4 month old length
What is the average baby length? Growth chart by month
Most newborn babies follow a predictable level of growth during their first year. People can track the length of their baby using average growth charts.
The average length of a full-term newborn baby is 19–20 inches (in), or 48.2–50.8 centimeters (cm). However, a length of around 18.5–20.9 in, or 47–53 cm, is also typical.
Male babies are slightly longer than female babies. Doctors measure a baby’s length from the top of their head to the heel of their foot.
This article looks at the average baby length, month-by-month, for the first year of life. We also discuss what it means when a baby is shorter or longer than average and when to speak with a doctor.
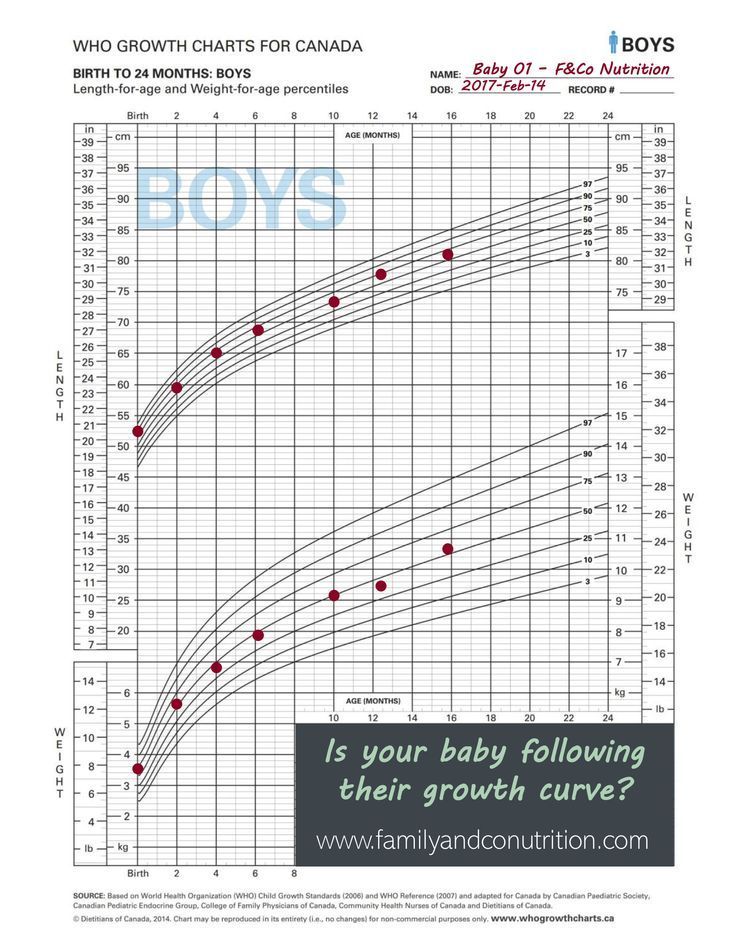
The World Health Organization (WHO) publishes standard infant growth charts according to the expected growth of children in six countries, including the United States, in optimal growth environments. This includes those who engage in breastfeeding.
It is important to note that most people use the terms “length” and “height” interchangeably. However, until the age of 2 years, most doctors will measure babies’ lengths lying down. In measurement terms, experts call this recumbent length. This is different from height, which doctors will measure after the age of 2 years when a child is able to stand.
In the first year of their lives, babies typically grow in length by 50%. According to the WHO’s growth charts, the average lengths for male babies and female babies by month are as follows:
| Age | Male baby | Female baby |
| Birth | 19.69 in (50 cm) | 19.29 in (49 cm) |
| 1 month | 21.65 in (55 cm) | 21.26 in (54 cm) |
| 2 months | 23.03 in (58.5 cm) | 22.44 in (57 cm) |
| 3 months | 24.21 in (61.5 cm) | 23.62 in (60 cm) |
| 4 months | 25. 20 in (64 cm) 20 in (64 cm) | 24.41 in (62 cm) |
| 5 months | 25.98 in (66 cm) | 25.20 in (64 cm) |
| 6 months | 26.77 in (68 cm) | 25.48 in (66 cm) |
| 7 months | 27.17 in (69 cm) | 26.38 in (67 cm) |
| 8 months | 27.95 in (71 cm) | 27.17 in (69 cm) |
| 9 months | 28.35 in (72 cm) | 27.56 in (70 cm) |
| 10 months | 28.74 in (73 cm) | 28.15 in (71.5 cm) |
| 11 months | 29.33 in (74.5 cm) | 28.74 in (73 cm) |
| 12 months | 29.92 in (76 cm) | 29.13 in (74 cm) |
It is important to note that the above numbers represent averages. Children can be healthy at a wide range of heights. No matter how long a baby is at birth, they are likely to grow at similar rates to other babies.
