What causes lactation
Causes & How It Works
Overview
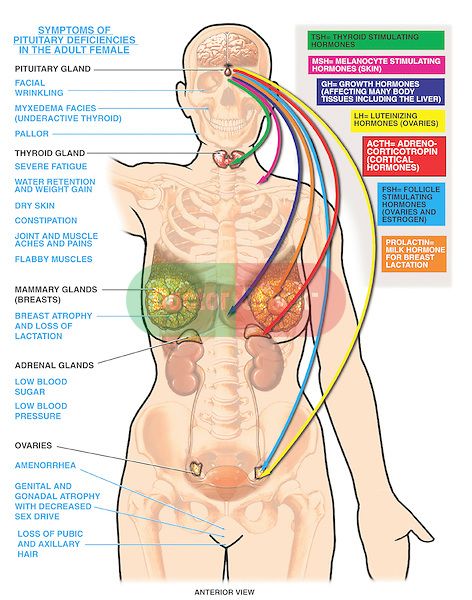
Lactation is the process of making human milk. It's driven by hormones and results in milk coming from your nipple.What is lactation?
Lactation is the process of producing and releasing milk from the mammary glands in your breasts. Lactation begins in pregnancy when hormonal changes signal the mammary glands to make milk in preparation for the birth of your baby. It’s also possible to induce lactation without a pregnancy using the same hormones that your body makes during pregnancy. Lactation ends once your body stops producing milk.
Feeding your baby directly from your breasts is called breastfeeding (or sometimes chestfeeding) or nursing. You can also feed your baby milk that you have expressed or pumped from your breast and saved in a bottle.
Where does human milk come from?
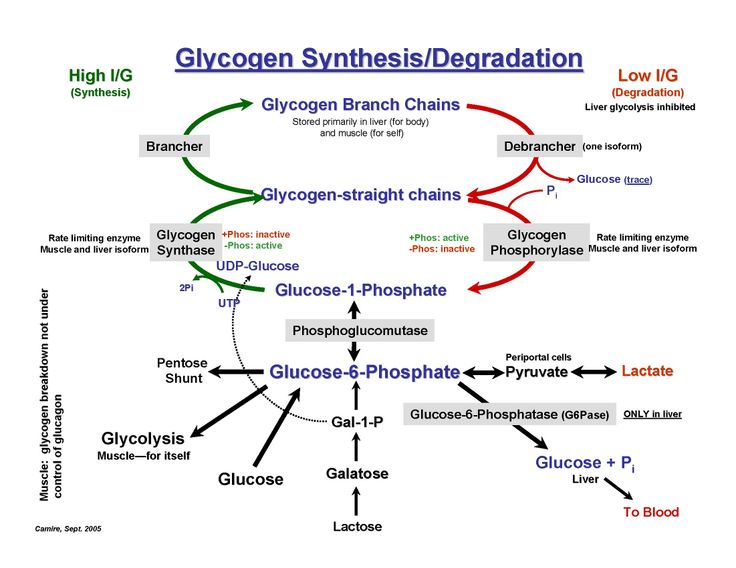
Human milk comes from your mammary glands inside your breasts. These glands have several parts that work together to produce and secrete milk:
- Alveoli: These tiny, grape-like sacs produce and store milk.
A cluster of alveoli is called lobules, and each lobule connects to a lobe.
- Milk ducts: Each lobe connects to a milk duct. You can have up to 20 lobes, with one milk duct for every lobe. Milk ducts carry milk from the lobules of alveoli to your nipples.
- Areola: The dark area surrounding your nipple, which has sensitive nerve endings that lets your body know when to release milk. To release milk, the entire areola needs stimulation.
- Nipple: Your nipple contains several tiny pores (up to about 20) that secrete milk. Nerves on your nipple respond to suckling (either by a baby, your hands or a breast pump). This stimulation tells your brain to release milk from the alveoli through the milk ducts and out of your nipple.
It helps to think of the lactation system as a large tree. Your nipple is the trunk of the tree. The milk ducts are the branches. The leaves are the alveoli.
Why do people lactate?
The primary reason people lactate is to feed a baby. Lactation is a biological, hormonal response that occurs during and after pregnancy to feed a newborn baby. Your body triggers specific hormones to initiate milk production and ejection (releasing of milk). All mammals lactate for this purpose and it’s possible to induce lactation in men and in non-pregnant women using the right hormone medications.
Lactation is a biological, hormonal response that occurs during and after pregnancy to feed a newborn baby. Your body triggers specific hormones to initiate milk production and ejection (releasing of milk). All mammals lactate for this purpose and it’s possible to induce lactation in men and in non-pregnant women using the right hormone medications.
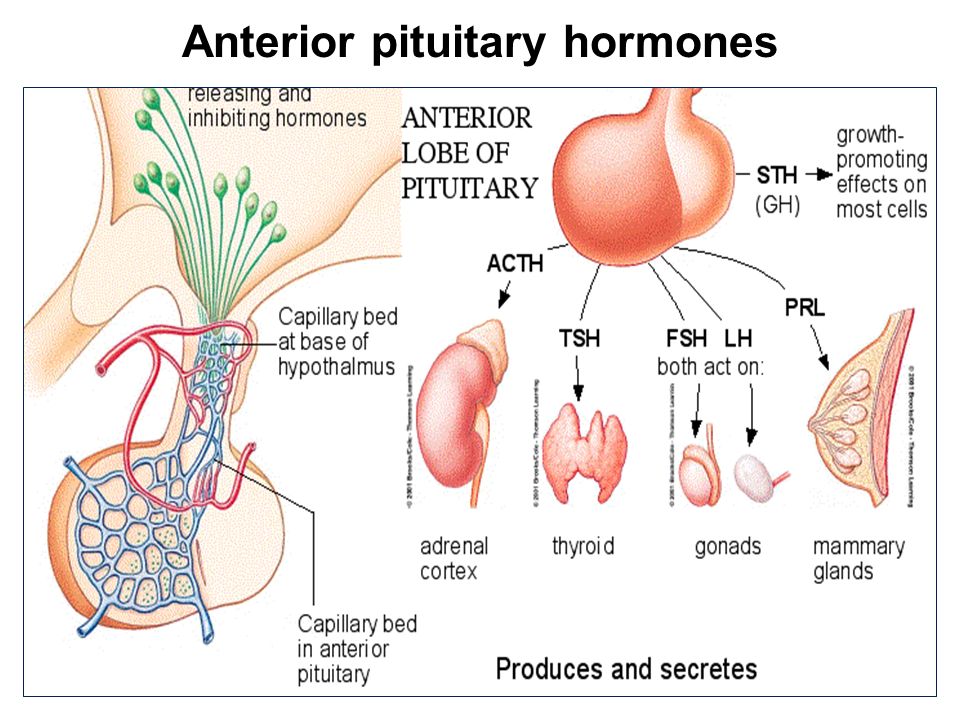
Function
What triggers lactation?
