Pregnancy sugar levels chart
Gestational Diabetes - Symptoms, Treatments
Gestational Diabetes
It can be a scary diagnosis, but it’s one that’s fairly common.
Nearly 10 percent of pregnancies in the U.S. are affected by gestational diabetes every year. So know that you’re not alone.
And know that it doesn’t mean that you had diabetes before you conceived or that you will have diabetes after you give birth. It means that, by working with your doctor, you can have a healthy pregnancy and a healthy baby. No matter what, you have all the support you need for both you and your baby.
We don’t know what causes gestational diabetes...
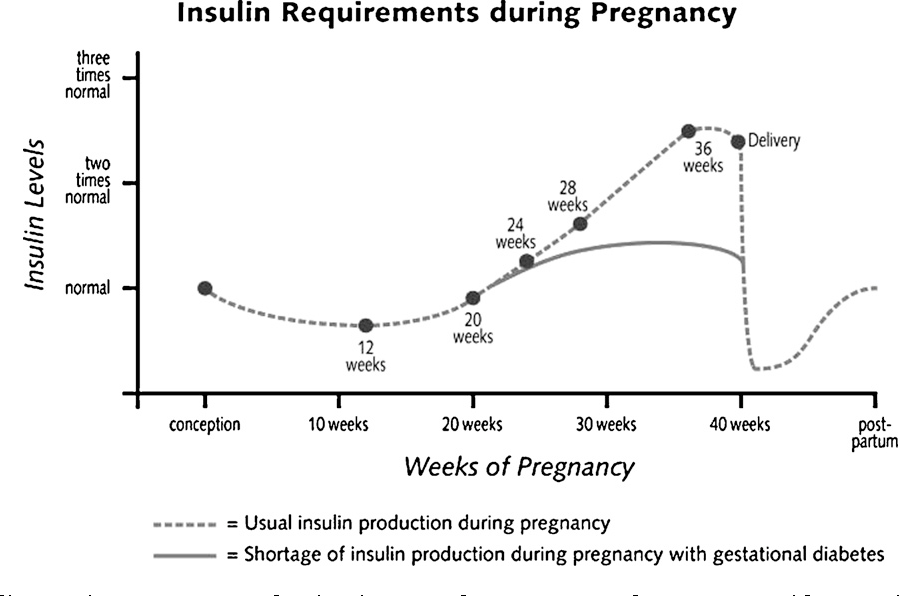
But we know that you are not alone. It happens to millions of women. We do know that the placenta supports the baby as it grows. Sometimes, these hormones also block the action of the mother’s insulin to her body and it causes a problem called insulin resistance. This insulin resistance makes it hard for the mother’s body to use insulin. And this means that she may need up to three times as much insulin to compensate.
Gestational diabetes can also start when the mother’s body is not able to make and use all the insulin it needs for pregnancy. Without enough insulin, glucose can’t leave the blood and be changed into energy. When glucose builds up in the blood, it’s called hyperglycemia.
Whatever the cause, you can work with your doctor to come up with a plan and maintain a healthy pregnancy through birth. Ask questions. Ask for help. There are many ways to combat gestational diabetes.
How You Can Treat ItThe key is to act quickly. As treatable as it is, gestational diabetes can hurt you and your baby.
Treatment aims to keep your blood glucose (blood sugar) levels normal. It can include special meal plans and regular physical activity. It can also include daily blood glucose testing and insulin injections.
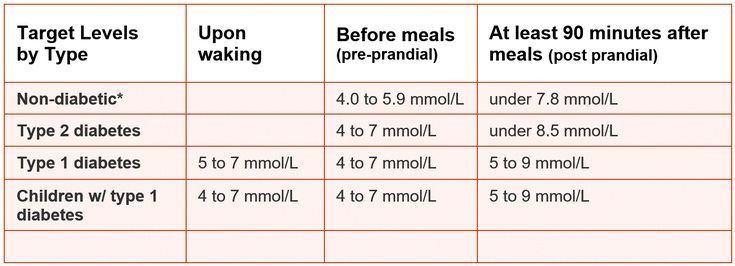
We suggest the following target for women testing blood glucose levels during pregnancy:
- Before a meal: 95 mg/dl or less
- One hour after a meal: 140 mg/dl or less
- Two hours after a meal: 120 mg/dl or less
Always remember that this is treatable—and working with your health care team can help ensure a healthy pregnancy.
As with all forms of diabetes, diet and exercise can help you gain the upper hand. With gestational diabetes, maintaining a balanced diet is integral to your success. Your doctor can help you develop a meal plan that makes sense for you, helping you identify the best foods and quick meal ideas that can help you stay healthy and strong.
Exercise is critical as well. Work with your doctor to determine the level of activity that’s safe for you and your baby throughout your pregnancy. Use our resources as well to stay in touch with ideas for daily activity. The important thing to remember is to take action as quickly as you can, to stay with it, and to stay on top of your condition. It’s treatable. It’s manageable. And it’s a fight that you can win.
Are you depressed?
Nutrition
Fitness
Pregnancy Diabetes Chart or Gestational Diabetes Mellitus Chart
Developed by Medindia Content Team | Calculator reviewed by The Medindia Medical Review Team Last Updated on Feb 10, 2022
Medically, Gestational (jes-TAY-shun-ul) Diabetes Mellitus (GDM) is defined as glucose intolerance, which is diagnosed during pregnancy. It is reported to affect approximately 7% of all pregnancies. GDM can adversely affect both the mother and the baby; hence a diagnosis, if made, should be taken seriously.
It is reported to affect approximately 7% of all pregnancies. GDM can adversely affect both the mother and the baby; hence a diagnosis, if made, should be taken seriously.
Advertisement
Gestational (jes-TAY-shun-ul) Diabetes Mellitus (GDM) is a form of diabetes that affects approximately 4% of pregnant women. In India an overall prevalence of 9 to 18% has been reported. GDM can adversely affect both the mother and the baby; hence a diagnosis, if made, should be taken seriously.
