What is the normal hcg level at 2 weeks
hCG levels | Pregnancy Birth and Baby
hCG levels | Pregnancy Birth and Baby beginning of content3-minute read
Listen
Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) is a hormone normally produced by the placenta. If you are pregnant, you can detect it in your urine. Blood tests measuring hCG levels can also be used to check how well your pregnancy is progressing.
Confirming pregnancy
After you conceive (when the sperm fertilises the egg), the developing placenta begins to produce and release hCG.
It takes about 2 weeks for your hCG levels to be high enough to be detected in your urine using a home pregnancy test.
A positive home test result is almost certainly correct, but a negative result is less reliable.
If you do a pregnancy test on the first day after your missed period, and it’s negative, wait about a week. If you still think you might be pregnant, do the test again or see your doctor.
hCG blood levels by week
If your doctor needs more information about your hCG levels, they may order a blood test. Low levels of hCG may be detected in your blood around 8 to 11 days after conception. hCG levels are highest towards the end of the first trimester, then gradually decline over the rest of your pregnancy.
The average levels of hCG in a pregnant woman’s blood are:
| 3 weeks | 6 – 70 IU/L |
| 4 weeks | 10 - 750 IU/L |
| 5 weeks | 200 - 7,100 IU/L |
| 6 weeks | 160 - 32,000 IU/L |
| 7 weeks | 3,700 - 160,000 IU/L |
| 8 weeks | 32,000 - 150,000 IU/L |
| 9 weeks | 64,000 - 150,000 IU/L |
| 10 weeks | 47,000 - 190,000 IU/L |
| 12 weeks | 28,000 - 210,000 IU/L |
| 14 weeks | 14,000 - 63,000 IU/L |
| 15 weeks | 12,000 - 71,000 IU/L |
| 16 weeks | 9,000 - 56,000 IU/L |
| 16 - 29 weeks (second trimester) | 1,400 - 53,000 IU/L |
| 29 - 41 weeks (third trimester) | 940 - 60,000 IU/L |
The amount of hCG in your blood can give some information about your pregnancy and the health of your baby.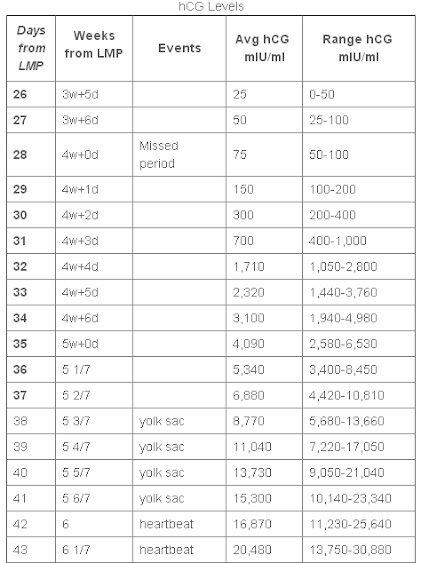
- Higher than expected levels: you may have multiple pregnancies (for example, twins and triplets) or an abnormal growth in the uterus
- Your hCG levels are falling: you may be having a loss of pregnancy (miscarriage) or risk of miscarriage
- Levels that are rising more slowly than expected: you may have an ectopic pregnancy – where the fertilised egg implants in the fallopian tube
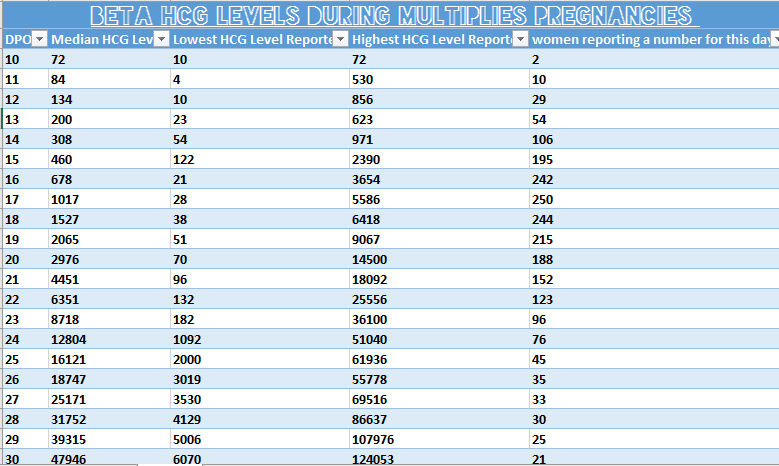
hCG levels and multiple pregnancies
One of the ways of diagnosing a multiple pregnancy is by your hCG levels. A high level may indicate you are carrying multiple babies, but it can also be caused by other factors. You will need an ultrasound to confirm that it’s twins or more.
Levels of hCG in your blood don’t provide a diagnosis of anything. They can only suggest that there are issues to look into.
If you have any concerns about your hCG levels, or wish to know more, speak to your doctor or maternity healthcare professional. You can also call Pregnancy, Birth and Baby to speak to a maternal child health nurse on 1800 882 436.
Sources:
UNSW Embryology (Human Chorionic Gonadotropin), Elsevier Patient Education (Human Chorionic Gonadotropin test), SydPath (hCG (human Chorionic Gonadotrophin), Pathology Tests Explained (Human chorionic gonadotropin), NSW Government Health Pathology (hCG factsheet)Learn more here about the development and quality assurance of healthdirect content.
Last reviewed: December 2020
Back To Top
Related pages
- Due date calculator
- Pregnancy tests
- Early signs of pregnancy
Need more information?
Human chorionic gonadotropin - Pathology Tests Explained
Why and when to get tested for hCG
Read more on Pathology Tests Explained website
Pregnancy testing - MyDr.
 com.au
com.au Pregnancy testing can be done from around the time that your period is due, and involves testing your urine for the pregnancy hormone called human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG).
Read more on myDr website
Pregnancy tests
Find out how a home pregnancy test works.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Pregnancy testing - Better Health Channel
Sometimes, a home pregnancy test may be positive when a woman isn’t pregnant.
Read more on Better Health Channel website
Molar pregnancy
A molar pregnancy is a type of pregnancy where a baby does not develop. A molar pregnancy can be either complete or partial.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Beta HCG Test | HealthEngine Blog
A Beta HCG (BHCG or Blood Pregnancy Test) May Be Performed by Your Doctor If They Suspect That You May Be Pregnant, or if You Suspect Pregnancy Yourself!
Read more on HealthEngine website
5 weeks pregnant: Changes for mum
Week 5 of pregnancy is probably when you’ll know that you’re pregnant because your period is missing. There are also subtle changes in your body which are symptoms of pregnancy such as changes to your breasts, and pregnancy symptoms like morning sickness and pregnancy heartburn. These changes are caused by pregnancy hormones, like hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin, produced by the placenta) which is the hormone detected by a pregnancy test.
Read more on Parenthub website
4 weeks pregnant: Key points
When you are 4 weeks pregnant your body and your new baby are undergoing rapid changes. The placenta forms and begins producing a hormone called human chorionic gonadotrophin (hCG), which is the substance a pregnancy test detects to confirm you are pregnant. The cells which are growing into your new baby establish membranes which connect them to the placenta and prepare themselves for differentiation into different types of cells, which will occur next week when you are 5 weeks pregnant. These developments may cause you to experience unusual emotions and also cause changes in your body such as darkening of the areolas of your nipples.
