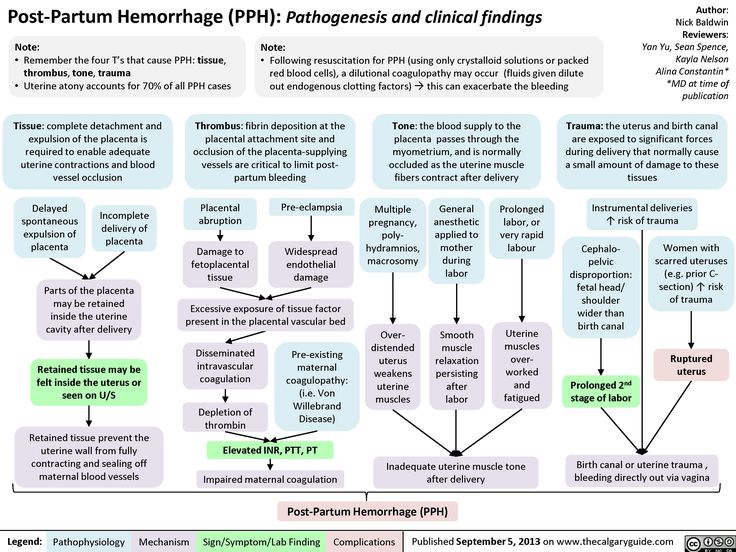
Retained placenta 8 weeks postpartum
Retained placenta | Pregnancy Birth and Baby
Retained placenta | Pregnancy Birth and Baby beginning of content3-minute read
Listen
A retained placenta is when the placenta is not delivered within 30 minutes of the baby’s birth. It is a serious problem since it can lead to severe infection or life-threatening blood loss.
Retained placenta is not a common condition, but because it’s serious, it will need to be managed by a medical team.
What causes retained placenta?
A placenta can be retained if your contractions aren’t strong enough to expel it, or if the cervix closes and traps the placenta inside your uterus.
You are more at risk of a retained placenta if you are over the age of 30, have a premature baby or if your first and second stages of labour were very long. It can also happen if you have a fibroid or another problem with your uterus.
Many women will have an injection of syntocinon (a synthetic version of the hormone oxytocin), which not only helps deliver the placenta but also helps reduce the risk of postpartum bleeding. Having this injection is called ‘active management’. If the mother chooses not to have the injection, it is called ‘expectant management’.
What are the symptoms of retained placenta?
The main symptom of retained placenta is that the placenta doesn’t completely come out of the uterus after the baby is born. Another symptom can be bleeding before the placenta comes out.
If a piece of placenta is left behind, you may develop symptoms days or weeks after the birth. These may include:
- fever
- a bad smelling discharge from the vagina
- heavy bleeding
- large pieces of tissue coming out of the vagina
- pain
What is the treatment for a retained placenta?
Sometimes retained placenta can be treated simply if you empty your bladder, change position and have the doctor or midwife gently pull on the umbilical cord.
If that doesn’t work, you will need a procedure to remove the placenta. You will be taken into surgery after the birth and given an epidural or anaesthetic so you don’t feel anything. Your doctor will use an instrument called a curette to scrape away the lining of the uterus.
While you’re waiting for surgery, the medical team will keep a close eye on you to check you're not bleeding heavily (postpartum haemorrhage). The procedure itself is quick, but you will need to be monitored for several hours after to make sure you are not bleeding.
If you do start to experience some of the symptoms mentioned above in the days and weeks after you have had your baby, it’s important to see your doctor immediately. It is not always obvious after the placenta has been delivered that some tissue may have been left behind and this can lead to infection and bleeding. If you are bleeding heavily after the birth, you will need surgery to investigate the cause.
Sources:
RANZCOG (Management of Postpartum Haemorrhage (PPH)), King Edward Memorial Hospital (Retained placenta), Women's and Newborn Health Westmead Hospital (The birth of your placenta), International Journal of Women's Health (Retained placenta after vaginal delivery: risk factors and management)Learn more here about the development and quality assurance of healthdirect content.
Last reviewed: February 2020
Back To Top
Related pages
- Placenta complications in pregnancy
- About the placenta
Need more information?
Labour complications
Even if you’re healthy and well prepared for childbirth, there’s always a chance of unexpected problems. Learn more about labour complications.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Asherman Syndrome
Read more on RANZCOG - Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists website
Why do some mums stop breastfeeding before 6 months?
Most new parents know 'breast is best', but while more than 9 out of 10 babies are breastfed at birth, few mums are breastfeeding exclusively 5 months later.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
What is freebirth?
Freebirth is when a woman chooses to birth her baby without medical or midwifery assistance, but this greater independence comes with some risks.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
About the placenta
The placenta develops inside the uterus (womb) during pregnancy. It gives your baby nutrients and oxygen. Find out more about the placenta here.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Postpartum haemorrhage
Postpartum haemorrhage is when you bleed more than normal after giving birth. It can be very serious and requires medical attention right away.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Disclaimer
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is not responsible for the content and advertising on the external website you are now entering.
OKNeed further advice or guidance from our maternal child health nurses?
1800 882 436
Video call
- Contact us
- About us
- A-Z topics
- Symptom Checker
- Service Finder
- Linking to us
- Information partners
- Terms of use
- Privacy
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is funded by the Australian Government and operated by Healthdirect Australia.
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is provided on behalf of the Department of Health
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby’s information and advice are developed and managed within a rigorous clinical governance framework. This website is certified by the Health On The Net (HON) foundation, the standard for trustworthy health information.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
This information is for your general information and use only and is not intended to be used as medical advice and should not be used to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any medical condition, nor should it be used for therapeutic purposes.
The information is not a substitute for independent professional advice and should not be used as an alternative to professional health care. If you have a particular medical problem, please consult a healthcare professional.
Except as permitted under the Copyright Act 1968, this publication or any part of it may not be reproduced, altered, adapted, stored and/or distributed in any form or by any means without the prior written permission of Healthdirect Australia.
Support this browser is being discontinued for Pregnancy, Birth and Baby
Support for this browser is being discontinued for this site
- Internet Explorer 11 and lower
We currently support Microsoft Edge, Chrome, Firefox and Safari. For more information, please visit the links below:
- Chrome by Google
- Firefox by Mozilla
- Microsoft Edge
- Safari by Apple
You are welcome to continue browsing this site with this browser. Some features, tools or interaction may not work correctly.
I Wish I’d Known About the Risks of a Retained Placenta After Bir
Health and wellness touch each of us differently. This is one person’s story.
Around this time three years ago, I was preparing for the birth of my first child. I’d spent hours diligently researching birth and the wide range of birth-related questions. So, when I went into labor, I thought I’d done all I could to prepare for any event.
So, when I went into labor, I thought I’d done all I could to prepare for any event.
The birth had several obstacles.
I lost a lot of blood, received an episiotomy, and remained mildly conscious as my son was removed with forceps.
What I remember the most — other than my mother’s horrified face because my blood was slow to coagulate — was the pain. When my placenta came out in pieces, it seemed less important at the time. But it significantly shaped my introduction to motherhood.
Little did I know then, it would take over a month and a half to be diagnosed with retained placenta. I’d experience weeks of pain as a consequence of my placenta not being expelled at once.
“If the placenta or a part of the placenta does not spontaneously deliver within 30 minutes after the baby has delivered, a retained placenta is diagnosed. Normally the placenta will separate and deliver from the uterus on its own once the baby has been born,” explains Sherry Ross, MD, OB-GYN.
