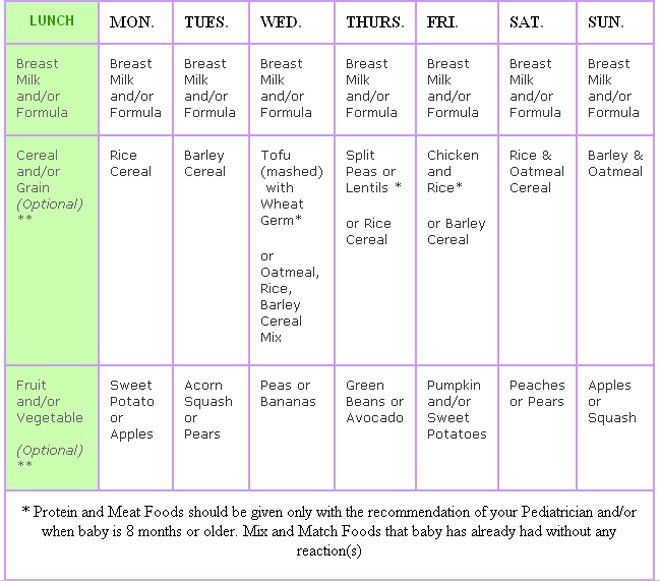
Solids and bottle feeding schedule
Sample Schedules for Starting Solids (6 to 12 Months)
Looking for sample schedules for starting solids? Ideas for how to introduce solids on a schedule. Including sample feeding schedule for 6 months old and beyond.
Ready to start solids with your babe? This is an exciting time!
Here’s everything you need to know about introducing solids safely including sample schedules for starting solids from 6 months to 12 months, plus recommended menu items.
Is Baby Ready for Solids?
The most important thing to consider as your baby approaches the 4-6 month mark, is whether they are showing signs of feeding readiness.
This includes things like:
- Baby is 6 months old (there is no benefit to starting solids before 4 months at the earliest)
- They are interested in food they see around them
- Baby is losing their tongue thrust reflex that keeps food out of their mouth
- They are sitting up on their own for at least 60 seconds at a time
If your baby is showing these signs, great! It’s time to start introducing some solids.
Note that baby should continue receiving breast milk and/or formula for at least the first year of life, as you begin the transition to solid foods.
What Are the Benefits of Solids?
Eventually, your baby’s diet will be predominantly solid foods, but it takes some time to get there.
Solid foods expose your baby to a wide variety of textures, shapes, consistencies, and colors. They’re also important for nutrition, providing an array of vitamins, minerals, fiber, protein, fat, and energy.
Eating solids is also important for physical growth and development. As your baby matures, they become prepared to try new foods and get more of their nutrients from solids than breast milk/formula.
Plus, it’s fun to play with and try new foods!
However you decide to introduce solids – using a traditional spoon-feeding/puree approach or a baby-led weaning approach – your baby benefits from the nutrition and exposure.
Recommended Solid Foods for Babies
Below are some nutritious first foods that have worked well for us:
- Tofu
- Avocado
- Oatmeal
- Hummus
- Pancakes
- Soft fruits, like bananas, kiwi, mango
- Soft-cooked vegetables, like zucchini, sweet potato, and broccoli
- Beans, peas, lentils
- Toast, cut into strips
As you design your baby’s menu, these are some great nutrient-dense foods to incorporate that can also be prepared and served in an age-appropriate way.
For a list of foods to avoid when starting solids, see this blog post.
Sample Schedules for Starting Solids
How you choose to design your baby’s solid feeding schedule depends on several things, including what your daily routine looks like.
We recommend beginning with 1 solid food meal per day for 6-month-old babes and increasing to 3 meals per day for 9-month-old babies.
Between these milestones, continue to slowly add new foods and increase how many meals/snacks you’re offering.
By 12 months old, your baby will be eating 3 meals and a few snacks per day of solid foods, using breast milk and/or milk/milk alternatives (e.g., fortified unsweetened soy or pea milk) as needed.
Keep in mind that it can take 10-15 times of offering a food before a baby even tries it, or decides whether they like it. If your baby doesn’t seem to be interested in a certain food, keep offering.
Below are a few example feeding schedules for offering solids to babes at least 6 months old.
