What is pregnancy implantation
What Is It? And When Does It Happen?
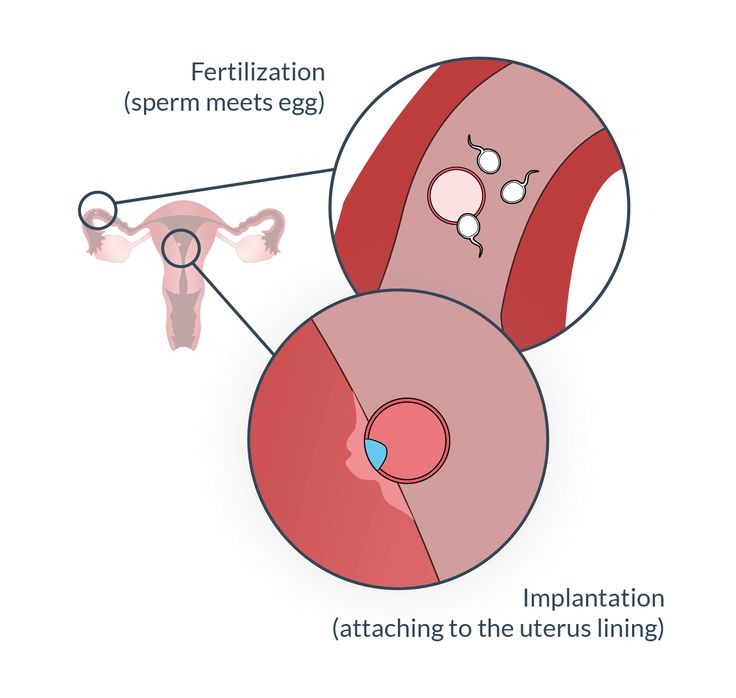
What is implantation?
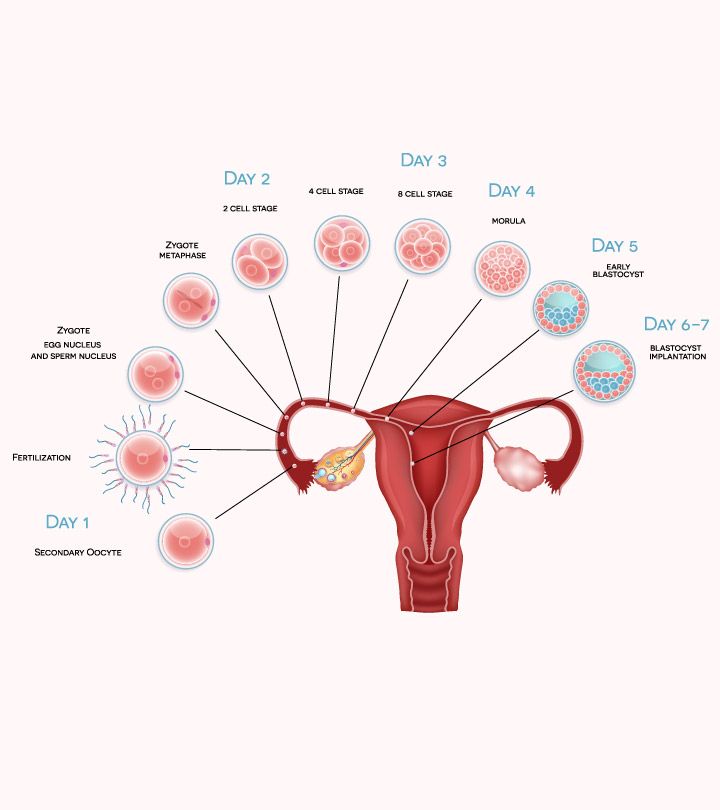
Generally speaking, “implantation” is the term used to describe when a fertilized egg attaches to your uterine lining.
An egg can only be fertilized when sperm successfully meets with a viable egg — this egg then travels from one of your tubes toward your uterine lining, where it attaches and begins to grow. It’s called implantation because the egg literally implants in your uterus in order to turn into a fetus.
Implantation usually occurs about 6 to 10 days after conception, and although this might seem incredibly early, knowing some of the signs of implantation can help you determine when to take a pregnancy test to get the most accurate results.
Take a quiz
Find out what you can do with our Health Assistant
When does implantation occur?
Implantation of a fertilized egg usually occurs about 6 to 10 days after conception. In order for you to be pregnant, your embryo needs to implant successfully into the uterine lining, which has thickened for this purpose between your last period and ovulation.
Once implantation happens, your body releases a hormone called human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), which produces changes in the body to support your pregnancy. Interestingly, this is the hormone pregnancy tests detect to deliver a positive result.
Implantation: Early signs of pregnancy, from bleeding to implantation cramps
Some women and people who menstruate are adamant that they “know” as soon as they are pregnant, and it’s true that implantation does sometimes come with early signs it has taken place. Things to look out for include light bleeding and light cramps.
The light bleeding, or spotting, that sometimes occurs is called implantation bleeding. It happens when the fertilized egg attaches to your uterine lining. Implantation bleeding is completely normal, so try not to worry if you notice it. Equally, not everyone will experience this symptom.
Depending on your cycle, implantation bleeding often shows up around the time you’d expect to start your period, which can be a little confusing.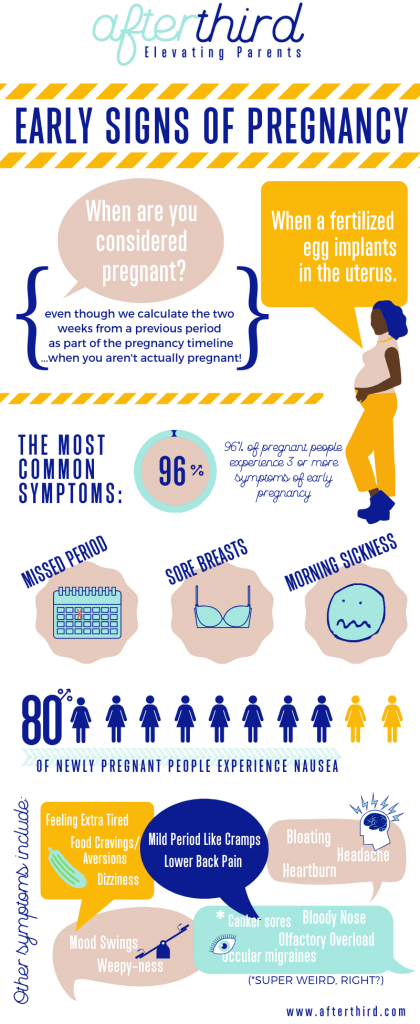 However, implantation bleeding is lighter than typical menstrual bleeding and usually doesn’t last as long either.
However, implantation bleeding is lighter than typical menstrual bleeding and usually doesn’t last as long either.
Cramps are another sign of implantation, which can happen as a result of the fertilized egg attaching to your uterine lining. Some feel these cramps in the abdomen, pelvis, or lower back, while others don’t feel any cramping at all.
What happens after implantation?
It’s important to remember that every pregnancy is unique — just as every baby is different — so try not to compare your experience to others. Some of us have every common symptom of pregnancy, while others only have a few (or none at all).
If your periods are usually as regular as clockwork, and you’ve missed your period date by a week or more, it could be an indication that implantation has taken place and you’re pregnant.
Remember that the first signs of pregnancy — things like tiredness, nausea, and sore or swollen breasts — appear around week six, so you won’t be able to tell if you’re pregnant right away.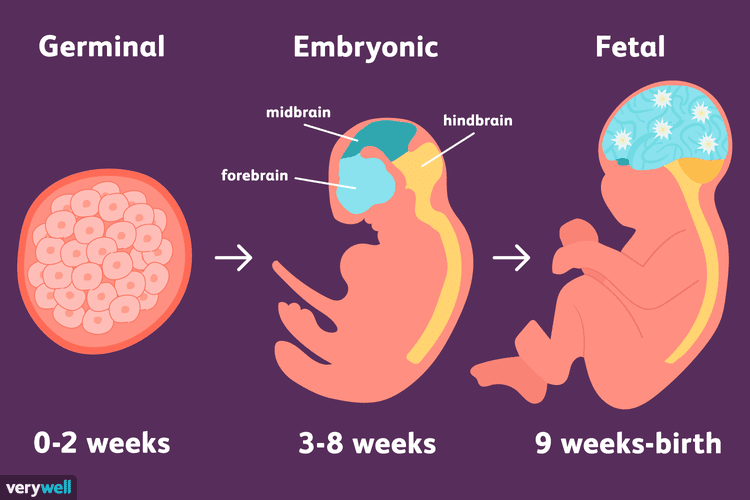 Taking a pregnancy test is the best way to find out.
Taking a pregnancy test is the best way to find out.
However, it’s worth keeping in mind that many of us have irregular menstrual cycles, in which case a missed period doesn’t necessarily indicate a pregnancy. Irregular menstrual cycles are very common and can happen for lots of reasons, including taking certain medicines or having medical conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome, eating disorders, or diabetes.
If your period is late and you think you might be pregnant, these are some early pregnancy symptoms you can look out for:
- Swollen and tender breasts and nipples — About one to two weeks after conception, you might experience sore breasts and tender nipples, which are a result of the hormone changes happening in your body. Breasts can also feel heavier or fuller than they did before. If this is the case, you might want to wear a looser bra or one without an underwire to feel less restricted.
