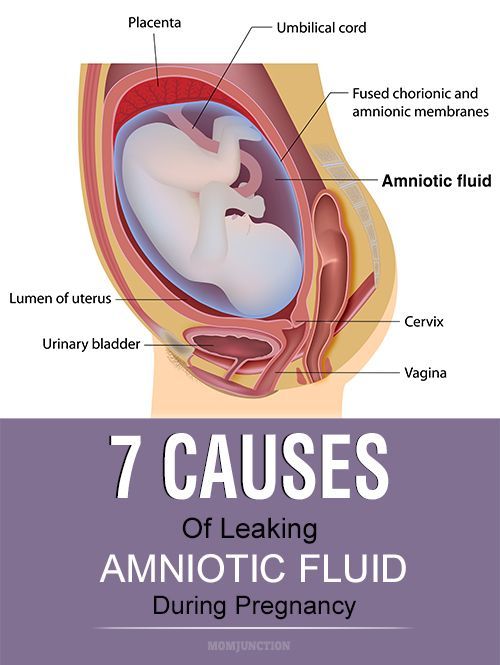
Sensitive vagina during pregnancy
10 Weird Ways Pregnancy Changes the Vagina
If you’re pregnant for the first time, you might feel a little worried. After all, pushing a baby through your lady bits kind of seems like squeezing a bowling ball through the eye of a needle.
But don’t worry — women have been doing this for literally thousands of years, and pregnancy will get your vagina delivery-ready by your due date. But what you may not realize is that to get there, there are many changes in store down below.
Those changes start earlier — a lot earlier, in fact.
So we’d like to introduce you to your changing anatomy and tell you what else you might expect over the next 9 months. This is your vagina on pregnancy:
When you think of a certain body part turning blue, you generally don’t think of a vagina — but that’s exactly what can happen when you’re newly pregnant.
Known as Chadwick’s sign, it’s caused by increased blood flow down below. Unless you’re literally looking for it, you may not even know that it’s happened since it doesn’t cause any discomfort. Regardless, the blue or purple hue should disappear shortly after you give birth.
This change of color in the vagina, labia, and cervix can occur as early as four weeks, making it one of the first indications that you could be pregnant.
During pregnancy, your body’s blood volume can increase by as much as 50 percent, and some of that extra blood heads downtown, making your nether regions swollen and extra sensitive.
Add higher-than-normal levels of oxytocin, estrogen, and progesterone to the equation and that just might translate into heightened arousal and bigger and better orgasms, as well as increased desire.
This can happen in the first and second trimesters, so remember to communicate any changes to your partner! Because on the flip side, this blood rush could lead to sensitivity and discomfort.
It’s not uncommon to develop these telltale bulging, purple blood vessels on your legs during pregnancy because of the added pressure and weight of your belly. But believe it or not, they can appear on your privatest of private parts as well.
But believe it or not, they can appear on your privatest of private parts as well.
According to one recent study, around 18 to 22 percent of pregnant women will develop this medical condition, usually in the second or third trimester. While not everyone will experience discomfort or even know they have this problem, some people will feel swelling, pressure, or pain.
The good news is that most vulvar varicosities will disappear a few weeks after childbirth.
To tackle varicose veins on the vagina, try:
- wearing special pregnancy undergarments with compression features
- using cool compresses on the afflicted area
- avoiding sitting or standing for too long
- increasing your water intake
- elevating your legs and hips when possible
Share on Pinterest
Translation: You’re likely going to smell and taste different — so heads up when your significant other is down under. That taste may be more “metallic or salty,” according to The Journal of Perinatal Education.
A change or increase in odor — while likely occurring because of your fluctuating hormones — may also seem more pungent to you because your olfactory senses are also heightened during pregnancy.
Still, if the smell seems overpowering or foul, or comes with burning or itching, you could have an infection and should definitely talk to your doctor.
And chances are no one told you this can happen. So when you’re actually experiencing it, you might end up calling your doctor in a panic because you legit think you’re dying.
But generally speaking, it’s nothing to worry about and is a pregnancy side effect known as “lightning crotch.” (Yep, really.)
