Ovulate week before period
Can You Get Pregnant Right Before Your Period? Chart, Test, More
Although it is possible to get pregnant in the days leading up to your period, it isn’t likely.
You can only get pregnant during a narrow window of five to six days a month.
When these fertile days actually occur depends on when you ovulate, or release an egg from your ovary.
Ovulation usually occurs in the middle of your menstrual cycle — about two weeks before your period — but not everyone’s cycle is regular.
Even for those with a regular cycle, it’s possible to ovulate earlier or later. This can shift the fertile window by a few days in a given month.
In other words, it’s difficult to pinpoint a time in your cycle where you can 100 percent guarantee that you will or won’t get pregnant.
| Chance of becoming pregnant | It’s unlikely | It’s possible | It’s likely |
| 14 days before | X | ||
| 10 days before | X | ||
| 5–7 days before | X | ||
| 2 days before | X | ||
| 1 day before | X | ||
| During menstruation | X | ||
| 1 day after | X | ||
| 2 days after | X | ||
| 5–7 days after | X | ||
| 10 days after | X | ||
| 14 days after | X |
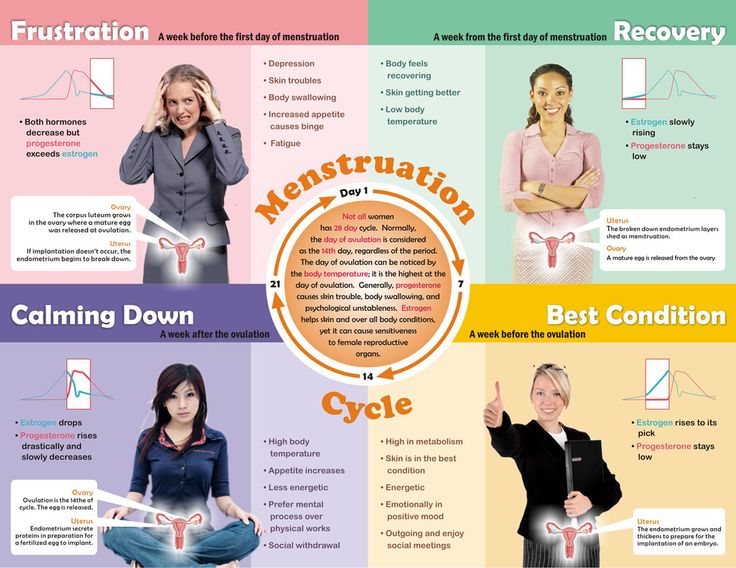
The average menstrual cycle is 28 days, with the first day of menstruation as cycle day 1.
Most periods last two to seven days. Pregnancy is uncommon during this time, because your peak fertility window is still about a week or so away.
Around days 6 to 14 of your cycle, your body will start releasing follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH).
This helps develop an egg inside your ovary. Your body will also begin rebuilding the endometrial lining in your uterus.
Pregnancy is slightly more likely during this time. Sperm can live up to five days inside the body, so it could still be present when the egg matures.
Once the egg is mature, your body will release lutenizing hormone (LH), triggering the egg’s release from your ovary (ovulation).
Ovulation usually occurs around cycle day 14. Pregnancy is likely on ovulation day.
That said, ovulation doesn’t always happen like clockwork. It can occur anywhere from four days before to four days after the midpoint of your menstrual cycle.
The bottom LineIf you ovulate later in your cycle or start your period sooner than usual, you could become pregnant if you have sex in the days leading up to your period.
Lots of people don’t have 28-day cycles. Some have cycles as short as 21 days and others as long as 35 days.
In fact, in one study, only about 30 percent of participants had their fertile window fall within days 10 to 17 of their cycle. Only 10 percent had ovulation fall exactly 14 days before their next period.
Stress and diet can also impact when ovulation occurs, as well as medical conditions such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) and amenorrhea.
Menstrual cycles can also be more irregular during adolescence or perimenopause.