The risk factors for GDM include A family history of diabetes, obesity or testing positive for glucose in the urine. Most pregnant women will undergo screening to check the blood glucose level. If the readings are high, they will be advised to undergo an Oral Glucose Tolerance Test. Blood samples are taken while fasting and also during one, 2 and 3 hours after having 100 gms of glucose. These samples are tested in the laboratory and the readings are interpreted.
| Sample drawn after 100-gram glucose drink (glucose load) | |
| Time of Sample Collection | Target LEVEL |
| Fasting* (prior to glucose load) | 95 mg/dL (5.3 mmol/L) |
| 1 hour after glucose load | 180 mg/dL (10.0 mmol/L) |
| 2 hours after glucose load | 155 mg/dL (8.6 mmol/L) |
| 3 hours after glucose load* | 140 mg/dL (7.8 mmol/L) |
| INDICATION: If two or more values meet or exceed the target level, gestational diabetes is diagnosed. | |
Reported prevalence of GDM in a region depends on the methods and criteria used to establish its diagnosis. For example - WHO uses 75 grams of oral glucose load and not 100 gms as described above.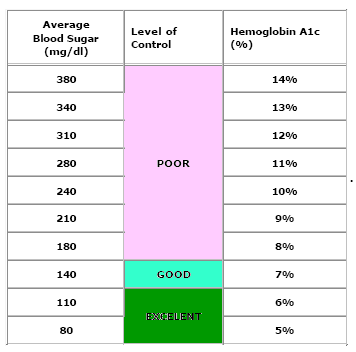 It also suggests only two samples of blood one while fasting and the other at 2 hours after consuming glucose. This method is more cost effective and is used frequently in India.
It also suggests only two samples of blood one while fasting and the other at 2 hours after consuming glucose. This method is more cost effective and is used frequently in India.
The National Institutes of Health Diabetes Data Group (NDDG) from the USA (Diabetes 1979;28:1039) and the values established by Carpenter and Coustan (Am J Obstet Gynecol 1982;144:768-73) uses a 100 gram glucose load. Their diagnosis is based on four measurements (fasting, 1, 2 and 3 hr. glucose levels).
Over the years different investigators have come up with different values with small variations as shown in the chart below.
| NDDG(1979) | Carpenter & Coustan (1982) | Sacks et al (1989) | |
| Fasting | 105 | 95 | 96 |
| 1 hour | 190 | 180 | 172 |
| 2 hour | 165 | 155 | 152 |
| 3 hour | 145 | 140 | 131 |
Remember that women diagnosed with GDM can develop diabetes later on in their life. Hence they are advised to undergo annual screening to enable early diagnosis or to rule out the condition.
Hence they are advised to undergo annual screening to enable early diagnosis or to rule out the condition.
Advertisement
References:
- clinical.diabetesjournals.org/content/23/1/17.full.pdf
- www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/pmc2582643/
- care.diabetesjournals.org/content/27/suppl_1/s88.full#sec-8
- www.hawaii.edu/hivandaids/Gestational%20Diabetes.pdf
Advertisement
Comments should be on the topic and should not be abusive. The editorial team reserves the right to review and moderate the comments posted on the site.
Recommended Reading
Top 12 Healthy Beverages for Diabetics
Diabetic patients need not be wary of drinks. Milk, detox water, whey drink, smoothies, cocoa, herbs or dairy-based drinks offer a wide palette to relish.
Type 1 Diabetes
An overview of type 1 diabetes, its contributing factors, management and adopting a healthy lifestyle to cope with it.
Ultrasound During Pregnancy
Ultrasound during pregnancy is a non-invasive procedure and is an integral part of the fetal monitoring during the pregnancy.
HbA1c or A1c Calculator for Blood Glucose
HbA1c calculator calculates average plasma and whole blood glucose levels. A1c test tells your average blood sugar level in the past 3 months and helps check whether your diabetes is in control.
Diabetes Risk Assessment Calculator
Almost one-third of the people are unaware of the risk factors of diabetes. Find out if you run the risk of diabetes by using Diabetes Risk Assessment calculator.
Quiz on Pregnancy
There is a general belief that a pregnant woman should eat for two people. How far is this true? This compilation of information, presented in the quiz, will tell you ...
Gestational diabetes
The condition is not caused by a lack of insulin, but by the action of hormones produced during pregnancy that blocks the action of insulin.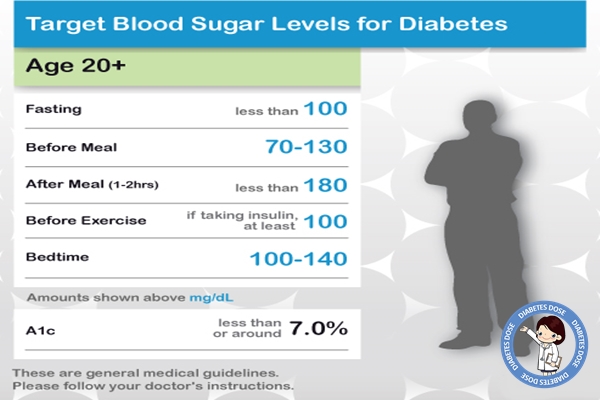
Pregnancy Confirmation Calculator
Are you pregnant? Use Medindia's simple and useful calculator to find out whether you are pregnant or not.
Multiple Pregnancy Calculator
Multiple Pregnancy Calculator assesses your pregnancy symptoms and finds if you are pregnant with twins or triplets or more. Multiple Pregnancy Calculator offers tips for pregnant women.
High Risk Pregnancy Group Calculator
Medindia offers you a useful calculator to find out if you fall under the high risk pregnant group. Take the precautionary steps and avoid complications during pregnancy.