A series of hormonal events, which begin when you’re pregnant, trigger the lactation process. That process is called lactogenesis.
Stage one lactogenesis: This begins around the 16th week of pregnancy and lasts until a few days after you give birth.
- Estrogen and progesterone rise and cause your milk ducts to grow in number and size. This causes your breasts to become fuller. Your mammary glands begin to prepare for milk production.
- Your nipples darken and your areolas become larger.
- Your Montgomery glands (small bumps on the areola) secrete oil to lubricate your nipple.
- Your body begins making colostrum. It’s highly nutritious and filling and serves as your baby’s first milk.
Stage two lactogenesis: This stage starts about two or three days postpartum (after giving birth). It’s when milk production intensifies.
- Once your baby and placenta are delivered, a sudden drop in your estrogen and progesterone causes the hormone prolactin to take over.
- Prolactin is the hormone that produces milk.
- You’ll notice your milk production increases dramatically at this stage. It’s often referred to as milk “coming in.”
- Your breasts are often engorged (or overly full of milk) to the point where they feel sore, painful or tender.
Stage three lactogenesis: This describes the rest of the time you lactate.
- Lactation generally continues as long as milk is removed from your breast.
- The more milk that’s removed, the more milk your body makes to replace it. Frequent feeding or pumping will cause your body to make more milk.

Hormones for lactation
The hormone prolactin controls the amount of milk you produce, and your body begins producing prolactin early in pregnancy. At first, the high levels of estrogen, progesterone and other pregnancy hormones suppress prolactin. Once you deliver the placenta, those pregnancy hormones drop and prolactin takes charge.
When your baby suckles, it stimulates nerves that tell your body to release prolactin and oxytocin. Prolactin causes the alveoli to make milk and oxytocin causes muscle contractions that push out of the alveoli and through the milk ducts.
When milk is released, it’s called a “letdown,” and it takes about 30 seconds of suckling before the letdown occurs. Because you can’t control which breast receives the hormones, the letdown can cause milk to drip from both nipples.
Inducing lactation in people who aren’t pregnant requires medication that mimics hormones your body makes during pregnancy. Suckling from the nipple can initiate lactation, either with a breast pump or by a baby. This is a complex process that involves working closely with a healthcare provider who understands the needs of non-pregnant people and has experience initiating lactation.
This is a complex process that involves working closely with a healthcare provider who understands the needs of non-pregnant people and has experience initiating lactation.
When do you lactate during pregnancy?
Lactation begins as early as a few weeks into the second trimester of your pregnancy. As estrogen and progesterone levels rise, your body prepares for lactation by increasing the number of milk ducts in your breasts, and those milk ducts will transport milk from the alveoli to your nipples. About midway through pregnancy, your body creates colostrum, which is your baby’s first milk.
Can you lactate when you’re not pregnant?
Yes, it’s possible to lactate if you’re not pregnant. Inducing lactation is a complex process that usually involves using hormone-mimicking drugs for several months to produce milk. The second part of lactation is expressing the milk through your nipple. Stimulation from infant suckling, pumping with a breast pump or hand-expressing signals the brain to release the milk. It’s common for people in this situation to receive assistance from a healthcare provider who understands the needs of non-pregnant people and has experience initiating lactation.
It’s common for people in this situation to receive assistance from a healthcare provider who understands the needs of non-pregnant people and has experience initiating lactation.
How do you stop lactation?
There are many reasons why you might need to stop producing milk, and you can stop lactating either naturally or with the help of hormonal drugs.
Natural milk suppression
Lactation is a supply-and-demand process. Your milk supply gradually goes down as your baby relies less on breast milk, or as you reduce the number of times you nurse or pump. Generally, if you decrease the volume of milk removed from your breasts, your body will slow milk production.
Suppressing your milk can feel uncomfortable and most people will become engorged (the term for overfilled breasts). You may also leak milk or develop a clogged milk duct. However, you can treat that pain by taking an over-the-counter pain reliever, wearing a firm bra or using an ice pack on your breasts.
Medication suppression
Medications can also be an option if you need to stop producing milk. Your healthcare provider can explain more about lactation-suppressing drugs, as well as the benefits and possible side effects.
Anatomy
Where are the mammary glands located?
Mammary glands are commonly called breasts and both genders have them. They are located on your chest and are composed of connective tissue, fat and special glandular tissue that makes milk. A woman’s glandular tissue is slightly different because it contains the alveoli and lobules necessary for producing milk. Women also have much more glandular tissue.
Conditions and Disorders
What are common conditions that affect your ability to lactate?
The ability to lactate and the length of time you’re able to produce milk varies. Some can produce milk for years, while others have trouble producing enough milk for their baby.
Some common factors that can impact lactation or breastfeeding are:
- Hormonal levels and conditions.

- Medications.
- Undergoing radiation therapy in the past.
- Trauma to your breast or nipples.
- Breast augmentation, reconstruction or other breast surgeries.
- Other medical conditions like HIV infection.
- Use of drugs and alcohol.
If you’re nursing or pumping your milk to bottle-feed your baby, you should always consult with your healthcare provider before starting any new medications or treatments. Many medications can pass to your baby through breast milk, which may have dangerous effects on your baby.
What is lactational amenorrhea?
Lactation amenorrhea (ah-men-oh-re-uh) means you aren’t menstruating (getting a period) due to lactation. When you’re lactating, your body produces prolactin, the hormone that produces milk. Prolactin reduces the amount of luteinizing hormone (LH) in your body, which helps trigger the release of an egg during ovulation. If you aren’t producing enough LH, you can’t ovulate or get your period. The length of time you can be amenorrheic due to lactation varies from a few months or until you’re completely done lactating.
The length of time you can be amenorrheic due to lactation varies from a few months or until you’re completely done lactating.
Does lactation reduce my risk of any diseases?
Studies have shown that breastfeeding reduces a woman’s risk of ovarian and breast cancers. It can also lower your risk for Type 2 diabetes and high blood pressure.
Care
How do you maintain milk production?
Maintaining lactation is mostly based on supply and demand. The more your baby breastfeeds or the more milk you express with a breast pump, the more your body will make. There are ways to suppress lactation with hormones or oral contraceptives. If you wish to maintain lactation, some things you should do are:
- Continue nursing on-demand or pump milk frequently (approximately every four hours).