In many cases, ovulation still happens around the middle of your cycle.
Try thisIf you’re trying to figure out when you might be ovulating, a good place to start is by determining the midpoint of your individual cycle.
But if your cycle length varies from month to month, it may be helpful to use a backup birth control method.
If you’re trying to get pregnant, you might consider formally tracking your ovulation.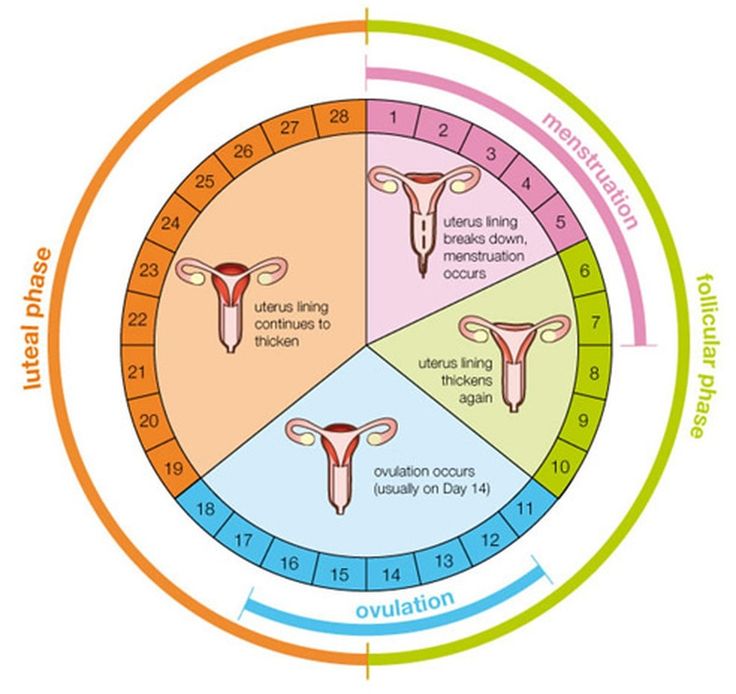 This can provide a more reliable view of your fertile window.
This can provide a more reliable view of your fertile window.
You can do this a number of ways, including:
- tracking your basal body temperature
- using an over-the-counter ovulation predictor kit
- wearing a fertility monitor
The only time you can get pregnant is during your fertile window.
An egg only lives for about 24 hours after being released from your ovary, and sperm can only live for up to five days inside the body.
That means you can only get pregnant if you have sex:
- in the four to five days leading up to ovulation
- on the day of ovulation
- on the day after ovulation
If you’re looking to conceive, the best time to have sex is right before ovulation. This will give sperm time to reach the fallopian tube and meet the egg there.
After that, if no sperm has fertilized the egg, it will dissolve. You won’t be able to get pregnant until your cycle restarts.
It isn’t impossible, but it’s unlikely.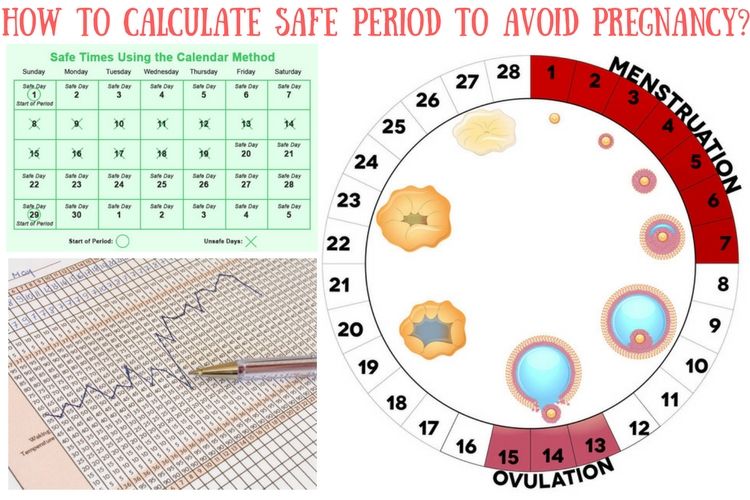 The timing would have to be perfect for the egg and sperm to reach each other in time.
