Waking up with swollen fingers
Over 15 Potential Causes, and When to See a Doctor
Swollen fingers can be an alarming symptom, especially if they’re accompanied by other symptoms such as redness and pain.
A wide variety of underlying conditions can cause your fingers to swell, and many of these conditions aren’t serious. However, when paired with other new or developing symptoms, swollen fingers may indicate something more serious.
In this article, we explore some of the common causes of swollen fingers and discuss when swelling in your fingers might be a cause for concern.
Water retention, sometimes referred to as fluid retention or edema, is one of the most common causes of swollen fingers. There are multiple causes of water retention, from diet to underlying health conditions.
When the body holds onto excess water, it can lead to swollen tissues in the extremities, especially in the fingers. Some other symptoms that may accompany water retention include bloating and puffiness.
Treatment for fluid retention often involves addressing the underlying cause. If you’re experiencing frequent or chronic fluid retention that’s causing your fingers to swell, consider speaking with your doctor to see if there’s an underlying cause.
Fluid retention caused by diet
Eating a diet high in salt can cause the tissues to retain extra water, leading to fluid retention in the fingers, hands, and other areas of the body.
Lowering sodium intake is one of the most common treatments for conditions that cause water retention. In fact, researchers explain that in some cases, sodium restriction and elevation of the extremities is the best treatment option.
Fluid retention from a blockage: lymphedema
Lymphedema is a type of fluid retention that results from a blockage in the lymphatic system. When the lymph nodes cannot circulate lymph fluid properly, this fluid builds up in the extremities.
Lymphedema commonly causes swollen fingers, hands, toes, and feet. Other symptoms of this condition may include:
- discoloration of the skin
- changes in the skin
- blisters and fluid leakage
Treatment of lymphedema includes compression therapy, daily exercise, and lymphatic drainage massage. In extreme cases when the lymphedema is severe, surgery may be necessary.
In extreme cases when the lymphedema is severe, surgery may be necessary.
Fluid retention from an allergic reaction: angioedema
Angioedema is another type of fluid retention that happens when fluid accumulates beneath the skin. Commonly caused by an allergic reaction, angioedema is often accompanied by the presence of large hives.
Although angioedema tends to appear in the face, head, and neck area, it can also cause swelling in the fingers. Other symptoms may include:
- a red rash
- local or body-wide swelling
Antihistamines and steroids are usually the first line of treatment for angioedema, as well as avoiding any triggers.
During a workout, such as running, hiking, or other forms of intense exercise, your body works hard to pump blood to your heart, lungs, and muscles. This directs blood flow away from the blood vessels in the hands, causing them to widen and the fingers to swell.
Swollen fingers after a workout are generally no cause for concern. However, you can reduce this post-exercise symptom by getting the hands and arms moving and making sure that you’re staying hydrated.
However, you can reduce this post-exercise symptom by getting the hands and arms moving and making sure that you’re staying hydrated.
Another potential reason for swollen fingers during and after working out or spending time outside in hot weather is increased body heat. In fact, exposure to heat, whether internal or external, can cause something called heat edema.
Heat edema commonly causes swelling in the extremities, especially in the fingers, hands, toes, and feet. While it’s generally not dangerous, it can indicate an imbalance in fluids and electrolytes. In some cases, it can also be linked to another underlying condition.
Luckily, you can reduce heat edema by keeping hydrated and cooling your body temperature back down as soon as possible.
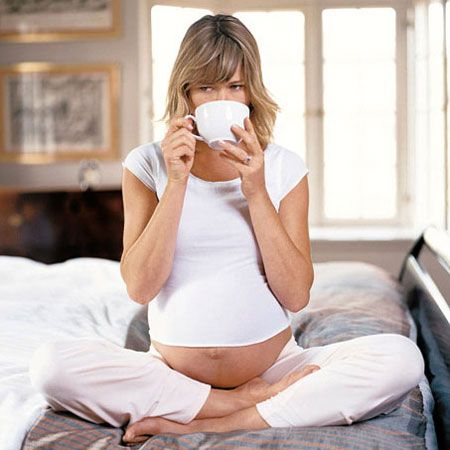
Hormonal changes, especially during menstruation and pregnancy, can cause symptoms such as bloating, swelling, mood changes, and more. These symptoms often occur due to a shift in hormones like estrogen and progesterone.
Swelling of the hands and fingers is a common symptom of premenstrual syndrome (PMS), and often appears during pregnancy, as well. Other symptoms of PMS may include:
- abdominal bloating and pain
- tender breasts
- gastrointestinal changes
- nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea
- fatigue
- headaches
- trouble sleeping
- mood changes
Treatment for PMS generally involves pain medications to help reduce any pain or tenderness. Getting regular exercise, eating a balanced diet, and practicing stress reduction techniques can also reduce PMS symptoms.
It is also common to notice swelling in the extremities, including in the fingers and toes, during late pregnancy.
Another potential cause of swollen fingers during pregnancy is a condition called preeclampsia. Preeclampsia often appears in late pregnancy and is characterized by the following symptoms:
- frequent, persistent headaches
- abnormally swollen face or hands
- vision changes
- weight gain
- abdominal pain
Early treatment for preeclampsia is crucial in ensuring a safe pregnancy and delivery. Treatment may include medications, frequent monitoring, or in some cases, early delivery.
Treatment may include medications, frequent monitoring, or in some cases, early delivery.
Swelling can sometimes occur in the hands and fingers when you wake up in the morning. While this can be caused by another underlying condition, such as arthritis, it can be made worse by certain sleeping positions.
