Pregnancy with spondylolisthesis
Spondylolysis and pregnancy--a risk analysis
. 1986;65(7):727-9.
doi: 10.3109/00016348609161490.
H Saraste
- PMID: 2949484
- DOI: 10.3109/00016348609161490
H Saraste. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 1986.
. 1986;65(7):727-9.
doi: 10.3109/00016348609161490.
Author
H Saraste
- PMID: 2949484
- DOI: 10.
3109/00016348609161490
Abstract
A possible interference of various musculo-skeletal anomalies with pregnancy is often discussed by obstetricians. Pregnancy as a risk factor for progression of spondylolisthesis, olisthesis as a risk factor for pregnancy complications, and pregnancy in women with spondylolysis as the cause of increased low-back symptoms, are questions hitherto not analysed. In the present study, a comparison between men, non-pregnant women, and women who had been pregnant, was made with respect to the degree of spondylolisthesis and its subsequent progression over an observation period of at least 20 years. Occurrence and intensity of low-back symptoms, and functional impairment due to low-back symptoms (such as change of work, sick-leave, sick-pension, limitation in non-occupational activities, and treatment) during this long observation time were also analysed. The mean values for the group of women who had been pregnant did not differ from those of the other groups as regards any of these variables. On the basis of these results, it is concluded that pregnancy does not constitute a risk for progression of spondylolisthesis, or for increased low-back symptoms in a woman with spondylolysis. Nor is spondylolysis, with or without olisthesis, a risk factor for pregnancy complications.
On the basis of these results, it is concluded that pregnancy does not constitute a risk for progression of spondylolisthesis, or for increased low-back symptoms in a woman with spondylolysis. Nor is spondylolysis, with or without olisthesis, a risk factor for pregnancy complications.
Similar articles
-
Symptoms in relation to the level of spondylolysis.
Saraste H. Saraste H. Int Orthop. 1986;10(3):183-5. doi: 10.1007/BF00266206. Int Orthop. 1986. PMID: 2945791
-
Occupational spondylolysis and spondylolisthesis.
Jakab G. Jakab G. Baillieres Clin Rheumatol. 1989 Apr;3(1):89-98. doi: 10.1016/s0950-3579(89)80038-x. Baillieres Clin Rheumatol. 1989. PMID: 2661033 Review.
-
Acute progression of spondylolysis to isthmic spondylolisthesis in an adult.
Stone AT, Tribus CB. Stone AT, et al. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2002 Aug 15;27(16):E370-2. doi: 10.1097/00007632-200208150-00023. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2002. PMID: 12195078 Review.
-
[Stress fractures. Spondylolysis and spondylolisthesis of the lumbar vertebrae among young athletes with back pain].
Halvorsen TM, Nilsson S, Nakstad PH. Halvorsen TM, et al. Tidsskr Nor Laegeforen. 1996 Jun 30;116(17):1999-2001. Tidsskr Nor Laegeforen. 1996. PMID: 8766639 Norwegian.
-
Long-term clinical and radiological follow-up of spondylolysis and spondylolisthesis.
Saraste H. Saraste H. J Pediatr Orthop. 1987 Nov-Dec;7(6):631-8. J Pediatr Orthop. 1987. PMID: 2963019
See all similar articles
MeSH terms
Spondylolisthesis and Pregnancy
Spondylolisthesis
Nicola V. Hawkinson, DNP, RN, RNFA
Adjunct Clinical Professor
**Question:** I have grade II spondylolisthesis, but I'm not experiencing any symptoms. What would happen if I became pregnant? Would the weight and pressure of the baby worsen my condition?
—Kingston, RI**Answer:** It's great that you're asking these questions now because it's important to deal with these concerns before becoming pregnant. And fortunately, although you cannot reduce spondylolisthesis, nor prevent possible worsening, there are ways to prevent symptom progression, especially during pregnancy.
But here's the unavoidable truth—pregnancy is hard on your back. In fact, approximately 80% of women report having back pain while pregnant, and many of those women don't have a pre-existing spinal disorder! Posture changes, weight gain, and loss of abdominal strength all directly affect the health of your back. You can learn more in our article about back care and pregnancy. So even though your spondylolisthesis hasn't produced any symptoms, becoming pregnant may exacerbate your condition.
So even though your spondylolisthesis hasn't produced any symptoms, becoming pregnant may exacerbate your condition.