The timing would have to be perfect for the egg and sperm to reach each other in time.
If you have sex toward the end of your period and you ovulate early, it’s possible for the egg and sperm to both be alive at the same time and for fertilization to occur.
It’s unlikely — though slightly more likely than if you have sex during your period.
If you have sex right after your period and you ovulate early that month, it’s possible to get pregnant.
This is more likely with people who have a shorter-than-average cycle, because ovulation occurs more frequently.
Your period will only start if the egg isn’t fertilized and the cells are reabsorbed.
This causes estrogen and progesterone levels to fall and menstruation to begin.
However, you may experience some spotting during early pregnancy.
One study found that 14 out of 151 participants experienced one day of vaginal bleeding in the first eight weeks of pregnancy.
Furthermore, 15 percent to 25 percent of people may experience spotting during the first three months of pregnancy.
Taking note of the timing and any other symptoms present can help you differentiate between typical menstruation and pregnancy-related spotting.
Implantation bleeding usually occurs 6 to 12 days after conception. It’s caused by the fertilized egg attaching to your uterus lining.
This light spotting usually only lasts 24 to 48 hours and is generally much lighter than the average period.
You may also experience spotting as a result of increased blood flow in the cervix. This type of spotting is most common after sex, a Pap test, or a pelvic exam.
If you’re experiencing unexpected bleeding, see a doctor or other healthcare provider.
If you had unprotected sex and want to avoid pregnancy, take emergency contraception (EC) as soon as possible.
There are two main types — the copper IUD and the hormonal EC pill — and they can both work up to five days after unprotected sex.
The IUD prevents pregnancy by producing an inflammatory reaction that’s toxic to sperm and eggs.
It’s more effective than the morning-after pill, but it’s only available by prescription and has to be inserted by a doctor within five days of unprotected sex.
The pill delivers a high dose of hormones to delay ovulation or prevent a fertilized egg from implanting to the uterus.
Plan B One-Step, Next Choice, and MyWay are all available over the counter.
Which should you use?As a general rule of thumb, EC pills may be less effective for people who have a higher body mass index (BMI).
There isn’t any research to suggest that the copper IUD is similarly affected by BMI, so this option may be more effective.
Talk to your local pharmacist or other healthcare provider about which EC option is right for you.
Wait until the first day of your missed period to take a home pregnancy test.
But if you can wait a little longer, taking the test one week after the date of your missed period may produce the most accurate result.
If you have an irregular cycle, wait one to two weeks after you had sex to take the test.
This will allow your body to develop high enough human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) levels to be detected by the test.
If you get a positive result, you might want to check again in a day or two since it’s possible to get a false positive. Then reach out to a medical provider to confirm the results.
Whether you’re trying to prevent pregnancy or trying to conceive, it’s always a good idea to talk about it with a doctor or other healthcare provider.
They can help you learn more about your cycle and discuss your options moving forward. This could include birth control, fertility awareness, or family planning.
Simone M. Scully is a writer who loves writing about all things health and science. Find Simone on her website, Facebook, and Twitter.
Can You Get Pregnant Right Before Your Period? Chart, Test, More
Although it is possible to get pregnant in the days leading up to your period, it isn’t likely.
You can only get pregnant during a narrow window of five to six days a month.
When these fertile days actually occur depends on when you ovulate, or release an egg from your ovary.
Ovulation usually occurs in the middle of your menstrual cycle — about two weeks before your period — but not everyone’s cycle is regular.
Even for those with a regular cycle, it’s possible to ovulate earlier or later. This can shift the fertile window by a few days in a given month.
