Vitamin for newborn
Vitamins for children - NHS
Vitamin supplements
The government recommends all children aged 6 months to 5 years are given vitamin supplements containing vitamins A, C and D every day.
Babies who are having more than 500ml (about a pint) of infant formula a day should not be given vitamin supplements. This is because formula is fortified with vitamins A, C and D and other nutrients.
Babies who are being breastfed should be given a daily vitamin D supplement from birth, whether or not you're taking a supplement containing vitamin D yourself.
Where you can get baby vitamin drops
Your health visitor can give you advice on vitamin drops and tell you where to get them.
You're entitled to free vitamin drops if you qualify for Healthy Start.
The Department of Health and Social Care only recommends vitamin supplements containing vitamins A, C and D.
But some supplements you can buy contain other vitamins or ingredients. Talk to a pharmacist about which supplement would be most suitable for your child.
Having too much of some vitamins can be harmful. Keep to the dose recommended on the label, and be careful not to give your child 2 supplements at the same time.
For example, do not give them cod liver oil and vitamin drops because cod liver oil also contains vitamins A and D. One supplement on its own is enough, as long as it contains the recommended dose of vitamin D.
Vitamin D
Vitamin D is only found in a few foods, such as oily fish and eggs. It's also added to some foods, such as fat spreads and breakfast cereals. But it’s difficult to get enough vitamin D from food alone.
But it’s difficult to get enough vitamin D from food alone.
The main source of vitamin D is summer sunlight on our skin. But it's important to keep your child's skin safe in the sun.
Children should not be out in the sun too long in hot weather. Remember to cover up or protect their skin before it turns red or burns.
Young children should still have vitamin drops, even if they get out in the sun.
The Department of Health and Social Care recommends:
- Babies from birth to 1 year of age who are being breastfed should be given a daily supplement containing 8.5 to 10 micrograms of vitamin D to make sure they get enough. This is whether or not you're taking a supplement containing vitamin D yourself.
- Babies fed infant formula should not be given a vitamin D supplement if they're having more than 500ml (about a pint) of infant formula a day, because infant formula is fortified with vitamin D and other nutrients.

- Children aged 1 to 4 years old should be given a daily supplement containing 10 micrograms of vitamin D.
Vitamin A
Vitamin A is important for babies and young children, and some may not be getting enough.
It's needed for a healthy immune system, can help their vision in dim light, and keeps skin healthy.
Good sources of vitamin A include:
- dairy products
- fortified fat spreads
- carrots, sweet potatoes, swede and mangoes
- dark green vegetables, such as spinach, cabbage and broccoli
Vitamin C
Vitamin C is important for your child's general health and immune system. It can also help their body absorb iron.
Good sources of vitamin C include:
- oranges
- kiwi fruit
- strawberries
- broccoli
- tomatoes
- peppers
A balanced diet for babies and young children
It's important for children to eat a wide variety of foods to make sure they're getting all the energy and nutrients they need to grow and develop properly.
Get more advice and information on a balanced diet for babies and young children:
- Your baby's first solid foods
- What to feed young children
- Young children and food: common questions
- Fussy eaters
Page last reviewed: 16 April 2021
Next review due: 16 April 2024
Supplements & Vitamins for Baby
RachelMS, RD, LDN, CSSD, CBS
Read time: 5 minutes
What to know about whether your baby needs extra vitaminsBreastmilk or formula provides your baby with most of the vitamins and minerals they need.1
Depending on the situation, possible supplements infants need include Vitamin K, Vitamin D, Vitamin B12, and iron.
During the first 6 months of life, your baby should exclusively be fed breastmilk and/or formula. Healthy full-term babies will likely get most of the vitamins and minerals they need from that breastmilk or formula.2,3
Healthy full-term babies will likely get most of the vitamins and minerals they need from that breastmilk or formula.2,3
As your baby begins eating solid foods, usually around 6 months, breastmilk and formula will continue to provide the majority of nutrients and calories.22,23 Adding a variety of fruits and vegetables, whole grains, and protein-dense foods will help your child get more of the nutrients they need. A multivitamin is usually not necessary for babies under 1 year old.1,3
Read more: Nutrient Needs and Feeding Tips for 6 to 12 Month Olds
When does my baby need extra vitamins?Some babies may need additional vitamins, such as:
Premature infants, born weighing less than 3.
 3 pounds, will likely need extra vitamins and minerals added directly to breastmilk or formula.4
3 pounds, will likely need extra vitamins and minerals added directly to breastmilk or formula.4Babies who are exclusively as well as partially breastfed are recommended to be given vitamin D and potentially iron.5,6
Babies born to mothers who follow a strict vegan diet may need a B12 supplement.9
Be sure to chat with your child’s pediatrician before starting any supplements.