According to Ross, a retained placenta is rare but dangerous, and affects just 2 percent of all deliveries.
1. Placenta adherents happens when the placenta doesn’t separate spontaneously from the uterus within 30 minutes of the baby being born. This is the most common type of retained placenta.
2. A trapped placenta happens when the placenta separates from the uterus but doesn’t spontaneously leave the uterus.
3. Placenta accreta happens when the placenta grows into the deeper layer of the uterus and is unable to spontaneously detach from the uterus. This is the most dangerous type of retained placenta and can lead to needing a hysterectomy and blood transfusions.
Ross also notes that retained placenta during a C-section is likely placenta accreta, and can be dangerous and the most difficult to treat.
My research had prepared me for the intellectualization of birth-related pain. However, the reality was much worse.
It hurt to sneeze, pee, and I thought I would die during each doctor’s checkup to see if my uterus deflated.
Sadly, research couldn’t prepare me for the physical experience. And my introduction to birth-related pain had only begun.
At first, I was too concerned with my son’s health and the troubles he was having with keeping food down to worry about how I felt.
Any parent who has ever had a child in the NICU for any amount of time will tell you that everything else in the world stops mattering. Your only concern becomes how to help your baby — despite often being powerless.
Thankfully, my son was cleared to come home after 5 days. For the first time in nearly a week, I was present in my body, not just my mind. And being present in my body hurt much more than I expected.
I was so distracted by the adjustment to motherhood that I was able to ignore my physical discomfort. Until it became too difficult to walk to get diapers.
In addition to extreme tiredness, I would experience intense bouts of abdominal pain at a moment’s notice.
I was three weeks postpartum and even though I had no knowledge of post-birth normalcy, an urge to push followed by lots of blood and large clots during a family outing let me know I needed to go to the emergency room.
But to my dismay, and despite informing them I was still passing large clots while being seen, the doctor declared my experiences a “normal part of the postpartum healing process.”
It didn’t matter what my initial postpartum checkup or the emergency room physician said — I knew something was wrong.
Each day post-birth, I felt progressively weaker instead of stronger
I was struggling so much that my relatives suggested I spend a few weeks in my hometown since my husband had returned to work. I was hesitant to leave my husband and travel with such a young baby. But I knew I couldn’t take care of a baby alone while my body was in such extreme pain.
I didn’t physically feel better there, but I had much more support. One day, I felt gross (pain and motherhood were a setback for self-care) and ambitiously tried to take a bath. The walk down the hall was too much for my body, and I started feeling faint. My son was nearby in his infant car seat but the pain intensified and I couldn’t reach him when he started crying.
The walk down the hall was too much for my body, and I started feeling faint. My son was nearby in his infant car seat but the pain intensified and I couldn’t reach him when he started crying.
I watched in horror as my bathwater became crimson from blood — I was passing clots again. And even though my son was less than 3 feet away, it might as well have been a mile.
Thankfully, my aunt returned shortly after and demanded we go to the hospital. I called the nurse line to inquire about my pain one more time and check that the visit would be covered by our insurance. I was told to go to the local emergency room.
I continued losing blood during the 5-hour wait to be seen in the ER, but the moment I was called back, the doctor knew something was wrong.
When my urine pregnancy test came back positive, I was immediately sent back from an ultrasound where I was diagnosed with retained placenta. I was put under anesthesia for a dilation and curettage (D & C), which is the procedure used to remove tissue left behind in the womb.
The rest was a blur.
Share on Pinterest
Unfortunately, thanks to my first birth experience, I’m at an increased risk for retained placenta if I have more children.
“Women who are high risk for a retained placenta include those who have had previous dilation and curettage (D & C), a premature delivery before 34 weeks, a stillborn, uterine abnormalities, or a long first or second stage of labor. If you have had a previously retained placenta, you are also at risk for having it again with future pregnancies,” Ross explains.
Because of this, it’s important to look out for the symptoms of retained placenta and advocate for yourself if you see them.
Signs of retained placenta “The most common sign of a retained placenta is when the placenta fails to deliver spontaneously after 30 minutes once the baby has been born. If pieces of the placenta have not delivered days or weeks after delivery, fever, persistent heavy bleeding with blood clots, cramping, pain, and a foul-smelling discharge may occur,” explains Ross.

I explained most, if not all, of those symptoms to a medical professional — so why wasn’t it caught sooner?
It could have been my race, considering the medical system has a long history of false beliefs relating to higher levels of pain tolerance for Black Americans. As a result, our discomfort is often overlooked.
It could have been my gender. Women regularly have their concerns ignored during birth. This mistreatment is one of many reasons things like birth trauma push women to opt out of multiple pregnancies due to the horrors of their first experiences.
And lastly, it could have been an intersection of these factors. The United States has the highest maternal mortality rates of any developed nation. While women of all races are at risk, Black women like myself are at a multiplied risk for complications and even death.
Through the experience, I felt ignored by my healthcare providers, and that hurt almost as much as my physical pain.
You may be at increased risk for a retained placenta if:
- you’re over age 30
- you give birth before the 34th week of pregnancy
- you experience a prolonged first or second stage of labor
- you have a stillbirth
I was lucky I got a diagnosis when I did. I was already over a month into motherhood and things could have easily gone differently.
I was already over a month into motherhood and things could have easily gone differently.
“Complications of a retained placenta include heavy bleeding, infection, uterine scarring, blood transfusion, and hysterectomy. Any of these complications can lead to death if not diagnosed and treated quickly,” noted Ross.
Retained placenta made the adjustment to new motherhood even more difficult.
I was too fatigued to perform small tasks, like getting diapers from the other side of the room. The condition would also be seen as a potential cause for the breastfeeding challenges I was having — I wasn’t producing very much milk.
The experience robbed me of my earliest memories of first-time motherhood and left in their place flashbacks of physical pain. But more importantly, my experience greatly impacted my trust in the medical system.
No one should have to jump through that many hoops to get answers about their health.
But, still, being armed with knowledge about the signs of retained placenta might help you get the right treatment more quickly.
Share on Pinterest
Rochaun Meadows-Fernandez is a diversity content specialist whose work can be seen in The Washington Post, InStyle, The Guardian, and other places. Follow her on Facebook and Twitter.
Complications after childbirth - causes and consequences
- Increased discharge
- Retention of part of the placenta in the uterine cavity
- Changes in the blood coagulation system
- Disorder of uterine muscle contraction
- Inflammatory process in the vagina or uterus
- Vaginal candidiasis (thrush)
- Postpartum endometritis
- Laktostasis and mastitis
- Postpartum pyelonephritis
- Venous thrombosis
- Discomfort in the area of postoperative sutures
- Urinary incontinence, feces, uterine prolapse
- Hemorrhoids
After giving birth, a woman often thinks that all worries and anxieties are behind her. But, alas, sometimes the first, happiest days or weeks of the life together of mother and baby can be overshadowed by various complications. In what cases are postpartum changes normal, and when should you see a doctor?
In what cases are postpartum changes normal, and when should you see a doctor?
