Pasteurized milk and pregnancy
People at Risk: Pregnant Women
Image
Download full-resolution infographic
Immune system changes in pregnant women place the women themselves, their unborn children, and their newborns at increased risk of foodborne illness. These illnesses can be worse during pregnancy and may lead to miscarriage or premature delivery. Some foodborne illnesses, such as Listeria and Toxoplasma gondii, can infect the fetus even if the mother does not feel sick. This is why doctors provide pregnant women with specific guidelines about foods that they should and should not eat.
Advice Regarding Seafood
Women who are pregnant or may become pregnant—as well as breastfeeding mothers and parents of young children – should make informed choices when it comes to seafood. Fish is one source of high quality protein, minerals, and vitamins that are beneficial to overall health. However, it is important to choose fish that are safe to eat and offer health benefits. Follow FDA and EPA’s advice on eating fish by using this chart and a set of frequently asked questions and answers to choose healthy and safe options.
Cook seafood thoroughly: All seafood dishes should be cooked to 145°F. Raw seafood may contain parasites or bacteria, including Listeria, that can make pregnant women ill and could potentially harm their babies. This means that you should avoid:
- Sushi
- Sashimi
- Raw Oysters
- Raw Clams
- Raw Scallops
- Ceviche
Take care with smoked seafood: Refrigerated smoked seafood presents a very real threat of Listeria. Don’t eat refrigerated smoked seafood unless it’s in a cooked dish, such as a casserole, that reaches an internal temperature of 165°F to kill harmful germs.
Refrigerated smoked seafood, such as salmon, trout, whitefish, cod, tuna, or mackerel, are often labeled as:
- Nova-style
- Lox
- Kippered
- Smoked
- Jerky
It is OK to eat smoked seafood during pregnancy if it is canned, shelf stable or an ingredient in a casserole or other cooked dish.
Don’t Drink Unpasteurized Juice or Cider
Unpasteurized juice, even fresh-squeezed juice, and cider can cause foodborne illness. These beverages have been linked to outbreaks caused by E. coli and other harmful germs. To prevent infection, either choose a pasteurized version or bring unpasteurized juice or cider to a rolling boil and boil for at least 1 minute before drinking.
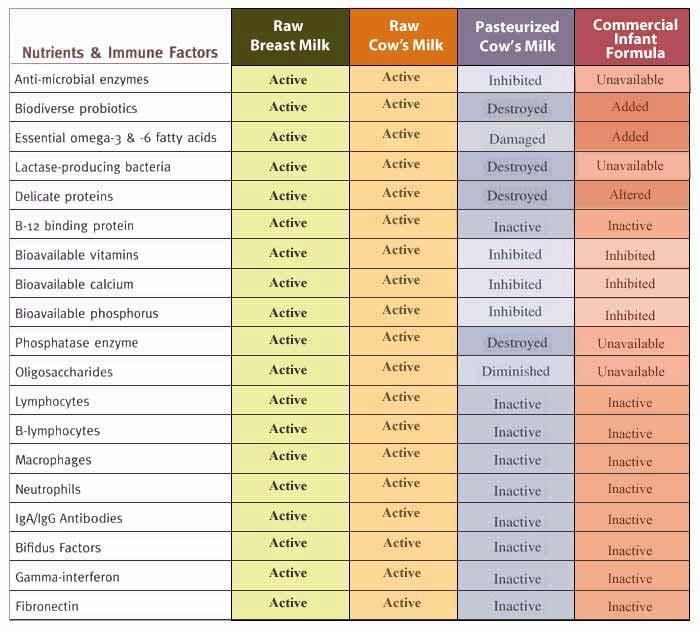
Avoid Raw Milk, Raw Milk Soft Cheeses, and Other Raw Milk Products
Raw milk is milk from any animal that has not been pasteurized to kill harmful bacteria. Raw milk, also called unpasteurized milk, may contain bacteria such as Campylobacter, E. coli, Listeria, Salmonella or the bacteria that causes tuberculosis. To avoid getting these foodborne illnesses, only consume pasteurized milk and milk products, including cheese.