Tell-tale signs / Yoga and Pregnancy
Through yogic practice, the phase of pregnancy can be transformed into a joyous, natural experience bringing about health and wellness to the mother and the baby
Trimester of pregnancy
Encyclopedia section of medindia explains in brief about confirmation of pregnancy in first trimester
Diabetes and Exercise
Regular exercise especially in type II diabetes not only helps reduce the sugar but also reduces the demand for medication by 20% and helps you stay healthy.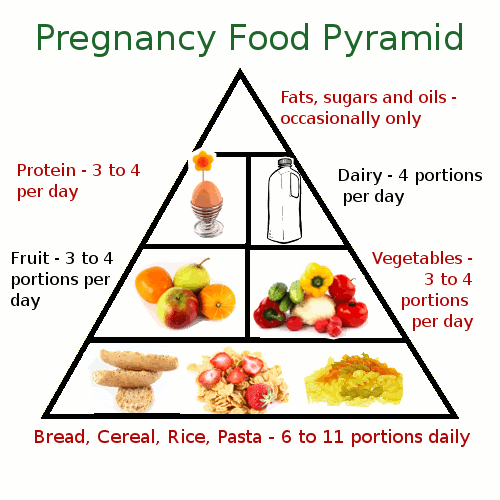
Blood Glucose Checks
Self-Monitoring Of Blood Glucose (SMBG) is recommended for the insulin-dependant and is desirable for all patients with diabetes
Diabetes
A comprehensive article on diabetes - both Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes, including : causes, signs, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, facts and a glossary on diabetes.
Pregnancy and Diet
Pregnant women should pay special attention to their diet. The diet before and during pregnancy should be rich in calories, proteins, vitamins and minerals.
Pregnancy and Complications
In-depth guide for expecting mothers to overcome health complications related to early or late pregnancy. Anemia, urinary infection, diabetes, premature labor to name a few.
Gestational diabetes in pregnancy - treatment and diagnosis of diabetes in pregnant women in Moscow, Clinical Hospital on Yauza
Consult a gynecologist
Service in two languages: Russian, English.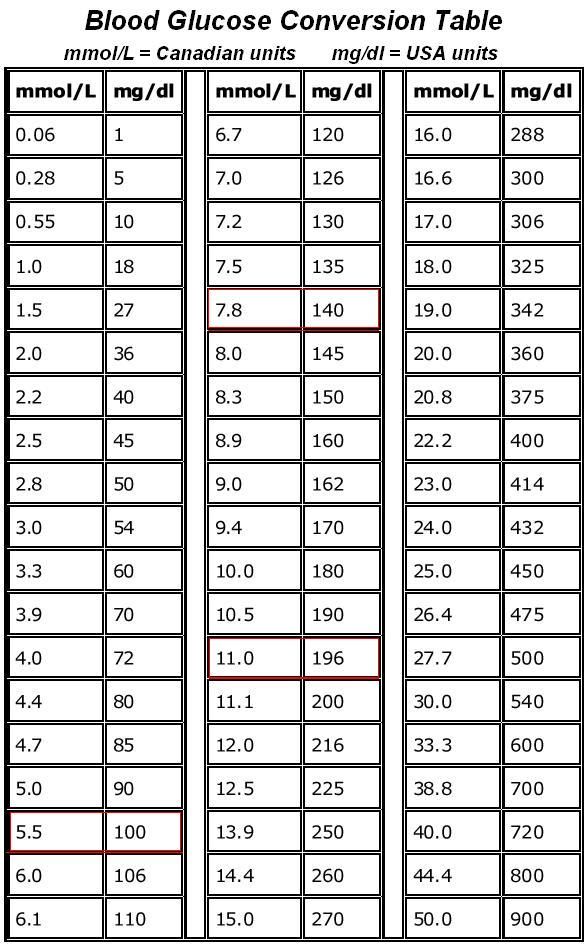
Leave your phone number and we will call you back.
Contents
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section should not be used for self-diagnosis or self-treatment. In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, only the attending physician should prescribe diagnostic tests. For diagnosis and proper treatment, you should contact your doctor. nine0006
Specialists of the Yauza Clinical Hospital diagnose and treat gestational diabetes and its complications. For a comfortable pregnancy and the safety of the expectant mother and baby, we exercise strict control over the blood sugar level of a pregnant woman, if necessary, prescribe a specially designed diet and medications.
Make an appointment with a gynecologist
- About 7% of pregnant women have manifestations of gestational diabetes. In 50% of cases, the disease is asymptomatic
- Gestational diabetes in pregnancy significantly increases the risk of pregnancy complications for both mother and fetus
- Perinatal mortality increases by 2-3% with a combination of diabetes mellitus and pregnancy
Pregnancy diabetes (gestational diabetes) is an increase in blood glucose that first occurs during pregnancy but is not high enough to warrant a diagnosis of diabetes mellitus. These are hidden disorders of carbohydrate metabolism that threaten to develop into diabetes mellitus. nine0006
These are hidden disorders of carbohydrate metabolism that threaten to develop into diabetes mellitus. nine0006
Pregnant blood glucose norm
During pregnancy, all women experience changes in insulin sensitivity and glucose tolerance. This is fine. The difference between the norm and pathology in the degree of change.
Blood tests for diabetes during pregnancy - norm and pathology
- If the test of venous blood taken on an empty stomach shows a glucose level of more than 5.1 mmol / l, this is the norm for pregnant women.
nine0022 From 5.1 to 7.0 mmol / l - gestational diabetes. - If 7.0 mmol / l or more - diabetes mellitus.
- Testing capillary blood (taken from a fingerstick) for the diagnosis of gestational diabetes mellitus is not recommended.
- If during an oral glucose tolerance test (when 75 g of glucose is taken orally during the study) after an hour the glucose level is more than 10.
 0 mmol/l, and after two hours the blood glucose level is in the range of 7.8-8.5 mmol/l - then for pregnant women this is a normal indicator. nine0023
0 mmol/l, and after two hours the blood glucose level is in the range of 7.8-8.5 mmol/l - then for pregnant women this is a normal indicator. nine0023
To better understand what gestational diabetes, or diabetes in pregnancy, is, you need to talk a little about hormonal changes in the body in pregnant women.
