What cold med can you take when pregnant
Which Cold & Flu Medication Is Safe to Take During Pregnancy? | UNM Health Blog
By Maria Montoya, MD | February 04, 2022
You are pregnant and start feeling sick. Before you reach for that bottle of cold or flu medicine, are you certain it is safe for your baby?
When you are pregnant, your baby will be exposed to everything you are exposed to. This means that when you are sick with a cold or flu your baby will not only be exposed to the cold or flu virus, but also any medication you may take.
Typically, with most viruses, you must wait for your immune system to fight the infection. Over-the-counter medications can help soothe your symptoms while you wait.
However, not all over-the-counter medicines are safe to take during pregnancy. Certain medications may hurt the baby or cause problems for you, such as increasing your blood pressure.
Use this quick list of pregnancy-safe natural cold and flu remedies and over-the-counter medications as a starting point. Remember, read the directions on the package for any medication you might take. It’s also a good idea to talk with your doctor or midwife before taking a cold or flu medication.
Natural, Pregnancy-Safe Remedies
Before you try any medications, there are natural remedies you may find adequate relief from first. Here are a couple of safe, natural remedies to try:
- Gargle warm salt water
- Get as much restful sleep as possible
- Sip honey in hot water
- Stay well hydrated
- Use nasal saline sprays
- Try a humidifier
While not all herbs and supplements are safe in pregnancy. You may be able to safely take:
- Vitamin C
- Zinc
- Manuka Honey
- Elderberry
Talk with your doctor or midwife before taking any supplements or trying at-home remedies or essential oils during pregnancy.
If natural remedies don’t provide enough relief, consider these pregnancy-safe medications.
Pregnancy-Safe Cold & Flu Medication
It is best to avoid taking medications when possible. If you do need to take something, follow the package directions carefully. Talk with your doctor or midwife before taking medication during pregnancy.
These over-the-counter medications are considered safe for most pregnant patients:
- Acetaminophen (Tylenol)
- Safe during the entire pregnancy.
- Take only as needed.
- Try to limit regular exposure.
- Not safe if you are allergic to it or have liver problems.
- Pseudoephedrine (Sudafed)
- Safe in the second and third trimester
- Not safe in the first trimester due to a small risk of abdominal wall birth defects
- Not safe if you have high blood pressure (hypertension) or a history of heart disease
- Chlorpheniramine (Chlor-Trimeton)
- Safe during pregnancy.
- Not safe while breastfeeding.
- Diphenhydramine (Benadryl)
- Safe throughout pregnancy.
Watch out for extra ingredients. Many cold and flu medications treat more symptoms than you may be experiencing. For example, Tylenol Cold Multi-Symptom treats headaches, fever, body aches, cough, chest congestion, stuffy nose, and more. If you just have a stuffy nose, this is more medication than you need.
A word about antibiotics. Some sinus infections are treated with antibiotics. In general, pregnant patients should not take antibiotics unless it is necessary. Make sure your health care provider knows you are pregnant if they prescribe antibiotics.
The dangers of high blood pressure in pregnancy
How to spot symptoms and get help
Read More
Medications to Avoid in Pregnancy
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory (NSAID) medications can hurt your developing baby. Do not take NSAIDs such as these when you are pregnant:
Do not take NSAIDs such as these when you are pregnant:
- Ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin)
- Naproxen (Aleve, Midol)
- Celecoxib (Celebrex)
- Aspirin (Bayer), unless your doctor or midwife prescribes daily low-dose aspirin.
Do not take these medications during pregnancy. These drugs can hurt the developing baby:
- Benzocaine (throat lozenges/throat sprays)
- Codeine (a pain and cough medication)
- Phenylephrine (i.e., Sudafed PE): it not considered safe while pregnant because studies with animals showed adverse effects to the fetus.
When you don’t feel well, the last thing you might want to do is read a medication label. However, it is worth taking a few extra moments to read the label and avoid additional risks. If you’re not sure what medicine is safe to take, call us. We are always here to help you.
To find out whether you or a loved one might benefit from Ob/Gyn care
Call 505-272-2245.
