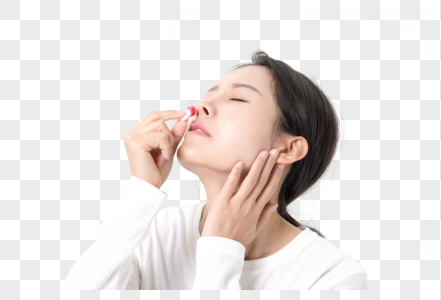
Signs of nose bleeding
Nosebleeds - Better Health Channel
Summary
Read the full fact sheet- Bleeding from the nose is common in children and is usually not a sign of any underlying problem.
- First aid treatment includes pinching the nostrils until the bleeding stops.
- If the nosebleed won’t stop, see a doctor or go to a hospital emergency department.
A nosebleed happens when one of the blood vessels in the lining of the nose bursts. Nosebleeds may be caused by infection, injury, allergic reaction, nose picking or an object being pushed into the nostril. Another name for nosebleed is epistaxis.
Bleeding from the nose is common in children and is usually not serious. Seek medical attention if nosebleeds are severe, frequent or prolonged.
Blood vessels in the nose are fragile
The small blood vessels in the septum (the firm tissue between the nostrils, which divides the nose into two halves) are fragile and can burst fairly easily, causing a nose bleed.
In children, the nose tends to bleed from only one side (unilateral).
Children usually grow out of the condition. If the bleeding is very heavy, prolonged or does not stop with first aid measures, take your child to a doctor or a hospital emergency department.
Symptoms of nosebleeds
The signs and symptoms of a nosebleed include:
- bleeding from either or both nostrils
- a sensation of flowing liquid at the back of the throat
- the urge to swallow frequently.
Causes of nosebleeds
A nosebleed can be caused by a range of factors, including:
- fragile blood vessels that bleed easily, perhaps in warm dry air or after exercise
- an infection of the nose lining, sinuses or adenoids
- an allergy that causes hay fever or coughing
- bumps or falls
- an object that has been pushed up the nostril
- nose picking
- occasionally, a bleeding or clotting problem.
First aid management for nosebleeds
To manage a nosebleed include:
- Reassure the person, especially children, as crying increases blood flow.
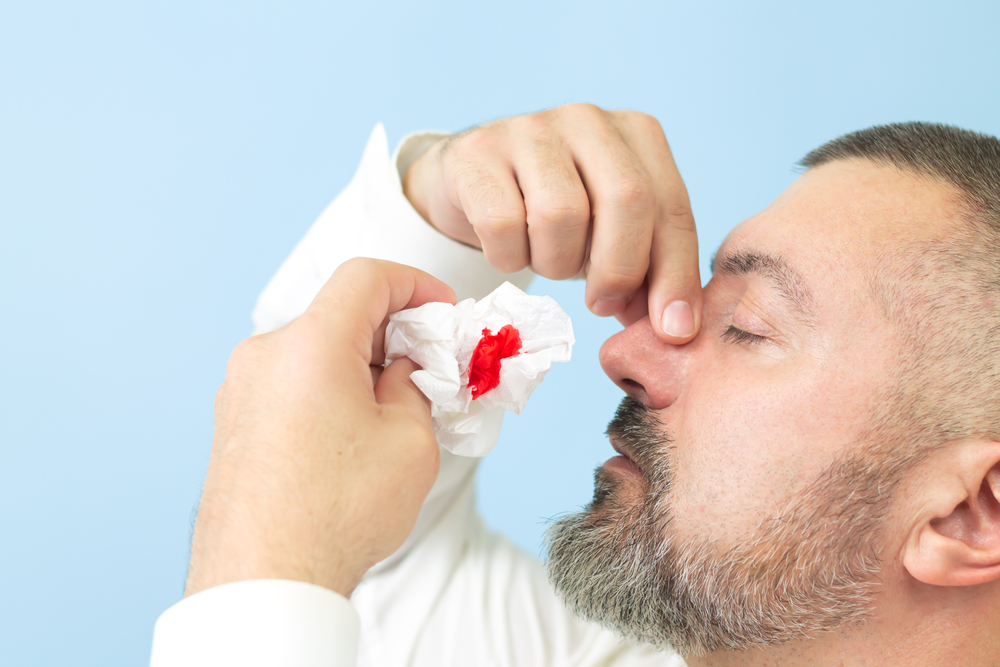

- Sit the person up straight and drop their head slightly forward.