Labor ends after the third stage of labor, that is, after the birth of the placenta. Following this, the uterus immediately significantly decreases in size, becomes spherical, its cavity is filled with blood clots; the bottom of the uterus at this moment is located approximately in the middle between the womb and the navel. The early postpartum period lasts for 2 hours and during this time the woman is in the maternity ward. Then comes the late postpartum period. This period lasts 6-8 weeks. During this time, there is a reverse development (involution) of all organs and systems that have undergone changes due to pregnancy and childbirth. The exception is the mammary glands, whose function reaches its peak precisely in the postpartum period. The most pronounced involutional changes occur in the genital organs, especially in the uterus. The rate of involutional changes is most pronounced in the first 8-12 days. The uterus and cervix are significantly reduced in size. After the birth of the placenta, a large wound surface remains in the uterus, which takes about 4-6 weeks to heal. During this period, the placental site in the uterus bleeds, spotting - lochia - in the first days is bloody in nature, gradually their color changes from red to reddish-brown, brownish, by the 4th week the discharge almost stops and soon disappear completely. In women who have undergone a cesarean section, everything happens more slowly, because, due to the presence of a suture on the uterus, it contracts worse. Their total amount of spotting during the postpartum period is 500-1500 ml.
The uterus and cervix are significantly reduced in size. After the birth of the placenta, a large wound surface remains in the uterus, which takes about 4-6 weeks to heal. During this period, the placental site in the uterus bleeds, spotting - lochia - in the first days is bloody in nature, gradually their color changes from red to reddish-brown, brownish, by the 4th week the discharge almost stops and soon disappear completely. In women who have undergone a cesarean section, everything happens more slowly, because, due to the presence of a suture on the uterus, it contracts worse. Their total amount of spotting during the postpartum period is 500-1500 ml.
What complications can occur after childbirth
You should consult a gynecologist in the following cases:
Increased amount of discharge
discharge does not stop for a long time, large blood clots appeared. When bleeding occurs, you need to contact an obstetrician-gynecologist, preferably at the maternity hospital where the birth took place. If the bleeding is very heavy (several pads are required within an hour), you do not need to go to the hospital yourself, you need to call an ambulance.
If the bleeding is very heavy (several pads are required within an hour), you do not need to go to the hospital yourself, you need to call an ambulance.
Retention of part of the placenta in the uterine cavity
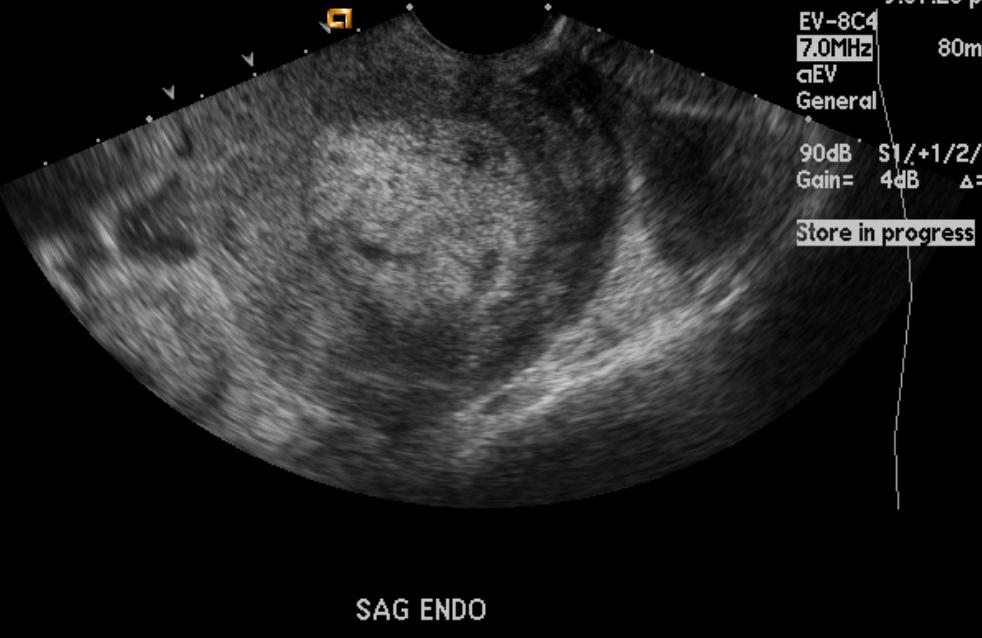
The most common cause of late postpartum hemorrhage (that is, those that occur later than 2 hours after birth) is the retention of a part of the placenta in the uterine cavity. The diagnosis in this case is confirmed by ultrasound. To remove the remnants of the placenta, the walls of the uterus are scraped under general intravenous anesthesia with mandatory subsequent antibiotic therapy to prevent infectious complications.
Changes in the blood coagulation system
In rare cases, the causes of bleeding may be changes in the blood coagulation system of a hereditary or acquired nature, blood diseases. In these cases, complex drug therapy is required.
Violation of contraction of the muscles of the uterus
Development of bleeding associated with impaired contraction of the muscles of the uterus is possible. This is the so-called hypotonic bleeding. In the subsequent period, the hypotonic state of the uterus can be caused by its overstretching due to polyhydramnios, multiple pregnancies, large fetuses, and underdevelopment of the uterus. A decrease in the contractility of the uterus is also caused by changes in its very wall (fibroids, the consequences of inflammatory processes, frequent abortions). These bleeding most often occur in the first hours after childbirth and require active treatment with medications, and in severe cases, surgery.
This is the so-called hypotonic bleeding. In the subsequent period, the hypotonic state of the uterus can be caused by its overstretching due to polyhydramnios, multiple pregnancies, large fetuses, and underdevelopment of the uterus. A decrease in the contractility of the uterus is also caused by changes in its very wall (fibroids, the consequences of inflammatory processes, frequent abortions). These bleeding most often occur in the first hours after childbirth and require active treatment with medications, and in severe cases, surgery.
A sharp, unexpected cessation of spotting should also alert the woman and requires urgent medical attention. In this case, the outflow of blood from the uterus may be disturbed, that is, lochia accumulate in the cavity and the so-called lochiometer develops. Blood clots are a good breeding ground for bacteria, so if the lochiometer is not treated in time, bacteria enter the uterine cavity and endometritis develops - inflammation of the uterine mucosa.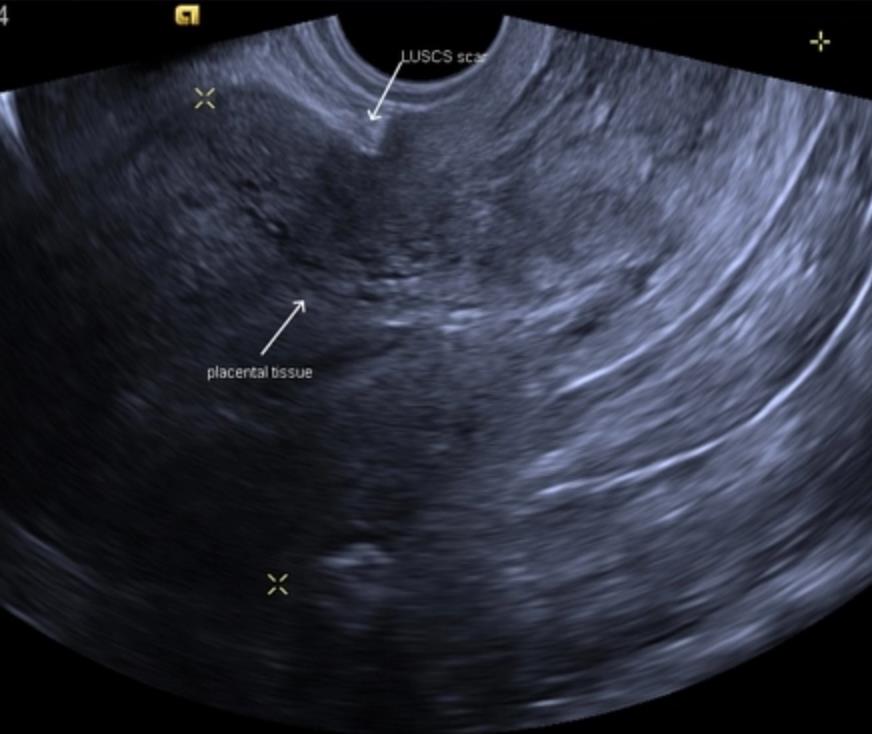 After a caesarean section, a lochiometer occurs more often than after a vaginal birth. Treatment consists in prescribing drugs that reduce the uterus, while using antispasmodics to relax the cervix and restore the outflow of lochia. In some cases, it is necessary to resort to vacuum aspiration of the contents of the uterus under general intravenous anesthesia and mandatory follow-up antibiotic therapy.
