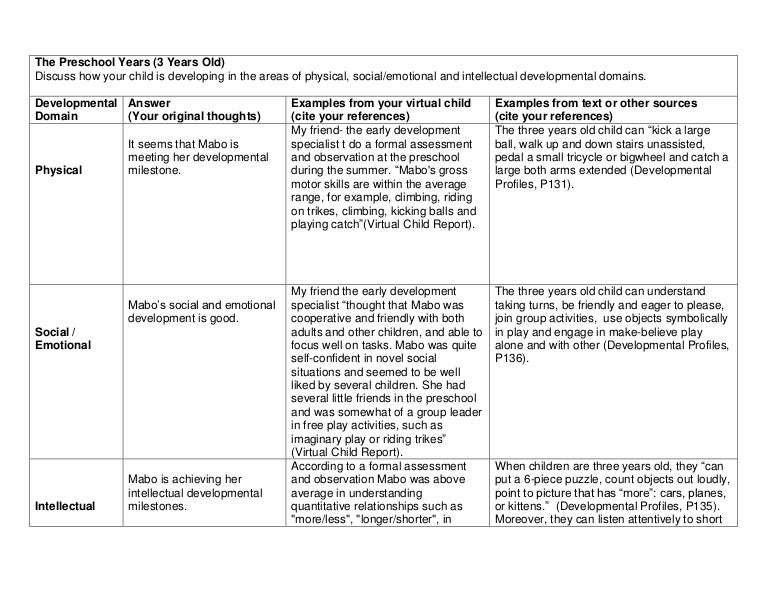
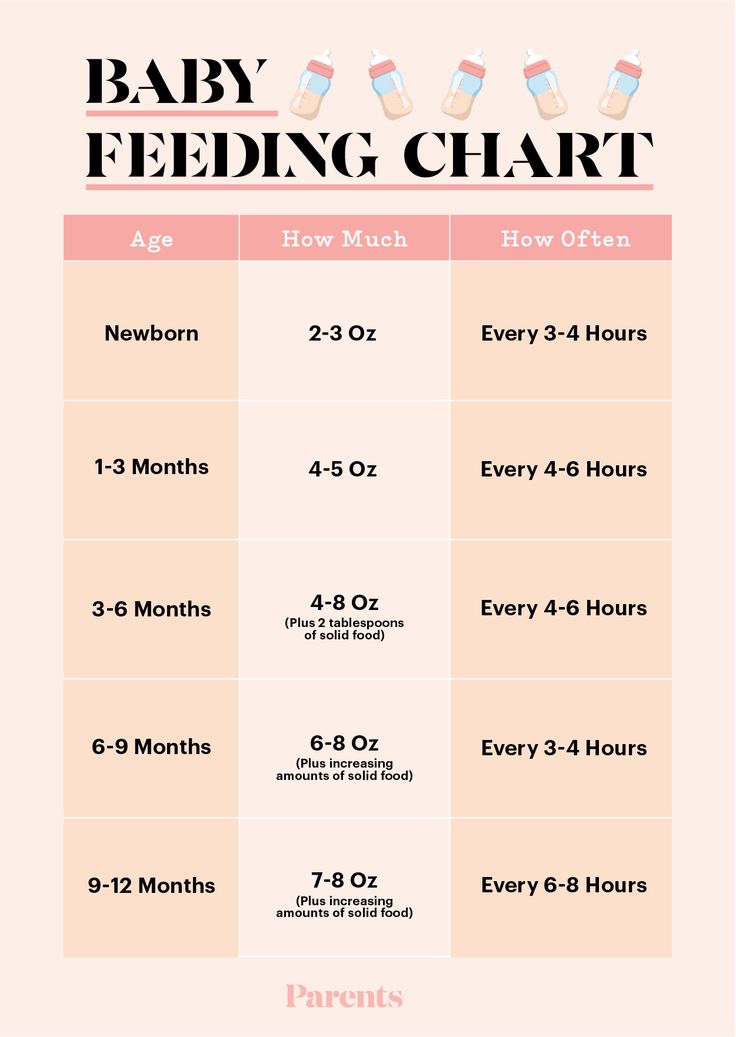
When baby starts solids how much milk
Formula Feeding FAQs: Starting Solids and Milk (for Parents)
Whether you plan to formula feed your baby from the start, want to supplement your breast milk with formula, or are switching from breast milk to formula, you probably have questions.
Here are answers to some common questions about formula feeding.
When Can My Baby Try Solid Foods?
Doctors recommend waiting until your baby is about 6 months old to start solid foods. Some babies may be ready for solids sooner than 6 months, but wait until your baby is at least 4 months old.