It’s caused by the baby pressing on certain nerves or because of cervical changes, and it often occurs in the third trimester when you’ve been sitting or lying in the same spot for a while and then get up.
Do what it takes to get yourself comfortable, if you feel this happening.
Methods to mitigate the pain:
- staying active
- limiting movements that involve bending or lifting
- trying a pregnancy massage
- swimming
- wearing a support brace
First up: yeast infections. This proliferates during pregnancy, thanks to increased estrogen levels and changes to your vagina’s pH levels.
This proliferates during pregnancy, thanks to increased estrogen levels and changes to your vagina’s pH levels.
Topical antifungals are preferred as a first line of defense, especially in light of a recent study that linked the common oral medication fluconazole (Diflucan) to a possible increased likelihood of miscarriage.
You may want to look into alternative remedies and lifestyle changes before trying any oral medication.
The other problem you might be facing throughout your pregnancy? Urinary tract infections (UTIs) — which aren’t only uncomfortable but also achieve the amazing feat of making you feel like you have to pee even more than you already do.
While a pregnant person’s odds of developing a UTI is only slightly higher than when not pregnant, the risk of having it progress to a kidney infection rises by a whopping 40 percent.
That, in turn, may lead to an increased risk of preeclampsia, preterm birth, and low birth weight.
Stock up on panty liners. Shortly after conception and often before you even realize you’re pregnant, your private parts go into hormonal overdrive, producing more discharge to keep your cervix protected and to help prevent infections.
Shortly after conception and often before you even realize you’re pregnant, your private parts go into hormonal overdrive, producing more discharge to keep your cervix protected and to help prevent infections.
The technical term for this discharge is leukorrhea, and it should be relatively thin in consistency, have a milky color, and smell mild — similar to your normal discharge, only heavier, more frequent, and stickier.
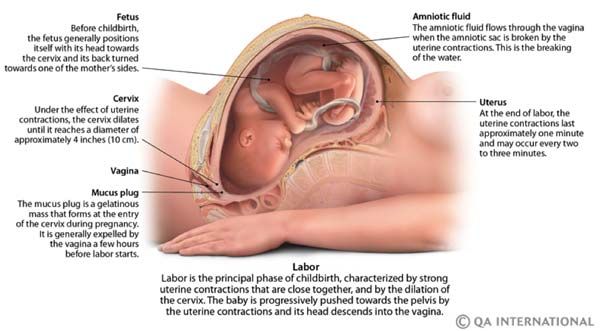
If, however, it takes on a yellow or green color, looks thick, or smells foul, you may have an infection and need antibiotics. Later in pregnancy, you may also lose the gooey mucus plug on your cervix, which indicates that labor is coming.
Even if you like giving cutesy nicknames to your private parts, Itchy and Scratchy probably isn’t what you had in mind. Unfortunately, itchiness down there is a common pregnancy symptom that can happen at any time.
The cause? The increased discharge and pH changes mentioned above, which could irritate sensitive skin, or a yeast infection.
Talk to your doctor if this annoyance doesn’t go away or is accompanied by other troubling symptoms, such as abnormal discharge, ulcers, or a burning sensation.
Share on Pinterest
Yep, your vagina is loaded with bacteria, which sounds unwanted but is actually completely normal. Starting in your first trimester of pregnancy, though, that bacterial environment can undergo changes.
Why does that matter as long as it doesn’t cause an infection? Because, according to multiple studies, people who are pregnant with lower vaginal levels of Lactobacillus have a greater likelihood of delivering early.
Someday, measuring vaginal bacteria will help determine whether the individual is at risk for preterm labor, but for now, more research is still needed.
Where, exactly? The perineum, the area between your vagina and anus that often remains tight and, as a result, tears during childbirth.