Categories: Women's Health
Which over-the-counter cold medications are safe during pregnancy? | Your Pregnancy Matters
Most people experience two to three colds during the winter and spring, and pregnant women are no exception. Colds are caused by viruses for which there is no real cure – you can treat the symptoms that make you feel crummy, but medicine doesn’t actually make the cold go away sooner.
Many over-the-counter (OTC) medications you can buy without a prescription come as multi-symptom formulas. These drugs are meant to treat every cold symptom: body aches, congestion, coughing, fever, headache, and sneezing. But not everyone develops every symptom of a cold, and pregnant women should avoid taking unnecessary drugs during pregnancy.
Instead of reaching for a multi-symptom drug, use the guidelines below to find an effective drug that’s safe for the symptoms you’re facing. And, as always, let your Ob/Gyn or nurse know about any OTC drug you take.
What to take for common cold symptoms
Cough
Dextromethorphan is a cough suppressant used in OTC medications such as Robitussin to reduce coughing. Cough suppressants can come in immediate-release and extended-release preparations. The maximum dose for pregnant women is 120 mg in 24 hours. The multi-symptom preparations that contain dextromethorphan often include “DM” in their name.
Guaifenesin is another medication frequently found in cough medications, such as Mucinex. It is an expectorant, so it helps thin mucus from your chest or throat so you can cough it up easier. It comes in immediate-release or extended-release formulations. The maximum dose you should take is 2,400 mg in 24 hours.
Cold medicines containing codeine were used in the past for cough suppression. I don’t recommend these for pregnant women because studies show they really don’t work well, and the fewer opioid-containing medications in our medicine cabinets, the better. For children, there is some evidence that honey can improve nighttime coughing. I certainly think this is an option for pregnant women as well. If you want to try honey, I suggest a spoonful of the real stuff – it’s not as clear that cold medicine with honey listed as a flavoring or ingredient is as effective.
I certainly think this is an option for pregnant women as well. If you want to try honey, I suggest a spoonful of the real stuff – it’s not as clear that cold medicine with honey listed as a flavoring or ingredient is as effective.
Stuffy nose and sinus pressure
Decongestant medications reduce stuffiness and sinus pressure by constricting the blood vessels in your nose, which reduces swelling. Pseudoephedrine and phenylephrine are available over the counter as Sudafed and are safe for many women to use during pregnancy. However, women who have high blood pressure should not take pseudoephedrine without first talking to a doctor. The drug can raise blood pressure and can cause jitters and racing heartbeats.
Because pseudoephedrine can be used to manufacture methamphetamine, it’s now kept behind the pharmacy counter. You’ll have to provide identification to purchase it, and stores track how much you purchase. The maximum dose of a typical decongestant is 240 mg in 24 hours.
Sneezing, runny nose, and watery eyes
These symptoms are the result of histamine release, which is an immune response to an invading virus. Chlorpheniramine, such as Triaminic Allergy, and diphenhydramine, such as Benadryl, are safe to take during pregnancy. However, both can cause drowsiness, so these are best taken at bedtime. The maximum dosage for chlorpheniramine is 32 mg in 24 hours.
When compared to placebos, antihistamines have the most successful results within the first couple days of treatment. Patients didn’t report any relief of symptoms between days three and 10. Newer antihistamines, such as loratadine (Claritin), are approved for allergies, not colds, so there isn’t information about how well they work for cold symptoms.