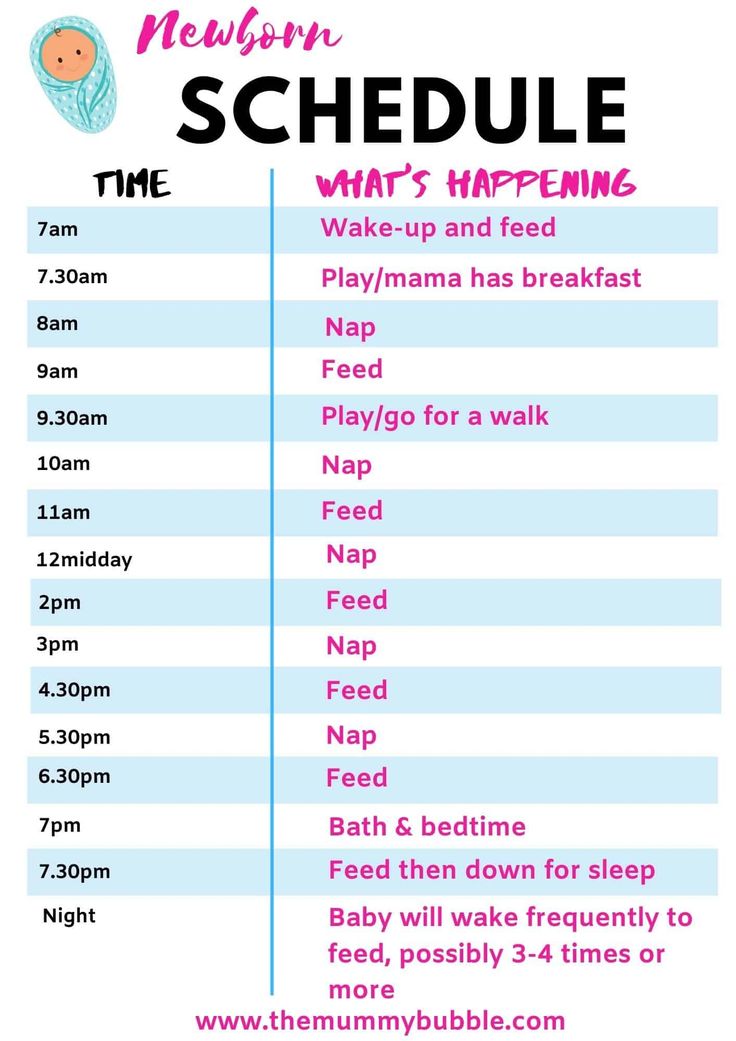
Feeding Schedule for 6 Months
- 7am: Breastfeed/bottle feed
- 8am: Breakfast – Iron-fortified baby oat cereal, peeled sliced peaches, avocado strips
- 11am: Breastfeed/bottle feed
- 2pm: Breastfeed/bottle feed
- 5pm: Breastfeed/bottle feed
- 7pm: Breastfeed/bottle feed
Note that you may continue to breastfeed/bottle feed babies this age during the night if they are still waking up.
Feeding Schedule for 9 Months
- 7am: Breastfeed/bottle feed
- 8am: Breakfast – Pancake strips, chopped raspberries and bananes
- 11am: Breastfeed/bottle feed
- 12pm: Lunch – Penne pasta with tomato sauce, green peas, melon slices with skin and seed removed
- 3pm: Breastfeed/bottle feed
- 5pm: Breastfeed/bottle feed
- 6pm: Dinner – Smashed black beans, tofu strips drizzled with thinned nut butter, sliced orange sections with outer membranes and pith removed
- 7pm: Breastfeed/bottle feed
Feeding Schedule for 12 Months
- 7am: Breast milk or milk/milk alternative
- 8am: Breakfast – Toast strips with mashed avocado, half of a banana (remove 2 inches of the skin, leaving the rest of the peel for easy handling)
- 10am: Mid-morning snack – chopped watermelon, diced grapes, hummus
- 12pm: Lunch – Quinoa-based veggie burger patty, steamed cauliflower and beet strips
- 3pm: Afternoon snack + breast milk or milk/milk alternative
- 6pm: Dinner – Lightly fried tempeh strips, kidney beans, roasted sweet potato cubes, steamed cucumber
- 7pm: Breast milk or milk/milk alternative
We hope these sample schedules for starting solids are helpful when your baby is ready for first foods. When you introduce solids on a schedule, this can help alleviate some of the stress of feeding while nourishing your baby well. Have fun with it!
When you introduce solids on a schedule, this can help alleviate some of the stress of feeding while nourishing your baby well. Have fun with it!
Chime In: If you’ve already done solids with your babe, what has your schedule looked like? Any other tips for new parents?
If you found this post helpful, we suggest you read these too:
- Spoon Feeding vs. Baby-Led Weaning
- Do Babies Really Need 11mg of Iron a Day?
- Plant-Based Baby-Led Weaning Grocery List
- How to Wean Baby to Plant-Based Milk
Balancing introducing solids with milk feeds
When to introduce solids?
At around 6 months of age babies need to start having solid foods as well as breastmilk or formula. Find out how to get started with solid foods and what are the best foods to start with.
At 6 months, your baby will still be getting most of their nutrition from breast milk or formula.
As you introduce solid foods, continue feeding with breastmilk or formula until at least 12 months of age.
Start to introduce solid foods at around 6 months of age when:
- your baby can sit up with support and has good head control
- your baby starts to show interest in food such as watching and reaching out when they see food
Even though some babies show these signs from an earlier age, continue to offer your baby breastmilk or formula if they appear hungry. This is usually all they need until around 6 months. It’s recommended that you don’t introduce solids before 4 months.
How to introduce solid foods into your baby’s diet
Start feeding your baby solids once a day. Your baby will take only small amounts of solid foods at first. Try one teaspoon at first of pureed vegetable, fruit, or rice cereal in between milk feeds.
From 6 to 9 months continue to give your baby breastmilk or formula first, then try solids after the milk.
From 9 months you can try to give solids first, then breastmilk or formula. This allows for your baby to naturally transition to solids by around 12 months.
At around 8 to 9 months try giving your baby solids as part of breakfast, lunch, and dinner.
Continue breastmilk or formula through the first year of life while foods are being introduced. From around 6 months you can try small amounts of cooled boiled water out of a sippy cup.
Which foods first?
From 6 months of age baby’s first foods should contain iron. Foods that have iron, include:
- iron-fortified baby cereals
- meat
- poultry
- fish
- cooked tofu
- legumes - lentils, beans, or chickpeas
Guidelines recommend that you can introduce foods in any order and at a pace that suits your baby, family, and cultural backgrounds, as long as some foods servings contain iron.
Your baby’s first foods can be smooth, mashed or have soft lumps.
Choose from the 5 food groups.
