Sti infections symptoms
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) - NHS
If you're worried because you think you've got an STI, go for a check-up at a sexual health clinic as soon as you can.
Do not have sex, including oral sex, without using a condom until you've had a check-up.
You can have an STI without knowing it and infect your partner during sex.
STI symptoms
The symptoms of an STI can include:
- an unusual discharge from the vagina, penis or anus
- pain when peeing
- lumps or skin growths around the genitals or bottom (anus)
- a rash
- unusual vaginal bleeding
- itchy genitals or anus
- blisters and sores around your genitals or anus
- warts around your genitals or anus
- warts in your mouth or throat, but this is very rare
Non-urgent advice: Go to a sexual health clinic if:
- you have symptoms of an STI
- a sexual partner has symptoms of an STI
- you're worried after having sex without a condom
- you're pregnant with symptoms of an STI
Many STIs have no symptoms at all, like HIV. The only way to know for sure is to get tested.
Find a sexual health clinic
Why you should go to a sexual health clinic
You can see a GP, but they'll probably refer you to a sexual health clinic if they think you may have an STI.
Sexual health clinics treat problems with the genitals and urine system. You can usually turn up without an appointment.
You'll often get test results quicker than from the GP and you may not have to pay a prescription fee for treatment.
You can feel comfortable sharing information about your sexual activities or orientation with a doctor. You do not need to give your real name or tell staff who the GP is if you do not want to.
No information about your visit to the clinic will be shared with the GP or anyone else outside the clinic unless you ask for it to be.
You can ask to see a female or male doctor or nurse if you wish.
What happens at a sexual health clinic
At a sexual health clinic, a doctor or nurse:
- will ask you some questions about your sex life
- may ask to look at your genitals or anus
- will tell you what tests they think you need
Some clinics offer home testing kits for some STIs.
If tests show you have an STI, you should tell your sexual partner and any ex-partners so they can get tested and treated as well.
If you do not want to do this, the clinic can usually do it for you without naming you.
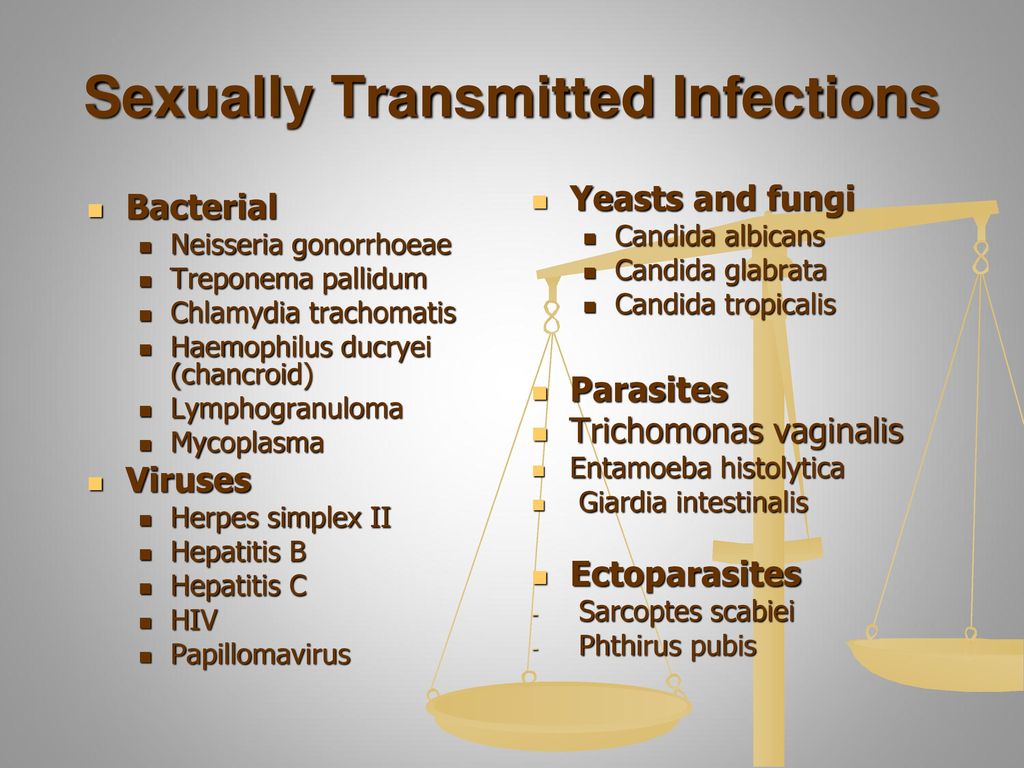
Common types of STI
Types of STI include:
- Chlamydia
- Gonorrhoea
- Trichomoniasis
- Genital warts
- Genital herpes
- Pubic lice
- Scabies
- Syphilis
- Human papillomavirus (HPV)
Page last reviewed: 25 June 2021
Next review due: 25 June 2024
How soon do STI symptoms appear?
It depends on which sexually transmitted infection (STI) you have.
Symptoms can develop within a few days or weeks, but sometimes they do not appear until months or even years later.
Often there are few or no symptoms and you may not know you have an STI.
If there's any chance you have an STI, go to a sexual health clinic or GP for a free and confidential check-up.
Chlamydia
Symptoms usually appear after 1 to 3 weeks but can start much later. Symptoms include:
- discharge from the vagina or penis
- pain when peeing
- vaginal bleeding between periods or after sex
- pelvic pain in women
- testicular pain in men
About 50% of men and 70% of women who are infected do not have any symptoms.
Find out more about chlamydia.
Genital herpes
Symptoms can appear after 4 to 7 days but might not start until months or years later. Symptoms include:
- small, painful blisters around the genitals
- pain when peeing
- a tingling or itching around the genitals
Most people do not have any symptoms when first infected.