- Fatigue — Pregnancy tiredness is a common symptom that can come on as early as one week after conception, and there’s a scientific reason for it.
 Your body is in overdrive to produce more progesterone, which is the hormone that helps maintain your pregnancy and promotes the growth of milk-producing glands in your breasts. Incredibly, the total blood volume in your body also increases to provide nutrients to the growing fetus. So it’s not surprising you might feel worn out.
Your body is in overdrive to produce more progesterone, which is the hormone that helps maintain your pregnancy and promotes the growth of milk-producing glands in your breasts. Incredibly, the total blood volume in your body also increases to provide nutrients to the growing fetus. So it’s not surprising you might feel worn out. - Headaches — The sudden increase in hormones might give you headaches while your body adjusts.
- Nausea or/and vomiting — We’ve all heard of the dreaded morning sickness, which affects 80 percent of us during pregnancy. The term “morning sickness” is actually quite misleading because it can strike at any point of the day, not just in the morning. Waves of nausea without vomiting are also common. Both of these symptoms may begin about two to eight weeks after conception and sometimes continue throughout the pregnancy.
- Food aversions or cravings — Developing a sudden dislike for some foods or strong cravings for others is a common pregnancy sign.
 Cravings and aversions can last your entire pregnancy or change throughout.
Cravings and aversions can last your entire pregnancy or change throughout. - Mood swings — The hormonal changes that occur during pregnancy can also cause intense mood swings. They usually start a couple of weeks after conception, so give yourself some TLC if you feel a little more up and down than usual.
- Frequent need to pee — Your blood volume increases during this period, causing your kidneys to process more fluid, which creates more urine.
- Bloating — The hormonal changes of early pregnancy can make you feel bloated. This feeling is very similar to how you might feel at the beginning of your period.
- Constipation — Again, thanks to ever-changing hormones, your digestive system can slow down, which can cause constipation. You can help constipation issues by ensuring you have enough fruit and fiber in your diet.
- Nasal congestion — Feeling stuffed up? That’s thanks to increased hormones and blood volume making your nasal mucous membranes swollen and more prone to bleeding.
 Although most medicines can’t be used during pregnancy, non-medication saline spray and mists can give you some relief from a stuffy nose.
Although most medicines can’t be used during pregnancy, non-medication saline spray and mists can give you some relief from a stuffy nose.
Implantation: The takeaway
So, we’ve learned that implantation is the moment when a fertilized egg attaches to your uterine wall, typically 6 to 10 days after conception. We also now know that there can be some early signs of pregnancy to look out for, from light bleeding to sore breasts and tiredness.
If you’re trying for a baby and you miss a period, the first thing to do is take a pregnancy test. Regardless of the result, we’d suggest making an appointment with your health care professional. They’ll be able to confirm you’re pregnant or get to the bottom of what caused your missed or delayed period.
Implantation Signs and Symptoms: Bleeding, Cramps, and More
Implantation is an essential early stage in conception when cells attach to the uterine wall. Signs of implantation include bleeding, cramps, discharge, and breast tenderness. These can be early signs of pregnancy.
These can be early signs of pregnancy.
We don’t know if we should blame Hollywood or the false reality of social media, but the phrase “getting pregnant” gets tossed around as if it’s a simple one-step process. But there are a ton of tiny, amazing things that need to happen in your body to result in pregnancy.
After the sperm and the egg join (conception), the combined cells start multiplying pretty quickly and moving through one of your fallopian tubes to your uterus. This cluster of rapidly growing cells is called a blastocyst.
Once in your uterus, this little bundle of cells has to attach, or implant, into your uterine wall. This step — known as implantation — triggers rising levels of all those fun pregnancy hormones (estrogen, progesterone, and hCG, or human chorionic gonadotropin).
If implantation doesn’t happen, your uterine lining is shed in your monthly period — a disappointment if you’re trying to get pregnant, but a reminder that your body is likely prepping for you to try again.
But if implantation does occur, your hormones — sometimes a nuisance, but doing their job — cause the placenta and the embryo (your future baby) to develop and your uterine lining to stay in place and support your pregnancy.
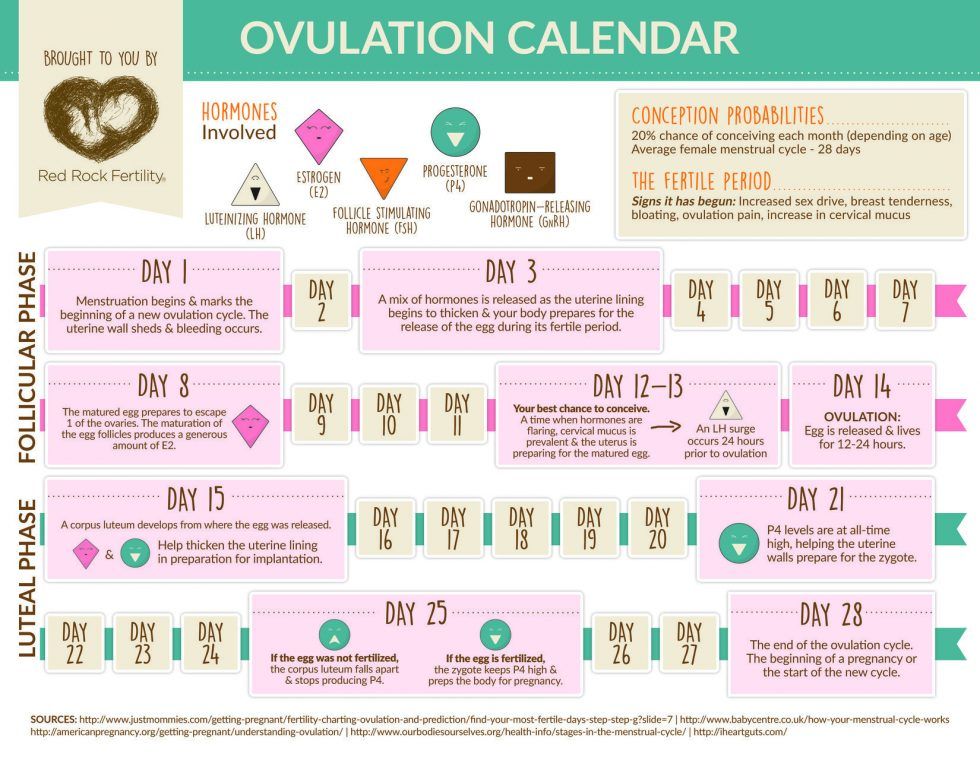
Implantation takes place anywhere between 6 and 12 days after you ovulate. It most commonly occurs 8 to 9 days after conception. So the exact date of implantation can depend on when you ovulated, and whether conception occurred early or late in the ovulation window.
When you’re hoping to get pregnant, it’s natural to be very aware of your body and notice every change, no matter how small.
Assuming a lack of symptoms means you’re not pregnant? Not so fast. Keep in mind that most experience no signs at all of conception or implantation — and are still pregnant! — though some do experience signs of implantation.
Let’s explore some symptoms you might notice if implantation has occurred, but keep our little disclaimer in mind:
Having the symptoms listed below doesn’t necessarily mean you’re pregnant — and having no symptoms doesn’t necessarily mean you’re not.
Bleeding
It’s a little unclear how common implantation bleeding is. Some sources claim that one-third of all women who become pregnant experience implantation bleeding, but this isn’t backed by peer-reviewed research. (Something on the internet that may not be true? Say it ain’t so!)
Here’s what we can tell you. Up to 25 percent of women experience bleeding or spotting in the first trimester — and implantation is one cause of first trimester bleeding.
This bleeding can be confusing, because it may happen around the time your period would start. Most commonly though, it will occur a few days to a week before you expect your menstrual period.
Other differences can help you determine whether you are experiencing implantation bleeding or your period:
- implantation bleeding is most likely to be light pink or brown (as opposed to the bright or dark red of your period)
- implantation bleeding is more like spotting than an actual flow of blood
This spotting may occur once, or last for a few hours, or even up to 3 days.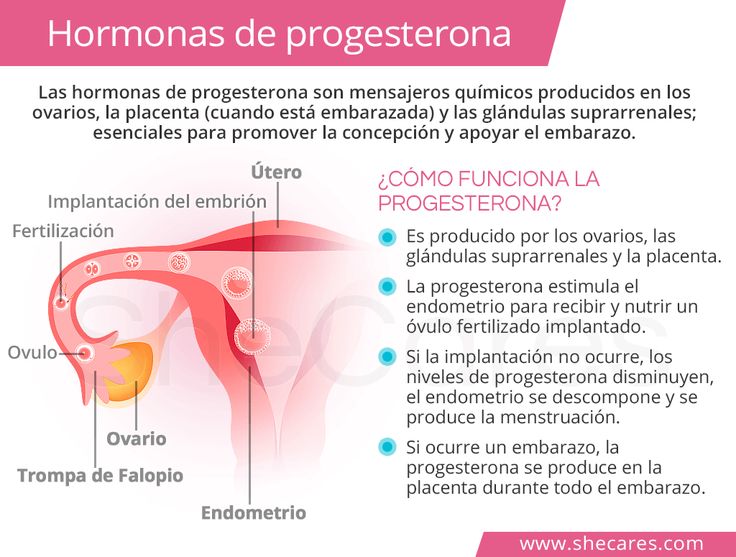 You may notice some pink or brown discharge when you wipe or on your underwear, but you won’t need a full pad or tampon — possibly not for many months!
