Swollen perineum pregnancy
How to Treat a Swollen Perineum During Pregnancy
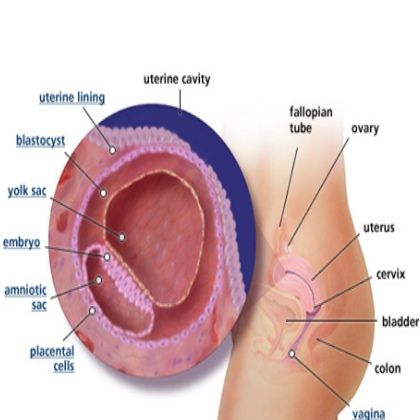
Your perineum is the small area of skin and muscle located between the vagina and the anus.
By the third trimester of pregnancy, your baby is gaining weight and dropping lower in your pelvis. The added pressure can lead to swelling of the genitals and perineum. At the same time, your perineum is starting to stretch in preparation for childbirth.
A sore perineum due to pregnancy is a temporary condition, though it can be uncomfortable.
The perineum is stretched even more during childbirth. It’s not uncommon for the perineum to tear as your baby passes through.
According to the American College of Nurse-Midwives (ACNM), anywhere from 40 to 85 percent of women have a tear during vaginal delivery. About two-thirds of them require stitches to repair the damage.
To decrease the chances of a ragged tear, your doctor may cut the perineum. This procedure is called an episiotomy. This gives baby more room to pass through without causing severe tears.
Whether you experience a tear or have an episiotomy, your perineum is a delicate area. Even tiny tears can cause swelling, burning, and itching. A large tear can be quite painful. Episiotomy stitches can feel sore and uncomfortable.
The symptoms can last a few days to several months. During that time, it may be difficult to sit or walk comfortably.
Pregnancy and childbirth are the most common causes of a sore perineum. Other things can lead to a sore perineum, but it’s not always easy to find the cause.
Something as simple as tight pants or sitting in an uncomfortable position for too long can cause soreness of the vulvar area or perineum. Intercourse without sufficient lubrication can also cause a sore perineum.
Generalized vulvodynia refers to a chronic pain in the vulvar area without an obvious cause. The pain can affect the entire area, including the labia, clitoris, and perineum.
Descending perineum syndrome occurs when the perineum balloons beyond its standard positioning. This might happen if you have an ongoing problem defecating or urinating and you strain too hard. If you have a descending perineum, the first step is to determine the cause.
This might happen if you have an ongoing problem defecating or urinating and you strain too hard. If you have a descending perineum, the first step is to determine the cause.
It could also be referred pain. If you have unexplained pain, a healthcare professional will likely begin with a complete gynecological examination to diagnose the concern.
A 2013 study indicated that some women have a higher risk for certain types of perineal tearing during childbirth. Risk factors include:
- delivering a baby when you’re an adolescent
- being 27 years old or over
- having a baby with a high birth weight
- having an instrumental delivery
Having more than one of these risk factors makes a perineal tear significantly more likely. In this case, your doctor may consider an episiotomy to try and prevent a tear.
If you have a sore perineum, sitting can make it worse. One simple and inexpensive fix is a hemorrhoid or donut cushion to keep your weight off of your perineum when you sit.
Massaging the area during pregnancy may help relieve soreness and prepare the perineum for childbirth.
Some women find that using an ice or a cold pack relieves symptoms such as swelling, itching, and burning of the perineum. However, a 2007 paper, updated in 2019, concluded that there’s only a small amount of evidence that cooling treatments are safe and effective in relieving perineal pain.
If you’ve experienced a tear or an episiotomy, your doctor will provide aftercare instructions. It’s important that you follow them carefully.
They’ll probably give you a perineal irrigation bottle. You can use it to squirt warm water on the area to clean and soothe it, especially after going to the bathroom.
To help prevent infection, you’ll need to keep the area very clean. A warm, shallow bath may help temporarily relieve discomfort. Use a clean towel to pat yourself dry rather than rubbing the area. You shouldn’t have a bubble bath or use other products with harsh ingredients until it’s completely healed.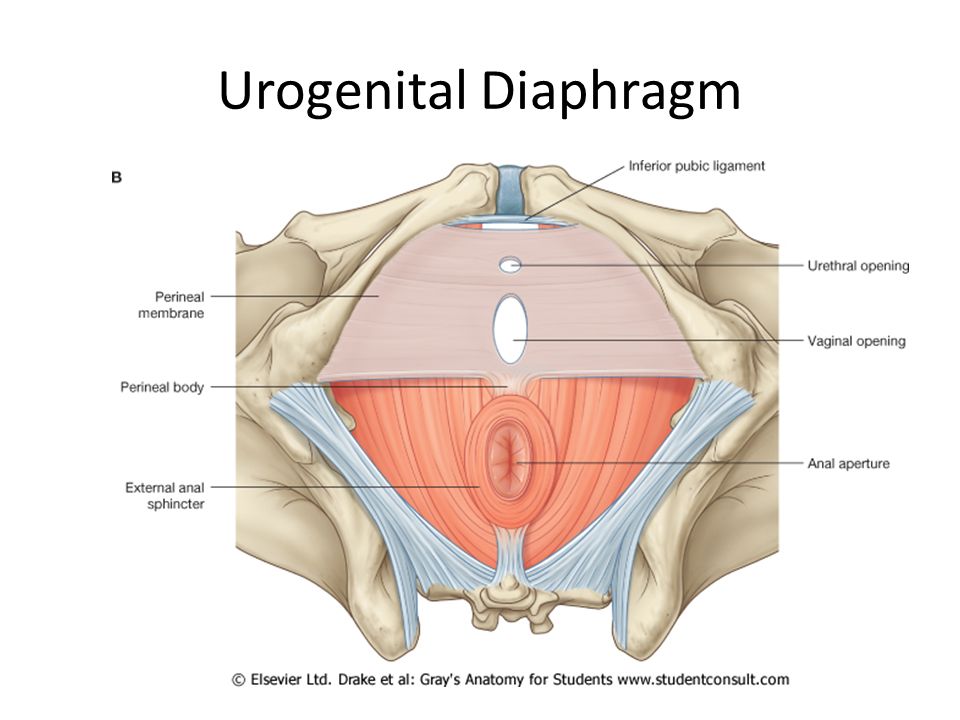
Taking care of vaginal tears: Are you missing a step?