Find out more about genital herpes.
Genital warts
If genital warts appear, symptoms could start from 3 weeks to many months or even years after contact with the virus that causes them. Symptoms include:
- small, fleshy growths or bumps on the genitals or around the anus – these are usually painless, but may be itchy
Most people with the virus that causes genital warts do not develop obvious warts.
Find out more about genital warts.
Gonorrhoea
Symptoms usually appear within 2 weeks of being infected but could start much later. They include:
- green or yellow discharge from the vagina or penis
- pain when peeing
About 10% of men and 50% of women who are infected do not have any symptoms.
Find out more about gonorrhoea.
Pubic lice
It can take several weeks before any symptoms of pubic lice appear. Symptoms are the same for men and women, and include:
- itching in the affected areas, especially at night
- inflammation and irritation caused by scratching
- black powder in your underwear
- blue spots or small spots of blood on your skin, such as on your thighs or lower tummy (caused by lice bites)
Find out more about pubic lice
Scabies
Symptoms of scabies can take up to 6 weeks to appear if you have never had them before.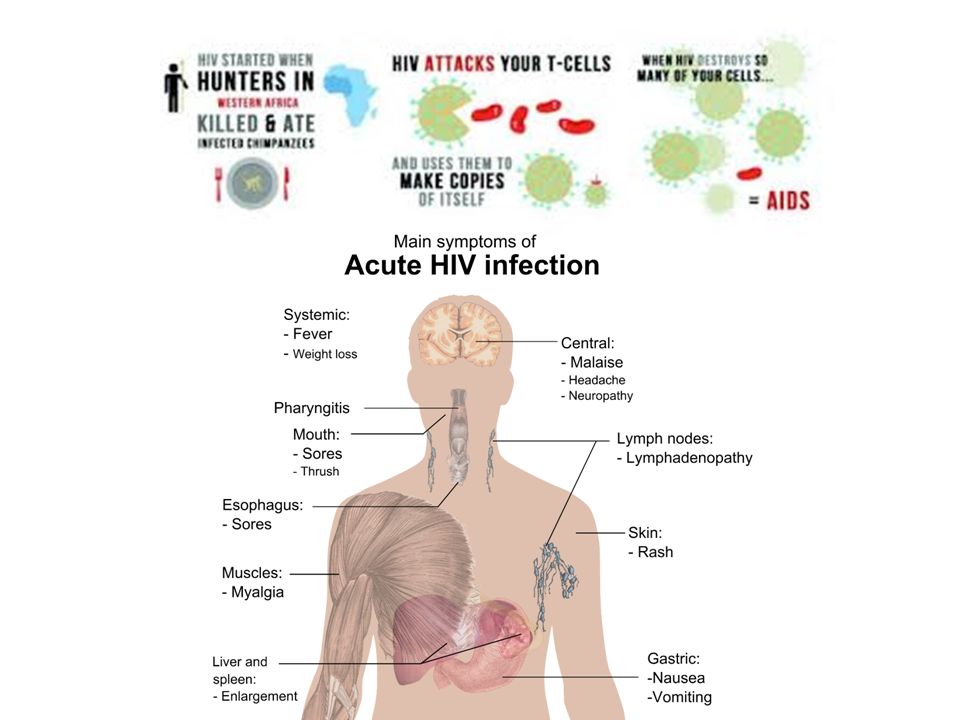 It may only take up to 4 days if you have had scabies before. Symptoms include:
It may only take up to 4 days if you have had scabies before. Symptoms include:
- itching around the genitals (usually worse at night)
- a spotty red rash
Find out more about scabies.
Syphilis
Symptoms usually appear after 2 to 3 weeks but could start earlier or much later. They include:
- one or more small painless sores or ulcers on the genitals
- a blotchy rash and flu-like symptoms that may follow a few weeks later
Symptoms are often not obvious and may come and go.
Find out more about syphilis.
Trichomoniasis
Symptoms usually appear within 4 weeks but could start months later. They include:
- discharge from the vagina or penis
- pain when peeing
- itchiness or discomfort around the opening of the vagina
About 50% of men and women who are infected do not have any symptoms.
Find out more about trichomoniasis.
HIV
The first symptoms may appear after 2 to 6 weeks. They can include:
- flu-like symptoms, such as a high temperature (fever), sore throat, headaches, and achy muscles or joints
- a red rash on the body
Not everyone gets these symptoms, but in people who do they usually last 1 to 2 weeks.
After the symptoms disappear, you may not have any further symptoms for many years, even though the infection remains in your body.
Find out more about HIV.
Further information:
- What should I do if I think I've got an STI?
- What services do sexual health clinics (GUM clinics) provide?
- Visiting an STI clinic
Page last reviewed: 22 November 2019
Next review due: 22 November 2022
What is STI?
STIs - sexually transmitted infections (STIs), are sexually transmitted, from one person to another, through unprotected sexual contact (vaginal, oral, anal).
CHLAMYDIA TRACHOMATIS (CHLAMYDIOSIS)
Chlamydia causes one of the most common sexually transmitted diseases (STDs), chlamydia. According to statistics from the World Health Organization (WHO), about 10 million new cases of the disease are registered annually in Western Europe. Among all STIs (sexually transmitted infection), chlamydia is from 5–10% (in men) to 10–30% (in women). Chlamydia trachomatis primarily affects the walls of the urethra, cervix, and rectum. The causative agent is also found on the conjunctiva of the eyes, in the pharynx and other organs. nine0007
Sexually transmitted infection chlamydia can be difficult to diagnose due to the lack of symptoms. It is believed that about 60% of women and 40% of men may not have any manifestations of this STI. If chlamydia is not recognized in time, it can cause serious complications: infertility, miscarriage, peritonitis, cystitis, pyelonephritis, chronic abdominal pain, reactive arthritis, decreased libido, etc.