The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists says that between 53 and 79 percent of those going through labor experience some sort of vaginal tearing, while other medical professionals put that number closer to 90 percent for first-time moms.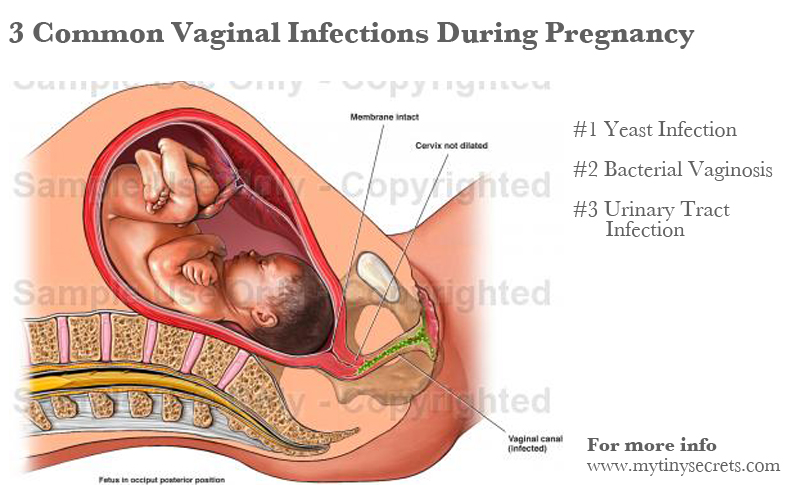
And according to one 2014 study, those who experience a severe tear during their first birth are 5 times more likely to experience another in subsequent births.
But there’s a potential solution: Massaging the area, especially in the last month of pregnancy, can cut down on your risk of experiencing this painful problem.
These vaginal changes may seem strange, but most of them are completely normal. Try to relax a little and remember that these pregnancy symptoms often reverse after you give birth.
Still, if any of these symptoms are getting in the way of your day to day (or do end up permanent), don’t hesitate to mention it to your doctor. They’ll be able to recommend treatments or alternatives.
After all, once you’re welcoming your gorgeous newborn into the world, there will be plenty of other life changes to keep your mind busy.
Share on Pinterest
Dawn Yanek lives in New York with her husband and their two very sweet, slightly crazy kids. Before becoming a mom, she was a magazine editor who regularly appeared on TV to discuss celebrity news, fashion, relationships, and pop culture. These days, she writes about the very real, relatable, and practical sides of parenting at Momsanity. You can also find her on Facebook, Twitter, and Pinterest.
Before becoming a mom, she was a magazine editor who regularly appeared on TV to discuss celebrity news, fashion, relationships, and pop culture. These days, she writes about the very real, relatable, and practical sides of parenting at Momsanity. You can also find her on Facebook, Twitter, and Pinterest.
Why It Happens and What to Do About It
Causes of vaginal pain during pregnancy
A growing fetus, dilation of the cervix, increased blood flow to the vagina, and fungal infections can all contribute to vaginal pain during pregnancy.
Growing fetus
As your baby and your uterus grow, your pelvic ligaments stretch to accommodate the extra weight. When ligaments and vaginal muscles are overstretched, it can cause a sharp, shooting pain. If you’re already feeling vaginal pain in the first trimester, though, be sure to consult your doctor.
Dilation of the cervix
Dilation refers to the eventual opening of your cervix. Occasionally, cervical dilation is to blame for sharp, shooting vaginal pains in the final stages of pregnancy. This is a perfectly normal process that helps the body prepare for labor and delivery. But should the pain present in the lower abdomen, consult a doctor right away.
Occasionally, cervical dilation is to blame for sharp, shooting vaginal pains in the final stages of pregnancy. This is a perfectly normal process that helps the body prepare for labor and delivery. But should the pain present in the lower abdomen, consult a doctor right away.
Take a quiz
Find out what you can do with our Health Assistant
During labor, uterine contractions open the cervix while the baby moves into the proper position. Effacement (when the cervix stretches and thins) and dilation allow the baby to pass through the birthing canal. This happens near the end of the third trimester, but varies with each individual. Some people start to efface and dilate over several weeks, and others shortly before the baby is born. First-time moms might not dilate until they’re in actual labor. An OB-GYN may check the cervix manually to monitor progress as part of prenatal care.
Increased blood flow
Increased blood flow to the vagina, accompanied by heavy vaginal discharge, are normal during pregnancy. Higher levels of estrogen and progesterone produce these changes. The increased overall volume of blood can cause vaginal discomfort or pain.