This means that if a baby is born longer than average, they are likely to stay this way during their first or second year of growth.
A baby’s growth in length during the first year almost always depends on their length at birth, unless they have significant issues, such as feeding difficulties or medical problems, that may cause insufficient length or weight gain.
For this reason, length alone does not reveal whether a baby is healthy. Weight is also an important consideration, especially since many newborns lose some weight after birth. Doctors will also look at factors, including gestational age and how much and how well a baby is eating.
Most healthy babies follow a similar growth pattern during the first year of life. After that, growth rates vary, and a baby’s length is not usually a good predictor of their height as an adult.
A parent or caregiver who takes their baby in for measuring should also know that an infant’s measured length can vary according to who is doing the measuring and how much the baby is moving around at the time. Research shows that length measurements during infant well checkups have the most measurement errors.
Therefore, if it seems there is an unexpected change in a baby’s length from one visit to the next, it can be due to differences in measuring. A person may wish to request another measurement during the visit or at the next one to rule out a legitimate issue.
Babies who are much smaller or larger than average in weight and length are more likely to experience health complications.
However, there is a wide variation in healthy birth weights, so parents and caregivers may not need to have concerns. A doctor will assess how closely they need to monitor a baby’s growth over time. Growth rates for length are fairly predictable among babies in the first year of life. Doctors are more interested in a baby’s overall growth pattern than their length.
A child who falls below the 5th percentile may have an atypical growth pattern. By the age of 12 months, having a length of 28.5 in as a male infant or 27.5 in for a female infant puts them below the fifth percentile.
However, this may not be apparent immediately. A baby who will be a tall adult may have a shorter length at birth and in the first year or two of life.
A baby who will be a tall adult may have a shorter length at birth and in the first year or two of life.
Numerous other factors may affect a child’s height, including:
- Genetics: Children are likely to be a similar height to their biological parents.
- The pregnancy: Research shows that factors, such as maternal anemia, high blood pressure, gestational diabetes, or obesity, may impact a baby’s growth after birth.
- Nutrition: Following a nutritious diet supports healthy growth.
- Hormones: Some children with hormonal imbalances grow slowly or more quickly than their peers.
- Health: A baby whose growth slows down that they fall into a much lower length group or whose length is persistently at a lower level may have a health issue. Some children with certain genetic conditions, such as Down syndrome, may be smaller than others.
- Medications: Some medications, such as steroids, including prednisone, may stunt growth.
People often do not see the effect of these issues on height in the first year of life.
During the first year of life, children should see their pediatrician at least seven times to monitor growth and overall health.
However, doctors’ recommendations may vary slightly. In general, a pediatrician will want to examine the baby at the following times in the first year:
- 3–5 days old
- 1 month old
- 2 months old
- 4 months old
- 6 months old
- 9 months old
- 12 months
A healthcare professional may recommend more frequent visits for a baby who loses a lot of weight after birth or has an unusual growth pattern.
In the early weeks of life, it can be difficult for parents or caregivers to know how much to feed a newborn. If the baby loses weight after birth, there could be feelings of pressure to help them regain the weight as quickly as possible, especially if the infant was born prematurely or has other health risk factors.
However, the amount of food newborns eat affects their weight much more than their length in the early stages of life. Insufficient weight gain needs to be present for a long time in infants before it affects their length.
Insufficient growth in length by itself in the first year is very uncommon and would more likely be due to a genetic syndrome or other uncommon condition.
How much should breastfed babies eat?
Most breastfed newborns eat every 1–3 hours. Over time, the time between feedings may expand to 2–4 hours. People can feed the baby on demand by following the baby’s feeding cues.
Since a nursing person cannot measure how much milk they are giving the baby, they can gauge whether the baby is getting enough milk by looking at the frequency of nursing and diaper changes. These indicators include the following:
- The baby is nursing at least 8–12 times in 24 hours
- By day 2, the baby should have at least two wet diapers in 24 hours. By day days 3 and 4, at least three or more wet diapers, and by day 5, at least six or more wet diapers.
