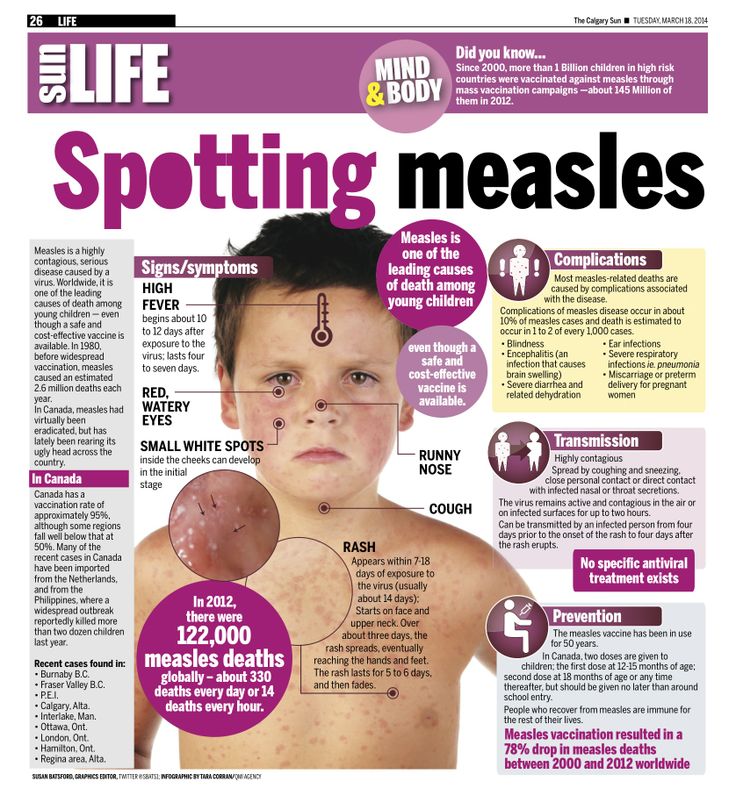
Physical fine motor skills
Toddler development - motor skills
Toddler development - motor skills | Pregnancy Birth and Baby beginning of content7-minute read
Listen
Children grow and develop fast during their toddler years. They start exploring their world more independently. Their coordination improves, and they begin doing more things for themselves. There are many ways in which you can help your toddler develop both their fine and gross motor (movement) skills.
What are motor skills?
Children develop 2 types of motor (movement) skills:
- fine motor skills
- gross motor skills
Fine motor skills involve using your hands and fingers to control small objects.
Gross motor skills involve using the large muscles in your body to make large movements.
Fine motor skills
Fine motor skills engage the small muscles in the hands and fingers so your child can:
- hold
- grasp
- grip
- pinch
Examples of fine motor skills are:
- buttoning up a shirt
- holding a pencil
- picking up food
Children develop fine motor skills so they can learn how to look after themselves. These skills help them to eventually learn to write.
Fine motor skills are important. Evidence suggests there's a link between fine motor skills development and language, literacy and brain development.
Other examples of fine motor skills include:
- clapping hands
- cleaning teeth
- picking up and putting objects down
- putting on shoes
- rolling playdough
- shaking musical instruments
At what age will my child develop fine motor skills?
While all children develop at their own pace, they do reach some milestones within certain age ranges.
Babies start to grasp objects using their hands (but not necessarily their thumbs) between 5 and 6 months old. They usually start to play with hand-held toys between 6 and 12 months.
By 18 months, most toddlers will attempt more complex skills. These may include:
- drinking from a cup independently
- trying to dress themselves
- using a crayon or pencil
From 2 years old, toddlers' fine motor skills become more sophisticated. They may start to show an interest in:
- scribbling
- drawing
- trying to write
Between 2 and 3 years old, they might be able to turn doorknobs and screw jar lids.
By 5 years old, your child might show a preference for one hand over the other.
How can I help my child improve their fine motor skills?
You can help your child grow and practise their newfound skills through play and activities.
- Paint, draw, glue and cut (with safety scissors).
- Pick up objects with tongs or toy tweezers.
- Play with blocks, Lego or do puzzles together.
- Roll playdough into shapes and cut with cookie cutters.
- Sand play using spades and buckets.
- Stacking cups or containers so they can pop the smaller ones into the larger ones. They can also use them to fill with water and practise pouring.
- Thread beads.
Gross motor skills
Gross motor skills involve the movement of the larger muscles in their arms, legs, and torso, such as:
- crawling
- jumping
- running
- throwing
You might notice that as your toddler builds their gross motor skills, they don't like to keep still.
When will my child develop gross motor skills?
Like fine motor skills, kids start developing gross motor skills when they're small babies. Even in their first 2 months, babies will kick their legs and wave their arms around.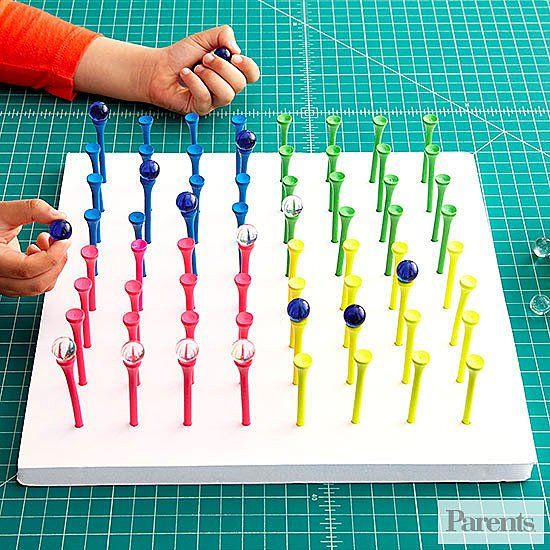
At 6 to 8 months old, your baby should be able to roll, reach and sit independently (if only briefly).
Between 12 and 18 months, most babies are walking.
By 2 years old, toddlers can typically:
- jump over small objects
- throw a small ball or object
- walk up and down stairs
Between 2 and 3 years, kids are capable of more complex movements such as:
- climbing stairs without holding the railing
- running faster
- avoiding obstacles
At 3 to 5 years old, movement may progress to:
- climbing on play equipment
- walking on a balance beam
How can I help my child improve their gross motor skills?