Babies who are ready to eat solids foods:
- are interested in foods (for example, they may watch others eat, reach for food, and open their mouths when food is near)
- hold up their heads well, and sit up with little or no help
- don't push food of their mouth (which is a natural tongue reflex that disappears when babies are 4–6 months old)
- usually weigh twice their birth weight, or close to it
Talk to your doctor about the right time to start solid foods.
How Do I Introduce Solid Foods?
When the time is right, start with a single-grain, iron-fortified baby cereal. Start with 1 or 2 tablespoons of cereal mixed with breast milk, formula, or water. Feed your baby with a small baby spoon. Don’t add cereal to a baby's bottle unless your doctor recommends it.
When your baby gets the hang of eating the first food, introduce other foods from all food groups, such as puréed meats, fruits, vegetables, grains, beans, and yogurt. Wait a few days between introducing new foods to make sure your baby doesn't have an allergic reaction.
You can include foods that are more likely to cause allergies — such as peanuts, eggs, cow’s milk, seafood, nuts, wheat, and soy — among the foods you introduce to your infant. Waiting to start these foods does not prevent food allergies.
Talk to your doctor before giving foods that contain peanuts if your baby has severe eczema or an egg allergy, as these conditions make an allergy to peanuts more likely. Eating peanut-containing foods early on may lower a child’s chances of developing a peanut allergy. But your doctor will need to decide if you can give peanuts to your baby, and the safest way to do it. Usually, this requires allergy tests.
Eating peanut-containing foods early on may lower a child’s chances of developing a peanut allergy. But your doctor will need to decide if you can give peanuts to your baby, and the safest way to do it. Usually, this requires allergy tests.
Should We Avoid Some Foods?
Yes, don’t give your baby:
- foods with added sugars or no-calorie sweeteners
- high-sodium foods
- honey until after the first birthday. It can cause botulism in babies.
- unpasteurized juice, milk, yogurt, or cheese
- regular cow's milk or soy beverages instead of breast milk or formula before 12 months. It’s OK to offer pasteurized yogurt and cheese.
- foods that may cause choking, such as hot dogs, raw carrots, grapes, popcorn, and nuts
Always supervise your child when eating. Make sure your child is sitting up in high chair or other safe place.
When Can My Baby Have Cow's Milk?
Before their first birthday, babies still need the nutrients in breast milk or formula. But after that, they’re ready to switch to cow's milk.
But after that, they’re ready to switch to cow's milk.
Most kids under age 2 should drink whole milk. If a toddler is overweight or there is a family history of obesity, high cholesterol, or heart problems, your doctor might recommend switching to reduced fat (2%) milk.
If your child can’t drink cow’s milk, choose an unsweetened soy beverage fortified with calcium and vitamin D. Other milk alternatives, like almond, oat, rice, or coconut milk, have less protein and may not be fortified.
How Do We Switch to Cow’s Milk?
You can switch your baby from formula to whole milk by replace bottles of formula with bottles — or sippy cups — of milk. By 1 year old, your baby should be eating a variety of solid foods and drinking about 16 to 24 ounces (480–720 milliliters) of milk per day.
When Can I Start Giving My Baby Water and Other Drinks?
In their first 6 months, healthy babies drinking enough formula usually don't need extra water. Once your baby is eating solid foods, you can offer a small amount of water between feedings, up to 4–8 ounces a day.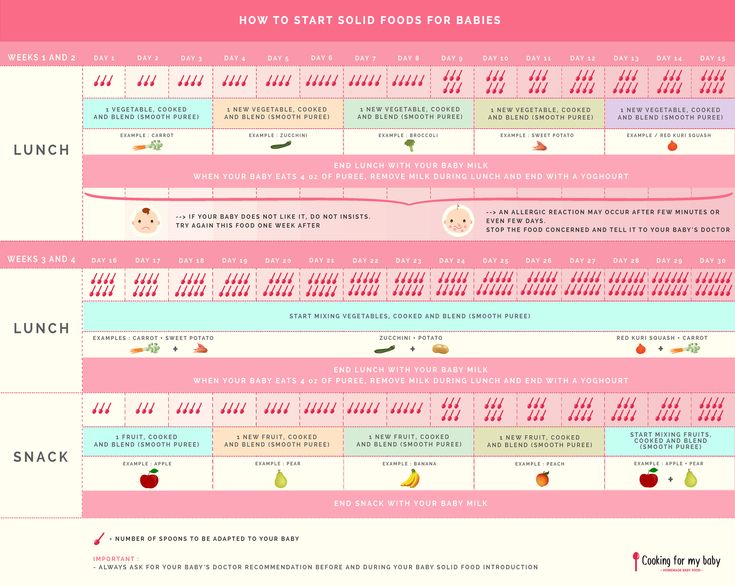
Water that has fluoride helps prevent tooth decay. If your water does not have fluoride, talk to your doctor or dentist about fluoride drops.