In other words, it’s difficult to pinpoint a time in your cycle where you can 100 percent guarantee that you will or won’t get pregnant.
| Chance of becoming pregnant | It’s unlikely | It’s possible | It’s likely |
| 14 days before | X | ||
| 10 days before | X | ||
| 5–7 days before | X | ||
| 2 days before | X | ||
| 1 day before | X | ||
| During menstruation | X | ||
| 1 day after | X | ||
| 2 days after | X | ||
| 5–7 days after | X | ||
| 10 days after | X | ||
| 14 days after | X |
The average menstrual cycle is 28 days, with the first day of menstruation as cycle day 1.
Most periods last two to seven days. Pregnancy is uncommon during this time, because your peak fertility window is still about a week or so away.
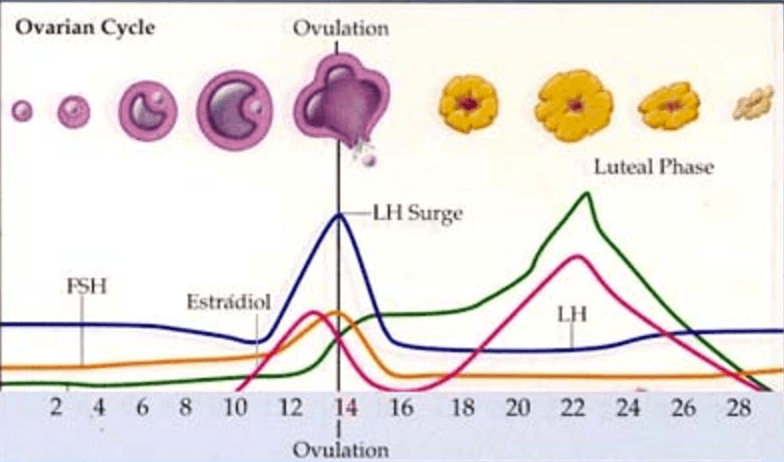
Around days 6 to 14 of your cycle, your body will start releasing follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH).
This helps develop an egg inside your ovary. Your body will also begin rebuilding the endometrial lining in your uterus.
Pregnancy is slightly more likely during this time. Sperm can live up to five days inside the body, so it could still be present when the egg matures.
Once the egg is mature, your body will release lutenizing hormone (LH), triggering the egg’s release from your ovary (ovulation).
Ovulation usually occurs around cycle day 14. Pregnancy is likely on ovulation day.
That said, ovulation doesn’t always happen like clockwork. It can occur anywhere from four days before to four days after the midpoint of your menstrual cycle.
The bottom LineIf you ovulate later in your cycle or start your period sooner than usual, you could become pregnant if you have sex in the days leading up to your period.
Lots of people don’t have 28-day cycles. Some have cycles as short as 21 days and others as long as 35 days.
In fact, in one study, only about 30 percent of participants had their fertile window fall within days 10 to 17 of their cycle. Only 10 percent had ovulation fall exactly 14 days before their next period.
Stress and diet can also impact when ovulation occurs, as well as medical conditions such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) and amenorrhea.
Menstrual cycles can also be more irregular during adolescence or perimenopause.
In many cases, ovulation still happens around the middle of your cycle.
Try thisIf you’re trying to figure out when you might be ovulating, a good place to start is by determining the midpoint of your individual cycle.
But if your cycle length varies from month to month, it may be helpful to use a backup birth control method.
If you’re trying to get pregnant, you might consider formally tracking your ovulation. This can provide a more reliable view of your fertile window.
This can provide a more reliable view of your fertile window.
You can do this a number of ways, including:
- tracking your basal body temperature
- using an over-the-counter ovulation predictor kit
- wearing a fertility monitor
The only time you can get pregnant is during your fertile window.
An egg only lives for about 24 hours after being released from your ovary, and sperm can only live for up to five days inside the body.