Give your child the space to safely explore their environment and practise their gross motor skills.
You can expect a few falls and bumps. They'll likely be testing their physical limits to know how far they can run, climb, and jump. You can:
- blow and chase bubbles outside
- dance to music at home
- encourage them to 'help' with everyday tasks, such as gardening or hanging clothes on the line
- throw a large ball to them, and have them throw it back
- visit playgrounds, parks, and the beach
- wheel, push or ride on large toy
Try to limit screen time, as this can inhibit movement and physical play.
When to seek help
It’s normal for children to take different amounts of time to reach different milestones. However, if you feel like your child's motor skills aren't developing well, seek advice. See your doctor or child health nurse if your 2 or 3-year-old:
- can't run
- can't walk up and down stairs, even with help
- has difficulty using small objects, like a crayon
- doesn't scribble or try to draw
- loses the physical skills they had before
Where can I get more information and support?
For resources on helping your child’s motor skills develop, you can visit the Learning Potential website.
You can call Parentline in your state or territory for advice and information:
- Parentline ACT: (02) 6287 3833, Mon to Fri, 9am – 5pm AEST / Sat, 10am – 12 midday
- Parent Line NSW: 1300 1300 52, Mon to Fri, 9am – 9pm / weekends, 4pm – 9pm
- Parentline Queensland and Northern Territory: 1300 30 1300, 7 days, 8am – 10pm
- Parent Helpline South Australia: 1300 364 100, 7 days, 7.
 15am – 9.15pm
15am – 9.15pm - Parent Line Tasmania: 1300 808 178, 24 hours, 7 days
- Parentline Victoria: 13 22 89, 7 days, 8am – 12 midnight
- Ngala Parenting Line WA: (08) 9368 9368 or 1800 111 546, Open 7 days a week, 8am – 8pm
Speak to a maternal child health nurse
Call Pregnancy, Birth and Baby to speak to a maternal child health nurse on 1800 882 436 or video call. Available 7am to midnight (AET), 7 days a week.
Sources:
International journal of environmental research and public health (A Network Perspective on the Relationship between Screen Time, Executive Function, and Fundamental Motor Skills among Preschoolers), Queensland Government Early Childhood Education and Care (Developing motor skills), Victoria State Government (Literacy Teaching Toolkit - Fine motor), Australian Children's Education and Care Quality Authority (Developmental milestones and the Early Years Learning Framework and the National Quality Standards), Children's Health Queensland Hospital and Health Service (Red Flags Early Identification Guide), Healthy WA (Child development)Learn more here about the development and quality assurance of healthdirect content.
Last reviewed: July 2022
Back To Top
Related pages
- Physical activity and exercise for children
- Young children and play
- Baby walkers and exercise jumpers
Need more information?
Toddler development: Getting dressed
Learning how to dress and undress are lifelong skills that start in childhood. Learn how to encourage your toddler to start dressing themselves.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Toddler development: Learning to feed themselves
Learning how to feed themselves, even if it's messy, is an important part of your toddler's development. Learn more here.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Handwriting skills for children | Raising Children Network
For toddlers and preschoolers, handwriting starts with drawing with crayons and chalk. Older children learn formal handwriting at school. Read how to help.
Older children learn formal handwriting at school. Read how to help.
Read more on raisingchildren.net.au website
Development milestones - your child at 3 years
Every toddler develops at their own pace but there are certain development milestones that should be reached at 3 years of age. Find out more.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Homemade toys and free activities for kids | Raising Children Network
A little imagination can turn ordinary items into homemade toys and free activities for kids. Get ideas for babies, toddlers, preschoolers and school kids.
Read more on raisingchildren.net.au website
Your baby's growth and development - 12 months old
At 12 months, your baby is now a toddler. If they haven’t already, it won’t be long now before they take their first steps, develop a sense of humour, and tell you they love you.
If they haven’t already, it won’t be long now before they take their first steps, develop a sense of humour, and tell you they love you.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Child development at 4-5 years | Raising Children Network
At 4-5 years, your preschooler is learning to express emotion and likes to be around people. Read how to help child development and spot delay at this age.
Read more on raisingchildren.net.au website
Development milestones - your child at 5 years
Turning 5 is a time of new experiences and changes. Find out what development milestones should be reached by this stage and what are areas of concern.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
7 ways play is beneficial for kids' health | Queensland Health
Playing benefits a child's physical, emotional and intellectual growth.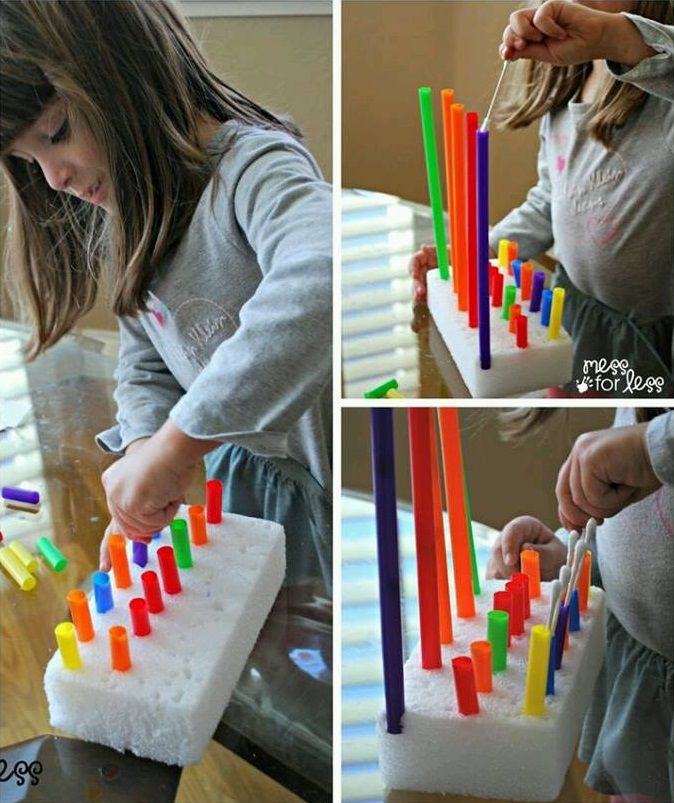
Read more on Queensland Health website
Playing with your baby
Not only is playing fun, but it's also the most effective way for children to learn. By playing, children can practise all the skills they'll need as they grow up.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Disclaimer
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is not responsible for the content and advertising on the external website you are now entering.