- Eat a healthy diet with enough calories. Low-calorie diets can decrease milk supply.
- Drink plenty of water to stay hydrated. Human milk is primarily water.
- Avoid smoking, drugs or alcohol.
 These can reduce your supply and transfer to your milk.
These can reduce your supply and transfer to your milk.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between lactation and colostrum?
Lactation describes the process of making and secreting milk from your breast. Colostrum is the first milk your breasts create during lactation and the first milk your baby drinks. It’s thick, yellow and commonly called “liquid gold.” Colostrum is high in protein, minerals, vitamins and antibodies.
What is hormone therapy for inducing lactation?
Couples or families who wish to induce lactation, maybe because of adoption, surrogacy or other reasons, can try hormone therapy. Induced lactation means you’re creating a milk supply without being pregnant. It’s a process that involves taking estrogen and progesterone for several months to make your body believe it’s pregnant. This helps prepare your breasts for lactation. Some medications and herbs are believed to help establish a milk supply, too.
Several weeks before your baby arrives, begin pumping your breasts with a breast pump. This encourages your body to release prolactin, which produces milk. Ideally, you express your milk several times a day, just like you would if you had a baby. This helps establish a supply. You can also freeze any milk you produce for use once your baby arrives.
This encourages your body to release prolactin, which produces milk. Ideally, you express your milk several times a day, just like you would if you had a baby. This helps establish a supply. You can also freeze any milk you produce for use once your baby arrives.
If you’re considering this as an option, you should talk to your healthcare provider about your desire to feed your baby with human milk. Induced lactation works for many people, but not all.
A note from Cleveland Clinic
If you want to feed your baby human milk, it’s helpful to understand the process of lactation so you know what to expect. Talk to your healthcare provider about how to best prepare for nursing or expressing milk. Remember, lactation can look different for everyone depending on your circumstances and health history. If you struggle with lactation at any point, you may feel embarrassed or even ashamed. But struggling with lactation is very common, and lactation specialists and other healthcare providers can help you as you try to overcome these difficulties.
Causes & How It Works
Overview
Lactation is the process of making human milk. It's driven by hormones and results in milk coming from your nipple.What is lactation?
Lactation is the process of producing and releasing milk from the mammary glands in your breasts. Lactation begins in pregnancy when hormonal changes signal the mammary glands to make milk in preparation for the birth of your baby. It’s also possible to induce lactation without a pregnancy using the same hormones that your body makes during pregnancy. Lactation ends once your body stops producing milk.
Feeding your baby directly from your breasts is called breastfeeding (or sometimes chestfeeding) or nursing. You can also feed your baby milk that you have expressed or pumped from your breast and saved in a bottle.
Where does human milk come from?
Human milk comes from your mammary glands inside your breasts. These glands have several parts that work together to produce and secrete milk:
- Alveoli: These tiny, grape-like sacs produce and store milk.
 A cluster of alveoli is called lobules, and each lobule connects to a lobe.
A cluster of alveoli is called lobules, and each lobule connects to a lobe. - Milk ducts: Each lobe connects to a milk duct. You can have up to 20 lobes, with one milk duct for every lobe. Milk ducts carry milk from the lobules of alveoli to your nipples.
- Areola: The dark area surrounding your nipple, which has sensitive nerve endings that lets your body know when to release milk. To release milk, the entire areola needs stimulation.
- Nipple: Your nipple contains several tiny pores (up to about 20) that secrete milk. Nerves on your nipple respond to suckling (either by a baby, your hands or a breast pump). This stimulation tells your brain to release milk from the alveoli through the milk ducts and out of your nipple.
It helps to think of the lactation system as a large tree. Your nipple is the trunk of the tree. The milk ducts are the branches. The leaves are the alveoli.
Why do people lactate?
The primary reason people lactate is to feed a baby. Lactation is a biological, hormonal response that occurs during and after pregnancy to feed a newborn baby. Your body triggers specific hormones to initiate milk production and ejection (releasing of milk). All mammals lactate for this purpose and it’s possible to induce lactation in men and in non-pregnant women using the right hormone medications.
Lactation is a biological, hormonal response that occurs during and after pregnancy to feed a newborn baby. Your body triggers specific hormones to initiate milk production and ejection (releasing of milk). All mammals lactate for this purpose and it’s possible to induce lactation in men and in non-pregnant women using the right hormone medications.
Function
What triggers lactation?
A series of hormonal events, which begin when you’re pregnant, trigger the lactation process. That process is called lactogenesis.
Stage one lactogenesis: This begins around the 16th week of pregnancy and lasts until a few days after you give birth.
- Estrogen and progesterone rise and cause your milk ducts to grow in number and size. This causes your breasts to become fuller. Your mammary glands begin to prepare for milk production.
- Your nipples darken and your areolas become larger.
- Your Montgomery glands (small bumps on the areola) secrete oil to lubricate your nipple.

- Your body begins making colostrum. It’s highly nutritious and filling and serves as your baby’s first milk.
Stage two lactogenesis: This stage starts about two or three days postpartum (after giving birth). It’s when milk production intensifies.
- Once your baby and placenta are delivered, a sudden drop in your estrogen and progesterone causes the hormone prolactin to take over.
- Prolactin is the hormone that produces milk.
- You’ll notice your milk production increases dramatically at this stage. It’s often referred to as milk “coming in.”
- Your breasts are often engorged (or overly full of milk) to the point where they feel sore, painful or tender.
Stage three lactogenesis: This describes the rest of the time you lactate.
- Lactation generally continues as long as milk is removed from your breast.
- The more milk that’s removed, the more milk your body makes to replace it. Frequent feeding or pumping will cause your body to make more milk.

Hormones for lactation
The hormone prolactin controls the amount of milk you produce, and your body begins producing prolactin early in pregnancy. At first, the high levels of estrogen, progesterone and other pregnancy hormones suppress prolactin. Once you deliver the placenta, those pregnancy hormones drop and prolactin takes charge.
When your baby suckles, it stimulates nerves that tell your body to release prolactin and oxytocin. Prolactin causes the alveoli to make milk and oxytocin causes muscle contractions that push out of the alveoli and through the milk ducts.
When milk is released, it’s called a “letdown,” and it takes about 30 seconds of suckling before the letdown occurs. Because you can’t control which breast receives the hormones, the letdown can cause milk to drip from both nipples.