If you’ve noticed that your fingers are frequently swelling in the morning, try these sleeping positions to keep the arms and hands elevated:
- Lying on your back. Use pillows under each arm to elevate your hands. You can even use additional, smaller pillows to raise your hands even further.
- Lying on your side. Use a pillow in front of you to elevate your top arm.
When we injure ourselves, the body produces an inflammatory response at the site of the injury. This inflammation is often indicated by swelling, redness, pain, and other symptoms.
Whether mild or serious, a hand injury can lead to swelling in the fingers, hand, and wrist. Other symptoms of injury and inflammation in the fingers might include:
Other symptoms of injury and inflammation in the fingers might include:
- tenderness
- bruising
- pain, especially when moving the fingers
- numbness or tingling
- visible breaks in the skin or bones
If you believe your swollen fingers are due to an injury, and you’re also experiencing the symptoms above, you should see a doctor immediately for medical treatment.
Similar to an injury, the inflammatory response is a necessary part of the healing process when an infection is present. Infections can cause a wide variety of symptoms, depending on the type and severity of the infection.
Infections of the arm and hand can cause swollen fingers, as well as infections in the joints of the fingers. Other signs and symptoms of an infection might include:
- a wound that’s having trouble healing
- pain
- tenderness
- fever
- fatigue
- swollen lymph nodes
- nausea or vomiting
An infection of the fingers, hand, or any other body part can be serious and require medical attention right away. Treatment may involve medications but ultimately depends on the infection.
Treatment may involve medications but ultimately depends on the infection.
Carpal tunnel syndrome occurs when the median nerve that runs through the center of the hand becomes compressed. This nerve affects feeling in the thumb, index, middle, and ring fingers.
If you develop carpal tunnel syndrome, you may notice the following symptoms in your hand and wrist:
- numbness
- tingling or pins and needles
- pain
- burning
- muscle weakness
Swollen fingers aren’t necessarily a defining symptom of carpal tunnel syndrome. However, according to the National Institute of Health (NIH), some people have reported feeling like their fingers are swollen.
Arthritis is an inflammatory condition that is characterized by pain, swelling, and stiffness in the joints. The two most common forms of arthritis include osteoarthritis (OA) and rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
Arthritis is commonly found in the joints of the hands, which can cause significant swelling in the fingers. Other symptoms of arthritis may include:
Other symptoms of arthritis may include:
- joint pain
- joint stiffness
- decreased range of motion
- skin redness
- fatigue
- loss of appetite
- fever
Treatment of arthritis can include anti-inflammatory medications, physical therapy, and, in some cases, surgery. Eating a diet high in anti-inflammatory foods can be helpful in keeping inflammation down.
One study also found that arthritis gloves can help apply pressure to the finger joints to reduce pain, swelling, and discomfort.
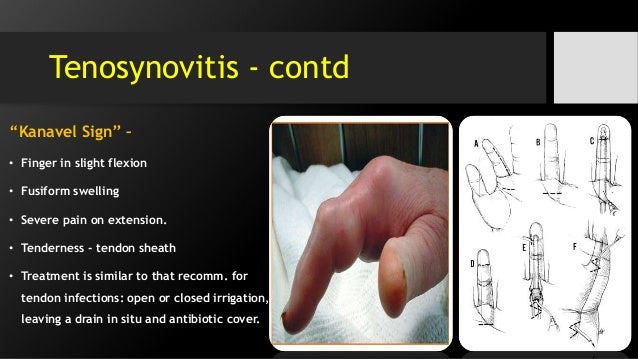
Tendonitis is an inflammatory condition that happens when the tendons become inflamed, leading to swelling, pain, and tenderness. Tendonitis commonly affects the tendons of the shoulders, arms, and legs.
There are three types of tendinitis that can cause swelling in the fingers:
- De Quervain’s tenosynovitis
- trigger finger
- trigger thumb
These types of tendinitis specifically affect the tendons in the fingers.
One of the initial interventions for reducing the pain and swelling associated with tendinitis is cold therapy. Applying ice to the swollen fingers can help to reduce blood flow to the area and reduce pain.
More serious cases of tendinitis usually require medical treatment.
Bursitis is another inflammatory condition. It’s caused by inflammation of the fluid-filled sacs that surround the joints. Bursitis tends to affect the larger joints’ bursae, such as those in the legs, arms, or hip.
If the bursae of the fingers become inflamed, it can cause swollen finger joints. Other symptoms of bursitis might include:
- pain
- redness
- thick bursae
Cold therapy is also helpful in reducing the inflammation and pain from bursitis. Physical therapy and injectable medications may also be used for more chronic cases. In some cases, surgery may be used to drain the inflamed bursae.
Gout is a condition that occurs when high levels of uric acid build up in the body and form crystals in the joints. Normally, the body excretes uric acid in the urine, but decreased kidney function can increase uric acid levels and trigger gout.
Normally, the body excretes uric acid in the urine, but decreased kidney function can increase uric acid levels and trigger gout.
Although gout commonly affects the feet, it can also cause swelling and pain in the joints of the fingers. Other symptoms of a gout attack may include:
- extreme pain
- redness and warmth in the skin around the joint
- hard lumps in the joint
Gout generally requires early intervention to prevent it from spreading or becoming chronic. Medications that help reduce pain and lower uric acid levels are often prescribed first.
A review published in 2017 also found that weight reduction, dietary modifications, and decreased alcohol intake can also reduce the frequency and severity of gout attacks.
