Pregnant with herpes outbreak
Pregnancy and herpes Information | Mount Sinai
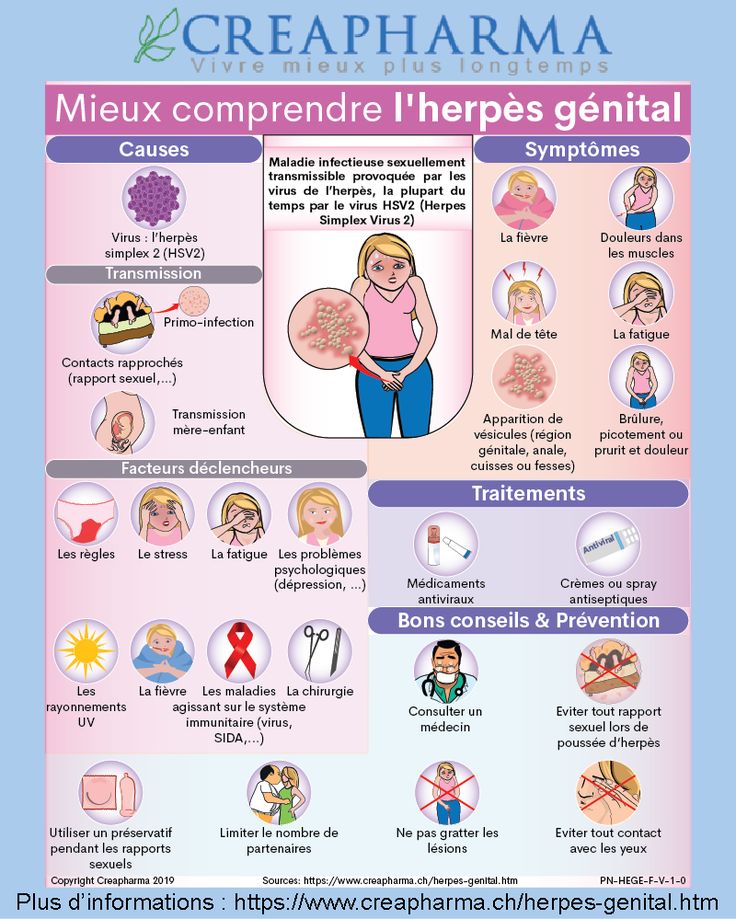
HSV; Congenital herpes; Herpes - congenital; Birth-acquired herpes; Herpes during pregnancy
Newborn infants can become infected with herpes virus during pregnancy, during labor or delivery, or after birth.
Infants may acquire congenital herpes from a mother with an active, possibly inapparent herpes infection at the time of birth. Aggressive treatment with antiviral medicine is required, but may not be effective in the case of systemic herpes.
Causes
Newborn infants can become infected with herpes virus:
- In the uterus (this is unusual)
- Passing through the birth canal (birth-acquired herpes, the most common method of infection)
- Right after birth (postpartum) from being kissed or having other contact with someone who has herpes mouth sores
If the mother has an active outbreak of genital herpes at the time of delivery, the baby is more likely to become infected during birth. Some mothers may not know they have herpes sores inside the vagina.
Some women have had herpes infections in the past, but are not aware of it, and may pass the virus to their baby.
Herpes type 2 (genital herpes) is the most common cause of herpes infection in newborn babies. But herpes type 1 (oral herpes) can also occur.
Symptoms
Herpes may only appear as a skin infection. Small, fluid-filled blisters (vesicles) may appear. These blisters break, crust over, and finally heal. A mild scar may remain.
Small, fluid-filled blisters (vesicles) may appear. These blisters break, crust over, and finally heal. A mild scar may remain.
Herpes infection may also spread throughout the body. This is called disseminated herpes. In this type, the herpes virus can affect many parts of the body.
- Herpes infection in the brain is called herpes encephalitis
- The liver, lungs, and kidneys may also be involved
- There may or may not be blisters on the skin
Newborn infants with herpes that has spread to the brain or other parts of the body are often very sick. Symptoms include:
- Skin sores, fluid-filled blisters
- Bleeding easily
- Breathing difficulties such as rapid breathing and short periods without breathing, which can lead to nostril flaring, grunting, or blue appearance
- Yellow skin and whites of the eyes
- Weakness
- Low body temperature (hypothermia)
- Poor feeding
- Seizures, shock, or coma
Herpes that is caught shortly after birth has symptoms similar to those of birth-acquired herpes.