Inducing lactation in people who aren’t pregnant requires medication that mimics hormones your body makes during pregnancy. Suckling from the nipple can initiate lactation, either with a breast pump or by a baby.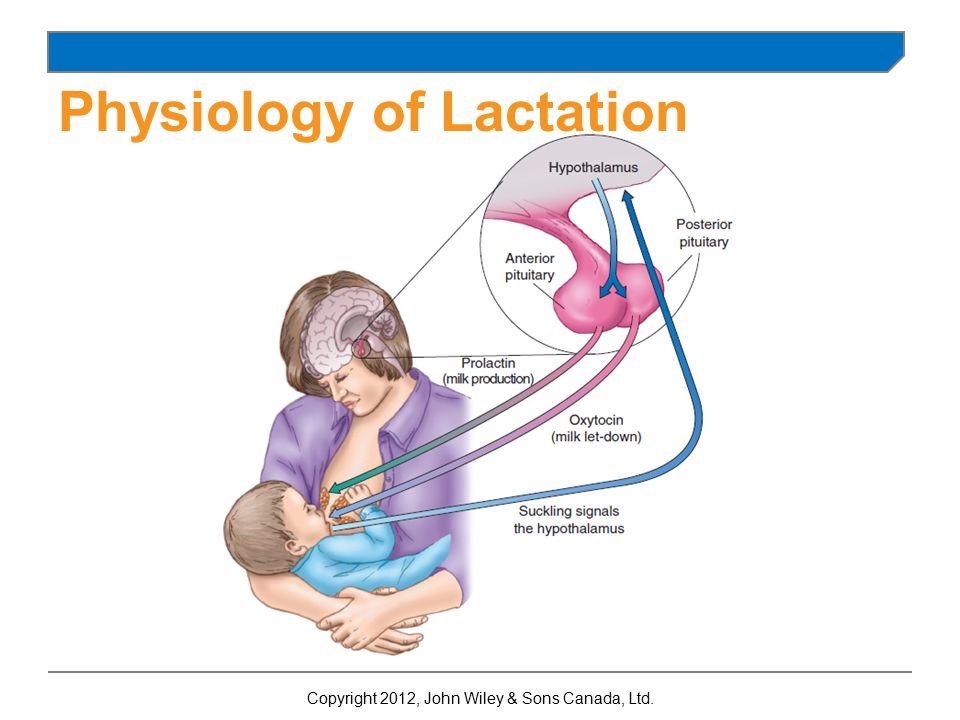 This is a complex process that involves working closely with a healthcare provider who understands the needs of non-pregnant people and has experience initiating lactation.
This is a complex process that involves working closely with a healthcare provider who understands the needs of non-pregnant people and has experience initiating lactation.
When do you lactate during pregnancy?
Lactation begins as early as a few weeks into the second trimester of your pregnancy. As estrogen and progesterone levels rise, your body prepares for lactation by increasing the number of milk ducts in your breasts, and those milk ducts will transport milk from the alveoli to your nipples. About midway through pregnancy, your body creates colostrum, which is your baby’s first milk.
Can you lactate when you’re not pregnant?
Yes, it’s possible to lactate if you’re not pregnant. Inducing lactation is a complex process that usually involves using hormone-mimicking drugs for several months to produce milk. The second part of lactation is expressing the milk through your nipple. Stimulation from infant suckling, pumping with a breast pump or hand-expressing signals the brain to release the milk. It’s common for people in this situation to receive assistance from a healthcare provider who understands the needs of non-pregnant people and has experience initiating lactation.
It’s common for people in this situation to receive assistance from a healthcare provider who understands the needs of non-pregnant people and has experience initiating lactation.
How do you stop lactation?
There are many reasons why you might need to stop producing milk, and you can stop lactating either naturally or with the help of hormonal drugs.
Natural milk suppression
Lactation is a supply-and-demand process. Your milk supply gradually goes down as your baby relies less on breast milk, or as you reduce the number of times you nurse or pump. Generally, if you decrease the volume of milk removed from your breasts, your body will slow milk production.
Suppressing your milk can feel uncomfortable and most people will become engorged (the term for overfilled breasts). You may also leak milk or develop a clogged milk duct. However, you can treat that pain by taking an over-the-counter pain reliever, wearing a firm bra or using an ice pack on your breasts.
Medication suppression
Medications can also be an option if you need to stop producing milk. Your healthcare provider can explain more about lactation-suppressing drugs, as well as the benefits and possible side effects.
Anatomy
Where are the mammary glands located?
Mammary glands are commonly called breasts and both genders have them. They are located on your chest and are composed of connective tissue, fat and special glandular tissue that makes milk. A woman’s glandular tissue is slightly different because it contains the alveoli and lobules necessary for producing milk. Women also have much more glandular tissue.
Conditions and Disorders
What are common conditions that affect your ability to lactate?
The ability to lactate and the length of time you’re able to produce milk varies. Some can produce milk for years, while others have trouble producing enough milk for their baby.
Some common factors that can impact lactation or breastfeeding are:
- Hormonal levels and conditions.

- Medications.
- Undergoing radiation therapy in the past.
- Trauma to your breast or nipples.
- Breast augmentation, reconstruction or other breast surgeries.
- Other medical conditions like HIV infection.
- Use of drugs and alcohol.
If you’re nursing or pumping your milk to bottle-feed your baby, you should always consult with your healthcare provider before starting any new medications or treatments. Many medications can pass to your baby through breast milk, which may have dangerous effects on your baby.
What is lactational amenorrhea?
Lactation amenorrhea (ah-men-oh-re-uh) means you aren’t menstruating (getting a period) due to lactation. When you’re lactating, your body produces prolactin, the hormone that produces milk. Prolactin reduces the amount of luteinizing hormone (LH) in your body, which helps trigger the release of an egg during ovulation. If you aren’t producing enough LH, you can’t ovulate or get your period.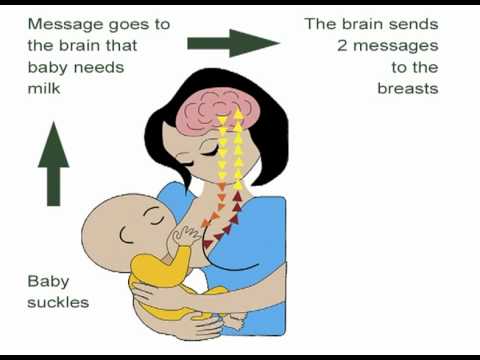 The length of time you can be amenorrheic due to lactation varies from a few months or until you’re completely done lactating.
The length of time you can be amenorrheic due to lactation varies from a few months or until you’re completely done lactating.
Does lactation reduce my risk of any diseases?