So what can you do? Focus on your health before getting pregnant. Since you have mild grade II spondylolisthesis (you can learn more about the grades of spondylolisthesis here), exercise is a great place to start.
Focus on exercises that engage your core muscles. Pelvic tilts are great for working your abdominals. Swimming and water aerobics are also effective, low-impact activities that increase muscle mass. Enroll in a Pilates class at your local gym. If you need a place to start, read our article about back pain exercises and stretches.
Focusing on your abdominal strength before getting pregnant is important, but it may seem like a waste of time because pregnancy causes your abdominal muscles naturally relax and lose tone. This allows your womb to expand as your baby grows.
Abdominal strength is connected to spine strength because your abdominals support _y_our back muscles.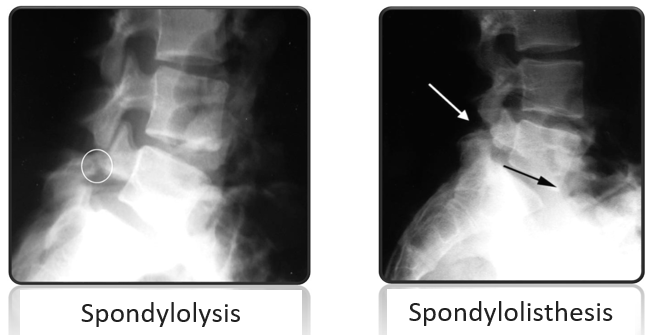 If you have a weak midsection, your back muscles will have to work harder to compensate.
If you have a weak midsection, your back muscles will have to work harder to compensate.
Building a strong core before you get pregnant will stave off the muscle relaxation process. As a result, you'll experience less pain throughout your pregnancy and your body will recover faster after you give birth.
Also, strong muscles will help prevent weight gain. Weight gain puts more pressure on the back and will likely worsen your spondylolisthesis.
Having spondylolisthesis doesn't mean that exercise is off limits. Be proactive about your health, especially if a baby is in your future. Of course, each case of spondylolisthesis is different. Talk to your doctor about your hopes of getting pregnant. He or she will recommend the next steps for you to take to give you the most successful pregnancy possible.
Notes: This article was originally published November 9, 2009 and most recently updated September 27, 2017.
Nicola V. Hawkinson, DNP, RN, RNFAAdjunct Clinical ProfessorNew York University College of Nursing
Dr. Nicola Hawkinson is Adjunct Clinical Professor at New York University College of Nursing in New York, NY. Since 2008 Nicola Hawkinson has been the founder and CEO of SpineSearch, a nationwide recruitment and continuing educational company. SpineSearch works with hospitals, private practices and ambulatory surgery centers to partner highly qualified individuals with specialized career opportunities.
Nicola Hawkinson is Adjunct Clinical Professor at New York University College of Nursing in New York, NY. Since 2008 Nicola Hawkinson has been the founder and CEO of SpineSearch, a nationwide recruitment and continuing educational company. SpineSearch works with hospitals, private practices and ambulatory surgery centers to partner highly qualified individuals with specialized career opportunities.