Read more on Parenthub website
Week by week pregnancy- 6 weeks pregnant
6 weeks pregnant is a time when embryo development is occurring rapidly and pregnant women often start experiencing pregnancy symptoms like morning sickness.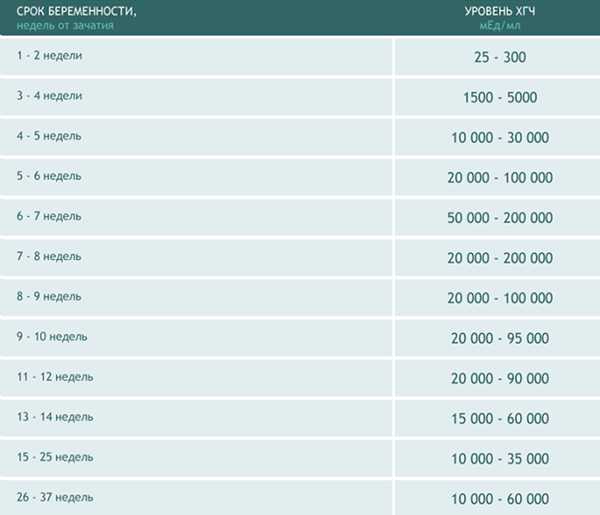 Pregnancy hormone human chorionic gonadotrophin (hCG), the hormone a pregnancy test detects, is usually evident in the woman’s blood in the sixth week of pregnancy. Antenatal care should be provided at a doctor appointment for women who have not already checked their pregnancy health. Find out more about the pregnancy changes which occur this week.
Pregnancy hormone human chorionic gonadotrophin (hCG), the hormone a pregnancy test detects, is usually evident in the woman’s blood in the sixth week of pregnancy. Antenatal care should be provided at a doctor appointment for women who have not already checked their pregnancy health. Find out more about the pregnancy changes which occur this week.
Read more on Parenthub website
5 weeks pregnant: Key points
The fifth week of pregnancy begins around the time your menstrual bleeding is due and is a good time to take a pregnancy test to confirm that you are pregnant. You are also likely to begin experiencing pregnancy symptoms like fatigue, morning sickness and changes to your breasts this week. Your baby is still only about 1.5mm long but it is developing rapidly and taking on a more human form. If you have not already visited your doctor the 5th week of pregnancy is a good time to do so.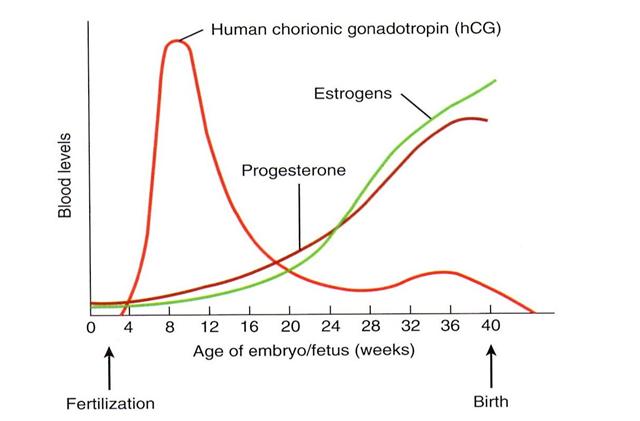
Read more on Parenthub website
Disclaimer
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is not responsible for the content and advertising on the external website you are now entering.
OKNeed further advice or guidance from our maternal child health nurses?
1800 882 436
Video call
- Contact us
- About us
- A-Z topics
- Symptom Checker
- Service Finder
- Linking to us
- Information partners
- Terms of use
- Privacy
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is funded by the Australian Government and operated by Healthdirect Australia.
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is provided on behalf of the Department of Health
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby’s information and advice are developed and managed within a rigorous clinical governance framework. This website is certified by the Health On The Net (HON) foundation, the standard for trustworthy health information.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
This information is for your general information and use only and is not intended to be used as medical advice and should not be used to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any medical condition, nor should it be used for therapeutic purposes.
The information is not a substitute for independent professional advice and should not be used as an alternative to professional health care. If you have a particular medical problem, please consult a healthcare professional.
Except as permitted under the Copyright Act 1968, this publication or any part of it may not be reproduced, altered, adapted, stored and/or distributed in any form or by any means without the prior written permission of Healthdirect Australia.
Support this browser is being discontinued for Pregnancy, Birth and Baby
Support for this browser is being discontinued for this site
- Internet Explorer 11 and lower
We currently support Microsoft Edge, Chrome, Firefox and Safari. For more information, please visit the links below:
- Chrome by Google
- Firefox by Mozilla
- Microsoft Edge
- Safari by Apple
You are welcome to continue browsing this site with this browser. Some features, tools or interaction may not work correctly.
Normal hCG Levels in Early Pregnancy
By:
Amos Grünebaum
Updated on March 4, 2021
What is hCG?hCG stands for human chorionic gonadotropin, the pregnancy hormone, which is produced by the placenta and detected in the blood within a few days after implantation. When you test at home with a pregnancy test, you actually test for the presence of hCG in the urine. If hCG is present, then the pregnancy test will be positive, and that means you are pregnant unless there is a false positive pregnancy test.
If hCG is present, then the pregnancy test will be positive, and that means you are pregnant unless there is a false positive pregnancy test.
Track your pregnancy
Get expert guidance and personalized insights to stay healthy through every week of your pregnancy.
Get the app!
How does hCG increase during early pregnancy?
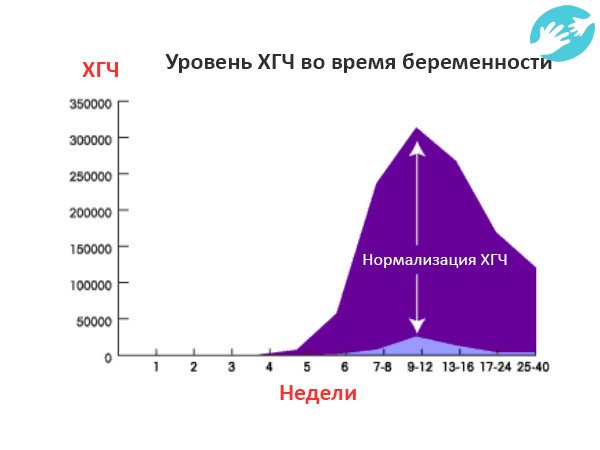
hCG usually doubles every 48-72 hours very early in pregnancy and every 3-4 days later on until about 9-10 weeks of the pregnancy when it levels off. There is no single "normal" hCG level during early pregnancy and there are wide ranges of normal levels that you can check with our hCG calculator.
What are normal hCG values and rise?
- Blood hCG under 5 mIU/ml: Negative. Not pregnant
- Blood hCG between 5-25 mIU/ml: "Equivocal". Maybe pregnant, maybe not. Repeat test in a couple of days
- Blood hCG over 25 mIU/ml: You are pregnant!
- One single hCG reading is not enough to make a clear diagnosis.
 Several hCG tests 2 or more days apart give a more accurate assessment of the situation.
Several hCG tests 2 or more days apart give a more accurate assessment of the situation. - The blood hCG levels should not be used to date a pregnancy since these numbers can vary so widely.
- For postmenopausal women, an hCG level up to 14 mIU/ml can be considered normal.
- In a study of 20 patients in the first 40 days of pregnancy, the hCG concentration rose by at least 66 percent every 48 hours in 85 percent of viable IUPs; but still, 15 percent of viable pregnancies had a rate of hCG rise less than this threshold. (Kadar 1981)
- An increase of >=35% in 48 hours can still be considered normal (Seeber 2006; Morse 2012)
- hCG levels are best checked based on ovulation/fertilization day because the day of the last period can vary.
How does implantation affect hCG?
Implantation occurs on average, 9 days after ovulation (with a range of 6-12 days) or about 5 days before a missed period. hCG levels are detected in the blood as early as 2-3 days, and in the urine 3-4 days, after implantation. A urine pregnancy test would be expected to be positive around the time of a missed period or 14-15 days after implantation (which can be as early as several days before a missed period).
A urine pregnancy test would be expected to be positive around the time of a missed period or 14-15 days after implantation (which can be as early as several days before a missed period).
Find out what your levels mean with our hCG calculator!
What are good hCG levels in early pregnancy?- In most normal pregnancies, at hCG levels below 1,200 mIU/ml, the hCG level usually doubles every 48-72 hours and normally increases by at least 60% every two days.
- In early pregnancy, a 48-hour increase of hCG by 35% can still be considered normal.
- As your pregnancy progresses, the hCG level increase slows down significantly.
- Between 1,200 and 6,000 mIU/ml serum, the hCG level usually takes 72-96 hours to double.
- Above 6,000 mIU/ml, the hCG level often takes over four or more days to double.