Causes of gestational diabetes
Hormonal changes that occur during pregnancy are associated with increased production of large amounts of steroid hormones. Some of them, such as cortisol and progesterone, have a significant effect on cell receptors, increasing their resistance to insulin. nine0005 This leads to an increase in blood glucose levels and requires a significant increase in insulin production by the pancreas. In cases where the compensatory capacity of the pancreas is not enough, sugar metabolism gets out of control and a condition called gestational diabetes or gestational diabetes develops.
This condition occurs quite often. Between 3 and 10% of pregnant women develop pathological insulin resistance leading to gestational diabetes.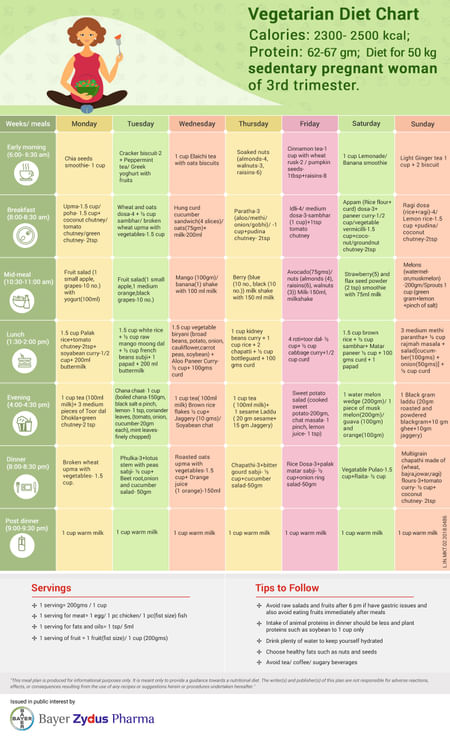 nine0005 Unlike diabetes mellitus diagnosed before pregnancy, pathological insulin resistance that occurs during pregnancy does not cause fetal malformations and in most cases does not require insulin treatment. But, nevertheless, uncompensated gestational diabetes can significantly complicate the course of pregnancy.
nine0005 Unlike diabetes mellitus diagnosed before pregnancy, pathological insulin resistance that occurs during pregnancy does not cause fetal malformations and in most cases does not require insulin treatment. But, nevertheless, uncompensated gestational diabetes can significantly complicate the course of pregnancy.
Specialists of the Yauza Clinical Hospital diagnose, treat and prevent diabetes in pregnant women and its complications, such as impaired fetal growth. The doctors of the Clinical Hospital on the Yauza strictly control the blood sugar level of a pregnant woman, if necessary, prescribe a specially designed diet. This ensures a comfortable pregnancy and the safety of the expectant mother and baby. nine0006
Pregnancy diabetes - consequences for the child
Large disproportionate fruit. The most important and frequent complication of gestational diabetes is fetal growth failure. Developing in conditions of increased blood glucose levels, which penetrate the fetoplacental barrier, the fetus is forced to compensate for the increased sugar level with its own insulin. Due to the fact that the structure of insulin and growth hormone are very similar, high levels of insulin stimulate the growth of the fetus. The problem is that a large fetus develops. In such a fetus, body proportions differ from those of normally developing newborns, in which the volume of the head is larger than the volume of the shoulder girdle. In fetuses with uncompensated gestational diabetes, the size of the shoulder girdle predominates, and the size of the abdomen increases. This leads to the fact that during childbirth after the fetus's head passes through the birth canal, the shoulders can get stuck (shoulder dystocia) and the child, along with the mother, can be severely injured or die. nine0006
Due to the fact that the structure of insulin and growth hormone are very similar, high levels of insulin stimulate the growth of the fetus. The problem is that a large fetus develops. In such a fetus, body proportions differ from those of normally developing newborns, in which the volume of the head is larger than the volume of the shoulder girdle. In fetuses with uncompensated gestational diabetes, the size of the shoulder girdle predominates, and the size of the abdomen increases. This leads to the fact that during childbirth after the fetus's head passes through the birth canal, the shoulders can get stuck (shoulder dystocia) and the child, along with the mother, can be severely injured or die. nine0006
Polyhydramnios or oligohydramnios. In addition, in gestational diabetes, the balance of the amount of amniotic fluid can be disturbed and either polyhydramnios or oligohydramnios develops. This is a serious risk factor for intrauterine fetal death or premature birth.
Underdevelopment of the lungs. In gestational diabetes, the lungs of the fetus mature later, as the production of surfactant (a special lubrication of the inner walls of the alveoli, where oxygen is exchanged in the lungs) is disrupted. Therefore, premature birth in gestational diabetes is especially dangerous. nine0006
Hypoglycemia and metabolic disorders in the fetus. Due to the constant increased production of its own insulin during pregnancy, immediately after birth, the child is in a state of hypoglycemia with electrolyte imbalance, which threatens his life.
All this dictates the need for the earliest possible detection of gestational diabetes in pregnant women, the level of sugar in the blood of a pregnant woman and to prevent the development of complications.
. nine0006
Diagnosis of diabetes in pregnant women at the Yauza Clinical Hospital
Signs of diabetes in pregnant women
Gestational diabetes in pregnancy is not usually associated with the classic symptoms of diabetes, such as thirst or excessive urination (polyuria).
Pregnancy tests for diabetes mellitus
First phase. At the first visit of a pregnant woman to a doctor at any time, she is tested for glucose levels in venous blood - fasting glucose, regardless of food intake, glycated hemoglobin. This is the first phase of research to detect diabetes mellitus or gestational diabetes in pregnant women. If diabetes mellitus is detected, the patient is referred for observation and treatment to an endocrinologist. nine0006
Second phase. For a period of 24-28 weeks, all patients who did not show identified disorders of carbohydrate metabolism at the first study are called for a glucose tolerance test (PGTT) to detect "hidden diabetes". This is done because the occurrence of gestational diabetes is associated with the development of insulin resistance under the influence of hormones produced by the placenta. Therefore, in the vast majority of cases, gestational diabetes develops in the second half of pregnancy after 24 weeks, when there is a peak in the production of placental hormones..jpg) nine0006
nine0006
Glucose tolerance test
It is carried out to detect pathological insulin resistance, characteristic of latent diabetes in pregnant women. Pregnant women undergo a two-hour test, only in the laboratory.