Higher levels of estrogen and progesterone produce these changes. The increased overall volume of blood can cause vaginal discomfort or pain.
Fungal infections
If you’re experiencing vaginal pain during pregnancy and suspect it’s the result of a fungal infection, talk to your physician. The most common infection is candida (yeast infection), which is common during pregnancy because of compromised immunity.
During pregnancy, recovering from candida might take longer than usual, as healthcare providers hesitate to prescribe cortisone medications. Consider treating it with an OTC antifungal cream or suppositories. Just remember to discuss this with your doctor first.
Lightning pain
Sometimes pain originating in the pelvic ligaments as they stretch to accommodate a baby can cause startling pain. It can be shocking enough to make some people think they’ve gone into labor. This is called lightning pain.
Some women naturally produce more relaxin and progesterone hormones, encouraging extra stretching and loosening of the ligaments. When round ligaments are stretched too quickly, it produces a sensation similar to that of lightning shooting through your crotch.
When round ligaments are stretched too quickly, it produces a sensation similar to that of lightning shooting through your crotch.
In certain cases, this does actually signal the start of labor. Constant back or lightning pain, contractions, or fluid leakage are all signs that the baby could be on their way. If you observe any of the above symptoms prior to 37 weeks, seek medical attention.
Ectopic pregnancy
Another potential cause of vaginal pain is ectopic pregnancy. This is when the fertilized egg implants anywhere other than the uterus. Most often, the fertilized egg will attach inside a uterine tube.
Ectopic pregnancies cannot be carried to term. The fertilized egg is unable to survive outside of the uterus. In certain cases, an ectopic pregnancy may cause the uterine tube to rupture, resulting in vaginal pain, bleeding, lightheadedness, and nausea. Seek medical help if you show any signs of ectopic pregnancy.
How to cope with vaginal pain during pregnancy
Vaginal pain occurs at some point during nearly every pregnancy. Besides pain medications (which should be approved by a doctor), there are a few different ways to find temporary relief:
Besides pain medications (which should be approved by a doctor), there are a few different ways to find temporary relief:
- Lying on the left side to improve blood circulation and reduce vaginal pressure
- Sitting elevated feet, which could also decrease pressure levels and alleviate vaginal pain
- Elevating the hips to lessen cervical pain during pregnancy (which usually aggravates existing vaginal discomfort)
- Taking warm baths to soothe and relax achy muscles throughout the body
- Engaging in activities such as yoga or swimming to help boost blood circulation and strengthen muscles.
- Getting a doctor-approved pelvic massage that can simultaneously offer much needed pelvic support and a reprieve from vaginal pain during pregnancy.
When to see a doctor
Vaginal pain is a normal part of pregnancy for most people. Although a few minor lifestyle changes can help, a doctor is the best source of guidance, especially in later trimesters.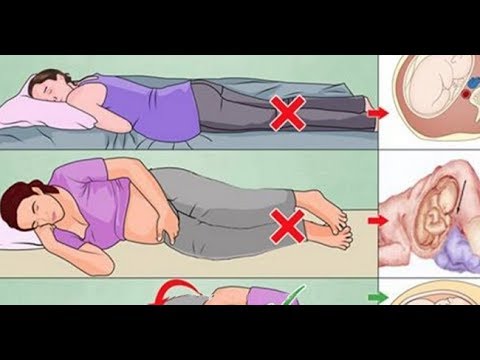
Additionally, there are various options available for treating vaginal pregnancy pain that you can research. Just remember that certain conditions, like infection or irregularities in the cervix, could potentially lead to miscarriage. That’s why it’s always a good idea to speak with a doctor about any questions, concerns, or possible treatments first.
Changes in a woman's body during pregnancy
From the very first days of pregnancy, the body of a pregnant woman undergoes profound transformations. These transformations are the result of the coordinated work of almost all body systems, as well as the result of the interaction of the mother's body with the child's body.