Sore throat
Pregnant women can take acetaminophen (Tylenol) for a sore throat with a limit of 3,000 mg in 24 hours. An antihistamine may help if the sore throat is due to postnasal drip because it can dry up those secretions.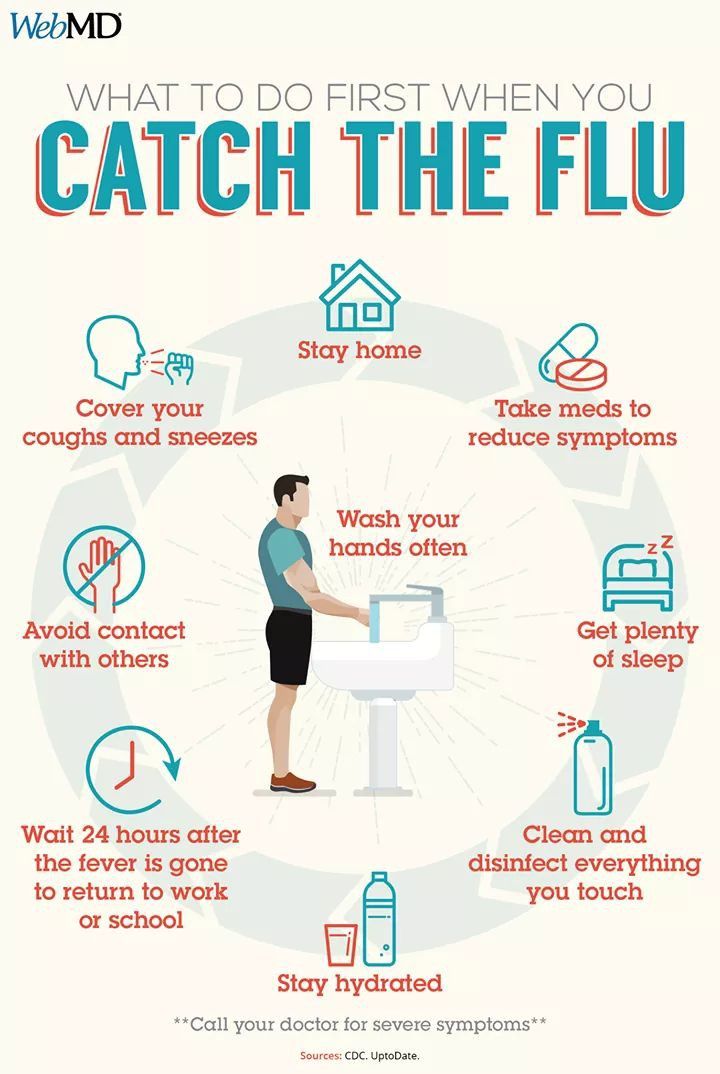
Sprays or lozenges that contain benzocaine, a local anesthetic, can help numb the throat. Menthol and phenol, such as Chloraseptic, are antiseptics that also help soothe throat discomfort. Sucking on hard candy can keep saliva flowing, which might reduce throat irritation.
A word about antibiotics
So many patients call asking for antibiotics for a cold, usually when they’ve had symptoms for several days. There are a few times when antibiotics are appropriate, for instance, strep throat or sinus infections caused by bacteria. But antibiotics simply don’t work against viruses that cause the common cold. Overprescribing antibiotics for viral illnesses leads to antibiotic resistance, which means the bacteria grow stronger over time and become tougher to beat with antibiotics.
If a doctor prescribes an antibiotic for cold symptoms, it’s usually a short, three-day round of drugs. The patient often feels better after finishing the medication but probably would have recovered in that timeframe anyway without the drug.
To sum up …
If you come down with a cold while pregnant and you want to take something for symptom relief, look for medications that are formulated for your specific symptoms. Avoid multi-symptom formulas, especially those containing acetaminophen. It can be easy to take more acetaminophen in a day than is safe because it’s in so many medications. Finally, be patient with cold symptoms – it can take a week or more for a cold to go away.
Sign up to receive Your Pregnancy Matters email alerts when we publish new stories.
Colds during pregnancy: how to treat?
Any cold or respiratory disease in early pregnancy, during the primary formation of the fetus, can lead to unpredictable consequences and complications. The matter is complicated by the fact that most medications are absolutely contraindicated for use during gestation.
In this regard, the treatment and prevention of colds in pregnant women is an important issue, which should be approached especially responsibly! The main thesis is: be careful with medicines and apply mild preventive measures based on alternative medicine methods to avoid respiratory diseases and flu.
"One for two - immunity"
This is a very fragile system, it is not necessary to interfere in its work, but it is necessary to support and strengthen it. Pregnancy belongs to the category of special, albeit temporary, conditions during which a woman needs additional protection.
This issue will help simple recommendations that are available to everyone:
• During the period of frequent weather changes, it is necessary to dress warmer, paying special attention to footwear.
• During an epidemic, it is better for a pregnant woman to refrain from being in crowded places - transport, metro, shops and hospitals. If there is an urgent need, to prevent possible infection, a protective respiratory mask should be worn before leaving the house.