Studies have shown that breastfeeding reduces a woman’s risk of ovarian and breast cancers. It can also lower your risk for Type 2 diabetes and high blood pressure.
Care
How do you maintain milk production?
Maintaining lactation is mostly based on supply and demand. The more your baby breastfeeds or the more milk you express with a breast pump, the more your body will make. There are ways to suppress lactation with hormones or oral contraceptives. If you wish to maintain lactation, some things you should do are:
- Continue nursing on-demand or pump milk frequently (approximately every four hours).
- Eat a healthy diet with enough calories. Low-calorie diets can decrease milk supply.
- Drink plenty of water to stay hydrated. Human milk is primarily water.
- Avoid smoking, drugs or alcohol.
 These can reduce your supply and transfer to your milk.
These can reduce your supply and transfer to your milk.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between lactation and colostrum?
Lactation describes the process of making and secreting milk from your breast. Colostrum is the first milk your breasts create during lactation and the first milk your baby drinks. It’s thick, yellow and commonly called “liquid gold.” Colostrum is high in protein, minerals, vitamins and antibodies.
What is hormone therapy for inducing lactation?
Couples or families who wish to induce lactation, maybe because of adoption, surrogacy or other reasons, can try hormone therapy. Induced lactation means you’re creating a milk supply without being pregnant. It’s a process that involves taking estrogen and progesterone for several months to make your body believe it’s pregnant. This helps prepare your breasts for lactation. Some medications and herbs are believed to help establish a milk supply, too.
Several weeks before your baby arrives, begin pumping your breasts with a breast pump. This encourages your body to release prolactin, which produces milk. Ideally, you express your milk several times a day, just like you would if you had a baby. This helps establish a supply. You can also freeze any milk you produce for use once your baby arrives.
This encourages your body to release prolactin, which produces milk. Ideally, you express your milk several times a day, just like you would if you had a baby. This helps establish a supply. You can also freeze any milk you produce for use once your baby arrives.
If you’re considering this as an option, you should talk to your healthcare provider about your desire to feed your baby with human milk. Induced lactation works for many people, but not all.
A note from Cleveland Clinic
If you want to feed your baby human milk, it’s helpful to understand the process of lactation so you know what to expect. Talk to your healthcare provider about how to best prepare for nursing or expressing milk. Remember, lactation can look different for everyone depending on your circumstances and health history. If you struggle with lactation at any point, you may feel embarrassed or even ashamed. But struggling with lactation is very common, and lactation specialists and other healthcare providers can help you as you try to overcome these difficulties.
Products that increase lactation and fat content in breast milk: a list, tips and tricks
Often the secretion of milk is reduced due to the wrong approach to breastfeeding. For example, a baby is bottle-fed and breastfed alternately. The child quickly chooses an easier sucking option - a bottle, and is too lazy to suck milk from the breast. As a result, the mother's body reduces the production of nutrient fluid. The use of a pacifier and feeding "on schedule", without taking into account the needs of the child, also affects. nine0003
In addition, the amount of milk decreases naturally over time. In the first time after childbirth, the mammary glands work in an enhanced mode, creating a kind of "reserve". The body then adapts to the needs of the child, producing as much nutrition as it needs. Another common occurrence during breastfeeding is a lactation crisis. In this state, milk is not secreted for several days, and then lactation resumes.
The state of health of the baby also affects the amount of milk. Infantile jaundice, short frenulum of the tongue, and even naturally increased drowsiness prevent the child from sucking milk from the breast to the end. nine0003
Infantile jaundice, short frenulum of the tongue, and even naturally increased drowsiness prevent the child from sucking milk from the breast to the end. nine0003
But the most important factor is the well-being of the mother. Often lactation stops in women with anemia, hypothyroidism, hormonal and postpartum problems. Chronic fatigue, taking certain medications and smoking have a negative effect.
Products with lactogenic properties help to improve the secretion of mother's milk. They speed up the metabolism and increase the level of the hormones oxytocin and prolactin, which are responsible for lactation. nine0003
How to check the volume and fat content of breast milk at home
On average, the mammary glands of a healthy woman produce up to 1.5 liters of milk per day. This amount fluctuates in different periods of feeding, and depends on many factors - the age, health status and, of course, the mother's nutrition.
The nutrient fluid is conventionally divided into "front" and "back". The first has a more liquid consistency, and contains more water, minerals and carbohydrates. She enters the stomach of the baby at the beginning of feeding, quenches thirst and stimulates appetite. The "back" portion is yellowish in color, thick and high in fat and protein. nine0003
The first has a more liquid consistency, and contains more water, minerals and carbohydrates. She enters the stomach of the baby at the beginning of feeding, quenches thirst and stimulates appetite. The "back" portion is yellowish in color, thick and high in fat and protein. nine0003
At home, it is impossible to measure exactly how much milk an infant sucks. But you can find out if he has enough nutrition by 3 signs:
- The baby looks relaxed and satisfied after feeding.
- There is a constant increase in weight. It is 130 - 230 g in the first 4 months, 115-130 g at the age of 5-8 months.
- The child urinates at least 10 times a day. nine0025
- Cereals. The most useful are oatmeal, pearl barley, brown rice and bulgur. They accelerate the synthesis of prolactin, give energy to the mother and child.
- Whole wheat bread. It is rich in vitamins B and E, which enhance the secretion of breast milk, as well as complex carbohydrates.
- Meat. To increase the protein content in milk, a nursing mother needs to eat turkey, chicken, lean veal.
- Spinach and beetroot. Vitamin C and iron found in leafy vegetables help to restore lactation in case of anemia. nine0024
- Carrot.
 This root vegetable contains beta-carotene, which speeds up the production of mother's milk and improves its taste.
This root vegetable contains beta-carotene, which speeds up the production of mother's milk and improves its taste. - Apricot. Potassium in the composition of the fruit works as a metabolic stimulant.
- Oily fish. Salmon, mackerel, salmon enrich the mother's body with Omega-3 fatty acids, which improve the synthesis of hormones and enzymes.
- Garlic. Just 1-2 slices of a spicy vegetable per day provide an increase in lactation by 5%. To reduce the intensity of the smell, you can add garlic to stews or soups. nine0024
- Nuts. Especially effective for lactation are almonds and walnuts, rich in omega-3 fats.
- Cow's milk. It contains a special secret iga, which forms antibodies that are useful for the intestines of the baby.
- Black sesame. It not only stimulates the production of breast milk, but also saturates it with calcium.
- Dill and basil.
 Fragrant greens are rich in lactogenic substances and vitamin C.
Fragrant greens are rich in lactogenic substances and vitamin C. - Omega 3. These organic substances stimulate the growth of the child's muscle mass, accelerate the development of the brain and retina, and strengthen the immune system.
