What causes itching in the nose
How to Get Rid of It and Causes
We include products we think are useful for our readers. If you buy through links on this page, we may earn a small commission. Here’s our process.
Healthline only shows you brands and products that we stand behind.
Our team thoroughly researches and evaluates the recommendations we make on our site. To establish that the product manufacturers addressed safety and efficacy standards, we:
- Evaluate ingredients and composition: Do they have the potential to cause harm?
- Fact-check all health claims: Do they align with the current body of scientific evidence?
- Assess the brand: Does it operate with integrity and adhere to industry best practices?
We do the research so you can find trusted products for your health and wellness.
Read more about our vetting process.Overview
A tickle in the nose can be very annoying. Typically, that tickling feeling in your nose only lasts for a few seconds, and then you sneeze. Sometimes, though, sneezing doesn’t relieve the problem. If you have a tickle in your nose that isn’t going away, there could be several possible causes, including viruses, allergies, and nasal polyps.
Viruses
The tickle in your nose may be caused by a virus like the common cold. Although colds are most common in the winter and spring, you can get them any time of year. In fact, most adults get two or three colds every year, and children have even more.
Your nose tickle may be your body’s way of telling you that you’re about to get a cold. When the germs that cause colds first infect your nose and sinuses, your nose tries to flush them out with mucus. Sneezing is another way that your body expels germs, which may explain the nose tickle. If you’re having trouble getting out that sneeze, these tips may help.
Allergies
Allergies occur when your body has an immune response to something in your environment.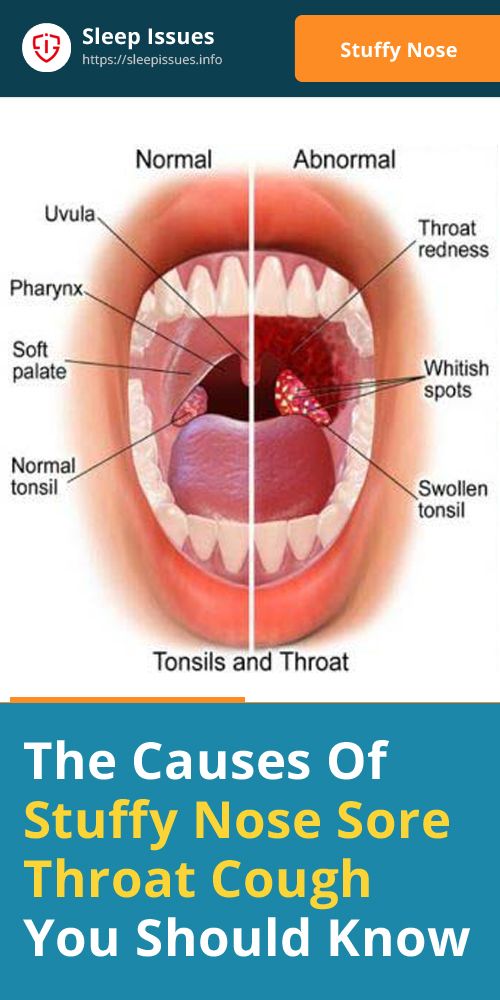 When you’re allergic to something, your body mistakes it for a foreign invader, like a flu virus. This can cause cold-like symptoms. Many people have allergies to both indoor and outdoor substances, such as pet dander, pollen, and dust mites.
When you’re allergic to something, your body mistakes it for a foreign invader, like a flu virus. This can cause cold-like symptoms. Many people have allergies to both indoor and outdoor substances, such as pet dander, pollen, and dust mites.
Allergies can be seasonal or last all year long. They can cause an irritating inflammation in your nose that may give you a tickly, itchy feeling.
Environmental irritants
There are things in the air that can be very irritating to the nasal passages (the spaces in your nose that fill with air). People who are bothered by irritants have what doctors call nonallergic rhinitis. The symptoms are similar to seasonal allergies, but your body doesn’t have an immune reaction. You may experience runny nose or other nasal irritation. Common irritants include fragrances, smoke, and cleaning products.
Sinusitis
Sinusitis can be either acute (lasting a short time) or chronic (lasting a long time). If you’ve felt a tickling sensation in your nose for more than a few weeks along with other symptoms, you could have chronic sinusitis.
Chronic sinusitis is a common condition that occurs when the passages become inflamed and swollen. It lasts at least 12 weeks and includes some of the following symptoms:
- difficulty breathing through your nose
- fatigue
- pain and tenderness around your eyes
Nasal polyps
Nasal polyps often occur in people with chronic sinusitis. They’re small, soft, noncancerous growths that hang down from the lining of your nasal passages. They can also be caused by asthma, allergies, drug sensitivity, or some immune disorders. Larger growths may be irritating and lead to breathing problems and a lost sense of smell.