• Be especially careful about hygiene after visiting the street and public places. Upon returning home, the first thing to do is wash your hands thoroughly.
Interesting: More than 90% of all acute respiratory infections are caused by viruses, about 10% are bacteria and other pathogens. Accordingly, any soap can be used, not necessarily antibacterial.
• Before going outside, you can lubricate the nasal mucosa with oxolin ointment. Upon returning home, flush the upper respiratory tract with soda solution.
• Rationalization of nutrition and intake of vitamins will strengthen the immune defense. It is especially useful to eat fruits and vegetables that are enriched with vitamins and have not undergone heat treatment.
Interesting: our grandmothers used to say: in order not to get sick, you need to drink chicken broth! Strange, but until recently, scientists did not attach much importance to this prophylactic. Pulmonologist Stefan Rennard decided to find out if this was true or not. The professor conducted a study and proved that the use of chicken broth affects the mobility of neutrophils, white blood cells that protect the body from infections and activate the immune system.
- Vitamins can be taken using ready-made pharmaceutical multivitamin complexes. Before choosing a drug, you should consult your doctor.
- Compliance with the regimen and duration of sleep - at least 9 hours a day. The possibility of psychotraumatic situations should be minimized.
- Maintaining cleanliness in the living quarters (ventilation, wet cleaning).
- Air humidification is an important aspect in the prevention of influenza and respiratory diseases. If air conditioners or heaters are used in the house of a pregnant woman, it would be best to purchase a mechanical humidifier.
Medications for prevention
- Grippferon - a drug in the form of drops for the nose, which provides prevention and treatment of influenza, is not contraindicated for pregnant and lactating women. The drug stimulates an increase in immunity, has a pronounced antiviral effect that can protect against colds, infections and influenza varieties.

- Ascorbic acid - can be used as a separate source of vitamin C in a synthetic version, with a reduced daily intake from food. Ascorbic acid not only prevents infection, but also fights viruses that have already entered the body of a woman.
- Viferon - nasal ointment, which is prescribed for the prevention of influenza and respiratory infections during an epidemic. The ointment has protective and immunomodulatory effects, and also allows you to deal with disorders that are already occurring in the body at the time of use. Viferon in the form of a nasal ointment has no contraindications for use in pregnant women at any time, including the first trimester.
- Aquamaris is a natural drug in the form of a nasal spray that allows you to moisturize the nasal mucosa, thereby reducing the risk of influenza viruses entering the nasal cavity.
I would like to say a few words about such a method of prevention as vaccination. Most often, the expectant mother may be at risk of infection due to the annual influenza epidemic. This disease is dangerous for a pregnant woman precisely because of its complications: pneumonia, bronchitis, otitis media. Influenza in a pregnant woman can also affect the health of the fetus. Most of all, it is dangerous in the early stages of pregnancy, when the tissues and organs of the human embryo are laid and formed. Viral intoxication or drug exposure can lead to pathology of the child's organs. In later pregnancy, there is a risk of infection of the fetus.
This disease is dangerous for a pregnant woman precisely because of its complications: pneumonia, bronchitis, otitis media. Influenza in a pregnant woman can also affect the health of the fetus. Most of all, it is dangerous in the early stages of pregnancy, when the tissues and organs of the human embryo are laid and formed. Viral intoxication or drug exposure can lead to pathology of the child's organs. In later pregnancy, there is a risk of infection of the fetus.
The most dangerous consequence of influenza in a pregnant woman is threatened miscarriage or premature birth!
It is quite natural that expectant mothers often wonder whether or not to vaccinate.
Studies have concluded that the use of inactivated ("killed") influenza vaccines does not have a teratogenic effect on the fetus and does not harm the health of a pregnant woman. After consulting with your doctor about such an inoculation, you can come to an optimal solution. If an influenza epidemic is inevitable, and the pregnant woman has no contraindications, then the vaccine should be given. If a pregnant woman has a negligible risk of infection, she does not come into contact with a large number of people, or is opposed to vaccination, then you can not do it. According to research, it is known that vaccination of mothers reduces the risk of influenza infection of a born child by 63%. Seasonal influenza prevention is carried out in September, October. Vaccinations for pregnant women are recommended from the second trimester of pregnancy.