OKNeed further advice or guidance from our maternal child health nurses?
1800 882 436
Video call
- Contact us
- About us
- A-Z topics
- Symptom Checker
- Service Finder
- Linking to us
- Information partners
- Terms of use
- Privacy
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is funded by the Australian Government and operated by Healthdirect Australia.
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is provided on behalf of the Department of Health
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby’s information and advice are developed and managed within a rigorous clinical governance framework. This website is certified by the Health On The Net (HON) foundation, the standard for trustworthy health information.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
This information is for your general information and use only and is not intended to be used as medical advice and should not be used to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any medical condition, nor should it be used for therapeutic purposes.
The information is not a substitute for independent professional advice and should not be used as an alternative to professional health care. If you have a particular medical problem, please consult a healthcare professional.
Except as permitted under the Copyright Act 1968, this publication or any part of it may not be reproduced, altered, adapted, stored and/or distributed in any form or by any means without the prior written permission of Healthdirect Australia.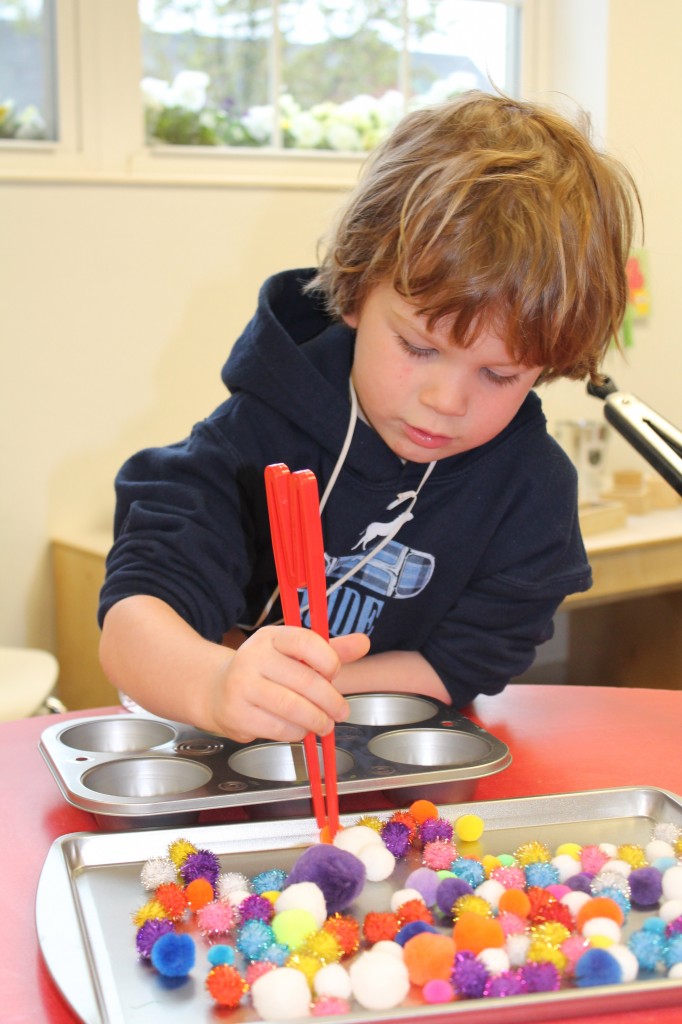
Support this browser is being discontinued for Pregnancy, Birth and Baby
Support for this browser is being discontinued for this site
- Internet Explorer 11 and lower
We currently support Microsoft Edge, Chrome, Firefox and Safari. For more information, please visit the links below:
- Chrome by Google
- Firefox by Mozilla
- Microsoft Edge
- Safari by Apple
You are welcome to continue browsing this site with this browser. Some features, tools or interaction may not work correctly.
Manipulation - Kid Sense Child Development
What is manipulation?Manipulation skills refer to the ability to move and position objects within one hand without the help of the other hand. Manipulation is used when holding a puzzle piece, keys , writing or even cutting with scissors. These are skills we sometimes take for granted.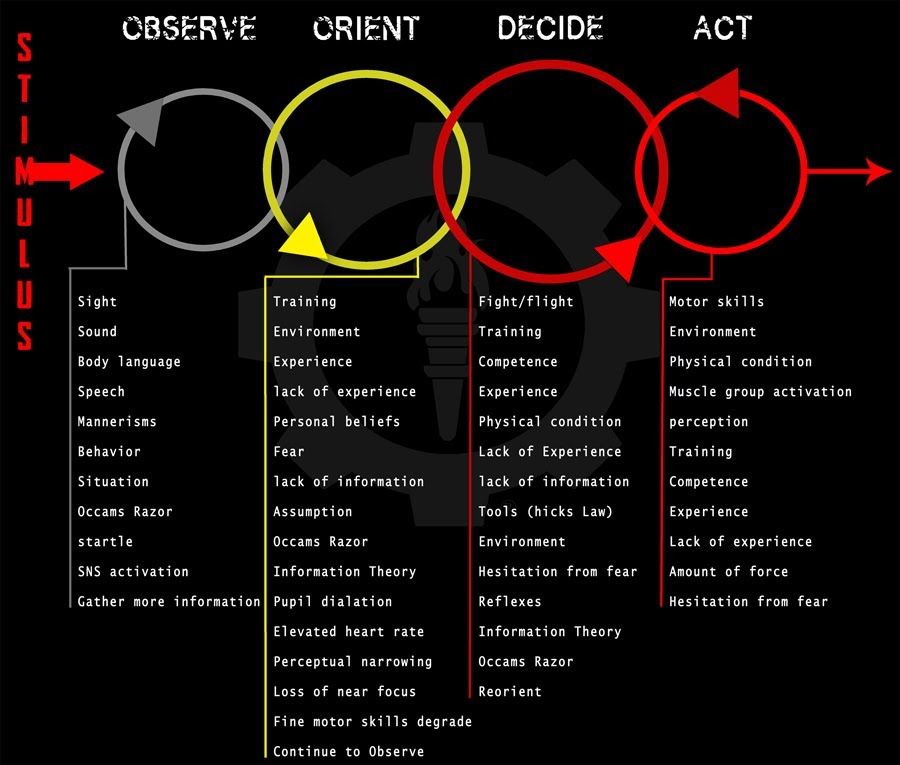 However, they all require the coordination of many skills for successful performance, including fine motor (muscle) control, bilateral integration, coordination and hand-eye coordination.