Sickle cell disease, or sickle cell anemia, is a rare genetic condition that affects red blood cells’ function. This disease causes “sickle” shaped red blood cells, which have trouble circulating properly around the body.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), one of the first symptoms of sickle cell disease is hand-foot syndrome, which can cause swelling in the fingers. Other symptoms of sickle cell anemia may include:
- fatigue
- irritability
- pain
- jaundice
- frequent infections
Sickle cell disease requires various types of treatment, depending on the severity and progression. However, an increase in fluids may help to at least decrease the swelling in the fingers.
Systemic scleroderma is an autoimmune condition that’s commonly characterized by changes in the skin. It can also cause changes in the connective tissues of the body, as well as the organs.
One of the initial symptoms of scleroderma is swelling of the hands and fingers, especially in the morning after waking up. Other symptoms of scleroderma may include:
- patches of thick, shiny skin
- hair loss
- joint pain
- shortness of breath
- gastrointestinal symptoms
Treatment for finger swelling associated with scleroderma includes frequently exercising the fingers and toes, sometimes with the help of an occupational therapist. Anti-inflammatory medications can also help more severe cases.
In some situations, swollen fingers can appear as a rare symptom in a few conditions.
- Diabetes mellitus. Much of the research on diabetes focuses on symptoms of diabetes in the feet. However, one report from 2012 mentions a condition called tropical diabetic hand syndrome, which can cause swelling of the fingers. In this report, two individuals were reported to have swollen fingers resulting from poorly controlled diabetes.
- Tuberculosis. There are multiple case reports describing swollen fingers as a rare symptom of tuberculosis. In one case study, a 25-year-old man diagnosed with tuberculosis presented with a swollen little finger and a history of frequent chest infections. In another case report, another 46-year-old man diagnosed with tuberculosis also reported having a swollen little finger.
- Sarcoidosis. According to the literature, the fingers’ swelling may be a rare symptom of an inflammatory condition called sarcoidosis.
In a case study from 2015, an older male with swelling of the middle finger was discovered to have a rare type of this condition called sarcoid tenosynovitis.
- Syphilis. If not treated early, syphilis can progress to a system-wide infection that affects various parts of the body, including the fingers. In 2016, a case study was published that described swelling and pain of the fingers in a 52-year-old male with untreated syphilis.
As you can see above, there are many health conditions that can cause swollen fingers. Most of these reasons, such as heat, exercise, or even hormones, are rarely dangerous. For these types of conditions, simple interventions can help with any swelling or discomfort you might feel in your fingers.
However, if you have chronic swollen fingers that are accompanied by other symptoms, it’s best to visit a doctor. They can help determine if there’s an underlying condition that needs to be addressed.
Over 15 Potential Causes, and When to See a Doctor
Swollen fingers can be an alarming symptom, especially if they’re accompanied by other symptoms such as redness and pain.
A wide variety of underlying conditions can cause your fingers to swell, and many of these conditions aren’t serious. However, when paired with other new or developing symptoms, swollen fingers may indicate something more serious.
In this article, we explore some of the common causes of swollen fingers and discuss when swelling in your fingers might be a cause for concern.
Water retention, sometimes referred to as fluid retention or edema, is one of the most common causes of swollen fingers. There are multiple causes of water retention, from diet to underlying health conditions.
When the body holds onto excess water, it can lead to swollen tissues in the extremities, especially in the fingers. Some other symptoms that may accompany water retention include bloating and puffiness.
Treatment for fluid retention often involves addressing the underlying cause. If you’re experiencing frequent or chronic fluid retention that’s causing your fingers to swell, consider speaking with your doctor to see if there’s an underlying cause.
Fluid retention caused by diet
Eating a diet high in salt can cause the tissues to retain extra water, leading to fluid retention in the fingers, hands, and other areas of the body.
Lowering sodium intake is one of the most common treatments for conditions that cause water retention. In fact, researchers explain that in some cases, sodium restriction and elevation of the extremities is the best treatment option.
Fluid retention from a blockage: lymphedema
Lymphedema is a type of fluid retention that results from a blockage in the lymphatic system. When the lymph nodes cannot circulate lymph fluid properly, this fluid builds up in the extremities.
Lymphedema commonly causes swollen fingers, hands, toes, and feet. Other symptoms of this condition may include:
- discoloration of the skin
- changes in the skin
- blisters and fluid leakage
Treatment of lymphedema includes compression therapy, daily exercise, and lymphatic drainage massage. In extreme cases when the lymphedema is severe, surgery may be necessary.
In extreme cases when the lymphedema is severe, surgery may be necessary.
Fluid retention from an allergic reaction: angioedema
Angioedema is another type of fluid retention that happens when fluid accumulates beneath the skin. Commonly caused by an allergic reaction, angioedema is often accompanied by the presence of large hives.
Although angioedema tends to appear in the face, head, and neck area, it can also cause swelling in the fingers. Other symptoms may include:
- a red rash
- local or body-wide swelling
Antihistamines and steroids are usually the first line of treatment for angioedema, as well as avoiding any triggers.
During a workout, such as running, hiking, or other forms of intense exercise, your body works hard to pump blood to your heart, lungs, and muscles. This directs blood flow away from the blood vessels in the hands, causing them to widen and the fingers to swell.
Swollen fingers after a workout are generally no cause for concern. However, you can reduce this post-exercise symptom by getting the hands and arms moving and making sure that you’re staying hydrated.
However, you can reduce this post-exercise symptom by getting the hands and arms moving and making sure that you’re staying hydrated.
Another potential reason for swollen fingers during and after working out or spending time outside in hot weather is increased body heat. In fact, exposure to heat, whether internal or external, can cause something called heat edema.