Will the soreness eventually get better?
How much soreness you have and how long it will last can vary depending on the person. It has a lot to do with the cause. If you’ve had extensive tearing and swelling, it may take longer to heal.
For most people, childbirth-related soreness of the perineum subsides within a few days to a few weeks. There are usually no long-term effects.
Reach out to a doctor if the soreness doesn’t seem to be improving or it’s getting worse. You should also call a doctor if you have:
- a fever
- foul-smelling discharge
- perineal bleeding
- difficulty urinating
- severe pain
- swelling
- problems with perineal stitches
If you’re prone to perineal soreness, try to avoid wearing pants that are too tight. You should also make sure you’re well lubricated before having intercourse.
If you’re pregnant, you might benefit from a perineal massage. According to Brighton and Sussex University Hospitals, studies show that in a first pregnancy, perineal massage after the 34th week can reduce perineal tearing.
According to Brighton and Sussex University Hospitals, studies show that in a first pregnancy, perineal massage after the 34th week can reduce perineal tearing.
To prepare for self-massage, the ACNM suggests you cut your fingernails short and wash your hands well. Relax, with your knees bent. Use pillows for added comfort.
You’ll need to lubricate your thumbs as well as the perineum. You can use vitamin E oil, almond oil, or vegetable oil. If you prefer, you can use a water-soluble jelly. Don’t use baby oil, mineral oil, or petroleum jelly.
To massage:
- Insert your thumbs about 1 to 1.5 inches into your vagina.
- Press down and to the sides until you feel it stretch.
- Hold for 1 or 2 minutes.
- Use your thumbs to slowly massage the lower part of your vagina in a U shape.
- Concentrate on keeping your muscles relaxed.
- Massage the perineum this way for about 10 minutes per day.
If you’re not comfortable doing it yourself, a partner can do it for you. Partners should use the same technique, but with index fingers instead of thumbs.
Partners should use the same technique, but with index fingers instead of thumbs.
Do perineal massages make labor less painful?
Five Tips to Help with Perineum Swelling
Perineum swelling is the inflammation of the area between the vaginal opening and the anus, commonly occurring during pregnancy as the baby grows.
Pregnancy is a beautiful time in a woman’s life, but it can also be filled with some uncomfortable side effects. Perineum swelling is perfectly normal and will go away after delivery. However, you can do a few things to help ease the discomfort and reduce the swelling. This blog post will discuss the cause of perineum swelling, what’s normal and when to seek help, and provide women with five tips for easing discomfort and reducing swelling.
Cause of Perineum Swelling
The perineum is the area of skin and muscle between the vagina and anus. This area stretches during childbirth to allow your baby to pass through. Perineum swelling can occur when the tissues around the perineum become stretched and thinned out from the added pressure.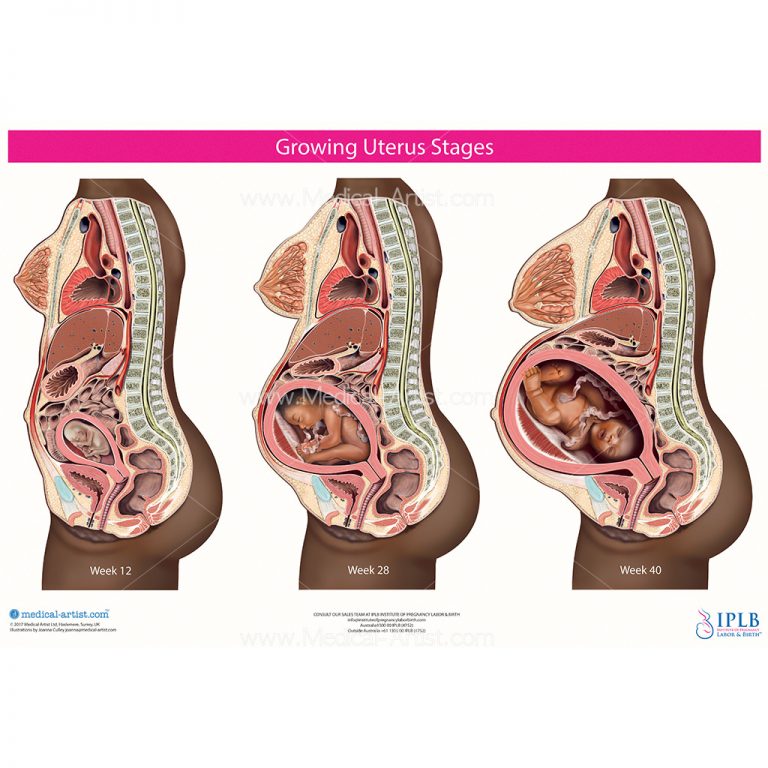 In some cases, perineal trauma can occur without any tearing. This is usually caused by excessive stretching or forceful pushing. Swelling is also common after an episiotomy, a surgical incision made in the perineum to enlarge the vaginal opening.