Do not give juice to babies younger than 12 months. After your child’s first birthday, limit 100% fruit juice to no more than 4 ounces a day. Always serve juice in a cup, not in a bottle. Don’t give your child sugar-sweetened beverages, including soda, juice drinks, sports drinks, and flavored milks.
Reviewed by: Mary L. Gavin, MD
Date reviewed: November 2021
How Much Milk Does a Baby Need When Eating Solids?
Some parents experience mixed emotions when they begin introducing solid food to their breastfed babies. They are excited that their baby is growing up and ready to try new foods, textures, and flavors, but at the same time this is the first step towards weaning. Now here comes the question: how much milk does a baby need when eating solids? That your baby is starting to eat solid foods does not mean that he shouldn’t have breast milk anymore.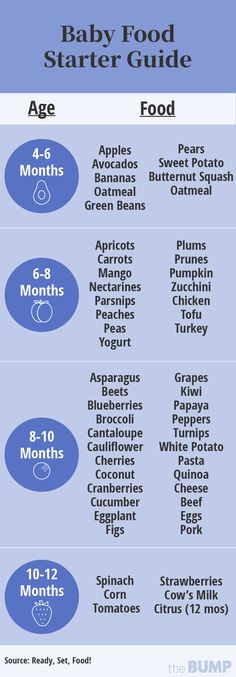 In fact, breast milk (or formula) will be your baby’s main source of nutrition until he is a year old and you can even keep breastfeeding after this as long as you and your baby are comfortable with it. Parents just beginning the transition to solid foods for their baby often wonder how much milk they need if they’re already eating solid foods and here is the answer.
In fact, breast milk (or formula) will be your baby’s main source of nutrition until he is a year old and you can even keep breastfeeding after this as long as you and your baby are comfortable with it. Parents just beginning the transition to solid foods for their baby often wonder how much milk they need if they’re already eating solid foods and here is the answer.
How Much Milk Does a Baby Need When Eating Solids?
1. Breastfeeding
Before your baby starts eating solids, he will probably have between 19 and 30 ounces of breast milk a day with the average amount being around 25 ounces. As you introduce solid foods into his diet, however, the milk intake will probably start decreasing. Despite this, you should always make sure that he gets enough breast milk to provide most of his nutrition until he is one year old. The amount of milk your baby needs will depend on many factors including how much solid food he is eating. One study that looked at the intake of breast milk found that it was about 30 ounces (875 ml) a day at seven months and about 19 ounces (550 ml) between 11 and 16 months with this final number only accounting for about 50% of daily calories).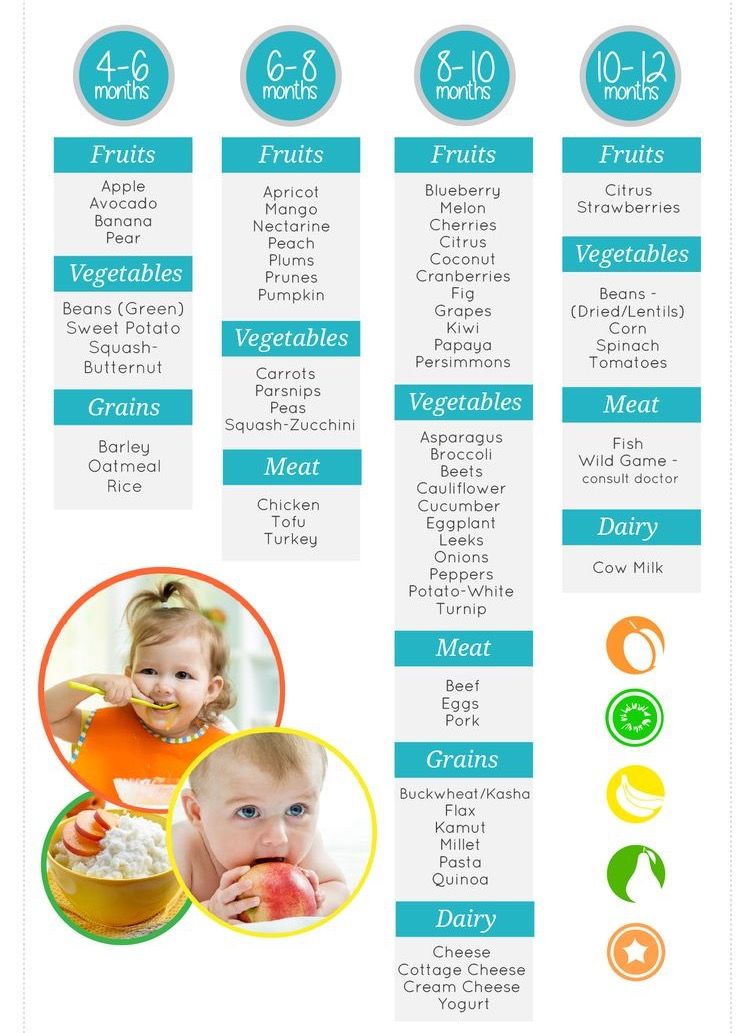
Other studies have looked at how much breast milk babies between one and two years usually have with numbers ranging from 14 to 19 ounces (400 to 550 ml). From 24 to 36 months, this average decreases to 10 to 12 ounces (300 to 360 ml) a day.