If a pregnant woman has a negligible risk of infection, she does not come into contact with a large number of people, or is opposed to vaccination, then you can not do it. According to research, it is known that vaccination of mothers reduces the risk of influenza infection of a born child by 63%. Seasonal influenza prevention is carried out in September, October. Vaccinations for pregnant women are recommended from the second trimester of pregnancy.
In the period of a planned pregnancy, a flu shot is given 1 month before it: the formation of immunity occurs 2-4 weeks. Protection after vaccination lasts about a year.
If infection does occur, action should be taken immediately if at least one symptom of the disease is detected. The health of a pregnant woman and her unborn child depends entirely on her responsibility and respect for her own body.
Proven folk remedies will be used first. Since pregnant women cannot steam their legs, steam their hands, and this will facilitate nasal breathing.![]() Bundle up, put on woolen socks and crawl under the covers: warmth, peace and sleep are good for colds. Do not forget to drink plenty of water - hot green tea with lemon and honey, lime blossom tea, cranberry juice, rosehip broth, dried fruit compote. Ginger in the form of tea also helps, not only with catarrhal symptoms, but with nausea in the morning.
Bundle up, put on woolen socks and crawl under the covers: warmth, peace and sleep are good for colds. Do not forget to drink plenty of water - hot green tea with lemon and honey, lime blossom tea, cranberry juice, rosehip broth, dried fruit compote. Ginger in the form of tea also helps, not only with catarrhal symptoms, but with nausea in the morning.
Various hot milk drinks are also suitable. Honey can be added to milk, and it is best to boil it on onions. It must be emphasized right away that not all herbs for colds during pregnancy can be used. Here is a list of medicinal plants that are contraindicated: aloe, anise, barberry, elecampane (grass and root), sweet clover, oregano, St. John's wort, strawberries (leaves), viburnum (berries), raspberries (leaves), lemon balm, lovage, wormwood, licorice root), celandine, sage. Accordingly, preparations containing these plants should not be taken.
The use of medicines for colds during pregnancy must be treated with great care!
It is contraindicated to use the following drugs : Pertussin, Tussin plus, Joset, Glycodin, Ascoril, Travisil, Broncholitin, ACC, Grippeks, Codelac, Terpinkod. Do not use lozenges and lozenges for sore throat or cough are also undesirable due to the likelihood of allergic reactions.
Do not use lozenges and lozenges for sore throat or cough are also undesirable due to the likelihood of allergic reactions.
Spray Pinosol, judging by the components indicated in the instructions, is not dangerous during pregnancy. However, the essential oils contained in the preparation - pine, peppermint, eucalyptus, thymol, guaiazulene (wormwood oil) - can lead to an allergic reaction with swelling of the nasal mucosa.
Viferon suppositories are allowed to be used only after 14 weeks from the start of conception. This drug contains recombinant human interferon alpha-2, ascorbic acid and alpha-tocopherol acetate and has antiviral, immunomodulatory and antiproliferative effects. It is used in the treatment of various infectious and inflammatory diseases in adults and children (including newborns). In the form of an ointment, Viferon is used to treat herpetic lesions of the skin and mucous membranes. The ointment is applied in a thin layer to the affected areas of the skin 3-4 times a day for 5-7 days.
The homeopathic preparation Stodal, which includes predominantly herbal ingredients, acts on various types of cough and has an expectorant and bronchodilator effect.
Viburkol - homeopathic suppositories - have analgesic, anti-inflammatory, sedative, antispasmodic action. They are prescribed in the complex therapy of acute respiratory viral infections and other uncomplicated infections (including in newborns), as well as in inflammatory processes of the upper respiratory tract and inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary system.
So, you can try to eliminate a slight ailment on your own, but there are conditions under which you need to call a doctor at home:
- Prolonged fever;
- Myalgia, fatigue, fatigue, general malaise;
- Difficulty breathing, nasopharyngeal lumps and dry or wet barking cough;
- A pregnant woman is troubled by severe pressing headache.
In conclusion, I would like to emphasize the importance of treating chronic diseases before pregnancy, a healthy lifestyle during childbearing and following all doctor's orders.