However, they all require the coordination of many skills for successful performance, including fine motor (muscle) control, bilateral integration, coordination and hand-eye coordination.
Why is manipulation important?
Many daily activities require object manipulation in one hand. Examples include positioning a pencil when writing and drawing; using scissors, holding a knife and a fork; and positioning buttons, zippers, snaps and laces for dressing. When these skills are difficult, children can become easily frustrated and avoid activities involving manipulation, resulting in less refined skills due to a lack of practice. Children who are lacking in these skills often have poor self esteem and confidence as a result.
What are the building blocks necessary to develop manipulation?
- Hand and finger strength: An ability to exert force against resistance using the hands and fingers, that uses muscle strength for task performance.
- Hand-eye coordination: The ability to process information received from the eyes to control, guide and direct the hands in the performance of a task such as manipulating a puzzle piece or pencil.
- Hand dominance: The consistent use of one (usually the same) hand for task performance, which allows refined manipulation skills to develop.
- Hand division: Using just the thumb, index and middle finger for manipulation, leaving the fourth and little finger tucked into the palm not participating but providing stability for the remaining 3 fingers.
- Bilateral integration: Using two hands together with one hand leading (e.g. threading with a string with one hand while the other hand helps by holding the bead).
- Postural control: The ability to stabilize the trunk and neck to enable coordination of the arm and hand for physical task performance.
- Body Awareness (Proprioception): Information the brain receives from our muscles and joints to make us aware of body position and body movement, that then guides future controlled movements.

How can you tell if my child has problems with manipulation?
If a child has difficulties with manipulation they might:
- Use both hands for activities that usually only require one (e.g. cutting or block building).
- Stabilise objects against their body or an external support (e.g. a table) to complete tasks rather than using the ‘helping’ hand to stabilise the object.
- Appear clumsy when handling objects.
- Be slow to complete activities requiring manipulation.
- Avoid activities requiring manipulation such as cutting, drawing and doing up buttons and zips.
- Prefer to get others to perform manipulation based activities for them such as when dressing or eating or in drawing (e.g. “Daddy, draw me a car” but refuses to try themselves).
- Have poor pencil and scissor skills.
What other problems can occur when a child has manipulation difficulties?
When a child has manipulation difficulties, they might also have difficulties with:
- Behaviour: The child may become angry or frustrated when attempting to manipulate small objects, so they are a described as having a ‘short fuse’ or small frustration tolerance.

- Self confidence: The child may have a limited belief in their ability to perform a task, so they avoid it.
- Self care: They might display avoidance, or demonstrate over reliance on adults to, perform everyday life activities (including dressing, eating, cleaning teeth).
- Fine motor skills: Finger and hand skills such as writing, cutting, opening lunch boxes, tying shoelaces, using a computer mouse, opening doors with a key.
- Construction activities such as Lego, block building, cut and paste.
What can be done to improve manipulation?
- Grasping and manipulating: Encourage participation in activities that involve grasping and manipulating small objects such as drawing, puzzles, opening containers, and threading.
- Finger games: Practice tasks that use just one or two fingers (e.g. poking games).
- Praise: Give lots of praise and encouragement when your child engages in these activities, especially if they persist when finding an activity difficult.
 Focus of the participation rather than the degree of skill in the performance.
Focus of the participation rather than the degree of skill in the performance. - Upper limb strength: Encourage play activities that develop upper limb (arm and shoulder) strength (e.g. climbing ladders, wheelbarrow walking).
- Postural control: Ensure the child is able to stabilise their trunk to allow refined movement of the arm and hands/fingers. This may involve reviewing the chair and table they typically use.
What activities can help improve manipulation?
- Small objects: Pick up a small object with fingers (bead, coin, M&M candy, popcorn) and hide it in your hand. Then pick up another then another, while still holding all in your hand.
- Transitioning skills: Move one item from your palm to your fingertips and place it down on the table (or put it in your mouth if it’s food) using just 3 fingers.
- Piggy bank: Place coins in a piggy bank, starting with several coins in the palm to move the coins from palm to finger tips using just 3 fingers.

- String beads: Hold 2 or 3 beads within the palm (as above).
- Pegboard games: Hold 2 or 3 pegs within the hand (as above).
- Twist open or closed lids on small bottles or toothpaste tube using fingers while they are held in the palm of the same hand.
- Cut with scissors: Practice holding the scissors with the thumb on top and adjusting the grip on the paper with the helping hand.
- Dressing: Practice buttoning, zipping and snapping snaps using both hands.
- Construction toys: Play with construction toys such as Duplo, Lego and K’nex.
- Craft activities: Activities that require using bottles to squeeze (e.g. glue, glitter glue, puffy paint, fabric paint).
- Threading: Lacing boards, sewing cards, and beads.
Why should I seek therapy if I notice difficulties with manipulation in my child?
Therapeutic intervention to help a child with manipulation difficulties is important to:
- Help them develop age appropriate self care skills such as dressing, tying shoelaces, opening lunch box items, using keys, putting on a watch.

- Enable the child to develop an appropriate pencil grip for successful academic performance.
- Prevent the child from under-performing.
- Enable the child to be able to effectively manipulate small objects such as blocks, beads and other small toys for confidence in play with peers.
- Enable the child to be able to hold and control scissors effectively.
If left untreated what can difficulties with manipulation lead to?
When children have difficulties with manipulation, they might also have difficulties with:
- Performing handwriting (in the academic setting) which is a leading cause of academic under-performance in children demonstrating their true intellectual capacity on paper.
