Where does ectopic pregnancy occur
Ectopic Pregnancy (for Parents) - Nemours KidsHealth
What Is an Ectopic Pregnancy?
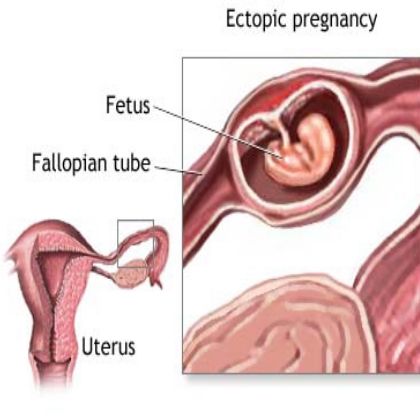
In a normal pregnancy, the fertilized egg implants and develops in the uterus. In an ectopic pregnancy, the egg implants somewhere other than the uterus — often, in the fallopian tubes. This is why ectopic pregnancies are commonly called "tubal pregnancies." The egg also can implant in the ovary, abdomen, or the cervix.
None of these areas has the right space or nurturing tissue for a pregnancy to develop. As the fetus grows, it will eventually burst the organ that contains it. This can cause severe bleeding and endanger the mother's life. A classical ectopic pregnancy does not develop into a live birth.
What Are the Signs & Symptoms of an Ectopic Pregnancy?
Ectopic pregnancy can be hard to diagnose because symptoms often are like those of a normal early pregnancy. These can include missed periods, breast tenderness, nausea, vomiting, tiredness, or frequent urination (peeing).
Often, the first warning signs of an ectopic pregnancy are pain or vaginal bleeding. There might be pain in the pelvis, abdomen, or even the shoulder or neck (if blood from a ruptured ectopic pregnancy builds up and irritates certain nerves). The pain can range from mild and dull to severe and sharp. It might be felt on just one side of the pelvis or all over.
These symptoms also might happen with an ectopic pregnancy:
- vaginal spotting
- dizziness or fainting (caused by blood loss)
- low blood pressure (also caused by blood loss)
- lower back pain
What Causes an Ectopic Pregnancy?
An ectopic pregnancy usually happens because a fertilized egg couldn’t quickly move down the fallopian tube into the uterus. The tube can get blocked from an infection or inflammation. The tube can get blocked from:
- pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)
- endometriosis, when cells from the lining of the uterus implant and grow elsewhere in the body
- scar tissue from previous abdominal or fallopian surgeries
- rarely, birth defects that changed the shape of the tube
How Is an Ectopic Pregnancy Diagnosed?
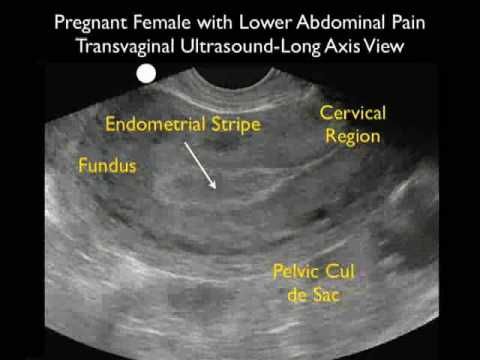
If a woman might have an ectopic pregnancy, her doctor may do an ultrasound to see where the developing fetus is. Often, pregnancies are too small to see on ultrasound until more than 5 or 6 weeks after a woman’s last menstrual period. If an external ultrasound can’t show the pregnancy, the doctor might do the test with a wand-like device in the vagina.
Often, pregnancies are too small to see on ultrasound until more than 5 or 6 weeks after a woman’s last menstrual period. If an external ultrasound can’t show the pregnancy, the doctor might do the test with a wand-like device in the vagina.
A woman might need testing every few days if the first tests can’t confirm or rule out an ectopic pregnancy.
How Is an Ectopic Pregnancy Treated?
How doctors treat an ectopic pregnancy depends on things like the size and location of the pregnancy.
Sometimes they can treat an early ectopic pregnancy with an injection of methotrexate, which stops the growth of the embryo. The tissue usually is then absorbed by the woman’s body.
If the pregnancy is farther along, doctors usually need to do surgery to remove the abnormal pregnancy.
Whatever treatment she gets, a woman will see her doctor regularly afterward to make sure her pregnancy hormone levels return to zero. This may take several weeks. An elevated level could mean that some ectopic tissue was missed.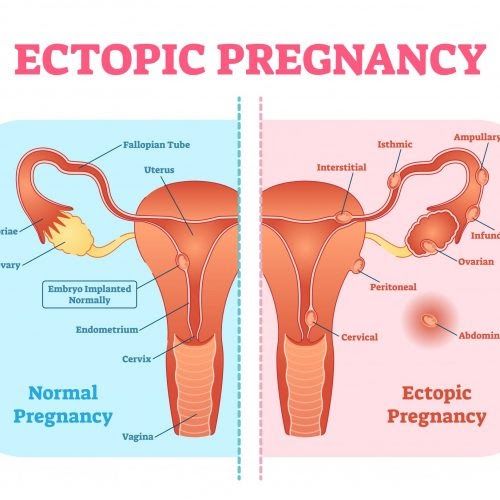 If so, she might need more methotrexate or surgery.
If so, she might need more methotrexate or surgery.
What About Future Pregnancies?
Most women who have had an ectopic pregnancy can have normal pregnancies in the future. Having had one ectopic pregnancy does increase a woman’s risk of having another one.
What Else Should I Know?
Any woman can have an ectopic pregnancy. But the risk is higher for women who are older than 35 and those who have had:
- PID
- a previous ectopic pregnancy
- surgery on a fallopian tube
- infertility problems or medicine to stimulate ovulation
Some birth control methods also can affect a woman's risk of ectopic pregnancy. Those who become pregnant while using an intrauterine device (IUD) might be more likely to have an ectopic pregnancy. Smoking and having multiple sexual partners also increase the risk of an ectopic pregnancy.
When Should I Call the Doctor?