In some cases, perineal trauma can occur without any tearing. This is usually caused by excessive stretching or forceful pushing. Swelling is also common after an episiotomy, a surgical incision made in the perineum to enlarge the vaginal opening.
Other causes of perineum swelling can include:
- Edema (fluid retention) can be caused by various things, such as standing for long periods, being overweight or hormone changes.
- A perineal infection may occur if bacteria enter the tissues through a tear or incision. UTI infection is also a common cause of perineum swelling.
- Hemorrhoids are swollen veins in the anus and rectum that cause pain and inflammation.
- As the baby grows, the woman’s blood volume increases, leading to swelling in other areas of the body, such as the perineum.
- Tight clothing, such as undergarments or jeans, can restrict blood flow and lead to perineal swelling.
What Is Normal and When to Seek Help
Perineum swelling is a common and normal occurrence during pregnancy.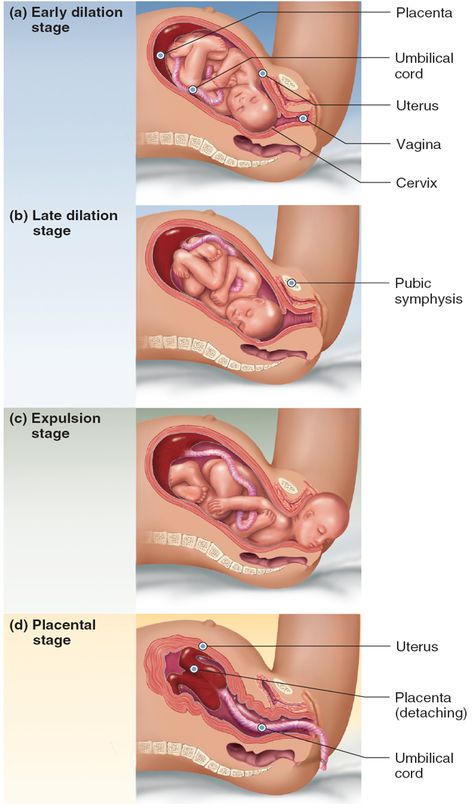 Swelling can range from mild to severe and usually goes away after delivery. In some cases, perineal trauma can occur without any tearing. This is usually caused by excessive stretching or forceful pushing. Swelling is also common after an episiotomy; you may experience the following:
Swelling can range from mild to severe and usually goes away after delivery. In some cases, perineal trauma can occur without any tearing. This is usually caused by excessive stretching or forceful pushing. Swelling is also common after an episiotomy; you may experience the following:
- Pain during sex.
- Difficulty urinating or having a bowel movement.
- Chronic pain in the perineum or vulva area.
If you’re experiencing any of the following symptoms, it’s important to seek medical attention:
- Bleeding from the perineum is not normal and should be evaluated by a doctor
- Thick, greenish discharge may indicate an infection.
- Fever, chills or nausea could be signs of a perineal infection.
- Swelling that lasts more than two weeks after delivery could be a sign of a seroma (a collection of fluid under the skin).
- A healthcare provider should evaluate unrelenting pain or discomfort in the perineum.
- Redness, warmth, soreness or itching in the perineum may be signs of an infection.
How to Ease Discomfort and Reduce Swelling
You can do a few things to ease the discomfort and reduce perineum swelling. Below are five tips:
- Apply a cold compress or use ice packs or frozen vegetables to reduce swelling. Applying a cold compress or placing the pack or veggies on the perineum area for fifteen minutes several times a day can help reduce inflammation and swelling.
- Take a warm bath. Soaking in a warm bath may help relieve pain and relax the muscles around the perineum. Add some soothing aromatherapy or Epsom salts to your bath for an extra level of relief.
- Wear loose-fitting clothing made from natural fibers such as cotton. Tight clothes, such as undergarments or jeans, can restrict blood flow and lead to perineal swelling. Opt for loose-fitting clothing instead to allow air to circulate around the area. You can also use perineal pads; these are special pads that you can wear during pregnancy and after delivery to help protect the perineum from further injury.