You may notice some pink or brown discharge when you wipe or on your underwear, but you won’t need a full pad or tampon — possibly not for many months!
Cramps
It’s no secret that early pregnancy causes a rapid shift of hormones. More specifically, implantation triggers the hormone surge — that’s why you can’t get that second pink line on a home pregnancy test until after implantation.
And the changing hormonal tide can also cause cramping. Furthermore, a lot is going on in your uterus as the fertilized egg implants and begins to grow.
While there’s no research indicating that implantation itself causes cramps, some women do feel abdominal tenderness, lower back pain, or cramping around the time of implantation. This may seem like a mild version of how you feel before your period starts.
Discharge
Let’s talk about what’s going on down there.
If you’ve been monitoring your cervical mucus, good work, future mama! Knowing what’s going on with your body can be empowering when trying to conceive.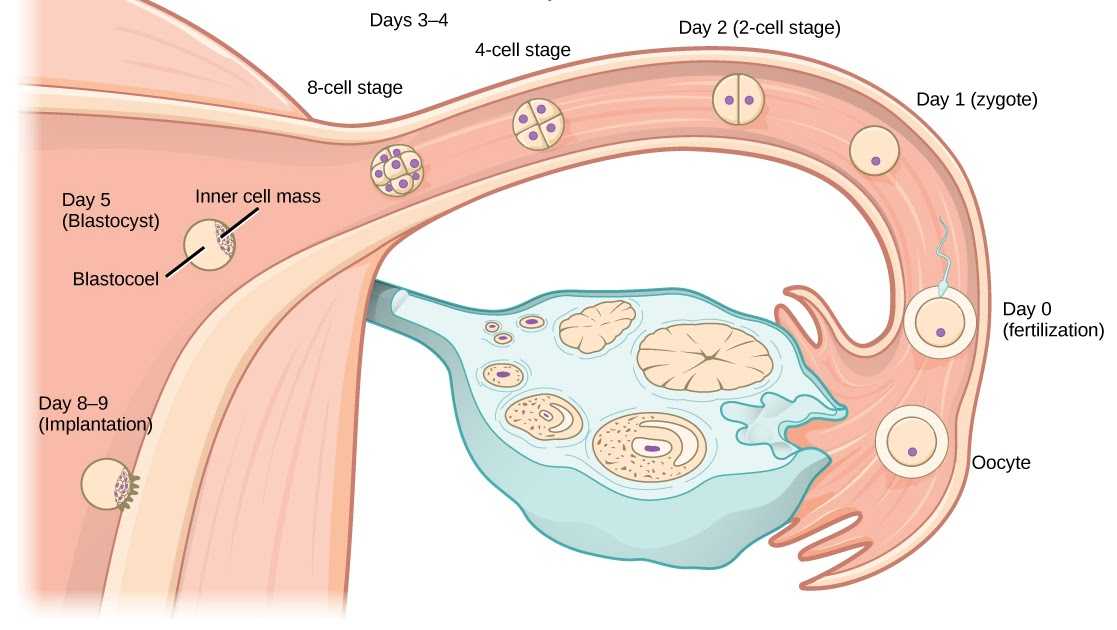
You may notice some cervical mucus changes around the time of implantation.
During ovulation, your cervical mucus will be clear, stretchy, and slippery (sort of like egg whites). You probably already know this as your green light to get your baby dance on.
After implantation occurs, your mucus might have a thicker, “gummier” texture and be clear or white.
And in the days of early pregnancy, rising progesterone and estrogen may cause your mucus to become even thicker, more profuse, and white or yellow.
We hate to say it, though: Cervical mucus can be affected by a number of things (hormones, stress, intercourse, pregnancy, implantation bleeding or your period, etc.) and may not be a reliable indicator of whether or not implantation has occurred.
Start tracking your cervical mucus while you’re not pregnant, and a more useful indicator may be how different it is from your norm during each stage of your cycle.
Bloating
Rising progesterone (which happens in early pregnancy) slows your digestive system down. This can make you feel bloated. But as so many of us know, this feeling can be a really common symptom of your period, too. Want to know why? Progesterone also rises when your period is imminent. Thanks, hormones.
This can make you feel bloated. But as so many of us know, this feeling can be a really common symptom of your period, too. Want to know why? Progesterone also rises when your period is imminent. Thanks, hormones.
Tender breasts
After implantation, levels of hCG, estrogen, and progesterone all increase rapidly. This can cause your boobs to feel very sore. (These hormones sure are multitaskers!) While many women experience breast swelling or tenderness before their periods, this is likely to be more noticeable than usual in very early pregnancy.
Nausea
Ah, arguably the most famous of the early pregnancy symptoms: nausea, aka “morning sickness” (though it can happen at any time of day).
Increased levels of progesterone following implantation can make you feel nauseous. But again, this occurs around 4 or 5 weeks of pregnancy (about the time you miss your period).
Progesterone slows down your digestion, which can contribute to nausea. Rising hCG levels and a more sensitive sense of smell can make the problem worse — so now might be a good time to avoid cooking liver and onions.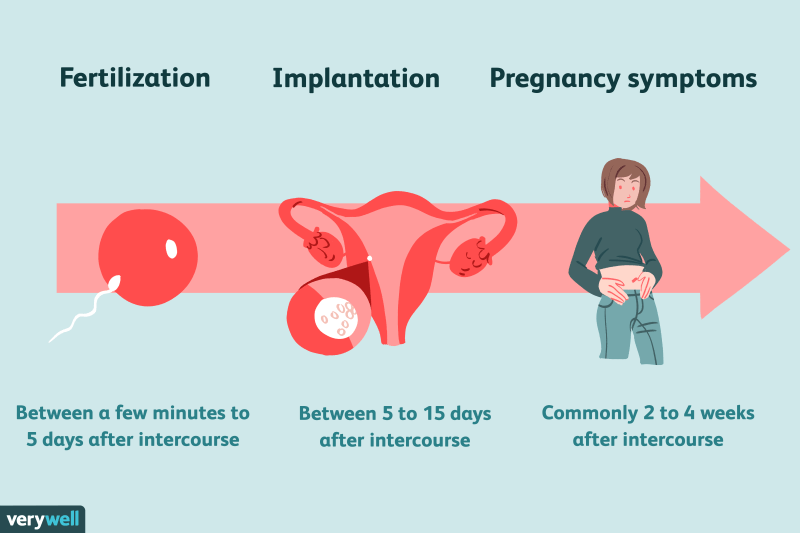
Headaches
While they’re good and necessary for a successful pregnancy, those wildly rising hormone levels (particularly progesterone) can also give you headaches following implantation.
Changes in mood
Find yourself content and happy one minute, and weeping at a commercial on TV the next? Or excited to see your partner in the evening and then biting their head off over nothing? You may be experiencing mood changes.
Estrogen and progesterone, as well as hCG, increase very quickly following implantation. This can make you feel “off” or moodier than usual.
Implantation dip
While this sounds like some weird appetizer, “implantation dip” refers to a 1-day decrease in your basal body temperature that can occur as a result of implantation.
If you’ve been tracking your basal body temperature (BBT) to help identify your most fertile days, you likely already have a log of your daily BBT over the course of a few months.
Typically, temperature is lower before ovulation and then increases, then drops again before her period starts. If you get pregnant, your temperature remains elevated.
If you get pregnant, your temperature remains elevated.
Simple, right? Except there’s something else.
Some women seem to experience a 1-day drop in temperature around the time of implantation. This is different than the drop in temperature that means your period is coming — in the case of an imminent period, your temperature would stay low.
In the case of implantation dip, your temp drops for one day and then goes back up. It’s thought that this might be due to a rise in estrogen, but it’s not entirely understood.
According to an analysis of more than 100,000 BBT charts from the popular app Fertility Friend, 75 percent of pregnant women using the app did not experience an implantation dip. Additionally, a dip was noted on approximately 11 percent of the charts of women who were not pregnant.
But it’s pretty interesting that 23 percent of app users who turned out to be pregnant did have a so-called implantation dip.