If you believe you're at risk for an ectopic pregnancy, meet with your doctor to talk about your options before you become pregnant. If you are pregnant and have any concerns about the pregnancy being ectopic, talk to your doctor — it's important to find it early. Your doctor might want to check your hormone levels or schedule an early ultrasound to ensure that your pregnancy is developing normally.
If you are pregnant and have any concerns about the pregnancy being ectopic, talk to your doctor — it's important to find it early. Your doctor might want to check your hormone levels or schedule an early ultrasound to ensure that your pregnancy is developing normally.
Call your doctor right away if you're pregnant and having any pain, bleeding, or other symptoms of ectopic pregnancy.
Ectopic pregnancy Information | Mount Sinai
Tubal pregnancy; Cervical pregnancy; Tubal ligation - ectopic pregnancy
An ectopic pregnancy is a pregnancy that occurs outside the womb (uterus).
Laparoscopy is performed when less-invasive surgery is desired. It is also called Band-Aid surgery because only small incisions need to be made to accommodate the small surgical instruments that are used to view the abdominal contents and perform the surgery.
It is also called Band-Aid surgery because only small incisions need to be made to accommodate the small surgical instruments that are used to view the abdominal contents and perform the surgery.
The ultrasound has become a standard procedure used during pregnancy. It can demonstrate fetal growth and can detect increasing numbers of conditions in the fetus including meningomyelocele, congenital heart disease, kidney abnormalities, hydrocephalus, anencephaly, club feet, and other deformities. Ultrasound does not produce ionizing radiation and is considered a very safe procedure for both the mother and the fetus.
External structures of the female reproductive anatomy include the labium minora and majora, the vagina and the clitoris. Internal structures include the uterus, ovaries, and cervix.
The uterus is a hollow muscular organ located in the female pelvis between the bladder and rectum.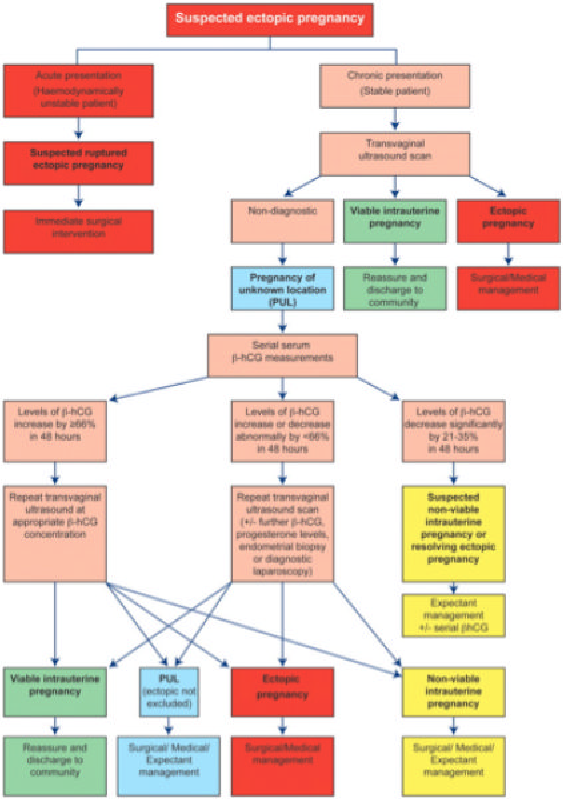 The ovaries produce the eggs that travel through the fallopian tubes. Once the egg has left the ovary it can be fertilized and implant itself in the lining of the uterus. The main function of the uterus is to nourish the developing fetus prior to birth.
The ovaries produce the eggs that travel through the fallopian tubes. Once the egg has left the ovary it can be fertilized and implant itself in the lining of the uterus. The main function of the uterus is to nourish the developing fetus prior to birth.
This is a normal ultrasound of a fetus at 19 weeks gestation. The right foot, including the developing bones, are clearly visible in the middle of the screen.
An ectopic pregnancy is one in which the fertilized egg implants in tissue outside of the uterus and the placenta and fetus begin to develop there. The most common site is within a Fallopian tube, however, ectopic pregnancies can occur in the ovary, the abdomen, and in the lower portion of the uterus (the cervix).
Causes
In most pregnancies, the fertilized egg travels through the fallopian tube to the womb (uterus). If the movement of the egg is blocked or slowed through the tubes, it can lead to an ectopic pregnancy.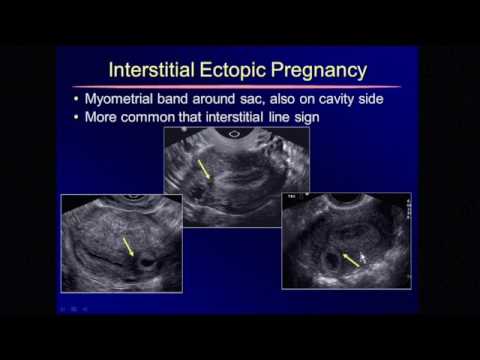 Things that may cause this problem include:
Things that may cause this problem include:
- Birth defect in the fallopian tubes
- Scarring after a ruptured appendix
- Endometriosis
- Having had an ectopic pregnancy in the past
- Scarring from past infections or surgery of the female organs
The following also increase risk for an ectopic pregnancy:
- Age over 35
- Getting pregnant while having an intrauterine device (IUD)
- Having your tubes tied
- Having had surgery to untie tubes to become pregnant
- Having had many sexual partners
- Sexually transmitted infections (STI)
- Some infertility treatments
Sometimes, the cause is not known. Hormones may play a role.
The most common site for an ectopic pregnancy is the fallopian tube. In rare cases, this can occur in the ovary, abdomen, or cervix.
An ectopic pregnancy can occur even if you use birth control.
Symptoms
Symptoms of ectopic pregnancy may include:
- Abnormal vaginal bleeding
- Mild cramping on one side of the pelvis
- No periods
- Pain in the lower belly or pelvic area
If the area around the abnormal pregnancy ruptures and bleeds, symptoms may get worse. They may include:
They may include:
- Fainting or feeling faint
- Intense pressure in the rectum
- Low blood pressure
- Pain in the shoulder area
- Severe, sharp, and sudden pain in the lower abdomen
Exams and Tests
The health care provider will do a pelvic exam. The exam may show tenderness in the pelvic area.