Herpes the baby gets in the uterus can cause:
- Eye disease, such as inflammation of the retina (chorioretinitis)
- Severe brain damage
- Skin sores (lesions)
Exams and Tests
Tests for birth-acquired herpes include:
- Checking for the virus by scraping from vesicle or vesicle culture
- EEG
- MRI of the head
- Spinal fluid culture
Additional tests that may be done if the baby is very sick include:
- Blood gas analysis
- Coagulation studies (PT, PTT)
- Complete blood count
- Electrolyte measurements
- Tests of liver function
Treatment
It is important to tell your health care provider at your first prenatal visit if you have a history of genital herpes.
- If you have frequent herpes outbreaks, you'll be given a medicine to take during the last month of pregnancy to treat the virus. This helps prevent an outbreak at the time of delivery.
- C-section is recommended for pregnant women who have a new herpes sore and are in labor.
Herpes virus infection in infants is generally treated with antiviral medicine given through a vein (intravenous). The baby may need to be on the medicine for several weeks.
Treatment may also be needed for the effects of herpes infection, such as shock or seizures. Because these babies are very ill, treatment is often done in the hospital intensive care unit.
Outlook (Prognosis)
Infants with systemic herpes or encephalitis often do poorly. This is despite antiviral medicines and early treatment.
This is despite antiviral medicines and early treatment.
In infants with skin disease, the vesicles may keep coming back, even after treatment is finished.
Affected children may have developmental delay and learning disabilities.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
If your baby has any symptoms of birth-acquired herpes, including skin blisters with no other symptoms, have the baby seen by the provider right away.
Prevention
Practicing safe sex can help prevent the mother from getting genital herpes.
People with cold sores (oral herpes) should not come in contact with newborn infants. To prevent transmitting the virus, caregivers who have a cold sore should wear a mask and wash their hands carefully before coming in contact with an infant.
Mothers should speak to their providers about the best way to minimize the risk of transmitting herpes to their infant.
Dinulos JGH. Sexually transmitted viral infections. In: Dinulos JGH, ed. Habif's Clinical Dermatology. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 11.
Kimberlin DW, Baley J; Committee on infectious diseases; Committee on fetus and newborn. Guidance on management of asymptomatic neonates born to women with active genital herpes lesions. Pediatrics. 2013;131(2):e635-e646. PMID: 23359576 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih. gov/23359576/.
gov/23359576/.
Kimberlin DW, Gutierrez KM. Herpes simplex virus infections. In: Wilson CB, Nizet V, Maldonado YA, Remington JS, Klein JO, eds. Remington and Klein's Infectious Diseases of the Fetus and Newborn Infant. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2016:chap 27.
Schiffer JT, Corey L. Herpes simplex virus. In: Bennett JE, Dolin R, Blaser MJ, eds. Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett's Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 135.
Last reviewed on: 7/1/2020
Reviewed by: John D. Jacobson, MD, Professor of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Loma Linda University School of Medicine, Loma Linda Center for Fertility, Loma Linda, CA. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
Genital herpes and pregnancy: Understanding the risks | Your Pregnancy Matters
Be honest with your doctor about your history with herpes – or if you suspect you may have herpes. This allows them to take additional precautions beyond what they might normally provide during pregnancy, labor, and delivery to safeguard your baby from contracting the virus.
This allows them to take additional precautions beyond what they might normally provide during pregnancy, labor, and delivery to safeguard your baby from contracting the virus. Genital herpes is one of the most common health conditions in the U.S. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) estimates that 1 in 6 people between the ages of 14 and 49 have it. Approximately 22% of pregnant women in the U.S. have genital herpes. Two percent contract it during pregnancy – that's 1 in 50 pregnant women.
Two viral strains can cause genital herpes. HSV-2 (herpes simplex virus) is the most common and typically spreads through sexual contact. HSV-1, which is best known for causing cold sores, can also produce genital lesions (blisters or open sores). More than half of adults in America get HSV-1 at some point in their lives.