Which vitamin supplements could a baby need?Vitamin KWhat does vitamin K do? Vitamin K is necessary to help with blood clotting.2,7
Who may need vitamin K? The American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) recommends that all babies receive a one-time vitamin K injection shortly after birth to reduce the risk of hemorrhagic disease. 11
11
What does vitamin D do? Vitamin D allows the body to absorb and retain calcium and phosphorus, both critical for building strong bones.27
What are symptoms of vitamin D deficiency? A vitamin D deficiency can lead to rickets, a bone-softening disease that still impacts children in the U.S., usually in the first two years of life.2,5
Who may need vitamin D? In many cases, breastmilk does not provide adequate vitamin D for baby.4,5 This is why the AAP and other health organizations recommend that all breastfed babies be supplemented with Vitamin D.6,8
Formula fed babies generally do not need additional vitamin D supplementation because formula has vitamin D already added. If your baby is drinking at least 32 ounces of formula per day, they are receiving adequate amounts of vitamin D.2,6
If your baby is drinking at least 32 ounces of formula per day, they are receiving adequate amounts of vitamin D.2,6
Read more: Why Vitamin D Matters for Babies, Tots and Mama
Vitamin B12What does vitamin B12 do? Vitamin B12 keeps the body’s nerve and blood cells healthy and helps make DNA, the genetic material in all cells.9 Vitamin B12 deficiency can cause a type of anemia called megaloblastic anemia that makes people tired and weak.10
What are symptoms of vitamin B12 deficiency? Signs and symptoms of vitamin B12 deficiency in infants include vomiting, lethargy, anemia, failure to thrive, hypotonia (low muscle tone), and developmental delay/regression.4,12 Breastfed infants may develop clinical signs of vitamin B12 deficiency before their mothers do. 4
4
Who may need vitamin B12? Breastfeeding people who may need vitamin B12 include: Vegans and some vegetarians, those who have had weight loss surgery, or people with malabsorption concerns.9 Taking B12 is often necessary for these groups to help make sure that both themselves and their babies are receiving adequate amounts.
Infant formulas must contain vitamin B12, so formula fed babies usually get enough of this nutrient.
If your family is vegan or there are other risk factors for low B12, discussing your family’s diet with a registered dietitian can help provide some insight on supplementation or food choices.13
Read more: Vegan Diet during Pregnancy, Breastfeeding, and for the Family
IronWhat does iron do? Iron plays an important role in the delivery of oxygen to tissues throughout the body.20 This mineral is also important for physical growth and brain development. 20
20
What are symptoms of iron deficiency? There are several levels of iron deficiency before iron deficiency anemia is diagnosed.20 Even mild and moderate deficiencies in babies and toddlers can cause symptoms such as shortness of breath, irritability, weakness, fatigue, and headaches.21
Who may need iron? Breastmilk is low in iron but most babies are born with sufficient reserves of iron while in the womb to protect them from anemia, at least until the age of 4-6 months.4 If you had poorly controlled gestational diabetes, or your baby was premature or smaller than 6 pounds at birth, your baby may not have gotten enough iron during pregnancy.4,14 There is also some research showing that delayed cord clamping at birth can help boost baby’s iron reserves. 5
5
Babies who are formula fed are recommended to be provided an iron-fortified formula to meet their needs.6
The AAP Committee on Nutrition recommends exclusively and partially breastfed infants receive 1 mg/kg/day of a liquid iron supplement starting at 4-6 months, continuing until iron-containing solid foods are introduced at about six months of age.6,16 However other major organizations, including the Academy of Breastfeeding Medicine as well as the United States Preventative Services Task Force, do not find the research on supplementing your baby compelling enough to recommend supplementation for breastfed babies.5,20
Speak with your baby’s doctor about iron supplementation and whether it’s right for you and your baby.18
Introduce iron-rich foods once your baby begins eating solids. When you begin to introduce your baby to solid food, choose foods that contain iron, like fortified cereals, meats, fish, beans, and vegetables every day.
When you begin to introduce your baby to solid food, choose foods that contain iron, like fortified cereals, meats, fish, beans, and vegetables every day.
Include vitamin C rich foods as well to help iron be absorbed better.25
If you are already supplementing your infant with iron when introducing iron-containing foods, chat with baby’s healthcare provider to see if the iron supplement should be stopped.4,5
Read more:
Why is Iron Important for my Baby and toddler?
What Should I Know about Iron Deficiency Anemia during Pregnancy?