A pregnancy test and vaginal ultrasound will be done.
Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) is a hormone that is produced during pregnancy. Checking the blood level of this hormone can detect pregnancy.
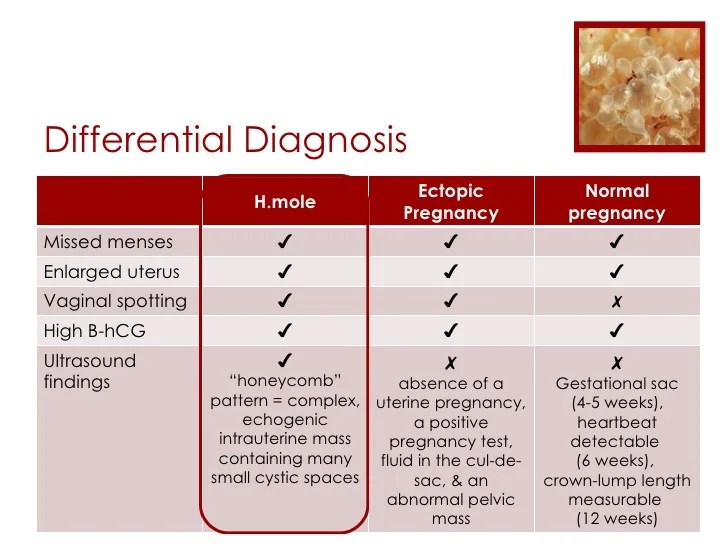
- When hCG levels are above a certain value, a pregnancy sac in the uterus should be seen with ultrasound.
- If the sac is not seen, this may indicate that an ectopic pregnancy is present.

You may need more than one exam, ultrasound, and blood test. Your provider will instruct you about signs to watch for until your next visit.
Treatment
Ectopic pregnancy may be life threatening. The pregnancy cannot continue to birth (term). Effective treatment requires either medical treatment to end the pregnancy or surgical removal of the pregnancy.
If the ectopic pregnancy has not ruptured, treatment may include:
- Surgery
- Medicine that ends the pregnancy, along with close monitoring by your doctor
You will need emergency medical help if the area of the ectopic pregnancy breaks open (ruptures). Rupture can lead to bleeding and shock.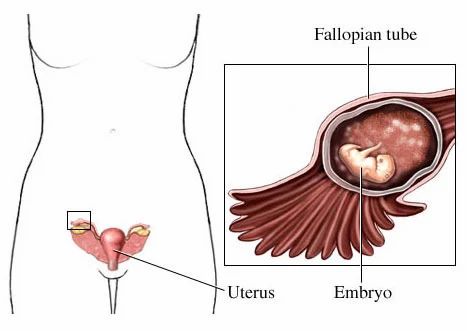 Treatment for shock may include:
Treatment for shock may include:
- Blood transfusion
- Fluids given through a vein
- Keeping warm
- Oxygen
- Raising the legs
If there is a rupture, surgery is done to stop blood loss and remove the pregnancy. In some cases, the doctor may have to remove the fallopian tube.
Outlook (Prognosis)
If diagnosed early, treatment is very effective. It's important to seek early care whenever you believe you may be pregnant so your provider may determine the location of the pregnancy.
One out of three women who have had one ectopic pregnancy can have a baby in the future. Another ectopic pregnancy is more likely to occur.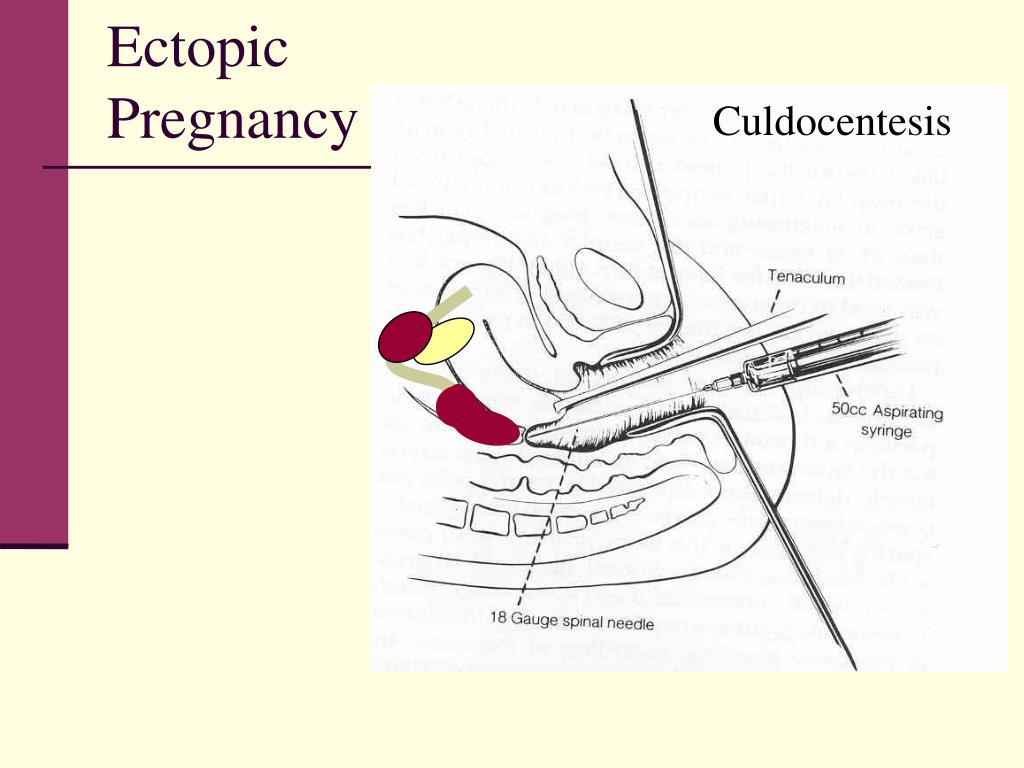 Some women do not become pregnant again.