Symptoms:
IN MEN
Usually (but remember that in almost 40% of cases the infection may be without symptoms) this is chlamydial urethritis - discharge of mucus or pus from the urethra, burning during urination, itching in the urethra and swelling around her, pain in the testicles is possible. nine0007
IN WOMEN
Vaginal discharge, burning during urination, bleeding between periods, pain in the abdomen and/or during intercourse. Pregnant women with untreated chlamydia infection who do not see a gynecologist or venereologist in time have an increased risk of preterm delivery, which is the most common cause of pneumonia and conjunctivitis in newborns.
Take care of your health — get STI-7 diagnostic right now! Find out the result on Chlamydia trachomatis (chlamydia) within 24-48 hours! nine0007
NEISSERIA GONORRHOEAE (GONORRHEA)
Neisseria causes a sexually transmitted disease - gonorrhea. Today it is believed that the incidence of STS is falling, but the reliability of these data is questioned by most doctors. For example, in Germany, gonorrhea is excluded from the list of mandatory disease registration, so it is impossible to track the real extent of the problem. In addition, gonorrhea often occurs without any symptoms: in women, this figure reaches 50%, in men - 10%. If we consider rectal and oral gonorrhea, it almost always has no clinical signs in both sexes. Resistant (not amenable to standard therapy) causative agents of gonorrhea are also of concern, which makes treatment extremely difficult. nine0007
Today it is believed that the incidence of STS is falling, but the reliability of these data is questioned by most doctors. For example, in Germany, gonorrhea is excluded from the list of mandatory disease registration, so it is impossible to track the real extent of the problem. In addition, gonorrhea often occurs without any symptoms: in women, this figure reaches 50%, in men - 10%. If we consider rectal and oral gonorrhea, it almost always has no clinical signs in both sexes. Resistant (not amenable to standard therapy) causative agents of gonorrhea are also of concern, which makes treatment extremely difficult. nine0007
Symptoms:
IN MEN
Most often, symptoms of this sexually transmitted infection occur in men within 2-7 days (very rarely up to 30 days). Up to 10% of men may have an infection without any symptoms. The most common symptoms are: discharge from the urethra, pain when urinating, burning in the urethra.
IN WOMEN
Only about 50% of women infected with gonorrhea will have severe symptoms: vaginal discharge, painful urination, burning or irritation of the vagina and urethra. In other cases, women will be carriers of gonorrhea, which may be detected, for example, when visiting a gynecologist and taking tests for any other reason. nine0007
In other cases, women will be carriers of gonorrhea, which may be detected, for example, when visiting a gynecologist and taking tests for any other reason. nine0007
Both men and women can have gonorrhea in other organs (mouth, anus).
Do not remain in doubt about your health — get a STI-7 diagnostic right now! Find out the result for Neisseria gonorrhoeae (gonorrhea) within 24-48 hours!
MYCOPLASMA GENITALIUM (MYCOPLASMOSIS)
Genital mycoplasma is part of the vaginal microflora - it colonizes it from childhood. Despite this, Mycoplasma genitalium can be pathogenic, depending on its genetic variability and the total number of bacteria. The onset of STI is associated with a change in sexual partner, and the incubation period of the disease lasts from 3 to 60 days. Since mycoplasmas are opportunistic pathogens, they may not cause disease at all, in which case the person will be their constant carrier. nine0007
nine0007
STIs of the lower urogenital tract (chlamydial urethritis, paraurethritis, bartholinitis, colpitis, endocervicitis) and ascending STIs (endometritis, salpingitis and salpingo-oophoritis, pelvioperitonitis) are distinguished according to the localization site. In women, mycoplasmosis doubles the risk of pelvic inflammatory disease, pregnancy complications, and infertility.
A new UK study found that about 94% of men and 56% of women infected with Mycoplasma genitalium were asymptomatic. nine0007
Symptoms:
IN MEN
Stinging or burning when urinating, discharge from the urethra.
WOMEN
Pelvic pain and/or pain during intercourse, vaginal discharge.
Get a STI-7 diagnostic and find out everything about your health right now! Get your Mycoplasma genitalium (mycoplasmosis) test result within 24-48 hours!
MYCOPLASMA HOMINIS (MYCOPLASMOSIS) nine0005
Mycoplasma hominis is detected with a frequency of 10–50% (according to some reports, up to 80%).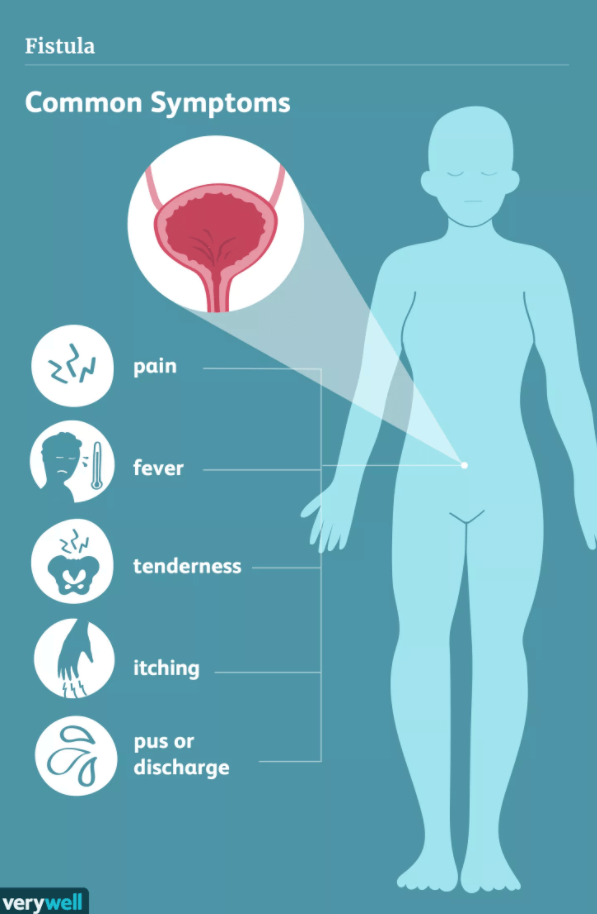 It, like Mycoplasma genitalium, is part of the normal microbiome of the genitourinary tract, but in some cases it can cause sexually transmitted infections (old name: sexually transmitted diseases, STDs). The most common are pelvic inflammatory disease, endometritis with puerperal and post-abortion fever, vaginitis, cervicitis, and urethritis.