- By day 4, at least 3–5 bowel movements a day.
- The baby is gaining weight.
How much should formula-fed babies eat?
Formula-fed babies may eat less frequently than breastfed babies. After the first few days, people typically feed formula-fed babies with 1–2 ounces (oz) of milk per feeding, which may increase to 2–4 oz by the end of the first month.
Like breastfed newborns, formula-fed infants should eventually eat 8–12 times in 24 hours, including at night. This will continue until they are approximately 6 months old when the child is ready to begin eating solid foods.
Like adults, babies are unique — there is no right or ideal length. As long as the infant is growing normally and does not suddenly fall well below their previous growth percentile, they are usually fine.
Before the age of 2 years, doctors usually measure a baby’s length lying down. After the age of 2 years, when a child is able to stand, a doctor can begin to measure their standing height.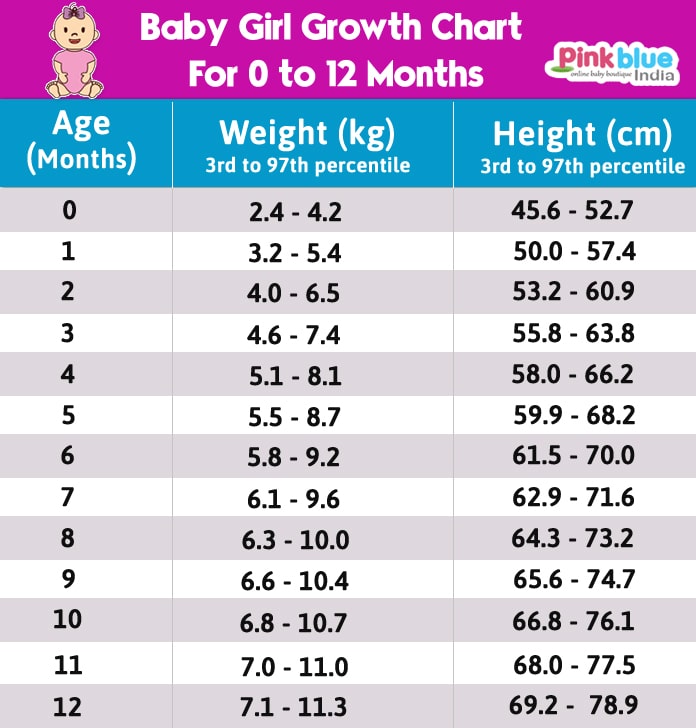
Caregivers should know that at this stage, doctors may switch from the WHO growth charts to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s (CDC) growth reference charts.
Since standing height measures slightly less than recumbent length, a child’s classification may change slightly at this point. The pediatrician can help parents and caregivers answer questions about length, growth, nutrition, and more.
What is the average baby length? Growth chart by month
Most newborn babies follow a predictable level of growth during their first year. People can track the length of their baby using average growth charts.
The average length of a full-term newborn baby is 19–20 inches (in), or 48.2–50.8 centimeters (cm). However, a length of around 18.5–20.9 in, or 47–53 cm, is also typical.
Male babies are slightly longer than female babies. Doctors measure a baby’s length from the top of their head to the heel of their foot.
This article looks at the average baby length, month-by-month, for the first year of life. We also discuss what it means when a baby is shorter or longer than average and when to speak with a doctor.
We also discuss what it means when a baby is shorter or longer than average and when to speak with a doctor.
The World Health Organization (WHO) publishes standard infant growth charts according to the expected growth of children in six countries, including the United States, in optimal growth environments. This includes those who engage in breastfeeding.
It is important to note that most people use the terms “length” and “height” interchangeably. However, until the age of 2 years, most doctors will measure babies’ lengths lying down. In measurement terms, experts call this recumbent length. This is different from height, which doctors will measure after the age of 2 years when a child is able to stand.