Migraine
Many people don’t know that headache is not the only symptom of migraines. Migraine attacks can include a variety of different symptoms, such as:
- facial numbness and tingling
- aura (flashes of light)
- nausea
- vomiting
- blurry vision
It’s possible to experience a migraine attack with no head pain at all.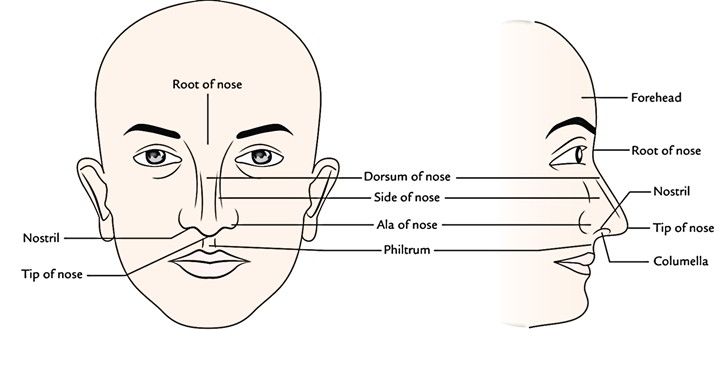 Migraines also come in stages, so a tingling nose could indicate that a migraine attack is on its way.
Migraines also come in stages, so a tingling nose could indicate that a migraine attack is on its way.
CPAP machine
If you use a continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) machine for sleep apnea, it could be causing your nose to itch. Nose itchiness is one of the most common complaints of new CPAP users. People say it feels like spiders or feathers in the nose.
If the itchiness is preventing you from wearing your mask, talk to your doctor. You can also try increasing the humidity or using mask liners.
Dry nose
When your nasal passages get dried out it can be uncomfortable, irritating, and painful. Dry nose is often caused by blowing your nose too much. Some medications for allergies and colds can also dry out your nose. Dry nose is common during the winter when the heat is turned on. There are several home treatments for dry nose.
Nasal tumors
Nasal and paranasal tumors are growths that form in and around your nasal passages. These tumors can be either cancerous (malignant) or noncancerous (benign).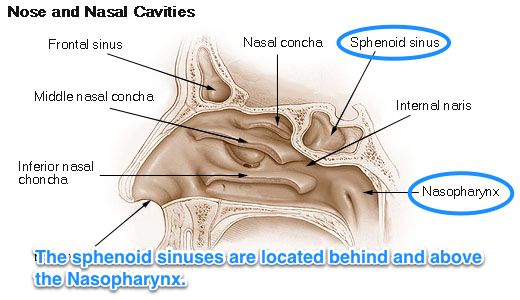 Cancer of the nasal passages is rare and often has no symptoms. Possible symptoms include loss of smell, congestion, sores inside the nose, and frequent sinus infections.
Cancer of the nasal passages is rare and often has no symptoms. Possible symptoms include loss of smell, congestion, sores inside the nose, and frequent sinus infections.
There are several things you can do to treat your nose tickle at home:
Avoid triggers. If you’re having a reaction to an allergen (pet dander, pollen, dust) or an irritant (smoke, perfume, chemicals), try to stay away.
Take over-the-counter (OTC) allergy drugs. OTC allergy medications can help with seasonal and indoor allergies. There are pills and nasal sprays available.
Take cold medicine. If your doctor says it’s safe, you can take an OTC cold remedy or decongestant.
Blow your nose less. Blowing your nose repeatedly can cause damage, dryness, and irritation.
Hands off. Don’t pick your nose or stick a tissue or Q-tip up there to try and remove debris. Your nose has ways of clearing debris on its own.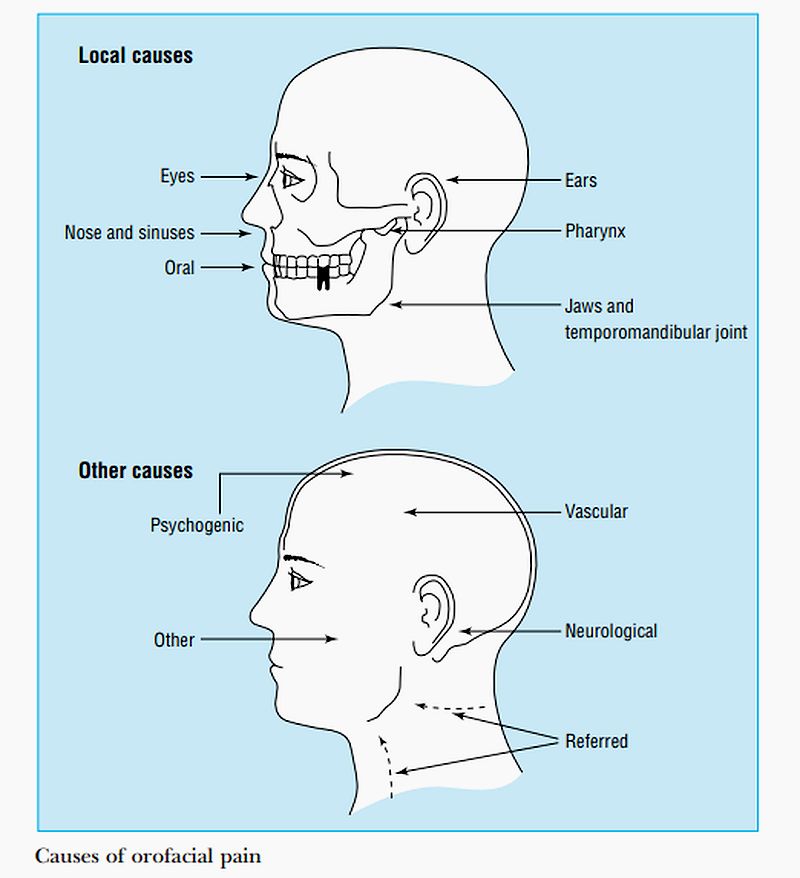
Use a humidifier. A humidifier can add moisture to dry winter air. It may be particularly useful at night.