Vegetables and legumes
Give your baby cooked and pureed:
- pumpkin
- sweet potato
- carrots
- potato
- peas
- broccoli
- cauliflower
- zucchini
Over time puree them less so the texture gets lumpier.
Then introduce vegetables that are cooked but not pureed.
Fruit
Give your baby stewed and pureed:
- apples
- pears
- peaches
- apricots
- berries
Your baby might also like to try mashed ripe banana.
Gradually introduce pieces of cooked fruit, banana, peach and grated raw apple.
Avoid larger pieces of raw apple; babies can choke on them.
Grains and cereals
Give your baby fortified infant cereals (e.g. rice cereal) to start.
Move to cooked rolled oats, wholegrain breakfast biscuits (Weetbix, Vita Brits) or thick infant cereals.
Don’t add sugar or honey or offer cereals with chocolate or added sugar.
Meat, fish, poultry, eggs, legumes, tofu
Meat, fish, poultry eggs, legumes, tofu should always be pureed when you start introducing solids.
When your baby accepts this, offer them bite size pieces of:
- chicken
- minced meat
- flaked fresh or canned fish (in spring water)
- mashed tofu
- mashed legumes
- scrambled or mashed boiled eggs
Don’t add salt. Also avoid processed meats as they have a lot of salt.
Also avoid processed meats as they have a lot of salt.
Milk, cheese, yoghurt
Formula should be used only until your baby is 12 months old. Then small amounts of milk can be added to foods like porridge. Breast feeding is recommended to continue until the age of 2 or longer.
Grated cheese is good in mashed vegetables.
Choose yoghurt without added sugar. Add fruit for extra flavour
What drinks should I be giving my baby?
After 12 months of age breastmilk, water (clean tap water or bottled water) and full fat cow’s milk should be the main drinks you offer your baby.
Keep breastfeeding for as long as you and your baby like.
Switch from formula to full fat ordinary cow’s milk after 12 months. Your child doesn’t need toddler milk products. Offer your baby a cup to drink from rather than a bottle. Your one-year-old should be exclusively drinking from a toddler cup.
From about 12 months, you can try rice milk and oat milk (fortified with at least 100mg calcium/100mL) if you want. But these drinks don’t have enough protein and vitamin B12. Your baby will need to have plenty of meat, poultry, fish, eggs, yoghurt, or cheese to make up for what they’re not getting from cow’s milk.
But these drinks don’t have enough protein and vitamin B12. Your baby will need to have plenty of meat, poultry, fish, eggs, yoghurt, or cheese to make up for what they’re not getting from cow’s milk.
How much should I feed my baby?
Your baby will grow at different rates at different times. Their appetite can vary, even from day to day.
Babies don’t know what to eat but they know how much. Provide wholesome, healthy unprocessed food choices. Take your cue from your baby. Babies tend to turn away or lose interest when they’ve had enough to eat.
Finger foods and self-feeding
By 9 to 12 months, most babies like finger foods. Finger foods are foods they can hold themselves.
Some also like to hold their own spoon at that age. It will be messy! But learning to feed themselves is important.
By 12 months, your baby can eat the same healthy food you serve your family.
Foods to limit or avoid when introducing solids
There are some foods and drinks you should limit or avoid:
- coffee and tea, herbal drinks are not recommended
- fruit juice
- honey until 12 months (to prevent botulism)
- processed foods
- raw or runny eggs (bacteria in raw eggs can be harmful to babies)
- sugar sweetened drinks
- unpasteurised milks
Low-fat milks are not recommended in the first 2 years of life. Goat’s milk, sheep’s milk, soy milk, coconut milk and almond milk should also be avoided before the age of 2 unless your doctor recommends them.
Goat’s milk, sheep’s milk, soy milk, coconut milk and almond milk should also be avoided before the age of 2 unless your doctor recommends them.
Avoid small hard foods such as whole nuts and uncooked vegetables until 3 years. These can be choking hazards.
If your family doesn’t use animal products, your baby may need a vitamin B12 supplement. Discuss this with your doctor.
Seek help from your health care professional if you are worried about your baby’s eating or development.
Fruit — give your baby stewed and pureed apples, pears, peaches, apricots and berries, or mashed ripe banana. Gradually introduce pieces of cooked fruit, banana, peach and grated raw apple. Avoid larger pieces of raw apple; babies can choke on them.
Grains and cereals — give your baby fortified infant cereals (e.g. rice cereal) to start. Move to cooked rolled oats, wholegrain breakfast biscuits (Weetbix, Vita Brits) or thick infant cereals. Don’t add sugar or honey and don’t use cereals with chocolate or added sugar.
Meat, fish, poultry, eggs, legumes, tofu — make them pureed at the start. When your baby accepts this, offer them pieces of chicken, minced meat, flaked fresh or canned fish (in spring water), mashed tofu, mashed legumes, scrambled or mashed boiled eggs. Don’t add salt and avoid processed meats as they also have a lot of salts.
Milk, cheese, yoghurt — breast milk or formula should be used for up to 12 months, then small amounts of milk can be added to foods like porridge. Grated cheese is good in mashed vegetables. Choose yoghurt without added sugar. Add fruit for extra flavour.
How much?
Babies grow at different rates at different times. Their appetite can vary even from day to day.
Babies don’t know what to eat but they know how much. Take your cue from your baby. Healthy babies turn away or lose interest when they’ve had enough.
Finger foods and self-feeding
By 9 to 12 months, most babies like finger foods.
Some also like their own spoon at that age. It will be messy, but learning to feed themselves is important.
By 12 months, serve the same healthy food you serve your family, but without hot spices.