 Omega-3 fats can be obtained from walnuts, flaxseeds, soybeans, and fatty fish. In a week, you should eat 2-3 dishes from these products. nine0024
Omega-3 fats can be obtained from walnuts, flaxseeds, soybeans, and fatty fish. In a week, you should eat 2-3 dishes from these products. nine0024 - Omega 6 They promote the division of brain cells. A large amount of Omega-6 is found in peanuts, sunflower and pumpkin seeds, Brazil nuts and olive oil.
- Monounsaturated fats. They lower cholesterol and blood sugar levels, are responsible for the health of the heart and blood vessels. Monounsaturated fats are found in poultry, avocados, nuts, peanut and olive oils.
- Alcohol. Ethyl alcohol quickly passes from the mother's blood into breast milk. It produces a dangerous effect on all organs and systems of the infant, but especially on the brain and digestive tract. nine0024
- Caffeine. It excessively excites the nervous system of the baby, causing insomnia, causeless crying and even convulsions. Therefore, coffee and chocolate are excluded from the menu in the first 4 months, and then consumed no more than 1 time per day, between feedings.
- Parsley, mint, sage. These herbs have the ability to reduce lactation. They can help with hypersecretion when mother's milk is in excess.
- Certain types of fish. The meat of shark, mackerel, eel and dorado concentrates mercury in itself, which is toxic to the child.
- Hot spices. Mustard, horseradish, red pepper disturb some babies. If a woman often used hot spices while pregnant, the baby does not show negative reactions. nine0024
- Garlic. The fragrant vegetable enhances the production of breast milk, but gives it a peculiar smell and taste. It does not affect children whose mothers often ate garlic during pregnancy.
- potential allergens. This group includes eggs, nuts, citrus fruits, fish, soy, dairy products, cereal gluten. They should be excluded from the diet if, 12-24 hours after feeding, the baby has allergy symptoms - a runny nose, cough and skin rash. Allergies are also indicated by colic, diarrhea, gas and vomiting. If the child normally tolerates foods, the mother can consume them in moderation - 2-3 times a week. nine0024
- Cocktail with sesame. For him, mix in a blender a glass of milk, 2 tbsp. spoons of black sesame, 1 teaspoon of sugar and 0.5 tsp. cinnamon powder. Drink once a day, preferably in the morning.
- Cumin infusion. Rich in iron, calcium and phosphorus, cumin seeds speed up metabolic processes. For infusion 2 tbsp. spoons of seeds are brewed with a glass of boiling water, poured into a thermos and left overnight. Strained infusion drink 6 times a day for 2 tbsp. spoons. nine0024
- Raspberry leaf tea. Raspberry leaf contains a high level of iron and vitamin C, which accelerate the synthesis of lactogenic hormones. 2 tbsp. spoons of fresh or dried leaves are brewed with a glass of boiling water. Infuse for 15 minutes, drink 0.5 cup 3-5 times a day.
- Nut smoothie. It is prepared from 200 g of chopped walnuts and 0.5 liters of boiling milk. The ingredients are combined in a thermos and infused for 4 hours.
 The finished smoothie is filtered through gauze and drunk half an hour before each feeding. nine0024
The finished smoothie is filtered through gauze and drunk half an hour before each feeding. nine0024 - A decoction of fenugreek. The seeds of this plant contain a lot of phytoestrogens that stimulate lactation. To get a healing agent, 2 teaspoons of grains are poured into a glass of cold water, left for 3 hours, then boiled for 10 minutes in a water bath. Drink a third of a glass 3 times a day, along with seeds.
- Plentiful drink
- herbal teas
- Products that increase lactation
- Vitamins and drugs that increase lactation
- Other ways to stimulate the production of prolactin.
 lactation crisis
lactation crisis
However, not only the quantity is important, but also the fat content of the product - at least 4%. You can measure it yourself by decanting 0.5 cups of “hind” milk. It is poured into a transparent container and put in the refrigerator for 6-7 hours. During this time, the milk fat will concentrate on top, forming a layer of cream.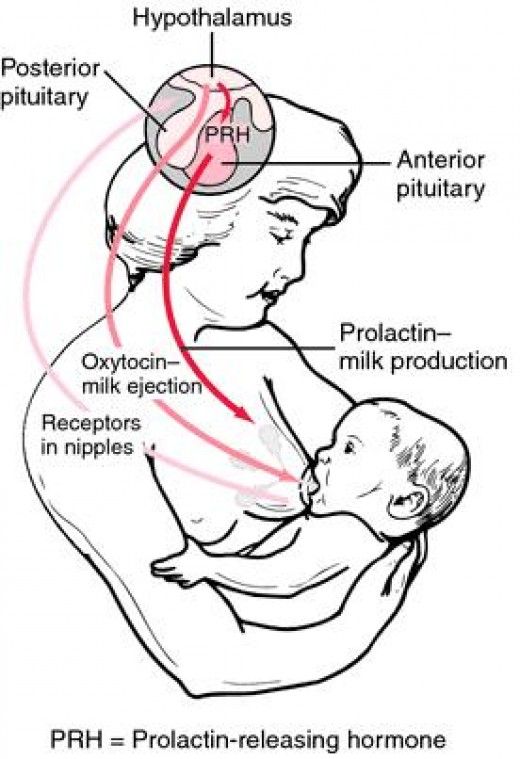 Its thickness is measured with a ruler. Each millimeter equals 1% fat.
Its thickness is measured with a ruler. Each millimeter equals 1% fat.
Which foods increase lactation
One of the keys to successful breastfeeding is the right diet for the mother. It should include proteins, poly- and monounsaturated fats, complex carbohydrates and fiber. With weak lactation, you need to use the most effective lactogens: nine0003
Some drinks also increase the secretion of breast milk - barley broth, coconut water, artificial coffee from chicory or dandelion roots.