It, like Mycoplasma genitalium, is part of the normal microbiome of the genitourinary tract, but in some cases it can cause sexually transmitted infections (old name: sexually transmitted diseases, STDs). The most common are pelvic inflammatory disease, endometritis with puerperal and post-abortion fever, vaginitis, cervicitis, and urethritis.
According to studies, Mycoplasma hominis can be found in tissues and amniotic fluid during preterm birth, miscarriage, ectopic pregnancy. In addition, this STI can be asymptomatic and accidentally detected at the appointment with a gynecologist, venereologist or urologist. nine0007
Symptoms:
MEN
Discomfort in the urethra, itching and/or burning. Frequent need to go to the toilet, pain when urinating.
IN WOMEN
Mucous or mucopurulent discharge from the vagina, pain and / or discomfort in the lower abdomen, pain of varying intensity during intercourse.
Do not put off the examination "for later" - get the diagnosis of STI-7 right now! Find out the result on Mycoplasma hominis (mycoplasmosis) within 24-48 hours! nine0007
TRICHOMONAS VAGINALIS (TRICHOMONIASIS)
The protozoan unicellular parasite Trichomonas vaginalis (Trichomonas) causes an unpleasant sexually transmitted disease - urogenital trichomoniasis.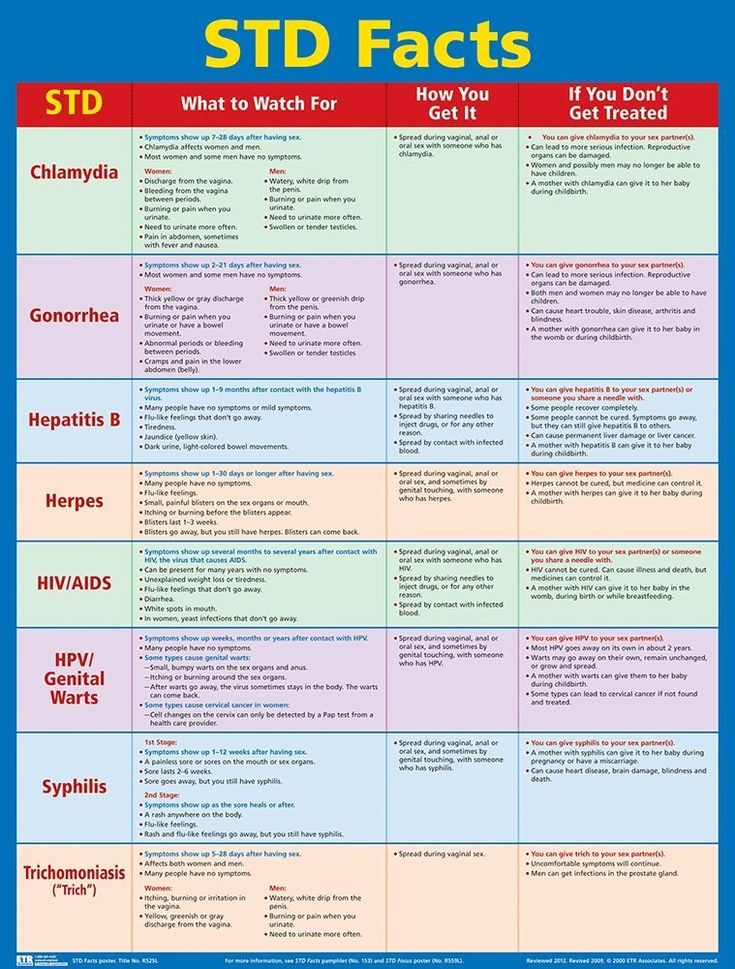 It can occur in different forms: acute, chronic or latent (carriage of Trichomonas). The latter option is especially dangerous, since a person does not know about his pathology and can infect partners. In women, Trichomonas affects the vagina and urethra, and in men - the urethra and prostate gland (less often). nine0007
It can occur in different forms: acute, chronic or latent (carriage of Trichomonas). The latter option is especially dangerous, since a person does not know about his pathology and can infect partners. In women, Trichomonas affects the vagina and urethra, and in men - the urethra and prostate gland (less often). nine0007
In pregnant women, infection may increase the risk of preterm birth and low birth weight. As with most STIs, Trichomonas vaginalis makes people more susceptible to HIV infection through unprotected sex with an HIV-infected partner.
Symptoms:
MEN
Discharge from the urethra, pain when urinating, frequent urination. Possibly a hidden carrier!
WOMEN
Vaginal discharge greenish-yellow - may be frothy, with an unusual odor. Pain when urinating and/or during intercourse. In women, the hidden carriage of Trichomonas is also possible (up to 50%)! nine0007
STI health check will protect not only you, but also your partners! Get STI-7 diagnostics right now and find out the result for Trichomonas vaginalis (trichomoniasis) within 24-48 hours!