Encourage infants to feed themselves.
If you have stopped breastfeeding, switch to ordinary cow’s milk after 12 months. Use a cup rather than a bottle. Limit the amount of cow’s milk to around 500ml per day. Under health professional supervision, you can use full fat rice milk or oat milk with at least 100mg calcium per 100mL if you want, as long as other sources of protein are included (meat, chicken, fish, eggs, legumes or nut butters).
Your child doesn’t need toddler milk products.
If your family doesn’t use animal products, your baby may need a vitamin B12 supplement. Discuss this with your doctor.
Learn more here about the development and quality assurance of healthdirect content.
table of the introduction of the first complementary foods by months, input scheme, the correct menu of the child on the IV, what can be given to the artificial
Contents: Hide
Formula-fed complementary foods
Inexperienced mothers of newborn babies are concerned about many problems: fighting colic, establishing a daily routine, performing hygiene procedures. However, time goes by and acute issues gradually become irrelevant. Inexorably, a new crucial stage is coming - the introduction of the first complementary foods begins. We will tell you how to properly introduce complementary foods with artificial feeding.
However, time goes by and acute issues gradually become irrelevant. Inexorably, a new crucial stage is coming - the introduction of the first complementary foods begins. We will tell you how to properly introduce complementary foods with artificial feeding.
Why does a baby need complementary foods
Both natural and bottle-fed babies are usually equally full of energy, active and inquisitive. The introduction of complementary foods allows you to gradually accustom the baby's gastrointestinal tract to new food, as well as give the growing body the vitamins and minerals that it needs at a particular stage of physical development. Also, with its help, you can gradually adapt the baby to the diet of adult family members and then painlessly transfer it to the common table. There are no exact norms and rules for the introduction of complementary foods. It is necessary to focus on the needs of the child and follow the recommendations of the pediatrician.
When can complementary foods be introduced with artificial feeding
Teaching children to adult food should be timely. The fact is that the gastrointestinal tract of an infant at a too early age (for example, 2-3 months) is not able to process certain foods. The mucous membrane of the digestive system is irritated, and this can provoke gastritis and other serious health problems.
The fact is that the gastrointestinal tract of an infant at a too early age (for example, 2-3 months) is not able to process certain foods. The mucous membrane of the digestive system is irritated, and this can provoke gastritis and other serious health problems.
IMPORTANT! At what age can you introduce your baby to new products? For children in good health, WHO recommends that complementary foods be introduced at 6 months of age. But for some babies, if there are certain medical indications, the doctor may advise you to do this earlier.
The recommendations do not provide a specific menu for each age, which must be followed. Much depends on the socio-cultural characteristics of different peoples and the individual pace of development of children. In most cases, the timing of the start of complementary foods varies from 4.5 to 6 months. Specialists distinguish the following signs of a child's readiness to try something new, in addition to the usual artificial mixture:
• the baby is not quite full of the mixture and asks to continue the meal;
• his first teeth have already erupted, he tries to chew them, takes and tries to taste food from adult plates;
• if you bring a spoon to the baby, he will begin to examine its contents and want to try it;
• the child sits confidently, can turn his head and control his body;
• The tongue thrust reflex fades so baby can drink water from a spoon without it dripping back out.
It is not necessary that all of the listed features be present at once. If several of them are observed, then it is quite possible to try to introduce the first complementary foods.
Read also: How much does a newborn eat per feeding?
When to delay feeding
It is better to delay feeding if:
• the child is ill;
• less than three days have passed since vaccination;
• the baby is teething, he does not sleep well and is naughty;
• there have been some changes in the family's lifestyle, such as moving to a new home, mother going to work, traveling to another city or country;
• the crumbs have manifestations of allergies, upset of the gastrointestinal tract;
• The weather is too hot outside.
Therefore, complementary foods should only be offered to a child when he is completely healthy, calm and in a good mood.
Basic rules for the introduction of complementary foods
Anna Levadnaya, pediatrician, Candidate of Medical Sciences, explains that the principles of introducing complementary foods on natural and artificial feeding are similar: it is recommended to focus on food interest, signs of a child's readiness for introducing complementary foods. The only thing is that with exclusive breastfeeding, it is not recommended to supplement the child with water, while bottle-fed children can be offered water.
The only thing is that with exclusive breastfeeding, it is not recommended to supplement the child with water, while bottle-fed children can be offered water.
Video: 10 rules for complementary foods
Author: pediatrician, Ph.D. Komarovsky E.O.
The rest of the principle is the same: for both breastfeeding and formula-feeding, offer your baby a new food before feeding, and then supplement with breast milk or formula.
In order for new products to bring benefits to the baby on artificial feeding and not harm his health, you should follow a number of simple recommendations.
1. Complementary foods are usually given in the morning before the main formula feeding. This allows you to track the reaction to unfamiliar food during the day and take action if necessary.
2. It is necessary to carefully monitor the cleanliness of children's dishes, pots and blenders. The gastrointestinal tract of an infant is very sensitive to infectious agents.
It is necessary to carefully monitor the cleanliness of children's dishes, pots and blenders. The gastrointestinal tract of an infant is very sensitive to infectious agents.
3. New food is introduced into the baby's diet from a quarter of a teaspoon. If he tolerated the product well, then within a week the portion is brought to one or two tablespoons. Then you should look at the desire of the child and his well-being, and also take into account the recommendations of the pediatrician.
4. The first dishes should be of a liquid consistency, then they are made into a puree, and only closer to a year can you give soft pieces to chew. Pediatricians advise adding butter and vegetable oils to them as vegetables and cereals are introduced into the diet.