- Completing assignments that involve cutting and pasting (e.g. poster presentations).
- Effectively holding and moving the mouse for IT work (e.g. mouse on a PC or stylus on an iPad).
- Dressing (e.
 g. doing up zips, button, tying shoes) and other self care skills (e.g. cleaning teeth).
g. doing up zips, button, tying shoes) and other self care skills (e.g. cleaning teeth). - Holding and using cutlery (knife and fork) to cut and prepare food.
- Frustration due to difficulties completing every day tasks such as eating, dressing and writing.
What type of therapy is recommended for manipulation difficulties?
If your child has difficulties with manipulation, it is recommended they consult an Occupational Therapist.
Development of fine motor skills. How to improve fine motor skills?
Read time: 5 minutes
5873 views
viewBox="0 0 18 18">Date: 29 07 2021
What is fine motor skills?
Fine motor skills are a set of coordinated human actions aimed at performing accurate small movements with hands and fingers. It depends on fine motor skills how a child will hold a spoon and a pen. How to use scissors and fasten buttons. nine0003
nine0003
But is it only on the work of the fingers and their dexterity that the success of the development of fine motor skills of the hands depends?
Fingers will not gain dexterity on their own if there is gross motor impairment. If you look deeper, then there are not even muscles in the fingertips. There are tendons, and the muscles themselves, which set the fingers in motion, are located on the forearm.
What if the handwriting is bad?
Let's look at a child with bad handwriting. Such children can press the pen hard, note pain in the thumb after prolonged writing. They cannot take a comfortable position at the table. These are just some of the symptoms that may be observed. Bottom line: it is difficult for a person to control his hand, not to mention more subtle actions. nine0003
About gross motor skills
In order to start working with fine motor skills correctly, it is necessary to restore gross motor skills. For this, too, there are a huge number of exercises and simulators. Exercise and massage help a lot. Coordination exercises are excellent. How can you speed up the process?
Exercise and massage help a lot. Coordination exercises are excellent. How can you speed up the process?
Download the practical guide in PDF format "Using the taping method for staging back-lingual sounds [K][G][X]" free of charge!
How to improve the effectiveness of classes? nine0009
Taping comes to the rescue. With the help of taping, all major joints of the hands can be affected, which improves both coordination and sensitivity of the hand.
You can work not only with the motor skills of the hands, but also with the legs, which will give a tangible result, since the development of the legs and arms is interconnected. And the violation of gross motor skills is not limited to the hands.
Watch a video about how speech is related to gross motor skills and put it into practice! nine0003
if you are not yet familiar with the possibilities of taping, then we recommend downloading our Guide "List of nosologies for the use of taping in speech therapy.
Download without payment.
Participation in the online workshop is free of charge.0003
Feedback from our students and their results
In the meantime, we want to share feedback from our online course! Taping is a modern physiological method that allows you to achieve fast and visible results in a short time!
Fine motor skills as a condition for the physical development of a child in preschool | Presentation for the lesson (senior, preparatory group) on the topic:
"Fine motor skills as a condition for the physical development of a child
in a kindergarten"
Raising children healthy and strong is the task of every preschool institution.
Therefore, it is very important to develop fine motor skills in a child from a very early age, even during physical education classes in kindergarten. Fine motor skills of the hands are a variety of movements with fingers and palms, and large motor skills are movements of the whole hand and the whole body.
Working with children of preschool age, I encounter such problems of children as poor development of the hand, poor memorization of color, shape, impaired motor skills of the hands, such children are dominated by slowness in performing movements, stiffness is observed. When performing tasks, the child begins to act up, his mood worsens. nine0038 Understanding the importance of this problem, I set myself a goal: to develop fine motor skills and coordination of hand movements in preschool children through a playful form of physical exercise.
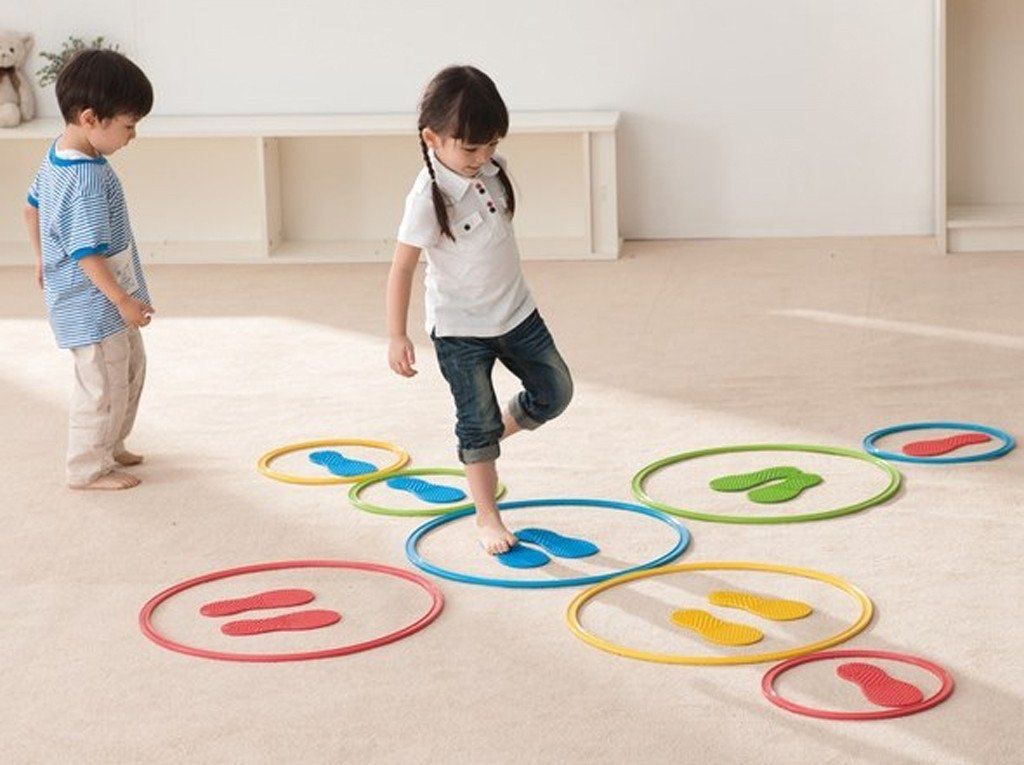
When working with children with it is necessary to pay great attention to physical exercises that contribute to the development of the child's hand. A variety of sports equipment will be used in exercises and games:
- balls of different diameters;
- hoops;
- skittles;
- tapes; nine0003
- flags
- massage balls, rollers, etc.