I wish expectant mothers and their loved ones to try to maintain a good mood: optimists live longer and happier, they are more productive. Remember your victories and pleasant moments more often and everything will be fine!
Antivirals for pregnant women - what to do if a pregnant woman has a cold at 1, 2, 3, trimester
January 17, 2022
17.01
5 minutes
5 minutes
39980
42
3
What is possible and what is not possible for pregnant women with a cold is one of the main issues that concern the expectant mother.
Article content
- Features of the treatment of acute respiratory viral infections in the 1st trimester
- Cold therapy in the 2nd trimester
- Treatment of acute respiratory viral infection in the 3rd trimester
- FAQ
Peculiarities of ARVI treatment in the 1st trimester
Perhaps the most difficult in the appointment of therapy.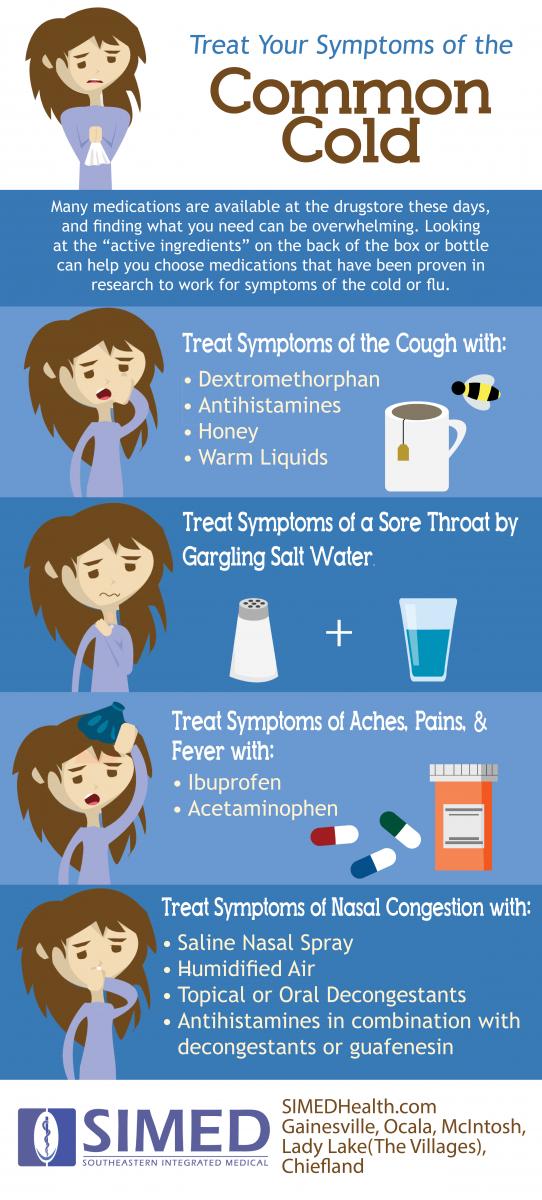 The fact is that it is at this time that the baby's internal organs are laid, as well as the nervous system. Exposure to various chemicals can adversely affect this process and cause the formation of malformations.
The fact is that it is at this time that the baby's internal organs are laid, as well as the nervous system. Exposure to various chemicals can adversely affect this process and cause the formation of malformations.
If the expectant mother fell ill in the first trimester, she is recommended to have more rest, take vitamins C and D, drink plenty of water and fresh cranberry juice. For sore throats, rinsing with a warm solution of furacilin or sage infusion is prescribed, rinsing the nose with sea water to treat a runny nose and inhaling with alkaline mineral water on a nebulizer when coughing.
At the first sign of a cold or SARS, you should consult a competent doctor. Our doctor will consult remotely: draw up a treatment regimen taking into account the well-being of the expectant mother, potential risks for the child and the timing of pregnancy.