Don’t eat the soft cheeses listed below unless they’re made with pasteurized milk. Make sure the label says “made with pasteurized milk. ”
”
- Brie
- Feta
- Camembert
- Roquefort
- Queso blanco
- Queso fresco
Cheese made with unpasteurized milk may contain E. coli or Listeria. Instead of eating soft cheese, eat hard cheese such as Cheddar or Swiss.
Pregnant woman should pay particular attention at farmers’ markets to make sure that fresh and soft cheeses are pasteurized.
Cook Eggs Thoroughly
Undercooked eggs may contain Salmonella. Cook eggs until the yolks and whites are firm to kill germs. If you are making a casserole or other dish containing eggs, make sure the dish is cooked to a temperature of 160°F. Make sure that foods that contain raw or lightly cooked eggs are made only with pasteurized eggs. Do not eat foods that may contain raw eggs, such as:
- Homemade eggnog
- Raw batter
- Homemade Caesar salad dressing
- Tiramisu
- Eggs Benedict
- Homemade ice cream
- Freshly made or homemade hollandaise sauce
Don’t Eat Premade Meat or Seafood Salad (Such as Deli Chicken or Tuna Salads)
Don’t buy or eat premade ham salad, chicken salad, or seafood salad which may contain Listeria. These items are commonly found in delis.
These items are commonly found in delis.
Do Not Eat Raw Sprouts
Raw or undercooked sprouts, such as alfalfa, clover, mung bean, and radish may contain E. coli or Salmonella. Cook sprouts thoroughly.
Avoid Undercooked Meat and Poultry
All meat and poultry should be thoroughly cooked before eating. A food thermometer should be used to ensure that the meat has reached the USDA-recommended safe minimum internal temperature. Visit minimum cooking temperatures for specific details.
Following the minimum recommend internal temperature is important because meat and poultry may contain E. coli, Salmonella, Campylobacter, or Toxoplasma gondii.
CDC recommends the following preventive measures to reduce the risk of contracting toxoplasmosis from eating meat:
- Cook meat to the USDA-recommended minimum safe internal temperature.
- Freeze meat for several days at sub-zero (0 °F) temperatures before cooking to greatly reduce chance of infection.

- Wash cutting boards, dishes, counters and utensils with hot, soapy water after contact with raw meat, poultry, seafood, or unwashed fruits or vegetables.
- Wash hands with soap and water.
Reheat Hot Dogs and Luncheon Meats
Reheat these meats to steaming hot or 165°F before eating, even though the label says precooked. These meat items may contain Listeria and are unsafe to eat if they have not been thoroughly reheated.
- Hot dogs
- Luncheon (deli) meats
- Cold cuts
- Fermented or dry sausage
- Any other deli-style meat and poultry
Be Selective with Meat Spreads or Pâté