- In general, when the hCG level reaches 7200 mIU/ml, a yolk sac should be seen.
- At an hCG level greater than 10,800 mIU/ml, there should be a visible embryo with a heartbeat.
It makes little sense to follow the hCG values above 6,000 mIU/ml as the increase is normally slower and not related to how well the pregnancy is doing. After 10-12 weeks, the hCG level increase will slow even further and eventually will even decline before reaching a plateau for the duration of the pregnancy.
A normal hCG rise over several days prior to 6 weeks of the pregnancy usually indicates a viable pregnancy.
Can hCG levels tell you if your pregnancy is healthy?
Pregnancy blood hCG levels are not recommended for testing the viability of the pregnancy when the hCG level is well over 6,000 and/or after 6-7 weeks of the pregnancy. Blood hCG levels are useless for testing the viability of the pregnancy if the hCG level is well over 6,000 and/or after 6-7 weeks days of the pregnancy. In general, after 6-7 weeks the best indication of a healthy pregnancy is a good fetal heartbeat. Instead of the hCG, after 6 weeks or an hCG above 6,000 mIU/cc, the health of the pregnancy can best be confirmed with a sonogram to confirm the presence of a fetal heartbeat.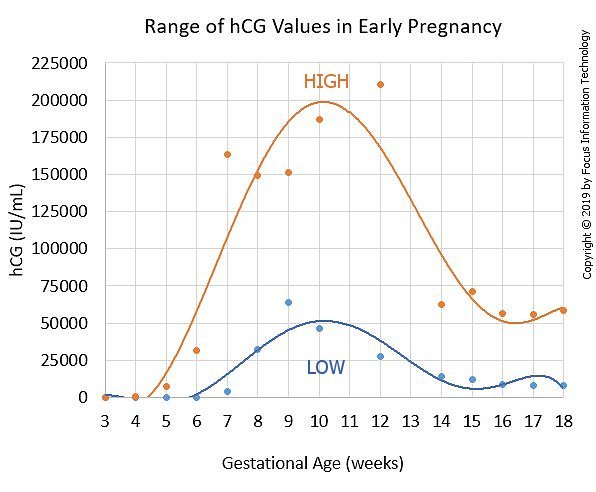 Once a fetal heartbeat is seen, the hCG levels don't tell you much more about the pregnancy viability.
Once a fetal heartbeat is seen, the hCG levels don't tell you much more about the pregnancy viability.
There is a wide range of normal hCG values and the values are different in blood serum or urine. Urine hCG levels are usually lower than serum (blood) hCG levels. There is no single normal human chorionic gonadotropin hCG level that always indicates a healthy pregnancy and there is a very wide range of human chorionic gonadotropin hCG levels values as the pregnancy progresses.
Read about slow-rising hCG levels.
Comparing slow rising and normal rising hCG levelsComparing changes in hCG titers with those of established expected curves can help the doctor determine what to do about the pregnancy and how to counsel the patient. However, there are many limitations to the serial assessment of hCG titers and the titers should never be used exclusively to replace clinical judgment based on symptoms or signs.
A normally rising hCG level would usually be a level that rises over 60% over a 48 period, though later on in pregnancy, the rise would be normally slower. Seebert et al reported in 2006 and Morse confirmed in 2012 that a rise of at least 35% over 48 hours was proposed as the minimal rise consistent with a viable intrauterine pregnancy.
Seebert et al reported in 2006 and Morse confirmed in 2012 that a rise of at least 35% over 48 hours was proposed as the minimal rise consistent with a viable intrauterine pregnancy.
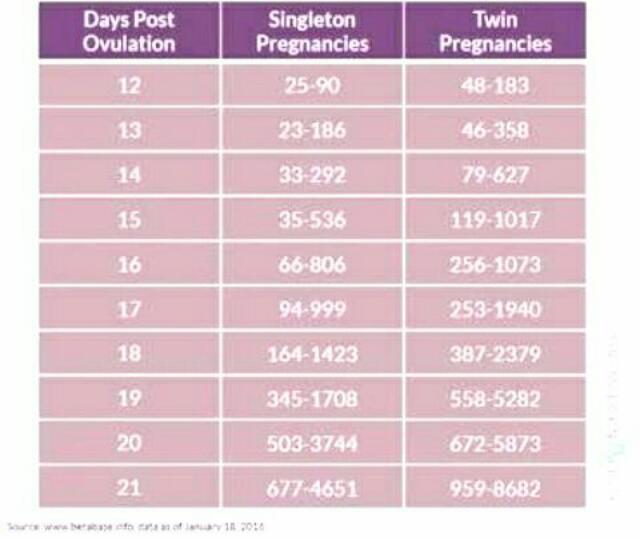
You cannot diagnose a twin pregnancy just from the hCG. There is no sufficient scientific evidence that with twins there is always a faster-than-usual rise in hCG. Normal hCG values can vary up to 20 times in normal pregnancies. Variations in hCG increases are not necessarily a sign that the pregnancy is abnormal or that there are two or more fetuses.
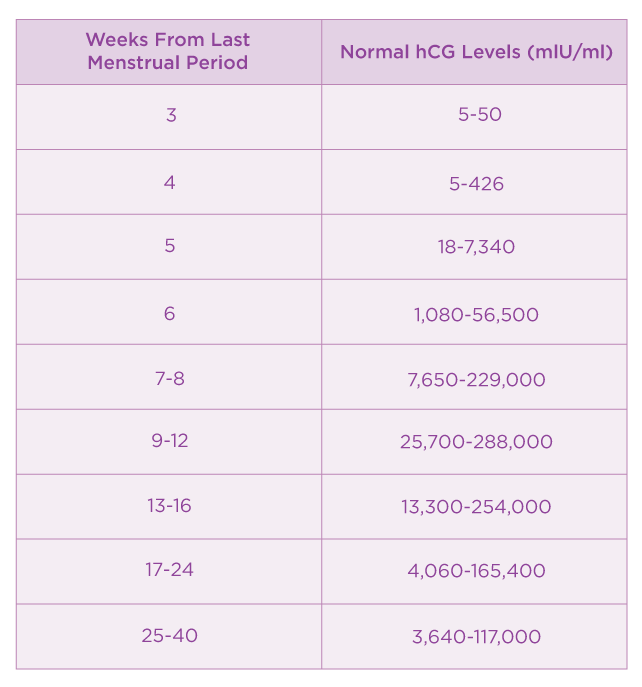
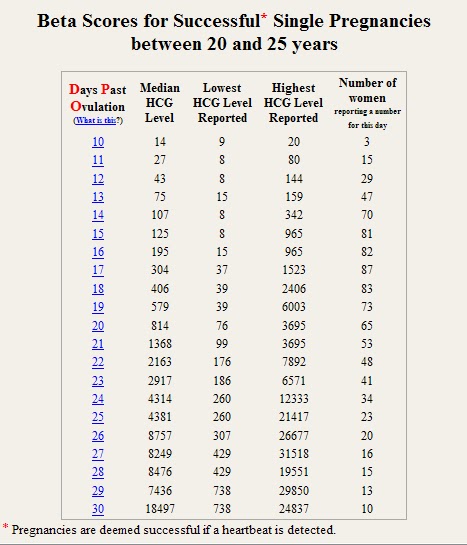
Normal amount of serum hCG levels by weeks
3 weeks: 5-50 mIU/cc
4 weeks: 4-426 mIU/cc
5 weeks: 19-7,340 mIU/cc
6 weeks: 1,080-56,500 mIU/cc
7 - 8 weeks: 7,650-229,000 mIU/cc
9 - 12 weeks: 25,700-288,000 mIU/cc
13 - 16 weeks: 13,300-254,000 mIU/cc
17 - 24 weeks: 4,060-165,400 mIU/cc
25 - 40 weeks: 3,640-117,000 mIU/cc
From Gnoth and Johnson
Everything you ever wanted to know about hCG- hCG is measured in milli-international units per milliliter (mIU/ml).
- There is a wide range of normal hCG levels and values and the values are different in blood serum or urine.