Heat edema commonly causes swelling in the extremities, especially in the fingers, hands, toes, and feet. While it’s generally not dangerous, it can indicate an imbalance in fluids and electrolytes. In some cases, it can also be linked to another underlying condition.
Luckily, you can reduce heat edema by keeping hydrated and cooling your body temperature back down as soon as possible.
Hormonal changes, especially during menstruation and pregnancy, can cause symptoms such as bloating, swelling, mood changes, and more. These symptoms often occur due to a shift in hormones like estrogen and progesterone.
Swelling of the hands and fingers is a common symptom of premenstrual syndrome (PMS), and often appears during pregnancy, as well. Other symptoms of PMS may include:
- abdominal bloating and pain
- tender breasts
- gastrointestinal changes
- nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea
- fatigue
- headaches
- trouble sleeping
- mood changes
Treatment for PMS generally involves pain medications to help reduce any pain or tenderness. Getting regular exercise, eating a balanced diet, and practicing stress reduction techniques can also reduce PMS symptoms.
It is also common to notice swelling in the extremities, including in the fingers and toes, during late pregnancy.
Another potential cause of swollen fingers during pregnancy is a condition called preeclampsia. Preeclampsia often appears in late pregnancy and is characterized by the following symptoms:
- frequent, persistent headaches
- abnormally swollen face or hands
- vision changes
- weight gain
- abdominal pain
Early treatment for preeclampsia is crucial in ensuring a safe pregnancy and delivery. Treatment may include medications, frequent monitoring, or in some cases, early delivery.
Treatment may include medications, frequent monitoring, or in some cases, early delivery.
Swelling can sometimes occur in the hands and fingers when you wake up in the morning. While this can be caused by another underlying condition, such as arthritis, it can be made worse by certain sleeping positions.
If you’ve noticed that your fingers are frequently swelling in the morning, try these sleeping positions to keep the arms and hands elevated:
- Lying on your back. Use pillows under each arm to elevate your hands. You can even use additional, smaller pillows to raise your hands even further.
- Lying on your side. Use a pillow in front of you to elevate your top arm.
When we injure ourselves, the body produces an inflammatory response at the site of the injury. This inflammation is often indicated by swelling, redness, pain, and other symptoms.
Whether mild or serious, a hand injury can lead to swelling in the fingers, hand, and wrist. Other symptoms of injury and inflammation in the fingers might include:
Other symptoms of injury and inflammation in the fingers might include:
- tenderness
- bruising
- pain, especially when moving the fingers
- numbness or tingling
- visible breaks in the skin or bones
If you believe your swollen fingers are due to an injury, and you’re also experiencing the symptoms above, you should see a doctor immediately for medical treatment.
Similar to an injury, the inflammatory response is a necessary part of the healing process when an infection is present. Infections can cause a wide variety of symptoms, depending on the type and severity of the infection.
Infections of the arm and hand can cause swollen fingers, as well as infections in the joints of the fingers. Other signs and symptoms of an infection might include:
- a wound that’s having trouble healing
- pain
- tenderness
- fever
- fatigue
- swollen lymph nodes
- nausea or vomiting
An infection of the fingers, hand, or any other body part can be serious and require medical attention right away. Treatment may involve medications but ultimately depends on the infection.
Treatment may involve medications but ultimately depends on the infection.
Carpal tunnel syndrome occurs when the median nerve that runs through the center of the hand becomes compressed. This nerve affects feeling in the thumb, index, middle, and ring fingers.
If you develop carpal tunnel syndrome, you may notice the following symptoms in your hand and wrist:
- numbness
- tingling or pins and needles
- pain
- burning
- muscle weakness
Swollen fingers aren’t necessarily a defining symptom of carpal tunnel syndrome. However, according to the National Institute of Health (NIH), some people have reported feeling like their fingers are swollen.
Arthritis is an inflammatory condition that is characterized by pain, swelling, and stiffness in the joints. The two most common forms of arthritis include osteoarthritis (OA) and rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
Arthritis is commonly found in the joints of the hands, which can cause significant swelling in the fingers. Other symptoms of arthritis may include:
Other symptoms of arthritis may include:
- joint pain
- joint stiffness
- decreased range of motion
- skin redness
- fatigue
- loss of appetite
- fever
Treatment of arthritis can include anti-inflammatory medications, physical therapy, and, in some cases, surgery. Eating a diet high in anti-inflammatory foods can be helpful in keeping inflammation down.
One study also found that arthritis gloves can help apply pressure to the finger joints to reduce pain, swelling, and discomfort.
Tendonitis is an inflammatory condition that happens when the tendons become inflamed, leading to swelling, pain, and tenderness. Tendonitis commonly affects the tendons of the shoulders, arms, and legs.
There are three types of tendinitis that can cause swelling in the fingers:
- De Quervain’s tenosynovitis
- trigger finger
- trigger thumb
These types of tendinitis specifically affect the tendons in the fingers.
One of the initial interventions for reducing the pain and swelling associated with tendinitis is cold therapy. Applying ice to the swollen fingers can help to reduce blood flow to the area and reduce pain.
More serious cases of tendinitis usually require medical treatment.
Bursitis is another inflammatory condition. It’s caused by inflammation of the fluid-filled sacs that surround the joints. Bursitis tends to affect the larger joints’ bursae, such as those in the legs, arms, or hip.
If the bursae of the fingers become inflamed, it can cause swollen finger joints. Other symptoms of bursitis might include:
- pain
- redness
- thick bursae
Cold therapy is also helpful in reducing the inflammation and pain from bursitis. Physical therapy and injectable medications may also be used for more chronic cases. In some cases, surgery may be used to drain the inflamed bursae.