After a caesarean section, a lochiometer occurs more often than after a vaginal birth. Treatment consists in prescribing drugs that reduce the uterus, while using antispasmodics to relax the cervix and restore the outflow of lochia. In some cases, it is necessary to resort to vacuum aspiration of the contents of the uterus under general intravenous anesthesia and mandatory follow-up antibiotic therapy.
Inflammatory process in the vagina or uterus
The discharge has acquired an unpleasant odor. This may indicate the development of an inflammatory process in the vagina or in the uterus. In the postpartum period, there was a significant increase in the composition of most groups of bacteria, including bacteroids, Escherichia coli, streptococci, staphylococci. Potentially, all of these species can be the cause of postpartum infectious diseases. A common problem for women after childbirth is the development of bacterial vaginosis. Bacterial vaginosis is a pathology of the vaginal ecosystem caused by the increased growth of predominantly anaerobic bacteria (that is, those that grow in an oxygen-free environment) that actively proliferate in the postpartum period in the woman's vagina and can be pathogens in postpartum endometritis or suppuration of the sutures of the vagina and cervix. Diagnosis of bacterial vaginosis is based on measuring the acidity of the vagina and detecting in a smear on the flora specific for this disease "key cells" (these are cells of the vaginal mucosa covered with anaerobic bacteria). Treatment of bacterial vaginosis in the postpartum period is carried out with local preparations.
Diagnosis of bacterial vaginosis is based on measuring the acidity of the vagina and detecting in a smear on the flora specific for this disease "key cells" (these are cells of the vaginal mucosa covered with anaerobic bacteria). Treatment of bacterial vaginosis in the postpartum period is carried out with local preparations.
Vaginal candidiasis (thrush)
The appearance of curdled discharge, itching, burning in the genital area, redness indicates the development of vaginal candidiasis (thrush). The risk of this complication increases with antibiotics. Diagnosis is based on the detection of a large number of yeast-like fungi in a smear on the flora. For treatment, local preparations are used in the form of vaginal suppositories or tablets.
Postpartum endometritis
Purulent discharge, lower abdominal pain, fever. These symptoms may indicate the development of a serious complication - postpartum endometritis (inflammation of the inner lining of the uterus).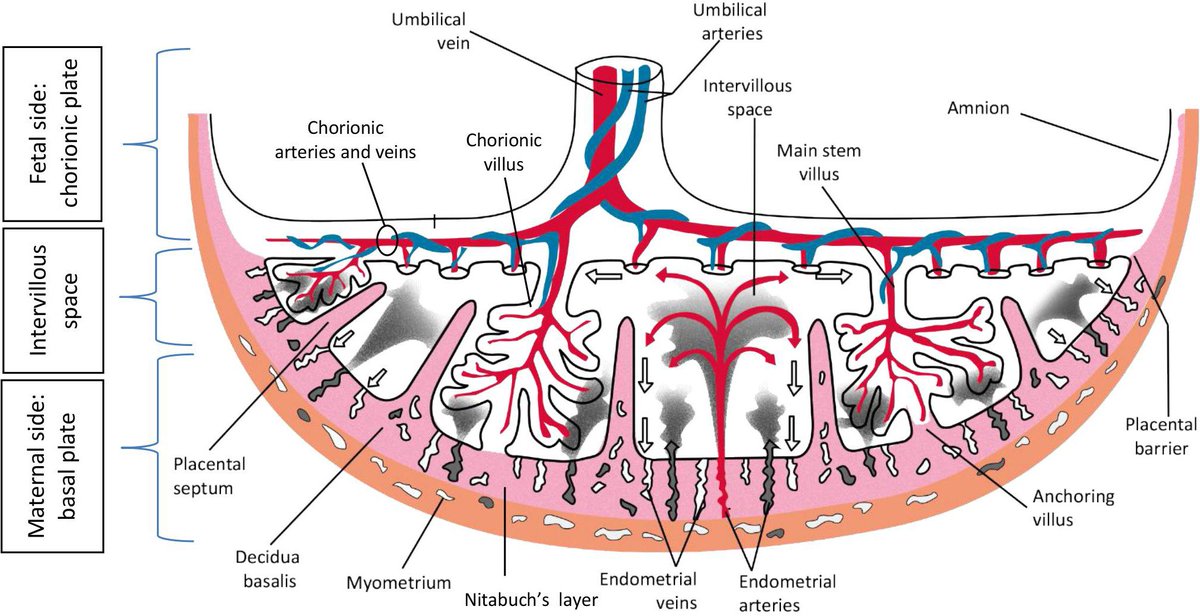 Most often, endometritis occurs in patients after cesarean section, manual examination of the postpartum uterus, manual separation of the placenta and removal of the placenta (if independent separation of the placenta is difficult due to a violation of the contractile function of the uterus), with a long anhydrous interval (more than 12 hours from the moment of amniotic fluid outflow to the birth of a baby), in women admitted to childbirth with inflammatory diseases of the genital tract (for example, against the background of sexually transmitted infections), in patients with a large number of abortions in the past. The classic form of endometritis occurs on days 1-5. Body temperature rises to 38-39degrees, heart rate increases to 80-100 beats per minute. They note depression of the general condition, chills, dryness and hyperemia of the skin, soreness of the body of the uterus, purulent discharge with a smell. The erased form appears on the 5-7th day, develops sluggishly. The temperature does not exceed 38 degrees, there is no chill.