Try capsaicin nasal spray. Capsaicin, the active ingredient in chili peppers, can overstimulate your nose all at once, making irritation less likely.
Try a neti pot. A neti pot flushes a salt water solution through your nasal passages. It’s a good way to clear out excess mucus and irritants and may feel refreshing
Get a lot of rest. If you have a cold or a flu, then there’s not much you can do except wait it out and get as much rest as possible.
Drink lots of water. Drinking fluids like water and tea while you’re sick keeps you hydrated while your body is fighting off an infection or virus.
Try dietary supplements. Researchers have looked into the possible benefits of honey, butterbur, capsaicin, astragalus, grapeseed extract, and omega-3 fatty acids for nasal issues.
There are many possible causes for a tickling sensation in your nose. Most can be resolved with home remedies and the passage of time. A tickle in the nose is rarely a sign of a serious problem, but you should talk to your doctor if your symptoms don’t improve.
Itchy Nose? 9 Reasons Your Nose is Itching
Normal episode of itchy skin
Itchy skin is also called pruritis. There are a number of "normal" causes for itching, meaning the cause is not disease-related and does not result in seriously damaged skin.
The most common causes are:
- Dry skin, due to bathing in soap or bubble bath that may be too harsh and is stripping the natural oils from the skin.
- Mild allergies, which may be caused by dust; certain plants and flowers; nickel-containing jewelry; and any sort of soap, detergent, lotion, or perfume.
- Pregnancy, due to stretching of skin or to a condition called prurigo. Prurigo causes small, itchy bumps which may be due to an autoimmune system dysfunction during pregnancy.

- Menopause, due to hormonal changes that may leave the skin overly dry.
Diagnosis is made through physical examination and sometimes allergy tests.
Treatment involves bathing only with mild, hypoallergenic soap; regular moisturizing with unscented lotion; wearing soft, loose, non-synthetic clothing; avoiding any substances that seem to provoke the itching; and sometimes prescription medicated creams.
Rarity: Common
Top Symptoms: feeling itchy or tingling all over
Symptoms that always occur with normal episode of itchy skin: feeling itchy or tingling all over
Urgency: Self-treatment
Non-specific insect bite
Insect bites are very common. They often cause itchiness, redness, and some swelling. Most insect bites can be treated at home.
Rarity: Common
Top Symptoms:
Urgency: Self-treatment
Non-allergic rhinitis
Rhinitis simply means "inflammation of the nose. " When it is caused by something other than allergies, it is called vasomotor rhinitis. "Vasomotor" simply refers to the constriction or dilation of blood vessels.
" When it is caused by something other than allergies, it is called vasomotor rhinitis. "Vasomotor" simply refers to the constriction or dilation of blood vessels.
Different substances can trigger the vasomotor reaction, even though it is not an allergic reaction. Common causes are certain medications; air pollution; and chronic medical conditions.
Symptoms include runny nose, sneezing, congestion, and postnasal drip. Since no allergy is involved, there will not be the scratchy throat or itchy eyes and nose of allergic rhinitis.
A medical provider should be seen for ongoing symptoms, since they can interfere with quality of life. Also, using over-the-counter medications meant for allergic rhinitis will not help in a case of vasomotor rhinitis.
Diagnosis is made through patient history, physical examination, and allergy tests, in order to rule out allergies as a cause of the symptoms.
Treatment involves using the appropriate medications to ease the symptoms, and avoiding any triggers as much as possible.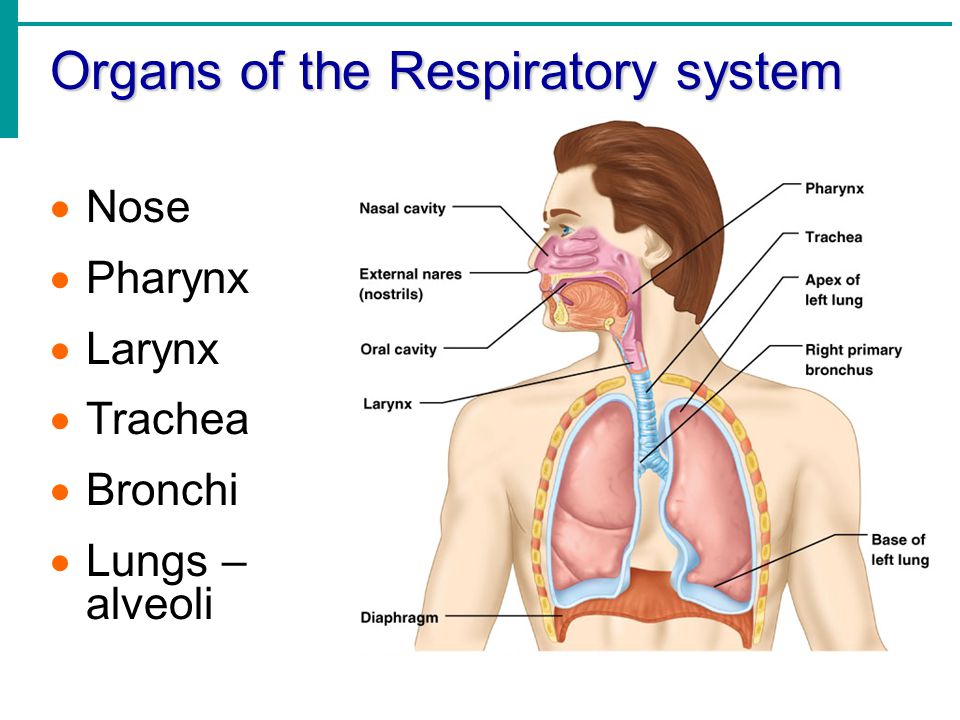
Rarity: Common
Top Symptoms: congestion, mucous dripping in the back of the throat, runny nose, frequent sneezing, eye itch
Symptoms that never occur with non-allergic rhinitis: fever, sinus pain, facial fullness or pressure
Urgency: Self-treatment
New-onset seasonal allergies
New-onset seasonal allergies, also called adult-onset seasonal allergies, are sensitivities to pollen, mold, and other irritants that cause nasal congestion, runny nose, sneezing, itchy eyes, and sore throat.