Gout is a condition that occurs when high levels of uric acid build up in the body and form crystals in the joints. Normally, the body excretes uric acid in the urine, but decreased kidney function can increase uric acid levels and trigger gout.
Normally, the body excretes uric acid in the urine, but decreased kidney function can increase uric acid levels and trigger gout.
Although gout commonly affects the feet, it can also cause swelling and pain in the joints of the fingers. Other symptoms of a gout attack may include:
- extreme pain
- redness and warmth in the skin around the joint
- hard lumps in the joint
Gout generally requires early intervention to prevent it from spreading or becoming chronic. Medications that help reduce pain and lower uric acid levels are often prescribed first.
A review published in 2017 also found that weight reduction, dietary modifications, and decreased alcohol intake can also reduce the frequency and severity of gout attacks.
Sickle cell disease, or sickle cell anemia, is a rare genetic condition that affects red blood cells’ function. This disease causes “sickle” shaped red blood cells, which have trouble circulating properly around the body.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), one of the first symptoms of sickle cell disease is hand-foot syndrome, which can cause swelling in the fingers. Other symptoms of sickle cell anemia may include:
- fatigue
- irritability
- pain
- jaundice
- frequent infections
Sickle cell disease requires various types of treatment, depending on the severity and progression. However, an increase in fluids may help to at least decrease the swelling in the fingers.
Systemic scleroderma is an autoimmune condition that’s commonly characterized by changes in the skin. It can also cause changes in the connective tissues of the body, as well as the organs.
One of the initial symptoms of scleroderma is swelling of the hands and fingers, especially in the morning after waking up. Other symptoms of scleroderma may include:
- patches of thick, shiny skin
- hair loss
- joint pain
- shortness of breath
- gastrointestinal symptoms
Treatment for finger swelling associated with scleroderma includes frequently exercising the fingers and toes, sometimes with the help of an occupational therapist. Anti-inflammatory medications can also help more severe cases.
Anti-inflammatory medications can also help more severe cases.
In some situations, swollen fingers can appear as a rare symptom in a few conditions.
- Diabetes mellitus. Much of the research on diabetes focuses on symptoms of diabetes in the feet. However, one report from 2012 mentions a condition called tropical diabetic hand syndrome, which can cause swelling of the fingers. In this report, two individuals were reported to have swollen fingers resulting from poorly controlled diabetes.
- Tuberculosis. There are multiple case reports describing swollen fingers as a rare symptom of tuberculosis. In one case study, a 25-year-old man diagnosed with tuberculosis presented with a swollen little finger and a history of frequent chest infections. In another case report, another 46-year-old man diagnosed with tuberculosis also reported having a swollen little finger.
- Sarcoidosis. According to the literature, the fingers’ swelling may be a rare symptom of an inflammatory condition called sarcoidosis.
 In a case study from 2015, an older male with swelling of the middle finger was discovered to have a rare type of this condition called sarcoid tenosynovitis.
In a case study from 2015, an older male with swelling of the middle finger was discovered to have a rare type of this condition called sarcoid tenosynovitis. - Syphilis. If not treated early, syphilis can progress to a system-wide infection that affects various parts of the body, including the fingers. In 2016, a case study was published that described swelling and pain of the fingers in a 52-year-old male with untreated syphilis.
As you can see above, there are many health conditions that can cause swollen fingers. Most of these reasons, such as heat, exercise, or even hormones, are rarely dangerous. For these types of conditions, simple interventions can help with any swelling or discomfort you might feel in your fingers.
However, if you have chronic swollen fingers that are accompanied by other symptoms, it’s best to visit a doctor. They can help determine if there’s an underlying condition that needs to be addressed.
How to remove swelling from the eyes after tears.
 Effective help
Effective help Contents:
➦What are the main causes of puffy eyes and panda effect?
➦ Why do my eyes swell when I wake up?
➦Quick relief from puffiness under the eyes
➦Professional and drugstore products
➦Unable to remove puffiness? Hide her!
➦Does puffy eyes mean I have some kind of disease?
➦How to treat puffy eyes
➦The main thing is not to be discouraged, the puffiness will definitely pass!
Our sympathetic nervous system reacts quite quickly to excessive stress. In an effort to protect us from the pathogen and perform an emotional reset in response to any strong adrenaline rush, it irritates the tear ducts inside the eye. An irritated canal provokes a copious release of tears, as well as redness of the face and swelling. Gradually, the heart rate returns to normal, the level of adrenaline decreases, but the puffiness from the eyes does not go away so easily. It turns out that swelling is caused by excessive tension of the channel, and you yourself provoke it by trying to wipe your eyes from tears with your hands or any other means at hand.
What are the main causes of puffy eyes and panda effect?
Tears are not the main cause of puffy eyes, but they provoke an excessive accumulation of fluid in the tissues of the skin. Since the skin around the eyes is very thin, when they swell, they form swellings that become visually noticeable. But why does fluid accumulate at all, forming a swelling of the eye?
Swollen eyes usually result from a variety of factors, including:
✦ Fluid retention
✦ Allergic reaction in the form of hay fever
✦ Problems with nasal sinuses and runny nose
✦ dehydration
✦ Fatigue and lack of sleep
✦ stress
✦ A large number of tears
✦ ATTRICTION
✦ Inherited facial features
Unfortunately, many people suffer from puffiness around the eyes due to hereditary factors that are inherent in their face type. Swelling under the eyes can be the result of age-related changes in adipose tissue. It is usually located around the bony part of the orbit and protects the eyeball from damage. With age, it begins to move forward and fill the spaces under the eye. These changes can only be stopped surgically or by a cosmetologist using special injections.