In the first year of their lives, babies typically grow in length by 50%. According to the WHO’s growth charts, the average lengths for male babies and female babies by month are as follows:
| Age | Male baby | Female baby |
| Birth | 19. 69 in (50 cm) 69 in (50 cm) | 19.29 in (49 cm) |
| 1 month | 21.65 in (55 cm) | 21.26 in (54 cm) |
| 2 months | 23.03 in (58.5 cm) | 22.44 in (57 cm) |
| 3 months | 24.21 in (61.5 cm) | 23.62 in (60 cm) |
| 4 months | 25.20 in (64 cm) | 24.41 in (62 cm) |
| 5 months | 25.98 in (66 cm) | 25.20 in (64 cm) |
| 6 months | 26.77 in (68 cm) | 25.48 in (66 cm) |
| 7 months | 27.17 in (69 cm) | 26.38 in (67 cm) |
| 8 months | 27.95 in (71 cm) | 27.17 in (69 cm) |
| 9 months | 28.35 in (72 cm) | 27.56 in (70 cm) |
| 10 months | 28.74 in (73 cm) | 28.15 in (71.5 cm) |
| 11 months | 29.33 in (74.5 cm) | 28.74 in (73 cm) |
| 12 months | 29.92 in (76 cm) | 29.13 in (74 cm) |
It is important to note that the above numbers represent averages. Children can be healthy at a wide range of heights. No matter how long a baby is at birth, they are likely to grow at similar rates to other babies.
Children can be healthy at a wide range of heights. No matter how long a baby is at birth, they are likely to grow at similar rates to other babies.
This means that if a baby is born longer than average, they are likely to stay this way during their first or second year of growth.
A baby’s growth in length during the first year almost always depends on their length at birth, unless they have significant issues, such as feeding difficulties or medical problems, that may cause insufficient length or weight gain.
For this reason, length alone does not reveal whether a baby is healthy. Weight is also an important consideration, especially since many newborns lose some weight after birth. Doctors will also look at factors, including gestational age and how much and how well a baby is eating.
Most healthy babies follow a similar growth pattern during the first year of life. After that, growth rates vary, and a baby’s length is not usually a good predictor of their height as an adult.![]()
A parent or caregiver who takes their baby in for measuring should also know that an infant’s measured length can vary according to who is doing the measuring and how much the baby is moving around at the time. Research shows that length measurements during infant well checkups have the most measurement errors.
Therefore, if it seems there is an unexpected change in a baby’s length from one visit to the next, it can be due to differences in measuring. A person may wish to request another measurement during the visit or at the next one to rule out a legitimate issue.
Babies who are much smaller or larger than average in weight and length are more likely to experience health complications.
However, there is a wide variation in healthy birth weights, so parents and caregivers may not need to have concerns. A doctor will assess how closely they need to monitor a baby’s growth over time. Growth rates for length are fairly predictable among babies in the first year of life. Doctors are more interested in a baby’s overall growth pattern than their length.
Doctors are more interested in a baby’s overall growth pattern than their length.
A child who falls below the 5th percentile may have an atypical growth pattern. By the age of 12 months, having a length of 28.5 in as a male infant or 27.5 in for a female infant puts them below the fifth percentile.
However, this may not be apparent immediately. A baby who will be a tall adult may have a shorter length at birth and in the first year or two of life.
Numerous other factors may affect a child’s height, including:
- Genetics: Children are likely to be a similar height to their biological parents.
- The pregnancy: Research shows that factors, such as maternal anemia, high blood pressure, gestational diabetes, or obesity, may impact a baby’s growth after birth.
- Nutrition: Following a nutritious diet supports healthy growth.
- Hormones: Some children with hormonal imbalances grow slowly or more quickly than their peers.

- Health: A baby whose growth slows down that they fall into a much lower length group or whose length is persistently at a lower level may have a health issue. Some children with certain genetic conditions, such as Down syndrome, may be smaller than others.
- Medications: Some medications, such as steroids, including prednisone, may stunt growth.
People often do not see the effect of these issues on height in the first year of life.
During the first year of life, children should see their pediatrician at least seven times to monitor growth and overall health.
However, doctors’ recommendations may vary slightly. In general, a pediatrician will want to examine the baby at the following times in the first year:
- 3–5 days old
- 1 month old
- 2 months old
- 4 months old
- 6 months old
- 9 months old
- 12 months
A healthcare professional may recommend more frequent visits for a baby who loses a lot of weight after birth or has an unusual growth pattern.
In the early weeks of life, it can be difficult for parents or caregivers to know how much to feed a newborn. If the baby loses weight after birth, there could be feelings of pressure to help them regain the weight as quickly as possible, especially if the infant was born prematurely or has other health risk factors.