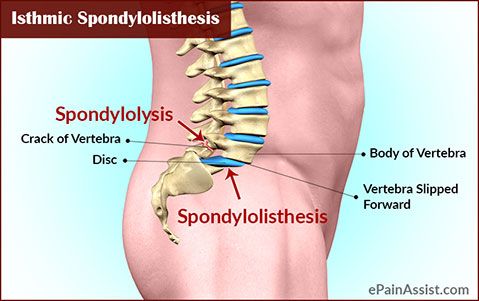
Displacement of the vertebrae
- Home >
- Center for Orthopedics >
- Displacement of the vertebrae
- Offset lumbar vertebrae
- Neck misalignment vertebrae
What is vertebral displacement
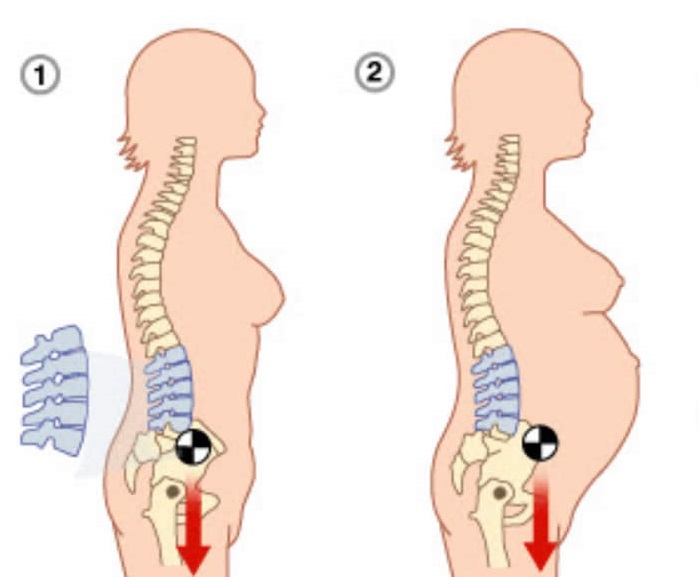
Vertebral displacement is a disease that can affect different age categories, the incidence of this disease is 4-7% in relation to the entire population. Such scale, this figure is quite significant. Pathology manifested in displacement of the vertebrae is commonly called the clinical term "spondylolisthesis".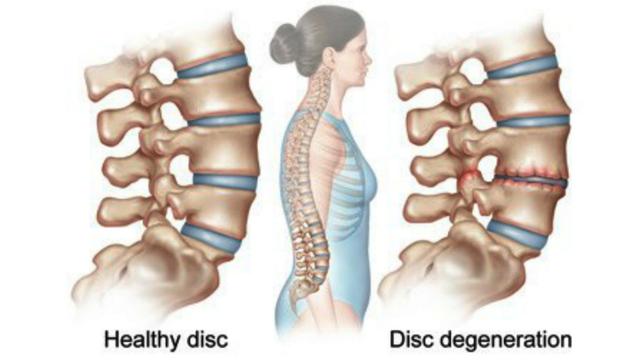 nine0019
nine0019
Among the number of classifications that apply to today, the most relevant divides the disease into degrees: 1st degree - this is the slipping of the vertebra a quarter from the underlying one; 2nd degree is a half shift; 3rd degree - three quarters the vertebra is displaced; 4th degree - more than three quarters.
Depending on the direction of displacement of the overlying vertebrae There are anterior, posterior and lateral spondylolisthesis. nine0019
In any part of the spinal column may occur the phenomenon of displacement of the vertebrae, or spondylolisthesis. However, there is statistic that says bias is most common vertebrae on the borders between the sections of the spine, i.e. often spondylolisthesis occurs at the level of L5 - Sl. Approximately 10% patients suffering from lumbar pain have a displacement of the vertebrae. In a smaller number of cases, this disease involves vertebra L4. It is extremely rare for vertebral displacements to occur in other sections of the spinal column. This is due primarily to the anatomical structure of these vertebrae, as well as the load that they have to. After all, the bulk of the load is distributed to lumbar region. nine0019
This is due primarily to the anatomical structure of these vertebrae, as well as the load that they have to. After all, the bulk of the load is distributed to lumbar region. nine0019
In case of traumatic displacement of the vertebrae in a pathological process may involve different parts of the spine.
Causes of vertebral displacement
Key role in the occurrence of lumbar vertebral displacement (67%) belongs to bilateral spondylolysis. spondylolysis, which is a major factor in the occurrence of vertebral slip relative to each other, characterized by a vertebral defect in the form violation of the integrity of the arc. This leads to destabilization of the spine column, since the static load provokes slipping of the bodies vertebrae relatively. nine0019
The main causes of vertebral mobility:
- Congenital anomalies in the development of the articular surfaces of the processes vertebrae. Such developmental defects are often accompanied by other stigmas of embryogenesis.
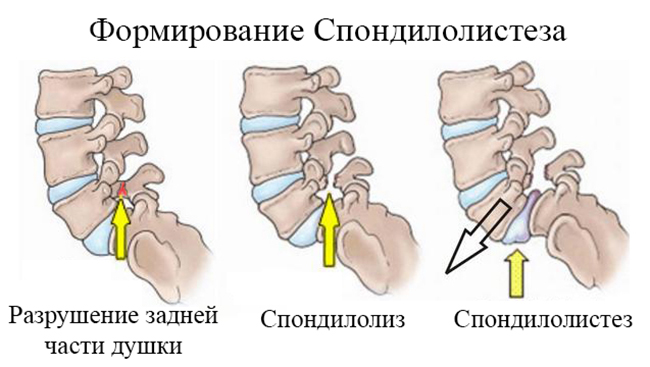
- Degeneratively altered facet (facet) joints. Arthrosis promotes destruction cartilage and joint dysfunction.