- Perineal massage involves massaging the perineum with your fingers in a circular motion. Start slowly and increase the pressure as needed. Massaging may help to reduce swelling and improve blood circulation.
- Elevate your legs and avoid sitting for long periods. Try to prop your legs up on a stool or pillow if you must sit. This will help to reduce the buildup of fluid in the perineal area.
These are just some tips that may help during your pregnancy. Speak with your doctor if you have any questions or concerns.
Please enable JavaScript to view the comments powered by Disqus.
Swollen perineum during pregnancy - is it worth panicking?
During the period of bearing a child, the entire body of a woman undergoes changes, if the labia is swollen during pregnancy, this may be a natural safe swelling or indicate an infectious etiology of this symptom. When the labia changes color during pregnancy, swelling, inflammation appears, this gives the woman considerable discomfort.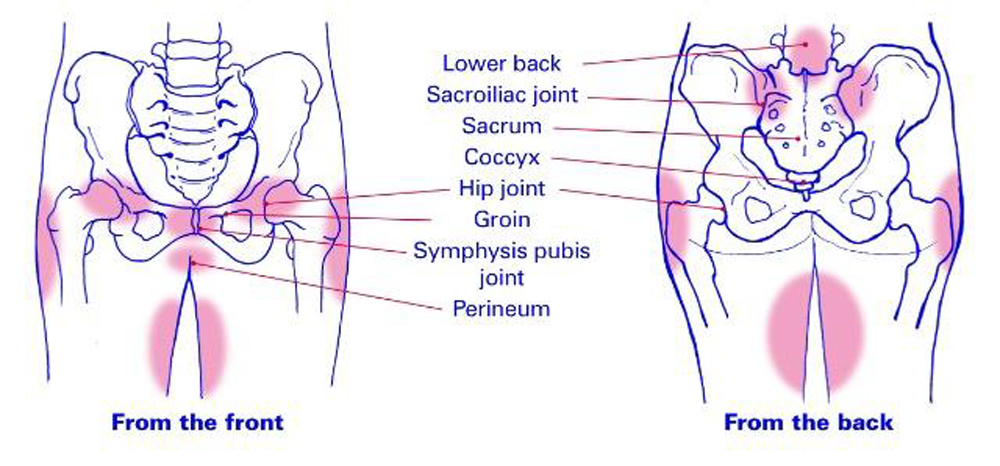 Often there is itching, an unpleasant odor, changes in the color of the discharge, which signals the development of diseases and requires immediate treatment. So, why do the small and large labia swell, how to alleviate this condition? Is vaginal swelling always a dangerous signal? nine0003
Often there is itching, an unpleasant odor, changes in the color of the discharge, which signals the development of diseases and requires immediate treatment. So, why do the small and large labia swell, how to alleviate this condition? Is vaginal swelling always a dangerous signal? nine0003
Why does the perineum swell during pregnancy?
During the period of bearing a baby, the genitals may change, which is explained by several reasons. This may be a hormonal restructuring of the body, an increase in body fat in the tissues associated with a general weight gain, preparing the body for childbirth. Swelling of the perineum during pregnancy can be observed in the later stages, when the uterus enlarges and presses on other organs of the small pelvis. If the natural changes in the body leading to a change in the shape of the labia are asymptomatic, then there is no need to worry, but it will be useful to consult with a gynecologist. After childbirth, the organs gradually return to their previous state.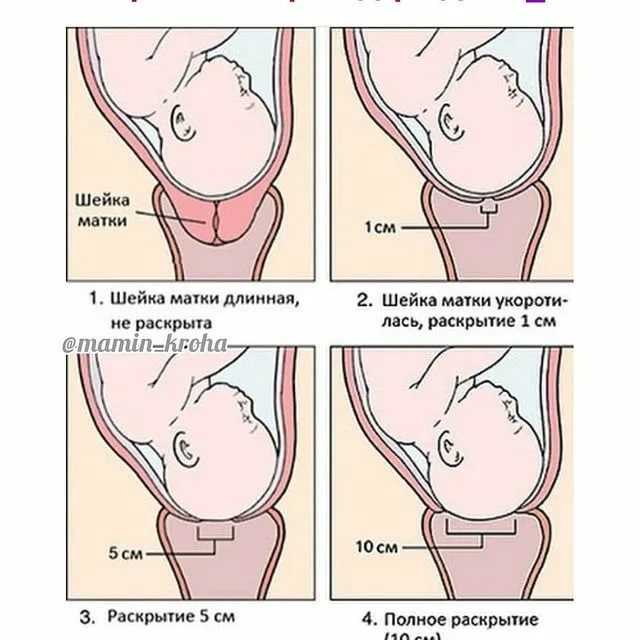 nine0003
nine0003
Changes in gait
After a prolapsed belly, it often becomes more difficult for a woman to walk, and sometimes even to sit and stand. After all, now the pressure on the lower abdomen has increased, sprain of the sacroiliac tissue, pain in the lower back may appear. Fetal pressure on muscles, ligaments, and nerve receptors can cause pain in the legs and lower abdomen.