Do not eat refrigerated pâtés or meat spreads from a deli or meat counter, or from the refrigerated section of a store. They can contain Listeria. Meat spreads and pâté that do not need refrigeration before opening, such as products in cans, jars, or sealed pouches, are a safer choice. Refrigerate these foods after opening.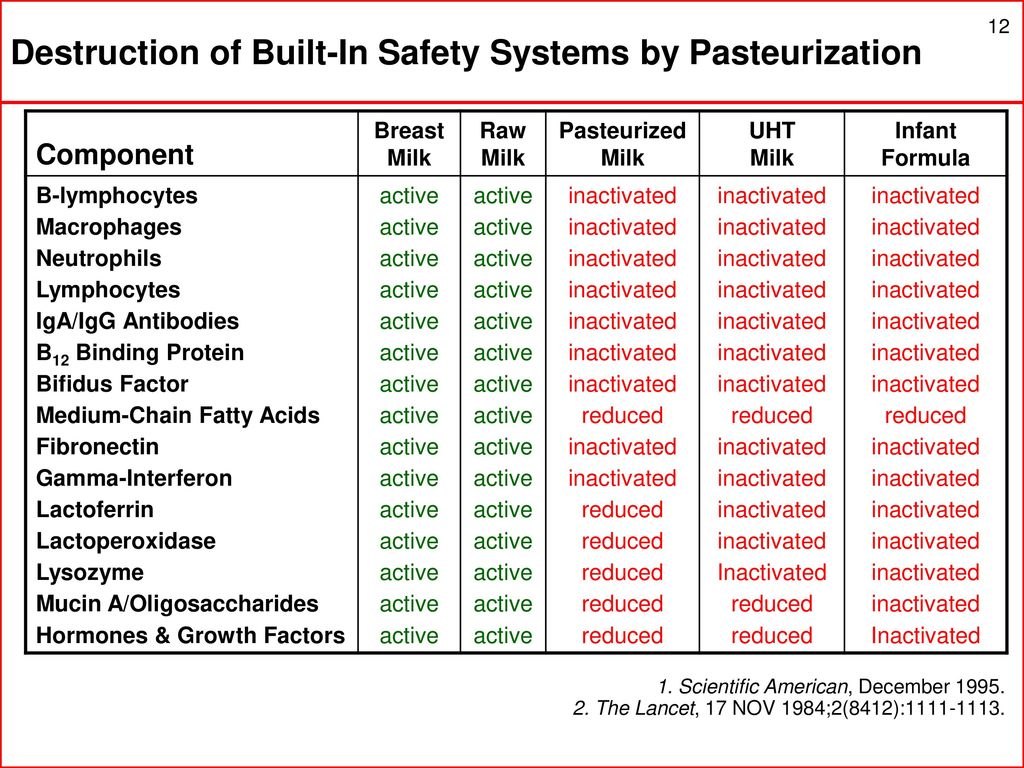
Don’t Eat Raw Dough
Unbaked (raw) dough or batter can make you sick. Flour hasn’t been treated to kill germs like E. coli. Raw eggs can contain Salmonella. Make sure batter is thoroughly baked or cooked before eating.
Additional Resources
Food Safety for Pregnant Women (FDA)
Listeria: Pregnant Women and Newborns (CDC)
Cultured Milk and Dairy During Pregnancy: Is It Safe?
Since it is advised that pregnant women steer clear of certain types of dairy, such as unpasteurized milk, you might wonder if you can have cultured milk and dairy products during pregnancy.
Overall, you can safely drink cultured milk, including buttermilk, and consume other cultured dairy products as long as they are pasteurized.
From milk to cheese and yogurt, let’s discuss the safety implications and nutritional information of cultured dairy products.
Covered in this Article:
Is Cultured Milk Safe When Pregnant?In general, cultured milk, which is commonly referred to as buttermilk, is safe for pregnant women as long as it is pasteurized.
Buttermilk is a low-fat or fat-free cow’s milk product that has lactic acid bacteria added in. This is why it is called cultured milk (source: California Dairy Press Room).
The result is a thicker and tangier milk product that many people love. Buttermilk can be consumed as a drink, just like regular milk. It is also often used in baking, cooking, and more.
All dairy products that you consume while you are pregnant, including milk, cheese, and yogurt, should be pasteurized (source: United States Food & Drug Administration [FDA]).
Pasteurization is the process of heating the milk to high temperatures to kill any bacteria that may be present. Pasteurization is essential for pregnant women, who are at an increased risk of developing foodborne illnesses.
More specifically, pasteurization kills any potential listeria bacteria that can cause listeriosis. Listeriosis can cause premature delivery, stillbirth, and more (source: FDA). Salmonella and E. Coli are also a concern in raw milk.
Otherwise, pasteurized buttermilk is an excellent source of calcium, protein, and other vitamins and minerals.
During pregnancy, you need more calcium in your diet than when you are not pregnant. Calcium supports the muscles, bones, nerves, and circulatory systems of you and your growing baby (source: American Pregnancy Association).
In fact, you need 1,000 milligrams of calcium per day when you are pregnant or lactating. For reference, one cup (or eight fluid ounces) of low-fat buttermilk contains 283 milligrams of calcium (source: United States Department of Agriculture [USDA]).
In other words, a serving of buttermilk has over a quarter of your calcium requirements for the entire day during pregnancy.