- Apply finger and thumb pressure on the soft part of nostrils below the bridge of the nose for at least 10 minutes.
- Encourage the person to breathe through their mouth while their nostrils are pinched.
- Loosen tight clothing around the neck.
- Place a cold cloth or cold pack over the person’s forehead and one around the neck, especially around the sides of the neck.
- After 10 minutes, release the pressure on the nostrils and check to see if the bleeding has stopped.
- If bleeding persist, seek medical aid.
- Tell the person not to sniff or blow their nose for at least 15 minutes and not to pick their nose for the rest of the day. (Having a nose full of clotted blood is unpleasant and children in particular may find it difficult to avoid sniffing or nose blowing for a few hours. Fifteen minutes will at least give some time for the clot to stabilise.)
You should go to the doctor or a hospital emergency department if the bleeding does not stop after simple first aid management. It is important to find and treat the cause of ongoing bleeding.
It is important to find and treat the cause of ongoing bleeding.
Frequent nosebleeds
If your child keeps having nosebleeds, see your doctor as the cause needs to be understood and treatment commenced. For example, if the cause is an ongoing infection, your doctor may prescribe an antibiotic ointment or medicine. Very occasionally, a child loses so much blood that this causes other health problems, such as anaemia.
Where to get help
- Your doctor
- NURSE-ON-CALL Tel. 1300 606 024 – for expert health information and advice (24 hours, 7 days)
- The nearest hospital emergency department
Things to remember
- Bleeding from the nose is common in children and is usually not a sign of any underlying problem.
- First aid treatment includes pinching the nostrils until the bleeding stops.
- If the nosebleed won’t stop, see a doctor or go to a hospital emergency department.
- Australian First Aid, 2012, 4th Edition, St John Ambulance Australia.
This page has been produced in consultation with and approved by:
Nosebleed causes & treatments | NHS inform
Most nosebleeds can be stopped without the need for medical attention, but occasionally further treatment may be required.
What to do
To stop a nosebleed:
- sit down and firmly pinch the soft part of your nose, just above your nostrils, for at least 10-15 minutes
- lean forward and breathe through your mouth – this will drain blood into your nose instead of down the back of your throat
- place an ice pack or bag of frozen vegetables covered by a towel on the bridge of your nose
- stay upright, rather than lying down as this reduces the blood pressure in the blood vessels of your nose and will discourage further bleeding
If the bleeding eventually stops, you won't usually need to seek medical advice. However, you should still follow the recovery advice outlined below.
When to seek medical advice
Contact your GP or call the NHS 111 service if:
- you're taking a blood-thinning medicine (anticoagulant) such as warfarin or have a clotting disorder such as haemophilia and the bleeding doesn't stop
- you have symptoms of anaemia such as heart palpitations, shortness of breath and a pale complexion
- a child under two years of age has a nosebleed (this is rare and there's a chance it's caused by something serious)
- you have nosebleeds that come and go regularly
Ask someone to drive you to your nearest accident and emergency (A&E) department or call 999 for an ambulance if:
- the bleeding continues for longer than 20 minutes
- the bleeding is heavy and you've lost a lot of blood
- you're having difficulty breathing
- you swallow a large amount of blood that makes you vomit
- the nosebleed developed after a serious injury, such as a car crash
Find your nearest A&E department
Medical treatment
If you see your GP or go to hospital with a nosebleed, you will be assessed to determine how serious your condition is and what's likely to have caused it. This may involve looking inside your nose, measuring your pulse and blood pressure, carrying out blood tests and asking about any other symptoms you have.
This may involve looking inside your nose, measuring your pulse and blood pressure, carrying out blood tests and asking about any other symptoms you have.
The main treatments that your GP or hospital doctor may use to stop your nose bleeding are described below.
Antibiotic ointment
Your doctor may prescribe an antibiotic ointment. This should be applied by squeezing a pea-sized amount onto the front of the nasal septum (wall between the nostrils).
This can reduce the inflammation and crusting in the nose and reduce the severity and frequency of nosebleeds.
Antibiotic ointment is particularly effective in children.
Cautery
If your doctor is able to identify exactly where the bleeding is coming from, they may carry out a minor procedure to seal the bleeding blood vessel by cauterising (burning) it.