In addition, the center of gravity has shifted, the shoulders lean back when walking, and the legs are slightly apart (“duck gait”) – the pregnant woman reflexively increases the area of support. nine0003
Warning symptoms
If swelling of the perineum occurs simultaneously with other symptoms, then there is a possibility of developing an infectious or viral disease. This is evidenced by the following symptoms:
Redness or other change in the natural color of the genitals.
Itching, burning.
Pain during or after intercourse.
Eruptions on the surface of the labia.
Unnatural discharge or excessive dryness of the vagina.
The above signs refer to the symptoms of gynecological diseases requiring treatment, as there is a risk of complications for pregnancy. If the labia is swollen during pregnancy and at least one of the above symptoms appears, then you should immediately consult a doctor for diagnostic measures. nine0003
Maturation of the cervix
Perhaps this is the only completely objective and reliable harbinger of the imminent onset of labor. And if we didn’t start the story with it, it’s only because it cannot be seen at home - the maturity of the cervix can only be seen during a medical examination. The cervix is very actively involved in the process of childbirth, and by the end of pregnancy it begins to prepare for it, "ripen"." This means that it becomes soft, stretchable, opens slightly, and its vaginal part shortens from three to four to one and a half centimeters. That is, the cervix is \u200b\u200bready for the onset of childbirth, and with the first contraction it will begin to open. However, sometimes a woman still may suggest that the cervix is maturing: the mucous plug comes out, the discharge becomes more abundant, slight tingling is felt. nine0003
However, sometimes a woman still may suggest that the cervix is maturing: the mucous plug comes out, the discharge becomes more abundant, slight tingling is felt. nine0003
Possible diseases
Swelling of the genital organs, which is accompanied by additional discomfort and pain, may indicate the following diseases:
Candidiasis or thrush. Refers to fungal pathologies, develops in connection with a violation of the microflora of the vagina. It is often found in pregnant women, since hormonal failure, nutrition, decreased immunity, and some other reasons can provoke the disease. Symptoms are manifested in the form of itching, discharge with a specific odor, resembling cottage cheese in structure. nine0007 Vulvovaginitis. Inflammatory process spreading on the surface of the mucous membrane of the genital tract. In addition to swelling of the genitals, there is reddening of the skin, dryness, discharge can be different in abundance, and also have differences in structure and color.
Genital herpes. A viral disease that goes into remission and may temporarily go away. Signs are general malaise, a rash on the genitals in the form of bubbles, itching. There is a high risk of infection of the child if the birth takes place naturally. nine0007 Bartholinitis. Infectious inflammation of the Bartholin glands located in the vestibule of the vagina. Passes with an increase in temperature, sometimes above 39 degrees. The labia not only swell, but become painful, acquire a dark red color.
Varicose veins. Pathology of a non-infectious nature, occurs due to a number of structural changes in the veins, can worsen during pregnancy. In the later stages, swelling of the labia is sometimes observed, associated with significant stress on the pelvic organs. There is a feeling of heaviness, the skin becomes blue due to protruding veins. nine0007 All of the above diseases can cause serious complications not only for the health of the expectant mother, but also for the development of the child.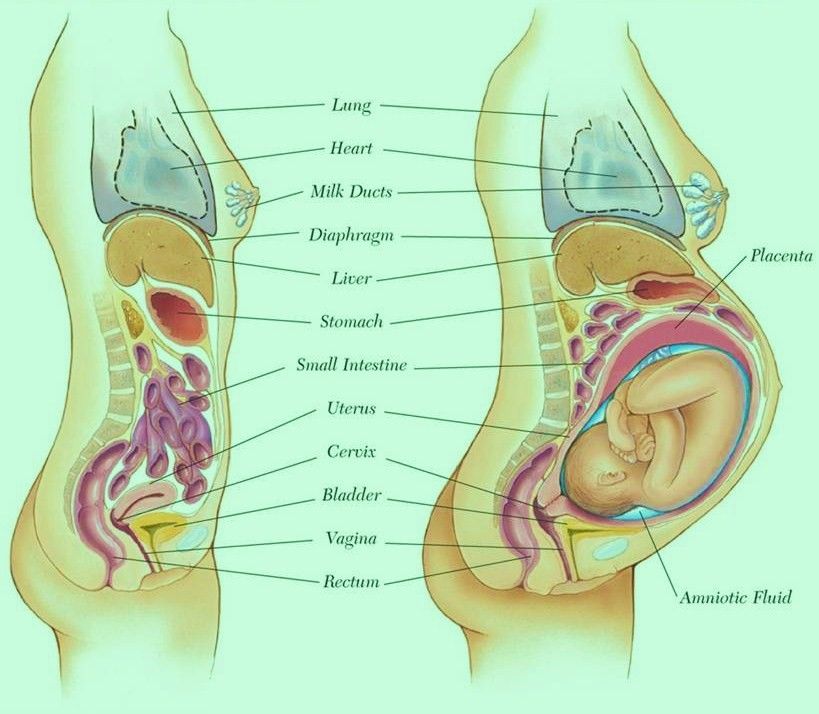 Untreated infections are transmitted at birth to the baby and getting rid of them in a newborn is much more difficult. With advanced stages, for example, genital herpes, a planned CS is prescribed.