Additionally, a cup of low-fat buttermilk contains just over eight grams of protein (source: USDA). During pregnancy, about 71 grams of protein are needed each day to help the baby grow and develop (source: Mayo Clinic). All dairy products, including yogurt, are a good source of protein.
Both pasteurized and unpasteurized cultured milk is available. The packaging should clearly state whether or not the milk is pasteurized. If it is not pasteurized, you will see a warning label. Store-bought buttermilk is likely pasteurized, but always check to make sure.
Avoid any dairy, including buttermilk or cultured dairy, that says it is raw or does not specify that it has been pasteurized, such as that from a farmer’s market, roadside stands, or health food store (source: FDA).
If you make cultured milk or buttermilk at home, ensure the cow’s milk base you are using specifies that it has been pasteurized.
Is Cultured Cheese Safe During PregnancyCultured cheese is a variety of cheese produced with bacteria. Cultured cheese can be made from a wide variety of different bacteria in a cheese culture.
Unless cultured cheese is pasteurized, it is not safe for pregnant women because of the increased risk of listeria and other dangerous bacteria.
Unfortunately, cultured cheese is more commonly unpasteurized than pasteurized. Therefore, to be on the safe side, it is best to avoid eating cultured cheese during pregnancy unless you are sure it was made from pasteurized milk.
Any type of cheese (even soft cheeses) can be safe for you during your pregnancy as long as you are sure it is pasteurized.
Is Cultured Yogurt Safe for Pregnant Women?While most yogurts can be defined as “cultured” because of the bacteria added in, it is essential to note that they must be pasteurized in order to be considered safe for pregnancy.
Reading the packaging is imperative to make sure yogurt is safe. Yogurts that are homemade or from a farmer’s market or roadside stand are most likely to be unpasteurized.
Is Cultured Yogurt Pasteurized?Most yogurt you find at your regular grocery store will be pasteurized. This includes regular yogurt, Greek yogurt, and most other varieties.
Overall, when you are pregnant, stick with commercially made and store-bought cheeses, yogurts, and milk to ensure they are pasteurized.
I hope this article helped provide information regarding cultured dairy products, such as milk, cheese, and yogurt, and how to choose which products to eat or drink during your pregnancy.
| This article has been reviewed and approved for publication in line with our editorial policy. |
Is it possible to milk, including coconut, almond, soy and oat during pregnancy?
Cow's milk is good to drink during pregnancy if it is pasteurized. This is a great way to get the calcium needed for your child's healthy bone and tooth development, as well as a source of iodine.
Plant-based milk is also good to drink during pregnancy.
Pasteurized and unpasteurized milk
During pregnancy, it is important to stick to pasteurized milk and dairy products. But don't worry too much, because all milk sold in supermarkets must be pasteurized. If you buy milk from a local farm, be sure to check if it is pasteurized before drinking. nine0003
If you buy milk from a local farm, be sure to check if it is pasteurized before drinking. nine0003
It is advised not to consume unpasteurized dairy products during pregnancy. This includes full-fat, skimmed, semi-skimmed and organic milk and applies whether you prefer to drink cow's, goat's or sheep's milk. This also applies to yogurt and cheese.
Pasteurization is a heat treatment process that helps keep dairy products such as milk, cheese and yogurt fresh and safe to consume. Named after Louis Pasteur who invented the idea, pasteurization kills listeria and other bacteria that could potentially cause disease. nine0003
Without this treatment process, there is a risk that your glass of milk may contain listeria bacteria. This can cause an infection called listeriosis, which can make your unborn baby very sick and increase the risk of miscarriage or stillbirth.
UHT milk
UHT milk is perfectly safe to consume during pregnancy. Just be sure to drink within the expiration date.
Regular pasteurized milk is usually heated to about 72°C for 15 seconds to kill most harmful bacteria. Ultra-heat-treated milk heats up in much less time - just three seconds - up to 140°C. This kills any bacteria present, which means that as long as the milk is stored in aseptic packaging, it can remain sterile for several months when stored at room temperature. nine0003
Plant based milk
Coconut milk, almond milk, soy milk and oat milk are fantastic healthy alternatives to animal milk and you can enjoy them during pregnancy.