That means you can only get pregnant if you have sex:
- in the four to five days leading up to ovulation
- on the day of ovulation
- on the day after ovulation
If you’re looking to conceive, the best time to have sex is right before ovulation. This will give sperm time to reach the fallopian tube and meet the egg there.
After that, if no sperm has fertilized the egg, it will dissolve. You won’t be able to get pregnant until your cycle restarts.
It isn’t impossible, but it’s unlikely. The timing would have to be perfect for the egg and sperm to reach each other in time.
The timing would have to be perfect for the egg and sperm to reach each other in time.
If you have sex toward the end of your period and you ovulate early, it’s possible for the egg and sperm to both be alive at the same time and for fertilization to occur.
It’s unlikely — though slightly more likely than if you have sex during your period.
If you have sex right after your period and you ovulate early that month, it’s possible to get pregnant.
This is more likely with people who have a shorter-than-average cycle, because ovulation occurs more frequently.
Your period will only start if the egg isn’t fertilized and the cells are reabsorbed.
This causes estrogen and progesterone levels to fall and menstruation to begin.
However, you may experience some spotting during early pregnancy.
One study found that 14 out of 151 participants experienced one day of vaginal bleeding in the first eight weeks of pregnancy.
Furthermore, 15 percent to 25 percent of people may experience spotting during the first three months of pregnancy.
Taking note of the timing and any other symptoms present can help you differentiate between typical menstruation and pregnancy-related spotting.
Implantation bleeding usually occurs 6 to 12 days after conception. It’s caused by the fertilized egg attaching to your uterus lining.
This light spotting usually only lasts 24 to 48 hours and is generally much lighter than the average period.
You may also experience spotting as a result of increased blood flow in the cervix. This type of spotting is most common after sex, a Pap test, or a pelvic exam.
If you’re experiencing unexpected bleeding, see a doctor or other healthcare provider.
If you had unprotected sex and want to avoid pregnancy, take emergency contraception (EC) as soon as possible.
There are two main types — the copper IUD and the hormonal EC pill — and they can both work up to five days after unprotected sex.
The IUD prevents pregnancy by producing an inflammatory reaction that’s toxic to sperm and eggs.
It’s more effective than the morning-after pill, but it’s only available by prescription and has to be inserted by a doctor within five days of unprotected sex.
The pill delivers a high dose of hormones to delay ovulation or prevent a fertilized egg from implanting to the uterus.
Plan B One-Step, Next Choice, and MyWay are all available over the counter.
Which should you use?As a general rule of thumb, EC pills may be less effective for people who have a higher body mass index (BMI).
There isn’t any research to suggest that the copper IUD is similarly affected by BMI, so this option may be more effective.
Talk to your local pharmacist or other healthcare provider about which EC option is right for you.
Wait until the first day of your missed period to take a home pregnancy test.
But if you can wait a little longer, taking the test one week after the date of your missed period may produce the most accurate result.
If you have an irregular cycle, wait one to two weeks after you had sex to take the test.
This will allow your body to develop high enough human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) levels to be detected by the test.
If you get a positive result, you might want to check again in a day or two since it’s possible to get a false positive. Then reach out to a medical provider to confirm the results.
Whether you’re trying to prevent pregnancy or trying to conceive, it’s always a good idea to talk about it with a doctor or other healthcare provider.
They can help you learn more about your cycle and discuss your options moving forward. This could include birth control, fertility awareness, or family planning.
Simone M. Scully is a writer who loves writing about all things health and science. Find Simone on her website, Facebook, and Twitter.