Most often, endometritis occurs in patients after cesarean section, manual examination of the postpartum uterus, manual separation of the placenta and removal of the placenta (if independent separation of the placenta is difficult due to a violation of the contractile function of the uterus), with a long anhydrous interval (more than 12 hours from the moment of amniotic fluid outflow to the birth of a baby), in women admitted to childbirth with inflammatory diseases of the genital tract (for example, against the background of sexually transmitted infections), in patients with a large number of abortions in the past. The classic form of endometritis occurs on days 1-5. Body temperature rises to 38-39degrees, heart rate increases to 80-100 beats per minute. They note depression of the general condition, chills, dryness and hyperemia of the skin, soreness of the body of the uterus, purulent discharge with a smell. The erased form appears on the 5-7th day, develops sluggishly. The temperature does not exceed 38 degrees, there is no chill.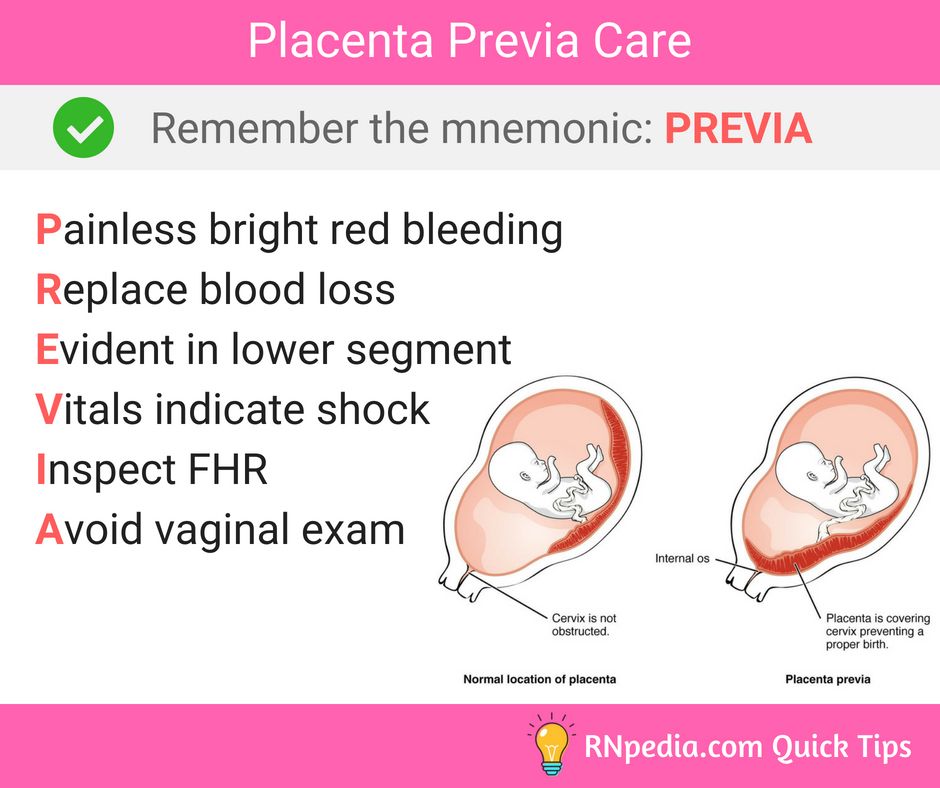 Endometritis after caesarean section always proceeds in a severe form.
Endometritis after caesarean section always proceeds in a severe form.
An ultrasound examination of the uterus and a complete blood count, which reveal signs of inflammation, help the doctor make a diagnosis. Treatment of endometritis should be started as early as possible. It is carried out in a hospital. Assign bed rest, with acute endometritis cold on the lower abdomen. Postpartum endomeritis is necessarily treated with antibiotics, along with them, agents that reduce the uterus are used. Currently, in many clinics and maternity hospitals, the uterine cavity is washed with cooled solutions of antiseptics. In severe cases, an intravenous infusion of saline solutions is required to improve blood circulation, relieve symptoms of intoxication.
In case of untimely treatment, there is a very high risk of spreading the inflammatory process to the entire uterus, small pelvis, the development of sepsis (the appearance of infectious agents in the blood), up to the death of the patient.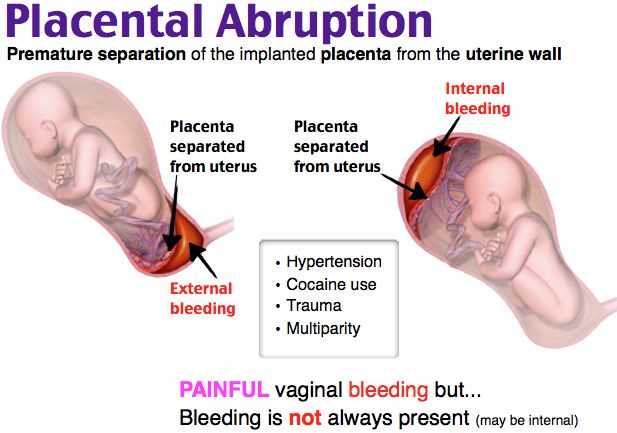
Laktostasis and mastitis
In the postpartum period, there may be pain in the mammary glands, a feeling of fullness, an increase in body temperature. When these symptoms appear, you should definitely consult a doctor - an obstetrician-gynecologist in a antenatal clinic or a surgeon.
Possible causes of pain in the mammary glands and the accompanying fever are lactostasis and mastitis.
Laktostasis (stagnation of milk in the gland), due to blockage of the excretory ducts. Most often, this condition develops when the baby is not properly attached to the chest, violation of the feeding regimen. Laktostasis often affects primiparous women. With the stagnation of milk, the mammary gland increases in volume, its dense enlarged lobules are determined. Body temperature can rise to 38-40 degrees. There is no redness of the skin and swelling of the gland tissue, which usually appear with inflammation. After decanting the mammary gland with lactostasis, the pain disappears, painless lobules with clear contours are small in size, and the body temperature decreases. If lactostasis is not eliminated within 3-4 days, mastitis (inflammation of the mammary gland) occurs, since when milk stagnates, the number of microbial cells in the milk ducts increases dramatically, milk is a good breeding ground for various bacteria, which contributes to the rapid progression of inflammation. With the development of mastitis, the body temperature constantly remains high, accompanied by chills. Symptoms of intoxication appear (general weakness, fatigue, headache). The patient is disturbed first by a feeling of heaviness, and then by pain in the mammary gland, which is accompanied by stagnation of milk. The mammary gland increases in volume, areas of redness are noted on the skin. Pumping milk is painful and does not bring relief, after pumping, dense painful areas remain, and a high body temperature persists. In severe cases, pus impurities can be determined in milk.
If lactostasis is not eliminated within 3-4 days, mastitis (inflammation of the mammary gland) occurs, since when milk stagnates, the number of microbial cells in the milk ducts increases dramatically, milk is a good breeding ground for various bacteria, which contributes to the rapid progression of inflammation. With the development of mastitis, the body temperature constantly remains high, accompanied by chills. Symptoms of intoxication appear (general weakness, fatigue, headache). The patient is disturbed first by a feeling of heaviness, and then by pain in the mammary gland, which is accompanied by stagnation of milk. The mammary gland increases in volume, areas of redness are noted on the skin. Pumping milk is painful and does not bring relief, after pumping, dense painful areas remain, and a high body temperature persists. In severe cases, pus impurities can be determined in milk.
To eliminate lactostasis, pumping, local anti-inflammatory ointments, and physiotherapy are used. Mastitis is treated with antibiotics. In some cases, lactation suppression and surgical treatment are required.
Mastitis is treated with antibiotics. In some cases, lactation suppression and surgical treatment are required.
Postpartum pyelonephritis
Fever, pain in the back or side, painful urination. These symptoms may indicate the development of postpartum pyelonephritis, that is, inflammation of the kidneys. Critical periods for the development of postpartum pyelonephritis, doctors consider 4-6 and 12-14 days of the postpartum period. The development of the disease is associated with infection in the urinary tract from the genital tract. Most often, the disease develops in puerperas, in the urine of which a small amount of bacteria was found during pregnancy. An ultrasound examination of the kidneys and bladder and a urine test help the doctor make the diagnosis.