During the 3 days leading up to the test, the woman should eat her usual diet, including carbohydrates (>150 g of carbohydrates per day), maintain her usual physical activity. The evening before testing, dinner should include 30-50 grams of carbohydrates. nine0005 On the day of the study, before the analysis, you should not smoke and take medications that can affect the level of glucose (vitamins, glucocorticoid hormones, iron preparations, which include carbohydrates, beta-agonists, beta-blockers). You can drink water.
Venous blood is taken on an empty stomach (after 8-14 hours of fasting, usually in the morning, before breakfast).
Then the patient takes a glucose solution (75 g).
And they take blood in an hour and two after the sugar load.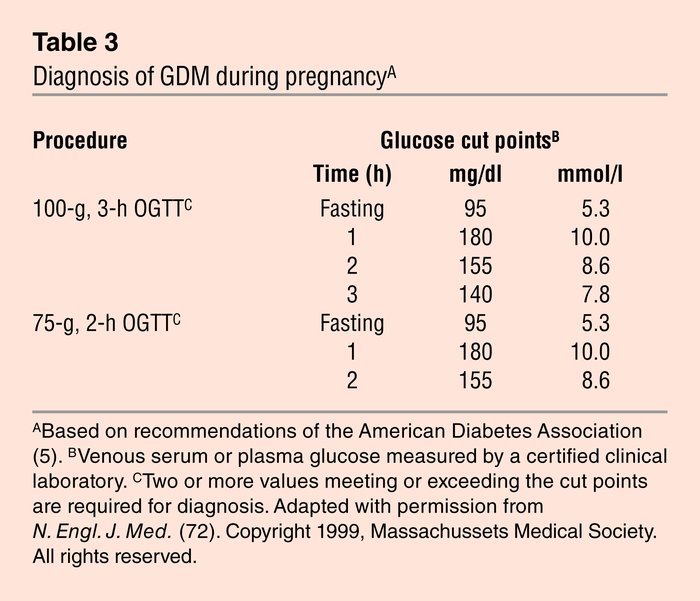 Normally, the level of glucose in the blood after a sugar load should not exceed an hour later - 10 mmol / l, after 2 hours - 8.5 mmol / l. nine0005 If manifest diabetes mellitus is detected, the patient is referred to an endocrinologist, gestational diabetes mellitus is treated by an obstetrician-gynecologist or therapist.
Normally, the level of glucose in the blood after a sugar load should not exceed an hour later - 10 mmol / l, after 2 hours - 8.5 mmol / l. nine0005 If manifest diabetes mellitus is detected, the patient is referred to an endocrinologist, gestational diabetes mellitus is treated by an obstetrician-gynecologist or therapist.
Glucose tolerance test contraindications
- Strict bed rest for a pregnant woman (until doctor's approval).
- Pronounced toxicosis of pregnant women (with nausea and vomiting).
- Acute infectious or inflammatory disease. nine0023
- Exacerbation of chronic pancreatitis.
- Dumping syndrome (syndrome of resected stomach).
Prenatal diabetes monitoring
Blood glucose monitoring, self-monitoring diary
When diagnosing gestational diabetes, it is necessary to establish strict control of sugar levels throughout the subsequent pregnancy and during childbirth. To do this, regularly examine the blood for sugar (glucose). In addition, the patient conducts self-monitoring using a glucometer. nine0006
In addition, the patient conducts self-monitoring using a glucometer. nine0006
It is recommended that a pregnant woman keep a diary of observations in which to record:
- blood glucose level (normal <5.1 mmol/l),
- the presence of ketone bodies in the urine, which is determined by test strips sold in a pharmacy (normally, ketone bodies are absent),
- blood pressure readings (normal <130|80 mmHg),
- fetal movements,
- body weight, nine0022 diet.
Expert ultrasound
Conducting an expert ultrasound examination reveals signs of intrauterine suffering of the fetus (diabetic fetopathy), polyhydramnios. Most often, this is a sign of chronically elevated blood glucose levels, penetrating into the blood of the fetus. This requires urgent correction of the diet and normalization of the level of glycemia (blood sugar). If necessary, insulin therapy.
Make an appointment nine0006
Treatment of gestational diabetes
Diet for gestational diabetes
In most cases, it is sufficient to follow a special diet recommended by a nutritionist based on the body mass index of the pregnant woman and her taste preferences. The effectiveness of diet therapy is determined by the maintenance of normal blood glucose levels. Diet in pregnancy diabetes recommends:
The effectiveness of diet therapy is determined by the maintenance of normal blood glucose levels. Diet in pregnancy diabetes recommends:
- Avoid simple carbohydrates - sweets, pastries, white bread, honey, sugar, jam, sweet drinks and fruits, ice cream. nine0023
- Limit complex carbohydrates - cereals (semolina, rice - exclude), potatoes, corn, legumes, durum wheat pasta. Distribute their intake evenly over several meals throughout the day to eliminate starvation (causes the formation of ketone bodies).
- Eat enough protein - meat, fish, seafood, poultry, mushrooms, eggs, hard cheese, dairy and sour-milk products of medium fat content (3-5%).
- It is necessary to enrich the diet with fiber and vitamins - greens, vegetables (except for boiled carrots and beets), sweet and sour berries (excluding grapes). nine0023
- Correctly choose fats, do not exceed their amount recommended by the doctor - vegetable oils (add to ready-made meals), nuts, seeds.
 Animal fats (butter, sausages) - limit.
Animal fats (butter, sausages) - limit. - When cooking, boil, stew, steam and bake dishes. Don't fry. Do not deep fry.
A detailed menu for a pregnant woman with gestational diabetes will be compiled by a doctor, taking into account the individual characteristics of each particular woman. nine0005 It is not worth using table No. 9 in its pure form for pregnant women with diabetes mellitus due to a significant restriction of its calorie content.