- Osteochondrosis leads to chronic progressive destruction of cartilage intervertebral disc. This leads to destabilization of the vertebral pillar. Osteochondrosis deprives the intervertebral disc of its properties, most contributing to the displacement of the vertebrae. nine0004
- Trauma is a universal mechanism for the occurrence of displacements vertebrae for all departments. Trauma causes damage spine, in which at the place of application of force occurs either separation of articular processes, or vertebral arches, or rupture of discs. As a result, there is a shift in the opposite direction applied force. But, due to the specifics of the anatomy of the vertebrae and the curvature spine, the thoracic region suffers from displacement of the vertebrae in the result of the application of a force more significant than in the case of the cervical and lumbar region.
 nine0004
nine0004 - Age-related changes associated with hormonal perestroika. Age-related changes lead to metabolic disorders calcium in the body. This leads to osteoporosis (washout of calcium from bone). Osteoporosis leads to the destruction of the vertebrae, on which account for the maximum load, and, most often, this lumbar vertebrae.
Predisposing factors for vertebral displacement
May play a role in causing vertebral displacement the following factors:
- history of osteochondrosis,
- menopause, as a period in which osteoporosis develops,
- spinal injuries,
- heavy static labor,
- sudden lifting of an excessively heavy load,
- pregnancy,
- history of pelvic trauma,
- congenital anomalies of the musculoskeletal system,
- violation of metabolic processes, nine0003 increased body mass index.
Prevention of vertebral displacement (spondylolisthesis)
For prevention, the following instructions must be observed:
- building materials, do it with someone's help,
- try as much as possible to maintain a normal body mass index,
- comply with safety regulations, avoid traffic injuries,
- during pregnancy, use corsets and bandages for maximum unloading of the lumbar region,
- avoid frequent wearing of high-heeled shoes, and when especially pregnancy,
- use hormonal prevention of osteoporosis in women in menopause.

Clinical picture
The clinic of vertebral displacement depends on the location of the pathology, the degree of involvement of the nervous tissue in this process, on the degree illness. Pain is an essential companion of patients. But Sometimes there is no pain. The painless form is found on initial stages of stable displacement. It intensifies with various kinds of static loads without changing position and rest. nine0019
Radicular symptoms occur when displaced vertebrae press on roots of the spinal cord. This is manifested by pain along the nerves, that originate from these roots, paresthesia, areflexia, violation of the trophism of the muscles for which this nerve is responsible.
Compression of the spinal cord causes more severe symptoms. At traumatic acute compression of the spinal cord at the level of the cervical vertebrae, spinal shock, respiratory and cardiac insufficiency, which without proper assistance can be fatal. nine0019
Flaccid paresis develops below the damaged area of the spinal cord and paralysis.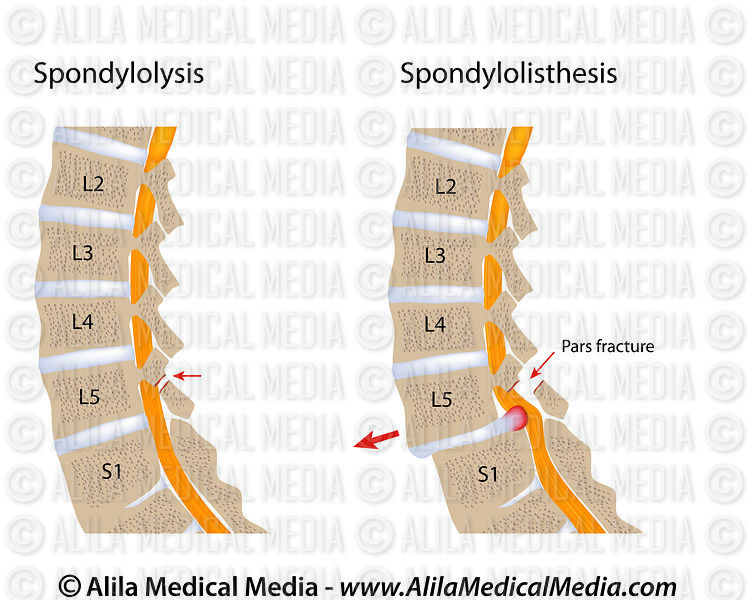 Sensitivity may be missing. Functions are broken pelvic organs. Tension symptoms occur. Decreased reflexes. AT in the lumbar region, the spinal cord passes into the terminal section - "ponytail". When it is damaged, intermittent claudication occurs, pain and weakness in the legs when standing and walking for a long time.