Treatment of pyelonephritis is mandatory with antibiotics.
Venous thrombosis
Pain in the legs, swelling, redness on the legs along the vein, increased pain when walking - these are symptoms of a serious pathology - venous thrombosis (formation of blood clots in the veins) and require an urgent visit to a surgeon or phlebologist.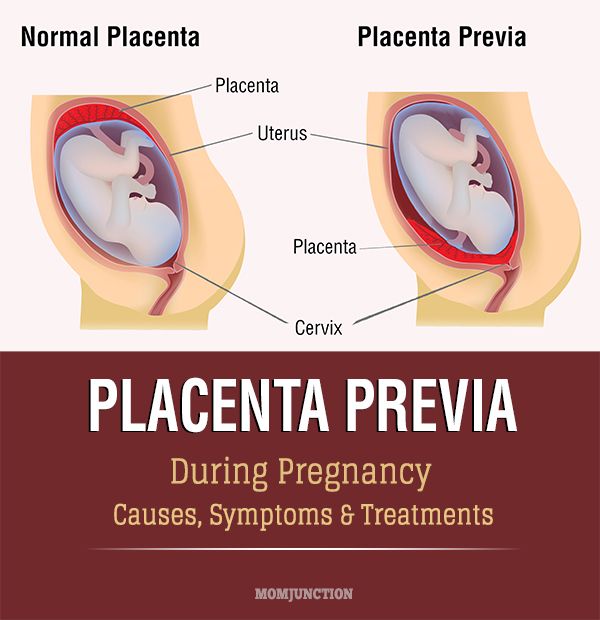 The most dangerous periods for the occurrence of thrombosis are considered 5-6 days after childbirth or cesarean section, less often thrombosis occurs 2-3 weeks after childbirth. The causes of thrombosis are changes in the blood coagulation system that occur during pregnancy and after childbirth. Physiologically, in the postpartum period, the activation of the coagulation system occurs. As the body tries to stop bleeding. At the same time, the tone of the vessels of the small pelvis and lower extremities is reduced, the veins have not yet had time to adapt to work in new conditions. These conditions trigger the mechanisms of thrombus formation. An important role in the development of postpartum venous thrombosis is also played by the hormonal background, which changes dramatically after the end of pregnancy.
The most dangerous periods for the occurrence of thrombosis are considered 5-6 days after childbirth or cesarean section, less often thrombosis occurs 2-3 weeks after childbirth. The causes of thrombosis are changes in the blood coagulation system that occur during pregnancy and after childbirth. Physiologically, in the postpartum period, the activation of the coagulation system occurs. As the body tries to stop bleeding. At the same time, the tone of the vessels of the small pelvis and lower extremities is reduced, the veins have not yet had time to adapt to work in new conditions. These conditions trigger the mechanisms of thrombus formation. An important role in the development of postpartum venous thrombosis is also played by the hormonal background, which changes dramatically after the end of pregnancy.
The risk of developing venous thrombosis is especially high in women with various pathologies of the blood coagulation system, which are detected even before pregnancy or during childbearing. There is a high probability of thromboembolic complications and in the presence of diseases of the cardiovascular system, overweight. The risk of thrombosis also increases in women in the age group after 40 years, in the presence of varicose veins of the lower extremities. The risk of thrombus formation is increased in women who have undergone a caesarean section. An ultrasound examination of the veins, with Dopplerography, that is, an assessment of blood flow in the vessels, helps the doctor in making a diagnosis. For the treatment of venous thrombosis, medications are used, wearing compression stockings.
There is a high probability of thromboembolic complications and in the presence of diseases of the cardiovascular system, overweight. The risk of thrombosis also increases in women in the age group after 40 years, in the presence of varicose veins of the lower extremities. The risk of thrombus formation is increased in women who have undergone a caesarean section. An ultrasound examination of the veins, with Dopplerography, that is, an assessment of blood flow in the vessels, helps the doctor in making a diagnosis. For the treatment of venous thrombosis, medications are used, wearing compression stockings.
A severe complication of venous thrombosis is the detachment of part of the thrombus and its movement along the vascular bed. In this case, blood clots, entering the vessels of the lung or brain, cause strokes (impaired cerebral circulation) or pulmonary embolism (blockage of the pulmonary arteries by a thrombus). This serious complication appears as a sharp cough, shortness of breath, pain in the chest, hemoptysis may begin - the appearance of blood streaks in the sputum when coughing. In severe cases, the work of the heart is disrupted and death can occur.
In severe cases, the work of the heart is disrupted and death can occur.
Unpleasant sensations in the area of postoperative sutures
Discomfort in the area of postoperative sutures after caesarean section or in the area of sutures on the perineum. Normally, after suturing vaginal tears, there may be slight pain for 1-2 days, but they quickly pass. Pain in the postoperative wound after cesarean section may be disturbing for 2 weeks, gradually decreasing. Feeling of heaviness, fullness, pain in the area of the postoperative wound may indicate the accumulation of hematoma (blood) in the area of the sutures. This usually happens in the first three days after childbirth and requires surgical treatment - removal of accumulated blood. Pain, burning, bleeding of the sutures, the appearance of discharge with an unpleasant odor, swelling in the area of the sutures, an increase in body temperature indicates the attachment of an infection and suppuration of the sutures. In these cases, you should also consult a doctor to treat the wound and decide on a further method of treatment.
In these cases, you should also consult a doctor to treat the wound and decide on a further method of treatment.
Urinary incontinence, feces, uterine prolapse
Violation of the physiological functions of the pelvic organs of varying degrees (bladder, rectum), which may appear as in the postpartum period - urinary incontinence, feces, uterine prolapse. The problem of genital prolapse occurs when the pelvic floor muscles have lost the ability to contract so much that individual organs or parts of them do not fall into the projection of the supporting apparatus. The most common cause of pelvic organ prolapse is trauma to the pelvic floor muscles during childbirth.
Hemorrhoids
Quite often, after childbirth, women are worried about the appearance of hemorrhoids - varicose veins of the rectum. The predisposing factor in this case is a significant increase in intra-abdominal pressure during pregnancy and during childbirth. In the case of hemorrhoids, formations appear in the anus, which can be painless, but most often - painful, bleeding and itchy.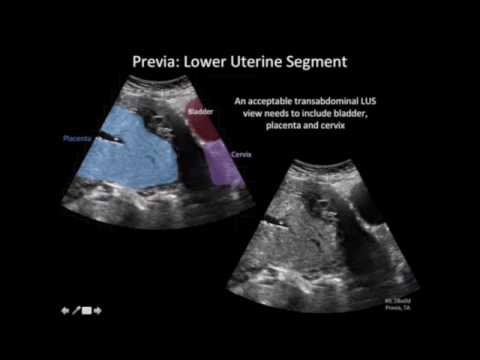 The appearance of intense pain in the anus, bloody discharge from the rectum are a reason to consult a doctor - a proctologist. Most often, uncomplicated forms of hemorrhoids are treated with local medications - creams and suppositories, in case of complications (nodule pinching, bleeding), surgical treatment is required.
The appearance of intense pain in the anus, bloody discharge from the rectum are a reason to consult a doctor - a proctologist. Most often, uncomplicated forms of hemorrhoids are treated with local medications - creams and suppositories, in case of complications (nodule pinching, bleeding), surgical treatment is required.
In any case, if you experience any symptoms that cause concern, it is advisable to consult a doctor, because any complication is best prevented or treated at the very initial stage.