This isn’t a peer-reviewed, medically conducted study.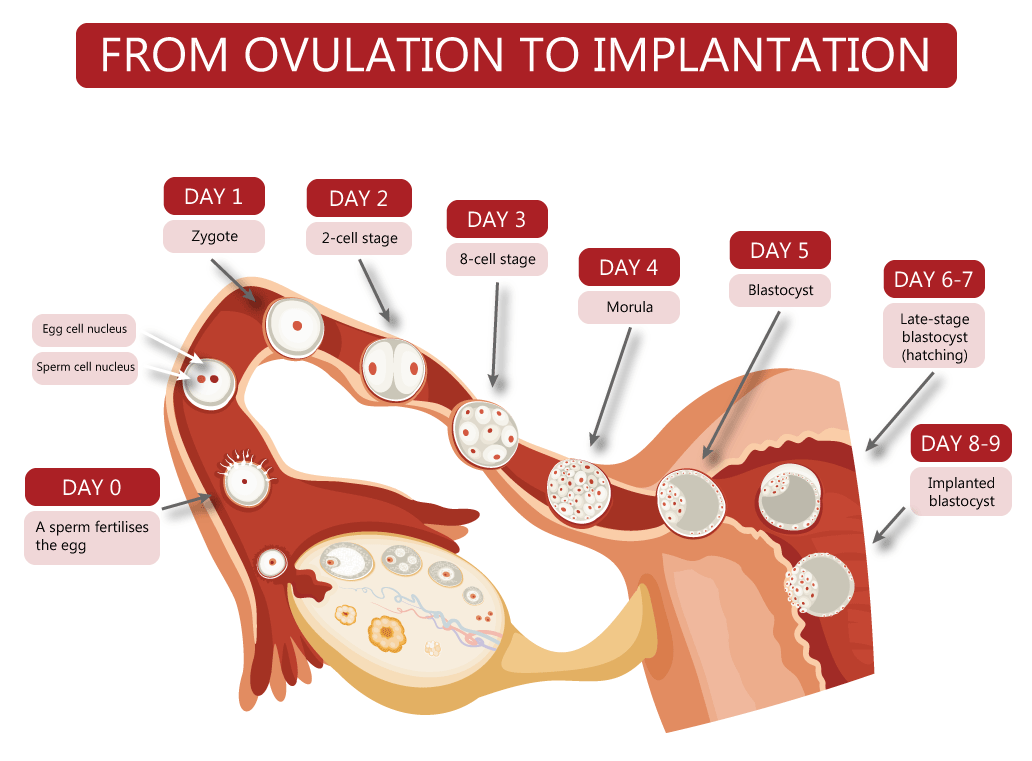 (We wish it were — when will researchers get on this?) But it may be helpful when it comes to interpreting your BBT chart. An implantation dip is more likely if you’re pregnant than if you’re not, but you can still be pregnant without a dip.
(We wish it were — when will researchers get on this?) But it may be helpful when it comes to interpreting your BBT chart. An implantation dip is more likely if you’re pregnant than if you’re not, but you can still be pregnant without a dip.
Trying to get pregnant can be both an exciting and nerve-wracking time. The days and months of your cycle can feel like forever when you’re waiting for a baby, and it’s easy to notice every tiny change in your body and wonder if it means you’re pregnant. This isn’t bad — knowledge is empowering — and in fact, it’s a very normal thing to do.
Some women do notice signs and symptoms that implantation has occurred. Signs may include light bleeding, cramping, nausea, bloating, sore breasts, headaches, mood swings, and possibly a change in basal body temperature.
But — and here’s the frustrating part — many of these signs are very similar to PMS. Additionally, most women experience no signs of implantation at all and are in fact pregnant.
The best way to know for sure if you’re pregnant is to take an at-home pregnancy test or call your doctor. (Keep in mind that even if you have implantation symptoms, it takes a few days for enough hCG to build up to turn a test positive.)
The “2-week wait” — the time between ovulation and when you can usually get a positive pregnancy test — can test all your patience. Keep paying attention to yourself and your body, find some activities you enjoy to take your mind off the wait — and know that you’re going to be an amazing parent.
Embryo implantation - Juno
Embryo implantation: content of the article
What is embryo implantation
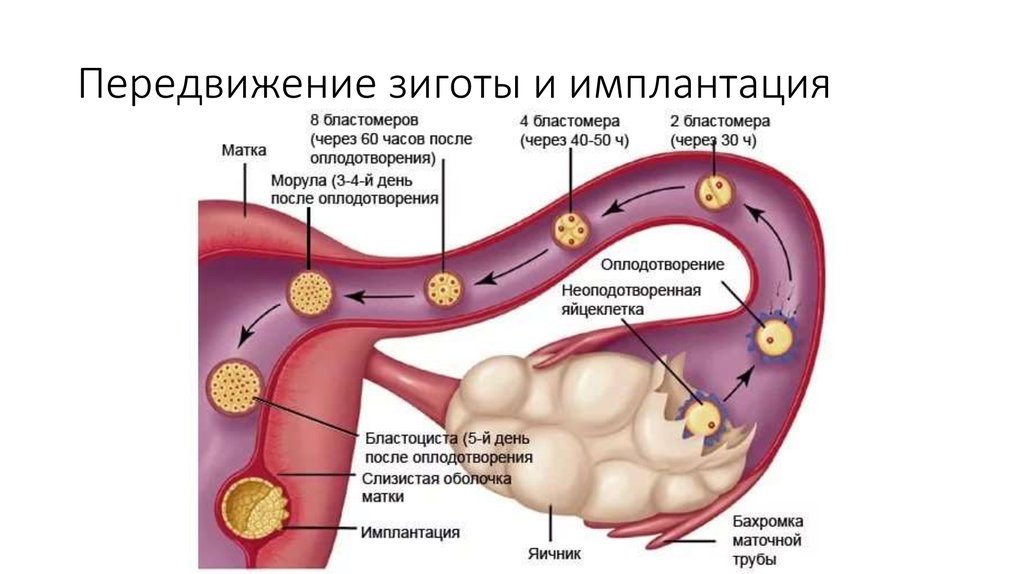
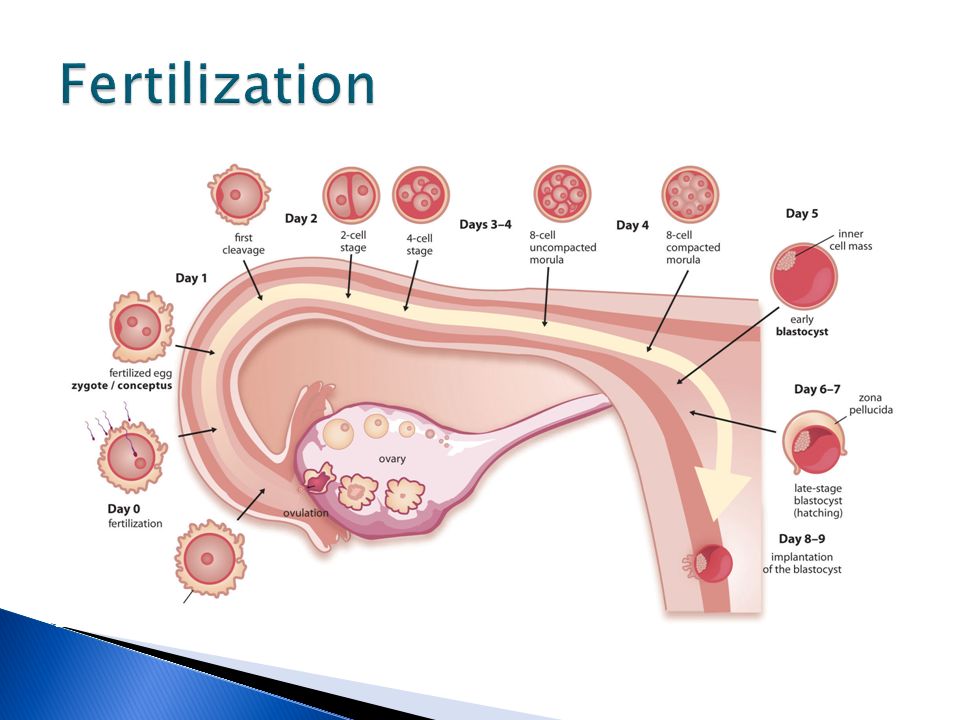
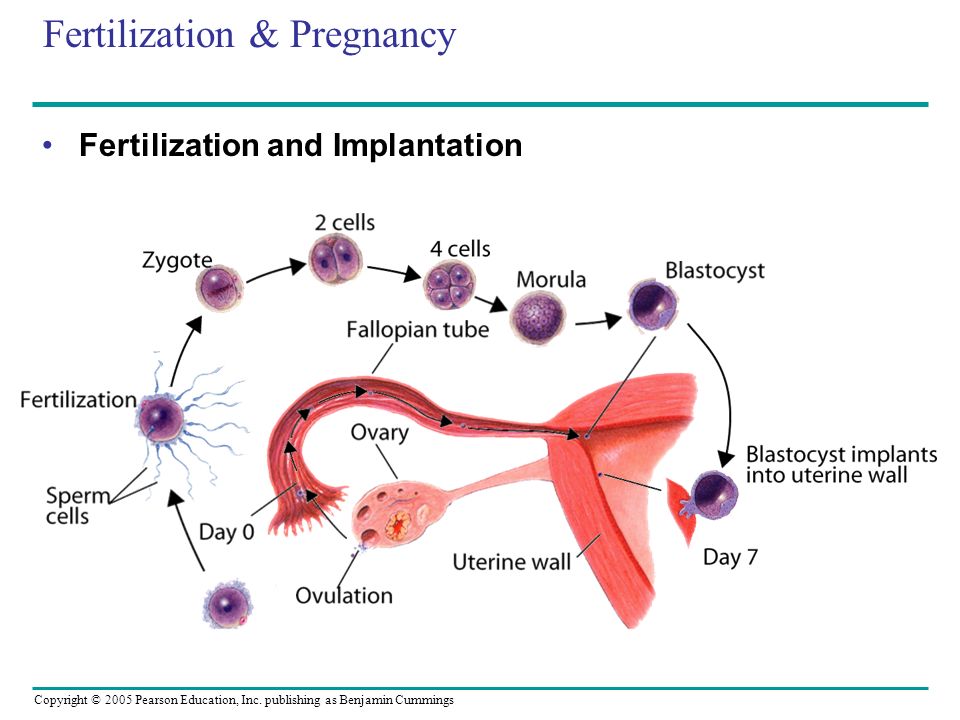
The egg matures in the follicle. At a certain moment, the follicle shell ruptures, the oocyte enters the abdominal cavity, then into the fallopian tube. If unprotected intercourse occurs, spermatozoa enter the female genital tract and begin to move through the tubes. There, one of them meets the egg, dissolves its shell and fertilizes it.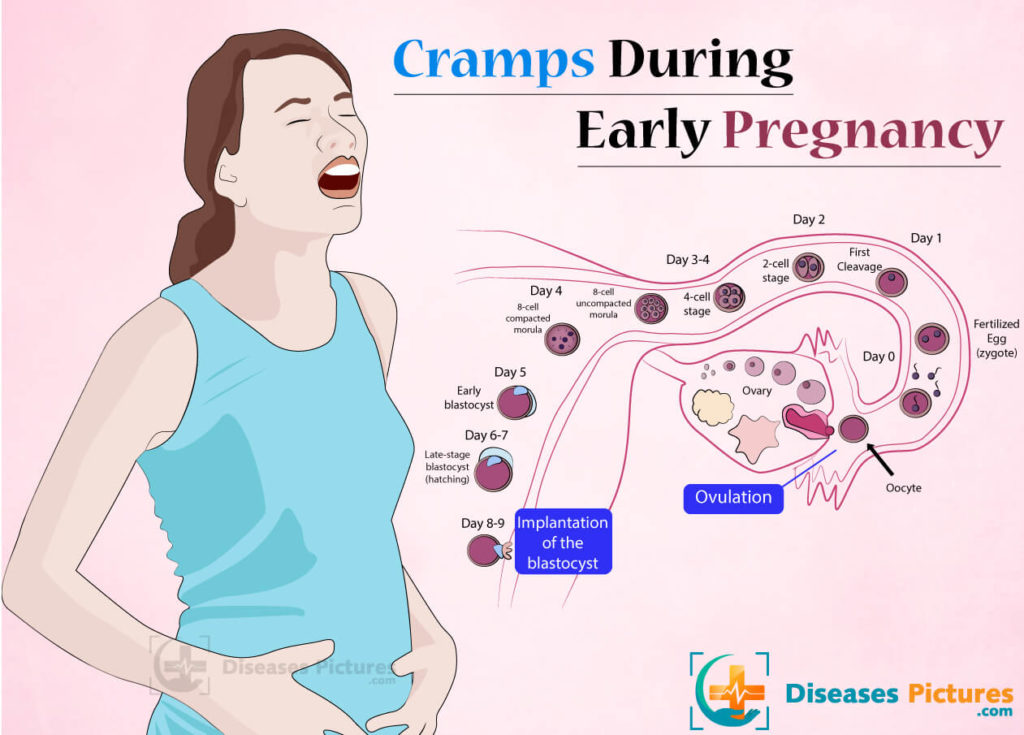
Then the process of division begins, during which the number of cells is constantly doubling. At the same time, the zygote moves along the fallopian tube towards the uterus. Its cells form the inner layer - the embryoblast, and the outer - the trophoblast. Due to the trophoblast, during implantation after conception, the embryo attaches to the wall of the uterus, growing into the endometrium, contacting the mother's body.
This process also takes place in stages. First, the embryo sticks to the mucous membrane - this is the adhesion stage. Then, villi are formed from the trophoblast, which grow into the endometrium, releasing substances that soften and destroy the inner lining of the uterus: vessels, connective tissue. Thus, a recess is formed on the surface of the uterus, or a depression into which the embryo is completely immersed - this is an invasion.
The villi of the trophoblast subsequently form the chorion, which ensures the supply of nutrients and oxygen, and releases hormones. Thanks to this, the fetus receives everything necessary for growth and development.
Thanks to this, the fetus receives everything necessary for growth and development.
When the embryo is implanted. Timing
It takes about 8-9 days from fertilization to attachment. The breakdown by stages is as follows:
- Conception is possible within 1 day after ovulation. On average, ovulation occurs on the 14th day of the menstrual cycle (the figure is given for a 28-day cycle). If your cycle is shorter or longer, you need to calculate the cherished date individually using tests, the calendar method or ultrasound folliculometry;
- Within 3-5 days after conception, the zygote moves along the fallopian tube towards the uterus;
- 6-7 days after conception, implantation begins, which lasts almost 2 days.
It turns out that, on average, attachment can occur on the 25th - 27th day of the menstrual cycle.
Can there be deviations and on what day after conception does implantation occur if the cycle is not 28 days? Deadlines may vary. Early implantation is distinguished - within a week after ovulation, and late - after the 10th day after. They are considered variants of the norm. But you need to take into account some nuances.
Early implantation is distinguished - within a week after ovulation, and late - after the 10th day after. They are considered variants of the norm. But you need to take into account some nuances.
For example, if the implantation of the embryo after conception occurred on the 6th day, by this time the endometrium may be “immature”, thin. As a result, the embryo does not completely sink into the endometrium, which is why there is a high probability of interruption and placental insufficiency. A similar deviation most often occurs with excessive production of progesterone.
And if the embryo enters the uterine cavity too late, the inner membrane undergoes some changes, which can also lead to a miscarriage in the first trimester. The reason for the delay in the advancement of the embryo may be the pathology of the fallopian tubes, when the contractions of the walls are too weak, adhesions and narrowing of the organ, a failure in the division of the cells of the embryo.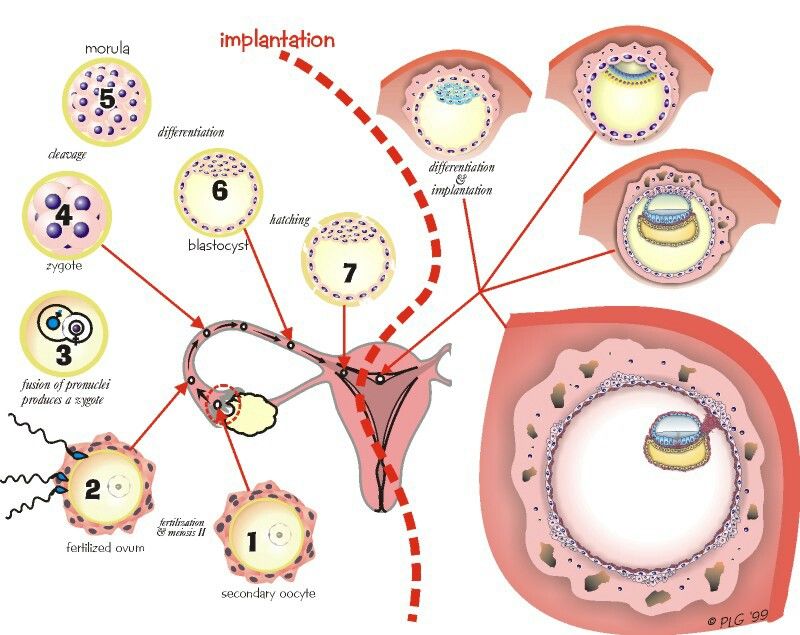
Symptoms
There are no signs that would speak with 100% certainty about embryo implantation. But judging by the reviews of many women, they physically felt the changes taking place in the body at that moment. Obviously, these sensations were associated with hormonal changes, which cause a cascade of changes in the body.
The characteristic subjective symptoms of implantation after conception are as follows:
- pain in the lower abdomen - pulling, twisting, accompanied by increased pulsation;
- weakness, malaise, vomiting, nausea, dizziness;
- slight increase in temperature to 37.5 degrees;
- emotional instability, irritability;
- taste change.
There are also objective symptoms that are determined by the doctor during the examination. Let's talk about them next.
Basal temperature
Basal temperature - the temperature in the rectal cavity, which is measured in the morning, depends on the level of hormones. During the cycle, its values change. So, in the first phase, when the follicle matures under the influence of estrogen, the thermometer shows numbers up to 36.4 degrees. Before ovulation, the temperature drops below - 36.2 degrees.
During the cycle, its values change. So, in the first phase, when the follicle matures under the influence of estrogen, the thermometer shows numbers up to 36.4 degrees. Before ovulation, the temperature drops below - 36.2 degrees.
After the follicle ruptures, a corpus luteum forms in its place - a temporary structure that synthesizes progesterone (pregnancy hormone). The hormone is needed for the maturation of the endometrium. In addition, it raises the temperature to 37.0 - 37.2 degrees. If conception occurs, and after it - implantation of the embryo, the level of progesterone decreases for a short time. On the temperature curve, you will see a sharp drop: in the region of 36.4 - 36.6 degrees. Then the concentration of progesterone rises again, and the basal temperature remains within 37.0 degrees throughout the pregnancy.