This is normally done using a stick of a chemical called silver nitrate. A local anaesthetic will be sprayed into your nose to numb it and the silver nitrate stick will be held against the bleeding point for up to 10 seconds.
Nasal packing
If cautery is ineffective or your doctor is unable to identify a specific bleeding point, they may recommend packing your nose with gauze or special nasal sponges to stop the flow of blood by applying pressure to the source of the bleeding.
Packing will usually be carried out after local anaesthetic has been sprayed into your nose. The gauze or sponges often need to be left in place for 24-48 hours before being removed by a health professional. You'll usually need to be admitted to hospital to be monitored during this time.
Further treatment
If the treatments above don't help, you may be referred to a hospital specialist such as an ear, nose and throat (ENT) doctor for further treatment.
Additional treatments that may be used in hospital include:
- electrocautery – an electric current running through a wire is used to cauterise the blood vessel where the bleeding is coming from
- blood transfusions – a procedure to replace the blood you've lost
- tranexamic acid – medication that can reduce bleeding by helping your blood to clot
- packing under anaesthetic – your nose is carefully packed with gauze while you are unconscious from general anaesthetic
- ligation – an operation using small instruments to tie off bleeding blood vessels in the back of your nose
Recovery
Once your nose has stopped bleeding, you should follow the advice below to reduce the risk of your nose bleeding again and to stop you picking up an infection:
- avoid blowing or picking your nose, heavy lifting, strenuous exercise, lying flat, and drinking alcohol or hot drinks for 24 hours
- don't remove any crusts that form inside your nose – these may be unpleasant, but they're a useful part of the healing process
- if you need to sneeze, try to sneeze with your mouth open to reduce the pressure in your nose
- avoid people with coughs and colds
If you see a GP or a hospital doctor about your nosebleed, they may give you a prescription for an antiseptic nasal cream once the bleeding stops. This should be applied to the inside of your nostrils several times a day for up to two weeks to help prevent further bleeding.
This should be applied to the inside of your nostrils several times a day for up to two weeks to help prevent further bleeding.
If your nose does start to bleed again, follow the first aid advice above and seek medical advice if the bleeding doesn't stop.
Frequent nosebleeds: what are the causes and what to do?
Other related articles: otolaryngologist, therapist
-
"Sedentary" diseases
-
10 examinations
-
COVID-19
-
adenovirus infection
-
Adenoids
-
Angina
-
Anemia
-
Meniere's disease
-
Bronchitis
-
Bronchoscopy
-
Types of ELI tests
-
All about flu
-
Sinusitis
-
Nasal hemangioma
-
Hypertension
-
Flu and SARS
-
flu during pregnancy
-
Diarrhea (diarrhea)
-
Eustachitis
-
iron deficiency
-
Ear diseases
-
immunity to coronavirus
-
Nose curvature
-
Nosebleeds
-
Nosebleed
-
Laryngitis
-
Lungs after COVID
-
Treatment of adenoids
-
Lymphadenitis
-
ENT diseases in children
-
mastoiditis
-
Medical examinations
-
Uric acid
-
Runny nose
-
Nasal septum
-
Surveys in autumn
-
Complications after angina
-
Pneumonia
-
Defeat the Flu
-
Items in the nose
-
Taking antibiotics
-
Signs of COVID-19
-
Application of ozone
-
Washing lacunae
-
Rheumatism
-
Sinusitis
-
Vaccine testing
-
Tonsillitis
-
Tuberculosis
-
Sulfur Plug Removal
-
Tick bite
-
Bed bug bites
-
Pharyngitis
-
ferritin
-
Chronic fatigue
-
nasal endoscopy
Bleeding from the nose due to trauma usually does not raise questions, but if it occurs without any mechanical impact, and even more often, this should alert
What can be the causes of frequent nosebleeds and how they can be cured - tells otorhinolaryngologist of the clinic "Semeynaya" Olga Pavlovna Soloshenko.
If the bleeding does not occur due to injuries and recurs periodically, it is better not to delay the visit to the ENT. After all, bleeding can be anterior and posterior - the second happens less often, but it is much more dangerous. With anterior bleeding, blood only goes out, with posterior bleeding, it flows into the mouth or stomach along the back of the pharynx. Posterior is usually caused by damage to larger vessels that are located deep in the nasal cavity. It is very difficult to stop back bleeding without a doctor.