Seasonal allergies commonly begin in childhood but can start at any age, especially among those with a family history. Moving to a different geographic location may trigger the allergy in someone with a genetic predisposition. Anyone with asthma is more likely to experience adult-onset seasonal allergies.
Sometimes the symptoms are actually from "pregnancy rhinitis" – nasal congestion and sneezing due to the effects of pregnancy hormones on the nasal tissue.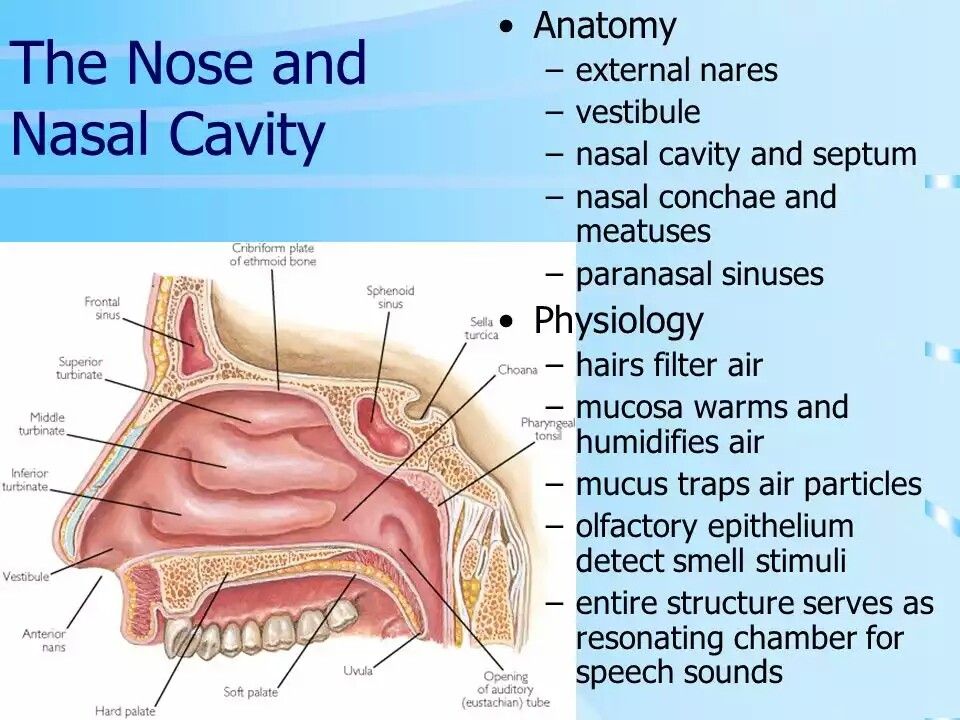
A new-onset allergy is often thought to be a cold, but a cold will clear up without treatment. Allergies persist, never getting better or worse, and can interfere with quality of life.
Diagnosis is made by an allergist, who will use skin tests and blood tests.
There is no cure for seasonal allergies but the symptoms can be managed for greater comfort and relief. Antihistamines, corticosteroid nasal sprays, and immunotherapy or "allergy shots" can be very effective.
Rarity: Common
Top Symptoms: sore throat, congestion, cough with dry or watery sputum, mucous dripping in the back of the throat, fatigue
Symptoms that never occur with new-onset seasonal allergies: fever, yellow-green runny nose, chills, muscle aches
Urgency: Self-treatment
Eczema (atopic dermatitis)
Atopic dermatitis, also called eczema, dermatitis, atopic eczema, or AD, is a chronic skin condition with an itchy rash.
AD is not contagious. It is caused by a genetic condition that affects the skin's ability to protect itself from bacteria and allergens.
AD is most often seen in infants and young children. Most susceptible are those with a family history of AD, asthma, or hay fever.
Infants will have a dry, scaly, itchy rash on the scalp, forehead, and cheeks. Older children will have the rash in the creases of elbows, knees, and buttocks.