It's a good idea to look for an unsweetened option when you buy plant-based milk. It is recommended to eat a healthy, balanced diet during pregnancy, so it is best to avoid milk containing added sugar. Look also for options with added calcium, as this is an important nutrient during pregnancy. nine0003
If you decide to drink plant-based milk during pregnancy, make sure you have enough iodine in your diet. Iodine is an essential nutrient during pregnancy because it is essential for your baby's brain development. Research shows that while cow's milk is rich in iodine, plant-based alternatives are poor sources of this important mineral. Fish and shellfish are also good sources of iodine, and some cereals also contain it, although you may benefit from a supplement if you are a vegan. nine0003
Research shows that while cow's milk is rich in iodine, plant-based alternatives are poor sources of this important mineral. Fish and shellfish are also good sources of iodine, and some cereals also contain it, although you may benefit from a supplement if you are a vegan. nine0003
Coconut milk
- Coconut milk is made from the white flesh of mature brown coconuts.
- Coconut milk is rich in vitamins and minerals, including vitamin C, potassium, fiber and iron.
- These nutrients will help support your immune system and aid digestion during pregnancy.
- Coconut milk is naturally high in calories and healthy fats called medium chain triglycerides. However, it also contains saturated fats. nine0036
- The healthy fats in coconut milk may improve metabolism. However, saturated fats can raise cholesterol levels.
- Be sure to avoid raw, unpasteurized coconut milk during pregnancy. It may contain harmful salmonella bacteria that can cause food poisoning.
Almond milk
- Almond milk is made from ground almonds and water.
- Almond milk is a fantastic source of Vitamin E, a powerful antioxidant that helps protect your body from free radical damage. nine0036
- Many brands are also fortified with additional vitamins and minerals, such as calcium, potassium, or vitamin D. These essential nutrients will help keep your bones and heart healthy during pregnancy.
- It is worth noting that almond milk has a low protein content compared to animal milk.
Soy milk
- Soy milk is made from soybeans and filtered water.
- Because soy milk is plant-based, it is lactose-free and low in saturated fat. nine0036
- Soy milk is an excellent source of potassium and may also help support heart health during pregnancy. It also contains as much protein as cow's milk.
- It's worth noting that soy is a common allergen, so be careful if you haven't tried it before.

Oat milk
- Oat milk is made by mixing steel-cut or rolled oats with water before straining them to separate the milk from the oats. nine0036
- Oat milk is rich in vitamin B12, dietary fiber, iron and calcium. These essential nutrients will aid digestion, support your immune system, and help keep your blood cells healthy during pregnancy.
- Oat Milk is lactose, soy and nut free, making it a great option for those with dietary restrictions.
- Oat milk contains beta-glucans, which may help lower cholesterol levels. nine0036
Vegetable milk is often enriched with vitamins and minerals. According to:
- Vitamin D and calcium work together to build strong bones and teeth.
- Vitamin C is a powerful antioxidant that enhances the body's natural defenses.
- Vitamin B12 supports healthy blood cells.
- Zinc is an essential mineral that supports cell growth and keeps your immune system strong.
 nine0047
nine0047
Chocolate milk
Chocolate milk is safe to drink as an occasional treat. However, it is quite high in sugar, so it is best not to consume it too often.
Cocoa powder contains a small amount of caffeine, so chocolate milk may also contain some caffeine. Most experts believe that it has about 2 mg of caffeine per glass, and it is unlikely to contain more than 10 mg.
You can consume up to 200 mg of caffeine per day, so keep an eye on your total intake if you drink a lot of tea or coffee or eat a lot of chocolate. nine0003
You can find your due date with our calculator
Pregnancy Calculator
and subscribe to our weekly Pregnancy Week Newsletter to stay up to date on the changes that are happening to you, your body and baby.
Newsletter
Subscribe to Vikids news at Facebook!