Postpartum hygiene
Congratulations! You have become a mother!
The postpartum period is no less important and responsible stage in the life of a family than pregnancy.
The postpartum period lasts 6-8 weeks (begins after the birth of the placenta and ends when the organs and systems that have changed during pregnancy return to their original state).
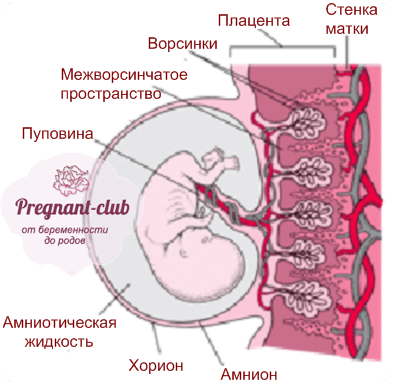
In the process of healing the inner surface of the uterus, postpartum discharge appears - lochia, which is a wound secret. Their character during the postpartum period changes: in the first days, lochia has a bloody character; from the 4th day, their color changes to reddish-brown; by the 10th day they become light, liquid, without blood, and after 3 weeks there is practically no discharge. There may be discomfort due to uterine contractions. To relieve discomfort, bend forward and gently massage your belly. If discomfort in the uterine area occurs during feeding, try choosing a different position. It is convenient to feed lying on your side. The stomach may ache for another reason. It hurts the abdominal muscles that were actively involved during childbirth, try to relax or do a light massage.
Their character during the postpartum period changes: in the first days, lochia has a bloody character; from the 4th day, their color changes to reddish-brown; by the 10th day they become light, liquid, without blood, and after 3 weeks there is practically no discharge. There may be discomfort due to uterine contractions. To relieve discomfort, bend forward and gently massage your belly. If discomfort in the uterine area occurs during feeding, try choosing a different position. It is convenient to feed lying on your side. The stomach may ache for another reason. It hurts the abdominal muscles that were actively involved during childbirth, try to relax or do a light massage.
In most non-nursing women, menstruation occurs on the 6-8th week after childbirth, more often it comes without the release of an egg from the ovary. However, ovulation and pregnancy may occur during the first months after childbirth. In lactating women, the time of the onset of the first menstruation after childbirth can be delayed for many months.
The normal postpartum period is characterized by a good general condition of the woman, normal temperature, sufficient lactation. For the prevention of infectious complications, strict adherence to sanitary and epidemiological requirements and personal hygiene rules is important.
POSTPARTUM HYGIENE
The strictest cleanliness is essential.
- The mother should take a shower twice a day (in the morning and in the evening), then wash the mammary gland with soap and brush her teeth.
- Particular attention should be paid to the cleanliness of hands. Nails should be cut short, hands should be washed more often with soap and be sure before each feeding of the child (if the hands are dirty, you can infect the child, infect the nipples).
- Among the hygienic measures of particular importance in the postpartum period is the maintenance of cleanliness of the external genitalia and the surrounding skin.
- Wash with warm water and soap (liquid with a dispenser, as microbes feel great on lumps) with a fluid stream, wash the genitals from front to back (from the pubis to the anus) after each visit to the toilet at least 4-5 times a day (you need to go to the toilet exactly at such a frequency that the filled bladder does not interfere with uterine contraction).

Wash hands cleanly before washing. - Keep the pads clean, change them every 3-4 hours, regardless of fullness. Remove pads from front to back to prevent microorganisms from entering the vagina from the anus. If there are seams on the perineum, they should be washed thoroughly enough - you can simply direct a jet of water at it. After washing, you need to dry the perineum and the seam area by blotting the towel from front to back.
- Do not take a bath for the first 6 weeks after giving birth. This is due to the fact that the entrance to the vagina is not yet closed enough and pathogenic microbes can penetrate into it along with water. It is clear that at this time you can not swim in the pool, river, lake, sea.
- The use of tight underwear is strictly excluded, as it puts significant pressure on the perineum, which disrupts blood circulation, preventing healing.
- If there are stitches on the perineum, a woman should not sit down for 7-14 days (depending on the degree of damage).
 At the same time, you can sit on the toilet already on the first day after childbirth. By the way, about the toilet. Many women are afraid of severe pain and try to skip bowel movements, as a result, the load on the muscles of the perineum increases and the pain intensifies.
At the same time, you can sit on the toilet already on the first day after childbirth. By the way, about the toilet. Many women are afraid of severe pain and try to skip bowel movements, as a result, the load on the muscles of the perineum increases and the pain intensifies.
To avoid constipation after childbirth, do not eat foods that have a fixative effect. If the problem of constipation is not new to you, drink a tablespoon of vegetable oil before each meal. The stool will be soft and will not affect the healing process of the stitches.
- Underwear and bed linen must be cotton. We change underwear daily, bedding - at least once every three to five days.
- Stitches after caesarean section do not require special care. After the stitches and bandage are removed, you can take a shower. Do not scrub the seam area with a washcloth. With painful sensations in the anterior abdominal wall, a postpartum or postoperative bandage, which must be worn for 4 months, will help to cope.
 Young mothers are often interested in: will the seams come apart if you carry a baby in your arms? For the first 2-3 months after surgery, it is recommended to lift no more than your child's weight.
Young mothers are often interested in: will the seams come apart if you carry a baby in your arms? For the first 2-3 months after surgery, it is recommended to lift no more than your child's weight.
It happens that redness, irritation, bloody or purulent discharge occurs at the suture site. This indicates suppuration or divergence of the seams. Then you should immediately consult a doctor in a antenatal clinic.
Sexual life after childbirth can be resumed after 6-8 weeks. By this time, the woman's body is already completely back to normal. Your doctor will advise you on contraceptives.
To fully recover from childbirth, at least two years must pass before the next pregnancy.
BREASTFEEDING
Feeding the baby should not go by the clock, but on demand, incl. in nighttime. At one feeding, put the baby on one breast so that he suckles for a long time and receives later milk, which contains brain and intelligence development factors, growth factors and immunoglobulins. Later, the milk comes in droplets like colostrum, the child sucks it intermittently. Sometimes the mother at this moment thinks that the child is indulging and tearing him off the breast. You don't need to do this. Let him let her go.
Later, the milk comes in droplets like colostrum, the child sucks it intermittently. Sometimes the mother at this moment thinks that the child is indulging and tearing him off the breast. You don't need to do this. Let him let her go.
Breast milk is the best food for a baby!
- After the baby has had enough, the mother should carefully feel the mammary gland. If the breast is soft and there is no soreness and seals anywhere, then pumping is not necessary. If necessary, you can wash the mammary glands with warm water after feeding, starting from the nipple and ending with the armpit, and dry with a clean towel.
Very useful for the breasts after childbirth and air baths, which are best taken after feeding, to give the breast a chance to rest, "breathe". The duration of such an air bath may not exceed 15-20 minutes, but the benefits of it are enormous.
- The nipple should be carefully inspected daily, the surface of which should not be cracked and, as a preventive measure, leave a drop of milk on the nipple and allow it to dry in the open air.
Only breast milk should be used as the main and only product for feeding a newborn. The use of nipples, horns and "pacifiers" is unacceptable, as this leads to a weakening of sucking in newborns and, accordingly, to incomplete emptying of the mammary gland, a decrease in prolactin production.
Are you worried about the question - do I have enough milk?