UREAPLASMA UREALITICUM (UREAPLASMA INFECTION)
Ureaplasma urealiticum refers to opportunistic microorganisms - they are part of the normal microflora of the genital organs. According to studies, the carriage of ureaplasma among sexually active people reaches 80%. nine0007
According to studies, the carriage of ureaplasma among sexually active people reaches 80%. nine0007
Ureaplasma urealiticum can cause infection of the urethra, upper urinary tract, and testicular inflammation (orchitis). Infected women may experience complications during pregnancy, there is a risk of premature birth, miscarriage and death during childbirth with low birth weight. In addition, the infection can spread and lead to serious problems in newborns such as pneumonia, sepsis, and meningitis.
Diagnosis of sexually transmitted infections (and in particular, ureaplasma) is based on laboratory tests. They are prescribed by gynecologists, venereologists or urologists, and are also performed at the request of the patients themselves. nine0007
Symptoms:
MEN
Discharge from the urethra, pain when urinating, frequent urination, decreased libido. A combination with mycoplasma and chlamydial STI is possible!
IN WOMEN
Discomfort when urinating, vaginal discharge, decreased libido.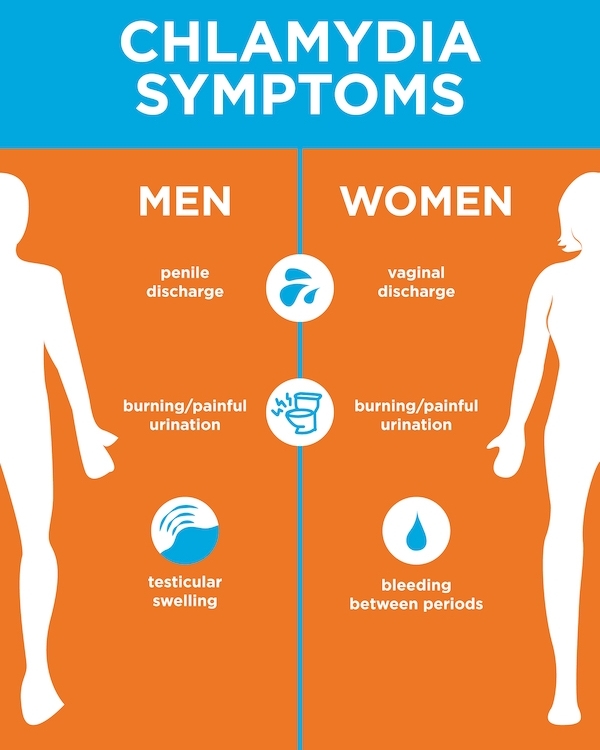 It is also possible to combine with mycoplasma and chlamydial STI or hidden carriage!
It is also possible to combine with mycoplasma and chlamydial STI or hidden carriage!
Diagnostics of STI-7 within 24-48 hours will give a reliable result for Ureaplasma urealiticum. Take the test right now! nine0007
UREAPLASMA PARVUM (UREAPLASMA INFECTION)
Ureaplasma parvum is an opportunistic bacterium and can be detected both in patients with ureaplasma infection and in clinically healthy individuals. According to scientific works, up to 87% of patients are carriers of Ureaplasma parvum and up to 19% - Ureaplasma urealiticum.
The clinic of ureaplasma infection has no characteristic signs and is similar to other sexually transmitted infections (sexually transmitted diseases). Ureaplasma parvum may not cause any symptoms, while having a negative impact on the course of pregnancy in women and the outcome of childbirth. This makes this disease especially dangerous, since it spreads "quietly", without external manifestations.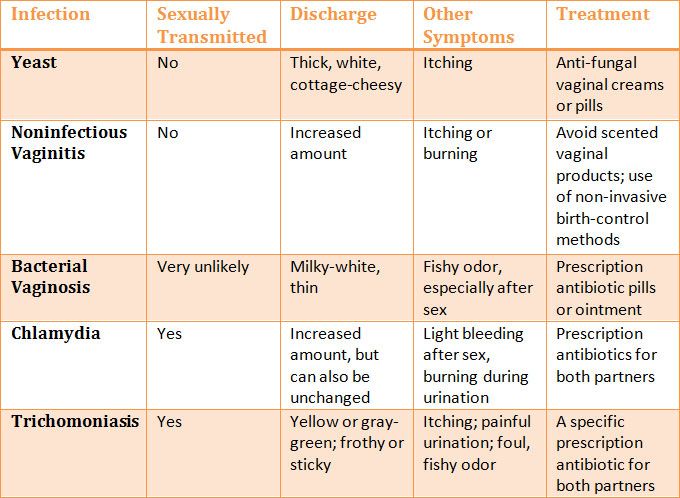 nine0007
nine0007
Symptoms:
MEN The clinic is nonspecific and similar to other STIs - discharge from the urethra, pain when urinating, frequent urination, decreased libido.
FOR WOMEN The clinic is also non-specific and similar to other STIs - discomfort during urination, vaginal discharge, decreased libido.
To find out the result on Ureaplasma parvum within 24-48 hours, go through the STI-7 diagnostic right now!
nine0004 If you want to do the STI 7 test to check yourself or your partner, you must:
- Collect urine sample
- Submit the collected urine sample to the laboratory (specify - sexually transmitted infections panel).