Physical exercises aimed at developing the child's hand are carried out:
- during morning exercises;
- at physical education sessions;
- in physical education classes;
- during outdoor games on walks, etc.
Such exercises allow you to develop the coordination of movements of all links of the hands and train the small muscles of the hands. The advantage of these exercises in comparison with other types of children's activities (drawing, modeling, appliqué, etc.) is the simultaneous training of both hands. Even if you have to perform a large number of exercises directly aimed at developing fine and precise hand movements, children never complain of fatigue, since all exercises are mostly playful in nature. nine0003
Carpal expander exercises help develop hand strength. The number of repetitions should be feasible and not cause severe muscle fatigue.
It is also helpful to have daily special exercises for the fingers and hands with children, for example: making a fist and unclenching it, showing fingers one at a time, tapping two fingers alternately on a smooth surface. Such exercises improve the motor skills of the hands, strengthen the muscles of the fingers, thin, small movements become more accurate, fast and dexterous. nine0003
nine0003
It is better to start all tasks in physical education classes with exercises that the child will get and give him pleasure. Perform exercises regularly, in a playful way. Instructions for performing exercises should be simple, short and precise. Its repetition, as well as pronunciation of actions in the process of implementation, facilitate the work of children.
Finger games develop in children the ability to work with their hands under the control of consciousness, they improve fine motor skills of the hands, precise finger movements, and develop an eye. nine0003
Finger games develop the child's brain, stimulate the development of speech, creativity, and fantasy. Simple movements help to remove tension not only from the hands themselves, but also to relax the muscles of the whole body.
Work on the development of fine motor skills of the hands should be carried out regularly, only then the greatest effect will be achieved. Tasks should bring joy, avoid boredom and fatigue.
Conclusion
Thanks to physical education classes, where there are many exercises aimed at developing fine motor skills in children, there is a positive trend, which indicates a positive effect of fine motor skills training on the overall physical development of children. nine0003
Games
Children come to class and cannot calm down, their attention needs to be switched, but how? Play with your fingers: make a circle with your fingers alternately, starting with the index one, say hello with your fingers, massage your fingers (pull your finger at the base, then at the middle, at the nail plate - on the side with two fingers of the other hand) and the attention of the children was focused, the children were carried away, heard you.
Sports relay races with objects: “From ice to ice”, “Pass the ball”, dribbling, roll the hoop,
Finger gymnastics "Orchestra" using only fingers to depict various instruments of the orchestra: noise, keyboards, percussion.
Self-massage of the fingers:
I will rub my hands strongly,
I will twist each finger,
I will greet him warmly
And I will start stretching.
I'll put my finger with a finger,
I'll close them with a padlock
And I'll keep warm.
I will release my fingers,
Let them run like bunnies! nine0003
Exercise-game with a handkerchief:
- Magician. We hold the handkerchief in our hand and slowly begin to collect it into a fist, working only with our fingers, until it completely disappears into the fist. Then you can turn your fist, showing that there is no handkerchief. Blow, throwing up a handkerchief and catch with the same hand. Option: hide the handkerchief in a fist, alternately pushing it with the fingers of the other hand into a clenched fist.
- "Washing a scarf." We imitate the movements of washing the handkerchief, in the slope we imitate the rinsing movement, we hold the handkerchief with the thumb and forefinger, imitating a clothespin.
 Then alternately, slightly tossing the handkerchief, we change fingers, intercepting it. nine0155
Then alternately, slightly tossing the handkerchief, we change fingers, intercepting it. nine0155
Exercises with a hoop:
- Handlebar. Turns to the right, to the left, we perform without turning the body.
- House. We raise the hoop above the head, lowering it slowly on the shoulders.
- Yula. Rotation of a vertically placed hoop with the fingers.
- Mirror. We hold the hoop in front of us, “good mirror” - we straighten our arms, “evil mirror” - turn the hoop over, bend our arms.
Clothespin exercise:
- Forest dwellers. We fix clothespins on pre-cut stencils of animals and depict the image of animals: a hare, a hedgehog, a bear, a fox, etc. nine0155
- Mom's helpers. Hanging scarves or other items of clothing on clothespins.
- Hide and Seek. With closed eyes, find clothespins fixed in advance on clothes.
- "Fairy Tale" Together with the children, the plot of familiar fairy tales is played out, while the role of the characters is played with clothespins, voice, imitation in motion.

Exercises with non-standard equipment, rope, wall bars, horizontal bars:
- Minibasketball. Exercises for the development of coordination, eye, large motor skills of the hands. Performing exercises step by step, from simple to complex. nine0155
- rotation, swinging in different directions.
- catching the ball with the hand, into the net.
- Magic wand. A rope 1 to 3 meters long is attached to a small stick, a ball or a car can be attached to the end. In the game - relay race, the child winds a rope on a stick, working simultaneously with two hands.
- "Barrings". Tug of war, you can use a stick - these exercises develop the strength of the muscles of the hands.
- Clever Monkeys. Climbing on the Swedish wall, hanging on the crossbar - these are the best exercises for the development of large and fine motor skills of the hands, the prevention of flat feet. nine0155
Exercises with the help "Cloud"
"Carousel"
Children, together with the teacher, spread and stretch the "cloud" around the entire circumference. Each child takes a colored sector with one hand. The children, together with the teacher, move in a circle and say the words:
Each child takes a colored sector with one hand. The children, together with the teacher, move in a circle and say the words:
Barely, barely
The carousels are spinning.
And then, then, then,
All run, run, run.
Hush, hush, slow down,
Stop the carousel. nine0003
One, two, one, two -
The kids turned around.
The game is repeated with a change of direction 4-6 times.