During pregnancy, many internal organs undergo significant restructuring. These changes are adaptive in nature, and, in most cases, are short-lived and completely disappear after childbirth. Consider the changes in the basic systems of the vital activity of a woman's body during pregnancy. nine0003
nine0003
The respiratory system during pregnancy works hard. The respiratory rate increases. This is due to an increase in the need of the mother and fetus for oxygen, as well as in the limitation of the respiratory movements of the diaphragm due to an increase in the size of the uterus, which occupies a significant space of the abdominal cavity.
Cardio The mother's vascular system has to pump more blood during pregnancy to ensure an adequate supply of nutrients and oxygen to the fetus. In this regard, during pregnancy, the thickness and strength of the heart muscles increase, the pulse and the amount of blood pumped by the heart in one minute increase. In addition, the volume of circulating blood increases. In some cases, blood pressure increases. The tone of the blood vessels during pregnancy decreases, which creates favorable conditions for enhanced
to supply tissues with nutrients and oxygen. During pregnancy, the network of vessels of the uterus, vagina, and mammary glands decreases sharply.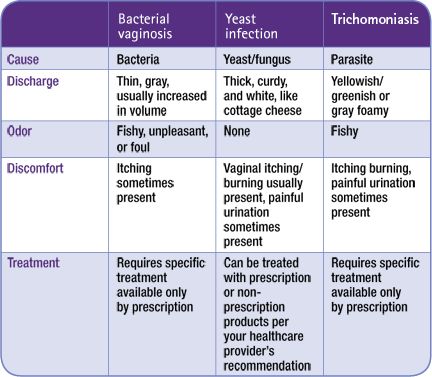 On the external genitalia, in the vagina, lower extremities, there is often an expansion of the veins, sometimes the formation of varicose veins. Heart rate decreases in the second half of pregnancy. It is generally accepted that the rise in blood pressure over 120-130 and a decrease to 100 mm Hg. signal the occurrence of pregnancy complications. But it is important to have data on the initial level of blood pressure. and changes in the blood system. During pregnancy, blood formation increases, the number of red blood cells, hemoglobin, plasma and bcc increases. BCC by the end of pregnancy increases by 30-40%, and erythrocytes by 15-20%. Many healthy pregnant women have a slight leukocytosis. ESR during pregnancy increases to 30-40. Changes occur in the coagulation system that contribute to hemostasis and prevent significant blood loss during childbirth or placental abruption and in the early postpartum period. nine0003
On the external genitalia, in the vagina, lower extremities, there is often an expansion of the veins, sometimes the formation of varicose veins. Heart rate decreases in the second half of pregnancy. It is generally accepted that the rise in blood pressure over 120-130 and a decrease to 100 mm Hg. signal the occurrence of pregnancy complications. But it is important to have data on the initial level of blood pressure. and changes in the blood system. During pregnancy, blood formation increases, the number of red blood cells, hemoglobin, plasma and bcc increases. BCC by the end of pregnancy increases by 30-40%, and erythrocytes by 15-20%. Many healthy pregnant women have a slight leukocytosis. ESR during pregnancy increases to 30-40. Changes occur in the coagulation system that contribute to hemostasis and prevent significant blood loss during childbirth or placental abruption and in the early postpartum period. nine0003
Kidneys work hard during pregnancy. They secrete decay products of substances from the body of the mother and fetus (the waste products of the fetus pass through the placenta into the mother's blood).
They secrete decay products of substances from the body of the mother and fetus (the waste products of the fetus pass through the placenta into the mother's blood).
Changes in the digestive system are represented by increased appetite (in most cases), craving for salty and sour foods. In some cases, there is an aversion to certain foods or dishes that were well tolerated before the onset of pregnancy. Due to the increased tone of the vagus nerve, constipation may occur. nine0003
The most significant changes, however, occur in the genitals of pregnant women. These changes prepare the woman's reproductive system for childbirth and breastfeeding.