- Blood hCG levels are not very helpful to test for the viability of the pregnancy if the hCG level is above 6,000 and/or after 6-7 weeks of the pregnancy. Instead, to test the health of the pregnancy better, a sonogram should be done to confirm the presence of a fetal heartbeat. Once a fetal heartbeat is seen, it is not recommended to check the pregnancy viability with hCG levels.
- Urine hCG levels are usually lower than serum (blood) hCG levels.
- Blood hCG testing is much more sensitive than urine HPT. This means that the blood test can detect pregnancy several days earlier than the urine test, as early as 2-3 days after implantation or 8-9 days after fertilization.
- Urine tests measure the urine hCG qualitatively, which means that the HPT results are either "positive" or "negative." Around the time of the first missed period (14+ days after ovulation), over 95% of HPTs are usually positive.
- Pregnancy test manufacturer's claim that their test is "99% accurate" means something different than what you think.
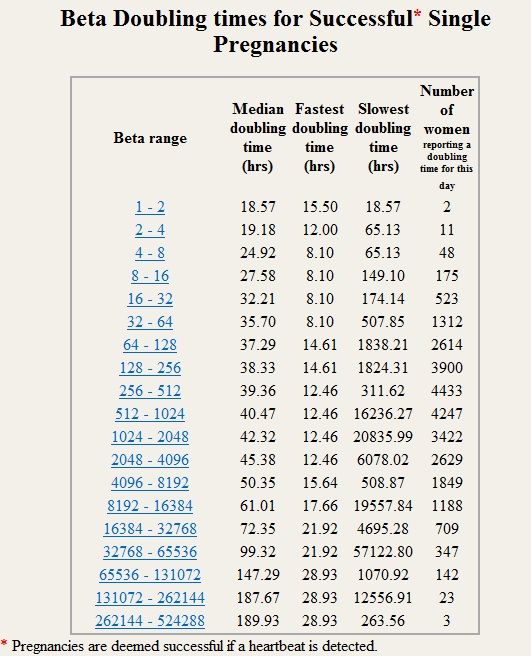
- About 85% of normal pregnancies will have the hCG level double every 48 - 72 hours. As you get further along into pregnancy and the hCG level gets higher, the time it takes to double can increase to about every 96 hours.
- Beta hCG levels usually double about every 2 days for the first four weeks of pregnancy.
- As pregnancy progresses the doubling time becomes longer. By 6 to 7 weeks beta hCG levels may take as long as 3 1/2 days to double.
- hCG normally reaches a peak level at about 8 to 10 weeks and then declines for the remainder of the pregnancy.
- The beta hCG level for a successful intrauterine pregnancy should be expected to increase by at least 35% in two days [Morse and coworkers (2012)].
- For women who are having a miscarriage, the beta hCG should be expected to fall 36 - 47% over two days. A fall that is slower than this is suggestive of an ectopic pregnancy.

- Serial hCG values should not be used alone to determine whether or not a pregnancy is likely to be a successful intrauterine pregnancy, a miscarriage, or an ectopic pregnancy. Serial hCG values should be used in combination with clinical judgment, evaluation of symptoms, and repeat ultrasound (as needed).
- Caution must be used in making too much of hCG numbers. A normal pregnancy may have low hCG levels and deliver a perfectly healthy baby. The results of ultrasound after 5 - 6 weeks gestation are much more accurate than using hCG numbers.
- An hCG of less than 5 mIU/cc is usually negative, over 25 mIU/cc usually positive, between 5 and 25 mIU/cc it's "equivocal" which simply means we don't know.
- hCG levels are also higher in women carrying a female fetus when compared to women carrying a male fetus, so it is possible that the pregnancy test becomes positive later in women carrying a male fetus.
- A transvaginal ultrasound should be able to see at least a gestational sac once the hCG levels have reached between 1,000 - 2,000mIU/ml.
 Because levels can differentiate so much and conception dating can be wrong, a diagnosis should not be made by ultrasound findings until the level has reached at least 2,000.
Because levels can differentiate so much and conception dating can be wrong, a diagnosis should not be made by ultrasound findings until the level has reached at least 2,000. - A single hCG reading is not enough information for most diagnoses. When there is a question regarding the health of the pregnancy, multiple testings of hCG done a couple of days apart give a more accurate look at assessing the situation.
- hCG levels should not be used to date a pregnancy since these numbers can vary so widely.
- There are two common types of hCG tests. A qualitative hCG test just looks to see if hCG is present in the blood. A quantitative hCG test (or beta hCG) measures the amount of hCG actually present in the blood.
- Other than for the diagnosis of pregnancy, hCG is also often monitored over time for reasons such as monitoring after a miscarriage, monitoring an ectopic pregnancy, and after a condition called "H.mole."
- The first detection of hCG in the blood depends on when implantation happens.
 Extremely sensitive tests (not usually available in a regular laboratory) can detect the hCG even before implantation. But with regular laboratory hCG tests, hCG is usually found in sufficient levels as early as 2-3 days after implantation.
Extremely sensitive tests (not usually available in a regular laboratory) can detect the hCG even before implantation. But with regular laboratory hCG tests, hCG is usually found in sufficient levels as early as 2-3 days after implantation. - Implantation happens as early as 6 days after ovulation/fertilization (usually about 9 days after ovulation), so blood hCG can be found as early as 8-9 days after ovulation/fertilization.
- Pregnant women usually attain blood serum concentrations of at least 10-50 mIU/cc in the 7-8 days following implantation.
- An equivocal test of between 5 and 25 mIU/cc requires a repeat within 2-3 days. If it goes higher then that's a good sign, but if it goes lower or stays about the same then that's a sign that the pregnancy has failed
- hCG monitoring is useful to assess the pregnancy before the fetal heart is seen (before 6-7 weeks after LMP), usually to rule out an ectopic pregnancy or an early miscarriage
- In an ectopic pregnancy, hCG increases at lower rates than in a normal pregnancy
- About 21% of ectopic pregnancies (pregnancies implanted outside of the uterus) have a rise in hCG similar to an intrauterine pregnancy and 8% of ectopic pregnancies have a fall in hCG similar to a miscarriage.
- In a nonviable pregnancy, it also rises slower.
- At hCG levels above 1,000-1,500 mIU/ml, vaginal sonography usually identifies the presence of an intrauterine pregnancy.
- Within the first 2-4 weeks after fertilization, hCG usually doubles every 48-72 hours.
- An increase of at least 35% in 48 hours in early pregnancy is still considered normal.
- Below 1,200 mIU/ml, hCG usually doubles every 48-72 hours, but 35%+ is still normal.
- Between 1,200 and 6,000 mIU/ml serum, the hCG usually takes 72-96 hours to double.
- Above 6,000 mIU/ml, the hCG often takes over four days to double.
- More than two in three normal pregnancies have a doubling of the hCG every 72 hours.
- There is a wide variation of normal hCG levels. An hCG that does not double every two to three days does not necessarily indicate a problem.
- A maximum level is usually reached by the 10th or 11th week.
- After 10 weeks or so, hCG normally decreases.
- Normal hCG values vary up to 20 times between different pregnancies.
- A single hCG value doesn't give enough information about the viability of the pregnancy.
- Pregnancies that will miscarry and ectopic (tubal) pregnancies are likely to show lower levels and slower rises but often have normal levels initially.
- Some normal pregnancies will have quite low levels of hCG — and deliver perfect babies.
- Once the fetal activity has been detected by ultrasound in a normal patient population, the chances of a normal delivery are about 95%.
- Normal levels of hCG can vary tremendously. After 5-6 weeks of pregnancy, sonogram findings are much more predictive of pregnancy outcome than are HCG levels. Once the fetal heart rate is seen, most doctors will monitor the fetal heart rate rather than drawing hCG.
- After hCG injections (Profasi, Pregnyl) to trigger ovulation or to lengthen the luteal phase, trace amounts of hCG can remain in the body as long as 14 days or longer after the last hCG injection.
 This may give a false positive on a pregnancy test.