2nd trimester cold therapy
In the second trimester, it is already easier for the doctor to choose drugs that are effective for the mother and safe for her baby for the treatment of colds.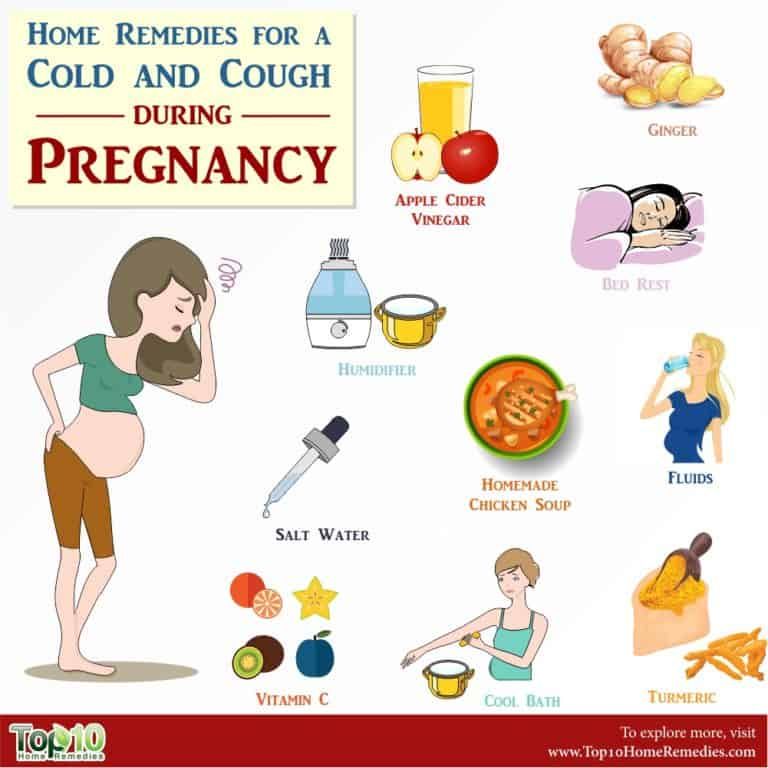 By this time, the placenta is formed in the uterus - a kind of barrier that can neutralize certain drugs. In the second trimester, antiviral drugs are already prescribed, most often interferon-based drugs, as well as antibiotics when bacterial complications are attached. Treatment of a runny nose, cough and sore throat is recommended in the same way as in the first trimester.
By this time, the placenta is formed in the uterus - a kind of barrier that can neutralize certain drugs. In the second trimester, antiviral drugs are already prescribed, most often interferon-based drugs, as well as antibiotics when bacterial complications are attached. Treatment of a runny nose, cough and sore throat is recommended in the same way as in the first trimester.
Pay attention! The lack of high-quality and comprehensive treatment of acute respiratory viral infection during pregnancy can cause placental insufficiency, a condition that is dangerous for the health and life of the child.
Treatment of acute respiratory viral infection in the 3rd trimester
At this time, the fetus is almost completely formed, so the list of approved drugs, including antiviral agents, is expanding. However, self-medication is still not recommended! It is very important to remember that some seemingly harmless plants can cause premature birth. So, for example, horsetail and sage stimulate the release of estrogen hormones into the blood, which stimulate the contraction of the smooth muscles of the uterus.
Example
A pregnant woman fell ill with ARVI for a period of 30 weeks. There were complaints of fever, cough and runny nose. They were prescribed: antiviral agents, antipyretic based on paracetamol, vitamins and inhalation on a nebulizer with alkaline mineral water and washing the nose with sea water. Against the background of the therapy, on the third day the woman felt an improvement, on the 7th day of the disease, the symptoms leveled off. Studies have shown that the fetus is fine.
The use of certain antiviral drugs should be discussed with a doctor. The fact is that not only the gestational age, but also the individual characteristics of the expectant mother can become a ban on their use. Contact our doctors by phone at any time of the day - they will check the drugs prescribed for you and give recommendations.
FAQ
How to treat SARS during pregnancy? Am I in 1st trimester?
+
Under the supervision of a doctor is the most important thing. It is recommended to rest more, ventilate the room more often, take vitamins C and D. If you have a sore throat, you can rinse with a warm solution of furacilin or sage infusion, rinse your nose with sea water if you have a cold, and inhale with alkaline mineral water if you cough.
It is recommended to rest more, ventilate the room more often, take vitamins C and D. If you have a sore throat, you can rinse with a warm solution of furacilin or sage infusion, rinse your nose with sea water if you have a cold, and inhale with alkaline mineral water if you cough.
What to do if a pregnant woman has a cold?
