessation are not very good signs. Normally, at 40 weeks of pregnancy, in 12 hours you should feel about 10 movements.
Like the mother, the baby is preparing for the birth. In order for the process of childbirth to go smoothly, the hormones adrenaline and norepinephrine are produced in the tiny body, which should reduce pain during the passage of the fetus through the birth canal.
By the 39th - 40th week of pregnancy, the baby's blood circulation is established, the digestive system is actively functioning, processing the amniotic fluid and dead skin cells. The meconium formed from them will leave the intestines of the child only after birth. The bones of the skull are still flexible, so that the fetus can pass through the birth canal unhindered.
The bones of the skull are still flexible, so that the fetus can pass through the birth canal unhindered.
The 40th week of pregnancy should be the final one, but in practice, only a few women give birth at the expected time. So be patient and wait, continuing to lead a normal life. In any case, very soon you will hug your baby.
YOUR WELL FEELING
If you have not yet had signs of childbirth, they may appear at the 40th week of pregnancy.
- Lowering of the abdomen. The baby in the uterus moves down and presses the head against the pelvic floor. Due to this, heartburn disappears in the expectant mother and it becomes much easier for her to breathe. But due to the strong pressure on the bladder, pregnant women at this time are forced to go to the toilet more often;
- Disorders of the food system. Approximately 24 to 48 hours before the onset of labor, stool liquefaction may occur;
- Loss of appetite;
- Weight loss.
 Before childbirth, body weight may decrease by 1 - 2 kg;
Before childbirth, body weight may decrease by 1 - 2 kg; - Mucus plug outlet. During 40 weeks of pregnancy, the cork closed the entrance to the cervix, protecting the baby from infections. Her separation (you will learn about this from lumps of mucus on panties) frees the birth canal for the child;
- Amniotic fluid discharge. Amniotic fluid is poured out immediately before childbirth. Most often it is transparent, but if meconium particles have got into it, the color may be yellowish or greenish;
- Painful and false contractions at 40 weeks. Primiparous women can confuse training contractions with real ones, especially since by the time of 39-40 weeks of pregnancy, false uterine contractions are also accompanied by pain and are repeated more often than in previous periods. To understand exactly what kind of contractions you have, change the position of the body during muscle contractions. Lie down or, conversely, stand up, walk around the room, then sit on a chair.
 If the contractions have stopped, then this is not childbirth.
If the contractions have stopped, then this is not childbirth.
RISK FACTORS
The main danger of 40 weeks of pregnancy is rapid delivery. A baby can be born very quickly, especially in multiparous women. Therefore, it is better to go to the hospital in advance, about a week before the expected date of birth. And if you live near a hospital, avoid long trips and tiring shopping trips.
At the 40th week of pregnancy, it is necessary to monitor the nature of the discharge. If they have changed their smell, color and texture (for example, they have become purulent or curdled), this indicates an infectious disease that requires immediate treatment. The presence of pathogenic microbes in the vagina creates a risk of infection of the child.
As at any time, anemia is dangerous at 39-40 weeks of gestation, due to which the level of oxygen in the tissues decreases. Low hemoglobin provokes fetal hypoxia, and the expectant mother faces an increased risk of developing late toxicosis and complications in childbirth.
Possible signs of anemia during pregnancy:
- Dry skin;
- Brittle nails and hair;
- Feeling weak and easily fatigued;
- Paleness of skin and mucous membranes;
- Insomnia;
- Headaches;
- Feeling of impending fainting;
- Arrhythmia and bradycardia;
- Constipation;
- Presence of taste perversions.
Anemia is treated with iron supplements and a special diet.
MEDICAL SUPERVISION
At the 40th week of pregnancy, you will have another trip to the doctor, where the usual procedures will be carried out: measuring blood pressure, weighing, determining the height of the fundus of the uterus and, of course, listening to the baby's heartbeat.
And in order to monitor the work of the kidneys, you will need to pass urine for analysis. If the date of delivery, which was set by the doctor, has passed, you may be prescribed a Doppler ultrasound. This study makes it possible to assess the blood flow of the fetus, blood circulation in the placenta and uterine vessels, and also to determine whether the baby receives enough oxygen and necessary substances. Another study, sometimes prescribed at 40 weeks of gestation, is cardiotocography, thanks to which the specialist will be able to exclude intrauterine hypoxia.
This study makes it possible to assess the blood flow of the fetus, blood circulation in the placenta and uterine vessels, and also to determine whether the baby receives enough oxygen and necessary substances. Another study, sometimes prescribed at 40 weeks of gestation, is cardiotocography, thanks to which the specialist will be able to exclude intrauterine hypoxia.
RECOMMENDATIONS
In the time remaining before the birth, try to relax properly, because after the birth of the child this is unlikely to work. It is very important to remain calm now, because your emotional state greatly affects the baby. Tune in to the upcoming birth and think only about the good.
At the 39th - 40th week of pregnancy, you should not experiment with nutrition. Eat foods high in protein and carbohydrates. They will help to accumulate strength and stock up on energy that you will need during childbirth. Don't forget about vitamins. Now the body needs vitamin K (it is found in spinach, in all types of cabbage, in asparagus, herbs, plums and prunes). This element improves blood clotting, which is very important for childbirth. You also need vitamin A, which is found in yellow, red and orange vegetables and fruits, beef liver, egg yolks and full-fat dairy products. Its lack can lead to a lack of baby weight. And at 39– At 40 weeks pregnant, you need B vitamins: they ensure not only the proper development of the fetus, but also the well-being of the mother. Their most valuable source is dry brewer's yeast, but they can be used only after consulting a doctor. Also, B vitamins are present in oatmeal, millet, meat, fish, eggs, legumes and dairy products.