Herpes is generally manageable in adults. However, it can cause serious health problems in newborns. During delivery, your baby may be exposed to the virus, even if you are not having an outbreak.
Herpes infection occurs in less than 1% of births, but it can cause severe illness in newborns, such as:
- Blindness
- Deafness
- Seizures
- Serious infections, such as viral meningitis
- Recurrent sores on the skin, eyes, genitals, or mouth
- organ damage, including to the liver, lungs, and heart
Tell your doctor if you or your partner have herpes or if you may have been exposed. By knowing, we can take extra precautions to reduce your baby's risk of infection during delivery and in their first few weeks at home. If you’re not certain but think you may have had herpes in the past, we can do a blood test to determine whether you have had the infection.
If you are concerned about privacy, we will note in your chart not to discuss the condition in front of anyone at your appointments – we are happy to accommodate this common request.
"Tell your doctor if you or your partner have herpes or if you may have been exposed.
Robyn Horsager-Boeher, M.D.By knowing, we can take extra precautions to reduce your baby's risk of infection during delivery and in their first few weeks at home."
How can I manage herpes during pregnancy?
There is no evidence to suggest pregnancy causes flare-ups. The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists says 75% of pregnant women who have herpes, however, can expect to have an outbreak during pregnancy.
During pregnancy, you should watch for symptoms of the virus becoming active, such as tingling, itching, or burning around where the sore will eventually appear.
If you have a history of herpes (or your blood test is positive), your provider may prescribe an antiviral medication such as acyclovir (Valtrex) to reduce the risk of spreading the virus or having an outbreak around the time of your delivery.
We typically recommend starting an antiviral at 36 weeks or sooner if you are at risk for preterm birth. The antiviral medications are safe during pregnancy. In fact, we can give the same medications to your baby if needed.
Will I need a C-section if I have herpes?
A cesarean (C-section) can’t completely prevent herpes transmission. But it does substantially decrease the risk to your baby if you have a lesion or report typical symptoms by bypassing contact with the vagina and labia.
Once you go into labor, we’ll carefully examine you for genital lesions. If we see something suspicious, we will recommend a C-section.
If you have no symptoms and no sores in the genital region, a vaginal delivery may be safe. Lesions can sometimes appear in other areas, such as the legs or back. If this is the case, we’ll cover them to make sure the baby doesn’t come into contact with them.
How can I protect my newborn from getting herpes?
If your partner has herpes and you don’t, do not have sex and oral sex the last few weeks of pregnancy. Condoms can reduce the risk of transmission but aren’t 100% effective. There’s no reason to risk a new infection close to delivery.
Condoms can reduce the risk of transmission but aren’t 100% effective. There’s no reason to risk a new infection close to delivery.
In the unlikely event your baby has been exposed, we’ll treat the baby with antiviral medications. HSV can’t be passed through breast milk, so unless you have sores or lesion on your breasts, breastfeeding is safe.
With visitors, do not allow anyone who has a cold sore or has had one recently to hold your baby. Same goes for people who have a cold or virus. Insist that anyone who wants to hold or touch your newborn wash their hands first – this should be the norm anyway due to COVID-19.
Genital herpes is a common condition, and we are well-equipped to help reduce your baby's risks. If you or your partner has a history of herpes, talk with your Ob/Gyn. We are eager to help you have a safe pregnancy and delivery.
To visit with an Ob/Gyn, call 214-645-8300 or request an appointment online.
Herpes during pregnancy - consequences of lichen for pregnant women
Herpes viruses are many-sided and very dangerous for humans.
 Of particular concern is the infection in a woman expecting a baby.
Of particular concern is the infection in a woman expecting a baby. Doctor's consultation
You can get the consultation of the necessary specialist online in the Doctis application
Laboratory
You can undergo a comprehensive examination of all major body systems nine0005
- Genital herpes in early pregnancy
- Genital herpes in late pregnancy
- Pregnancy herpes test
- Chicken pox and herpes zoster during pregnancy
- Prevention of infection of the newborn with chickenpox
- Treatment and prevention of exacerbations of herpes
There is an opinion that if a pregnant woman is infected with the herpes simplex virus, then the unborn danger! But everything is not so scary if the disease does not manifest itself (is in stable remission) or a pregnant woman with an active form of the disease is observed by an infectious disease specialist. Today approaches to maintaining patients with genital herpes changed
Today approaches to maintaining patients with genital herpes changed
Why is herpes dangerous during pregnancy
I am pregnant, short term, and I have genital herpes. Does this mean that I need to terminate the pregnancy?