2. Bottle-feeding
When you first start feeding solids to your baby, his daily formula intake will usually start to decrease gradually until it reaches around 720 ml.
Once he is eating solids regularly, this number will decrease to about 500 to 600 ml a day of formula in addition to a healthy and varied diet. If your baby doesn’t want to drink this much milk, try giving him foods with milk such as yogurt, rice pudding, or custard.
After your baby reaches a year of age, he can switch from formula to drinking full-fat cow’s milk.
Want to know more about how much milk your baby needs when eating solids? Check out the video below:
Milk and Solids—How Much Is Enough for Your Baby?
Most babies have around 24 to 32 ounces of breast milk or formula a day when they are about 6 months old. When they reach a year, the number will be between 16 and 24 ounces and the remaining nutrition will be from solid foods. Most of the time, babies between 8 and 9 months are already having three meals of “solid” foods each day, but each baby is different.
When they reach a year, the number will be between 16 and 24 ounces and the remaining nutrition will be from solid foods. Most of the time, babies between 8 and 9 months are already having three meals of “solid” foods each day, but each baby is different.
When your baby is young, he doesn’t eat for pleasure, so experts recommend that you let him regulate how much to eat. He will only do so when hungry. After their morning milk, wait one or two hours and let him eat as much solid food as he wants. Simply offer a nutritious option and let him do the rest.
Many parents are tempted to know exactly how much food their child consumes on a daily basis or want a specific guideline to follow. In reality, your only job as a parent is to give your child healthy foods. He will decide how much he needs to eat. It is important to start encouraging children to eat if they are hungry and then stop when they get full while they are still young.
How to Introduce Milk to Your Baby When Eating Solids
1.
 Breastfeeding
BreastfeedingExperts suggest that you give your child breast milk for their first meal in the morning. Then you can wait a half hour to an hour and give them solid foods. The goal with young babies is not to fill up on solids and sacrifice milk. Until they are a year old, the breast milk is the most important source of nutrition.
By the time your baby starts eating solid foods, he will already be signaling when he wants to breastfeed and when he is full. He will start doing the same thing with solid foods. Most babies can start eating solids when they are around six months old as they can sit up by themselves, won’t push food out of their mouth, and can hold the food themselves.
2. Bottle-feeding
As soon as you start introducing solid foods into your baby’s diet, mealtime will get more exciting. The following steps can make it easier and more enjoyable for both your baby and you.
- Keep your baby seated while eating. You can start off with an infant seat or have him sit on your lap and then when he can sit up by himself, move on to a highchair.
- Encourage your baby to play with and explore his food while eating. This is a great way to help with his development and you can prevent messes with a drop cloth.
- Let your baby hold onto a spoon while you feed him with another to start introducing the idea of utensils. Eventually encourage him to start feeding himself.
- When your child reaches nine months or so, he might be ready to start drinking from a cup. Try filling it with breast milk (or formula) to help wean him off a bottle.
- Always put out individual servings. Chances are your baby won’t finish an entire container of food and saliva can ruin the leftovers. You can refrigerate the rest of the food for three days.
- Don’t force your baby to try a new food if he doesn’t want to. Instead, try it again next time.
- If your baby indicates he is full, listen to him. If he is following the growth charts and his doctor is happy with his growth, he is eating enough.
what products are possible, features of complementary foods
It is no secret that young and not very experienced mothers receive information on the nutrition of an infant, including recommendations on how to introduce the first complementary foods, mainly from two sources: grandmother's stories and from the Internet. Unfortunately, both of these respected sources of information may voluntarily or not voluntarily, but be very mistaken, since grandmothers grew up in a more prosperous time in terms of environmental conditions, and the Internet is littered with various articles that are rarely written by professionals, moreover, they rely either on explicit outdated guides on baby food, or frankly on unverified information. nine0003
Unfortunately, both of these respected sources of information may voluntarily or not voluntarily, but be very mistaken, since grandmothers grew up in a more prosperous time in terms of environmental conditions, and the Internet is littered with various articles that are rarely written by professionals, moreover, they rely either on explicit outdated guides on baby food, or frankly on unverified information. nine0003
In this article, I will try to combine the latest scientific data and recommendations on how to introduce the first complementary foods with many years of observations from the experience of a practical pediatrician and an allergist-immunologist.