These changes in rectal temperature are characteristic only for a normal ongoing pregnancy. If a woman has hormonal disorders, the general body temperature is increased due to an inflammatory process, temperature fluctuations cannot be considered a symptom of implantation after conception.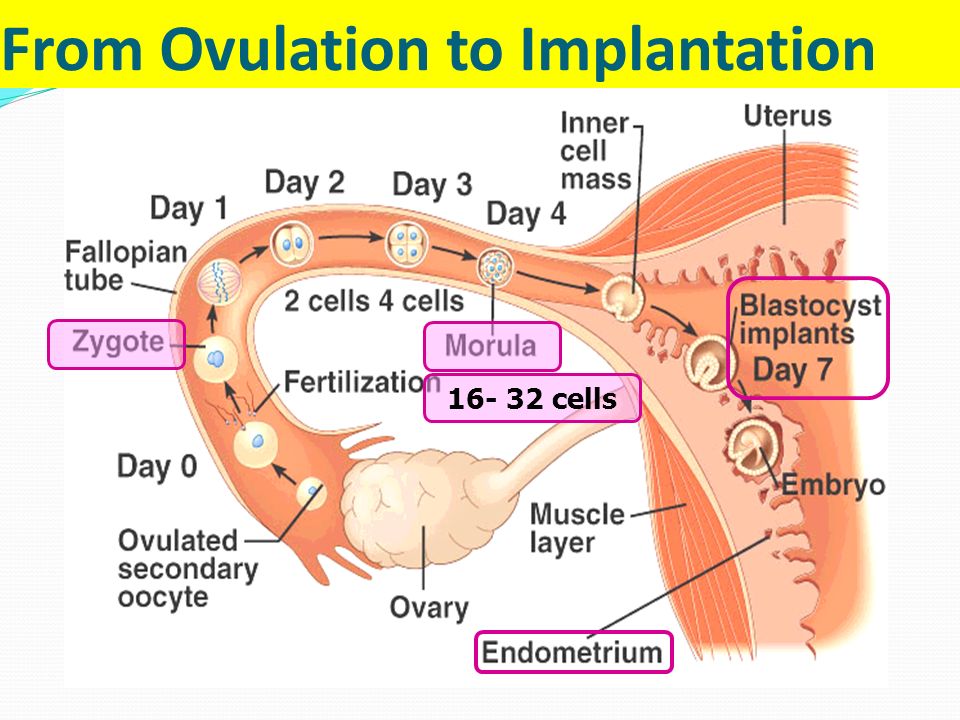
Bleeding
Implantation bleeding is caused by damage to small blood vessels during the ingrowth of trophoblast filaments into the endometrium. Passes within two days. The amount of blood loss is small: pinkish spots just appear on the linen. A woman may not even notice the discharge.
There is no heavy bleeding during embryo implantation. If you see that the amount of discharge is significant, consult a doctor. It is necessary to exclude uterine bleeding, clotting disorders and other conditions that require adequate therapy.
All of the listed symptoms, both objective and subjective, must be evaluated as a whole. For example, an increase in only basal temperature, or only nausea and weakness, is not evidence of the implantation of the embryo after conception.
Breast and cervical changes
Chorionic gonadotropin, which begins to be released after conception and implantation of the embryo, affects the condition of the mammary glands.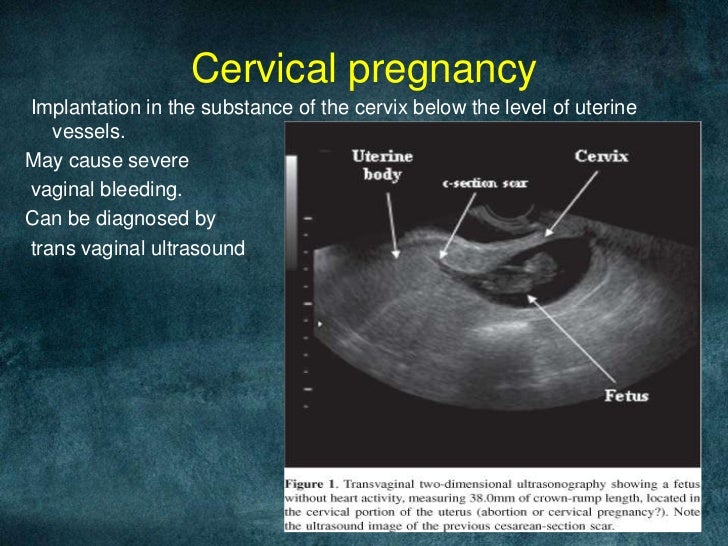 It stimulates the development of the glandular tissue of the mammary glands, thus preparing the body for lactation. The chest hurts, the nipples darken, the vascular network becomes visible.
It stimulates the development of the glandular tissue of the mammary glands, thus preparing the body for lactation. The chest hurts, the nipples darken, the vascular network becomes visible.
The blood supply to the reproductive organs increases after conception. Therefore, the cervix becomes soft, changes color from pink to bluish. Upon examination, the doctor will determine its low location, which is associated with an increase in the size of the uterus.
IVF implantation
In IVF, fertilization is carried out outside the woman's body: in a test tube under laboratory conditions. At the first stage, doctors stimulate ovulation to get more eggs. Then the ovaries are punctured and oocytes are taken, fertilized with the husband's or donor's sperm. When the embryos reach a certain degree of maturity, 1 or 2 of them are transferred to the uterine cavity.
Implantation of an embryo in an IVF cycle occurs differently than during natural conception, and the duration of the process itself is longer than 40 hours. Attachment of 3-day-old embryos is possible not earlier than 3 days after the transfer. If cryopreserved embryos are used, the process takes even longer. But 5-day material is able to grow in after a few hours. At the same time, the probability of successful replanting is also higher in older embryos.
Attachment of 3-day-old embryos is possible not earlier than 3 days after the transfer. If cryopreserved embryos are used, the process takes even longer. But 5-day material is able to grow in after a few hours. At the same time, the probability of successful replanting is also higher in older embryos.
Implantation of the embryo directly occurs in the same way as with natural conception. Since in women who decide on artificial insemination, the problem often lies in the pathology of the endometrium, it is important to properly prepare for the protocol. Both too thick and too thin are undesirable. Therefore, a woman undergoes an examination, during which they find out the condition of the reproductive organs.
If the inner lining of the uterus is thinner than necessary for the implantation of the embryo after conception, it is increased with the help of hormonal preparations. All processes must take place synchronously so that by the time of transplantation the shell is of the required thickness.
Why is attachment not happening
In some cases, the couple conceives, and there are problems with the implantation of the embryo. We will analyze what reasons can lead to such a result.
Parent factors:
- endocrine pathology - thyroid disease, deficiency of female hormones, due to which the endometrium does not mature to the desired thickness;
- immune pathology - as a result of a malfunction in the immune system, cells begin to perceive the embryo as a foreign body and attack it;
- defective endometrium - due to operations, injuries, curettage and termination of pregnancy;
- diseases of the uterus - endometritis, cysts, endometriosis, large fibroids, developmental anomalies;
- concomitant pathology of a woman - diseases of the cardiovascular and nervous system, overweight;
- bad habits - worsen the condition of the reproductive organs, reduce the quality of oocytes;
- defective spermatozoa due to bad habits, concomitant diseases of a man.
fruit factors:
- chromosomal abnormalities;
- delayed development of the embryo.
Implantation of the embryo after conception depends on another structure - the pinopodium. These are outgrowths on the surface of the uterus, to which the future fetus is directly attached. With a decrease in the number of pinopodiums, attachment may not occur.
Abnormal embryo attachment
The implantation of an embryo outside the body of the uterus is called an ectopic pregnancy. The embryo can attach to the wall of the fallopian tube (in most cases), to the surface of the ovaries and peritoneum, in the cervix. Hormonal disorders, inflammatory processes, obstruction of the tubes, volumetric formations of the uterus lead to an abnormal process.
A woman will complain of pain, the intensity of which increases as the pregnancy progresses. Possible bleeding, weakness. To prevent rupture and internal bleeding, early diagnosis (ultrasound of the pelvic organs) and timely surgical operation are necessary.
How to increase the chances of successful implantation
Thus, in the process of fertilization and subsequent attachment, the following are involved:
- Egg - you need to ovulate, the egg was healthy. In order for the oocyte to be of high quality, it is necessary to normalize the hormonal background. In the period of preparation for pregnancy, it is recommended to undergo an examination, based on the results of which the doctor will prescribe a correction for the detected violations. It is also important to eliminate other factors that can negatively affect embryo implantation: lose weight, remove strong coffee and tea, and canned foods from the diet. Instead, it is useful to eat more vegetables and fruits, greens. If necessary, the doctor may prescribe vitamin and mineral complexes. Be sure to take folic acid (folates) to prevent malformations of the nervous system;
- Endometrium - the most important parameter is the thickness. Endometrium under the influence of hormones matures, thickens.