This may give a false positive on a pregnancy test. - Two consecutive quantitative hCG beta blood tests can determine whether the hCG is from an injection or pregnancy. If the hCG level increases by the second test, you are likely pregnant.
- At a blood hCG level in early pregnancy below 1,200 mIU/ml, the hCG usually doubles every 48-72 hours and it should normally increase by at least 60% every two days.
- Between 1,200 and 6,000 mIU/ml serum levels in early pregnancy, the hCG usually takes 72-96 hours to double.
- Above 6,000 mIU/ml, the hCG often takes over four or more days to double.
- The gestational sac is usually seen on a transvaginal ultrasound once the hCG levels have reached between 1,000 – 2,000mIU/ml.
- At an hCG level greater than 12,000 mIU/ml there should be a visible embryo with a heartbeat, though it could take up to an hCG level of 22,000 mIU/ml to first see the fetal heartbeat.
- After 9-10 weeks of pregnancy levels normally decrease.
- It makes little sense to follow the hCG level above 6,000 mIU/ml as the increase is normally slower at this point and not related to how well the pregnancy is progressing. After two to three months the level of hCG will slow even further and may even decline before reaching a plateau for the duration of the pregnancy.
- For postmenopausal women, an hCG level up to 14 mIU/ml can be considered normal.
[bmed_ad]
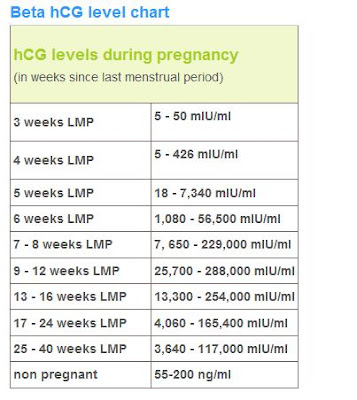
Chart of hCG level by week
| Days from LMP | Weeks | Events | Avg hCG | Range hCG |
| 26 | 3w+5d | 25 | 0-50 | |
| 27 | 3w+6d | 50 | 25-100 | |
| 28 | 4w+0d | Missed period | 75 | 50-100 |
| 29 | 4w+1d | 150 | 100-200 | |
| 30 | 4w+2d | 300 | 200-400 | |
| 31 | 4w+3d | 700 | 400-1,000 | |
| 32 | 4w+4d | 1,710 | 1,050-2,800 | |
| 33 | 4w+5d | 2,320 | 1,440-3,760 | |
| 34 | 4w+6d | 3,100 | 1,940-4,980 | |
| 35 | 5w+0d | 4,090 | 2,580-6,530 | |
| 36 | 5 1/7 | 5,340 | 3,400-8,450 | |
| 37 | 5 2/7 | 6,880 | 4,420-10,810 | |
| 38 | 5 3/7 | yolk sac | 8,770 | 5,680-13,660 |
| 39 | 5 4/7 | yolk sac | 11,040 | 7,220-17,050 |
| 40 | 5 5/7 | yolk sac | 13,730 | 9,050-21,040 |
| 41 | 5 6/7 | yolk sac | 15,300 | 10,140-23,340 |
| 42 | 6 | heartbeat | 16,870 | 11,230-25,640 |
| 43 | 6 1/7 | heartbeat | 20,480 | 13,750-30,880 |
| 44 | 6 2/7 | heartbeat | 24,560 | 16,650-36,750 |
| 45 | 6 3/7 | embryo seen | 29,110 | 19,910-43,220 |
| 46 | 6 4/7 | embryo seen | 34,100 | 25,530-50,210 |
| 47 | 6 5/7 | embryo seen | 39,460 | 27,470-57,640 |
| 48 | 6 6/7 | embryo seen | 45,120 | 31,700-65,380 |
| 49 | 7 | 50,970 | 36,130-73,280 | |
| 50 | 7 1/7 | 56,900 | 40,700-81,150 | |
| 51 | 7 2/7 | 62,760 | 45,300-88,790 | |
| 52 | 7 3/7 | 68,390 | 49,810-95,990 | |
| 53 | 7 4/7 | 73,640 | 54,120-102,540 | |
| 54 | 7 5/7 | 78,350 | 58,200-108,230 | |
| 55 | 7 6/7 | 82,370 | 61,640-112,870 | |
| 56 | 8 | 85,560 | 64,600-116,310 |
Read More:
hCG Levels and Sex of Fetus
hCG Chart and Calculator
Sources:
Barnhart KT, Sammel MD, Rinaudo PF, et al.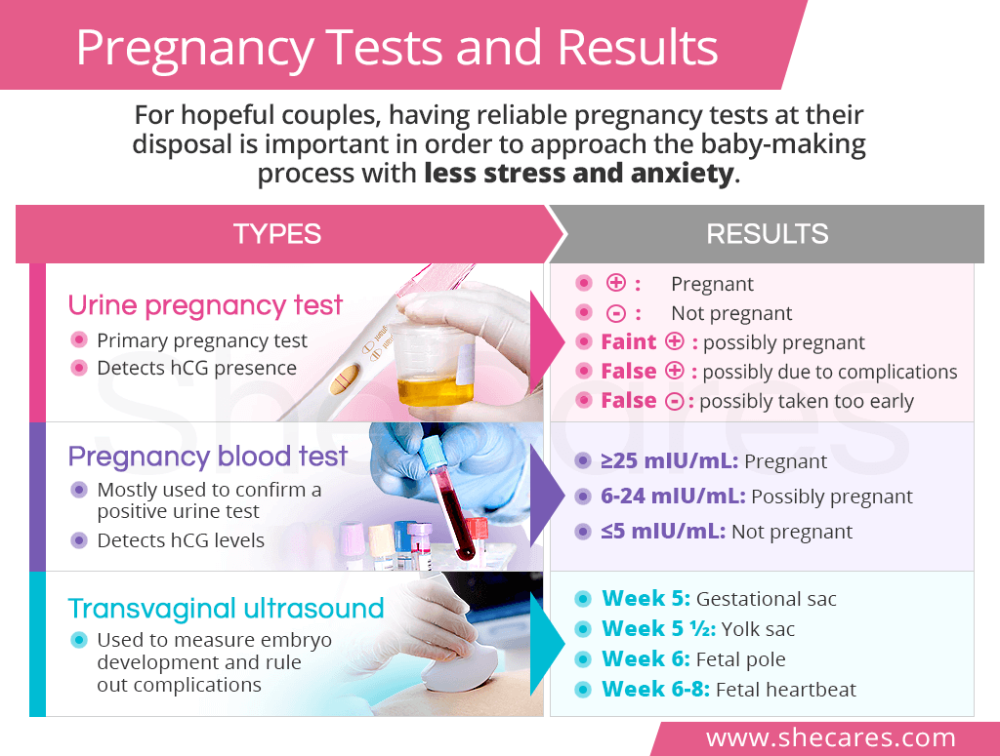 Symptomatic patients with an early viable intrauterine pregnancy: HCG curves redefined. Obstet Gynecol 2004; 104:50.
Symptomatic patients with an early viable intrauterine pregnancy: HCG curves redefined. Obstet Gynecol 2004; 104:50.
Silva C, Sammel MD, Zhou L, et al. Human chorionic gonadotropin profile for women with ectopic pregnancy. Obstet Gynecol 2006; 107:605.
Kadar N, Caldwell BV, Romero R. A method of screening for ectopic pregnancy and its indications. Obstet Gynecol 1981; 58:162.
Seeber BE, Sammel MD, Guo W, et al. Application of redefined human chorionic gonadotropin curves for the diagnosis of women at risk for ectopic pregnancy. Fertil Steril 2006; 86:454.
Morse CB, Sammel MD, Shaunik A, et al. Performance of human chorionic gonadotropin curves in women at risk for ectopic pregnancy: exceptions to the rules. Fertil Steril 2012; 97:101.
Kadar N, DeVore G, Romero R. Discriminatory hCG zone: its use in the sonographic evaluation for ectopic pregnancy. Obstet Gynecol 1981; 58:156.