No way! Genital herpes is not an indication for abortion. Virus crosses the placenta extremely rarely. But for a child, herpes is dangerous if it first appeared a month before birth. or repeated a few days before the birth, since there is a risk of infection of the baby at the time of his passage through the infected birth canal. If infected, the infant will develop severe the disease is neonatal herpes, often occurring with damage to the central nervous system. nine0005
Although during pregnancy the risk of transmission of herpes virus from mother to fetus minimal, tolerate the manifestations of genital herpes and not take antiviral drugs, being afraid the consequences of treatment for the unborn child are not worth it.
After 14 weeks of pregnancy, if genital herpes occurs, treatment with an antiviral drug is possible acyclovir. After 22 weeks, therapy with valaciclovir is possible.
In the vast majority of cases, the herpes simplex virus is transmitted from the mother child during childbirth, so the closer to the end of pregnancy there is a recurrence of genital herpes, the higher the risk of infection of the child and the more relevant the treatment of the disease. nine0037If primary genital herpes or recurrence occurs at or after 36 weeks of gestation, clinicians do not limit treatment to 5-10 days, but continue the entire period until the moment of delivery. As in the case very frequent recurrences of genital herpes during pregnancy (one outbreak in 1-2 months) - at week 36, proactive treatment with acyclovir or its analogues begins and continues until the moment childbirth. The goal of proactive treatment is to prevent recurrence shortly before delivery and to reduce the likelihood of asymptomatic carriage.
nine0005
It must be remembered that it is the asymptomatic shedding of the virus from the urogenital tract that can often be cause of infection of the child during childbirth.
Even when there seems to be no cause for concern, since the manifestations genital herpes are absent in the last months of pregnancy, still at 32-34 weeks pregnancy, it is necessary to conduct a smear (scraping) examination from the cervical canal for the presence of DNA herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2 by PCR. nine0037This analysis is necessary for primary genital herpes or its recurrence in the 1st and / or 2nd trimester, relapses genital herpes before pregnancy, relapses of genital herpes in a sexual partner, lesions urogenital tract of unknown cause, antibodies to herpes simplex virus type 1 and type 2 IgM class, detected during a routine examination during pregnancy.
For rashes or virus shedding on Wednesday within 7 days before delivery, especially in the presence of genital herpes by the beginning of childbirth, a caesarean section is performed to reduce the risk of transmission virus from mother to child.nine0037
I'm just planning a pregnancy. And I want to get rid of herpes recurrences that have been haunting me for a long time me. How do you feel about the treatment of genital herpes with interferon inducers and immunomodulators?
Widespread use of immunomodulators and interferon preparations in Russian medical centers (viferon, polyoxidonium, isoprinosine, etc.) for the treatment of herpesvirus infections is completely unreasonable. The so-called "ozone therapy" will not help the patient either. You will not find these methods in international protocols, recommendations for the treatment of viral infections in children and adults, including pregnant women women. Neither in Russia nor abroad have studies been conducted proving the effectiveness of these drugs in accordance with all international regulations. nine0005
An infectious disease specialist, a professional in his field, will never turn to immunomodulators and inducers interferon, but will look for the cause of the disease and prescribe therapy that acts on the pathogen itself - drugs acyclovir, valaciclovir or famaciclovir.With primary genital herpes for 10 days, with relapses diseases - in appropriate doses for 5 days.
Therapy should be started as early as possible at the very first signs of an exacerbation. Application possible antiherpetic drugs as a preventive treatment - 2-3 days before the expected relapse, if the patient is aware of the factors that provoke it, and for the entire period of the risk factor. If genital herpes disturbs a person more than 6 times a year and / or relapses reduce the quality of life of the patient and bring him not only physical, but also serious psychological discomfort, should be discussed with the patient long-term (at least 12 months) daily suppressive antiviral therapy (for example, valaciclovir). The effectiveness of such treatment tactics for the prevention of recurrence of herpes infection has been proven. all international rules. nine0005
Sequelae of chickenpox during pregnancy
How dangerous are chicken pox and shingles for a pregnant woman?