 The moment when this shell is maximally ready to "accept" the embryo is called the "implantation window". Couples who are planning a pregnancy should determine the period that is favorable for them. It lasts no more than 2 days, which means that sexual contact should take place during this period. The state of the inner shell is affected by the pathology of the reproductive system. If there are any violations, then it is necessary to undergo a course of treatment long before the intended conception;
The moment when this shell is maximally ready to "accept" the embryo is called the "implantation window". Couples who are planning a pregnancy should determine the period that is favorable for them. It lasts no more than 2 days, which means that sexual contact should take place during this period. The state of the inner shell is affected by the pathology of the reproductive system. If there are any violations, then it is necessary to undergo a course of treatment long before the intended conception; - Pinopodium - protrusion of endometrial cells. The maximum number of these structures is observed in the middle of the cycle, that is, it coincides in time with the “implantation window”. And they appear 6-9 days after ovulation, disappear after 1-2 days. To accurately determine the pinopodium, the doctor may prescribe a biopsy - taking the inner lining of the uterus and examining it;
- Spermatozoa - qualities such as viability, mobility, quantity are important. The quality of sperm is affected by the general health of a man, previous diseases, surgeries, and injuries.
 Particular attention should be paid to mumps: a childhood infection affects the glandular organs, which include the testicles. Also, the future dad needs to be examined, and if diseases are detected, to be treated in a timely manner. Doctors recommend giving up bad habits, improving lifestyle and nutrition. A man should also take folic acid to prevent abnormalities of the nervous system of the unborn baby.
Particular attention should be paid to mumps: a childhood infection affects the glandular organs, which include the testicles. Also, the future dad needs to be examined, and if diseases are detected, to be treated in a timely manner. Doctors recommend giving up bad habits, improving lifestyle and nutrition. A man should also take folic acid to prevent abnormalities of the nervous system of the unborn baby.
What to do after sex?
With natural conception, there are no restrictions in sexual life. If artificial insemination was carried out, it is necessary to observe sexual rest: both arousal and coitus with orgasm increase the tone of the uterus, which reduces the likelihood of successful implantation of the embryo. For the first day, a strict bed rest is recommended for the expectant mother, then she can slowly get up and move, being careful. She cannot lift weights, make sudden movements.
Any drugs during this period can be taken only after agreement with the doctor.
Will pregnancy tests show?
After the embryo attaches to the wall of the uterus, a chorion is formed, which synthesizes hCG - chorionic gonadotropin. Pregnancy tests react specifically to them: a reagent is applied to the test strip, which stains upon contact with the pregnancy hormone.
The fact is that the test can "catch" the hormone only from a certain level. At the very beginning of pregnancy, the concentration is very low, so the study will show a negative result. If you take the most sensitive test, it will reliably show a positive result after 7 - 9days after embryo implantation. Low-sensitivity test strips are informative only from the 14th day after fertilization.
Tips for future parents
If you are planning to become parents, think about your health long before conception. This recommendation is relevant for both the expectant mother and father. Embryo implantation is a complex, multi-stage process that is influenced by many factors. It is advisable to undergo an examination in advance, adjust the daily routine and diet, and give up bad habits. By following these steps, you will greatly increase your chances of successful fertilization and implantation.
It is advisable to undergo an examination in advance, adjust the daily routine and diet, and give up bad habits. By following these steps, you will greatly increase your chances of successful fertilization and implantation.
1-4 weeks of pregnancy
From a tiny fetus to a small person, a child's body develops in just 9 months. What changes are happening to the expectant mother and what changes are observed inside her during this difficult and joyful period of life?
Each new life begins with the union of the egg and sperm. Conception is the process by which a sperm enters an egg and fertilizes it.
It should be noted that the embryonic and obstetric terms are different. The thing is that among specialists it is customary to consider the period from the first day of the last menstruation, that is, the obstetric period includes the period of preparation for pregnancy. So it turns out that the embryo has just appeared, and the gestation period is already two weeks.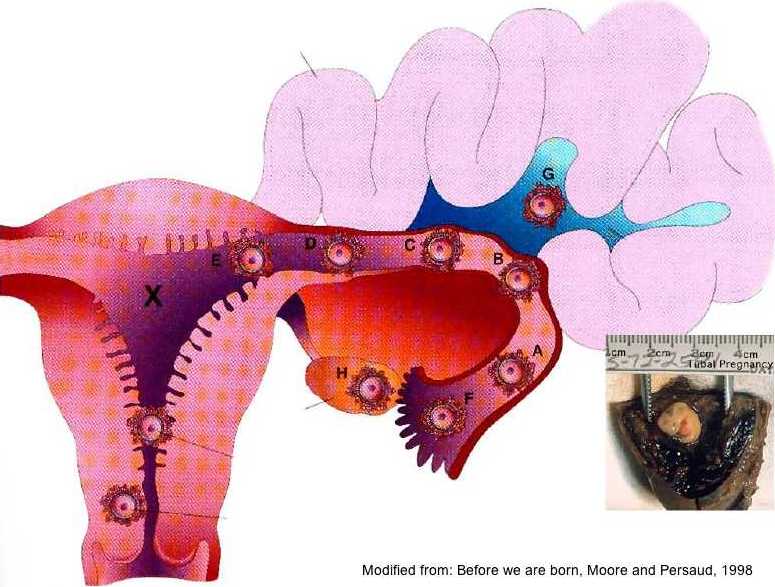 It is the obstetric period that is indicated in all the documents of a woman and is the only reporting period for specialists.
It is the obstetric period that is indicated in all the documents of a woman and is the only reporting period for specialists.
Until the moment of the meeting, the spermatozoon and the ovum lived for a certain time, being in the stage of development and maturation. The development of the future fetus significantly depends on the quality of these processes.
First week
Growth and maturation of the egg starts from the first day of the cycle. A mature egg contains 23 chromosomes as the genetic material for the future embryo, and also contains all the nutrients necessary to start its development. It contains reserves of carbohydrates, proteins and fats, designed to support the embryo during the first days after its occurrence.
A certain number of eggs are laid in each ovary of a girl before she is born. During the childbearing period, they only grow and develop, the process of their formation does not occur. By the time a girl is born, the number of cells from which eggs can develop in the future reaches a million, but this number decreases significantly over the course of life. So, by the time of puberty, there are several hundred thousand of them, and by maturity - about 500.
So, by the time of puberty, there are several hundred thousand of them, and by maturity - about 500.
The ovary each month gives the opportunity to develop most often one egg, the maturation of which occurs inside a vesicle with a liquid called a follicle. From the first day of the cycle, the uterine mucosa begins to prepare for a possible pregnancy. For implantation, i.e., the introduction of the resulting embryo into the wall of the uterus, an optimal environment is created. To do this, due to the influence of hormones, the endometrium thickens, it becomes covered with a network of vessels and accumulates the nutrients necessary for the future embryo.
Male reproductive cells are formed in the gonads - in the testicles or testes. The maturation of spermatozoa occurs in the epididymis, into which they move after formation. The liquid structure of semen is formed due to the secretion of the seminal vesicles and the prostate gland. A liquid medium is necessary for storing mature spermatozoa and creating favorable conditions for their life.
The number of spermatozoa is quite large: tens of millions in one milliliter. Despite such a significant number, only one of them will be able to fertilize the egg. In spermatozoa, there is exclusively genetic material - 23 chromosomes, which are necessary for the appearance of the embryo.
Spermatozoa are characterized by high motility. Once in the female genital tract, they begin their movement towards the egg. Only half an hour or an hour passes from the moment of ejaculation, when sperm enter the uterine cavity. It takes one and a half to two hours for spermatozoa to penetrate into the widest part, which is called the ampulla. Most spermatozoa die on the way to the egg, meeting the folds of the endometrium, getting into the vaginal environment, cervical mucus.
Second week
In the middle of the cycle, the egg fully matures and leaves the ovary. It enters the abdominal cavity. This process is called ovulation. With a regular cycle of 30 days, ovulation occurs on the fifteenth.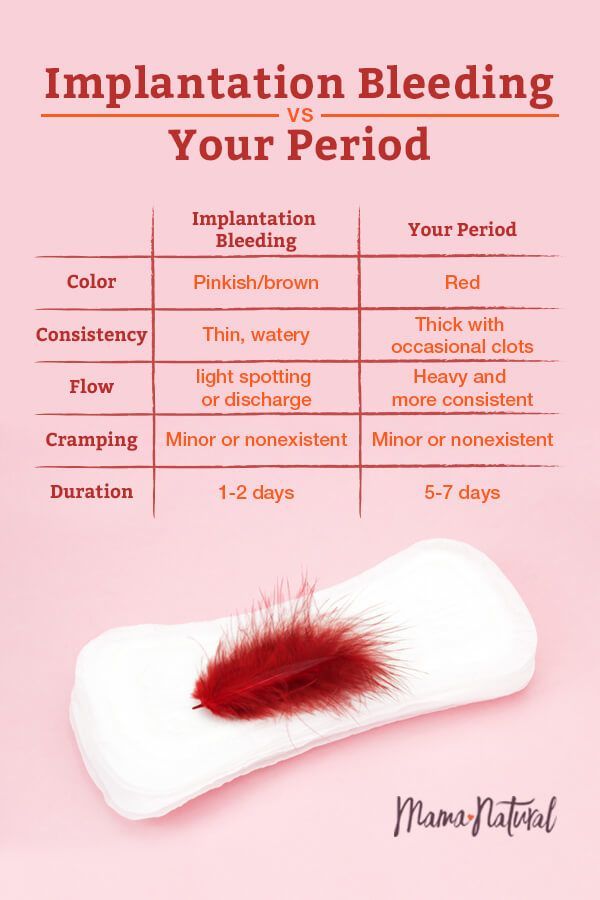 The egg is unable to move on its own. When she leaves the follicle, the fimbriae of the fallopian tube ensure her penetration inside. The fallopian tubes are characterized by longitudinal folding, they are filled with mucus. The muscular movements of the tubes have a wave-like character, which, with a significant number of cilia, creates optimal conditions for transporting the egg.