In detail, what you can eat with diabetes in pregnant women will be told by the doctor at an in-person consultation.
Pharmacotherapy
In cases where the diet fails to achieve the desired control of the level of glycemia in the blood, there are signs of a negative effect on the fetus - they resort to prescribing drugs - insulin. In case of diabetes in pregnant women, antidiabetic drugs in tablets should not be used. Insulin therapy is prescribed by an endocrinologist. Pregnant women with diabetes who are on insulin therapy are jointly managed by an endocrinologist, an internist and an obstetrician-gynecologist. nine0006
nine0006
Physical activity
Patients are recommended regular physical activity - walking in the fresh air (at least 150 minutes per week), swimming.
Prenatal diabetes - childbirth
With a compensated course of gestational diabetes, normal development of the fetus and the condition of the woman, childbirth is carried out in time in a natural way. The question of early delivery, caesarean section may arise if there are relevant indications from the mother or fetus. nine0006
Specialists of the Yauza Clinical Hospital have included mandatory fetal development screenings and tests to diagnose sugar metabolism disorders in the pregnancy monitoring program. Recommendations are given on a special diet for women with manifestations of gestational diabetes. If necessary, strict glycemic control is carried out throughout pregnancy, ensuring its successful completion and the birth of a healthy child.
Make an appointment nine0006
Cost of services
Prices for services you can see in the price list or check by phone listed on the site.
Attention! Website prices may vary.
Please check the current cost with the administrators by phone.
BOOK AN APPOINTMENT. WE WORK WITHOUT DAYS OFF
Service in two languages: Russian, English.
Leave your phone number and we will call you back. nine0006
Benefits of the clinic
More than 100
specialists
More than 35 000
satisfied clients
Hospital
with 15 beds
More than 30
Gestational diabetes specialties
Gestational diabetes mellitus is a disease characterized by hyperglycemia (increased blood glucose levels) that was first diagnosed during pregnancy. Most often, a woman's glycemia normalizes after childbirth, but there is a high risk of developing diabetes in subsequent pregnancies and in the future. nine0006
Gestational diabetes during pregnancy is a fairly common disease in Russia and the world as a whole..jpg) The incidence of hyperglycemia during pregnancy, according to international studies, is up to 18%.
The incidence of hyperglycemia during pregnancy, according to international studies, is up to 18%.
Disturbance of carbohydrate metabolism can develop in any pregnant woman, taking into account those hormonal and metabolic changes that occur sequentially at different stages of pregnancy. But most high risk of developing gestational diabetes in pregnant women with:
- Overweight/obese and over 25 years of age
- The presence of diabetes in the immediate family
- Impaired carbohydrate metabolism identified prior to present pregnancy (impaired glucose tolerance, impaired fasting glycemia, gestational diabetes in previous pregnancies
- Birth of a child weighing more than 4000 g
In a healthy pregnant woman, in order to overcome physiological insulin resistance and maintain a normal blood glucose level for pregnancy, a compensatory increase in insulin secretion by the pancreas occurs approximately three times (the mass of beta cells increases by 10-15%). nine0006
nine0006
However, in pregnant women, especially those with a hereditary predisposition to diabetes mellitus, obesity (BMI over 30 kg/m2), etc., the existing secretion of insulin does not always allow overcoming the physiological insulin resistance that develops in the second half of pregnancy. This leads to an increase in blood glucose levels and the development of gestational diabetes. With the blood flow, glucose is immediately and freely transferred through the placenta to the fetus, contributing to its production of its own insulin. nine0006
Fetal insulin, having a "growth-like" effect, leads to stimulation of the growth of its internal organs against the background of a slowdown in their functional development, and excess glucose coming from the mother through its insulin is deposited from the 28th week of pregnancy in the subcutaneous depot in the form of fat. As a result, chronic maternal hyperglycemia harms the development of the fetus and leads to the formation of the so-called "diabetic fetopathy".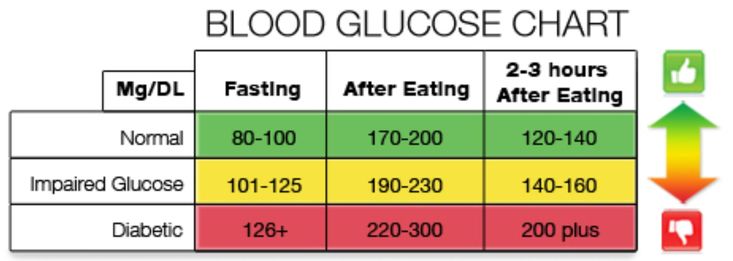
These are fetal diseases that occur from the 12th week of intrauterine life until birth:
- Large fruit weight; violation of body proportions - large belly, wide shoulder girdle and small limbs