Without treatment, a child may have trouble sleeping due to the intense itching. Constant scratching may cause skin infections and the skin may turn thickened and leathery.
Diagnosis is made through physical examination, patient history, and allergen skin tests.
AD cannot be cured, but can be controlled through prescribed medications, skin care, stress management, and treatment of food allergies. Those with AD often have allergies to milk, nuts, and shellfish. Keeping the skin clean and moisturized helps prevent flareups.
Dermatofibroma of the nose
A dermatofibroma is a fairly common skin growth that usually appears on the lower legs, but may appear anywhere on the body. These mole-like growths are benign (noncancerous.)
These mole-like growths are benign (noncancerous.)
The cause is not known, though a dermatofibroma may appear after a minor injury. The growths are not contagious.
Dermatofibromas are most common in adults and are rarely found in children.
Symptoms include a hard, raised growth that is red, pink, or brown and less than half an inch across. They are usually painless but may be tender or itchy, and may appear alone or in groups.
Any new growth on the skin should be seen by a medical provider, especially if the growth is very dark in color or changes its shape or appearance quickly.
Diagnosis is made through physical examination and sometimes biopsy.
A dermatofibroma does not require treatment unless it is interfering with clothing or is unsightly. They can be surgically removed, though this will leave a scar and the growth may eventually return.
Rarity: Rare
Top Symptoms: nose itch, small nose lump, skin-colored nose bump, pink or red nose bump, marble-size nose lump
Urgency: Wait and watch
Allergic contact dermatitis of the nose
Allergic contact dermatitis means the skin has touched something that provoked an allergic reaction, causing inflammation and irritation.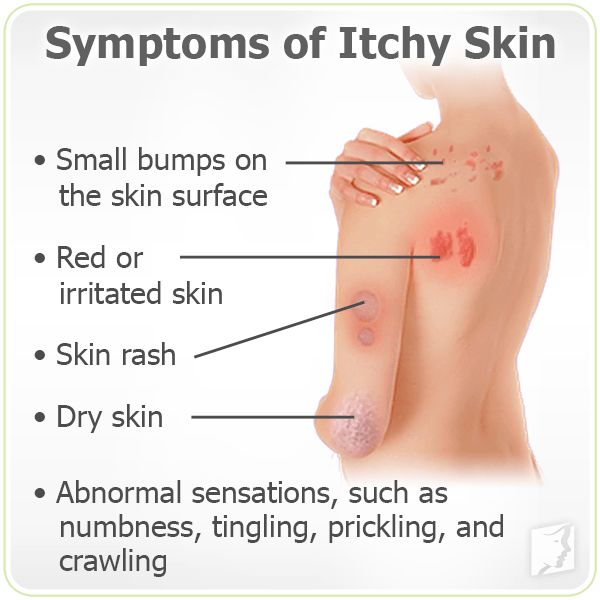
"Contact" means the allergic reaction came from touching something, not from consuming something. The first exposure to the substance sensitizes the immune system, and then the second exposure actually causes the symptoms.
The most common causes of allergic contact dermatitis are:
- Nickel, a metal often used in belt buckles, the buttons on pants, and jewelry, including piercing jewelry.
- Poison ivy.
- Various types of perfumes, including those founds in soaps, fabric softeners, and detergents.
- Of course, there are many more.
Symptoms include red, itching, scaling, flaking skin that may be painful due to the irritation and inflammation.
Diagnosis is made through first avoiding contact with any suspected substance, to see if the dermatitis clears. Patch testing can be done if the results are not certain.
Treatment involves fully avoiding the allergy-provoking substance and using topical steroid cream as prescribed. Cool compresses and calamine lotion can help to ease the discomfort.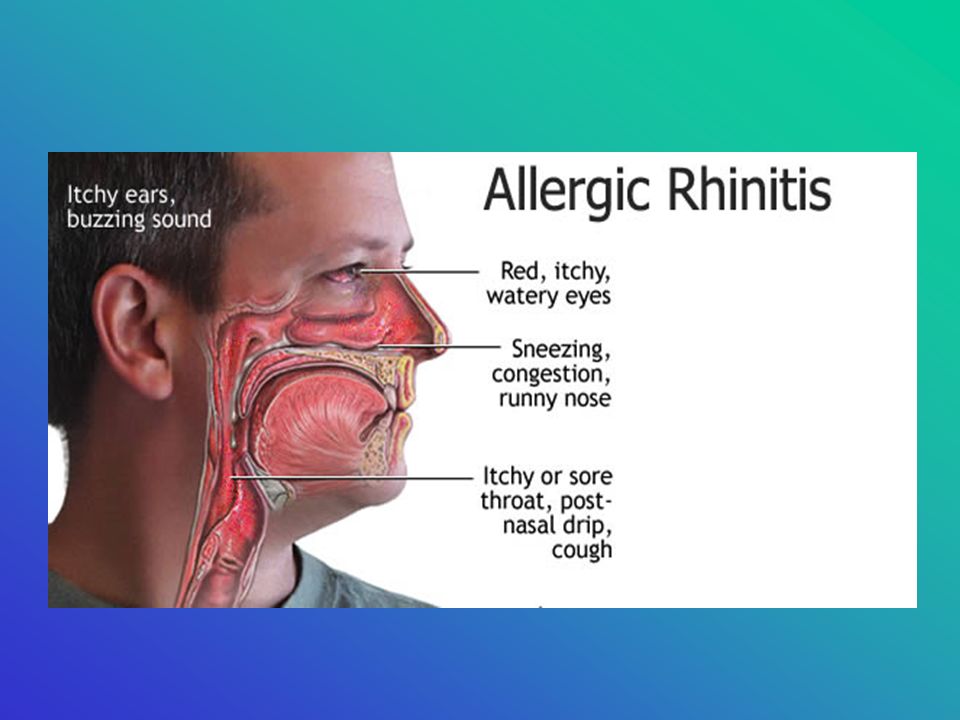
Rarity: Common
Top Symptoms: nose itch, nose redness, scabbed area of the nose
Symptoms that always occur with allergic contact dermatitis of the nose: nose redness
Urgency: Self-treatment
Chronic allergies
Allergies are an overreaction by the immune system to something that does not bother most other people. Many people who have allergies are sensitive to pollen, but other things such as dust mites, animal dander, cockroaches, and mold can also cause a reaction.