At what age is it time to introduce the first complementary foods
According to the recommendations of the Research Institute of Nutrition of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences, the first complementary foods can be introduced from 4.5 - 5 months, regardless of the type of feeding. This is "average". In practice, the choice of when to start introducing complementary foods still depends on the individual characteristics of the child. For example, for a child with widespread atopic dermatitis (diathesis), we will not introduce complementary foods until at least acute skin symptoms, such as cracks, weeping or secondary eczema, have steadily disappeared. Increased dryness and flaking of the skin, of course, require constant application of moisturizers to the skin, but in no case are they a contraindication to the start of the introduction of the first complementary foods. nine0003
In practice, the choice of when to start introducing complementary foods still depends on the individual characteristics of the child. For example, for a child with widespread atopic dermatitis (diathesis), we will not introduce complementary foods until at least acute skin symptoms, such as cracks, weeping or secondary eczema, have steadily disappeared. Increased dryness and flaking of the skin, of course, require constant application of moisturizers to the skin, but in no case are they a contraindication to the start of the introduction of the first complementary foods. nine0003
Another important point when choosing the time to start introducing complementary foods is the dynamics of the child's weight gain. The more intensively the child gains in height and weight, the sooner he may need additional calories, since the energy value of breast milk or artificial formula alone will most likely not be enough for a child who grows faster than his peers by 4 - 5 months. We must not forget that natural products contain a fairly large range of minerals and vitamins, and a mother’s body, alas, cannot be an eternal and bottomless source of useful nutrients, somewhere something will gradually begin to be missed. nine0003
nine0003
In addition, the nature of lactation in the mother has a great influence on the timing of the introduction of complementary foods. If a nursing mother begins to feel a lack of milk, I would prefer to first give her advice on stimulating lactation, and at the same time begin to introduce complementary foods. It will be better than introducing an artificial mixture. But I repeat that the earliest start date for the introduction of the first complementary foods is the age of 4 months, before the child's body is not yet ready, the risk of developing allergies is also high.
So, we agree with you that the first complementary foods can be introduced no earlier than 4 months of a child's life.
First complementary foods: Which foods to choose?
The first complementary foods, as a rule, should consist of vegetable or fruit purees, but in no case juices. Still, juices, even for children, are highly filtered, mainly contain a large amount of organic acids and “light” carbohydrates (that is, sugar, to make it clear to everyone). I will not waste time explaining why juices are harmful to an infant, but I will describe a clinical case from practice. nine0003
I will not waste time explaining why juices are harmful to an infant, but I will describe a clinical case from practice. nine0003
Parents with an 8-month-old girl came to the reception. Somewhere from 5 months she practically did not gain weight, although before that all indicators were normal. In the analyzes, apart from visible signs of iron deficiency, slightly reduced hemoglobin, no pathology was also detected. The main complaint: "does not eat anything." And when I began to find out what she still eats, it turned out that the child drinks half a liter of juice every day. But porridge or cottage cheese, or mashed potatoes cannot be forced together, they spit everything out. I don't like the taste. And so - for three months. The child, of course, became very nervous, yelling at night, demanding juice. nine0003
So draw your own conclusions and be careful.
For the first feeding, this is now recognized by everyone, the best dishes are vegetable purees from green varieties of vegetables: zucchini, cauliflower, broccoli.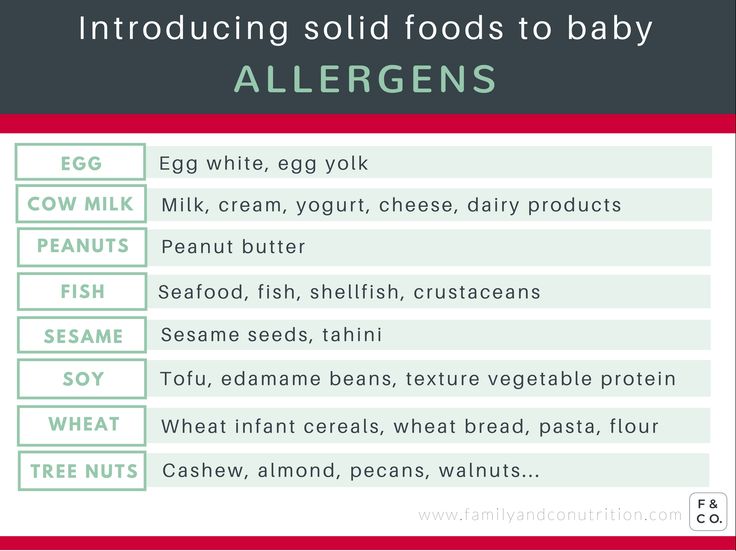 The first complementary foods are introduced, starting with half a teaspoon, in the morning for three days, then gradually increase the amount of the product to 40-50 grams per week. Supplemented with breast milk or formula.