Some women do not become pregnant again.
The likelihood of a successful pregnancy after an ectopic pregnancy depends on:
- The woman's age
- Whether she has already had children
- Why the first ectopic pregnancy occurred
- The health of her fallopian tubes
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if you have:
- Abnormal vaginal bleeding
- Lower abdominal or pelvic pain or
- Suspect you might be pregnant
Prevention
Most forms of ectopic pregnancy that occur outside the fallopian tubes are probably not preventable. You may be able to reduce your risk by avoiding conditions that may scar the fallopian tubes. These steps include:
You may be able to reduce your risk by avoiding conditions that may scar the fallopian tubes. These steps include:
- Practicing safer sex by taking steps before and during sex, which can prevent you from getting an infection
- Getting early diagnosis and treatment of all STIs
- Stopping smoking
Alur-Gupta S, Cooney LG, Senapati S, Sammel MD, Barnhart KT. Two-dose versus single-dose methotrexate for treatment of ectopic pregnancy: a meta-analysis. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2019;221(2):95-108.e2. PMID: 30629908 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30629908/.
Henn MC, Lall MD. Complications of pregnancy. In: Walls RM, eds. Rosen's Emergency Medicine: Concepts and Clinical Practice. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 173.
Hur HC, Lobo RA.. Ectopic pregnancy: etiology, pathology, diagnosis, management, fertility prognosis.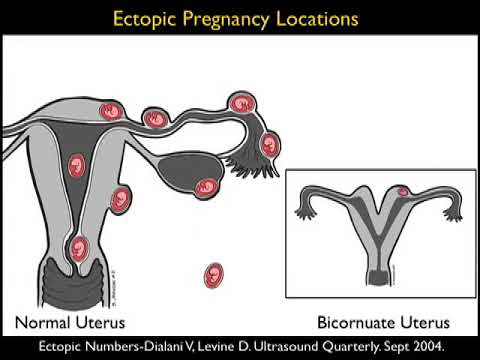 In: Gershenson DM, Lentz GM, Valea FA, Lobo RA, eds. Comprehensive Gynecology. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 17.
In: Gershenson DM, Lentz GM, Valea FA, Lobo RA, eds. Comprehensive Gynecology. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 17.
Nelson AL, Gambone JC. Ectopic pregnancy. In: Hacker NF, Gambone JC, Hobel CJ, eds. Hacker & Moore's Essentials of Obstetrics and Gynecology. 6th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2016:chap 24.
Last reviewed on: 1/10/2022
Reviewed by: John D. Jacobson, MD, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Loma Linda University School of Medicine, Loma Linda, CA. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
Ectopic pregnancy - signs, causes, symptoms, treatment and prevention
Ectopic pregnancy
Table of contents
- What is an ectopic pregnancy and how does it develop?
- Signs and symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy
- Causes of an ectopic pregnancy
- Diagnosis of an ectopic pregnancy
- Treatment of an ectopic pregnancy
- Consequences of an ectopic pregnancy
- Why should you visit the Mama Papa Ya clinic?
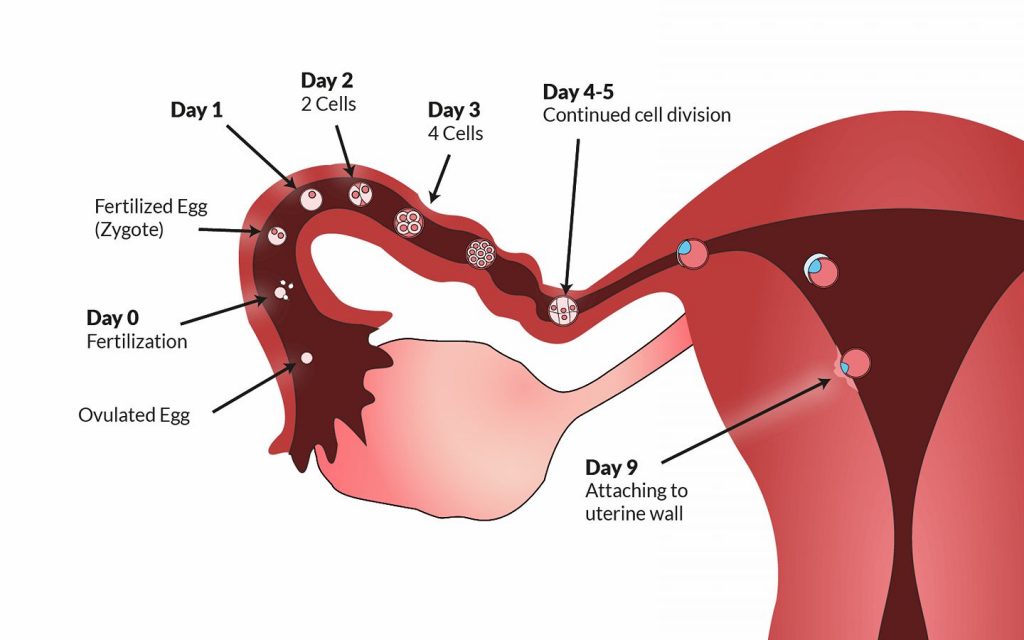
After fertilization, the egg moves sequentially through the cilia of the epithelium along the fallopian tube and attaches to the inner surface of the uterus.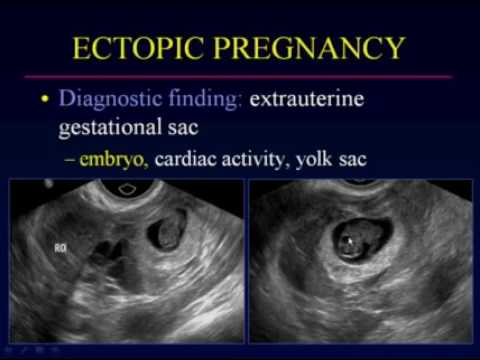 Symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy occur when such implantation occurs outside the surface of the endometrium. This happens in 2% of all conceptions.
Symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy occur when such implantation occurs outside the surface of the endometrium. This happens in 2% of all conceptions.
What is an ectopic pregnancy and how does it develop?
In this condition, the egg is attached not in the uterus, but in the fallopian tube, on the surface of the peritoneum or cervix. At this time, a home pregnancy test will be positive, but the fetal egg will not be able to fully develop and will inevitably die.
Early symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy are a medical emergency. Prompt treatment reduces a woman's risk of complications and increases her chance of having a baby in the future.
Signs and symptoms of ectopic pregnancy
When a patient develops an ectopic pregnancy, early signs are normal. Observed:
- delayed menstruation;
- breast tenderness;
- fatigue;
- nausea;
- frequent urination.
Later signs of ectopic pregnancy appear after 6 to 8 weeks of delayed menstruation:
- slight discharge of blood from the vagina;
- abdominal or pelvic pain.
With further development, the following signs and symptoms of ectopic pregnancy occur:
- pain in the lower abdomen, aggravated by movement; at first, it may suddenly appear on one side, and then spread to the entire pelvic area;
- severe vaginal bleeding;
- soreness during intercourse or gynecological examination;
- dizziness or fainting due to internal bleeding;
- pale skin, cold sweat, shortness of breath, weak rapid pulse, impaired consciousness (signs of shock).
Causes of ectopic pregnancy
The most common type of pathology is tubal, in which a fertilized egg develops in the fallopian tube. Causes of an ectopic pregnancy in such a case include:
- smoking: it interferes with the ability of the fallopian tube to move the fetus into the uterine cavity;
- an inflammatory disease such as gonorrhea or chlamydia that has caused scarring in the tubal cavity;
- previous fallopian tube operation;
- previous ectopic pregnancy.
Risk factors for pathology:
- woman's age over 35;
- surgery for diseases of the abdominal organs;
- multiple abortions;
- endometriosis;
- malformations of the fallopian tubes;
- pregnancy resulting from the use of an intrauterine device.
Diagnosis of ectopic pregnancy
At the beginning of its development, such a pregnancy proceeds as normal, and its termination resembles a spontaneous abortion. How to recognize an ectopic pregnancy? It is very difficult to do this on your own, since such a measureable sign as basal temperature during ectopic pregnancy is not informative - the schedule before the loss of the embryo is the same as during normal gestation.
Diagnosis of ectopic pregnancy is carried out using the following methods:
- gynecological examination, revealing the absence of signs of uterine pregnancy and pathological formation, for example, in the tube;
- Ultrasound, which makes it possible to determine the pathology from 1 - 2 weeks of delayed menstruation, when a fetal egg is not found in the uterus;
- analysis for hCG with an interval of 48 hours, normally the indicator doubles during this time, with an ectopic pregnancy, its increase in the blood is not so great.
Treatment of ectopic pregnancy
A child cannot develop outside the uterus, and the spontaneous interruption of such a pathological process is dangerous for a woman's life. Therefore, the treatment of ectopic pregnancy is only surgical:
- salpingostomy - a longitudinal incision of the tube with subsequent restoration of its wall;
- salpingectomy - removal of part of the tube when it is ruptured.
Both operations can be performed laparoscopically or laparotomically.
There is also a medical method of treatment - methotrexate. It is used only in the earliest stages when the operation is impossible.
Consequences of an ectopic pregnancy
Usually the consequences of an ectopic pregnancy are relatively favorable: although a woman's ability to conceive is reduced by about 40%, she can still carry and give birth to a child. Another negative factor is the increased risk of recurrence of such a pathology.
Recovery from an ectopic pregnancy occurs during the next menstrual cycle. Much more harm to a woman is brought not by physical, but by psychological trauma. Full rehabilitation requires the support of relatives, communication on appropriate forums, and sometimes individual and group psychotherapy.
The negative consequences of an ectopic pregnancy can be reduced if the causes of the disease are immediately looked for and eliminated.
Why should you visit the Mama Papa Ya clinic?
The network of medical clinics "Mama Papa Ya", whose branches are located in Moscow and other cities, offers medical services at affordable prices that will help to avoid the development of pathology or diagnose it in time:
- consultation of a qualified gynecologist on pregnancy planning;
- individual pregnancy management program “Waiting for you, baby!”;
- tests necessary for expectant mothers, including determining the level of hCG;
- gynecological ultrasound for the diagnosis of the disease at an early stage.

All consultations and procedures are carried out at a convenient time for the patient, without waiting and queues.
If you miss your period, we recommend that you take a home pregnancy test and, regardless of the results, make an appointment with a gynecologist. This can be done by calling the nearest clinic or on the website.
Reviews
Good clinic, good doctor! Raisa Vasilievna can clearly and easily explain what the essence of the problem is. If something is wrong, she talks about everything directly, not in a veiled way, as other doctors sometimes do. I don't regret that I went to her.
Anna
I would like to thank the staff of the clinic Mom, Dad, me. The clinic has a very friendly atmosphere, very friendly and cheerful staff and highly qualified specialists. Thank you very much! I wish prosperity to your clinic.
Anonymous user
Today I removed a mole on my face at the dermatologist Kodareva I.A. Doctor is very thorough! Correct! Thanks a lot! Administrator Borshchevskaya Julia is friendly, clearly fulfills her duties.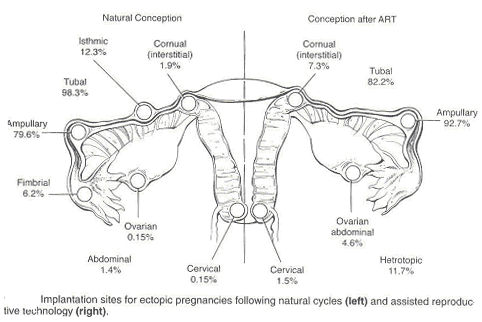
Belova E.M.