How to increase the fat content of mother's milk
The lack of fat in the diet of the baby affects, first of all, its growth and development. But it is not so much the amount that matters, but the type of fatty acids. Poly- and monounsaturated fats help the absorption of vitamins and proteins that accelerate cell division in a growing organism. nine0003
A mother's diet cannot affect the fat content of breast milk, but it can determine the type of substances that are passed on to the baby. Here are the most valuable fatty acids that should be included in the menu of a nursing woman:
To increase the nutritional value of milk, it is useful for mom to use special drinks - for example, milkshakes with protein powder and hot tea with walnuts and sugar-free condensed milk. nine0003
What foods should not be eaten while breastfeeding
Modern doctors believe that a nursing mother should not limit her diet to rigid limits. You can eat everything that a woman is used to, the main thing is that the calorie content of the diet is 3200 - 3500 kcal per day. However, there are a number of products that are extremely harmful to lactation:
However, there are a number of products that are extremely harmful to lactation:
A few more products are considered conditionally harmful - they cause negative consequences only in some cases. Among them:
Among them:
How to increase lactation with folk remedies
Phytochemicals - leaves, fruits and seeds of medicinal plants - help to strengthen the production of milk. Here are 5 proven remedies:
Here are 5 proven remedies:
Ordinary culinary dishes also help to improve lactation - chicken soup with barley, beetroot salad, oatmeal with dried fruits. nine0003
How to increase the lactation of a breastfeeding mother
PreviousNext
Contents:
Today we're going to talk about how to give your baby optimal nutrition. And, of course, we are talking about breastfeeding and ways to increase lactation. nine0003
First, a few praises for breast milk.
Only breast milk is the ideal food for newborns and infants. In terms of nutritional value, the balance of the chemical composition and the degree of digestibility of nutrients, none of the most perfect and adapted milk formula can be compared with breast milk. The nutritional value of breast milk - a product created by nature itself - ensures the rapid growth and development of a child in the first year of life. But it brings the greatest benefit for the baby precisely in the first months, when there is no other complementary food yet. Therefore, it is important to establish breastfeeding immediately after the birth of a child. How to do it right, read here. nine0003
And, of course, mothers, especially beginners, are interested in ways to increase lactation.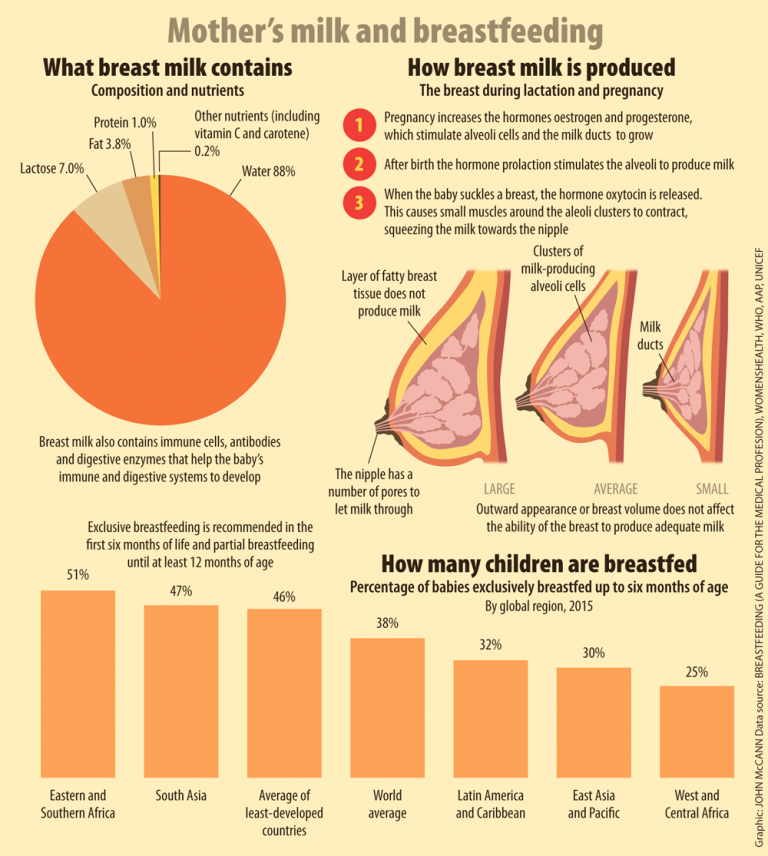 Let's consider the most effective of them in more detail:
Let's consider the most effective of them in more detail:
Plentiful drink
It is difficult to overestimate the importance of this factor. For reference: the amount of food for a child in the first year of life starts from 700 ml (1/5 of body weight), gradually increasing to 1 liter per day. Accordingly, the volume of liquid consumed by a nursing mother should also increase by at least 1 liter. At home, there should always be herbal teas in a thermos and boiled water (mineral water, compotes or fruit drinks) at the same time. Especially effective is the combination of drinking hot herbal decoctions with feeding: you put a mug on the table and, periodically drinking, put the baby to your chest. A wonderful feeling of rush in the chest is guaranteed! nine0003
Did you know that...
Baby's skin is several times thinner and more delicate than that of adults, so the diaper should be as soft as a cloud. And we took care of it! 4 in 1: soft, absorbent, breathable, hypoallergenic! All these are new smart diapers Huggies Elite Soft
Herbal teas
Most herbal preparations contain oregano, anise, fennel, lemon balm, dill, nettle, wild strawberry leaves. All of these herbs have a calming, antispasmodic effect, which has a beneficial effect on the production of oxytocin, one of the two main hormones responsible for lactation. Therefore, during stress, overwork, nervous exhaustion, when the production of oxytocin decreases, herbal preparations are absolutely indicated for use. But sage and thyme (thyme) should be treated with caution - they have a depressing effect on the production of breast milk. From a lack of food, babies can often be capricious and lose a lot of weight, so it is important not to deviate from the daily diet. How much a newborn should eat per feeding - read here.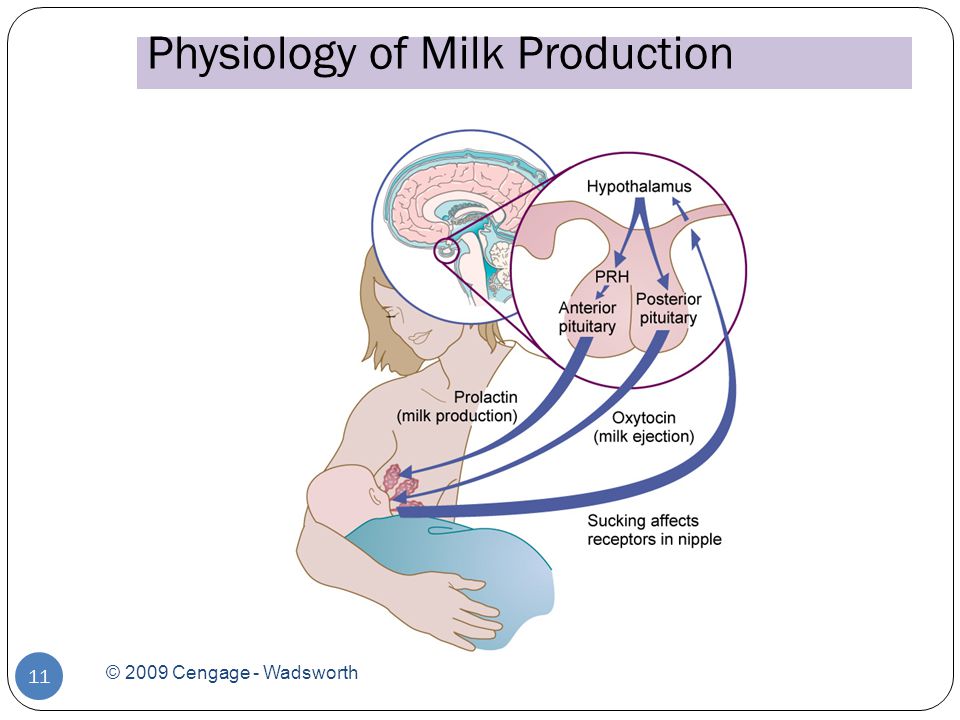 nine0003
nine0003
Herbs can be prepared in advance by yourself, bought at a pharmacy to make a collection at home, or you can buy ready-made herbal teas, including in filter bags.