With age, it begins to move forward and fill the spaces under the eye. These changes can only be stopped surgically or by a cosmetologist using special injections.
This process is almost inevitable, but at a certain age you can influence it with the help of cosmetics and procedures. It occurs due to tissue aging and thinning of the membranes that hold fatty deposits that accumulate on the upper and lower eyelids. As the membrane becomes thinner, the fat expands and moves forward. This causes puffy eyes, dark circles and bags under the eyes.
Why do my eyes swell when I wake up?
For some, this fact may be surprising, but during sleep we do not blink. Our eyes are tightly closed and under the eyelids there is a chaotic movement of the eyeball. Unfortunately, some people may develop puffy eyes after prolonged sleep. The process of blinking is very similar to walking or playing sports. When you are not moving, your limbs may swell, which causes significant discomfort. As soon as you begin to make movements, the fluid in the body accelerates and is distributed evenly throughout it, so the swelling goes away. A similar action occurs with the centuries.
As soon as you begin to make movements, the fluid in the body accelerates and is distributed evenly throughout it, so the swelling goes away. A similar action occurs with the centuries.
Being in a closed position during sleep and not moving the eyelids can potentially swell in some people who are prone to this problem. So you may wake up in the morning with unusually swollen eyelids. When you wake up and start blinking, some of the puffiness will gradually go away. Dark circles under the eyes can form due to stress or lack of sleep.
Quick relief for swelling under the eyes
There are too many reasons that cause us to cry, and to keep them in ourselves is not only harmful, but it also does not always work out. What to do if, after uncontrollable sobbing, you urgently need an important event? Or did you wake up in the morning with puffiness under your eyes, and two hours later you have to go to work and have an important meeting? There is an exit.
- One of the quickest and easiest remedies is washing with cold water.
 The contrast temperature will help reduce swelling quickly. For a more targeted effect, ice or something cold can be applied under the eyes.
The contrast temperature will help reduce swelling quickly. For a more targeted effect, ice or something cold can be applied under the eyes. - Take a couple of drops of rosemary oil, dilute it with olive oil, then gently apply the mixture on the eyelids and under the eyes. Hold for a couple of seconds, rinse off the remnants with a damp cotton pad. Rosemary is an excellent anti-inflammatory agent, and olive oil will further moisturize the skin.
- Milk "baths" are an excellent compress for puffiness. Swabs soaked in cold milk should be kept under the eyelids for 5-10 minutes.
- In summer, ordinary cucumber slices can be the first remedy for swollen eyelids. For a more pronounced effect, it can be ground into a kind of gruel.
Lightly tap or massage the area to stimulate blood flow
You can increase blood flow to the affected area by gently tapping or massaging around the eyes:
- Work the pressure points on the brows for a few seconds before moving your fingers from the inner corner of the eye to the outer.
 This helps drain the inflamed area.
This helps drain the inflamed area. - Then tap the sinuses with two fingers on each hand, starting on both sides of the nose and moving outward. You may even feel fluid movement in the area.
- You can also lightly massage the lymph nodes in your neck to improve fluid flow. Move down, away from your face, in a smooth motion and don't press too hard.
- Continue with general massage for about 3 minutes and repeat for several days if necessary.
Top eye puffiness products
More in Eye Care
Professional & Pharmacy Products
Some brands of professional cosmetics produce special eye creams, one of the effects of which is to relieve fatigue and eliminate puffiness. You can pick up such products in the Fitomarket "Face Care" section of the online store. Regular intake of vitamin E will help restore skin elasticity, smooth wrinkles and get rid of swelling in the eye area. In addition, you can try massage and various types of eye exercises. They will improve blood circulation and can speed up the process of eliminating edema.
In addition, you can try massage and various types of eye exercises. They will improve blood circulation and can speed up the process of eliminating edema.
Eye drops are another way to reduce puffiness in the eyelids. They can be used to relieve any symptoms, from dryness to replenish natural tearing. There are also vasoconstrictors that can help with the redness that invariably comes with crying or allergies. To avoid further irritation, try choosing preservative-free solutions containing fewer synthetic additives. Most formulas are not recommended for contact lens wearers, so read labels carefully and consider removing lenses before use.
If you happen to have witch hazel lying around in your first aid kit. Then you should know that this astringent is great for inflammation and redness. This is a good choice of natural ingredient to combat puffy eyes. For a quick result, apply witch hazel to a cotton pad and apply it to the eye area for 5-10 minutes.
Among professional skin care products, patches under the eyes are considered a panacea in this matter. Thanks to natural extracts of green tea, aloe juice or other additives, they improve blood microcirculation, relieve inflammation and puffiness. Be sure to make sure that the package with patches indicates the presence of a draining effect, which is responsible for removing swelling from the eyes.
Thanks to natural extracts of green tea, aloe juice or other additives, they improve blood microcirculation, relieve inflammation and puffiness. Be sure to make sure that the package with patches indicates the presence of a draining effect, which is responsible for removing swelling from the eyes.
Again, cooling the eye area soothes the skin, stimulates the lymphatic system and constricts the blood vessels. Try chilling your favorite face cream or eye patch before applying. Then the effect will be stronger, and you will feel a pleasant coolness during the procedure.
Can't get rid of puffiness? Hide her!
The skin under the eyes may swell or darken after crying. Possible consequences of a tantrum are also redness around the nose or other spots on the face. A good concealer will help mask these obvious signs and give you a fresh look through color correction.