Today I was served in the clinic, I was satisfied with the staff, as well as the gynecologist. Everyone treats patients with respect and care. We thank them very much and continue to prosper.
Anonymous
The Mama Papa Ya clinic in Lyubertsy is very good. The team is friendly and responsive. I recommend this clinic to all my friends. Thanks to all doctors and administrators. I wish the clinic prosperity and many adequate clients.
Iratiev V.V.
Visited the clinic "Mama Papa Ya" with a child. I needed a consultation with a pediatric cardiologist. I liked the clinic. Good service doctors. We didn't stand in line, everything was the same price.
Evgeniya
I liked the first visit. I was carefully examined, additional examinations were prescribed, and good recommendations were given. I will continue the treatment further, I liked the conditions in the clinic.
Kristina
The doctor carefully examined my husband, ordered an ECG and made a preliminary diagnosis.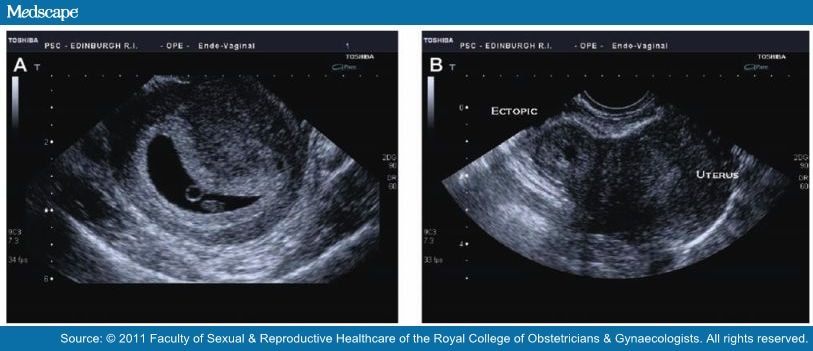 She made recommendations about our situation and ordered additional examinations. So far, there are no comments. Financial agreements have been met.
She made recommendations about our situation and ordered additional examinations. So far, there are no comments. Financial agreements have been met.
Marina Petrovna
I really liked the clinic. Helpful staff. Was at the appointment with the gynecologist Mikhailova E.A. Satisfied, there are more such doctors. Thanks!!!
Olga
Recommended for reading:
- Symptoms of the abscess
- Symptoms and adenoma treatment in men
- Signs of adnexitis in women
- adrenogenital syndrome
Causes
Signs
Diagnosis
Treatment
What to do
Ectopic pregnancy is one of the most dangerous pathological conditions in which the fetus develops outside the uterine cavity. The place of its implantation can be the fallopian (uterine) tubes, as well as other organs of the abdominal cavity and small pelvis.
Termination of an ectopic pregnancy is accompanied by intra-abdominal bleeding and severe complications requiring surgical intervention.
In the female body, normal gestation is possible only in the uterus, but in practice, the location of the embryo, in addition to the uterus, may vary.
There are several types of ectopic pregnancy: tubal, ovarian, abdominal, cervical and with a location in the rudimentary horn of the uterus.
The sites listed are unfavorable for gestation, so an ectopic pregnancy is terminated at 4 to 8 weeks to prevent serious complications.
Attached in an atypical place, the vessels of the fetal egg grow into the surrounding tissues. Other organs, besides the uterus, are not able to stretch and form blood vessels for the placenta. As a result, damage to surrounding tissues occurs, exfoliation of the fetal egg, as a result, severe bleeding occurs that threatens the life of the patient.
The appearance of a tubal form of pathology is associated with the presence of obstacles in the movement of a fertilized egg.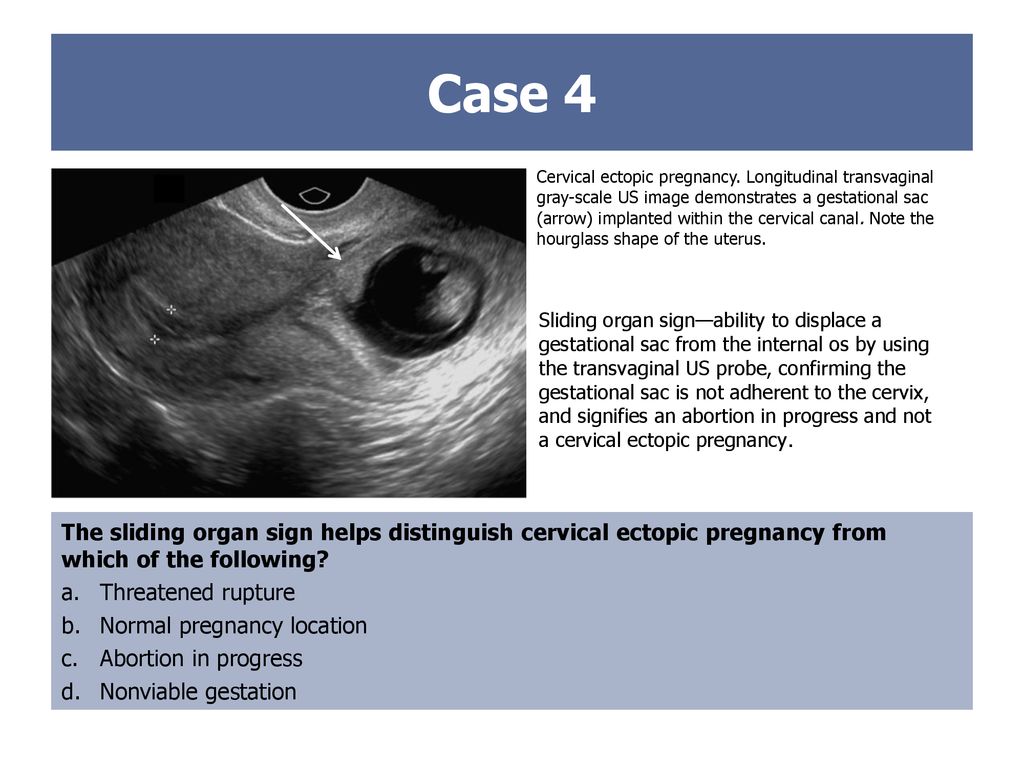 If the fertilized egg does not reach the uterine cavity, then it is implanted in the fallopian tube. Ectopic fetal development occurs in approximately 2% of cases among all types of pregnancy, of which 9 fall on the tubal form.eight%. Fetal implantation in other parts of the uterus and appendages, as well as in the abdominal cavity, is much less common.