Ovulation: how to calculate? | Clinic MEDEL
It is impossible to sneeze with your eyes open.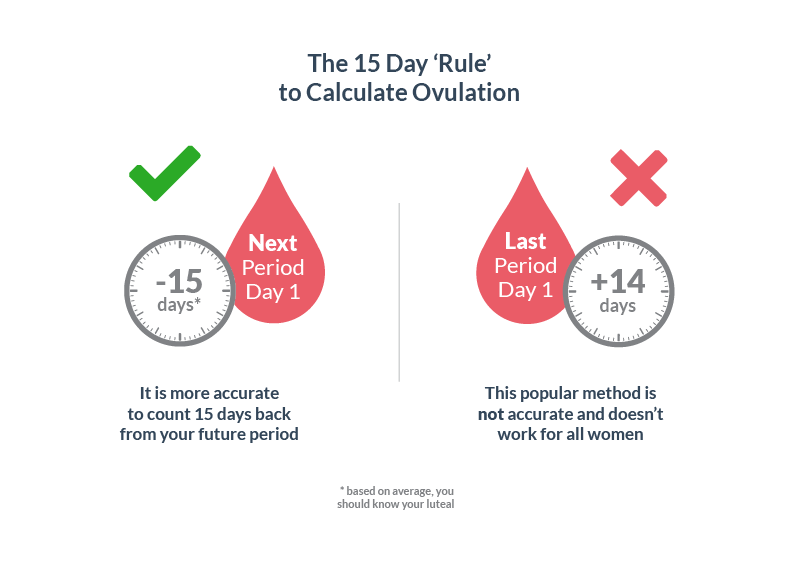
The phase of a woman's menstrual cycle when an unfertilized egg is released from the ovary, travels through the fallopian tubes and into the uterus, is called ovulation.
This is the stage of the menstrual cycle during which pregnancy can occur if the released egg is fertilized by sperm.
We'll show you how to calculate the length of your menstrual cycle to determine when you might be ovulating.
How many days after menstruation does ovulation last?
Ovulation usually occurs about 14 days before your next period. Count the number of days from the first day of your period to the day before your next period to determine the length of your cycle. Then subtract that number by 14 to determine which day after your period you will ovulate. If your average menstrual cycle is 30 days, you will ovulate 16 days after your period starts (30-14 = 16).
In predicting ovulation, there may be a margin of error of at least 2 days.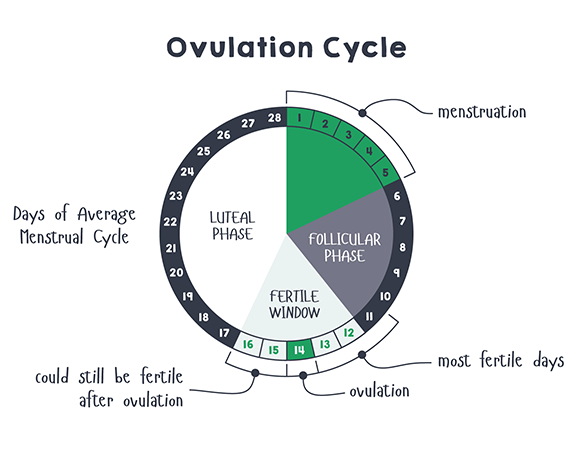
If you want to get pregnant, many doctors recommend having sex a few days before ovulation because sperm can live up to 5 days in a woman's reproductive tract.
When is the highest chance of getting pregnant?
The day before ovulation and on the day of ovulation. If you're trying to conceive, it's a good idea to have sex every day or every other day for a week to maximize your chance of pregnancy.
You are unlikely to get pregnant immediately after your period, although this can happen if you have an abnormally short menstrual cycle in which ovulation can occur just a few days after your period ends.
Here is an example:
First day of menstruation - January 1
The next one will start on January 31 (that is, in 30 days)
Ovulation will take place from January 17 to January 21 (10-14 days before the next period). These days are the most likely to conceive.
Keep in mind that women with irregular cycles may not be able to predict when they will ovulate because their cycle length varies from month to month. Some women with irregular cycles may ovulate immediately after their period, but this is very rare.
Some women with irregular cycles may ovulate immediately after their period, but this is very rare.