This element improves blood clotting, which is very important for childbirth. You also need vitamin A, which is found in yellow, red and orange vegetables and fruits, beef liver, egg yolks and full-fat dairy products. Its lack can lead to a lack of baby weight. And at 39– At 40 weeks pregnant, you need B vitamins: they ensure not only the proper development of the fetus, but also the well-being of the mother. Their most valuable source is dry brewer's yeast, but they can be used only after consulting a doctor. Also, B vitamins are present in oatmeal, millet, meat, fish, eggs, legumes and dairy products.
If at 40 weeks of pregnancy you feel the onset of contractions, do not rush to go to the hospital. Before childbirth, you should replenish energy reserves, and for this you can drink sweet tea, jelly or compote, eat a little low-fat cottage cheese or yogurt. As soon as the duration of the contractions reaches 1 minute, and the interval between them is 5-7 minutes, go to the hospital.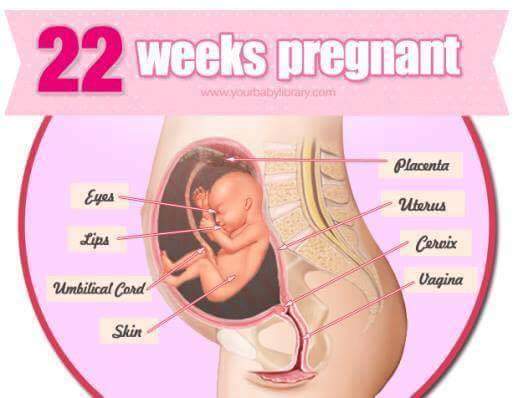
Many future parents are interested in the question of whether it is harmful to have sex at the 39th - 40th week of pregnancy. In the absence of contraindications, this is not prohibited. And in some cases, sexual intercourse is even recommended as a means of preparing for childbirth. The semen contains the hormone prostaglandin, which softens the cervix, and the orgasm experienced by a woman stimulates the onset of contractions.
Pregnancy and childbirthNinth month of pregnancy: changes in the female body and fetal development by week
Newborn careDowry for a newborn
What do you need to have at home for discharge, what stroller and crib to choose, and what equipment to buy?
Pregnancy and childbirthWhat to take with you to the hospital
Pregnancy and childbirthPsychology of pregnancy and motherhood
Positive attitude and overcoming fears during pregnancy, psychological hygiene and well-being of a woman.
How to Prepare for Pregnancy
How to properly organize your life before childbirth and how to choose a maternity hospital.
Communication with a childHow to prepare for the birth of a baby?
How to build a relationship between an older and younger child and what you need to be prepared for.
Breast-feedingAll About Breastfeeding
Let's dispel the most popular misconceptions about breastfeeding.
40 week
39 week 41 weeks
Calm before childbirth
By the 40th week of pregnancy, the baby is completely ready for childbirth. He calms down before childbirth, saving strength. The diameter of the head and the volumes of the child have changed very little. At this time, there is a risk of oxygen starvation of the child, so you need to carefully monitor the movements. It is better to once again appear at the doctor who will listen to the child, measure the heart rate, and do an ultrasound. The risk of intrauterine infection also increases, so a woman should be very attentive to herself.
He calms down before childbirth, saving strength. The diameter of the head and the volumes of the child have changed very little. At this time, there is a risk of oxygen starvation of the child, so you need to carefully monitor the movements. It is better to once again appear at the doctor who will listen to the child, measure the heart rate, and do an ultrasound. The risk of intrauterine infection also increases, so a woman should be very attentive to herself.
Health
Before childbirth, there are frequent urges to go to the toilet, because the baby's head is down and presses on the bladder, perineum, and pelvic vessels. Because of this, pain occurs and hemorrhoids appear or intensify, sometimes with bloody discharge from cracks in the nodes of the anus. Colostrum is secreted from the nipples. For a child, this is a concentrate of nutrients and mother's antibodies to various infections. Colostrum will be secreted for another three days after birth, then it will become more liquid milk. In the first days of feeding, cracks appear on the nipples, which are covered with very delicate skin.
In the first days of feeding, cracks appear on the nipples, which are covered with very delicate skin.
Important to avoid overwearing
The fetus before childbirth begins to receive less oxygen and nutrients due to the aging of the placenta. If the pregnancy is delayed, then the fetus begins to suffer from oxygen starvation. The sutures and fontanelles on his skull harden (it will be more difficult for him to go through the birth canal), oligohydramnios develops (he swallows water during pregnancy, receiving protein), the risk of infection of the child increases, he becomes passive, lethargic. His central nervous and cardiovascular systems begin to suffer. A true pregnancy delay is considered after the 42nd week, and the reason for this is the disturbed hormonal balance. If a woman is past her term, and the child has no signs of overmaturity, the pregnancy can be called prolonged. The child is closely monitored through monitors. With the onset of signs of the child's suffering, the woman will be urgently prepared for delivery.