If the fertilized egg does not reach the uterine cavity, then it is implanted in the fallopian tube. Ectopic fetal development occurs in approximately 2% of cases among all types of pregnancy, of which 9 fall on the tubal form.eight%. Fetal implantation in other parts of the uterus and appendages, as well as in the abdominal cavity, is much less common.
The release of a fertilized egg into the abdominal cavity with further implantation to the omentum, peritoneum or intestine leads to the development of abdominal pregnancy. One of the causes of this pathology may be in vitro fertilization.
In cervical pregnancy, the egg is implanted in the columnar epithelium of the cervical canal. As a result of deep penetration of the embryonic villi into the muscular layer of the cervix, the pregnancy ends in very heavy bleeding.
Causes of pathology
The development of pregnancy outside the uterine cavity occurs as a result of failures of natural processes that prevent the penetration of a fertilized egg into it. The most common causes of ectopic pregnancy include:
The most common causes of ectopic pregnancy include:
- previously transferred infectious lesions of the appendages caused by pathogenic microflora;
- the presence of adhesions in the fallopian tubes;
- defects in the structure of the genital organs;
- installed IUD in the uterus;
- infantilism;
- the presence of a tumor in the appendages or uterus;
- use of assisted reproduction methods;
- use of hormonal contraceptives;
- the presence of an inflammatory focus in the pelvic cavity;
- previously transferred surgical interventions on the appendages;
- stimulation of the ovulation process;
- history of abortions;
- endometriosis.
Features
It is not possible to determine the pathology at home. In this regard, timely registration can play a decisive role in the correct diagnosis.
At an early stage of development, an ectopic pregnancy has no distinguishing features.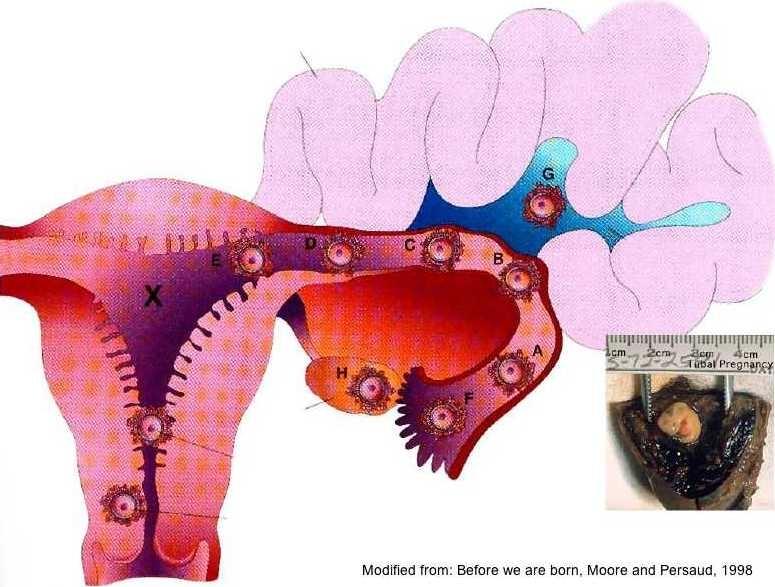 As a rule, it is characterized by:
As a rule, it is characterized by:
- absence of menstruation;
- breast engorgement;
- manifestations or absence of toxicosis;
- positive pregnancy test, although in the presence of ectopic pathology, it is not pronounced;
- painful sensations in the lower abdomen with irradiation to the rectum, as well as "spotting" discharge from the vagina.
Clinical manifestations of fetal development in the fallopian tube
An ectopic pregnancy can have a progressive form, in which case the growing fetal egg penetrates the muscular layer of the fallopian tube, leading to its gradual destruction. The patient has all the symptoms of pregnancy, but there are small bleeding from the genitals.
Also ectopic pregnancy can be terminated:
- as a tubal abortion. In this case, there is a partial or complete detachment of the membranes of the embryo from the wall of the tube and its entry into the abdominal cavity.
 Symptoms of manifestations depend on the severity of bleeding. Characterized by the presence of vaginal discharge in the form of blood clots. A pronounced soreness in the lower abdomen joins. Bimanual examination reveals an increase in the size of the uterus and appendages. Palpation of the posterior vaginal fornix is very painful;
Symptoms of manifestations depend on the severity of bleeding. Characterized by the presence of vaginal discharge in the form of blood clots. A pronounced soreness in the lower abdomen joins. Bimanual examination reveals an increase in the size of the uterus and appendages. Palpation of the posterior vaginal fornix is very painful; - is like a ruptured fallopian tube. May occur after the 6th week of pregnancy. This condition is life threatening due to internal bleeding. Patients complain of very severe pain in the lower abdomen on both sides. There is a protrusion of the posterior fornix of the vagina and a "floating" uterus during a bimanual examination.
How to detect an ectopic pregnancy
In the initial period, it is difficult to diagnose pathology. Symptoms indicate, as a rule, the presence of pregnancy, but there are no signs typical for the pathology.
Diagnosis is carried out by examining a woman in a gynecological chair, as well as using additional research methods:
- blood test for B-hCG, which in case of ectopic pregnancy shows a period less than it actually is;
- Ultrasound, which will give more complete information about the development of the fetal egg and its location.

Interrupted tubal pregnancy is accompanied by intra-abdominal bleeding. Typical symptoms of a pipe rupture will be:
- acute pain in the lower abdomen radiating to the anus, lumbar region, legs;
- secretion of blood from the genital tract;
- rapid, weak pulse;
- sudden drop in blood pressure;
- loss of consciousness.