5. In order to protect the child's body from pathogens that may be contained in unprocessed food, complementary foods should first be boiled, stewed or baked. The baby is offered slightly warm food: the optimum temperature is 36-37 degrees.
6. It is advisable to try the products immediately from a spoon. If the baby gets used to the bottle, this will slow down the formation of the skill of chewing food and may subsequently affect diction.
7. A food diary can help you reliably identify what your child has an allergic reaction to. It should record everything that the baby ate during the day, in what quantity and at what time. You can also record in a diary whether he liked the new dish or not.
8. Complementary foods should be introduced only from mono-products. Only after making sure that vegetables, cereals, juices, fruits or protein products are well tolerated by the child, you can offer their mixes.
9. The interval between introduced and new complementary foods should be at least a week. Such a period of time will allow the child's body to adapt to the expanded diet and perceive other dishes without unpleasant surprises.
10. If an allergy occurs to any product, it should be immediately removed from the menu and consulted by a pediatrician. It will be possible to return to this complementary food no earlier than in a month.
It will be possible to return to this complementary food no earlier than in a month.
11. It is desirable that with the introduction of complementary foods, the infant receives a sufficient amount of liquid. It can be both ordinary water and compotes.
12. Do not offer your child foods that are considered highly allergenic as first foods: full-fat cow's milk, citrus fruits, gluten-containing cereals, chicken eggs, etc.
13. Do not force-feed a child, even if you think that he is hungry. A small person has the right to defend his opinion in the choice of dishes.
14. Feed your baby exclusively in a sitting or reclining position to avoid the risk of aspiration. Very convenient for this special children's chairs made of easy-to-wash material.
From 7–8 months, formula-fed mashed or pureed food, such as a banana, can be used as complementary foods. If semi-solid food is not introduced into his diet in time, problems may arise with the intake of solid food in the future: after a year, the child will refuse it completely. From 8–9 months, the child should be offered the so-called finger food: cut soft fruits and vegetables into pieces, such as boiled carrots, potatoes, and offer them to the baby. If you follow this scheme, by the year the child will be ready to eat solid food from the common table, Levadnaya explains.
From 8–9 months, the child should be offered the so-called finger food: cut soft fruits and vegetables into pieces, such as boiled carrots, potatoes, and offer them to the baby. If you follow this scheme, by the year the child will be ready to eat solid food from the common table, Levadnaya explains.
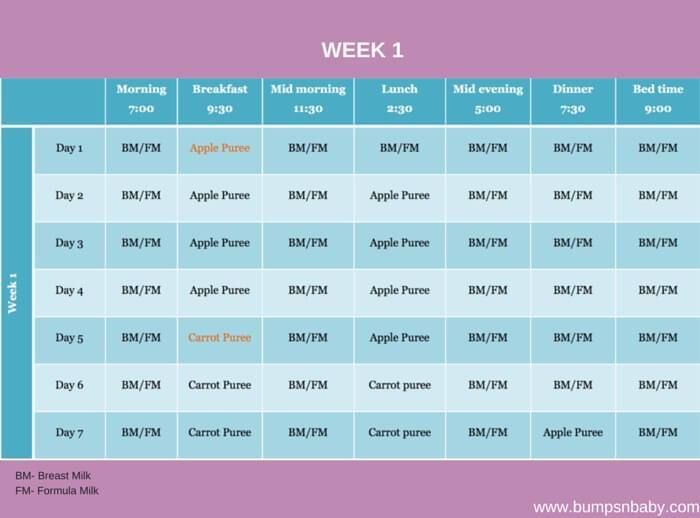
Complementary Feeding Schedule
We provide a suggested complementary feeding schedule for up to a year to guide you unless advised otherwise by your doctor. As a standard formula-fed babies with normal weight gain are offered products in approximately the following order:
• vegetable puree;
• cereals;
• fruit puree;
• kefir;
• butter and vegetable oil;
• children's biscuits and bread;
• meat puree;
• fish puree.
The earlier introduction of vegetable puree rather than fruit puree is due to the fact that the former has a more insipid taste. Having fallen in love with sweet apples and bananas, the child may subsequently refuse to eat zucchini, pumpkin, etc. However, if the infant is underweight, the doctor may recommend porridge as the first complementary food for him. They are more high-calorie and allow you to gain the missing kilograms faster. Each type of complementary food is described in the table.
However, if the infant is underweight, the doctor may recommend porridge as the first complementary food for him. They are more high-calorie and allow you to gain the missing kilograms faster. Each type of complementary food is described in the table.
| Vegetables | They are usually offered to children in the following order:
Tomatoes, white cabbage and cucumbers are recommended to be included in the menu already after a year. |
| Fruit | Seasonal fruits are recommended. The approximate order of their introduction: apples, pears, peaches, apricots and bananas. If the baby suffers from constipation, you can carefully and with the permission of the pediatrician offer him plums. |
| Kashi | To start complementary foods, choose gluten-free cereals: buckwheat, rice, corn grits. After the child is 8 months old, you can gradually give him a taste of oatmeal, wheat and barley porridge. It is better to refuse semolina altogether, since it contains very few useful substances and at the same time it is very high in calories. Cereals can be ground in a coffee grinder or mashed from ready-made cereals in a blender. |
| Protein products | Fermented milk products do not need to be introduced earlier than 8 months, since only by this time do children begin to produce the enzymes necessary for their processing. From meat, children under one year old should be given rabbit, chicken, turkey and veal. Sea fish is more suitable - hake, cod or flounder. Meat and fish are offered to kids in grated form as part of vegetable dishes and cereals. Cottage cheese can be prepared for the baby yourself. |
IMPORTANT! It is undesirable to add salt, sugar and spices to food for a child. His taste buds are not yet accustomed to strong stimuli, so it is better for him to appreciate the natural taste of the food offered. Soup should be boiled only on vegetable broths, and meat should be added to an already prepared dish. Meat broth may be too heavy for the baby's kidneys.