- Test result usually available within 24-48 hours (check with lab)
After receiving the results of the test for the presence of sexually transmitted infections: nine0005
- If the test is negative, you can rule out the 7 most common infections
- If the test is positive, please see a doctor who will prescribe the appropriate treatment for you
- If you have any complaints but the test result is negative, please contact your doctor as there is a risk of another infection or disease
Rotavirus - treatment and prevention
Rotavirus - treatment and preventionRemote consultations with a doctor are available in our center! Read more
8 812 380 02 38 St.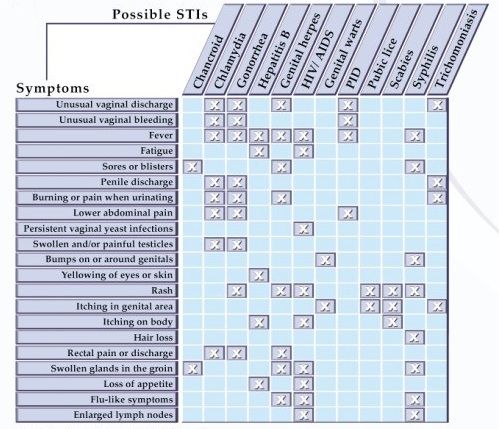 Petersburg
Petersburg
Sign up for an appointment
Moiseeva Tatyana Sergeevna
Pediatrician, infectious media
with intestinal infections Early or late, almost every person collishes. After acute respiratory viral infections (ARVI and influenza), this is the most common reason for visiting a doctor in childhood. They are a problem not only for the child, but for the whole family. Perhaps the most common intestinal infection at the moment is rotavirus or, as its parents often call it, "intestinal flu." nine0007
Regardless of the social status of the family and the sanitary and hygienic situation in the house, from birth to 5 years, almost all children suffer from rotavirus gastroenteritis . According to statistics, more than 137 million people worldwide carry this infection every year, about a quarter of whom are hospitalized.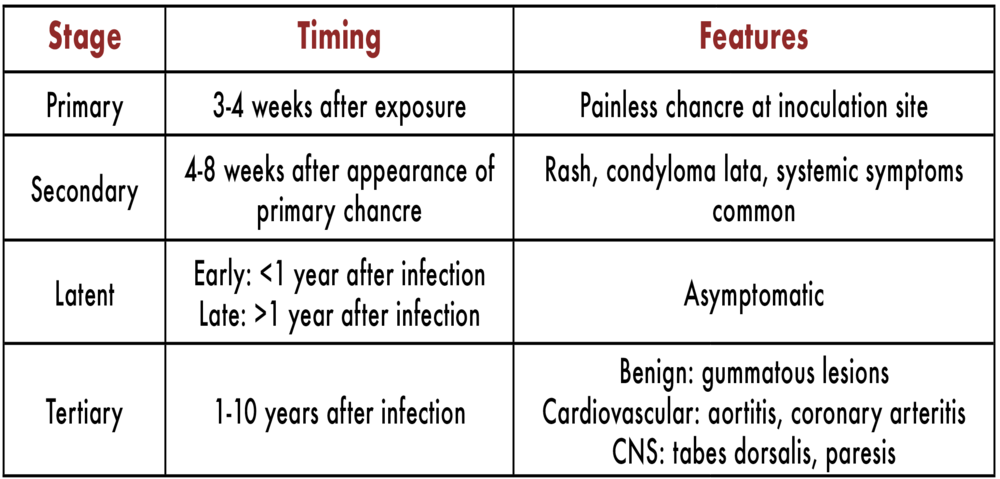 Unfortunately, there are cases with a fatal outcome, including in children. Rotavirus gastroenteritis is most severe in children when they first encounter the virus, which usually occurs between the ages of 6 and 18 months. In formula-fed babies, the risk of infection and a more severe course is slightly higher. nine0007
Unfortunately, there are cases with a fatal outcome, including in children. Rotavirus gastroenteritis is most severe in children when they first encounter the virus, which usually occurs between the ages of 6 and 18 months. In formula-fed babies, the risk of infection and a more severe course is slightly higher. nine0007
Adults are also susceptible to this infection. During life, you can become infected repeatedly, since natural immunity to the virus is type-specific (protects only against a specific type of rotavirus and does not protect against others). With repeated exposure to the virus, as a rule, the disease is less pronounced, but the person is contagious and can spread the infection.
So, what is rotavirus? There is an opinion that the rotavirus got its name because it enters the human body through the mouth, this is not true, the virus is called that because it looks like a wheel in its structure (from lat. - rota), hence the name. There are several types that differ slightly from each other in structure, but cause the same clinical picture of the disease.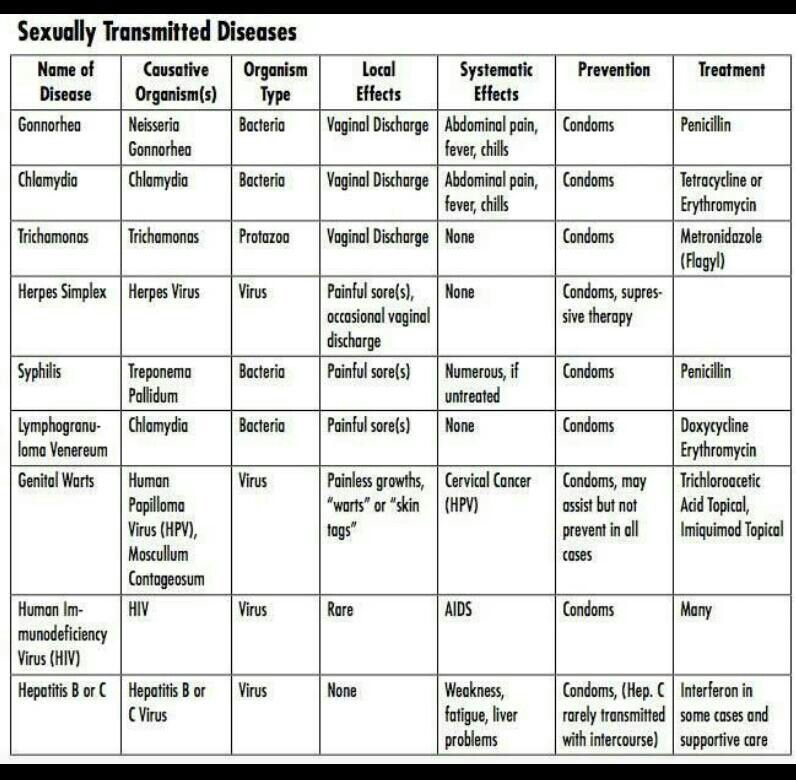 nine0007
nine0007
The route of transmission of this infection is fecal-oral, that is, to put it simply, it is a “disease of dirty hands”. The virus is highly contagious, only 10 particles of the virus are enough to get sick. Rotavirus persists for a long time on any surface, even with thorough cleaning. Therefore, very often this infection affects several family members at the same time, including adults, there are outbreaks in children's groups. It is worth noting that you can get infected only from a sick person, pets do not get sick with “human” rotaviruses. nine0007
The incubation period for rotavirus infection ranges from a few hours to 5-7 days. It is characterized by general malaise, weakness, refusal to eat, fever and symptoms of damage to the gastrointestinal tract (frequent watery loose stools, vomiting, abdominal pain). At the first sign of illness, seek medical attention! After examining the child, the doctor will assess his condition, the need for hospitalization, prescribe an examination and treatment. nine0007
nine0007
For the diagnosis of infection, a stool test for rotavirus is used by PCR (polymerase chain reaction) and ELISA (enzyme immunoassay), the result is usually ready in 1-2 days. But treatment must be started at the first symptoms of the disease, without waiting for the results. Therapy is carried out according to the symptoms, and practically does not depend on the results of the tests. Tests are prescribed to make sure that it is a rotavirus infection and in case of complications, so that doctors understand what exactly they are dealing with. nine0007
For the treatment of children who do not need hospitalization and stay at home under the supervision of a pediatrician, the so-called pathogenetic therapy is used, aimed at compensating for fluid losses that the child loses during illness with loose stools and vomit.