Untreated infections are transmitted at birth to the baby and getting rid of them in a newborn is much more difficult. With advanced stages, for example, genital herpes, a planned CS is prescribed.
Home Remedies
Increase your water intake, which not only helps reduce the burning sensation, but also the chance of spreading infection, as bacteria are flushed out of the body when you go to the toilet. nine0007 Cold compresses can be used to relieve inflammation and reduce swelling. In addition, you can also do baths with cool water.
The antifungal and antibacterial properties of garlic are effective in dealing with this problem. You can make a paste of garlic and apply it on the affected area for a few days to get rid of the swelling.
There are some studies showing that increasing your intake of probiotics can help balance your vaginal flora. Studies have used probiotic capsules (with bacteria Lactobacillus acidophilus and L. rhamnosus), but live yogurt can be tried and consumed regularly. nine0007 The antibacterial properties of apple cider vinegar can help relieve swelling. You can add some vinegar to the bath and soak in it for 10-15 minutes.
nine0007 The antibacterial properties of apple cider vinegar can help relieve swelling. You can add some vinegar to the bath and soak in it for 10-15 minutes.
What should I do if my labia is swollen?
If there is swelling of the small lips during pregnancy or the entire perineum is swollen, you should immediately consult a doctor, without waiting for a scheduled appointment. Additional tests may be required, for example, a smear, blood and urine donation. Based on the data obtained and the examination, treatment will be prescribed if there are pathological processes in the form of infection. It may include restorative measures, the use of external agents, in extreme cases, antibiotics adapted for the body of pregnant women are used, with the exception of viral diseases. Their treatment is carried out according to a special scheme, including antiviral agents. nine0003
Diagnosis
In order to cure swelling of the labia during pregnancy, you must first undergo a qualified diagnosis:
Examination of the genitals by a gynecologist,
Clinical analysis of blood, urine,
Scraping for pathogenic flora,
Analysis of feces for helminths,
Coprogram
You can leave a comment or trackback on your site.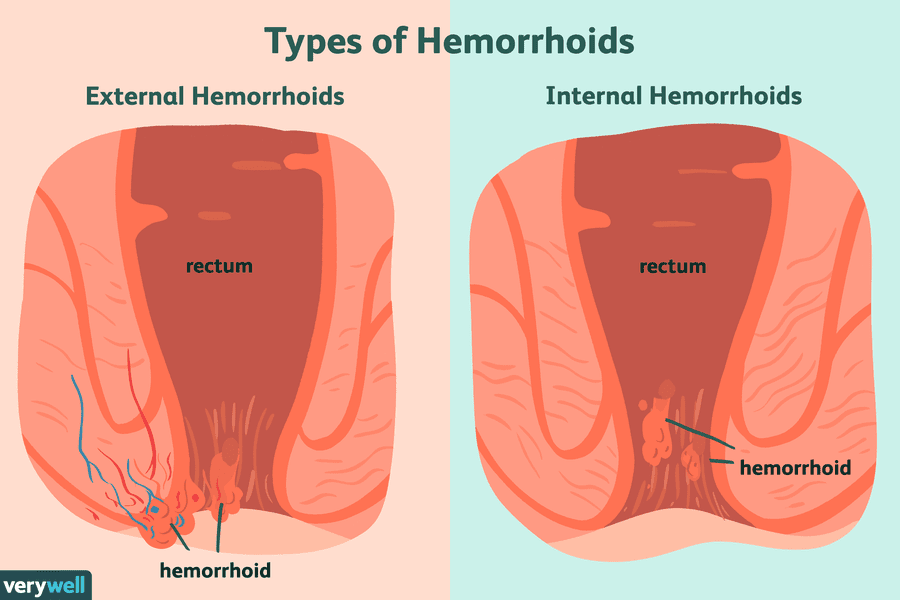
Changes in a woman's body during pregnancy
From the very first days of pregnancy, the body of a pregnant woman undergoes profound transformations. These transformations are the result of the coordinated work of almost all body systems, as well as the result of the interaction of the mother's body with the child's body.
During pregnancy, many internal organs undergo significant restructuring. These changes are adaptive in nature, and, in most cases, are short-lived and completely disappear after childbirth. Consider the changes in the basic systems of the vital activity of a woman's body during pregnancy. nine0003
The respiratory system during pregnancy works hard. The respiratory rate increases. This is due to an increase in the need of the mother and fetus for oxygen, as well as in the limitation of the respiratory movements of the diaphragm due to an increase in the size of the uterus, which occupies a significant space of the abdominal cavity.