Sensitivity may be missing. Functions are broken pelvic organs. Tension symptoms occur. Decreased reflexes. AT in the lumbar region, the spinal cord passes into the terminal section - "ponytail". When it is damaged, intermittent claudication occurs, pain and weakness in the legs when standing and walking for a long time.
On examination, there is a symptom of "reins", which indicates hypertonicity of the back extensor muscles. Touching and tapping in the area of displacement of the vertebrae causes pain. There is a characteristic "gait of a tightrope walker". On the abdomen, a specific skin fold, which indicates a pronounced lordosis and disease high degree. nine0019
Diagnosis of vertebral displacement
Before resorting to instrumental and hardware methods research, the patient is subject to a thorough examination, which can identify the extent of the process and complications.
MRI is a modern high-precision method diagnostics used gradually more and more often, instead of radiography. Magnetic resonance imaging allows you to distinguish all soft structures that are under compression. Perform MRI at lack of objective data on X-ray examination. On the picture you can see the displacement of the vertebrae, narrowing of the vertebral channel, the degree of spondylolisthesis, pronounced lordosis, the presence spondylolysis, osteochondrosis. nine0019
Magnetic resonance imaging allows you to distinguish all soft structures that are under compression. Perform MRI at lack of objective data on X-ray examination. On the picture you can see the displacement of the vertebrae, narrowing of the vertebral channel, the degree of spondylolisthesis, pronounced lordosis, the presence spondylolysis, osteochondrosis. nine0019
The diagnosis of "displacement of the vertebrae" is determined by yourself impossible. First, the displacement of the vertebrae is often secondary disease, a consequence of other pathologies. Second, before a certain state, the process can be asymptomatic and how once in a while effective measures can be taken therapeutic and preventive measures. In any case, the appearance of back pain due to injuries, over the age of 45, those who already have a diagnosis, associated with diseases of the spine - a reason to turn to neurologist nine0019
Treatment of vertebral displacement at the MART clinic
Treatment of the pathology in question at the MART clinic includes complex of conservative methods. In order to get started to conservative treatment of vertebral displacement, it is necessary to determine indications, contraindications and concomitant diseases.
Indications for conservative treatment:
- vertebral displacement in children and adolescents within the first degrees, nine0003 severe pain syndrome,
- elderly patients,
- patient with a repeated attack of exacerbation of this pathology, previously helped by conservative therapy.
Methods of conservative treatment used in the MART clinic, include:
- Advice to the patient on a long stay restriction regimen time on your feet, exclusion of loads and heavy lifting.
- Determination of the need to wear support bandages and corsets. In this case, you can use corsets of various degrees. rigidity. nine0004
- Medication is needed to control pain. For analgesics, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are used drugs, a course of B vitamins, drugs that improve blood supply.
 In case of strong pain impulses, it is prescribed drug therapy in the form of blockades of analgesics.
In case of strong pain impulses, it is prescribed drug therapy in the form of blockades of analgesics. - Therapeutic exercise is one of the main directions in treatment, as it is responsible for activating the forces and capabilities patient versus pathology. All exercises are for reduction in lumbar lordosis. Exercises are performed on the back, on swedish hill or on an incline. The less pain syndrome, the more exercises you can do in a standing position. In while doing physiotherapy exercises, muscles are strengthened back and abdomen. nine0004
- Massage designed to stimulate flow blood to the muscles, which allows you to relieve spasm and normalize their tone. Apply at least 2 massage courses of 10-20 sessions.
- Physiotherapy procedures, held at the MART clinic always have a positive impact, in the absence of contraindications. Usually they are not prescribed during the period acute phase with severe pain syndrome. The main methods physiotherapy for displacement of the vertebrae are: nine0002
- thermal effect of various fields,
- erythemal ultraviolet doses,
- diadynamic currents,
- sinusoidal modulated currents,
- ultrasound UVF,
- UHF electric field,
- electrophoresis, laser phoresis, magnetophoresis of painkillers substances,
- low frequency magnetotherapy, nine0003 vacuum therapy,
- peloidophoresis (mud therapy).