How to choose complementary foods
The main recommendations for choosing specific foods to start complementary foods are as follows:
1. It is recommended that your baby's diet be based on products grown in the region where he/she lives. If the period of the first feeding falls on the winter, it is advisable to stock up vegetables, fruits and berries from your garden in advance, putting them in the freezer for safekeeping.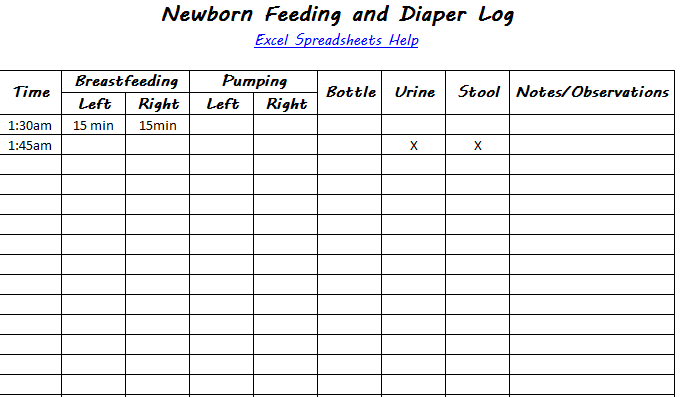 In the event that this is not possible, you can give preference to ready-made canned mashed potatoes. They undergo mandatory certification confirming the quality.
In the event that this is not possible, you can give preference to ready-made canned mashed potatoes. They undergo mandatory certification confirming the quality.
2. It is advisable not to buy store-bought juices for your child in large quantities. Compotes will be much more useful for him. You can also offer decoctions of dried fruits.
3. If you decide to buy ready-made food for your baby, then pay attention to the label and the release date. The product must be age appropriate and fresh. The composition should not contain salt, sucrose, dextrose and other extraneous additives.
In general, it is worth remembering that the first food offered to a child should be puree-like, not too viscous products, consisting of one ingredient, soft consistency, without added sugar, salt and spices, says Andrey Mosov, head of the expert direction of NP Roskontrol, doctor on nutritional hygiene of children and adolescents. He insists that preference should be given to industrial prepared meals, as such products have been tested and certified. There are no guarantees with mashed homemade vegetables.
There are no guarantees with mashed homemade vegetables.
Introduction of complementary foods to formula-fed premature babies
The question of the correct introduction of complementary foods to a premature baby should be discussed individually at a pediatrician's appointment. In order for the body to be able to process a new product, organs and systems must be sufficiently mature and prepared. The quality of food digestion largely depends on the production of special enzymes, so you should not be self-motivated in compiling the baby's menu.
The schedule for the introduction of complementary foods will be determined by the presence or absence of anemia, the rate of weight gain, the tendency to allergies, and some other nuances. Formula-fed premature babies are usually advised to start introducing meat and egg yolk earlier. It is advisable to cook porridge on a vegetable broth or mixture, and not on water, since then they will be more nutritious and healthy.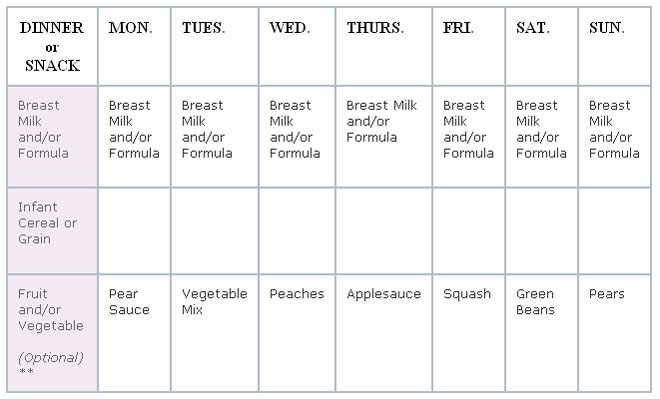
IMPORTANT! However, the course of complementary foods must be monitored by a pediatrician. The doctor monitors the child's reaction to new products, evaluates the dynamics of growth and general physical development. The scheme may change if any deviations from the norm are detected during routine inspections.
Answers to frequently asked questions for mothers
• What foods should not be given to babies under one year old?
It is forbidden to give cow's milk to babies under the age of one, as it can cause allergic reactions and digestive disorders. It is perfectly replaced by adapted mixtures from modern manufacturers. In addition to milk, it is not recommended to include nuts, citrus fruits, exotic fruits and vegetables, red fish and honey in the menu of the crumbs of the first year of life.
• What should I do if my child absolutely does not want to eat complementary foods?
Wait a while and try to offer food again, but don't insist on another refusal. Perhaps the baby did not like the new dish because of the unfamiliar taste. Children are big conservatives and are often wary of change. Be patient, do not rush to introduce complementary foods. Show your child with what appetite you yourself eat from your plate, and then he may have a desire.
Perhaps the baby did not like the new dish because of the unfamiliar taste. Children are big conservatives and are often wary of change. Be patient, do not rush to introduce complementary foods. Show your child with what appetite you yourself eat from your plate, and then he may have a desire.