These diseases are caused by the varicella-zoster virus (VZV), which also belongs to the herpesvirus family.
infect women are most often children who easily tolerate the disease. At the same time, chickenpox in an adult can be severe and dangerous to his health.
Infection is transmitted by airborne droplets from person to person already 48 hours before the onset of the rash, during the entire period of the rash and for a week after appearance of the last bubbles. nine0037Expectant mothers who catch chickenpox may develop severe herpes pneumonia. Therefore, when sick chickenpox during pregnancy should be observed by an infectious disease specialist and in most cases of antiviral therapy.
In maternal varicella at 8 to 20 weeks of gestation infection fetus with the varicella-zoster virus can lead to fetal chickenpox with the development of a "syndrome congenital chicken pox" with severe malformations - damage to the brain, eyes, skeletal defects. Therefore, if a woman falls ill with chicken pox in the 1-3rd month of pregnancy, the doctor the woman should be informed about all possible risks of the disease for the fetus and discussed with her the question of a possible termination of pregnancy.
nine0005
Second and third trimesters infectious disease doctor monitors the state of the future mothers. If the infection is severe or the infection occurred in the last month of pregnancy, prescribe antiviral treatment with acyclovir or its analogues. If ultrasound does not detect fetal pathology, pregnancy is not interrupted.
Within 96 hours (preferably within the first 48 hours) after contact a pregnant woman with chickenpox in the absence of IgG class antibodies to VVZ it is possible to introduce a specific VVZ-immunoglobulin as a measure to prevent the development of the disease. Immunity persists for 3-4 weeks, may be re-introduced after 21 days. nine0037If the mother-to-be becomes ill with chicken pox in the last month of pregnancy , then the child may be born with skin rashes. If a woman falls ill in the last few days of pregnancy or in the first days after childbirth in a newborn infected during childbirth, the symptoms of chickenpox appear in the first 11 days of life.
Chickenpox is most severe in infants whose mothers fell ill 5 days before or 2-3 days after delivery. In case of chickenpox in mothers, newborn children are given a specific immunoglobulin to prevent the development of the disease. In case of its severe course - appoint acyclovir for intravenous administration. nine0005
Infection of a child with VVV a few days after birth may manifest as postnatal varicella in the period of 12-28 day of his life. This form of the disease is less severe, it is possible to introduce a specific immunoglobulin with the risk of the disease and the appointment of intravenous acyclovir for destructive skin lesions.
Vaccination against the varicella-zoster virus is not given to pregnant women because this is a live vaccine. Therefore, if a young woman does not have IgG antibodies to VVZ before planning pregnancy, it is advisable to vaccinate against chicken pox. nine0037Herpes zoster ("secondary" VVZ infection) in a pregnant woman is not dangerous for a child.
Contact seronegative pregnant woman with herpes zoster is not desirable, although the threat of her infection There is practically no VVZ.
I'm just planning a pregnancy. And I want to get rid of herpes recurrences that have been haunting me for a long time me. How do you feel about the treatment of genital herpes with interferon inducers and immunomodulators?
nine0002 Widespread use of immunomodulators and interferon preparations in Russian medical centers (viferon, polyoxidonium, isoprinosine, etc.) for the treatment of herpesvirus infections is completely unreasonable. The so-called "ozone therapy" will not help the patient either. You will not find these methods in international protocols, recommendations for the treatment of viral infections in children and adults, including pregnant women women. Neither in Russia nor abroad have studies been conducted proving the effectiveness of these drugs in accordance with all international regulations.nine0005
Infectionist, a professional in his field will never turn to immunomodulators and interferon inducers, but will look for the cause of the disease and prescribe an effective pathogen therapy - drugs acyclovir, valaciclovir or famaciclovir. With primary genital herpes for 10 days, with relapses of the disease - in appropriate doses for 5 days.Therapy should be started as early as possible at the very first signs of an exacerbation. Application possible antiherpetic drugs as a preventive treatment - 2-3 days before the expected relapse, if the patient is aware of the factors that provoke it, and for the entire period of the risk factor. If genital herpes disturbs a person more than 6 times a year and / or relapses reduce the quality of life of the patient and bring him not only physical, but also serious psychological discomfort, should be discussed with the patient long-term (at least 12 months) daily suppressive antiviral therapy (for example, valaciclovir).