The MART clinic has a physiotherapy room where experienced certified specialists, exercise therapy doctors. For each patient develops an individual system of exercises, using various simulators, including Thera Band. The attending physician controls and doses the load depending on from contraindications, observes the dynamics of the patient's condition, adjusts the curriculum. nine0019
A course of physical therapy carried out under the supervision of the attending physician, as a rule, brings immediate relief, improving day by day day.
A set of various procedures performed at the MART clinic, necessarily brings a patient with a disease of displacement of the vertebrae relief, stable condition, restoration of physical performance. About 90% of our patients diagnosed "spondylolisthesis" get rid of pain for a long time, with further compliance with the recommendations of doctors and constant care of one's own health, including regular exercise therapy exercises and periodically undergoing supportive courses of physiotherapy treatment.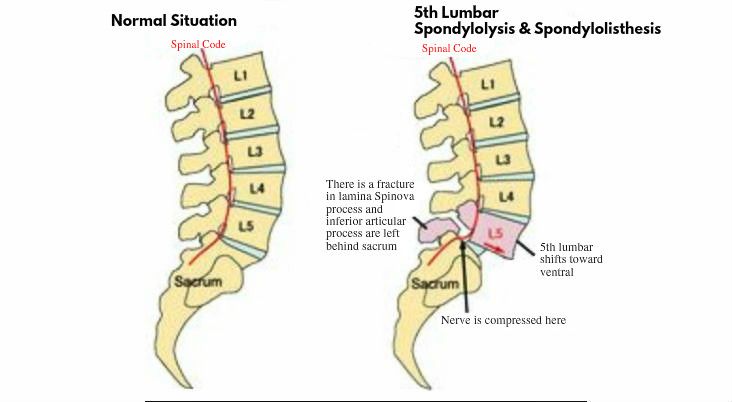 nine0019
nine0019
The article was reviewed by
MD, professor Shvartsman Grigory Isaakovich,
North-Western Medical university. I.I. Mechnikov.
Sign up at the MART medical center in St. Petersburg (see below). card)
by phone: 8 (812) 308-00-18, 8 (921) 947-22-61 or leave a request on the website.
© 2014 - 2023. LLC Medical Center "MART"
There are contraindications. Consult with doctor. 16+
Information on the site is not public offer and is for reference only (Article 437 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
Development, maintenance and promotion of the site spb123.ru
L5-S1 spondylolisthesis and vaginal delivery
nealex
Newbie
- #1 nine0009
- nine0004
- #2
- nine0003 #3
- #four
My wife has L5-S1 spondylolisthesis. She is now 37 weeks pregnant. During pregnancy, there is no worsening of the condition, neuralgic pains, etc. How big are the risks associated with natural rds with such a problem? Which childbirth is better - vertical or traditional horizontal. What is the best hospital to give birth in?
She is now 37 weeks pregnant. During pregnancy, there is no worsening of the condition, neuralgic pains, etc. How big are the risks associated with natural rds with such a problem? Which childbirth is better - vertical or traditional horizontal. What is the best hospital to give birth in?
MRI report:
Statics of the lumbosacral region is not broken. The spinal canal is not narrowed. There is an anterior listesis of the L5 vertebra up to 17 mm. nine0171 The height of the vertebral bodies is not changed. Reactive changes in the end plates of adjacent surfaces L5 and S1 are determined (pronounced subchondral sclerosis).
The contours of the vertebral bodies are minimally deformed due to single marginal osteophytes.