Keyword Tags:
hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin)
HCG norms by weeks of pregnancy
HCG norms by weeks of pregnancy - Private maternity hospital Ekaterininskaya Clinics
Content
- Table of average hCG norms
- Table of average hCG norms for carrying twins
- Table of average hCG values after IVF with engrafted twins
- Guidelines for free β-hCG subunit
- Norm РАРР-А
- What if I am at high risk? nine0008
- How to confirm or deny the results of screening?
- The doctor says I need an abortion.
 What to do?
What to do?
One of the main tests during pregnancy is the study of the level of pregnancy hormone - hCG or human chorionic gonadotropin. If future mothers want to know if the hormone level is normal, we made a summary table of values
Table of average hCG norms:
| Gestation period | nine0031 HCG in honey/mlHCG in mIU/ml | HCG in ng/ml | |
| 1-2 weeks | 25-156 | 5-25 (doubtful result) | - |
| 2-3 weeks | 101-4870 | 5-25 (doubtful result) | - |
| 3-4 weeks | 1100 – 31500 | 25-156 | - |
| 4-5 weeks | 2560 – 82300 | nine0031 101-4870- | |
| 5-6 weeks | 23100 – 151000 | 1110 -31500 | - |
| 6-7 weeks | 27300 – 233000 | 2560 -82300 | - |
| 7-11 weeks | 20900 – 291000 | 23100 -233000 | 23. 7 - 130.4 7 - 130.4 |
| 11-16 weeks | 6140 – 103000 | 20900 -103000 | 17.4 - 50.0 | nine0039
| Weeks 16-21 | 4720 – 80100 | 6140 – 80100 | 4.67 - 33.3 |
| 21-39 weeks | 2700 – 78100 | 2700 -78100 | - |
Table of average hCG norms for carrying twins:
| Gestation period, weeks | Average range of hCG concentration (mU/ml) |
| 1-2 weeks | 50 - 112 |
| 2-3 weeks | 209 – 9740 |
| 3-4 weeks | 2220 – 63000 |
| 4-5 weeks | 5122 – 164600 |
| 5-6 weeks | 46200 – 302000 |
| 6-7 weeks | 54610 – 466000 |
| 7-11 weeks | 41810 – 582000 |
| 11-16 weeks | 12280 – 206000 |
| 16-21 weeks | 9440 – 160210 |
| 21-39 weeks | 5400 – 156200 |
Table of average values of hCG after IVF with accustomed twins:
| Gestational age, weeks | HCG range, mU/ml |
| 1-2 weeks | 50 – 600 |
| 2-3 weeks | 3000 – 10000 |
| 3-4 weeks | 20000 – 60000 |
| 4-5 weeks | 40000 – 200000 |
| 5-6 weeks | 100000 – 400000 |
| 6-7 weeks | 100000 – 400000 |
| 7-11 weeks | 40000 – 200000 |
| 11-16 weeks | 40000 – 120000 |
| 16-21 weeks | 20000 – 70000 |
| 21-39 weeks | 20000 – 120000 |
Free hCG β-subunit limits
Free hCG β-subunit measurement is more accurate in determining the risk of Down syndrome in an unborn child than measuring total hCG.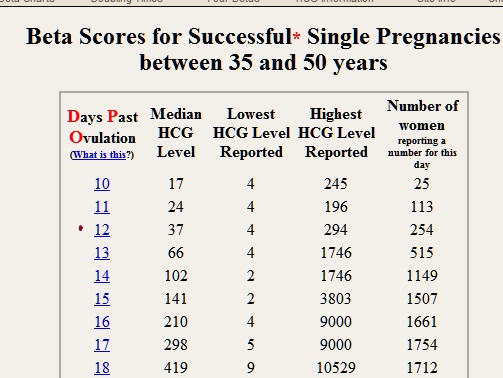
Norms for free β-hCG subunit in the first trimester:
| Gestational period, weeks | HCG in ng/ml |
|---|---|
| 9 weeks | 23.6 - 193.1 ng/mL or 0.5 - 2 MoM |
| 10 weeks | 25.8 - 181.6 ng/mL or 0.5 - 2 MoM |
| 11 weeks | 17.4 - 130.4 ng/mL or 0.5 - 2 MoM |
| 12 weeks | 13.4 - 128.5 ng/mL or 0.5 - 2 MoM |
| 13 weeks | 14.2 - 114.7 ng/mL or 0.5 - 2 MoM |
Norms in ng / ml may vary in different laboratories, therefore the data indicated is not final, and in any case you should consult your doctor. If the result is indicated in MoM, then the norms are the same for all laboratories and for all analyzes: from 0.5 to 2 MoM. nine0349If hCG is not normal, then:
- If the free β-hCG subunit is higher than normal for your gestational age, or more than 2 MoM, then the child has an increased risk of Down syndrome.
- If the free hCG β-subunit is below normal for your gestational age, or is less than 0.5 MoM, then the baby is at increased risk of Edwards syndrome.
PAPP-A norm
PAPP-A, or "pregnancy-associated plasma protein A" as it is called, is the second indicator used in biochemical screening of the first trimester. The level of this protein constantly increases during pregnancy, and deviations in the indicator may indicate various diseases in the unborn child. nine0003
Norm for PAPP-A depending on the duration of pregnancy:
Gestational period, weeks HCG in ng/ml 8-9 weeks 0.17 - 1.54 mU/ml, or 0.5 to 2 MoM 9-10 weeks 0.32 - 2.42 mU/ml or 0.5 to 2 MoM 10-11 weeks 0.46 - 3.73 mU/ml, or 0.5 to 2 MoM 11-12 weeks 0.79– 4.76 mU/ml, or 0.5 to 2 MoM 12-13 weeks 1. 03 - 6.01 mU/ml, or 0.5 to 2 MoM
13-14 weeks 1.47 - 8.54 mU/ml, or 0.5 to 2 MoM
Norms in ng / ml may vary in different laboratories, therefore the data indicated is not final, and in any case you should consult your doctor. If the result is indicated in MoM, then the norms are the same for all laboratories and for all analyzes: from 0.5 to 2 MoM. nine0349If PAPP-A is abnormal:
- If PAPP-A is lower for your gestational age, or less than 0.5 MoM, your baby is at increased risk of Down syndrome and Edwards syndrome.
- If PAPP-A is higher than normal for your gestational age, or more than 2 MoM, but other screening values are normal, then there is no cause for concern.
Studies have shown that women with elevated PAPP-A levels during pregnancy are not at greater risk of fetal disease or pregnancy complications than other women with normal PAPP-A. nine0003
What if I am at high risk?
If your screening reveals an increased risk of having a baby with Down syndrome, then this is not a reason to terminate the pregnancy.
You will be referred for a consultation with a geneticist who, if necessary, will recommend examinations: chorionic villus biopsy or amniocentesis
How to confirm or refute the screening results?
If you think that the screening was not done correctly, then you should be re-examined at another clinic, but for this you need to retake all the tests and undergo an ultrasound. This method is possible only if the gestational age at the time of the examination does not exceed 13 weeks and 6 days. nine0003
The doctor says I need an abortion. What to do?
Unfortunately, there are times when a doctor strongly recommends or even forces an abortion based on the screening results. Remember: no doctor has the right to such actions. Screening is not a definitive method for diagnosing Down syndrome and, based on poor results alone, a pregnancy should not be terminated.
Say that you want to consult a geneticist and undergo diagnostic procedures for Down syndrome (or other disease): chorionic villus biopsy (if you are 10-13 weeks pregnant) or amniocentesis (if you are 16-17 weeks pregnant).
nine0003
The author of the article:
Ananyina Anna Alexandrovna
Obstetrician-gynecologist
Work experience since 2010
Sign upEat more foods rich in iron: beef tongue, liver, buckwheat and oatmeal, prunes, dried apricots, green apples, etc. But diet alone will not work to raise hemoglobin. nine0455 Medical therapy with iron supplements is required. If the problem is associated with insufficient intake of iron into the body, one set of drugs is needed, if with absorption, another. The doctor must select drugs.
Injection therapy may be required for more severe anemia.If there are no contraindications, natural childbirth is possible. Only an obstetrician-gynecologist should decide on the possibility of EP.