• What should I do if my baby has problems with stool while weaning?
If a child has a stool retention of more than three days during the introduction of complementary foods, then we can talk about constipation. In this case, you need to visit a pediatrician, as well as immediately exclude fixing foods from the menu and give more fluids to drink. If the stool has become too frequent (more than 5 times a day), then this may be due to indigestion or an intestinal infection. Be sure to consult your doctor about this.
• What should I do if I have an allergy to complementary foods?
It is advisable to take care of this issue even before the introduction of complementary foods, asking the pediatrician observing the child to prescribe an antihistamine drug that is optimal for his age. You should also carefully fill out the food diary at first. With it, it will be possible to identify a possible allergen and exclude it from the baby's menu, preventing more serious health consequences.
You should also carefully fill out the food diary at first. With it, it will be possible to identify a possible allergen and exclude it from the baby's menu, preventing more serious health consequences.
• How do you know if a baby tolerates complementary foods well?
Normal weight and height gain, regular bowel movements, and the absence of allergic skin rashes indicate the successful introduction of complementary foods. If the baby is cheerful, active, he has a good appetite and a good sleep, most likely, this means that you are doing everything right and the selected diet suits him.
However, it is impossible to completely refuse artificial formula when introducing complementary foods, even when the infant eats complementary foods with appetite. His body is not yet ready for a complete change in the type of food and may malfunction. This often manifests itself in the form of allergies, stool disorders or growth retardation. Remember that the baby should enjoy the new food.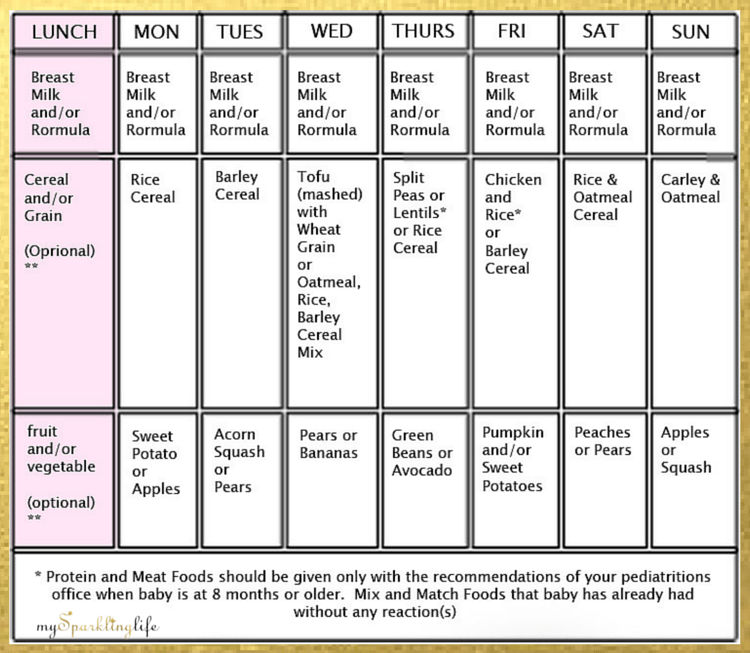 Only under this condition will he form the correct eating behavior.
Only under this condition will he form the correct eating behavior.
#Nutrition for children up to a year #Complementary food
newborn diet on IV, how to properly bottle feed a baby
The desire for a child to grow up strong and healthy is natural for mothers. And the health of a newborn begins with proper nutrition. Mother's milk has always been considered the best option for feeding - the most healthy and nutritious food for infants. However, in some cases, breastfeeding is not possible. And then mixtures come to the aid of mothers.
Contents: Hide
- When is it necessary to switch to artificial feeding
- How to choose a mixture
Medical contraindications to breastfeeding. There are a number of diseases in which breast milk is prohibited. On the mother's side, these are HIV, an open form of tuberculosis, dangerous infections, and a serious state of health. On the part of the child, these are leucinosis, galactosemia, and individual food intolerance.
 It is not necessary to take tests after hearing the terrible names of diseases. All newborns are checked in maternity hospitals for their presence. But allergies are not so easy to identify. Many newborns have skin rashes and redness, which may be due to a reaction to an aggressive environment. Only a strict diet for the mother can help here, so that her milk does not contain allergens, monitoring the baby and consulting a doctor.
It is not necessary to take tests after hearing the terrible names of diseases. All newborns are checked in maternity hospitals for their presence. But allergies are not so easy to identify. Many newborns have skin rashes and redness, which may be due to a reaction to an aggressive environment. Only a strict diet for the mother can help here, so that her milk does not contain allergens, monitoring the baby and consulting a doctor. Lack of lactation or its complete cessation. This is the second objective reason for transferring a child from breast milk to formula. Lactation does not always come in the right amount and it can be increased. It happens that milk disappears a few days after the birth of the crumbs. This often depends on the individual characteristics of the mother's body. So that the child does not starve, he is first transferred to mixed, and then completely to artificial feeding.
Insufficient nutritional value of mother's milk. Usually this problem can be solved without resorting to the transition to IoT, but this is not always possible.
 A woman may have a lot of milk, but it will be like water in both color and consistency. In such cases, doctors give advice to the mother on nutrition in order to increase the fat content of milk and its usefulness. If the milk remains watery, the child stops eating, cries of hunger, loses weight. The only way out in this situation is the transition to the mixture.