The most important rule for a mother with rotavirus is to solder the child, several sips every 5-10 minutes.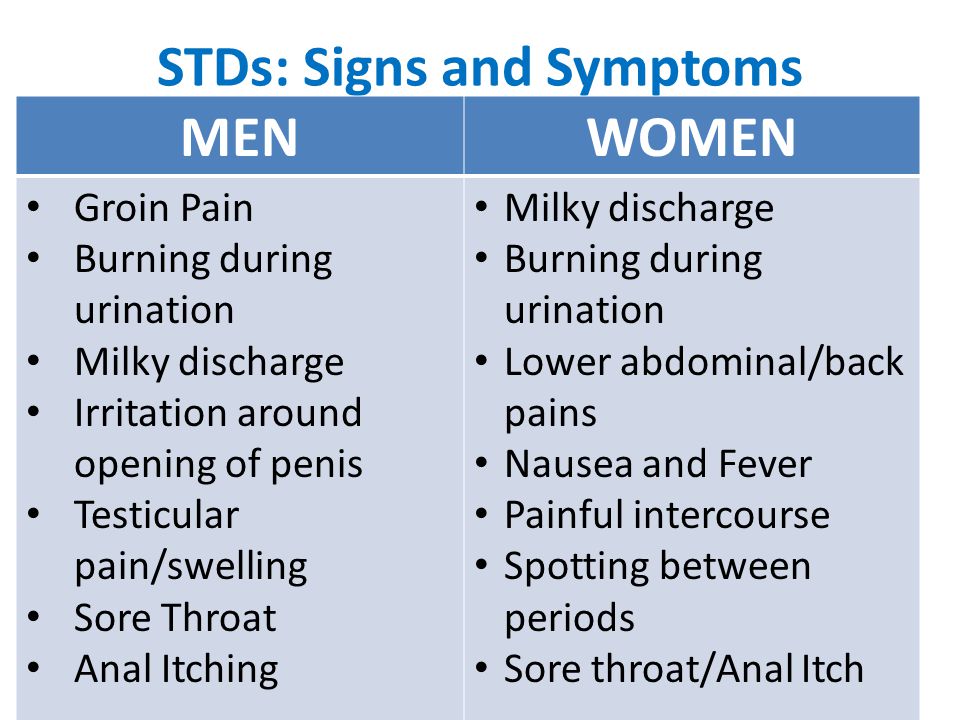 If the child refuses, then drink it from a spoon or from a syringe (after removing the needle). Do not let your child drink large amounts of liquid at one time, even if he is very thirsty, as this may cause him to vomit. It is necessary to be patient and constantly, despite the protests, drink-drink-drink. It is soldering that helps to avoid dehydration and hospitalization. nine0007
If the child refuses, then drink it from a spoon or from a syringe (after removing the needle). Do not let your child drink large amounts of liquid at one time, even if he is very thirsty, as this may cause him to vomit. It is necessary to be patient and constantly, despite the protests, drink-drink-drink. It is soldering that helps to avoid dehydration and hospitalization. nine0007
In addition to water, special saline solutions from a pharmacy are used to solder a child, containing salts that are just lost by the body during illness (Hydrovit, Humana, Electrolyte, Gastrolit, Regidron, etc.). In the absence of special preparations, until the moment of their purchase, you can use a home-made solution. You can prepare it by taking a liter of boiled water, adding 1-2 tablespoons of sugar (without a slide), half a teaspoon of table salt and one third of a teaspoon of baking soda. The finished solution can be stored for no more than a day. It is impossible to solder children with milk, juices, fruit drinks, vegetable broths, carbonated drinks. nine0007
nine0007
The second important component of the treatment of rotavirus infection is diet therapy . For the duration of an acute illness and 2-3 weeks after it, the child is prescribed a sparing diet, with the exception of dairy products, juices, raw fruits and vegetables. The child should eat more often than usual, in small portions. Food should be as gentle as possible for the stomach - not spicy, not greasy, not hot, not fried.