The intensity of the MR signal from the intervertebral disc L5-S1 and its height are reduced - manifestation of dehydration, the disc is deformed, circularly prolapses
(with minimal lateralization to the right). maximum size up to 8 mm with compression of both root holes.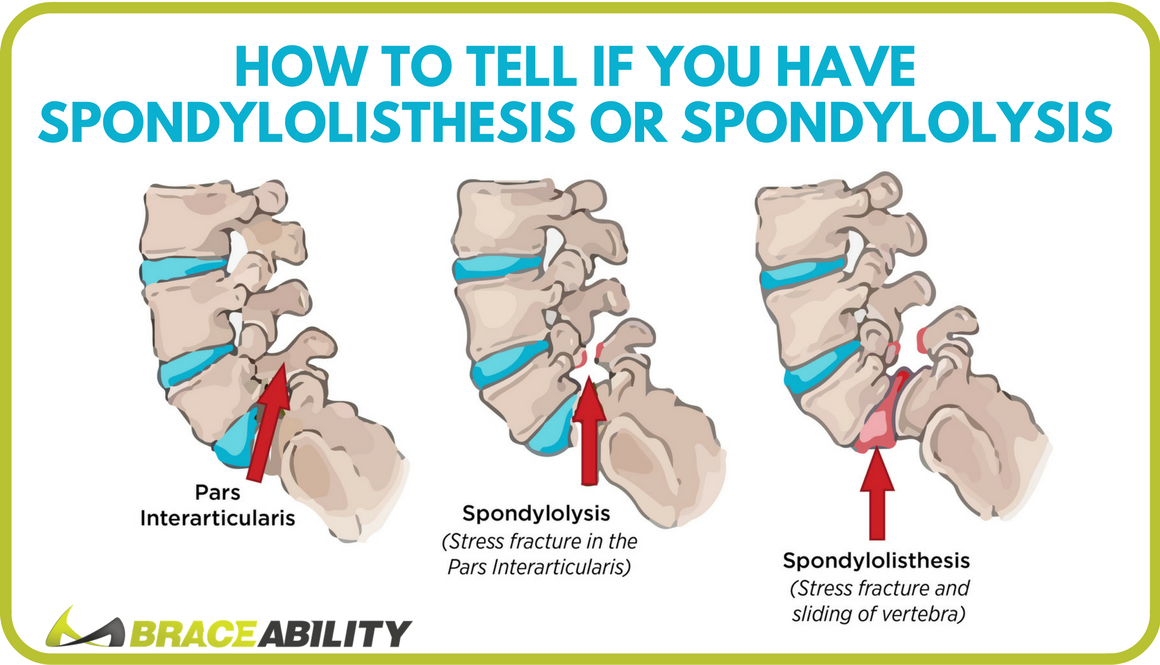 nine0171 At the level of L4-L5, the posterior central protrusion of the disc on the wide base is up to 3.5 mm in size with slight compression of the anterior subarachnoid space.
nine0171 At the level of L4-L5, the posterior central protrusion of the disc on the wide base is up to 3.5 mm in size with slight compression of the anterior subarachnoid space.
The terminal sections of the spinal cord (ends at the level of L1-L2) and elements of the cauda equina are visualized.
The spinal cord has the correct location, homogeneous structure, smooth contours, normal diameter.
The roots of the spinal nerves and elements of the cauda equina have a typical course, normal size and shape. nine0171 CONCLUSION: MRI of anterior listhesis L5, circular protrusion of the L5-S1 disc with reactive changes in the adjacent surfaces of the bodies of these vertebrae, minimal protrusion of the L4-L5 disc against the background of initial manifestations of osteochondrosis of the lumbosacral spine.
Thank you in advance.
Doctor Stupin
Doctor
Answer: L5-S1 spondylolisthesis and natural childbirth
Rather Caesarean.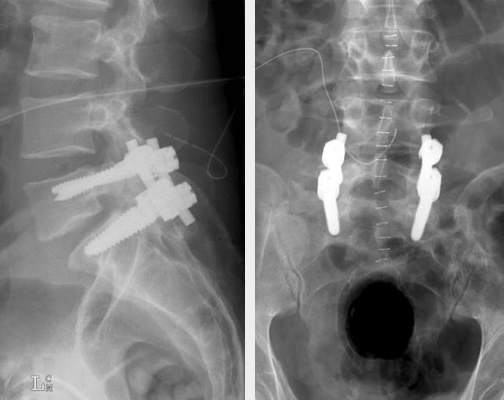
Guzel
Newbie
I also have spondylolisthesis L5 anteriorly by 8mm, I am concerned about the question: is such a diagnosis not a contraindication for pregnancy? How can this threaten me and the child?
Vladimir Vorotyntsev
Physician - chiropractor, rehabilitation specialist
Guzel! Get pregnant and give birth to health! Childbirth can be both natural and caesarean section.