A woman may have a lot of milk, but it will be like water in both color and consistency. In such cases, doctors give advice to the mother on nutrition in order to increase the fat content of milk and its usefulness. If the milk remains watery, the child stops eating, cries of hunger, loses weight. The only way out in this situation is the transition to the mixture. Impossibility of regular feeding. Children who, for a number of reasons, are separated from their mother for long periods of time are transferred to artificial feeding: the woman is in a hospital, going to work or study, business trips, etc. If the break in breastfeeding is one-time, then restoring lactation and breastfeeding is still possible . However, more often in such cases, breastfeeding has to be abandoned.
Mother's personal wish. Unfortunately, there are cases when a woman, having every opportunity to breastfeed her baby, refuses to breastfeed for various subjective reasons. In this case, lactation is interrupted, and the baby is transferred to the mixture.

See also: Newborn weight gain by month
How to choose a formula
If you are going to transfer your baby to artificial feeding, then the first thing you will encounter will be the choice of nutrition. Today there are a large number of different mixtures: adapted and non-adapted, dairy and sour-milk, dry and liquid. There are mixtures against regurgitation, hypoallergenic, for premature babies, etc. How to choose the optimal replacement for mother's milk from such a variety?
- Make your choice only after consulting a pediatrician. The doctor will examine the baby and give all the necessary recommendations.
- Monitor your child. When adapting to a new diet, the child may have small rashes, but they disappear if the body begins to absorb the mixture normally. The baby eats with appetite, he has a normal stool and no colic. Otherwise, the mixture must be changed.
- If there is a need to replace the mixture with a thicker one (against spitting up), choose the same brand of food that was previously used.
- Consider the age of the baby. All mixtures have a gradation by months of life.
- Prefer adapted formulas, they are usually easier to digest
Basic rules for formula feeding save you a lot of problems.
1. Choose proven blends. This applies not only to the choice of brand, but also to the packaging itself. Look at its integrity, check the expiration date.
2. Observe the storage conditions of the opened package at home (in a dry and cool place, but in no case in the refrigerator, the mixture must not become damp). Remember that the open mixture is stored for three weeks. After this period, it can no longer be used.
3. Strictly follow the instructions when preparing meals. It is indicated on the packaging. Water for the preparation of the mixture must be purified and boiled. The optimal temperature for preparing the mixture is 36–37 °C. You can cook food right in the bottle. This is quite convenient, since baby bottles have a volume scale that makes it easier to calculate the right amount of scoops.
 The mixture must be stirred until completely dissolved, and then cooled to an acceptable temperature so that the baby can drink without burning himself. You can check if the milk is hot by dropping it on your wrist - there the skin is most tender and sensitive. If the temperature is almost not felt, then the mixture can be given to the child.
The mixture must be stirred until completely dissolved, and then cooled to an acceptable temperature so that the baby can drink without burning himself. You can check if the milk is hot by dropping it on your wrist - there the skin is most tender and sensitive. If the temperature is almost not felt, then the mixture can be given to the child. 4. Sterilize baby dishes. Baby bottles and nipples should be thoroughly rinsed using a special brush so that no food residue remains. You can use children's dishwashing detergents. Do not wash bottles with common cleaning products that you are used to using, no matter how good they are. After washing, be sure to place the dishes in boiling water. This helps to kill harmful bacteria. It is recommended to sterilize children's dishes during the entire first year of a baby's life. Then you can limit yourself to just a thorough wash.
5. Hold the bottle in a semi-vertical position when feeding. The milk should completely fill the nipple.
 This prevents the child from swallowing air. After feeding, it is necessary to hold the baby in a column for several minutes to avoid spitting up.
This prevents the child from swallowing air. After feeding, it is necessary to hold the baby in a column for several minutes to avoid spitting up. 6. Monitor the amount of formula consumed and the feeding schedule. Maintaining a balance is extremely important for the healthy and full development of the baby.
- Calculate the amount of formula to be prepared based on the baby's weight. It is body weight, and not the age of the crumbs, that is the main indicator when calculating the daily nutritional intake. You can find out the required volume of the mixture for feeding either at a pediatrician’s appointment, or on your own (it is recommended to use Maslov’s caloric method when calculating).
- Observe the breaks between feedings. During the day they should be 3.5 hours, at night - 6. Try not to break the schedule.
- Give your child water. Supplementation with water is a necessity for artificial feeding. Water should be given somewhere in the middle of the interval between feedings or 10-15 minutes after it.
 Avoid supplementation before meals.
Avoid supplementation before meals.
Major mistakes in artificial feeding
Overfeeding. The desire to feed the child is understandable, but in the case of mixtures, feeding must be approached strictly. On artificial feeding, the child is normally gaining weight very well. Excess body weight is an additional burden on the body and health problems. Even an adult can find it difficult to cope with problems from being overweight. What to say about the tiny weak body of a newborn? Follow the diet and control the daily milk intake. Fortunately, you can always see how much the child ate.
Unreasonable replacement of the mixture. If the child eats the current mixture well, then it is not necessary to change it. The baby will have to go through a difficult period of adaptation again, and it’s not a fact that his body will accept new food just as well.
Use of old mix. The child's food must be fresh. If the child has not finished eating, then literally after half an hour the milk can only be poured out.


 This will require pasteurized milk 2.5% fat and sourdough. After the milk turns sour, it is placed in a water bath and heated over low heat until the whey leaves. Then it remains only to drain the liquid through a colander or gauze and grind the resulting curd to make it more tender.
This will require pasteurized milk 2.5% fat and sourdough. After the milk turns sour, it is placed in a water bath and heated over low heat until the whey leaves. Then it remains only to drain the liquid through a colander or gauze and grind the resulting curd to make it more tender.