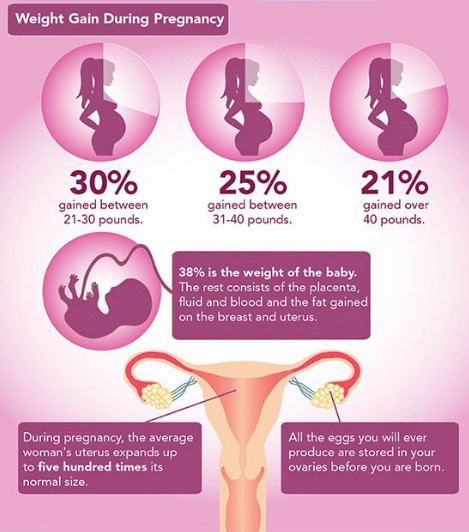
The uterus of a pregnant woman increases significantly in size. Its mass increases from 50 g - at the beginning of pregnancy to 1200 g - at the end of pregnancy. The volume of the uterine cavity by the end of pregnancy increases by more than 500 times! The blood supply to the uterus is greatly increased. In the walls of the uterus, the number of muscle fibers increases. The cervix is filled with thick mucus that clogs the cavity of the cervical canal. The fallopian tubes and ovaries also increase in size. In one of the ovaries, there is a "corpus luteum of pregnancy" - a place for the synthesis of hormones that support pregnancy. nine0003
In the walls of the uterus, the number of muscle fibers increases. The cervix is filled with thick mucus that clogs the cavity of the cervical canal. The fallopian tubes and ovaries also increase in size. In one of the ovaries, there is a "corpus luteum of pregnancy" - a place for the synthesis of hormones that support pregnancy. nine0003
The walls of the vagina will loosen and become more elastic.
External genitalia (labia minor and major) also increase in size and become more elastic. The tissues of the perineum are loosened. In addition, there is an increase in mobility in the joints of the pelvis and a divergence of the pubic bones. The changes in the genital tract described above are of extremely important physiological significance for childbirth. Loosening the walls, increasing the mobility and elasticity of the genital tract increases their throughput and facilitates the movement of the fetus through them during childbirth. nine0003
Skin in the genital area and in the midline of the abdomen usually becomes darker in color. Sometimes "stretch marks" form on the skin of the lateral parts of the abdomen, which turn into whitish stripes after childbirth.
Sometimes "stretch marks" form on the skin of the lateral parts of the abdomen, which turn into whitish stripes after childbirth.
Mammary glands increase in size, become more elastic, tense. When pressing on the nipple, colostrum (first milk) is released. Changes of the bone skeleton and muscular system . An increase in the concentration of the hormones relaxin and progesterone in the blood contributes to the leaching of calcium from the skeletal system. This accomplishes two goals. On the one hand, this helps to reduce the rigidity of the joints between the pelvic bones (especially the pubic joint) and increase the elasticity of the pelvic ring. Increasing the elasticity of the pelvis is of great importance in increasing the diameter of the internal bone ring in the first stage of labor and further reducing the resistance of the birth tract to fetal movement in the second stage of labor. Secondly, calcium, washed out of the mother's skeletal system, is used to build the skeleton of the fetus. nine0003
nine0003
It should be noted that calcium compounds are washed out of all bones of the maternal skeleton (including the bones of the foot and spine). As shown earlier, a woman's weight increases during pregnancy by 10 -12 kg. This additional load against the background of a decrease in bone stiffness can cause foot deformity and the development of flat feet. A shift in the center of gravity of the body of a pregnant woman due to an increase in the weight of the uterus can lead to a change in the curvature of the spine and the appearance of pain in the back and pelvic bones. Therefore, for the prevention of flat feet, pregnant women are advised to wear comfortable shoes with low heels. It is advisable to use insoles that support the arch of the foot. For the prevention of back pain, special physical exercises are recommended that can unload the spine and sacrum, as well as wearing a comfortable bandage. Despite an increase in calcium loss by the bones of the skeleton of a pregnant woman and an increase in their elasticity, structure and bone density (as is the case with osteoporosis in older women). nine0003
nine0003
Changes in the nervous system . In the first months of pregnancy and at the end of it, there is a decrease in the excitability of the cerebral cortex, which reaches its greatest degree by the time of the onset of childbirth. By the same period, the excitability of the receptors of the pregnant uterus increases. At the beginning of pregnancy, there is an increase in the tone of the vagus nerve, in connection with which various phenomena often occur: changes in taste and smell, nausea, increased salivation, etc.