Rarity: Common
Top Symptoms: fatigue, irritability, trouble sleeping, runny nose, congestion
Symptoms that never occur with chronic allergies: fever, yellow-green runny nose, chills, muscle aches
Urgency: Self-treatment
Mosquito bite
Mosquito bites are bites from flying insects that feed on the blood of animals, including humans.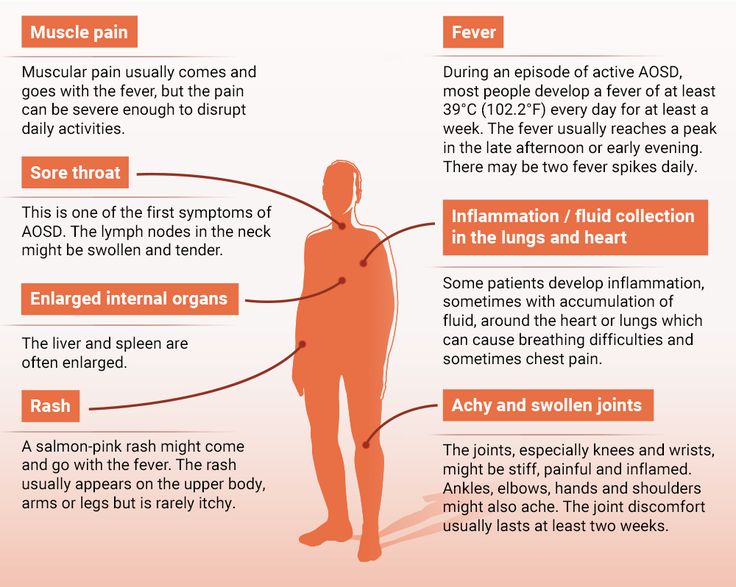 Mosquito bites are more common during the summer or in warmer climates, at dawn or dusk, and near bodies of water.
Mosquito bites are more common during the summer or in warmer climates, at dawn or dusk, and near bodies of water.
In most cases, mosquito bites will cause a local skin reaction that gets better on ..
How to get rid of burning and itching in the nose
Burning and itching in the nose cause anxiety, distract from work, interfere with communication with people. Often associated symptoms are sneezing and nasal secretion. In order to quickly overcome the discomfort, it is worthwhile to figure out in which cases itching occurs in the nose and how to soothe the irritated mucosa.
Causes, symptoms, treatment
Most often, itching in the nose is the result of an allergic reaction or infectious inflammation. Dry and polluted air, injuries, abuse of certain medications can also trigger the mechanism of protective reactions, one of the signs of which is itching in the nasal cavity. nine0003
Allergy
Any allergic reaction is based on the body's hypersensitivity to a specific irritant. When the latter settles on the mucous membrane of the upper respiratory tract, a chain of immune reactions develops, resulting in swelling, increased secretion of mucus, irritation of nerve endings, which causes itching and sneezing. Thus, hypersecretion and sneezing act as protective mechanisms aimed at the speedy removal of the allergen from the body.
When the latter settles on the mucous membrane of the upper respiratory tract, a chain of immune reactions develops, resulting in swelling, increased secretion of mucus, irritation of nerve endings, which causes itching and sneezing. Thus, hypersecretion and sneezing act as protective mechanisms aimed at the speedy removal of the allergen from the body.
In addition to itching and frequent sneezing, allergic inflammation of the nasal mucosa is characterized by:
- copious rhinorrhea in the form of clear liquid discharge;
- hyperemia of the conjunctiva, lacrimation, sometimes swelling of the eyelids and even the face;
- dry cough due to mucus running down the throat;
- with a protracted course, asthenic syndrome develops.
Allergies may be seasonal or occur spontaneously through accidental contact with an irritant. Seasonal hay fever is associated with the body's reaction to the antigen of one or more types of pollen. It is with this type of allergy that the symptoms, including itching, are especially acute. nine0003
It is with this type of allergy that the symptoms, including itching, are especially acute. nine0003
In the case of persistent allergic rhinitis, when the irritant is present in a person's life almost all year round, itching in the nose is mild and occurs periodically. Such permanent allergens are usually small mites that parasitize on dust particles, pet hair, some ingredients of household chemicals, cosmetics, and food.