Cardio The mother's circulatory system has to pump more blood during pregnancy to ensure an adequate supply of nutrients and oxygen to the fetus. In this regard, during pregnancy, the thickness and strength of the heart muscles increase, the pulse and the amount of blood pumped by the heart in one minute increase. In addition, the volume of circulating blood increases. In some cases, blood pressure increases. The tone of the blood vessels during pregnancy decreases, which creates favorable conditions for enhanced
to supply tissues with nutrients and oxygen. During pregnancy, the network of vessels of the uterus, vagina, and mammary glands decreases sharply. On the external genitalia, in the vagina, lower extremities, there is often an expansion of the veins, sometimes the formation of varicose veins. Heart rate decreases in the second half of pregnancy. It is generally accepted that the rise in blood pressure over 120-130 and a decrease to 100 mm Hg. signal the occurrence of pregnancy complications. But it is important to have data on the initial level of blood pressure. and changes in the blood system. During pregnancy, blood formation increases, the number of red blood cells, hemoglobin, plasma and bcc increases. BCC by the end of pregnancy increases by 30-40%, and erythrocytes by 15-20%. Many healthy pregnant women have a slight leukocytosis. ESR during pregnancy increases to 30-40. Changes occur in the coagulation system that contribute to hemostasis and prevent significant blood loss during childbirth or placental abruption and in the early postpartum period. nine0003
signal the occurrence of pregnancy complications. But it is important to have data on the initial level of blood pressure. and changes in the blood system. During pregnancy, blood formation increases, the number of red blood cells, hemoglobin, plasma and bcc increases. BCC by the end of pregnancy increases by 30-40%, and erythrocytes by 15-20%. Many healthy pregnant women have a slight leukocytosis. ESR during pregnancy increases to 30-40. Changes occur in the coagulation system that contribute to hemostasis and prevent significant blood loss during childbirth or placental abruption and in the early postpartum period. nine0003
Kidneys work hard during pregnancy. They secrete decay products of substances from the body of the mother and fetus (the waste products of the fetus pass through the placenta into the mother's blood).
Changes in the digestive system are represented by increased appetite (in most cases), craving for salty and sour foods. In some cases, there is an aversion to certain foods or dishes that were well tolerated before the onset of pregnancy. Due to the increased tone of the vagus nerve, constipation may occur. nine0003
In some cases, there is an aversion to certain foods or dishes that were well tolerated before the onset of pregnancy. Due to the increased tone of the vagus nerve, constipation may occur. nine0003
The most significant changes, however, occur in the genitals of pregnant women. These changes prepare the woman's reproductive system for childbirth and breastfeeding.
The uterus of a pregnant woman increases significantly in size. Its mass increases from 50 g - at the beginning of pregnancy to 1200 g - at the end of pregnancy. The volume of the uterine cavity by the end of pregnancy increases by more than 500 times! The blood supply to the uterus is greatly increased. In the walls of the uterus, the number of muscle fibers increases. The cervix is filled with thick mucus that clogs the cavity of the cervical canal. The fallopian tubes and ovaries also increase in size. In one of the ovaries, there is a "corpus luteum of pregnancy" - a place for the synthesis of hormones that support pregnancy. nine0003
nine0003
The walls of the vagina will loosen and become more elastic.
External genitalia (labia minor and major) also increase in size and become more elastic. The tissues of the perineum are loosened. In addition, there is an increase in mobility in the joints of the pelvis and a divergence of the pubic bones. The changes in the genital tract described above are of extremely important physiological significance for childbirth. Loosening the walls, increasing the mobility and elasticity of the genital tract increases their throughput and facilitates the movement of the fetus through them during childbirth. nine0003
Skin in the genital area and in the midline of the abdomen usually becomes darker in color. Sometimes "stretch marks" form on the skin of the lateral parts of the abdomen, which after childbirth turn into whitish stripes.