However, the amount of food newborns eat affects their weight much more than their length in the early stages of life. Insufficient weight gain needs to be present for a long time in infants before it affects their length.
Insufficient growth in length by itself in the first year is very uncommon and would more likely be due to a genetic syndrome or other uncommon condition.
How much should breastfed babies eat?
Most breastfed newborns eat every 1–3 hours. Over time, the time between feedings may expand to 2–4 hours. People can feed the baby on demand by following the baby’s feeding cues.
Since a nursing person cannot measure how much milk they are giving the baby, they can gauge whether the baby is getting enough milk by looking at the frequency of nursing and diaper changes. These indicators include the following:
These indicators include the following:
- The baby is nursing at least 8–12 times in 24 hours
- By day 2, the baby should have at least two wet diapers in 24 hours. By day days 3 and 4, at least three or more wet diapers, and by day 5, at least six or more wet diapers.
- By day 4, at least 3–5 bowel movements a day.
- The baby is gaining weight.
How much should formula-fed babies eat?
Formula-fed babies may eat less frequently than breastfed babies. After the first few days, people typically feed formula-fed babies with 1–2 ounces (oz) of milk per feeding, which may increase to 2–4 oz by the end of the first month.
Like breastfed newborns, formula-fed infants should eventually eat 8–12 times in 24 hours, including at night. This will continue until they are approximately 6 months old when the child is ready to begin eating solid foods.
Like adults, babies are unique — there is no right or ideal length. As long as the infant is growing normally and does not suddenly fall well below their previous growth percentile, they are usually fine.
Before the age of 2 years, doctors usually measure a baby’s length lying down. After the age of 2 years, when a child is able to stand, a doctor can begin to measure their standing height.
Caregivers should know that at this stage, doctors may switch from the WHO growth charts to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s (CDC) growth reference charts.
Since standing height measures slightly less than recumbent length, a child’s classification may change slightly at this point. The pediatrician can help parents and caregivers answer questions about length, growth, nutrition, and more.
| Age and physical characteristics | Skills |
| At birth Height (length) - 49-50 cm Weight - 3200-3300 g Head circumference - 34-34.5 cm Chest circumference - 32-34 cm | Moves legs and arms while awake. Starts and starts to blink at sharp sounds. Responds to a stimulus by crying. |
| 1 month Height (length) - 54-55 cm Weight - 4200-4500 g Head circumference - 36.5-37 cm Chest circumference - 36-36.5 cm | Tries to raise the head in the prone position and hold it for up to 5 seconds. Follows moving bright objects and an adult's face. Responds to harsh sounds. Replies with a smile. Starts babbling. |
| 2 months Height (length) - 57-58 cm Weight - 5100-5600 g Head circumference - 38-39 cm Chest circumference - 38-39 cm | Holds the head for a long time. Turns to the sound of an adult speaking. Grabs objects reflexively. Actively interested in the outside world. hoots. |
| 3 months Height (length) - 60-61.5 cm Weight - 5800-6400 g Head circumference - 39.5-40.5 cm Chest circumference - 40-42 cm | Holds head well in upright position. Looks at objects for a long time. Makes different sounds. Supported under the armpits by legs. Raises on the forearms in the prone position. Turns on its side from the back. Emotionally responds to the conversation, shows dissatisfaction with loud crying. Sucking fingers or cam |
| 4 months Height (length) - 62-64 cm Weight - 6400-7000 g Head circumference - 40.5-41.5 cm Chest circumference - 41.5-42 cm | Confidently raises his head, lying on his tummy. Handles mother's breast or bottle during feeding. Laughs and smiles when playing. Long hums. Grabs hanging objects with hands. Rolls over from back to stomach. In the position on the stomach, he rises with support on the palm of his hand. Lying on the back, raises the head and shoulders. |