The egg is unable to move on its own. When she leaves the follicle, the fimbriae of the fallopian tube ensure her penetration inside. The fallopian tubes are characterized by longitudinal folding, they are filled with mucus. The muscular movements of the tubes have a wave-like character, which, with a significant number of cilia, creates optimal conditions for transporting the egg.
Through the tubes, the egg enters their widest part, which is called the ampulla. This is where fertilization takes place. If there is no meeting with the sperm, the egg dies, and the female body receives the appropriate signal to start a new cycle. There is a rejection of the mucous membrane, which was created by the uterus. The manifestation of such rejection is bloody discharge, which is called menstruation.
Waiting time for fertilization of the egg is short. On average, it takes no more than a day. Fertilization is likely on the day of ovulation and maximum on the next. Sperm have a longer lifespan, averaging three to five days, in some cases seven. Accordingly, if a spermatozoon enters the female genital tract before ovulation, there is a possibility that it will be able to wait for the appearance of an egg.
Accordingly, if a spermatozoon enters the female genital tract before ovulation, there is a possibility that it will be able to wait for the appearance of an egg.
When the egg is in a state of waiting for fertilization, certain substances are released that are designed to detect it. If spermatozoa find an egg, they begin to secrete special enzymes that can loosen its shell. As soon as one of the spermatozoa penetrates the egg, the others can no longer do this due to the restoration of the density of its shell. Thus, one egg can only be fertilized by one sperm.
After fertilization, the chromosome sets of the parents merge - 23 chromosomes from each. As a result, one cell is formed from two different cells, which is called a zygote. The sex of the unborn child depends on which of the chromosomes, X or Y, was in the sperm. Eggs contain only X chromosomes. When XX is combined, girls are born. If the spermatozoon contains a Y chromosome, that is, with a combination of XY, boys are born. As soon as a zygote is formed in the body, a mechanism is launched in it aimed at maintaining pregnancy. There are changes in the hormonal background, biochemical reactions, immune mechanisms, and the receipt of nerve signals. The female body creates all the necessary conditions for the safe development of the fetus.
As soon as a zygote is formed in the body, a mechanism is launched in it aimed at maintaining pregnancy. There are changes in the hormonal background, biochemical reactions, immune mechanisms, and the receipt of nerve signals. The female body creates all the necessary conditions for the safe development of the fetus.
Third week
As soon as a day has passed after the formation of the embryo, he will need to make his first journey. The movements of the cilia and the contraction of the muscles of the tube direct it into the uterine cavity. During this process, inside the egg, fragmentation into identical cells occurs.
After four days, the appearance of the egg changes: it loses its round shape and becomes vine-shaped. This stage is called morula, embryogenesis begins - an important stage in the development of the embryo, during which the formation of the rudiments of organs and tissues occurs. Cleavage of cells continues for several days, on the fifth day their complexes are formed, which have different functions.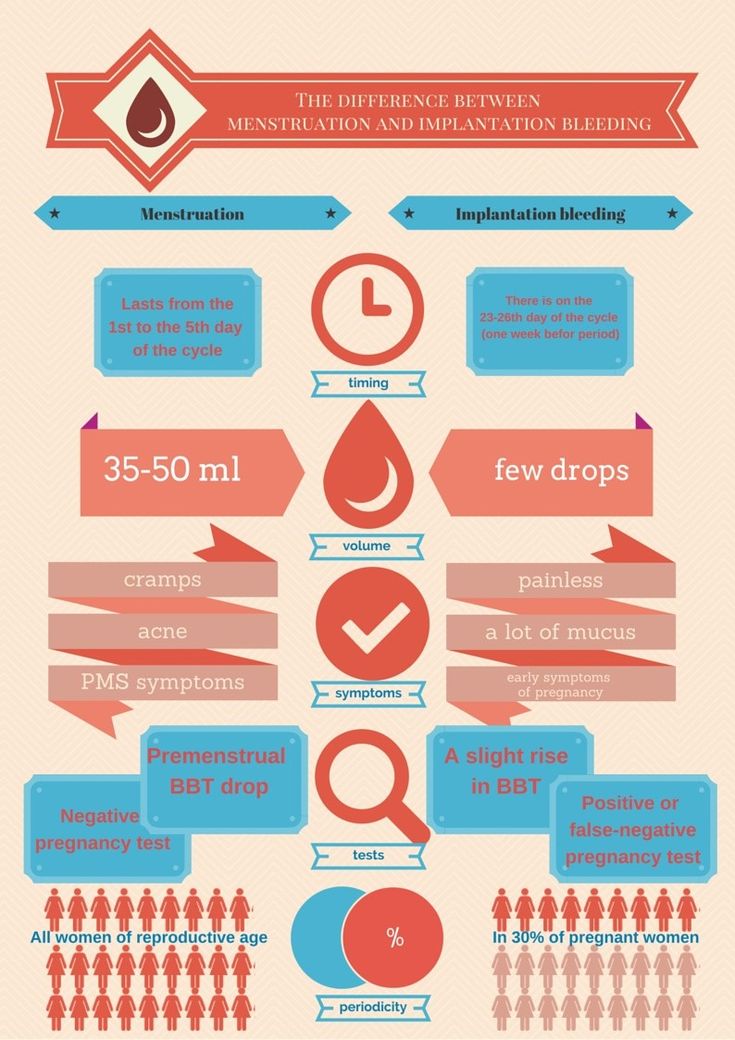 The central cluster forms directly the embryo, the outer one, called the trophoblast, is designed to melt the endometrium - the inner layer of the uterus.
The central cluster forms directly the embryo, the outer one, called the trophoblast, is designed to melt the endometrium - the inner layer of the uterus.
It takes 5-7 days for the embryo to reach the uterus. When implantation occurs in its mucous membrane, the number of cells reaches one hundred. The term implantation refers to the process of implantation of the embryo into the endometrial layer.
After fertilization on the seventh or eighth day implantation takes place. The first critical period of pregnancy is this stage, since the embryo will have to demonstrate its viability for the first time.
During implantation, the outer cells of the embryo actively divide, and the process itself takes about forty hours. The number of cells outside the embryo increases dramatically, they stretch, they penetrate into the uterine mucosa, and the thinnest blood vessels are formed inside, which are necessary for the supply of nutrients to the embryo. Time will pass, and these vessels will be transformed first into the chorion, and subsequently into the placenta, which will be able to supply the fetus with everything necessary until the baby is born.
The embryo at this stage of life is called a blastocyst. It contacts with the endometrium, melts the cells of the endometrium with its activity, creates a path for itself to the deeper layers. The blood vessels of the embryo intertwine with the mother's body, which allows it to immediately begin to extract useful and necessary substances for development. This is vital, because by this time the stock that the mature egg carried in itself is exhausted.
Next, the production of the trophoblast cells, i.e., the outer cells of human chorionic gonadotropin, the hCG hormone, begins. The distribution of this hormone throughout the body notifies it of the onset of pregnancy, which causes the launch of active hormonal changes and the beginning of corresponding changes in the body.
After fertilization and before the start of hCG, it usually takes eight or nine days. Therefore, already from the tenth day after fertilization, it becomes possible to determine this hormone in the mother's blood. Such an analysis is the most reliable confirmation of the onset of pregnancy. The tests that are offered today to determine pregnancy are based on the detection of this hormone in the urine of a woman. After the first day of delayed menstruation with its regular cycle, it is already possible to determine pregnancy using a test on your own.
Such an analysis is the most reliable confirmation of the onset of pregnancy. The tests that are offered today to determine pregnancy are based on the detection of this hormone in the urine of a woman. After the first day of delayed menstruation with its regular cycle, it is already possible to determine pregnancy using a test on your own.
What happens to a woman in the third week of pregnancy
If a woman is planning a pregnancy, 21-24 days, subject to a regular cycle, should become important for her. This is a period of possible implantation, when you should pay special attention to your own lifestyle. During this period, thermal effects and excessive physical exertion are undesirable, and the influence of various kinds of radiation should also be prevented.
The woman does not feel anything at this stage, because the implantation has no external signs. If you adjust your lifestyle in accordance with the simple rules listed above, you will be able to create optimal conditions for successful implantation.
Fourth week
In the fourth obstetric week or the second week of the fetus's life, its body consists of two layers. Endoblast - cells of the inner layer - will become the beginning of the digestive and respiratory systems, ectoblast - cells of the outer layer - will start the development of the nervous system and skin.
The size of the embryo at this stage is 1.5 mm. The flat arrangement of the cells determined the name of the embryo of this age - the disc.
The fourth week is characterized by intensive development of extra-embryonic organs. Such organs should surround the embryo and create the most favorable conditions for its development. The future fetal membranes at this stage are called the amniotic sac, the chorion also develops, which will later become the placenta, and the yolk sac, which is a warehouse of nutrients needed by the embryo.
What happens to a woman in the fourth week of pregnancy
If a woman experiences changes in the fourth week, they are very minor.