"Sun and cloud"
Children hold the stretched canvas by the loops with both hands. A larger ball is thrown onto the "cloud" in relation to the hole in the middle of the allowance. Children, by joint actions, pulling or weakening the material, try to roll the ball into the middle. After the ball is rolled, the guys on the team throw the ball up so that the ball does not fall to the floor. The game is repeated 5-6 times. nine0003
The game "Salute"
"A cloud lies on the floor, children pick up balls from a pool of two colors (yellow - boys, red - girls) take the cloud with both hands and slowly raise and lower it to the count of "one, two, three" . After the word "three!" throw the balls up, lower the "cloud" to the floor and scatter to collect the balls. The balls are collected and the game is repeated again.
After the word "three!" throw the balls up, lower the "cloud" to the floor and scatter to collect the balls. The balls are collected and the game is repeated again.
Su-Jok massager is a unique tactile gymnastics that has a total effect on the cerebral cortex, which protects its individual zones from overwork, evenly distributing the load on the brain. Game self-massage with a massager is carried out in the form of 5-minute exercises between the main parts of the lesson (dynamic pauses). nine0038 Exercises to relax the fingers and hands:
• “Let's pet the kitten” - smooth movements illustrating the corresponding action, performed first with one hand, then with the other. (3-5 times).
• "Bunny" - and. p .: the hand rests on the elbow; the index and middle fingers are straightened and spread apart, the remaining fingers are clenched into a fist.
• “Ring” – i. n. the same; the thumb and forefinger are connected into a ring, the remaining fingers are straightened and spread apart.
Su-Jok Sample Exercises :
Rectilinear movements of a prickly ball:
- On the back and palmar side of the hand (first ask the child to depict the sun, spreading the fingers of the massaging hand). The direction of movement is from the fingertips to the wrist joint.
Circular movements on the palm:
- First of one hand;
- Then the other hand.
Spiral movements:
- On the back and palmar surfaces of the hand with the pads of two to five fingers (from the fingertips to the wrist joint). nine0038 Zigzag movements:
- On the palms of both hands (you can use the game image in communicating with children: draw the child's attention to the fact that the hand resembles a tree: the forearm is the trunk, and the hand with spread fingers is the crown).
Slight tingling of all fingers:
- Pads of one hand;
- Pads of the other hand.
Exercises with various small balls
| No. | Exercises | Corrective orientation |
| With small balls (rubber, tennis, etc.): c) Tossing the ball in front of you with your right (left) and catching with two. d) Throwing the ball with the right, catching with the left and vice versa with a gradual increase in flight height | Hand coordination, attention concentration, tracking movements. Concentration of attention, differentiation of efforts in time and space | |
| Throwing the ball high up and before catching, performing various movements (clapping in front, behind, under the knee), turning right, left, around time and space. Switching attention | ||
| a) Hitting the ball on the floor and catching it with both hands. | Differentiation of efforts, visual analysis of the dependence of the height of the ball rebound on the strength and direction of impact, ori | |
| cotton front, back, under the knee, turning around | Differentiation of force and direction of movement, regulation of muscle direction, switching speed, spatial accuracy | |
| a) Circular movements of the hands to the right and left with tennis balls in both hands, b) Alternately tossing balls and catching with the right, then left, c) Simultaneous tossing of 2 balls and catching with both hands after hitting the balls on the floor | Mobility in the wrist joint, distribution of attention, fine differentiation of temporal, power and spatial characteristics of movement, simultaneous solution of two motor tasks (right and left) | |
| , d) Throwing with the right and catching with the right e) Throwing with the left and catching with the left, f) Throwing the ball at a target at close range , distribution of attention | ||
| Throwing at a horizontal target (hoop) from a distance of 4-6 m. | Differentiation of tactile sensations, effort and distance . Manual dexterity, responsiveness to switching, speed-strength qualities | |
| The same, but at a vertical target (target, hoop) located on the wall at eye level | Differentiation of tactile sensations, comparison of effort and space, the ability of vision to distinguish distance, speed-strength qualities in hands, with the end of the music, they should stand near the “stump” (“pills” from the “Alma” equipment) of the same color as the leaves.  nine0155 nine0155 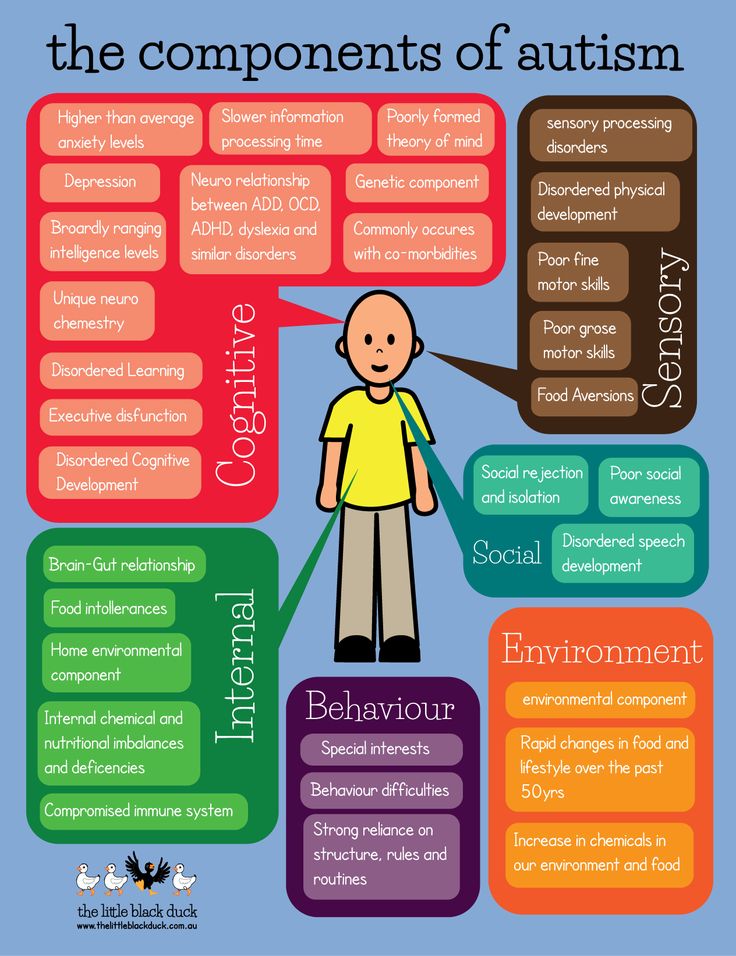 Each team (who is faster) must quickly collect the petals and lay out a flower from them. nine0155 Each team (who is faster) must quickly collect the petals and lay out a flower from them. nine0155   " Whoever stands near the “cap” faster, he puts on the cap and stands in the center. nine0155 " Whoever stands near the “cap” faster, he puts on the cap and stands in the center. nine0155  Each hoop has an equal number of fish. Children sit on a chair or “stumps” and catch fish (whoever catches a fish faster). Each hoop has an equal number of fish. Children sit on a chair or “stumps” and catch fish (whoever catches a fish faster). An exemplary set of exercises also used in physical education classes with a massage ball (according to Ermakova I.A.) 1. The ball is between the palms of the child, the fingers are pressed together. Make circular motions, rolling the ball over your palms.2. The ball is between the palms of the child, the fingers are pressed to each other. Make massage movements by rolling the ball back and forth. 3. Holding the ball with your fingertips, rotate forward (as if you were screwing on a cap). 4. Holding the ball with the balls of your fingers, press firmly on the ball (4-6 times) . 