- Anticipation of intrauterine development - with ultrasound, an increase in the main dimensions of the fetus in comparison with gestational age
- Edema of fetal tissues and subcutaneous fat
- Chronic fetal hypoxia (impaired blood flow in the placenta as a result of prolonged uncompensated hyperglycemia in a pregnant woman)
- Delayed formation of lung tissue
- Birth injuries
- High risk of perinatal mortality
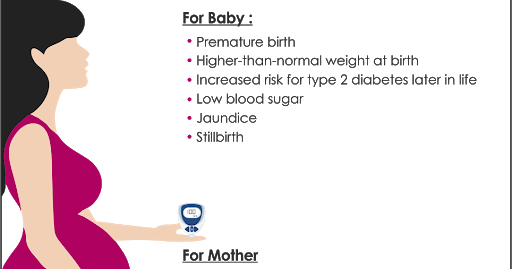
At birth, children with diabetic fetopathy are more common:
- Macrosomia (newborn weight ≥4000 g, or ≥90 percentile in preterm pregnancy)
- Violation of adaptation to extrauterine life, which is manifested by the immaturity of the newborn, even with a full-term pregnancy and its large size
- Respiratory disorders
- Asphyxia
- Neonatal hypoglycemia
- Organomegaly (enlarged spleen, liver, heart, pancreas)
- Cardiomyopathy (primary lesion of the heart muscle)
- Jaundice
- Disturbances in the blood coagulation system, increased content of erythrocytes (red blood cells) in the blood
- Metabolic disorders (low blood glucose, calcium, potassium, magnesium levels)
Children born to mothers with undiagnosed, uncompensated gestational diabetes are more likely to:
- Neurological diseases (cerebral palsy, epilepsy) due to birth trauma
- During puberty and thereafter, the risk of developing obesity, metabolic disorders (in particular, carbohydrate metabolism), and cardiovascular diseases is increased
On the part of a pregnant woman with gestational diabetes mellitus, the following are more common:
- Polyhydramnios
- Infections of the urinary system
- Toxicosis of the second half of pregnancy (a pathological condition that develops in the second half of pregnancy and is manifested by the appearance of edema, increased blood pressure)
- Pre-eclampsia, eclampsia
- Prematurity
- Anomalies of labor activity
- Birth injuries
- Delivery by caesarean section
Gestational diabetes mellitus does not have any clinical manifestations associated with hyperglycemia (dry mouth, thirst, increased urine output per day, itching, etc.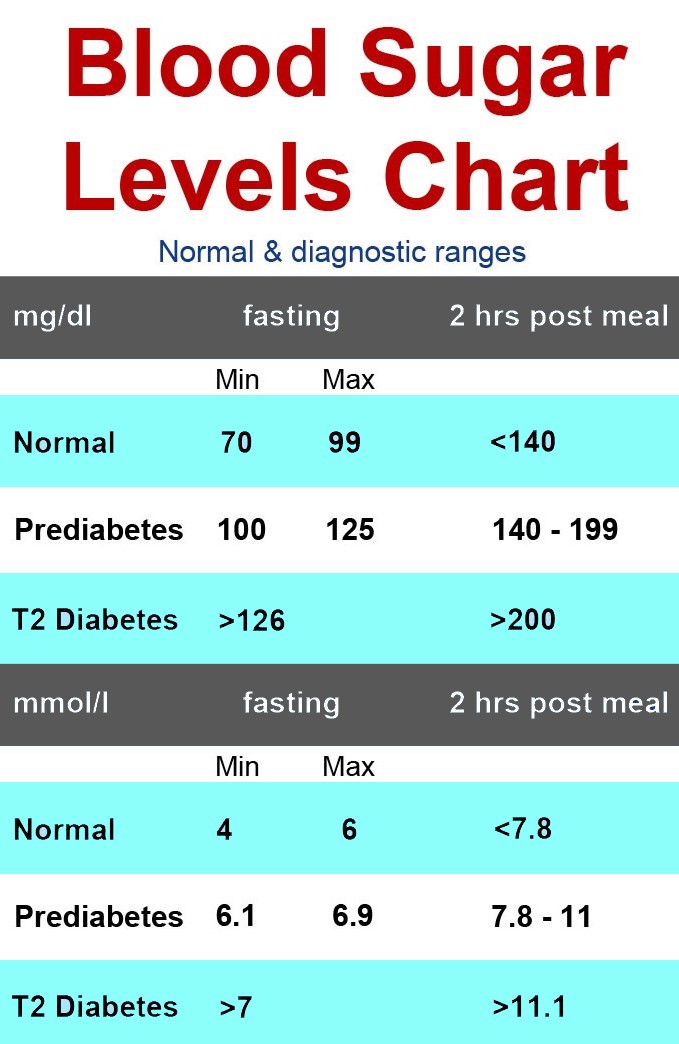 ), and therefore active detection of this disease in all pregnant women is required.
), and therefore active detection of this disease in all pregnant women is required.
Analysis and testing for diabetes in pregnant women
It is mandatory for all pregnant women to test fasting venous blood plasma glucose, in the laboratory - against the background of a normal diet and physical activity - at the first visit to the antenatal clinic or perinatal center, no later than 24 weeks of pregnancy. nine0006
If the results of the study correspond to normal indicators during pregnancy, then an oral glucose tolerance test - OGTT ("load test" with 75 g of glucose) is mandatory at 24-28 weeks of gestation in order to actively identify possible disorders in carbohydrate metabolism.
OGTT with 75 g of glucose is a safe and the only diagnostic test for detecting carbohydrate metabolism disorders during pregnancy.
Rules for conducting OGTT:
- OGTT is performed with a normal diet (at least 150 g of carbohydrates per day) and physical activity for at least 3 days prior to the study
- The test is performed in the morning on an empty stomach after 8-14 hours of overnight fasting
- The last meal must necessarily contain at least 30-50 g of carbohydrates
- Drinking plain water is not forbidden
- The patient must be seated during the test
- Drugs that affect blood glucose levels (multivitamins and iron preparations containing carbohydrates, glucocorticoids, β-blockers), if possible, should be taken after the end of the test
- Determination of venous plasma glucose is performed only in the laboratory on biochemical analyzers or on glucose analyzers.
 The use of portable self-monitoring devices (glucometers) for testing is prohibited
The use of portable self-monitoring devices (glucometers) for testing is prohibited
Stages of implementation of PGTT
After taking the first sample of venous blood plasma on an empty stomach, the patient drinks a glucose solution for 5 minutes, consisting of 75 g of dry glucose dissolved in 250-300 ml of non-carbonated drinking water, or 82.5 mg of glucose monohydrate. The start of taking a glucose solution is considered the beginning of the test. The next blood samples to determine the level of venous plasma glucose are taken 1 and 2 hours after the glucose load.
Norms of venous plasma glucose for pregnant women:
- Fasting
- 1 hour after glucose load
- 2 hours after glucose load
Diagnosis of gestational diabetes mellitus is established by detecting glycemia above or equal to the above indicators. To establish a diagnosis, it is enough to obtain an abnormal result in one of the three points.