To eliminate the manifestation of allergic rhinitis, it is necessary to take an antihistamine tablet and thoroughly rinse the nasal cavity with saline solution (half a teaspoon to a glass of boiled water). As a symptomatic agent that facilitates nasal breathing, vasoconstrictor sprays or sprays based on corticosteroids are used. Further treatment is determined by the doctor, taking into account the characteristics of the course of the disease and the results of laboratory tests. nine0003
Respiratory infection
If we talk about the infectious origin of itching in the nose, it is most pronounced at the initial stage of a viral infection. The introduction of the virus into the cells of the mucous epithelium causes an immune system reaction, which is manifested by edema and increased secretion. The result of inflammation of the mucosa will be itching, sneezing, runny nose. After 1-2 days, the discomfort in the nose usually goes away.
The introduction of the virus into the cells of the mucous epithelium causes an immune system reaction, which is manifested by edema and increased secretion. The result of inflammation of the mucosa will be itching, sneezing, runny nose. After 1-2 days, the discomfort in the nose usually goes away.
Concomitant symptoms:
- sore throat and sore throat, hyperemia of the pharynx; nine0016
- possible cough;
- general malaise;
- temperature is normal or subfebrile.
For bacterial rhinitis, itching in the nose is less characteristic, especially since this kind of inflammation most often develops on the basis of the destruction of the nasal epithelium by a viral agent. An increase in temperature, symptoms of intoxication, problems with nasal breathing come to the fore.
At the first sign of a viral infection, flush the nose with saline. Complex preparations based on Paracetamol, Ibuprofen will help reduce the temperature and alleviate the general condition. At the initial stage of viral rhinitis, in the absence of fever, it is advisable to resort to warming procedures (blue lamp, dry heat, paraffin applications). nine0003
At the initial stage of viral rhinitis, in the absence of fever, it is advisable to resort to warming procedures (blue lamp, dry heat, paraffin applications). nine0003
In the treatment of bacterial rhinitis, antimicrobial drops and sprays, nasal irrigation with salt solutions, antiseptics, herbal decoctions are used. The choice of the main drug of systemic action is best left to the doctor.
Dry polluted air
Characteristics of the air environment have a significant impact on the condition of the mucous membranes. Dryness, high temperature, high concentration of dust in the air, chemical agents, including occupational hazards, contribute to the drying of the mucosa and disruption of the protective functions of the epithelium. The initial hypersecretion is eventually replaced by dryness of the mucosa up to the formation of small ulcers. As a result, there is itching and burning in the nose. nine0003
Regular rinsing of the nose with an isotonic solution of NaCl, lubrication of the mucous membranes with sea buckthorn, peach and similar oils will help restore the mucous membrane.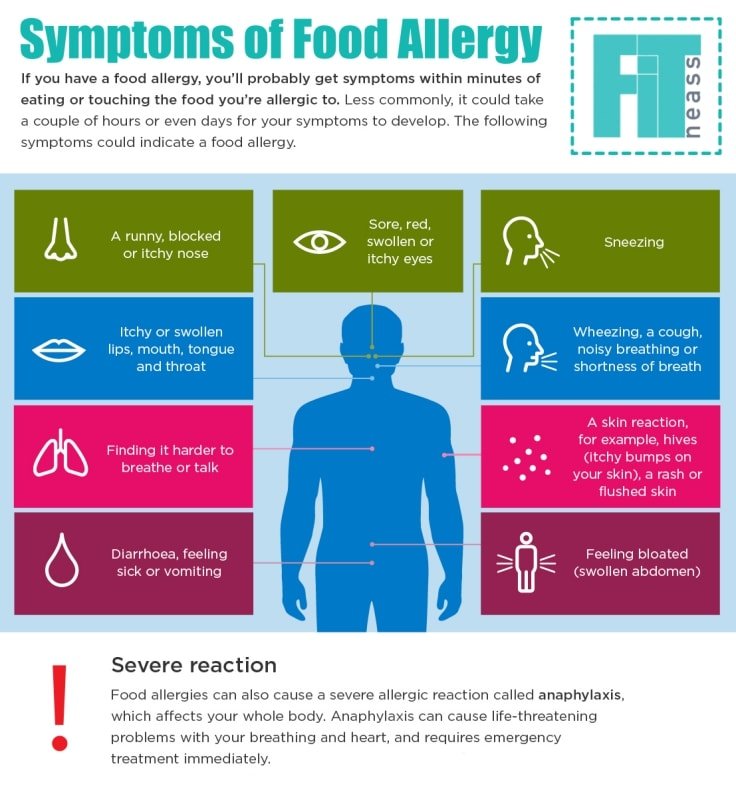 Pinasol drops, which include eucalyptus extract and an oil solution of vitamin A, have a good regenerating effect. It is necessary to stop smoking, eat right, periodically take vitamin complexes, including vitamins A, E and group B.