Mammary glands increase in size, become more elastic, tense. When pressing on the nipple, colostrum (first milk) is released. Changes of the bone skeleton and muscular system . An increase in the concentration of the hormones relaxin and progesterone in the blood contributes to the leaching of calcium from the skeletal system. This accomplishes two goals. On the one hand, this helps to reduce the rigidity of the joints between the bones of the pelvis (especially the pubic joint) and increase the elasticity of the pelvic ring. Increasing the elasticity of the pelvis is of great importance in increasing the diameter of the internal bone ring in the first stage of labor and further reducing the resistance of the birth tract to fetal movement in the second stage of labor. Secondly, calcium, washed out of the mother's skeletal system, is used to build the skeleton of the fetus. nine0003
Changes of the bone skeleton and muscular system . An increase in the concentration of the hormones relaxin and progesterone in the blood contributes to the leaching of calcium from the skeletal system. This accomplishes two goals. On the one hand, this helps to reduce the rigidity of the joints between the bones of the pelvis (especially the pubic joint) and increase the elasticity of the pelvic ring. Increasing the elasticity of the pelvis is of great importance in increasing the diameter of the internal bone ring in the first stage of labor and further reducing the resistance of the birth tract to fetal movement in the second stage of labor. Secondly, calcium, washed out of the mother's skeletal system, is used to build the skeleton of the fetus. nine0003
It should be noted that calcium compounds are washed out of all bones of the maternal skeleton (including the bones of the foot and spine). As shown earlier, a woman's weight increases during pregnancy by 10 -12 kg.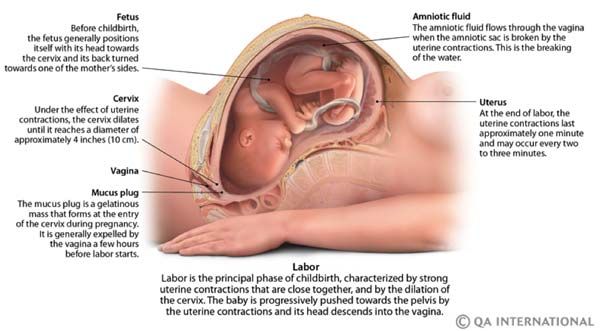 This additional load against the background of a decrease in bone stiffness can cause foot deformity and the development of flat feet. A shift in the center of gravity of the body of a pregnant woman due to an increase in the weight of the uterus can lead to a change in the curvature of the spine and the appearance of pain in the back and pelvic bones. Therefore, for the prevention of flat feet, pregnant women are advised to wear comfortable shoes with low heels. It is advisable to use insoles that support the arch of the foot. For the prevention of back pain, special physical exercises are recommended that can unload the spine and sacrum, as well as wearing a comfortable bandage. Despite an increase in calcium loss by the bones of the skeleton of a pregnant woman and an increase in their elasticity, structure and bone density (as is the case with osteoporosis in older women). nine0003
This additional load against the background of a decrease in bone stiffness can cause foot deformity and the development of flat feet. A shift in the center of gravity of the body of a pregnant woman due to an increase in the weight of the uterus can lead to a change in the curvature of the spine and the appearance of pain in the back and pelvic bones. Therefore, for the prevention of flat feet, pregnant women are advised to wear comfortable shoes with low heels. It is advisable to use insoles that support the arch of the foot. For the prevention of back pain, special physical exercises are recommended that can unload the spine and sacrum, as well as wearing a comfortable bandage. Despite an increase in calcium loss by the bones of the skeleton of a pregnant woman and an increase in their elasticity, structure and bone density (as is the case with osteoporosis in older women). nine0003
Changes in the nervous system . In the first months of pregnancy and at the end of it, there is a decrease in the excitability of the cerebral cortex, which reaches its greatest degree by the time of the onset of childbirth.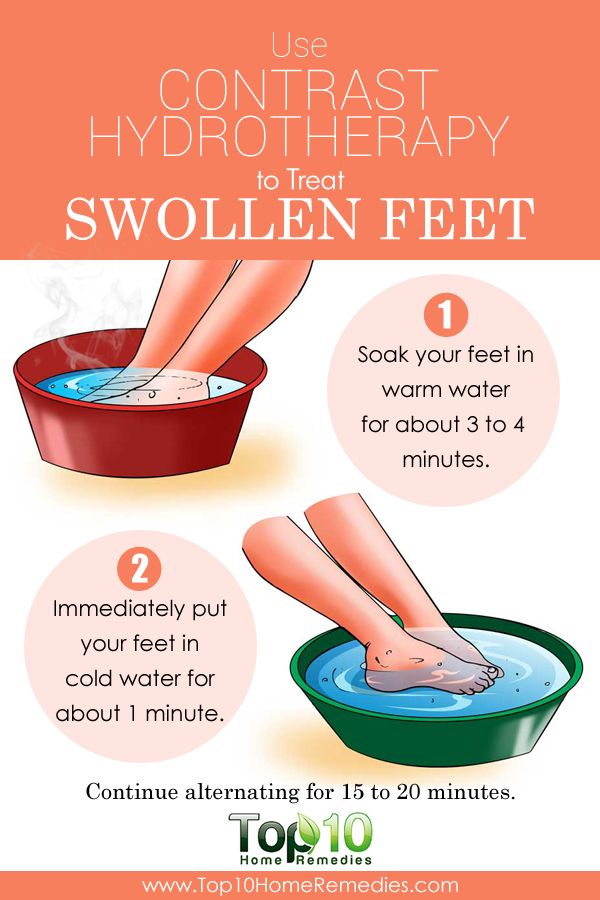 By the same period, the excitability of the receptors of the pregnant uterus increases. At the beginning of pregnancy, there is an increase in the tone of the vagus nerve, in connection with which various phenomena often occur: changes in taste and smell, nausea, increased salivation, etc.
By the same period, the excitability of the receptors of the pregnant uterus increases. At the beginning of pregnancy, there is an increase in the tone of the vagus nerve, in connection with which various phenomena often occur: changes in taste and smell, nausea, increased salivation, etc.
Active endocrine glands there are significant changes that contribute to the proper course of pregnancy and childbirth. Changes in body weight. By the end of pregnancy, a woman's weight increases by about 10-12 kg. This value is distributed as follows: fetus, placenta, membranes and amniotic fluid - approximately 4.0 - 4.5 kg, uterus and mammary glands -1.0 kg, blood - 1.5 kg, intercellular (tissue) fluid - 1 kg , an increase in the mass of adipose tissue of the mother's body - 4 kg.
Conclusion. nine0006 Summarizing the facts concerning changes in a woman's body during pregnancy, it is worth emphasizing that these changes reflect the processes of physiological adaptation of the mother's body to the process of intrauterine development of the fetus.

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/hemorrhage-in-miscarriage-meaning-2371523-FINAL-f2ab04cab1cc491e964a45e682f93da5.png)