The first complementary foods are introduced, starting with half a teaspoon, in the morning for three days, then gradually increase the amount of the product to 40-50 grams per week. Supplemented with breast milk or formula.
For problems with stools, constipation, it’s good to start introducing prune puree, green apple, you can try pumpkin, even apricot puree, but in no case start with carrots. Beta-carotenoids, which are abundant in carrots, are generally poorly absorbed and can cause allergies in a child. nine0003
Second food. Porridge or meat?
Even 5 - 6 years ago, we taught students at the medical institute that from 5 - 5.5 months old, an infant should begin to give cereal porridge for complementary foods. This is rice, buckwheat, corn. The first week you can cook 5% porridge: 5 grams of ground cereal per 100 ml of water. Then the porridges are cooked already denser: 10 grams of cereal per 100 ml of water. But now, basically everyone uses instant (soluble) cereals, which are diluted with water according to the instructions on the package. In addition, ready-to-eat liquid cereals are on sale: for example, Bellakt, Frutonyanya, etc. nine0003
In addition, ready-to-eat liquid cereals are on sale: for example, Bellakt, Frutonyanya, etc. nine0003
Why meat? You ask. According to modern recommendations (they really began to change quite often), but in this case I support: if a child has a pronounced decrease in hemoglobin in the blood below 100 g / l by the age of 5 months, it makes sense to start introducing fruit or vegetable purees as a second types of complementary foods - meat purees as a source of the most well-absorbed heme iron. You need to choose from varieties such as turkey, rabbit, lamb. Beef and veal can only be offered to children who did not have red cheeks and diathesis. nine0003
In the absence of problems with low hemoglobin, feel free to introduce porridge as the second meal of complementary foods, especially if the child is small and does not gain weight very well. In this case, we can recommend breeding cereals with the addition of breast milk or a mixture (Nan, Nutrilon, Celia, Nanny). With mixtures based on goat's milk, parents of children with a predisposition to allergies should be very careful. Goat milk formulas are not the best choice for babies who are allergic or intolerant to cow's milk protein, whatever the internet says. Believe me, there are serious scientific articles by foreign authors, which provided data on a very high frequency of cross-allergy between cow and goat milk proteins in children who were transferred to goat milk mixtures. And I saw it myself in my practice, when a child with dermatitis was transferred to a mixture of goat's milk, there was a clear improvement for a month or two, and then all over again and with a doubled degree of allergic skin damage. nine0003
Goat milk formulas are not the best choice for babies who are allergic or intolerant to cow's milk protein, whatever the internet says. Believe me, there are serious scientific articles by foreign authors, which provided data on a very high frequency of cross-allergy between cow and goat milk proteins in children who were transferred to goat milk mixtures. And I saw it myself in my practice, when a child with dermatitis was transferred to a mixture of goat's milk, there was a clear improvement for a month or two, and then all over again and with a doubled degree of allergic skin damage. nine0003
Introduction to fermented milk products
This is the most difficult question. I am sure that most of our grandparents demand that their stupid parents start drinking milk and kefir as soon as possible. In a number of cases, children really start to absorb sour-milk products quite well after 6 months, but before this age I am very careful even with sour-milk Agusha, and even introducing milk or kefir before 6 months is a bad form, believe me, and can lead to very bad consequences for the child. I understand the Western European medical community, which has recently banned its pediatricians from recommending fermented milk products for complementary foods for children under 3 years of age, just imagine! nine0003
I understand the Western European medical community, which has recently banned its pediatricians from recommending fermented milk products for complementary foods for children under 3 years of age, just imagine! nine0003
They (the Europeans) need to do something with their artificial milk formulas. Even 20 years ago, we did not know other mixtures after the "two", that is, the second formula for children from 6 to 12 months. Then there were formulas for children from 1 to 2 years old, then from 2 to 3 years old, and now there are already mixtures for children up to 4 years old, and I think if this goes on, then until the age of sixteen there will be their own milk substitutes. Dismiss me, I don't think this approach is correct. But the fact is that our grandparents had much better genetics than the generation of our children, alas. In the context of the growth of the possibilities of medicine, genetically determined diseases are also growing, and in this case - intolerance to cow's milk protein, and with every 10 years there are more and more such people among us. But if a child really suffers from an allergy to cow's milk protein or he is severely deficient in enzymes, then he will carry this peculiarity through his whole life, and most likely he will not drink milk or kefir himself, and there is no need to force him if he himself won't want to! nine0003
But if a child really suffers from an allergy to cow's milk protein or he is severely deficient in enzymes, then he will carry this peculiarity through his whole life, and most likely he will not drink milk or kefir himself, and there is no need to force him if he himself won't want to! nine0003
But you are lucky with genetics, and no one in the family has ever had an allergy (which is hard to imagine in our time), and most importantly, if your child has always had perfectly clean skin, then the first of the dairy products - cottage cheese, you will begin to offer your child with 7 months, kefir - from 10 months. Milk - after a year. It will be better this way.