Look for a green concealer that will successfully neutralize redness. Green is the opposite of red on the color wheel, causing the two colors to cancel each other out. You can apply the concealer to the affected areas and blend well with your fingers or a cosmetic blender.
You can apply the concealer to the affected areas and blend well with your fingers or a cosmetic blender.
Another distraction that can help hide puffiness is dark blue eyeliner. It has long been used to emphasize the whiteness of proteins. Narrowline is a technique that is similar to waterline tracking. It is sometimes referred to as "invisible eyeliner" because it mimics the natural dark area on the lash line.
You can also use pink eye shadow or blush. Pink color elsewhere on the face can reduce redness around the eyes and nose. To do this, try applying blush on your cheeks and bright lipstick on your lips. Apply blush to the cheek area after applying concealer and foundation.
Does puffy eyes mean I have some kind of disease?
If your eyelids have never been swollen before, and now you notice swelling that has arisen for no apparent reason, this may be a sign of a serious health problem. For example, patients with hypo- and hyperthyroidism may suffer from a general swelling of tissues and muscles. In addition, bulging eyes can signal a serious thyroid condition known as Graves' disease.
In addition, bulging eyes can signal a serious thyroid condition known as Graves' disease.
One of the symptoms of an allergy may be watery eyes, itching and swelling. Typically, such reactions occur on certain foods or chemicals. Allergies have a wide range of symptoms, including a runny nose, cough, and shortness of breath. During an allergic reaction, certain cells in the body release a chemical called histamine. Which can provoke an outflow of fluids from the blood vessels, which will lead to swelling of the surrounding tissues, including the appearance of bags under the eyes.
Puffy eyelids and dark circles under the eyes can occur if you have an eye infection such as conjunctivitis. In some cases, inflammation due to dry eye syndrome also causes swelling. Kidney failure and other systemic diseases can cause swelling throughout the body, including around the eyes.
How to treat puffy eyes
If your eyelids are painful or sensitive to the touch, the cause is most likely an infection, cyst, or stye. It is important to determine the cause of a swollen eyelid, as treatment options depend on what is causing it.
It is important to determine the cause of a swollen eyelid, as treatment options depend on what is causing it.
✅ Cyst
If your upper or lower eyelid is swollen, it could be a cyst or a chalazion. The chalazion usually swells in the middle part of the eyelid. These cysts may disappear within a few weeks and some will turn into a hard lump.
Treatment: for relief, press a damp, heated cloth, heating pad, or boiled egg against the eye. Heat helps with oil secretion and blockage of blood vessels and skin. You can do this four to five times a day. If the cyst persists, see your doctor.
✅ Barley
Styes are formed due to an infection at the base of the eyelid near the eyelashes. It can be internal or external, but often appears as a well-defined red bump. Once the pus comes out of the stye, your eye will usually get better.
Treatment: A warm compress can be used to facilitate and speed up healing. It usually goes away after a few weeks. Avoid wearing makeup during a stye as this can cause reinfection.
Avoid wearing makeup during a stye as this can cause reinfection.
✅Conjunctivitis
Pink eye is caused by a bacterial, viral or allergic infection that causes inflammation on the surface of the eye. It can start in one eye and spread to both. Often, pus or sticky deposits appear on the eyelashes and in the corners of the eyes.
Treatment: you can clean sticky and crusty eyelids with warm water and cotton. The eye may heal on its own without treatment. Avoid touching your eyes during this time and keep your pillowcases clean. Avoid eye makeup and contact lenses.
The main thing is not to lose heart, the puffiness will definitely pass!
These methods will help relieve the symptoms that occur after a prolonged tantrum, accompanied by sobbing. They can also help to recognize other causes of puffy eyes and distinguish between heavy tears and a serious condition. In addition to controlling the outward signs of a tantrum, it is important to understand that self-care and love are important during times of sadness or stress. Set aside time for yourself every day, even if it's just a few minutes.
Set aside time for yourself every day, even if it's just a few minutes.
Better yet, express your thoughts or simply relax with a close friend or family member. Another good option is a professional therapist. They can help you sort out your feelings and prescribe medication if needed. Just remember that you don't have to go through what you will face alone.
SM-Clinic cardiologist spoke about the causes of hand swelling in adults
Edema of the hands occurs quite often, and can be a manifestation of physiological changes or one of the symptoms of pathology. When should edema alert and where to address the problem?
ALENA PARETSKAYA
Pathophysiologist, immunologist, member
St. Petersburg Society of Pathophysiologists
ANDREY GRACHEV
Leading cardiologist of the holding
SM-Clinic, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Academician of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences
Swelling of the hand is a cause for concern if it occurs frequently or almost daily, is accompanied by additional symptoms, is aggravated or is not eliminated by simple methods.
What you need to know about hand swelling
- Why your hand is swollen
- How to relieve swelling
- Questions and answers
Why the hand swells in adults
Swelling of the arm or both at once may be physiological or be a sign of pathology. It may be localized or spread to surrounding tissues. With swelling, the limb increases in volume, discomfort, soreness, and inconvenience when performing precise finger movements may be felt. It is difficult to remove the rings from the fingers or the watch from the wrist.
Swelling in the right or left arm occurs when the blood or lymphatic vessels are compressed by items of clothing during sleep. Swelling of the fingers and hands, which is especially noticeable if you remove rings or watches, occurs after alcohol or excess salty foods, fluids at night.