Causes of nosebleeds:
- Injuries. Injury to the nose is often fraught with cartilage fractures. As a rule, this is accompanied by swelling and pain.
- High blood pressure. Very common cause. Due to a sharp jump, the walls of the capillaries easily burst. Pressure rises due to overload, as well as in the presence of diseases of the cardiovascular system.
- Sunstroke and any sudden increase in body temperature.

- Overwork.
- Hormonal changes. Bleeding may occur in women during the months of pregnancy or menopause, and in adolescents at puberty.
- Dry air. It causes dryness of the mucous membrane.
- Poor blood clotting.
- ENT diseases. Sinusitis, sinusitis, rhinitis - all of them can cause bleeding, especially with the constant use of drugs that thin the mucous membrane.
- Vascular problems. Even infectious diseases such as chickenpox, measles, influenza, etc. can lead to them.
- Polyps, adenoids, tumors. In addition to occasional bleeding, they simply make breathing difficult.
- Foreign body - can damage the mucous membranes and blood vessels.
- Deficiency of vitamins K, C and calcium.
First aid rules for nosebleeds:
- Lie down (or position the patient) with legs down
- Tilt head forward
- Place a cold compress on the bridge of the nose for a few minutes
- Cover nose with hand or insert swab pre-soaked in hydrogen peroxide
- Drops for vasoconstriction can be instilled
Attention, this must not be done!
- Throwing the head back (contrary to popular belief) - blood can enter the respiratory tract
- Blow your nose - so as not to increase bleeding without it.

Which cases require an immediate call to a doctor and an ambulance
- In case of loss of consciousness
- For excessive bleeding
- Blood flows with clear fluid (this may occur after trauma and indicate a skull fracture)
- If vomiting of blood occurs (possibly indicating bleeding in the esophagus or stomach)
- Foamy blood (possible with lung injury)
- In a patient with diabetes mellitus
- If the patient is known to have poor blood clotting
Treatment
Treatment of bleeding is carried out in a complex manner. Often, an otorhinolaryngologist works in conjunction with a general practitioner, neurologist, endocrinologist, and hematologist.
At the first examination, the doctor determines the type of bleeding - anterior or posterior. Also, the patient is required to pass a general blood test and a coagulogram (analysis of blood coagulation indicators). In addition, it is important to measure the pressure, because if it is above the norm (the absolute norm is 120/80 mm Hg, but these figures change depending on age), the blood will not stop until it decreases.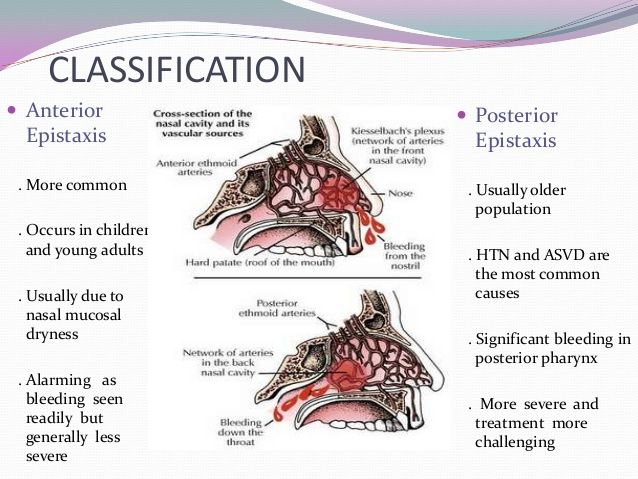
In case of significant blood loss, the patient may be left in the hospital.
As a treatment for bleeding, it is possible to pack the nasal cavity, cauterize vessels (with drugs, laser, ultrasound, etc.), remove polyps. If there is no result, surgical ligation of vessels in problem areas is performed. In addition, drugs are prescribed that increase blood clotting.
Prevention
- Taking drugs that strengthen the walls of blood vessels
- Nutrition rich in vitamins and minerals
- Air humidification during the heating season
- Injury Prevention
- Monitoring blood pressure and taking medications to lower it
Nosebleeds are not only unpleasant, but also dangerous. Therefore, as soon as it begins to bother you regularly, it is important to see a doctor as soon as possible. It is better to exclude all the most terrible causes of such a phenomenon as soon as possible and then it is already calmer to engage in further treatment.