Get tested
- Chest X-ray
- KSR
- Hepatitis B HBsAg
- Hepatitis C Anti-HCV
- Rubella IgM
- Rubella IgG
- HIV
- B/P for flora and senses.
- from throat
Specialist consultation:
- General practitioner consultation
With an increase in the duration of pregnancy and the growth of the baby, the uterus increases - this can lead to increased tone. Sometimes tension arises in response to the movements of the child. Strong physical exertion, stress, overwork of a pregnant woman can also lead to increased tone. nine0455 In early pregnancy, uterine tone may be associated primarily with reduced progesterone production. In this case, the doctor prescribes the patient treatment with progesterone preparations.
Symptoms of increased tone
All pregnant women experience tone differently. Someone - like heaviness and tension in the lower abdomen. Others - as a pulling pain in the lumbar region. In the 2nd and 3rd trimesters of pregnancy, a woman can feel the tone by putting her hand on her stomach: the uterus becomes "stone", then relaxes. nine0003Obstetrician-gynecologist
Doctor of the first category
Specify the cost of admission
in the Call-centerObstetrician-gynecologist nine0451
Doctor of the first category
Admission fee
2500 ₽Obstetrician-gynecologist
Doctor of the highest category
Candidate of Medical SciencesCheck the cost of admission
in the Call-centerObstetrician-gynecologist
Doctor of the first category
Check the cost of admission
in Call-centerObstetrician-gynecologist
Doctor of the highest category
Specify the cost of admission
nine0495 Obstetrician-gynecologist / Gynecologist
in the Call-centerDoctor of the highest category
Candidate of Medical SciencesAdmission fee
2500 ₽Obstetrician-gynecologist nine0451
Doctor of the highest category
Admission fee
2500 ₽Obstetrician-gynecologist
Doctor of the second category
Check the cost of admission
in Call-centerMobile application of the clinic
You can make an appointment with a doctor, get tests
and much more...
Fill out the form to make an appointment or order a call back
I agree with personal data processing policy and user agreement I also give my consent to the processing of personal data.
Sign up for a consultation
I agree with personal data processing policy and user agreement I also give my consent to the processing of personal data.
By continuing to use rd.clinic23.ru, you agree to the use of cookies. How to ban the use of certain cookies can be found in Politics
HCG rate during pregnancy. Table of hCG values by week. Elevated HCG. Low HCG. HCG in ectopic pregnancy. hCG during IVF (hCG after replanting, hCG at 14 dpo). nine0001
hCG or beta-hCG or total hCG - human chorionic gonadotropin - a hormone produced during pregnancy. HCG is formed by the placenta, which nourishes the fetus after fertilization and implantation (attachment to the wall of the uterus).
- What is hCG (= beta-hCG)
- When to donate blood for hCG
- HCG norm. Deciphering the analysis of hCG. HCG level during pregnancy
- Normal HCG doubling time
- HCG norms by week. HCG table
- Low hCG. What does hCG below normal mean?
- Negative hCG or hCG indicative of non-pregnancy with missed period
- hCG and biochemical pregnancy
- hCG and ectopic pregnancy
- Elevated hCG. What can hCG levels above normal mean?
- HCG and multiple pregnancy. hcg and twins.
- Blister drift
- HCG test after embryo transfer. HCG for IVF
- hCG and ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome
- Elevated hCG levels in non-pregnant women and men
- How does hCG change after miscarriage, abortion, childbirth?
- What medications affect hCG levels?
What is hCG (= beta-hCG)
HCG or beta-hCG or total hCG - human chorionic gonadotropin - a hormone produced during pregnancy.
HCG is formed by the placenta, which nourishes the fetus after fertilization and implantation (attachment to the wall of the uterus). HCG is measured in mIU/mL (mile international units per milliliter). nine0003
HCG partially crosses the placental barrier. The level of hCG in newborns is approximately 1/400 of the level in maternal blood. And it is approximately 10-50 mIU / ml at birth. The half-life is 2-3 days. Thus, at 3 months of life, the level in newborns corresponds to the norm of hCG for an adult.
When to donate blood for hCG
An increase in hCG in the blood can be detected a few days before the expected menstruation. The optimal time for a blood test to determine hCG is after a missed period. nine0003
A single determination of hCG cannot be used to diagnose miscarriage or ectopic pregnancy.
HCG norm. Deciphering the analysis of hCG. HCG level during pregnancy
An hCG level of less than 5 mIU / ml indicates the absence of pregnancy or that the test was taken too early.
The level of hCG is above 25 mIU / ml - about the presence of pregnancy.
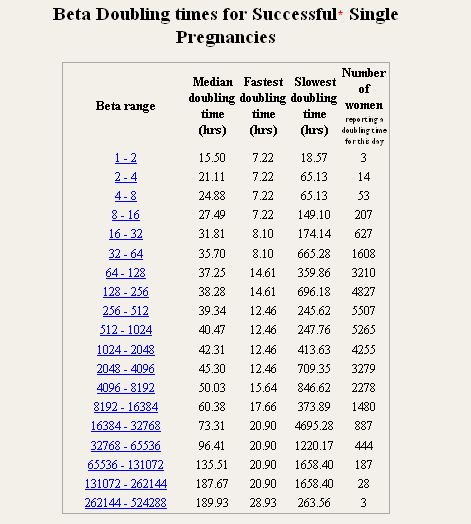
On average, a doubling of hCG levels occurs every 36-72 hours. HCG levels peak at term 9-11 weeks of pregnancy (from the date of the last menstruation) and further decreases until the 15th week of pregnancy, remaining unchanged during the remainder of the pregnancy. In 85% of cases, the level of hCG in the early stages doubles every 48-72 hours. As pregnancy progresses, the doubling time for hCG levels increases to 96 hours.
Normal HCG doubling time
HCG level Doubling time
1200 mIU/ml 48-72 hours
1200 – 6000 mIU/ml 72-96 hours
More than 6000 mIU/ml More than 96 hourshcg calculator
At what hCG value should an ultrasound be done?
After reaching an hCG level of 1000 - 2000 mIU / ml, a fetal egg can be visualized by ultrasound. Since the level of hCG has a large variability, and the date of conception can be erroneous, the gestational age is determined by ultrasound or IVF data, but not by hCG.
A single determination of hCG is not enough, since it is important to evaluate the growth dynamics of the hormone every 48-72 hours. nine0003HCG norms by week. HCG table
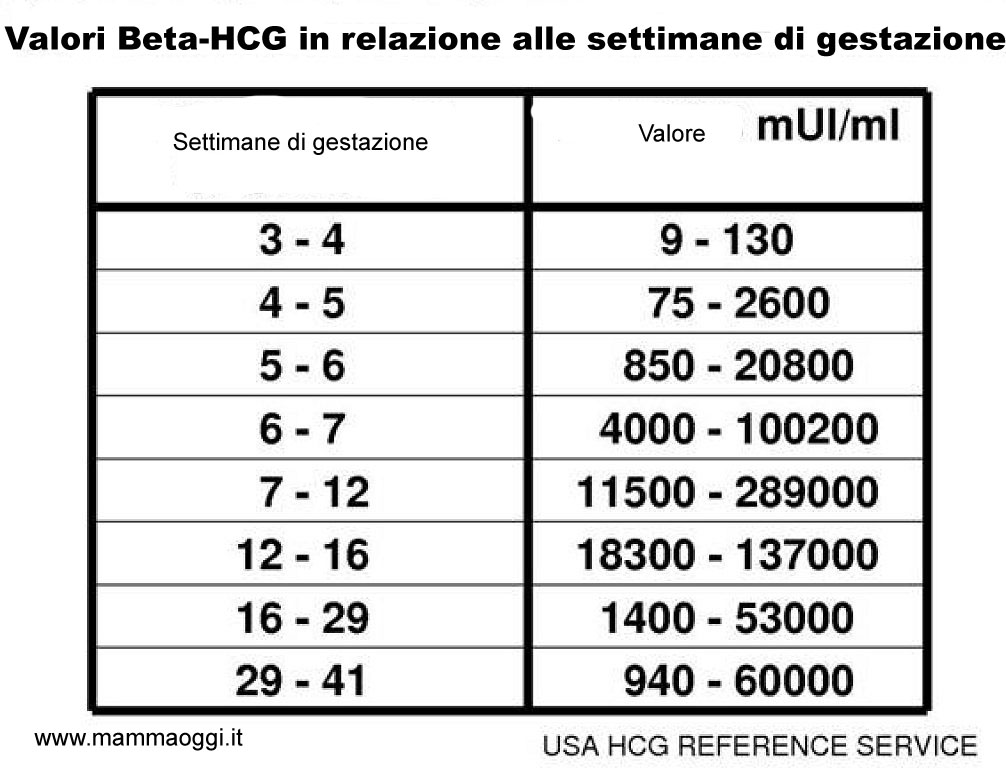
Indicator (p.m. - from the date of the last menstruation) Minimum Maximum Non-pregnant women 0 5.3 Pregnancy 3 - 4 weeks sixteen nine0032 156 Pregnancy 4 - 5 weeks 101 4870 Pregnancy 5 - 6 weeks 1110 31500 Pregnancy 6 - 7 weeks 2560 82300 nine0032 Pregnancy 7 - 8 weeks 23100 151000 Pregnancy 8 - 9 weeks 27300 233000 Pregnancy 9 - 13 weeks 20900 291000 Pregnancy 13 - 18 weeks 6140 103000 Pregnancy 18 - 23 weeks 4720 80100 Pregnancy 23 - 41 weeks 2700 78100 These ranges are provided as a guide and should not be used to interpret a particular hCG assay.