Right hand
A small local edema, if the mobility of the limb is preserved, is possible with bruises. In the area of edema, there may be soreness, redness, bruises or abrasions may appear. If it is a hematoma, the edema will be more pronounced, a seal is determined under the skin, in the center of which fluctuation (fluid movement) is felt. Swelling is typical for sprains in the area of the carpal, elbow or shoulder joint, with torn ligaments or their rupture. Severe pain is characteristic, which increases with movement, if the ligaments are torn, it is almost impossible to move the hand.
In the area of edema, there may be soreness, redness, bruises or abrasions may appear. If it is a hematoma, the edema will be more pronounced, a seal is determined under the skin, in the center of which fluctuation (fluid movement) is felt. Swelling is typical for sprains in the area of the carpal, elbow or shoulder joint, with torn ligaments or their rupture. Severe pain is characteristic, which increases with movement, if the ligaments are torn, it is almost impossible to move the hand.
Edema is possible with fractures of bones, dislocations of joints. Then there is pain, limb deformity, complete impossibility of movement.
Edema may appear with frostbite of the fingers, burns, infectious processes in the area of the hand, forearm or shoulder.
Left hand
Swelling of the finger of the left hand (as well as the right one) is possible with panaritium - suppuration in the phalanx. If it is a deeper lesion, the edema passes to the hand. Carbuncles or boils on any part of the arm can also lead to swelling. In this case, cyanosis or a purple area with suppuration is visible in the center of the inflamed focus. Edema is possible with suppuration of wounds, erysipelas, purulent arthritis and osteomyelitis.
Carbuncles or boils on any part of the arm can also lead to swelling. In this case, cyanosis or a purple area with suppuration is visible in the center of the inflamed focus. Edema is possible with suppuration of wounds, erysipelas, purulent arthritis and osteomyelitis.
Joint damage in other forms of arthritis also leads to tissue swelling. With rheumatoid arthritis, the joints of both hands are symmetrically affected, with gout, the fingers swell, with psoriasis, the joints of the fingers and hand.
Edema is typical for joint damage - thrombosis. In addition to edema, a feeling of fullness, pain, thickening of tissues, discoloration of the skin, crawling, and a change in sensitivity are typical.
Morning
Lymphatic edema is possible after operations to remove the mammary gland, if the axillary lymph nodes were excised. Puffiness may increase or appear in the morning with malformations of the lymphatic capillaries, with post-burn scars, thrombophlebitis, lymphadenitis. Without treatment, swelling can become permanent.
Without treatment, swelling can become permanent.
Hand edema also occurs against the background of heart failure. In the morning they are minimal, intensify in the evening. In contrast, renal swelling of the hands is most pronounced in the morning and decreases or disappears during the day.
Pregnancy
Puffiness in the fingers or hands is due to hormonal changes, especially as the pregnancy progresses. In the first trimester, a slight swelling of the fingers is typical, which is almost not noticeable. By the third trimester, swelling can be pronounced, making it difficult to wear rings, watches, bracelets. Puffiness gradually disappears in the first days after childbirth.
However, pathological edema associated with hypertension, excess weight gain and the development of preeclampsia is also possible in pregnant women. Then the appearance of protein in the urine, a pronounced weight gain per week, severe swelling of the arms and legs, face, and body are typical.
How to relieve hand swelling in adults
At home or for first aid, you need to give your hand an elevated position.
If this is an injury, the hand should be immobilized with a bandage or splint, a cold compress should be applied to the affected area, and an anesthetic should be taken.
If these are diseases of the joints, it is necessary to use painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs locally and orally. If the swelling develops quickly, with severe pain and dysfunction of the hand, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Doctors can use two options for treating edema - conservative and surgical. It depends on the cause, the severity of the condition, and possible complications. In case of injuries, emergency care, bandages, anti-inflammatory drugs, anesthesia are indicated.
In vascular edema, antispasmodic, angioprotective and phlebotonic drugs are used.
Physiotherapy, gymnastics, massage or manual therapy are also prescribed.
If the injury is serious or severe lesions of blood vessels, bones, joints are detected, the edema is not eliminated, surgical interventions are used.
FAQ
Edema can be a short-term phenomenon and does not threaten anything. But sometimes they are symptoms of dangerous conditions. Andrey Grachev, a cardiologist, helped us figure out the problem.
Why is hand swelling dangerous?
Swelling is often a sign of a serious infection, cancer, heart or kidney problems. And if the swelling is persistent, then the disease has worsened or is rapidly progressing. Edema can be complicated by tissue malnutrition, skin inflammation, stretch marks, and discoloration.
When should I see a doctor for swollen hands?
In any situation when you notice swelling of the hands - in the morning, in the evening or during the day, you need a doctor's consultation and at least a minimal set of tests and examinations. Edema itself is a symptom of problems in the body, and you need to find out what caused it.
Edema itself is a symptom of problems in the body, and you need to find out what caused it.
Is it possible to remove swelling of the hands with folk remedies?
There are a number of diuretic decoctions and infusions, but it is extremely dangerous to use them on your own, not knowing what the causes of edema are. This can lead to a worsening of the situation, an electrolyte imbalance, a sharp decrease in pressure, dehydration and malaise.
In addition, various traditional medicines can cause allergies, worsen the condition, negatively affect the effects of the drugs taken and have a number of contraindications for taking. Folk remedies are not equal to the concept of "safe".
What if only one arm is swollen?
If one arm is swollen, see a surgeon or physician, depending on the suspected cause. At the time of the examination, it is worth disturbing the sore arm less, giving it an elevated position so that the liquid flows more easily, do not sleep on this side, do not press the arm to the body.