For infants who are breastfed or artificially fed, the issue of further feeding is decided on an individual basis with a pediatrician. With continued frequent liquid stools, in artificially fed children, a temporary transition to a mixture with a low lactose content (lactose-free, low-lactose, etc.) is possible. In infants, the issue of partial replacement of breast milk with a mixture with a low lactose content or the addition of special enzymes to breast milk that help milk to be absorbed in the intestines of the child (lactase enzyme preparations) is being resolved.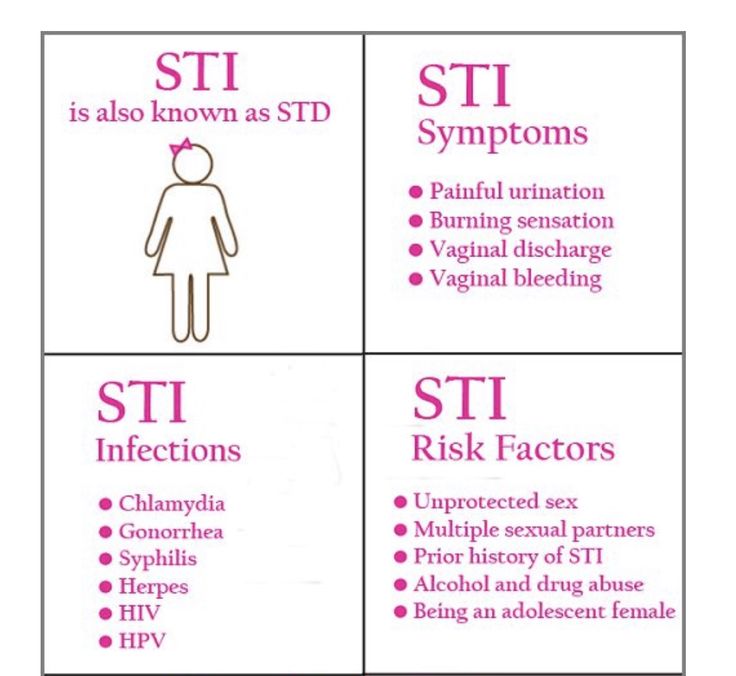 nine0007
nine0007
Also used in therapy are such groups of drugs as: enterosorbents (Smecta, Filtrum-sti, Enterosgel, etc.), probiotics (Enterol, Lineks, Bifiform, Acipol, etc.), prebiotics (Hilak-forte, Dufalac et al.), enzymes (Creon 10000, Mezim-forte, Pancreatin). You should not give these drugs to your child on your own, you need to consult a doctor, as you need to understand the advisability of taking them at different periods of the disease.
antiviral and immunomodulatory therapy may be performed according to indications . The decision to prescribe drugs in this group is made only by a doctor.
antibacterial therapy is worth mentioning separately. Antibacterial therapy for uncomplicated rotavirus infection is not carried out. But in some cases, doctors still prescribe antibiotics. And it's not just habit. This is due to the fact that acute intestinal infections are not only viral, but also bacterial in nature (E.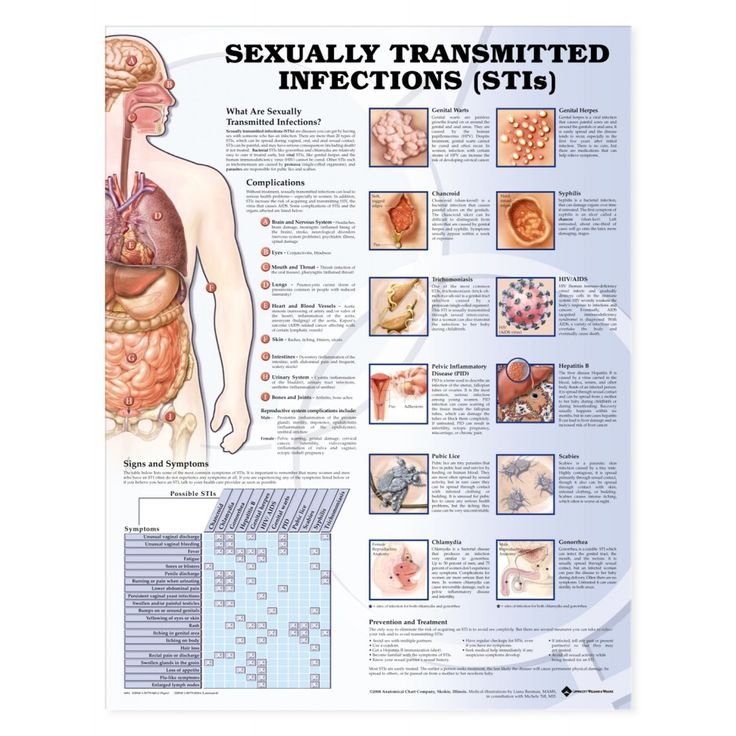 coli, Salmonella, Yersinia, and some more). And it is not always possible to determine with 100% accuracy by the symptoms what caused the symptoms: a viral infection, a toxic infection or a bacterial one. There are also mixed causes and an atypical course of the disease, so the question of prescribing antibacterial drugs is at the discretion of the attending physician. nine0007
coli, Salmonella, Yersinia, and some more). And it is not always possible to determine with 100% accuracy by the symptoms what caused the symptoms: a viral infection, a toxic infection or a bacterial one. There are also mixed causes and an atypical course of the disease, so the question of prescribing antibacterial drugs is at the discretion of the attending physician. nine0007
Very important! If the soldering of the child turned out to be ineffective and the child continues to vomit, weakness increases, he urinates less than usual (the interval is 3-4 hours), then there are direct indications for the hospitalization of the baby in a hospital, where he will be prescribed infusion therapy (intravenous fluid).
Now there is a unique opportunity to protect your baby from rotavirus infection. The Rotatek® vaccine has been certified in Russia and has been successfully used abroad for several years. The vaccine protects against the five most common types of rotavirus and prevents severe forms of the other types of the virus.