5. Holding the ball with your fingertips, rotate backwards (as if opening a lid). nine0003 6. Throw the ball with both hands to a height of 20-30 cm and catch it. 7. Grab the ball between your palms, fingers interlocked, elbows out to the sides. 8. Shift the ball from one hand to the other, gradually increasing the pace. The finger game "Our fingers are walking" is very interesting for children, where the coordination of finger movements is trained, where in a playful way children walk along the path along with a fictitious little man. nine0003 At the end of the lesson, in order to relieve fatigue and stress, I use such rhymed finger games as: “Orange” We shared an orange. "Ladushki" Ladushki, patty Development of fine motor skills of hands in children of primary and middle preschool age as part of physical education The younger preschool age is characterized by a high intensity of physical and mental development. The activity of the child increases, its purposefulness increases; movements become more diverse, including fine motor skills of the hand. The most important achievement of this age is that the child's actions become purposeful. Fine motor skills of the hands are developed by various games with fingers, where it is necessary to perform certain movements in a certain sequence; also develop physical exercises. These are various hangings and climbing (on a sports complex, along a ladder, etc.). Games can be played both collectively and individually. Observing how children perform funny game tasks, one can assess with a sufficient degree of accuracy the level of physical fitness, the degree of development of physical qualities, and the level of maturity of nervous processes. Usually a child with a high level of development of fine motor skills is able to reason logically, he has sufficiently developed memory, attention, coherent speech. Therefore, work on the development of fine motor skills should begin long before entering school. nine0003 Therefore, exercises and activities in which the little fingers of the child participate are extremely important for his mental and mental development. Fine motor skills, sensory skills, coordination of movements are key concepts for the period of primary preschool age. In their physical education classes in the younger group, fine motor skills exercises are included at all stages of the lesson. At the beginning of the lesson, for example, the game "Sun - fence" is used during the warm-up. The purpose of the exercise: warm up and prepare your hands for work. nine0003 As well as various counters for fingers, for example: We count and bend fingers. In the main part of the lesson, I practiced such exercises as: Hanging and wall bars, which develop grip strength. In the process of performing general developmental exercises, I use elements of finger exercises. For example, during bending with a gymnastic stick, 1 - stick up, 2 - tilt, put the stick on the floor, 3 - straighten up, arms up, move your fingers, 4 - bend over, take the stick. nine0003 Also used are exercises with clapping above the head or behind the back and with massage balls, in particular hand massage by rolling the ball with one hand, along the other hand from the palm to the shoulder and back. This exercise promotes the development of fine motor skills in children. Development of fine motor skills of hands in children of senior preschool age as part of physical education classes By the age of 5-7, the maturation of the corresponding areas of the cerebral cortex, the development of small muscles of the hand, is basically completed. It is important that by this age, the child is prepared to learn new motor skills, and not be forced to correct incorrectly formed old ones. Children are more willing to study if everything they are shown and offered is of a playful nature: competitive spirit, accuracy of execution. At the beginning of the lesson, children are offered self-massage of the hands and fingers: 1. Pressing with strongly clenched four fingers of one hand on the base of the thumb, the middle of the palm, the base of the fingers of the other hand. Then the position of the hands changes. 2. Rubbing the palms up and down. 3. Rubbing the side surfaces of interlocked fingers. nine0003 4. Kneading, then rubbing each finger lengthwise, then across. 5. Kneading the right hand with the fingers of the left and vice versa, then alternately rubbing. In the main part of the lesson, I practiced such exercises as: Hanging and wall bars, which develop grip strength. During general developmental exercises, I used exercises to develop fine motor skills of hands with small balls, handkerchiefs, massage balls. Rolling the massage ball with the older group is carried out not only over the arm, but also over the head with a change of hands, starting from the palm of, for example, the left hand and ending at the palm of the right hand. Here, massage of the belt of the upper limbs and the development of motor skills of finger movements are also practiced. Rolling the ball between the palms is carried out in walking (normal, on toes, side steps). Outdoor games use such items for the development of fine motor skills as clothespins, handkerchiefs, ribbons. nine0003 Example: Handkerchief Burners Number of Players: Any |
 b) The same, but catching with the right (left) hand
b) The same, but catching with the right (left) hand  Throwing at a target with three balls (plastic, rubber and tennis), different in weight and material
Throwing at a target with three balls (plastic, rubber and tennis), different in weight and material  Press your palms on the ball (4-6 times).
Press your palms on the ball (4-6 times). 
 Such exercises strengthen the palms and fingers of the baby, develop muscles. A kid who is allowed to climb and hang better masters exercises aimed directly at fine motor skills. nine0003
Such exercises strengthen the palms and fingers of the baby, develop muscles. A kid who is allowed to climb and hang better masters exercises aimed directly at fine motor skills. nine0003 

 nine0003
nine0003  nine0003
nine0003