Articles
Return to the list
MEdel Multidisciplinary Clinic
We are waiting for you at the following addresses:
Kazan, st. Siberian tract, 34, bldg. 5
Kazan, st. Adoratskogo, d. 17
Kazan, st. Yuliusa Fuchik, 91a
Mail: [email protected]
How to get to Kazan Clinics
Working hours:
Mon-Fri 8:00 - 20:00
Saturday 8:00 - 17:00 02 day off.
* Data processing policy
Review of the clinic Information search
Late ovulation and pregnancy: its causes and features | Mamovedia
Fertility and ovulation: is it possible to get pregnant if ovulation occurs after the twenty-first day of the menstrual cycle? Let's talk today about late ovulation and how it affects female fertility
Women always pay close attention to ovulation, especially with regard to the timing in which it occurs. This is because knowing when a woman ovulates allows her to control her fertility: whether she wants to conceive a child or avoids it.
This is because knowing when a woman ovulates allows her to control her fertility: whether she wants to conceive a child or avoids it.
There are various disorders of ovulation, which in 25-30% of cases are the cause of female infertility.
Terms of ovulation
To understand the essence of the consequences of late ovulation, it is necessary to know the process of maturation of the egg (oocyte) to prepare for fertilization.
During the menstrual cycle, several oocytes mature in the female body, but only one (dominant) is a candidate for fertilization. This complex mechanism does not always begin in the same way in all women, as it depends on several factors.
It is believed that ovulation occurs around the 14th day of the menstrual cycle , but these are very approximate data, and there is no complete certainty that ovulation will occur on this day. Often there is early ovulation, or in the case of interest to us, late ovulation also occurs, that is, that which occurs after the twenty-first day of the monthly cycle, closer to the next.
Late ovulation: its causes
Each menstrual cycle consists of three different phases : follicular, actual ovulation and luteal phase.
The luteal phase is the phase that usually has the same duration, while the follicular phase is the most unstable and can last from 10 to 16 days. And, if the follicular phase is prolonged, ovulation occurs later, or may be completely absent.
Variables that affect the duration of the follicular phase and ovulation itself are different, but they are all associated with hormonal imbalance . They can be temporary or long-term:
- severe stress, both physical and mental
- polycystic ovary syndrome
- thyroid disorders
- certain antidepressants or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
- drug use
Even cycles of chemotherapy and other cancer treatments can have serious consequences on the hormonal level, and accordingly on the timing of ovulation.
You also need to take into account the age of the woman . Teenagers and older women are more likely to have irregular cycles and therefore late ovulation. Those who are overweight (as well as underweight) may also be predisposed to late ovulation episodes.
Breastfeeding is also the cause of late ovulation. The production of prolactin, the hormone responsible for milk production, cancels ovulation and menstruation. But, it should be remembered that this mechanism should not be considered as a contraceptive method. Some studies show that 2% of women who use breastfeeding as a method of contraception, within six months after giving birth, were again in position.
Late ovulation with regular cycles
The phenomenon of late ovulation is not uncommon even in women with regular cycles. The reason is very simple: the timing of ovulation is very variable, and it is not a mechanism that repeats itself at the same time: only 30% of women are fertile between the 10th and 17th day of the menstrual cycle. This means that two-thirds of women, even if they have regular periods, can ovulate after this period. Therefore, it is important that every woman is aware of this possible unpredictability of her body, and that her body is not an automaton that gives out "eggs" on demand.
Late ovulation: what are the symptoms?
As we can see, ovulation is a very variable mechanism that can be seen in some of the physical changes that occur in the body. For example, an increase in cervical mucus or an increase in basal temperature may indicate ovulation. Sometimes, late ovulation can be accompanied by abdominal pain and bleeding (you should pay close attention to this).
Late ovulation and conception
All ovulation disorders directly affect fertility and conception. In the case of late ovulation, we are talking about one of the most common cases of female infertility, since it is more difficult to determine the period in which the relationship should be conceived. Late ovulation does not mean that it is impossible to get pregnant, but it will be more difficult to do so.