Clinical manifestations of an interrupted tubal pregnancy should be differentiated from appendicitis and ovarian apoplexy. When the embryo is located in the cervical region, pregnancy should be distinguished from incomplete abortion and tumors.
An ectopic pregnancy can be confirmed or denied after ultrasound diagnostics and a blood test for B-hCG.
Treatment
Treatment of ectopic pregnancy is carried out only by surgery. All the efforts of doctors are aimed at maintaining the integrity and function of the fallopian tube, into which the implantation of the fetal egg has occurred. With timely detection of pathology and a small blood loss, a laparoscopic operation is performed.
With timely detection of pathology and a small blood loss, a laparoscopic operation is performed.
When localizing the embryo in the tube, the following types of surgical intervention are used:
- tubotomy (removal of the fetal egg while preserving the tube). In the case of choosing this method, the possibility of recurrence of the pathology is taken into account;
- tubectomy (excision of the tube) - performed in the presence of severe damage.
The choice of methodology is influenced by the following factors:
- whether the woman plans to have a child in the future;
- repeated ectopic pregnancy will require removal of the tube;
- whether there is an adhesive process in the small pelvis;
- change in the structure of the wall of the fallopian tube.
If the blood loss is large, then in order to save a life during an ectopic pregnancy, it is necessary to perform an abdominal operation, in which the fetal egg and tube are removed.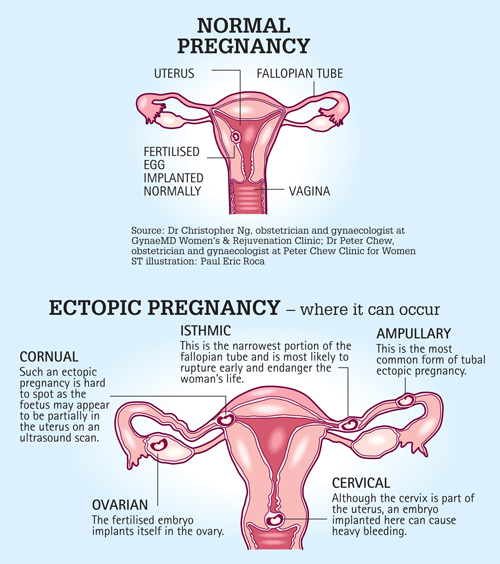 Plasma transfusion may be required to restore blood loss. It is important that the remaining second pipe fully retains its function.
Plasma transfusion may be required to restore blood loss. It is important that the remaining second pipe fully retains its function.
How to deal with an ectopic pregnancy
To avoid serious complications that can occur during a pathological pregnancy, a timely visit to an obstetrician-gynecologist will help. Attempts to save the fetus can lead to sad consequences: as a result of a ruptured tube, blood flows into the abdominal cavity, which leads to fatal hemorrhagic shock.
When a patient is diagnosed with an ectopic pregnancy, urgent hospitalization is required to terminate the pregnancy.
The author of the article:
Shklyar Aleksey Alekseevich
obstetrician-gynecologist, surgeon, KMN, head of the direction "Obstetrics and Gynecology"
work experience 10 years
reviews leave feedback
Clinic
m. Sukharevskaya
Go to doctor's profile
Services
- Title
- Appointment, consultation of an obstetrician-gynecologist primary3590
- Reception, consultation of an obstetrician-gynecologist repeated2200
- Reception, consultation of the doctor of the head of the department of gynecology / Ph.
 D. primary4300
D. primary4300 - Reception, consultation of the head of the department of gynecology / Ph.D. repeated2750
Health articles
All articlesAllergistGastroenterologistHematologistGynecologistDermatologistImmunologistInfectionistCardiologistCosmetologistENT ENT doctor (otolaryngologist)MammologistMassageNeurologistNephrologistOzone therapyOncologistOphthalmologistProctologistPsychotherapistPulmonologistRheumatologistTherapistTraumatologistTrichologistUltrasound (ultrasound examination)UrologistPhysiotherapistPhlebologistSurgeonFunctional diagnostics and Energist 905 years. Red Gates. AvtozavodskayaPharmacy. Glades. Sukharevskaya. st. Academician Yangelam. Frunzenskaya ZelenogradOkocha Victoria Alexandrovna
obstetrician-gynecologist, reproductive specialist, gynecologist-endocrinologist, ultrasound doctor
reviews Make an appointment
Clinic
m.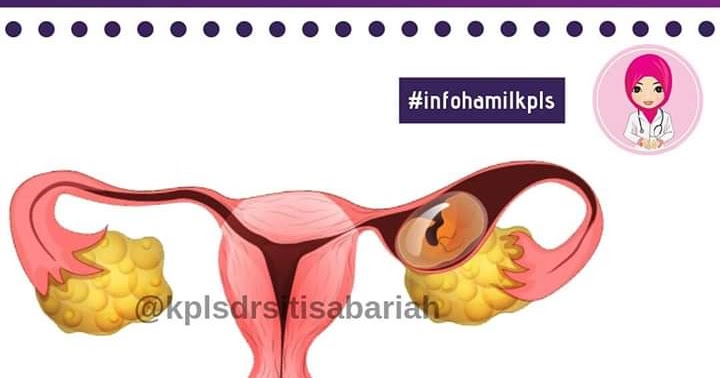 Frunzenskaya
Frunzenskaya
Ellinskaya Anastasia Aleksandrovna
obstetrician-gynecologist, ultrasound doctor
reviews Make an appointment
Clinic
m. Smolenskaya
m. Polyanka
Akabirova Shakhlooy Anvarovna
obstetrician-gynecologist, endocrinologist, ultrasound doctor, KMN
reviews Make an appointment
Clinic
m. Red Gate
m. Avtozavodskaya
Gazdieva Irina Khasanovna
obstetrician-gynecologist
reviews Make an appointment
Clinic
m. Street 1905 Goda
Zharova Natalya Anatolyevna
obstetrician-gynecologist
reviews Make an appointment
Clinic
m.