| 5 months Height (length) - 64-66 cm Weight - 6900-7500 g Head circumference - 41.5-42.5 cm Chest circumference - 43-44 cm | Recognizes mother and other close people. Consciously follows the object with his eyes. Rolls over from tummy to supine position. Grabs and holds objects with both hands. Takes an item from an adult's hand. Sitting with support. Long humming in a singsong voice. Responds to heard nursery rhymes and songs. Looking at pictures. |
| 6 months Height (length) - 66-67.5 cm Weight - 7300-7900 g Head circumference - 42-43 cm Chest circumference - 44-45.5 cm | Sitting without support. Stretches hands towards an object of interest. Picks up a toy that has fallen out of hand. Tries objects "by the tooth". Begins to crawl. Learns to eat from a spoon. Begins to say syllables. Tries to stand on his feet, holding on to a support. Responds to a name. Listens carefully to an adult. Looks for an object that an adult is talking about. |
| 7 months Height (length) - 67-69 cm Weight - 7600-8300 g Head circumference - 43-44 cm Chest circumference - 45-46.5 cm | Crawls and sits well. Stands with both hands supported. Holds an irregularly shaped object in his hand. Plays with toys for a long time, studying their properties. Drinks from a mug with the help of an adult. Tries to sit up. Displays body parts. |
| 8 months Height (length) - 69-70.5 cm Weight - 7900-8600 g Head circumference - 43.5-44.5 cm Chest circumference - 46-47 cm | Looking for a toy that has fallen. Transfers an item from one pen to another. Gets up holding onto a support. Crawls fast. Sits down, lies down, steps over objects. Babbles with intonation. Enjoys other children. Shows familiar objects when asked where? Independently holds solid food (rusk, biscuits). Afraid to part with mother. |
| 9 months Height (length) - 70-72 cm Weight - 8200-8900 g Head circumference - 44-45 cm Chest circumference - 47-48 cm | Tries to stand and take the first steps. Imitates other children. Reaches for an object of interest and tries to get it. Consciously manipulates toys. Shows human body parts and toys. Tears and crumples paper. Holding onto a support, dancing to the music. |
| 10 months Height (length) - 71.5-73 cm Weight - 8500-9200 g Head circumference - 44-45.5 cm Chest circumference - 47-48 cm | Begins to pick up small objects with fingers. Puts fingers in holes, opens drawers. Plays hide and seek. Walks with the support of two hands of an adult. Can go up and down stairs (3-4 steps). Understands adult requests. Repeats gestures and sounds after an adult. Simulates animal voices. Waving at parting and meeting. Tries to eat on his own with a spoon. |
| 11 months Height (length) - 73-74. Weight - 8700-9400 g Head circumference - 44.5-46 cm Chest circumference - 48-49 cm | Stands alone. Walks with one hand supported. Lifts objects without crouching (bending down). Able to crouch without support. Assembles a pyramid. Adds cubes. Begins to say "easy" words. Plays patty. Reacts vividly to a stranger or new toys, as well as to praise. Interested in books and musical toys. |
| 12 months Height (length) - 74-76 cm Weight - 8900-9600 g Head circumference - 45-46 cm Chest circumference - 48-49 cm | Tries to walk independently. Gets up from a squatting position. Drinks from a cup independently. Can refuse unloved food. Bites off biscuits and other hard foods. Understands the words "don't" and "may". Recognizes animals and shows them in pictures and on the street. Knows how to use some items. Pronounces 10-15 words. |
Size charts - AnnyBaby
Sizes for newborns
In large stores, clothes are sorted by the height of the child. In the department for newborns, undershirts, bodysuits, panties, overalls are hung or laid out in accordance with growth. The European dimensional grid of children's clothing is more and more widely used in Russian everyday life. The European size grid corresponds to the height of the baby in centimeters, a new size is every 6 cm. In the department for newborns, you will find sizes 50, 56, 62, 68. Most newborns start wearing clothes from size 56, and after one and a half to two months they grow up from it and move on to the next size.
It is difficult to accurately measure the height of a newborn. The easiest way to remember what height was measured at the doctor's appointment, but for this you need to help the nurse measure the growth of your child, put the newborn evenly, not in a hurry, fix it for a second so that the measurement is reliable.