But if your family does not have a very close and joyful relationship with milk, then even the introduction of kefir and yogurt into complementary foods for a child should be postponed until the age of 18 months. nine0003
Fish day and first meal
Fish is a very healthy product, rich in vitamins and antioxidants, but it must also be introduced carefully. I advise you to start introducing the first fish food at about 7-8 months. It is better to start with species such as cod, hake, haddock. The rules are the same: the first three days on the "gram," then slowly add. If there are no problems in a week or two, you can try such delicacies as tuna or salmon, of course, canned children, if you can find it. It is better not to mess with trout and salmon in the first year of life, this fish is all stuffed with dyes and antibiotics. nine0003
I advise you to start introducing the first fish food at about 7-8 months. It is better to start with species such as cod, hake, haddock. The rules are the same: the first three days on the "gram," then slowly add. If there are no problems in a week or two, you can try such delicacies as tuna or salmon, of course, canned children, if you can find it. It is better not to mess with trout and salmon in the first year of life, this fish is all stuffed with dyes and antibiotics. nine0003
No matter how hard I tried, the article about the first complementary foods turned out to be long. Thank you for reading to the end, I hope it will be useful. If you have questions about the introduction of complementary foods, you can write your appeals on our website in the question to a specialist section. A short answer can be obtained on the Internet, but in order to make a diagnosis and give a detailed consultation, of course, you need to come to a face-to-face appointment with a pediatrician and a pediatric allergist.
how many spoons, grams per day
nine0002 Published: 06/21/2020Reading time: 4 min.
Number of reads: 22296
The author of the article: Ponomareva Yuliya Vladimirovna
Pediatrician, Candidate of Medical Sciences, Allergist-Immunologist
The introduction of complementary foods is a responsible and necessary period in the life of both parents and children. In essence, this is a transitional stage of nutrition, when the baby's body gradually moves from easily digestible, maximally adapted breast milk to a varied adult diet. nine0003
Content: Hide
- Individual program
- Rules for introduction
- at what time and how often to give
- child refuses to eat
- Individual intolerance
- Preparation of complementary foods
Individual program 9000
of introduction, and also also The order of choice of products is always individual. Ideally, parents should work with their pediatrician to develop a complementary feeding schedule for their baby. It takes into account many factors, such as the state of health of the child, whether the baby was born full-term, how he gains height and weight every month, whether the mother has enough milk, and how the process of maturation of the baby's digestive system occurs. As the first product of complementary foods, experts recommend choosing vegetable puree or porridge. It is better to prefer specialized industrial products with a high level of safety, raw material quality and modern manufacturing technologies. nine0003
It takes into account many factors, such as the state of health of the child, whether the baby was born full-term, how he gains height and weight every month, whether the mother has enough milk, and how the process of maturation of the baby's digestive system occurs. As the first product of complementary foods, experts recommend choosing vegetable puree or porridge. It is better to prefer specialized industrial products with a high level of safety, raw material quality and modern manufacturing technologies. nine0003
Introduction Rules
Any new complementary foods should be started when the baby is healthy, without interfering with preventive vaccinations or any planned significant events in the baby's life. The mother herself should avoid eating foods that are unusual for her traditional diet these days in order to objectively assess the reaction to the product introduced to the baby. It is always necessary to start with a monocomponent composition, that is, from one type of vegetable or cereal without the addition of salt and sugar, and also initially prefer products with a low risk of developing allergic reactions. Any new product should be introduced gradually, starting with a small amount. “How much to give complementary foods for the first time?” is a traditional question for many parents. Start introducing complementary foods with ½-1 teaspoon, which corresponds to about 5-10 grams of vegetables or cereal. nine0003
Any new product should be introduced gradually, starting with a small amount. “How much to give complementary foods for the first time?” is a traditional question for many parents. Start introducing complementary foods with ½-1 teaspoon, which corresponds to about 5-10 grams of vegetables or cereal. nine0003
When and how often to give