Make an appointment with an otolaryngologist
Be sure to consult a qualified specialist in the field of nose diseases at the Semeynaya clinic.
For prices for pediatric appointments or other questions, follow the link below
Tags OtolaryngologistTherapist
Epistaxis - causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment
Please, specify the information by phone. +7(925)793-45-41
-
Epistaxis is the outflow of blood from the nasal cavity. Blood can either flow out through the nostrils or drain inward along the back of the throat. Usually, such bleeding stops on its own, as the damaged vessels are of small diameter. Very rarely, this condition requires medical attention.
Causes
The causes of bleeding are divided into local and general. Local include:
- Head and/or nose injuries.

- Infectious diseases of the nasopharynx, larynx and trachea.
- Operations on the nasal cavity.
- Neoplasms in the nose.
- Inhalation of irritants (hot vapour, acid and alkali fumes, gas).
- Increased air dryness.
Common causes:
- Sudden increase/decrease in blood pressure.
- Hereditary or acquired bleeding disorder.
- Increased vascular fragility.
- Willebrand-Diana disease (hereditary blood disorder).
- Infectious diseases, especially influenza.
Symptoms
The most obvious symptom of anterior bleeding is bleeding from one or both nostrils, in streams or drops. Posterior nosebleeds do not manifest themselves in any way until the blood enters the gastrointestinal tract. Then patients experience nausea, vomiting (coffee grounds), hemoptysis, tarry stools.
Clinical manifestations depend on the amount of blood loss. If it is only a few milliliters, the person's condition will not change, but people with hemophobia may faint.
 If the bleeding is prolonged and continues, the person complains of dizziness, flies before the eyes, weakness, tinnitus, tachycardia. At the same time, his skin is pale, covered with sweat.
If the bleeding is prolonged and continues, the person complains of dizziness, flies before the eyes, weakness, tinnitus, tachycardia. At the same time, his skin is pale, covered with sweat. Diagnosis
A surgeon, otorhinolaryngologist or therapist listens to the patient's complaints, collects an anamnesis and necessarily specifies the presence of chronic diseases, such as arterial hypertension, pathology of the liver, blood vessels, hemophilia. In addition, it is important to know if the patient has had recent surgeries and is taking any medications. Be sure to find out how often nosebleeds recur.
After the interview, the doctor examines the nasal cavity, mouth and throat, measures blood pressure. Perform a complete blood count to evaluate the number of red blood cells, platelets, hemoglobin and color index. A coagulogram and a biochemical blood test are also prescribed to check liver function.
Treatment
A person can stop nosebleeds on their own.
 To do this, it is enough to tilt your head forward and strongly press the wings of the nose against the septum for 5 minutes. Contrary to a well-known myth, it is forbidden to throw your head back, as blood will run into your throat.
To do this, it is enough to tilt your head forward and strongly press the wings of the nose against the septum for 5 minutes. Contrary to a well-known myth, it is forbidden to throw your head back, as blood will run into your throat. First aid:
- pressing the wings of the nose;
- cold compress on the nose;
- insertion into the nostril of a tampon soaked in adrenaline;
Mechanical ways to stop bleeding from the nose:
- anterior and posterior tamponade;
- cauterization of a bleeding vessel;
- hemostatic therapy;
- surgical methods: flashing of vessels, their embolization, ligation of arteries.Preventive measures include:
- Air humidification.
- Wetting of the nasal mucosa.
- Avoidance of head injury.
- Prevention of SARS.
- Blood pressure control.
- Head and/or nose injuries.
Licenses
Reviews
Your name:
Phone number:*
* I agree with the rules for processing personal data set out in the privacy policy
Fields marked with "*" are mandatory.
×
Ask a doctor a question
Your name
Your e-mail "*"
Message
for filling.
×
Order hospitalization
Your name:
Phone number:*
Comment:
* I agree with the rules for processing personal data set out in the privacy policy
Fields marked with "*" are required.
×
leave a review
×
Send a letter
Your name
Your e-mail
Topic
Message
0366
×
Take the first step - make an appointment
Leave your contacts and we will contact you as soon as possible.
Your name:
Phone number or e-mail:*
Select date:
Note:
required to fill out.