+
Do not self-medicate, but immediately consult a doctor. Of course, most of us know how to treat a cold on our own and have such experience. But this knowledge cannot be useful in this situation, because now it is important not only to effectively treat the disease in the mother, but also not to harm the baby. Therefore, a doctor is needed - a specialist who will assess the risks and help you choose the most effective and at the same time safe treatment.
What is the treatment for SARS during pregnancy in the 1st trimester?
+
At this time, the laying of the internal organs of the fetus occurs, so you need to act as delicately as possible. Preparations during this period must be selected carefully so as not to disrupt the processes of organ formation and not provoke malformations.
Preparations during this period must be selected carefully so as not to disrupt the processes of organ formation and not provoke malformations.
How to bring down the temperature during pregnancy?
+
The temperature during pregnancy can be brought down in several ways - with the help of physical cooling, for example, a cool compress on the forehead or rubbing the body with cold water. It is only important to understand that hypothermia will not benefit and act carefully. Of the antipyretic drugs, paracetamol-based products are recommended for expectant mothers.
What pills can pregnant women?
+
The expectant mother can take the drugs prescribed by a competent doctor. The specialist will assess the need for a particular remedy, as well as the potential risk to her baby. I also recommend that you always read the annotations to the drugs, there is a section "use during pregnancy" and breastfeeding. It contains information about whether these tablets and capsules are allowed for the expectant mother.
It contains information about whether these tablets and capsules are allowed for the expectant mother.
What can a low temperature during pregnancy in the 3rd trimester mean?
+
Most often, this situation is observed with a decline in strength and a decrease in immunity. If the situation persists for 2-3 days, it is recommended to consult a doctor observing the pregnancy. It also makes sense to double-check the thermometer readings by measuring the temperature on the control device.
What antipyretics can I take during pregnancy in the 3rd trimester?
+
The temperature during pregnancy in the 3rd trimester can be paracetamol-based. Such drugs do not have a negative effect on the fetus, while helping the mother - they reduce fever and reduce pain, which often accompanies colds.
What antiviral can be used during pregnancy in the 3rd trimester?
+
Interferon-based antiviral drugs are well suited for the treatment of SARS in the third trimester. It is important that the annotation states that the drug is approved for use during pregnancy and the period of breastfeeding.
It is important that the annotation states that the drug is approved for use during pregnancy and the period of breastfeeding.
We publish only verified information
Article author
Menshikova Maria Viktorovna obstetrician-gynecologist
Experience 38 years
Consultations 1816
Articles 46
Specialist with extensive practical experience. He has a certificate of a mammologist, a certificate of professional certification. Participates in foreign business trips and individual training programs (Los Angeles).
He has a certificate of a mammologist, a certificate of professional certification. Participates in foreign business trips and individual training programs (Los Angeles).
- 1982 - 1986 NPO MONIIAG - obstetrician-gynecologist
- 1987 - 1989 VNITs OZMIR - obstetrician-gynecologist
- 1989 - 1992 departmental polyclinic st. Moscow - Kurskaya - obstetrician-gynecologist
- 1992 - 2001 NPO MONIIAG - obstetrician-gynecologist
- 2007 - 2008 NP KMIKM - doctor administrator
- 2009 - 2013 Pereslavl Central District Hospital, women's consultation - obstetrician-gynecologist
- 2020 to present Teledoctor24 LLC - doctor - consultant (gynecologist)
Sources
- ... P.V.Budanov, A.N.Strizhakov, V.V.Malinovskaya, Yu.V.Kazarova, “Discoordination of systemic inflammation in intrauterine infection”, Issues of gynecology, obstetrics and perinatology, 2009.

- ... Guidelines for the diagnosis, treatment and prevention of influenza in pregnant women, 2014
- ... Klimanova R.R., Malinovskaya V.V., Parshina O.V., Guseva T.S., Novikova S.V., Torshina Z.V., Zarochentseva N.V. "The effect of viral infections on the cytokine profile in pregnant women with a burdened obstetric history and immunocorrective therapy with interferon
Share:
Category: Pregnancy and childbirth
About health Pregnancy and childbirth About children healthy lifestyle Psychology Neurology Gastroenterology Personal care Medicines and dietary supplementsPrevious article
Medical interruption .