Introduce the new product once a day in the morning, before breastfeeding. When the baby is hungry, he will be more willing to try a product that tastes very different from his usual milk or formula. When you start complementary foods in the morning, you have time to observe possible reactions to a new food. If you do not notice any significant changes in the baby's health, repeat the introduction of the same type of complementary foods in the amount of 1 teaspoon in the next two days. Increase the amount of product introduced gradually, so the child's digestive tract will smoothly adapt to the new food. If complementary foods are well tolerated, in about 10 days, bring the amount to the required amount recommended at this age.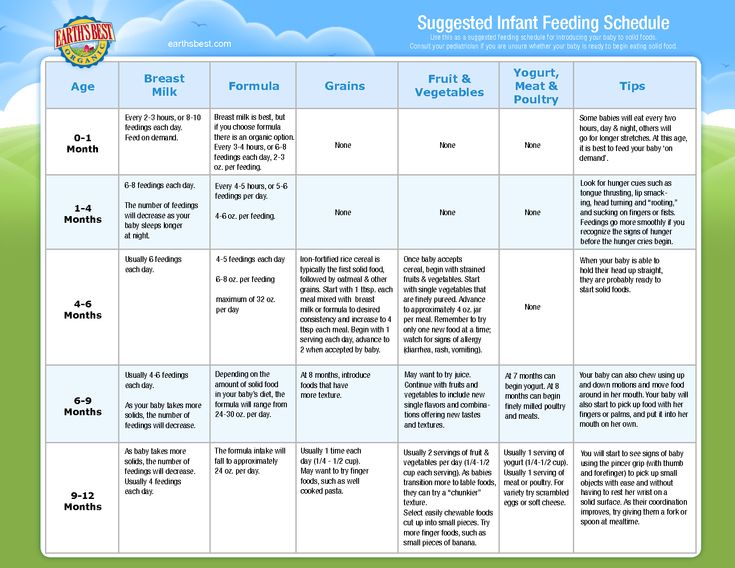 For an infant at 5 months, the volume of feeding should be about 150 ml. Do not be upset if the child at first eats only half of the prescribed volume. Each baby has his own characteristics and preferences, if he starts to turn away from the spoon, stop and supplement him with breast milk. nine0003
For an infant at 5 months, the volume of feeding should be about 150 ml. Do not be upset if the child at first eats only half of the prescribed volume. Each baby has his own characteristics and preferences, if he starts to turn away from the spoon, stop and supplement him with breast milk. nine0003
The child refuses to eat
Read also: How much does a newborn eat per feeding?
The best option is when the baby is happy to eat a new complementary food and tolerates it without any reactions. But what if the baby is naughty and rejects the offered food? Do not panic, this situation occurs quite often, because for a child it is completely different from the usual food. He needs to adapt to the innovations in his life. Do not insist that the baby necessarily eat the offered food, but the next day give him the opportunity to try it again. It often takes 10-15 attempts for a child to get used to a new taste and taste the product. Another secret that can improve the perception of the baby is the addition of mother's milk to the complementary foods. Familiar smells and tastes will increase your child's interest in new foods. Use expressed milk to make porridge by warming it up a little in a water bath, and then add the right amount for the desired consistency of the finished dish. You can also add a small amount of mother's milk to vegetable puree during the adaptation period. nine0003
Familiar smells and tastes will increase your child's interest in new foods. Use expressed milk to make porridge by warming it up a little in a water bath, and then add the right amount for the desired consistency of the finished dish. You can also add a small amount of mother's milk to vegetable puree during the adaptation period. nine0003
Individual intolerance
The problem is when the baby not only refuses a new food, but he has signs of intolerance. Most adverse reactions occur within the first 6 hours after eating. Always carefully examine the baby's skin for a rash, watch for changes in the digestive system, pay attention to the baby's behavior and sleep. After taking a new product, the child should not have vomiting, abdominal pain, loose stools or retention. There may be a temporary change in the consistency of feces or the appearance of heterogeneous lumps, this is the norm at this stage. In the event of an undesirable reaction, it is necessary to stop the introduction of a new product; in case of serious violations of the baby's health, it is necessary to seek the advice of a pediatrician. It is possible to resume the introduction of complementary foods only after the condition is normalized, not earlier than 7 days after the reaction. In this situation, it is better to introduce another possible food group into the diet next. So, if regurgitation or abdominal pain was noted against the background of the introduction of vegetable puree, you can try porridge instead. nine0003
It is possible to resume the introduction of complementary foods only after the condition is normalized, not earlier than 7 days after the reaction. In this situation, it is better to introduce another possible food group into the diet next. So, if regurgitation or abdominal pain was noted against the background of the introduction of vegetable puree, you can try porridge instead. nine0003
Preparing complementary foods
Remember to offer a fresh complementary food each time. Vegetable puree of industrial production can be stored in an airtight package in the refrigerator for no more than a day, and porridge must be diluted immediately before use each time. When preparing complementary foods, follow the manufacturer's instructions, adjusting the consistency by adding water or breast milk. At the beginning of the introduction of complementary foods, dilute the porridge to a semi-liquid state, gradually increasing the density as the baby matures and adapts. Any complementary food product, regardless of volume and consistency, should be offered to eat with a spoon and not use a bottle, which is used only for the introduction of breast milk substitutes.




:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/hemorrhage-in-miscarriage-meaning-2371523-FINAL-f2ab04cab1cc491e964a45e682f93da5.png)