The effectiveness of such treatment tactics for the prevention of recurrence of herpes infection has been proven. all international rules. nine0005
If you have any questions, you can ask your doctor obstetrician-gynecologist or infectious disease specialist online at Doctis app.
The author of the article: Vasily Iosifovich Shakhgildyan
Herpes and pregnancy: what to do? | Mamovedia
Recently, in pregnant women, along with well-known microorganisms such as Trichomonas, gonococci, chlamydia, which provoke the occurrence of inflammatory diseases of the genital tract, more and more often diagnose herpes virus lesions. nine0005
What should a pregnant woman who has been diagnosed with herpes do?
Ideally, of course, for a good pregnancy, a woman needs to plan it in advance and pass all tests for infections in advance, since drugs that are contraindicated for pregnant women are used in the treatment of herpes.
But, if this was not possible and herpes is detected, then you should not panic either. It is necessary to strictly follow all the doctor's instructions, since herpes can pose a threat to the health of the fetus and cause malformations and pathologies in it. nine0005
There are two types of herpes virus that can affect pregnant women.
The first type infects the mucous membranes of the eyes, lips, nose and skin of a woman, and the second type of virus infects the mucous membrane of the genital organs. Sometimes it happens that the body of a pregnant woman is affected by two types of herpes virus at the same time.
The herpes virus is transmitted by airborne droplets, as well as through dishes, household items, through kissing and sexual contact. After the herpes virus enters the body of a pregnant woman, it immediately penetrates into the blood and lymph, and through them into other organs. Once in a woman's body, the herpes virus remains there for the rest of her life.
nine0005
Most gynecologists tend to believe that if the pregnancy proceeds normally and has no complications, then herpes on the lips will not affect the condition of the fetus. In the event that a woman suffers from this problem in her life, then during pregnancy, antibodies to the herpes virus penetrate the placenta into the blood of the fetus and thus protect the unborn child from the negative effects of the virus. Treatment of herpes on the lips is carried out using local remedies that are not absorbed into the bloodstream and do not adversely affect the development of the fetus. nine0005
Unlike herpes on the lips, genital herpes that occurs during pregnancy, especially in the first trimester, poses a serious danger to the fetus. But at the same time, a woman also has a fairly high probability of carrying and giving birth to a healthy baby, since it is the primary episode of infection during pregnancy that is dangerous. If there is a relapse, the doctor may decide on the need for a caesarean section in order to avoid infection of the fetus.
It is impossible to completely remove the herpes virus from the body. Nevertheless, it is necessary to treat herpes without fail. A very important step in the treatment of herpes in a pregnant woman is to strengthen the immune system, which will increase the body's resistance against the virus and this will prevent the herpes virus from developing further and appearing more actively. In order to increase immunity, you need to improve nutrition, walk more in the fresh air, play sports and physical activity, and, if possible, harden. But with the use of immunostimulants, you must be very careful and do not start using them without first consulting with the doctor who is pregnant. nine0005
According to the recommendations of the World Health Organization, in the event that a woman has a primary infection with the herpes virus before twelve weeks of pregnancy, then, in most cases, the pregnancy is recommended to be terminated. If an outbreak of the herpes virus in a pregnant woman occurs repeatedly, then the risk of infection with this virus of the fetus is quite low and is only 0-8%.
This is due to the fact that the concentration of the herpes virus in the mother's blood is lower and the period of its exposure is shorter. And in this case, with proper treatment, pregnancy will have a successful outcome. nine0005
Atypical forms of chronic genital viral infection are quite dangerous for the fetus. Such a virus can provoke the development of congenital herpes in an unborn child. Also, with such a herpes virus in newborns, a fairly high mortality rate is observed - from 50-70%. This fact once again confirms the need for a married couple (both a woman and a man) to undergo a comprehensive examination for the presence of herpes and other sexual infections in the body before starting pregnancy. All infections, including herpes infection, detected before pregnancy, are subject to successful treatment under the supervision of an experienced doctor. nine0005
For the treatment of herpes in a pregnant woman, the doctor prescribes drugs that inhibit the pathogen, as well as drugs that help strengthen and increase the woman's immunity.