If you have more questions about whether your baby could benefit from vitamins or other supplements, reach out to our team of registered dietitians and moms are available from Monday – Friday 8 am – 6 pm (ET). Chat now!
What to do to make sure baby is meeting their vitamin and mineral needsIf formula feeding, continue to feed your baby with iron-fortified formula through the first yearYour baby is receiving adequate iron and vitamin D in their formula therefore it’s important to continue feeding them infant formula through the first year of life. 6
6
If you are breastfeeding, chat with your infant’s healthcare provider about supplementing with iron and vitamin D. They’ll let you know if your little one needs a supplement, how much to give, and how long to supplement for.
Tip: One way to supplement your infant is to place the liquid supplement on your nipple before latching baby to feed. Chat with your child’s healthcare provider for more tips on how to give your baby the supplements they may need.
Understand that your preemie may have different needsIf your baby was born prematurely, they may need more iron than a term baby or need larger amounts of other nutrients.9 Speak with your baby’s doctor about your baby’s specific needs.
Do not introduce cow’s milk until after your baby’s first birthday
Babies who are fed cow’s milk (instead of breastmilk or iron-fortified formula) during the first year of life are more likely to develop iron-deficient anemia because the cow’s milk proteins can affect your child’s iron status. 15,24
15,24
Note that while cups of cow’s milk are not recommended before a year, it is safe for your little one to have the small amounts of milk used in baking and cooking. And as long as your child does not have a cow’s milk protein allergy or lactose intolerance, it is also safe for them to eat cheese and yogurt in the texture they can handle.26
Let's Chat!
We know parenting often means sleepless nights, stressful days, and countless questions and confusion, and we want to support you in your feeding journey and beyond.
Our Happy Baby Experts are a team of lactation consultants and registered dietitians certified in infant and maternal nutrition – and they’re all moms, too, which means they’ve been there and seen that. They’re here to help on our free, live chat platform Monday - Friday 8am - 6pm (ET).Chat Now!
Read more about the experts that help write our content!
For more on this topic, check out the following articles:
Meal Plan for 6 to 9 Month Old Baby
Why does Vitamin C Matter for Babies, Tots and Mama
Meeting Your Needs and Baby’s on a Vegetarian Diet
Does your Toddler need Vitamins or Supplements
Why does Vitamin B12 Matter for Babies, Tots, and Mama?
Sources
Vitamins for babies
Before taking vitamin D, be sure to consult a pediatrician, because. An overdose of vitamin D can lead to sad consequences. Vitamin D itself is a rather “uncommon” vitamin that is produced by the body when it interacts with sunlight. And it is very interesting that taking vitamin D by a child is useless if the child does not spend at least half an hour a day under diffused sunlight. In foods, this vitamin is quite rare: in fish and eggs. nine0003
An overdose of vitamin D can lead to sad consequences. Vitamin D itself is a rather “uncommon” vitamin that is produced by the body when it interacts with sunlight. And it is very interesting that taking vitamin D by a child is useless if the child does not spend at least half an hour a day under diffused sunlight. In foods, this vitamin is quite rare: in fish and eggs. nine0003
Now on the shelves of pharmacies you can find vitamins for children up to a year in the form of gels, drops, powders. Each mother herself can choose a more convenient form of vitamins for her child after consulting a competent pediatrician or immunologist.
The whole truth about immunity
Why do some kids get sick often, while others, who also attend kindergarten, clubs and schools, rarely? Children get sick due to a weakened immune system. There are several main signs of poor health:
- recurring (4-6 times a year) acute respiratory viral infections, often with complications;
- slow healing and difficult recovery of immunity after illness;
- the occurrence of fungal diseases, especially in the spring or after taking antibiotics;
- occurrence of allergic reactions.

Note that allergies can also occur in the general well-being of the child as a separate disease. The connection between weakened immunity and intolerance to any substances is said in cases where treatment is delayed. Then the weakened immune system becomes too sensitive and begins to destroy those cells that do not pose a danger to it. This is how allergies develop. nine0003
Weakening of the immune system is also evidenced by fatigue, decreased attention, drowsiness, irritability and bowel problems, diarrhea, bloating and pain often begin for no apparent reason.
How to strengthen the immunity of a child?
If the doctor has determined that the child's immunity is reduced, it is necessary to start improving health. From spring to mid-autumn, it is recommended to give more fruits, berries and vegetables, fresh juices: carrot, blackcurrant, cherry, grape, apple, orange, tomato and many others. You can cook infusions from wild rose. Onions and garlic are useful in moderation, as they protect the body from colds. nine0003
Summer is the easiest time to teach a child to harden. To do this, it is not necessary to douse them with cold water. Less stressful methods are now known, such as moving from a warm room to a cooler one.