After the diagnosis of gestational diabetes mellitus is established, all women need constant monitoring by an obstetrician-gynecologist, a general practitioner together with an endocrinologist
Management of pregnancy in case of diagnosed gestational diabetes mellitus:
In women with gestational diabetes mellitus, taking into account the characteristics of the course of the pathological condition , nutrition should be adjusted.
Diet for diabetes in pregnancy
Easily digestible carbohydrates are completely excluded from the diet (quickly absorbed from the intestines and increase blood glucose levels within 10-30 minutes after ingestion):
- Sugar, fructose, jam, honey, caramel, lozenges, chocolate
- Fruit juices (including juices dispensed at antenatal clinics)
- Lemonades
- Ice cream, cakes, cakes, condensed milk
- Bakery products made from fine flour
- Sweet pastries (buns, buns, pies)
Foods with a high glycemic index are completely excluded from the diet. nine0016
nine0016
Glycemic index (GI) is a measure of the effect of food on blood sugar levels. Each food is assigned a score from 0 to 100 based on how quickly it raises blood glucose levels. Glucose has a GI of 100, which means it enters the bloodstream immediately, a benchmark against which other foods are compared.
Another indicator that helps predict how high blood sugar will rise after eating and how long it will stay at this level - Glycemic Load (GL)
Calculated as:
GL = [GI (%) x amount of carbohydrates per serving (g)] / 100
, but a large amount of carbohydrates will not be effective in maintaining normal blood sugar after a meal.
For example, let's compare the glycemic load of different foods:
Watermelon:
GI - 75, carbohydrates - 6.8 g per 100 g of product, GL \u003d (75x6.8) / 100 \u003d 6.6 g. g per 100 g of the product, GN = (76x38. 8) / 100 = 29.5 g. 6)/100 = 15.3 g. products increases with an increase in the amount of carbohydrates consumed and the glycemic index. Accordingly, it is possible to control the glycemic load by eating low GI foods in small portions several times a day. nine0006
8) / 100 = 29.5 g. 6)/100 = 15.3 g. products increases with an increase in the amount of carbohydrates consumed and the glycemic index. Accordingly, it is possible to control the glycemic load by eating low GI foods in small portions several times a day. nine0006
Glycemic load scale:
During one meal
- Low to 10 g
- Medium 11 to 19 g
- High - more than 20
During the day
- Low to 80 g
- Medium 100 to 120 g
- High - more than 120
It is necessary to give preference to foods with a medium and low glycemic load, eating food in small portions, several times a day, excluding the intake of easily digestible carbohydrates. nine0006
High GI foods should be excluded:
- Sweet fruits and berries: grapes, bananas, persimmons, figs, cherries, melons, dates
- Vegetables: Potatoes, parsnips, pumpkin, boiled beets, boiled carrots, canned sweet corn and peas
- Cereals - millet, wheat groats, semolina, millet, polished rice varieties, and all instant porridges
- Homemade noodles, rice noodles
- Milk
- White or black bread made from premium flour
Also, do not eat foods containing a large amount of hidden fat, so as not to put on too much weight:
- Meat delicacies
- Sausages
- Sausages
- Sausages
- Carbonates
- Ham
- Salo nine0022 Baked ham
- Offal
Preference is given to products with medium and low GI:
- Vegetables: Any cabbage (white cabbage, broccoli, cauliflower, Brussels sprouts, leafy, kohlrabi), salads, herbs (onion, dill, parsley, cilantro, sorrel, mint, basil, asparagus, spinach, wild garlic, tarragon), eggplant, zucchini, pepper, radish, radish, cucumber, tomato, asparagus, onion, garlic, squash, turnip, paprika, capsicum, raw carrot nine0022 Legumes: peas, beans, lentils, beans
- Mushrooms
- Fruits: Grapefruit, lemon, lime, kiwi, orange, apples, pears, tangerines
- Berries: chokeberry, lingonberry, blueberry, blueberry, blackberry, feijoa, currant, wild strawberry, strawberry, raspberry, gooseberry, cranberry, cherry
- Fermented milk products - kefir, fermented baked milk, curdled milk, ayran, tan (no more than 1 glass at a time), yogurt, cottage cheese, cheese
- Meat, chicken, fish.
 During cooking, visible fat is removed and it is melted as much as possible. Best Food Processing—Boiling, Steaming, Roasting, Open Fire
During cooking, visible fat is removed and it is melted as much as possible. Best Food Processing—Boiling, Steaming, Roasting, Open Fire
How to lower your glycemic index and glycemic load:
- Pair medium GI starchy foods with low GI vegetables
- Pasta made from durum wheat flour without vegetables is worse than the same pasta with vegetables
- Do not cook durum wheat pasta until sticky
- Eat cereals made from whole grains (preference is given to barley, buckwheat, oatmeal, wheat, spelt, bulgur) and wholemeal bread with bran
- Kashi (buckwheat, oatmeal) is better to just brew with boiling water and keep warm for several hours. Then the starch under the influence of water and high temperature will not go into a state easily and quickly absorbed by the body
- The more crushed the product, the higher its glycemic index. Nothing Not to Puree
- Eat whole fruits (unlike juices, they contain fiber, which lowers the GI)
- Prefer raw vegetables.
 Vegetables subjected to heat treatment should not be boiled. Fiber is not destroyed during such processing
Vegetables subjected to heat treatment should not be boiled. Fiber is not destroyed during such processing - Try to consume fruits and vegetables as much as possible with the skin, which consists of whole fiber
- Combine protein foods with vegetables, eat starches at the same time as proteins
- Dress salads with a little olive oil (1 tablespoon) with lemon juice
- Fat also lowers the glycemic index
- If you really want something sweet, eat it along with proteins and foods rich in fiber and fat
- Foods containing high fiber carbohydrates should not exceed 45% of the daily caloric intake, they should be evenly distributed throughout the day (3 main meals and 2-3 snacks) with a minimum carbohydrate content for breakfast, as . the contra-insular effect of increased levels of maternal hormones and the feto-placental complex in the morning enhances tissue insulin resistance
- Breakfast should be "protein" (cottage cheese, egg, meat, fish, chicken with vegetables).