Registration
Share on your timeline
'+ '
' + ' nine0003
' + '
What not to eat during pregnancy
A pregnant woman needs to take care of her own health and provide her baby with everything necessary, so she must strictly monitor her diet.:strip_icc():format(jpeg)/kly-media-production/medias/1587493/original/004712900_1494216364-Perfect-Day-milk4-1.jpg) What not to eat during pregnancy?
What not to eat during pregnancy?
Food is a source of vitamins, trace elements, proteins, carbohydrates and fats necessary for the normal development of the fetus. But there are foods that are better to limit or completely eliminate from the diet of a pregnant woman.
Every pregnant woman should know which foods to avoid. The list of prohibited foods is below. nine0003
Sweets
A pregnant woman should limit sweets in her diet - marmalade, cakes, ice cream, cakes, muffins, sweets and pies. They practically do not contain vitamins. The composition of sweets is dominated by carbohydrates. Eating such food, the expectant mother quickly gains weight, which is useless during pregnancy. The baby also gains weight, which can cause complications in childbirth.
In addition, many sweets contain dyes, leavening agents and stabilizers, which adversely affect the functioning of the liver and other organs of mother and baby. nine0003
Raw meat
Prohibited foods during pregnancy include raw or undercooked meat. With insufficient heat treatment of meat, one cannot be sure of its safety. It may contain pathogens of dangerous diseases and helminths.
With insufficient heat treatment of meat, one cannot be sure of its safety. It may contain pathogens of dangerous diseases and helminths.
Sushi
Raw fish may also contain pathogens and helminths. Pregnancy is a contraindication for the use of antihelminthic drugs, so it will be very difficult for the expectant mother to deal with helminthic invasion. In addition, the parasite will compete with the child for nutrients. nine0003
In addition, some types of fish contain high levels of mercury, which can affect pregnancy. In this list: perch, tuna, swordfish, orange Australian ruff, shark, king mackerel. Eating a large amount of this fish can lead to hearing and vision disorders, kidneys, and the baby's nervous system. Safe fish - salmon, cod, flounder, sardine, herring. But it must also be thermally processed.
Unpasteurized milk
Pregnancy requires a constant supply of nutrients to the body. Milk contains many trace elements necessary for the development of the fetus. However, if you use milk unpasteurized. It can pose a serious danger due to possible contamination with bacteria - salmonella, E. coli. Contamination of milk can occur during the collection, processing, storage of milk. Pregnancy is not the time to tempt fate. Buy only pasteurized milk.
However, if you use milk unpasteurized. It can pose a serious danger due to possible contamination with bacteria - salmonella, E. coli. Contamination of milk can occur during the collection, processing, storage of milk. Pregnancy is not the time to tempt fate. Buy only pasteurized milk.
Canned food
Canned food contains a lot of vinegar and preservatives. They are harmful because they inhibit the production of certain proteins. And protein, as you know, is a building material that a growing baby needs.
Spicy food
Spicy and spicy food can cause heartburn which often accompanies pregnancy. This brings pronounced discomfort for the pregnant woman, and the illness of the mother always affects the condition of the child.
Salt
Pregnancy is sometimes accompanied by complications, which are characterized by the development of edema (eg preeclampsia of pregnancy). The use of salt in excess contributes to water retention in the body and swelling increases. Doctors sometimes recommend giving up salt completely a few weeks before giving birth.
Doctors sometimes recommend giving up salt completely a few weeks before giving birth.
Coffee and tea
If the pregnancy proceeds without complications, a pregnant woman can afford a cup of her favorite coffee, but it should not be abused. Scientists say that excessive consumption of coffee increases the likelihood of miscarriage. Caffeine increases the risk of preterm birth and low birth weight. Remember that drinks like cola and tea also contain caffeine. nine0003
Raw eggs
Do not eat raw eggs during pregnancy. There is a risk of contracting salmonellosis or other foodborne infections. Pregnancy is accompanied by a decrease in the body's defenses, so the risk of getting food poisoning increases. Vomiting and diarrhea cause dehydration and can affect the condition of the baby, causing premature labor.
Alcohol
It is necessary to give up bad habits when planning a pregnancy. Alcohol use can cause serious problems in a child's development.