Each child is recommended to develop a hardening program according to their state of health.
If the restoration of immunity falls on winter time, then vitamins should be given to children. It is important to choose a balanced complex that will fully compensate for the lack of nutrients in the body. The following vitamins are especially important for the health of babies:
- A (retinol) - helps with allergic reactions, improves the condition of the nervous system, relieves dry skin and improves vision;
- C (ascorbic acid) - protects against chronic forms of colds if you start taking the vitamin in a timely manner. Ascorbic acid increases the elasticity of blood vessels and slows down the aging of the body;
- E (tocopherols, tocotrienols) - fights cancer, microbes and viruses;
- B1 (thiamine) - prevents weakness of the nervous system, due to which the child has tearfulness, headache, irritability; nine0012
- D (ergocalciferol, cholecalciferol) - ensures normal blood clotting, heart function and the immune system; necessary for the formation of strong bones.

It is much more difficult to restore a child's immunity in winter than in summer. Children at this time are exposed to the action of viruses. Therefore, we will pay special attention to protecting the body during the cold season.
Vitamin D3 for children and newborns | Which vitamin D3 is better | Dosage (Daily Value) of Vitamin D3
Vitamin D3 is an important component for the healthy development of children. It helps to form strong bones and teeth, healthy nails and hair, and muscle tissue. In addition, it is involved in maintaining immunity.
At the same time, people living in central Russia and to the north are at risk of developing a shortage of this substance due to the small number of sunny days. Its deficiency is very dangerous for infants and toddlers of the first year of life, especially those born from October to March.
In what doses to give it to newborns and older babies, what forms and preparations exist, we will consider in this article. The recommendations are based on the National Program of the Ministry of Health, released in 2018 - "Vitamin D deficiency in children and adolescents of the Russian Federation: modern approaches to correction." nine0003
The recommendations are based on the National Program of the Ministry of Health, released in 2018 - "Vitamin D deficiency in children and adolescents of the Russian Federation: modern approaches to correction." nine0003
What is vitamin D3 for
It regulates the absorption of phosphorus and calcium in our body. Parents most often know that it is essential for bone growth. However, its benefit also lies in the following:
- regulates the timing of teething,
- is responsible for muscle growth,
- improves skin condition and reduces the likelihood of its diseases,
- is involved in tuning the immune and endocrine systems,
- reduces the risk of inflammation,
- reduces the likelihood of oncology and autoimmune conditions.
D or D3 - what's the difference
Vitamin D (calciferol) is a whole group of substances, but it is the D3 form that is produced by the body on its own and is the component that helps to absorb calcium and phosphorus. Therefore, speaking further about vitamin D, we will mean its form D3 or cholecalciferol. nine0003
Therefore, speaking further about vitamin D, we will mean its form D3 or cholecalciferol. nine0003
Vitamin D3 sources
The peculiarity of this substance is that our body receives it from two sources:
- Firstly, it is produced in our skin under the influence of ultraviolet rays. That is why it is so useful to walk on sunny days. It does not have to be under the scorching sun. In the shade of trees will have the same effect. Just 20 minutes of walking with an open face and palms is enough to provide yourself with cholecalciferol for several days. nine0012
- Secondly, the source of this substance is food. It is found in significant quantities in fish, caviar and eggs.
Reasons for shortages
When the intake of a vitamin from food or its production by the body is limited, its deficiency develops. Main reasons:
- Prolonged lack of sun exposure
- Putting to bed on a glassed-in balcony - ultraviolet does not penetrate through the glass.
 nine0012
nine0012 - Genetically poor ability to absorb cholecalciferol
- Vegetarian diet for nursing mothers
- Prematurity - the baby's body did not have time to get enough of the necessary substances. This process takes place during the last two months of pregnancy.
Deficiency symptoms
D3 deficiency in babies of the first year is fraught with the occurrence of rickets. In our country, the practice of making this diagnosis “by eye” is very common. In fact, rickets is a very rare disease. In developed countries, it occurs in 1 in 200,000 children. Diagnosis is based on x-ray and blood tests. nine0003
Possible symptoms of rickets:
- Softening and thinning of the skull bones
- Enlargement of frontal and parietal tubercles
- Late dentition with poor enamel
- Rachitic rosary - indurations on bones, on ribs, e.g.