To resolve this issue, you need to observe the child, if he urinates more than 6 times a day, then he receives a sufficient amount of milk. The reason for the decrease in the amount of milk can be:
- rare feeding break (3 or more hours)
- if you do not feed at night
- short feedings or by the hour
To increase the amount of milk, you need to reorganize the feeding regimen, feed often and for as long as you want child. Try to feed with one breast so that the baby sucks out milk later, you can strain the empty breast for 10 minutes, thereby increasing the flow of milk. It is necessary to improve the mother's nutrition or use herbal teas to increase lactation.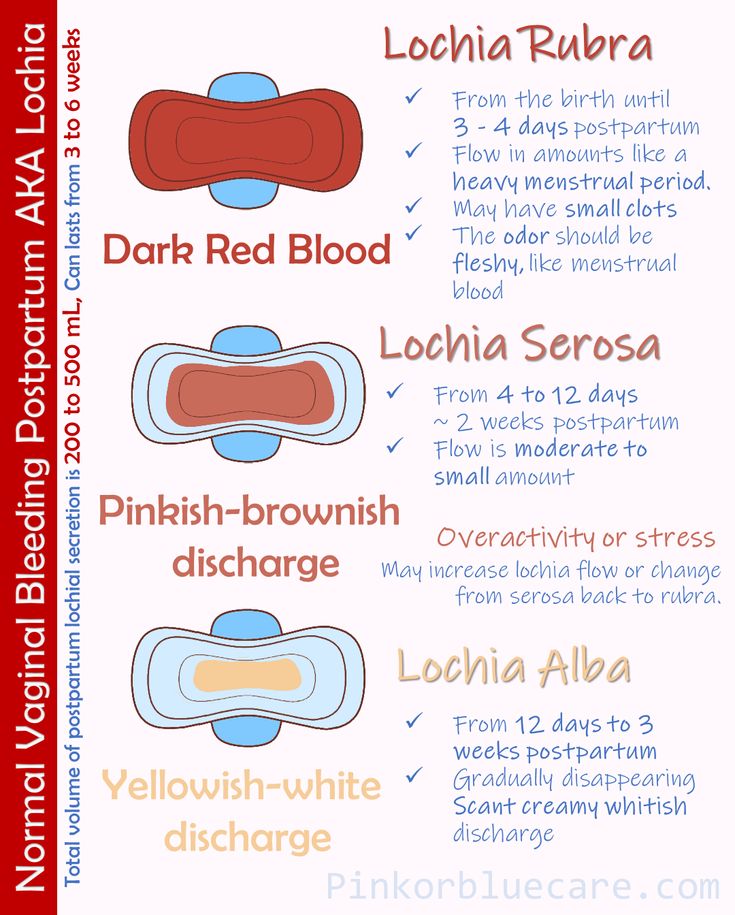
NUTRITION
Nursing mother's diet should be rich in calories (3200 kcal), balanced with the proper amount of proteins, fats, carbohydrates, vitamins and microelements. This diet will be dominated by lactic acid, protein foods, fresh fruits and vegetables. Food should be rich in vitamins and minerals. Spicy, fatty, fried, smoked foods, canned food, sausages, alcohol and potential allergens for the child (chocolate, citrus fruits, coffee) should be excluded from the diet.
The food of the puerperal should be 5-6 times a day. It is necessary to distribute products in the daily menu in such a way that those that are rich in protein and are much more difficult to digest in the gastrointestinal tract (meat, fish, cereals) would be used during the first half of the day, and in the second half it is advisable to give preference to milk. - vegetable food.
Conditions requiring special attention
Unfortunately, the first month after childbirth does not always go smoothly. Situations may arise, when medical attention is needed . Monitor your well-being, regularly measure your body temperature, as fever is most often the first sign of complications in the postpartum period.
Situations may arise, when medical attention is needed . Monitor your well-being, regularly measure your body temperature, as fever is most often the first sign of complications in the postpartum period.
All complications of the postpartum period can be divided into several groups:
1. Complications of the uterus.
Subinvolution of the uterus - a decrease in the rate of contraction of the uterus, due to a delay in the uterus of postpartum discharge. The disease often occurs 5-7 days after childbirth, due to the closure of the cervical canal with a blood clot or a piece of membranes, as well as the inflection of the uterus due to relaxation of the ligamentous apparatus.
Infection of the contents of the uterus can lead to inflammation of the uterine mucosa - endometritis. Predisposing factors for the occurrence of endometritis are difficult childbirth, violations of the separation of the placenta during childbirth, infections of the genital tract during pregnancy, impaired immunity, abortion. Symptoms of the disease are: fever, unpleasant odor in lochia, aching pain in the lower abdomen. If these symptoms appear, you should consult an obstetrician-gynecologist at the place of residence. To clarify the diagnosis, an ultrasound examination is performed and, if necessary, surgery, during which the contents are removed from the uterine cavity (washing or curettage of the uterus). After surgery, antibiotics must be prescribed.
Symptoms of the disease are: fever, unpleasant odor in lochia, aching pain in the lower abdomen. If these symptoms appear, you should consult an obstetrician-gynecologist at the place of residence. To clarify the diagnosis, an ultrasound examination is performed and, if necessary, surgery, during which the contents are removed from the uterine cavity (washing or curettage of the uterus). After surgery, antibiotics must be prescribed.
2. Breast complications.
Laktostasis - stagnation of milk in the mammary gland. At the same time, the chest swells and becomes painful, foci of seals appear, a short-term rise in body temperature is possible. In itself, lactostasis is not a disease, requiring only gentle pumping of the breast, restriction of fluid intake, and frequent feeding of painful breasts. However, when an infection joins, it turns into lactational mastitis, requiring immediate medical attention , antibiotic therapy, and sometimes surgery. The question of the possibility of breastfeeding with mastitis is decided individually, depending on the stage of the disease.
The question of the possibility of breastfeeding with mastitis is decided individually, depending on the stage of the disease.
Another complication of the chest is the appearance of cracks in the nipples. The main reason for their appearance is improper attachment of the baby to the breast, when the baby captures only the nipple, and not the entire areola. Such a seizure is very painful for the mother - and this is the main danger signal. Breastfeeding doesn't have to be painful. Good advisory and practical help for lactostasis and cracked nipples is provided by breastfeeding consultants. Treatment of cracks consists in treating the nipple with wound healing drugs.
Hypogalactia - insufficient milk production. In order to increase the amount of milk, a mother needs to increase the frequency of feedings, not skip night feedings, offer her baby both breasts in one feeding, drink more, eat well and sleep a lot.
3. Complications from the tissues of the cervix, vagina and skin.
Inflamed wounds of these tissues are called postpartum ulcers. When an infection is attached, these wounds swell, become covered with a purulent coating, and their edges are painful. For the purpose of treatment, they are treated with various antiseptics, sometimes they require surgical treatment.
4. Complications of the venous system.
Hemorrhoids (varicose veins of the rectum) also cause pain. When infringed, they increase, become swollen, tense and painful. Thorough hygiene helps to reduce pain (shower after each visit to the toilet), applying ice to the perineum. Certain medications can be used as prescribed by a doctor.
Thrombophlebitis is a disease of the veins characterized by inflammation of the venous wall and thrombosis of the vein. After childbirth, thrombophlebitis of the pelvic veins most often occurs. Usually this disease occurs in the third week after childbirth. In terms of symptoms, it is very similar to endometritis, but requires a different treatment.