Each manufacturer of children's clothing has its own standards. But since for newborns the cut of clothes is wide, free, the difference is not significant and it is enough to focus on the growth of the newborn. If we talk about the standards of manufacturers, then European manufacturers do not have a single standard and each company sews according to its own standard. Pants are sewn with the diaper in mind. Large Russian manufacturers of children's clothing sew in accordance with GOST. You will find a table of standard sizes according to GOST below, in the section about sliders for newborns. Here is a table of average standard sizes for a variety of manufacturers. I repeat, due to the wide cut of undershirts, bodysuits, overalls for newborns, differences in standards do not greatly affect the result, the main indicator when choosing the size of clothes for a newborn is the growth of the baby.
| Size | 50 | 56 | 62 | 68 | 74 | 80 | 86 | 92 |
| Height in cm | to 50 | 51-56 | 57-62 | 63-68 | 69-74 | 75-80 | 81-86 | 87-92 |
| Chest in cm | 40-43 | 42-45 | 44-47 | 46-49 | 48-51 | 50-53 | 51-55 | 52-56 |
| Waist in cm | 40-43 | 42-45 | 44-47 | 46-48 | 47-50 | 49-51 | 50-52 | 51-53 |
| Hips in cm | 42-44 | 44-46 | 46-48 | 48-50 | 50-52 | 52-54 | 54-56 | 56-58 |
| Estimated age | 0 months | 0-1. 5 months 5 months | 1.5-3 months | 3-6 months | 6-9 months | 9-12 months | 1-1.5 years | 2 years |
Newborn overall sizes
Winter and demi-season overalls for newborns are sized by height in centimeters. They are sewn loose enough to wear blouses, pants, a diaper under the overalls. When choosing a size, keep in mind that a newborn and a baby up to a year old grows very quickly, and the cold season lasts several months, therefore, when buying an expensive thing for growth, it is easy to make a mistake with the size. We recommend buying a jumpsuit for a newborn on the eve of the season.
Newborn slider sizes
For the first time, most mothers encounter the Russian dimensional grid when choosing rompers, panties, and T-shirts. The Russian dimensional grid of children's clothing differs from the European one not only in standard metric indicators, but also in the main size. If you see size 18, 20, 22 on Russian-made clothes, then this is a Russian dimensional grid. You can find a table with the Russian dimensional grid of clothes for newborns here, just below.
If you see size 18, 20, 22 on Russian-made clothes, then this is a Russian dimensional grid. You can find a table with the Russian dimensional grid of clothes for newborns here, just below.
We would like to draw your attention to the fact that the Russian dimensional grid is focused on not very well-fed children. Today, most newborns are larger than 30-50 years ago, when GOST was created. Therefore, when choosing a size according to the table below, pay attention not only to height, but also to the circumference of your child's chest. First, according to the height of the newborn, find the appropriate size in the table, then compare what chest girth in the table and the baby. If the newborn has a smaller bust than in the table, choose the size corresponding to the height. If the newborn has a larger chest circumference than indicated in the table, take a larger size.
| Size | 18 | 20 | 22 | 24 | 26 |
| Height in cm | 50-56 | 62-68 | 74 | 80 | 86-92 |
| Chest in cm | 40 | 44 | 44 | 48 | 52 |
| Waist in cm | 40 | 44 | 45 | 48 | 52 |
| Hips in cm | 42 | 46 | 50 | 54 | 56 |
| Estimated age | 0-1. 5 months 5 months | 1.5-6 months | 6-9 months | 9-12 months | 1-2 years |
Sock sizes for newborns and toddlers up to two years
The size of the socks is determined by the length of the foot in centimeters. Foot length is measured from heel to toe. It is convenient for a newborn to measure the leg when he sleeps. For the most reliable measurement, try tracing the outline of the foot on paper and measure the length of the foot on the paper.
Children's socks have different sizes. Most often there is a grid after 2 cm for even values, for example, in most Russian manufacturers. Some manufacturers produce socks according to the size grid in 1 cm.