Active endocrine glands there are significant changes that contribute to the proper course of pregnancy and childbirth. Changes in body weight. By the end of pregnancy, a woman's weight increases by about 10-12 kg. This value is distributed as follows: fetus, placenta, membranes and amniotic fluid - approximately 4.0 - 4.5 kg, uterus and mammary glands -1.0 kg, blood - 1.5 kg, intercellular (tissue) fluid - 1 kg , an increase in the mass of adipose tissue of the mother's body - 4 kg.
Conclusion. nine0008 Summarizing the facts concerning changes in a woman's body during pregnancy, it is worth emphasizing that these changes reflect the processes of physiological adaptation of the mother's body to the process of intrauterine development of the fetus. Therefore, measures aimed at preventing the pathology of pregnancy should be, first of all, natural, physiological. This is a proper and balanced diet, smoking cessation, a sufficient level of physical activity and fluid intake. In a healthy woman, such approaches ensure the normal course of pregnancy and adequate preparation of the mother's body for childbirth and breastfeeding. nine0003 Prepared by: Head of the Pregnancy Pathology Department Teressa Ivanovna Vorobieva. Pregnancy is one of the important and responsible stages in a woman's life. In most cases, this is 9 months of anxious waiting to meet your baby. Discomfort in the vagina often manifests itself in the form of itching, burning, irritation and swelling. The main thing, when these symptoms appear, is to understand that it is necessary to establish their cause and eliminate it as soon as possible, because there are risks of harming the health of the fetus. Various sexual infections can affect the appearance of discomfort in the perineum. Unfortunately, during pregnancy, a woman is prone to various infectious diseases. As mentioned above, bearing a baby causes a restructuring of the hormonal background in a woman's body: the level of the hormone progesterone rises and the activity of the immune system naturally decreases, which creates favorable conditions for the exacerbation of chronic infections and the emergence of new ones. How dangerous is the development of infectious diseases of the vagina and vulva during the bearing of a baby? Normally, during pregnancy, the amniotic bladder and water, as well as the mucous plug of the cervix, protect the fetus from various infections and bacteria, so your unborn baby is safe. The presence in the body of a woman in an interesting position of an infectious disease and the lack of necessary therapy can adversely affect the course of pregnancy. For example, an untreated infection can lead to damage to the membranes, the fluid in which the unborn child is located, and the fetus itself. nine0003 There is also a high probability of physical contact of the child with the infection during passage through the birth canal. Therefore, in case of any discomfort in the intimate area during pregnancy, you should consult a specialist. You can suspect the appearance of an infection of the vagina and vulva by a series of symptoms: cramps, itching, burning. Bacterial vaginosis can also cause discomfort. This pathology, caused by a decrease in the number of lactobacilli in the vagina, as a result, their place is taken by other microorganisms that are always present in the vagina, but in excess lead to the development of dysbiosis. Bacterial vaginosis can occur without symptoms, but sometimes it occurs with clinical manifestations. It is usually accompanied by discomfort, as well as vaginal discharge that is white, gray, or yellow-green in color with an unpleasant "fishy" odor. nine0003 Bacterial vaginosis also adversely affects the course of pregnancy, can provoke inflammation of the pelvic organs, premature birth, chorioamnionitis - inflammation of the amniotic membranes and infection of the amniotic fluid. Itching in the intimate area during pregnancy can appear with vulvovaginal candidiasis - infection of the mucous membranes of the vulva and vagina with yeast-like fungi of the genus Candida. It should be noted that the first episode of the incidence of vulvovaginal candidiasis is observed during pregnancy. This is due to changes in hormonal levels, reduced immunity. This disease, in addition to discomfort in the groin area, itching and burning, is characterized by: moderate hyperemia, white and thick discharge like cottage cheese, sour smell from the vagina, pain during sexual intercourse and urination. nine0003 However, itching and burning are not always symptoms of serious pathologies. Occasionally, discomfort can occur with the use of poorly fitting underwear or aggressive pH soaps. Feeling discomfort in the groin, you should consult with a specialist. The specialist can conduct an examination, collect an anamnesis and prescribe, if necessary, laboratory and / or other diagnostic tests. In order to prevent the appearance of discomfort in the intimate area and not spoil the pleasant waiting time for the addition, it is necessary to follow preventive recommendations. Treatment of discomfort in the intimate area will be different. The diagnosed disease will influence the choice of therapy. Spray Epigen Intim can be included in the complex treatment of diseases accompanied by discomfort - nonspecific colpitis (vaginitis), bacterial vaginosis, thrush, herpes. nine0003 More Buy The drug has antipruritic and anti-inflammatory action. The drug is successfully used to treat viral infections (caused by the human papillomavirus, genital herpes), diseases associated with a decrease in local immunity (nonspecific vaginitis, thrush, bacterial vaginosis), etc. It can be used to treat exacerbations in conjunction with antiviral, antifungal and antimicrobial drugs, and for the prevention of these vaginal infections. more nine0003 why does it occur and how to solve the problem?