- Decreased muscle tone or change in bone sensitivity
- Slow growth
These are just possible symptoms. You can not draw a conclusion only on their basis. The diagnosis is made only after an X-ray examination of the bones, analyzes of the content of phosphorus, calcium, vitamin D and some hormones. nine0003
You can not draw a conclusion only on their basis. The diagnosis is made only after an X-ray examination of the bones, analyzes of the content of phosphorus, calcium, vitamin D and some hormones. nine0003
Symptoms that are not symptoms of rickets:
- Excessive sweating
- Erased hair at the back of the head
- Anxiety
- Capriciousness
- Crooked legs
- Hypertonus
In children who are breastfed, rickets almost never occurs, because the baby receives the necessary dose of the substance with mother's milk. Here, it is much more important for a mother to monitor its amount in her body and take care of how to replace the lack of sun. nine0003
Formula-fed babies used to be at risk, but now in almost all mixtures of this substance there is a sufficient amount to prevent the development of the disease.
You should check with your pediatrician if you have any doubts that your baby is getting enough vitamin D.
Daily requirement and how to take
A child from one month to a year needs 1000 IU (international units) of vitamin D. A pediatrician can prescribe the drug from the first days of life. Healthy full-term newborns are prescribed 500 IU until they reach the age of one month. nine0053 The National Program of the Ministry of Health recommends the following dosages for healthy babies:
| Age | Prophylactic daily dose | Daily dose for residents of the European North of Russia |
| term newborn | 500 IU | 500 IU |
| 1 - 6 months | 1000 IU | nine0165 1000 IU|
| 6 to 12 months | 1000 IU | 1500 IU |
| 1 to 3 years | 1500 IU | 1500 IU |
| 3 to 18 years old | 1000 IU | 1500 IU |
Modern mixtures, as well as breast milk, contain vitamin D, which, however, is not enough to prevent deficiency among Russians. Therefore, the indicated dosages are prescribed for babies, regardless of the type of feeding. nine0003
Therefore, the indicated dosages are prescribed for babies, regardless of the type of feeding. nine0003
You can get acquainted with the recommended dosages for premature babies, children at risk and therapeutic dosages in the National Program.
Overdose symptoms
An overdose leads to a violation of the absorption of calcium and is the cause of allergic reactions. However, it is incorrect to talk about an allergy to cholecalciferol. Allergies are the consequences of its overabundance.
Other symptoms are increased nervous excitability and, as a result, sleep disturbance. nine0003
Taking prophylactic doses does not lead to an excess of vitamin D. In accordance with the National Program, the drug is recommended to be taken continuously, including the summer months.
Vitamin D oil or water based
Calciferol is a fat-soluble substance, therefore, special additives are used to dissolve it in water. You can find a list of them in the composition of excipients in the instructions for the drug.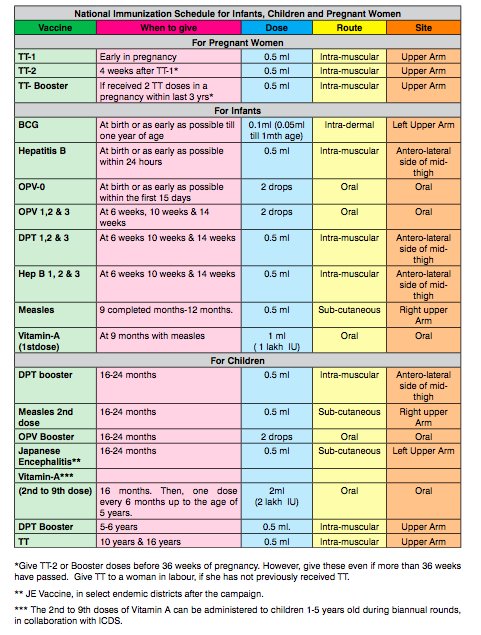 Stabilizers are also added to such preparations so that the solution retains its shape and preservatives, which most often is ethyl alcohol. Auxiliary components are contained in scanty doses, so you should not be afraid of this. Store the aqueous solution in the refrigerator. nine0003
Stabilizers are also added to such preparations so that the solution retains its shape and preservatives, which most often is ethyl alcohol. Auxiliary components are contained in scanty doses, so you should not be afraid of this. Store the aqueous solution in the refrigerator. nine0003
There are cases when only an aqueous solution is suitable for children. These are babies with diseases of the intestines and pancreas, which do not absorb fats well.
The oil solution contains only oil and cholecalciferol. In this case, oil acts as a natural preservative. Oil-based preparations are stored at room temperature.
A healthy, non-allergic child is given any option to prevent deficiency of this substance. In any case, the questions: which vitamin D is better - on a water or oil basis, how to give and up to what age, and what is the correct dosage, your pediatrician should answer. nine0003
Zinaida Rassadina
Pediatrician, experience - 14 years
Israeli children's vitamin D3
On our website you can buy an oil-based drug from two Israeli manufacturers.