| Size | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 |
| Russian size | 10 | 12 | 14 | ||||||
| Foot length in cm | to 6.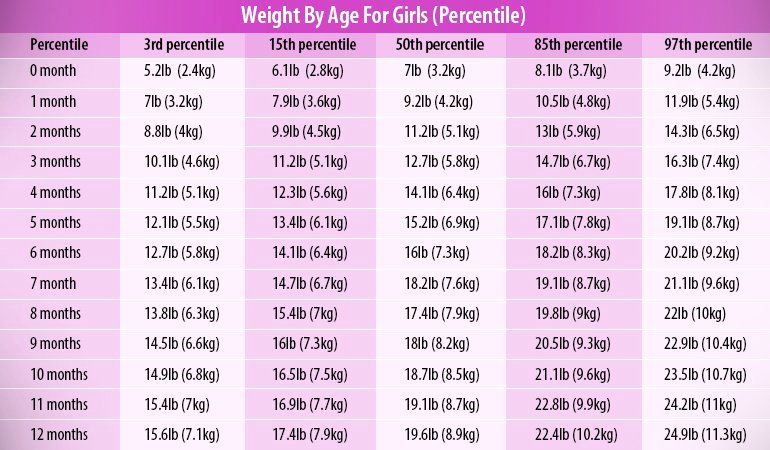 4 4 | 6.5-7.4 | 7.5-8.4 | 8.5-9.4 | 9.5-10.4 | 10.5-11.4 | 11.5-12.4 | 12.5-13.4 | 13.5-14.4 |
| Estimated age | 0-1 month | 0-1.5 months | 0-3 months | 1.5-3 months | 3-6 months | 6-9 months | 9-12 months | 1-1.5 years | 1.5-2 years |
Children's tights sizes
Children's tights are measured by height in centimeters. Manufacturers provide a standard foot length (see size chart). If the baby has a large leg, take stretchy tights. For a chubby newborn, choose tights for the next size chart.
Tights are double sized, but sizes vary from manufacturer to manufacturer. Some manufacturers sew children's tights in sizes 50-56, 62-68, 74-80, 86-92. Others - 56-62, 68-74, 80-86. Which is very convenient, because. allows you to choose the size of the newborn tights. Large children's stores sell tights in both sizes.
Large children's stores sell tights in both sizes.
In the table we present both dimensional grids of children's tights at the same time, in sizes for newborns and babies up to two years old.
| Size | 50-56 | 56-62 | 62-68 | 68-74 | 74-80 | 80-86 | 86-92 |
| Foot length in cm | 7 | 8 | 9 | 9-10 | 11-12 | 12-13 | 13-14 |
| Estimated age | 0-1.5 months | 0-3 months | 1.5-6 months | 3-9 months | 6-12 months | 9-18 months | 1-2 years |
Sizes of baby caps and caps
Sizes of baby caps and caps are determined by the head circumference in centimeters. You need to measure your head exactly along the eyebrows, above the ears and further to the back of the head. We measure the newborn when he lies, then lower the centimeter from the eyebrows to the back of the head vertically. If the newborn is already holding the head, it is better to measure the circumference of the head when someone is holding it. If the baby is already sitting, measure while sitting. Then we clasp the head with a centimeter strictly horizontally.
You need to measure your head exactly along the eyebrows, above the ears and further to the back of the head. We measure the newborn when he lies, then lower the centimeter from the eyebrows to the back of the head vertically. If the newborn is already holding the head, it is better to measure the circumference of the head when someone is holding it. If the baby is already sitting, measure while sitting. Then we clasp the head with a centimeter strictly horizontally.
Caps for newborns and children's hats are very different in size: letter and number, single and double, according to size grids in 1, 2 or 4 cm. Most manufacturers sew caps and hats according to size grids with double sizes 36-38, 40 -42 or 38-40, 42-44 or according to the size grid after 2 cm, for example, 36, 38, 40, 42. Sometimes, along with the volume of the head, the height of the newborn is indicated, for example, 36/56, 40/62, 44 / 68, or the age of the child.
For the sake of safety and health, we recommend wearing bonnets and caps, especially for newborns, in size.
| Age of boys | 0 months | 1 month | 2 months | 3 months | 6 months | 9 months | 1 year | 1.5 years | 2 years |
| Medium head circumference | 34-39 | 37-41 | 39-43 | 41-45 | 43-47 | 45-48 | 47-49 | 48-50 | 48-51 |
| Age of girls | 0 months | 1 month | 2 months | 3 months | 6 months | 9 months | 1 year | 1.5 years | 2 years |
| Medium | 32-38 | 35-40 | 37-42 | 39-44 | 41-46 | 43-47 | 45-48 | 47-49 | 48-50 |
If you have come across the letter designation of the cap size for a newborn or baby hat, then the table below will help you determine the appropriate size:
| XXS | XS | S | M | |
| Head circumference | 40-43 | 44-46 | 47-49 | 50-52 |
Baby & Toddler Mittens & Mittens Sizes
The Russian size of children's mittens and mittens is determined by the girth of the palm, excluding the thumb in centimeters.



 5 cm
5 cm