Products that increase lactation
Lactation is a very energy intensive process. Before the introduction of complementary foods, you feel like a sort of small dairy. And nutrition during feeding should be balanced - taking into account not only losses with breast milk, but also the energy spent on its creation in the mammary gland. Therefore, when breastfeeding, not only the volume of food increases (mainly due to liquid), but also its calorie content. But not at the expense of cakes and pastries! A sufficient amount of protein-containing foods will ensure adequate lactation with good milk quality. Low-fat meats, fish (no more than 2 times a week), cottage cheese, cheese, dairy products, eggs must be in the diet of a nursing woman. Hot soups and broths made from lean veal, chicken, turkey, and rabbit are especially good at stimulating lactation. They should be on the menu every day. nine0003
They should be on the menu every day. nine0003
But alcohol, including the legendary beer, as a means of increasing milk production, is under an absolute ban. In the case of using beer, including with sour cream, the main effect is calming and relaxing, which positively affects the production of oxytocin. Herbal teas have the same effect, and the effects of alcohol on a child's body can be catastrophic. But you can use brewer's yeast as a source of B vitamins.
Any new product should be introduced with caution, observing the child's reaction to it within 2-3 days. And one of the main indicators is the nature of the chair. For a healthy child of the first month of life, the norm is the passage of stool after each feeding. And here, Huggies ® Elite Soft diapers for newborns can become your assistant, which have a unique Soft Absorb absorbent layer that absorbs loose stools and moisture in seconds. And for even more tenderness as part of the new Huggies ® Elite Soft contains 100% organic cotton. The elastic waistband of the diaper fits perfectly to the baby's body, and a special pocket for loose stools will provide additional protection against leakage. Use with pleasure!
The elastic waistband of the diaper fits perfectly to the baby's body, and a special pocket for loose stools will provide additional protection against leakage. Use with pleasure!
Good to know
In the first months of a baby's life, mothers have so many questions! Look for answers to them at Huggies Parents School
Vitamins and drugs that increase lactation
During lactation, the woman's body's need for vitamins and trace elements increases. The resulting relative hypovitaminosis can contribute to a decrease in the function of the mammary gland. Preference is given to multivitamin complexes containing retinol (vitamin A), tocopherol (vitamin E), thiamine (vitamin B 1 ), ascorbic acid, microdoses of iodine, glutamic and lipoic acid.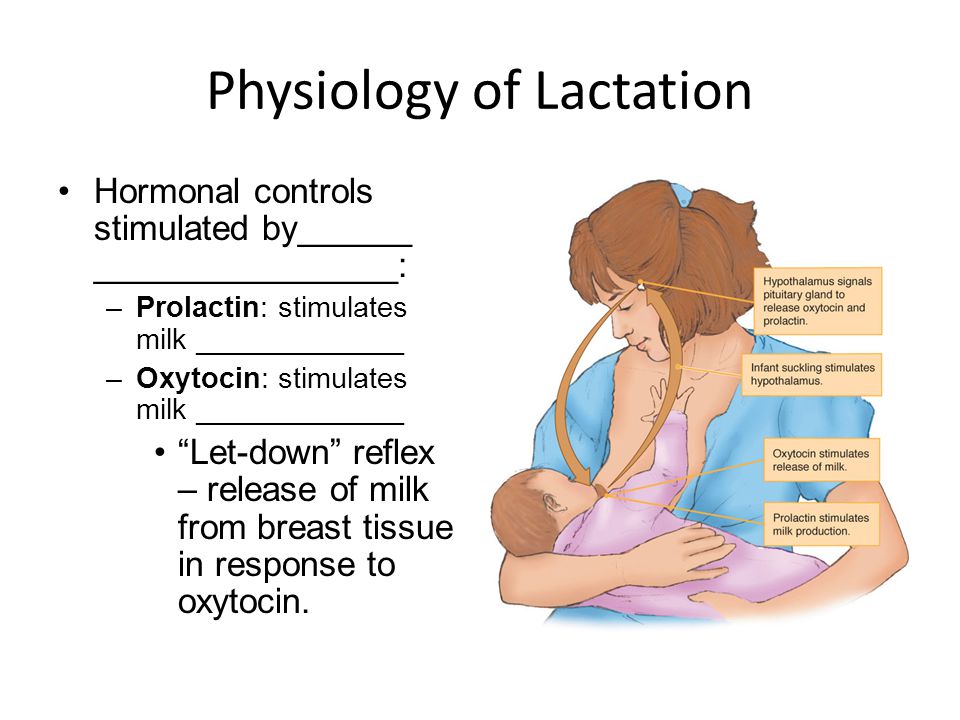 Of the biogenic stimulants, Apilak, Laktogon are used.
Of the biogenic stimulants, Apilak, Laktogon are used.
Considering that almost all drugs pass into breast milk and, accordingly, to the child, medications to increase lactation should be used only as directed by a doctor.
Other ways to stimulate the production of prolactin. Lactation crisis
It should be noted that the production of breast milk is a cyclical process. There is the concept of lactation crises that occur every 1.5–2 months, when the amount of milk a woman may slightly decrease. In this situation, the most important thing is not to reduce the number of feedings, but, on the contrary, to put the baby to the breast more often. This stimulates milk production. And the child, as a rule, feels the approach of a lactation crisis and “stocks up” food in advance, increasing his appetite a day or two before the start of the decline in lactation. You can not refuse night feedings. The maximum production of prolactin occurs at night, and with proper stimulation by applying to the chest, lactation is easily restored.