nine0003
Low hCG. What does hCG below normal mean?
- Not pregnant
- Error in calculating the gestational age
- Pregnancy arrest or miscarriage, biochemical pregnancy
- Ectopic pregnancy
- Threat of spontaneous abortion
Negative hCG or hCG indicative of non-pregnancy with missed period
It is necessary to repeat the analysis for hCG in 1-2 days, perhaps the pregnancy came later than expected. If the level of hCG does not rise, it is necessary to look for other reasons for the delay in menstruation.
hCG and biochemical pregnancy
The so-called "biochemical pregnancy" is a condition in which an increase in hCG above normal was detected, but the pregnancy did not continue to develop. The level of hCG in this case rises slightly, and then in a short time decreases to zero values. nine0003
HCG and ectopic pregnancy
An ectopic pregnancy is a pregnancy in which the fertilized egg is outside the uterine cavity.
With an ectopic pregnancy, there may be pain in the lower abdomen, spotting. The level of hCG during an ectopic (ectopic) pregnancy may not increase as quickly and not as significantly as with a normally developing uterine pregnancy. However, the low level of hCG does not allow such a conclusion to be made unambiguously. Starting with an hCG level of 1000 mIU / ml, a fetal egg can be detected in the uterine cavity. With an hCG level of 2000 mIU / ml and the absence of a fetal egg in the uterine cavity during ultrasound, the likelihood of an ectopic pregnancy is significant. nine0003
Increased hCG. What can hCG levels above normal mean?
- Error in calculation of gestational age
- Blister drift
- Multiple pregnancy
- Complications of pregnancy (preeclampsia)
- Maternal diabetes mellitus
- Taking synthetic gestagens
- Risk of fetal malformations
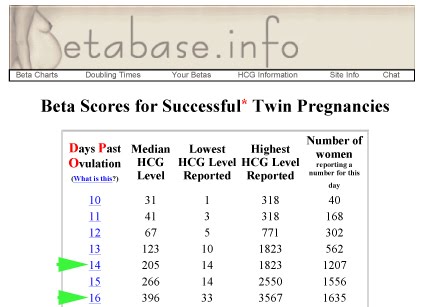
HCG and multiple pregnancy. hcg and twins.
nine0612
The level of hCG in a multiple pregnancy is higher than in a single pregnancy, but the rate of increase in hCG is the same in both cases.
Blister
Vesicular drift is a rare complication of pregnancy in which the level of hCG will be significantly increased, on average 2 times higher than the average value for a given period. For example, the possible level of hCG with cystic mole for 36 days from the first day of the last menstruation can reach 200,000 mIU / ml, while with a normally developing pregnancy, hCG will be from 1,200 to 36,000 mIU / ml. nine0003
HCG test after embryo transfer. HCG in IVF
An hCG test is performed approximately 2 weeks after embryo transfer (12-14 days after transfer (dpp)). Usually the level of hCG at 14 dpo is more than 100 mIU / ml.
If the hCG level is less than 25 mIU / ml, pregnancy has not occurred. If the hCG level is more than 25, the test is repeated after 2 days, with the development of pregnancy, its level should increase.
The hCG level will double approximately every 48 hours until 21 days after infusion. nine0003
Higher hCG values (300-400 mIU / ml) are more likely to indicate multiple pregnancy.
hCG and ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome
In patients with ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome, hCG levels should be interpreted with caution. These patients may develop edema, which leads to thickening of the blood, which can lead to a false increase in the level of hCG, and when the blood composition is normal, to a false absence of an increase in the level of hCG. nine0003
HCG in later pregnancy
The test for hCG is also included in the prenatal screening of the second trimester - an analysis that allows you to assess the risk of developing fetal defects.
Elevated hCG levels in non-pregnant women and men
Outside of pregnancy, hCG can be produced by the cells of some tumors (seminoma, testicular teratoma, neoplasms of the gastrointestinal tract (including pancreas, liver, colorectal cancer and stomach cancer).
nine0003
With successful treatment of an hCG-producing tumor, the hCG level should decrease to normal.
How does hCG change after miscarriage, abortion, childbirth?
In most cases, the level of hCG decreases. The half-life of hCG is 24-36 hours. The speed of reaching zero hCG values depends on what exactly happened: spontaneous miscarriage, abortion, childbirth, curettage) and how high the hCG level was at the time of pregnancy loss. Doctors recommend continuing to assess hCG levels until levels are below 5 mIU/mL. If the hCG level remains high, you should consult a doctor. nine0003
What drugs affect hCG levels?
The level of hCG is affected by drugs that contain hCG (Pregnil, Horagon).
- nine0007
ToRCH infections and pregnancy
What are ToRCH infections, what are the dangers of these infections during pregnancy, how and when is the examination performed, how to interpret the results. Perinatal infections account for approximately 2-3% of all congenital fetal anomalies.
Pregnancy tests in the CIR Laboratories
In our laboratory, you can undergo a complete examination at the onset of pregnancy, take tests at any time, and in our clinics you can conclude an agreement on pregnancy management.
Online hCG calculator during pregnancy
The hCG calculator is used to calculate the increase in hCG (the difference between two tests taken at different times).
The increase in hCG is important for assessing the development of pregnancy. Normally, in the early stages of pregnancy, hCG increases by about 2 times every two days. As the hormone levels increase, the rate of increase decreases. nine0003
False positive pregnancy test or why hCG is positive but not pregnant?
When can a pregnancy test be positive?
The norm of a complete blood count during pregnancy. Hemoglobin, platelets, hematocrit, erythrocytes and leukocytes during pregnancy. Clinical blood test during pregnancy.
Hematological changes during pregnancy.
Translation of materials from UpTodate.com
A normal pregnancy is characterized by significant changes in almost all organs and systems to adapt to the requirements of the fetoplacental complex, including changes in blood tests during pregnancy.Risk assessment of pregnancy complications using prenatal screening
Prenatal screening data allow assessing not only the risks of congenital pathology, but also the risk of other pregnancy complications: intrauterine fetal death, late toxicosis, intrauterine hypoxia, etc.
Parvovirus B19 and parvovirus infection: what you need to know when planning and getting pregnant.
What is a parvovirus infection, how is the virus transmitted, who can get sick, what is the danger of the virus during pregnancy, what tests are taken for diagnosis.
Pregnancy planning
Obstetrics differs from other specialties in that during the physiological course of pregnancy and childbirth, in principle, it is not part of medicine (the science of treating diseases), but is part of hygiene (the science of maintaining health).