Pinasol drops, which include eucalyptus extract and an oil solution of vitamin A, have a good regenerating effect. It is necessary to stop smoking, eat right, periodically take vitamin complexes, including vitamins A, E and group B.
not less than 60%, carry out regular wet cleaning, airing, get rid of materials and objects on which dust is fixed. nine0003
Other factors
Itching in the nose is sometimes due to trauma - mechanical, thermal or chemical. Minor damage to the mucosa can sore and itch, they must be treated with antiseptic solutions. If the nose itches due to the ingestion of a foreign body, it is important to remove it as quickly as possible. In order not to aggravate the situation with your own attempts, it is better to contact a specialist.
Thermal damage to the inner wall of the nose will require restorative therapy as described above. If chemicals enter the nose, it is necessary to rinse the nose with a large amount of liquid, and the acid burn is neutralized with a solution of soda, and with an alkaline one, a little vinegar or citric acid is added to the water. Further assistance, if necessary, is provided in a medical facility. nine0003
Further assistance, if necessary, is provided in a medical facility. nine0003
A serious problem is atrophic processes arising from prolonged use of vasoconstrictor sprays that form persistent angiospasm. As a result, the mucous membrane is overdried, thinned and prone to the slightest irritation, which explains the causes of itching in the nose with medical rhinitis. In this case, in addition to restorative procedures at home, qualified assistance will be required.
Itchy sensations inside the nose due to an infiltrate or boil, which, despite the treatment with antiseptics, do not always undergo spontaneous regression. Antibiotic therapy or minor surgery may be required. nine0003
Preparations Aqualor
Washing the nose with saline solutions is the basic procedure for lesions of the nasal mucosa of any etiology. The composition for irrigation can be prepared independently or you can use ready-made Aqualor products. These are sterile isotonic and hypertonic solutions of sea water enclosed in spray bottles.
If itching in the nose is provoked by swelling and hypersecretion of mucus, the saturated salt component of Aqualor Forte will help remove excess fluid from the mucous membrane and provide an antiseptic effect. In addition, due to the active circulation of fluid from the nasal cavity, bacteria, viruses, and allergens are washed out. nine0003
In case of degenerative processes in the mucosa caused by dry air, bad habits or occupational hazards, regular irrigation of the nasal cavity with isotonic solutions of Aqualor Baby, Soft or norms is useful. They promote hydration and regeneration of the epithelium, reduce the viscosity of mucus, increase the resistance of the nasal wall to microbes and toxic factors.
We treat itching in the nose with effective methods, an individual approach
When a person develops itching in the nose , this causes a lot of discomfort. Inside the nose, as if something tickles, burns and itches. Also, reddening of the skin of the wings of the nose is often observed, mucus flows from the nostrils, and breathing becomes difficult. In addition to discomfort, itching can be dangerous. After all, he is a consequence of serious pathologies that can lead to serious complications.
In addition to discomfort, itching can be dangerous. After all, he is a consequence of serious pathologies that can lead to serious complications.
Why does it itch in the nose
When there is itching in the nose, 9 reasons0082 may be associated with allergic reactions, infection and other factors.
Allergy
When an allergen comes into contact with the nasal mucosa, it causes irritation. As a result, there is swelling, itching in the nose, copious secretion of mucus. It also often makes breathing difficult. In such cases, it is necessary to take the necessary drugs as soon as possible in order to relieve an allergic attack.
Inflammatory diseases
Itching may be a sign infectious inflammation in nasal cavity . Common causes are rhinitis, nasal mycosis, and sycosis of the nasal vestibule. In case of an infectious disease , it is important to consult a doctor in time to prevent the spread of the inflammatory process.
Other reasons
When a person itches in the nose, the reasons for may be as follows:
- mechanical injuries ;
- mucosal burns; nine0016
- dry polluted air;
- inhalation of vapors from caustic substances;
- abuse of cigarettes.
What should I do if my nose is itchy?
The best solution is to see an ENT doctor. He will diagnose and determine the cause of the problem, then select the appropriate therapy. Our doctors are often asked how to get rid of itchy nose at home . We want to immediately warn that self-medication is not only useless, but also dangerous. Diseases that cause this symptom, are capable of lead to severe complications. Therefore, they should be treated only under medical supervision.
Contraindications for itchy nose
If you have itchy nose is not recommended:
- ignore the problem - itching will not go away on its own, but will only intensify;
- use vasoconstrictor drops - they may aggravate the problem;
- gargle with saline solution - salt will cause dehydration and more itching; nine0159 to be treated with folk methods - they do not give a result and can provoke complications.
How to cure an itchy nose
If you are concerned about itchy nose, treatment is available at our ENT Center for children and adults. Our doctors will conduct a comprehensive diagnosis and carefully analyze symptoms . They will select a therapy regimen aimed at treating the underlying disease. Our center uses modern medical protocols and an individual approach to each patient. Treatment will depend on the nature of the itch, the diagnosis, and your general condition. For more details, sign up! nine0003
What itching can cause
Itchy nose is a manifestation of the body's defense responses to allergens, pollution, infections, etc. And it is important to eliminate the irritant that causes it as soon as possible. Otherwise, the underlying pathology will progress. For example, with allergic itching, attacks of bronchial asthma can reach. And inflammatory diseases of the nasal cavity spread to other organs and systems.