 However, during pregnancy, a woman's body undergoes major hormonal changes and pleasant emotions can go hand in hand with painful and uncomfortable sensations in different areas of the body. Including unpleasant symptoms may appear in the intimate area. nine0003
However, during pregnancy, a woman's body undergoes major hormonal changes and pleasant emotions can go hand in hand with painful and uncomfortable sensations in different areas of the body. Including unpleasant symptoms may appear in the intimate area. nine0003  nine0003
nine0003  Often, sexual infections provoke colpitis - inflammation of the mucous membrane of the vagina and the vaginal part of the cervix. By itself, colpitis often causes discomfort in the groin of pregnant women. It can be provoked not only by sexual infections, but also by endocrine or chronic diseases, stress, lack of hygiene. nine0003
Often, sexual infections provoke colpitis - inflammation of the mucous membrane of the vagina and the vaginal part of the cervix. By itself, colpitis often causes discomfort in the groin of pregnant women. It can be provoked not only by sexual infections, but also by endocrine or chronic diseases, stress, lack of hygiene. nine0003 
 All this will help to establish a diagnosis and choose an individual treatment regimen. nine0003
All this will help to establish a diagnosis and choose an individual treatment regimen. nine0003
 Epigen Intim gel contains activated glycyrrhizic and lactic acids in its composition. Its pH is slightly acidic, which corresponds to the normal acid-base balance of the skin of the intimate area. The tool helps to eliminate discomfort (irritation) due to wearing panty liners or not very comfortable underwear. It has a very pleasant aroma and helps to neutralize unpleasant odors in the intimate area with constant use. nine0101
Epigen Intim gel contains activated glycyrrhizic and lactic acids in its composition. Its pH is slightly acidic, which corresponds to the normal acid-base balance of the skin of the intimate area. The tool helps to eliminate discomfort (irritation) due to wearing panty liners or not very comfortable underwear. It has a very pleasant aroma and helps to neutralize unpleasant odors in the intimate area with constant use. nine0101 Spray Epigen Intim
Epigen Intim Spray
 Thanks to the active ingredient - activated glycyrrhizic acid, Epigen Intim spray helps to eliminate itching and irritation. It also helps to eliminate inflammation, swelling and redness of tissues. The drug is also able to increase the local immunity of the vagina, by stimulating the production of its own interferons. Spray Epigen Intim promotes healing and restoration of the integrity of the damaged mucosa, due to which the protective function of the mucosa will be restored and the number of lactobacilli will increase. nine0003
Thanks to the active ingredient - activated glycyrrhizic acid, Epigen Intim spray helps to eliminate itching and irritation. It also helps to eliminate inflammation, swelling and redness of tissues. The drug is also able to increase the local immunity of the vagina, by stimulating the production of its own interferons. Spray Epigen Intim promotes healing and restoration of the integrity of the damaged mucosa, due to which the protective function of the mucosa will be restored and the number of lactobacilli will increase. nine0003
By the way, while carrying a baby, the use of many drugs sold in pharmacies is limited or prohibited.